The Influence of Parenting Style and Time Management Tendency on Internet Gaming Disorder among Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Effects and Prevalence of Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD)
1.2. Factors Influencing Adolescents’ Internet Gaming Disorder
1.2.1. Family and Parenting Factors: Parenting Style
1.2.2. Personality Factors: Time Management Tendency
1.3. Research Purpose
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Internet Gaming Disorder
2.2.2. Parenting Style
2.2.3. Time Management Tendency
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Pearson Correlations
3.3. Chi-Squared Analysis
3.4. Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| The Path | Indirect Effect Coefficient | Standard Error | 95% Confidence Interval | Mediation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bounds | Upper Bounds | p | ||||
| 1. Father’s rejection → time management tendency → online game addiction | −0.014 | 0.013 | −0.042 | 0.010 | 0.217 | none |
| 2. Father’s emotional warmth → time management tendency → online game addiction | −0.255 | 0.068 | −0.421 | −0.143 | <0.001 * | full |
| 3. Father’s over-protection → time management tendency → IGD | 0.020 | 0.013 | −0.003 | 0.052 | 0.133 | none |
| 4. Mother’s rejection → time management tendency → IGD | −0.003 | 0.011 | −0.025 | 0.018 | 0.798 | none |
| 5. Mother’s emotional warmth → time management tendency → IGD | −0.041 | 0.012 | −0.069 | −0.021 | 0.010 * | full |
| 6. Mother’s over-protection → time management tendency → IGD | 0.027 | 0.012 | 0.004 | 0.053 | 0.037 * | partial |
References
- Block, J.J. Issues for DSM-V: Internet addiction. Am. J. Psychiatry 2008, 165, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, H.; Mihara, S.; Higuchi, S. Treatment and risk factors of Internet use disorders. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 71, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, K. Internet game addiction, parental attachment, and parenting of adolescents in South Korea. J. Child Adolesc. Subst. Abuse. 2015, 24, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Namkoong, K.; Ku, T.; Kim, S.J. The relationship between online game addiction and aggression, self-control and narcissistic personality traits. J. Eur. Psychiatry 2008, 23, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sublette, V.A.; Mullan, B. Consequences of play: A systematic review of the effects of online gaming. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2012, 10, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, A.; Kattner, F.; Bradford, D.; Gentile, D.A.; Choo, H.; Chen, V.H.H.; Khoo, A.; Green, C.S. The role of game genres and the development of internet gaming disorder in school-aged children. J. Addict. Behav. Ther. Rehabil. 2015, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbein, F.; Kliem, S.; Baier, D.; Mößle, T.; Petry, N.M. Prevalence of internet gaming disorder in German adolescents: Diagnostic contribution of the nine DSM-5 criteria in a state-wide representative sample. Addiction 2015, 110, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Internet Network Information Center. Statistical Report on China’s Internet Development. Available online: http://www.cac.gov.cn/2019-02/28/c_1124175677.htm (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Long, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Hao, W.; Maurage, P.; Billieux, J. Prevalence and correlates of problematic online gaming: A systematic review of the evidence published in Chinese. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2018, 5, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jiang, X.; Mo, P.H.; Cai, Y.; Ma, L.; Lau, J.F. Prevalence and interpersonal correlates of internet gaming disorders among Chinese adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Imani, V.; Broström, A.; Årestedt, K.; Pakpour, A.H.; Griffiths, M.D. Evaluating the psychometric properties of the 7-item Persian Game Addiction Scale for Iranian adolescents. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, S.; Karakoc, A.; Can Gurkan, O.; Onan, N.; Barlas, G.U. Investigation of the online game addiction level, sociodemographic characteristics and social anxiety as risk factors for online game addiction in middle school students. Community Ment. Health J. 2020, 56, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.W.; Dorstyn, D.; Delfabbro, P.H.; King, D.L. Global prevalence of gaming disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2020, 4867420962851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.X.; Ofir, T.; Yu, F.Y. Online game addiction among adolescents: Motivation and prevention factors. Eur. J. Inform. Syst. 2012, 21, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, S. The role of cognitive distortion in online game addiction among Chinese adolescents. J. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2013, 35, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Hums, M.A.; Bum, C.H. Impact of the family environment on juvenile mental health: ESports online game addiction and delinquency. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinhua News Agency, Game Supervision Starting from Classification. Available online: https://xhpfmapi.zhongguowangshi.com/vh512/share/9266815?channel=weixin&from=timeline (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- People’s Daily. Game Addiction, Can This Disease Be Cured? Available online: http://paper.people.com.cn/rmrbhwb/html/2020-09/07/node_865.htm (accessed on 28 October 2020).
- Mihara, S.; Higuchi, S. Cross-sectional and longitudinal epidemiological studies of Internet gaming disorder: A systematic review of the literature. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 71, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berte, D.Z.; Mahamid, F.A.; Affouneh, S. Internet addiction and perceived self-efficacy among university students. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.J.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, A.; Kim, B.M.; Park, M.K.; Jung, M.H.; Choi, J.S. Self-efficacy and clinical characteristics in casual gamers compared to excessive gaming users and non-gamers in young adults. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.L.; Chou, C.; Chen, C.H. The moderating effects of parenting styles on the relation between the internet attitudes and internet behaviors of high-school students in Taiwan. Comput. Educ. 2016, 94, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Lin, S.L.; Wu, C.P. The effects of parental monitoring and leisure boredom on adolescents’ internet addiction. Adolescence 2009, 44, 993–10041. [Google Scholar]
- Floros, G.D.; Siomos, K.E.; Fisoun, V.; Dafouli, E.; Geroukalis, D. Adolescent online cyberbullying in Greece: The impact of parental online security practices, bonding, and online impulsiveness. J. School Health 2013, 83, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.Q.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, M.C.; Wang, J.N.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, R. Mental health, personality, and parental rearing styles of adolescents with internet addiction disorder. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2010, 13, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siomos, K.; Floros, G.; Fisoun, V.; Evaggelia, D.; Farkonas, N.; Sergentani, E.; Lamprou, M.; Geroukalis, D. Evolution of internet addiction in Greek adolescent students over a two-year period: The impact of parental bonding. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2012, 21, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lei, H.; Tian, L. A meta-analysis of the relationship between parenting style and internet addiction among mainland Chinese teenagers. Soc. Behav. Personal. 2018, 46, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y. Factors affecting pathological internet use among Chinese university students. Soc. Behav. Personal. 2017, 45, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaer, Y.; Akdemir, D. Parenting styles, perceived social support and emotion regulation in adolescents with internet addiction. Compr. Psychiatry 2019, 92, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floros, G.; Siomos, K. The relationship between optimal parenting, Internet addiction and motives for social networking in adolescence. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 209, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.P.; Bai, B.Y.; Jiang, S.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Q. Parenting styles and internet addiction in Chinese adolescents: Conscientiousness as a mediator and teacher support as a moderator. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 101, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.T.; Wong, H.T.; Yu, K.F.; Fok, K.W.; Yeung, S.M.; Lan, C.H. Parenting approaches, family functionality, and internet addiction among Hong Kong adolescents. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wilkinson, J.S. Parenting style, personality traits, and interpersonal relationships: A model of prediction of internet addiction. Int. J. Commun. U. S. 2020, 14, 2163–2185. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, W.E.; Johnson, J.L. Time use efficiency and the five-factor model of personality. Education 2005, 125, 511–515. [Google Scholar]
- Butter, R.; Born, M.P. Enhancing criterion-related validity through bottom-up contextualization of personality inventories: The construction of an ecological conscientiousness scale for Ph. D. candidates. Hum. Perform. 2012, 25, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Ho, R.T.H.; Chan, C.L.W.; Tse, S. Exploring personality characteristics of Chinese adolescents with internet-related addictive behaviors: Trait differences for gaming addiction and social networking addiction. Addict. Behav. 2015, 42, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittek, C.T.; Finserås, T.R.; Pallesen, S.; Mentzoni, R.A.; Hanss, D.; Griffiths, M.D.; Molde, H. Prevalence and predictors of video game addiction: A study based on a national representative sample of gamers. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2016, 14, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boers, E.; Afzali, M.H.; Newton, N.; Conrod, P. Association of screen time and depression in adolescence. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Du, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, F.; Huang, B.; Zhang, M.; Xie, J. Intrinsic motivation, favorability, time management, and achievement: A cross-lagged panel analysis. Learn. Motiv. 2020, 72, 101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, C.A.; Won, S.; Hussain, M. Examining the relations of time management and procrastination within a model of self-regulated learning. Metacognition Learn. 2017, 12, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.T.; Zhang, Z.J. The compiling of adolescence time management disposition inventory. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2001, 4, 338–3438. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, S.S.; An, L. The measurement of college students’ time management tendency and its relationship to culture orientation. Psychol. Sci. 2011, 4, 894–898. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Sun, L.; Feng, K. The mediating effect of college students’ time management tendency on the relation between fatigue and test anxiety. China J. Health Psychol. 2018, 12, 1867–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, V. A study of time management: The correlation between video game usage and academic performance markers. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2007, 10, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, S.I.; Lee, J.Z.; Huang, D.H. Video game addiction in children and teenagers in Taiwan. J. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2004, 7, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.T. Problems with the concept of video game “addiction”: Some case study examples. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2008, 6, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, D.; Hu, J.; Zhen, S.; Yu, C.; Li, B.; Chang, X.; Zhang, W. Dimensions of emotional intelligence and online gaming addiction in adolescence: The indirect effects of two facets of perceived stress. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malatras, J.W.; Israel, A.C.; Sokolowski, K.L.; Ryan, J. First things first: Family activities and routines, time management and attention. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2016, 47, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Shirley, L.Y. Relations of perceived parental autonomy support and control with adolescents’ academic time management and procrastination. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2018, 61, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysan, M.; Kiral, E. Associations between procrastination, personality, perfectionism, self-esteem and locus of control. Br. J. Guid. Couns. 2017, 45, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.S. Factors related to Taiwanese adolescents’ academic procrastination, time management, and perfectionism. J. Educ. Res. 2017, 110, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. Predicting adolescent problematic online game use from teacher autonomy support, basic psychological needs satisfaction, and school engagement: A 2-year longitudinal study. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2015, 18, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D. Pathological video-game use among youth ages 8 to 18: A national study. Psychol. Sci. 2009, 20, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Lu, Z.R.; Jiang, B.J.; Xu, Y. Preliminary revision of the Chinese version of the parenting style questionnaire. Xīn Lǐ Fā Zhǎn Yǔ Jiāo Yù 2010, 1, 94–99. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y. Parenting Styles, Effortful Control, and Academic Outcomes among Chinese Adolescents: The Mediating Effect of Activation Control. Master’s Thesis, Syracuse University, New York, NY, USA, August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Lynch, J.G., Jr.; Chen, Q. Reconsidering baron and kenny: Myths and truths about mediation analysis. J. Consum. Res. 2010, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cheung, H.Y.; Fan, X.; Wu, J. Factors related to resilience of academically gifted students in the Chinese cultural and educational environment. Psychol. Sch. 2018, 55, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Scrimin, S.; Moscardino, U. Perceived parental guan and school adjustment among Chinese early adolescents: The moderating role of interdependent self-construal. J. Adolesc. 2019, 71, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedini, Y.; Zamani, B.E.; Kheradmand, A.; Rajabizadeh, G. Impacts of mothers’ occupation status and parenting styles on levels of self-control, addiction to computer games, and educational progress of adolescents. Addict. Health 2012, 4, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Květon, P.; Jelínek, M. Parenting styles and their relation to videogame addiction. Int. J. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 2016, 10, 1961–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgur, H. Online game addiction among Turkish adolescents: The effect of internet parenting style. Malays. Online J. Educ. Technol. 2019, 7, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi Payam, A.; Mirzaeidoostan, Z. Online game addiction relationship with cognitive distortion, parenting style, and narcissistic personality traits in students. Iran. J. Psychiatry Clin. Psychol. 2019, 25, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Miao, N.F.; Chen, P.H.; Lee, C.M.; Chiang, J.T.; Pan, Y.C. The relationship between parental mediation and internet addiction among adolescents, and the association with cyberbullying and depression. Compr. Psychiatry 2015, 57, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Research on the correlation between college students’ time management tendency and their parenting style. Hēi Lóng Jiāng Gāo Jiāo Yán Jiù 2017, 1, 43–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.L.; Jiang, X.Y. Relationship between internet addiction and time management tendency of college students. Zhōng Guó Gōng Gòng Wèi Shēng 2011, 27, 764–765. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y. Effects of time management on college students’ mobile phone addiction. Adv. Psychol. 2019, 9, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, C.S.; Griffiths, M.D.; Gjertsen, S.R.; Krossbakken, E.; Kvam, S.; Pallesen, S. The relationships between behavioral addictions and the five-factor model of personality. J. Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Xia, M.; Jiang, G.R.; Wei, H. Self-esteem and internet game addiction-the mediating role of self-control. Zhōng Guó Lín Chuáng Xīn Lǐ Xué 2012, 20, 58–60. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R.A. A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological internet use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2001, 17, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Methodology in the Social Sciences. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
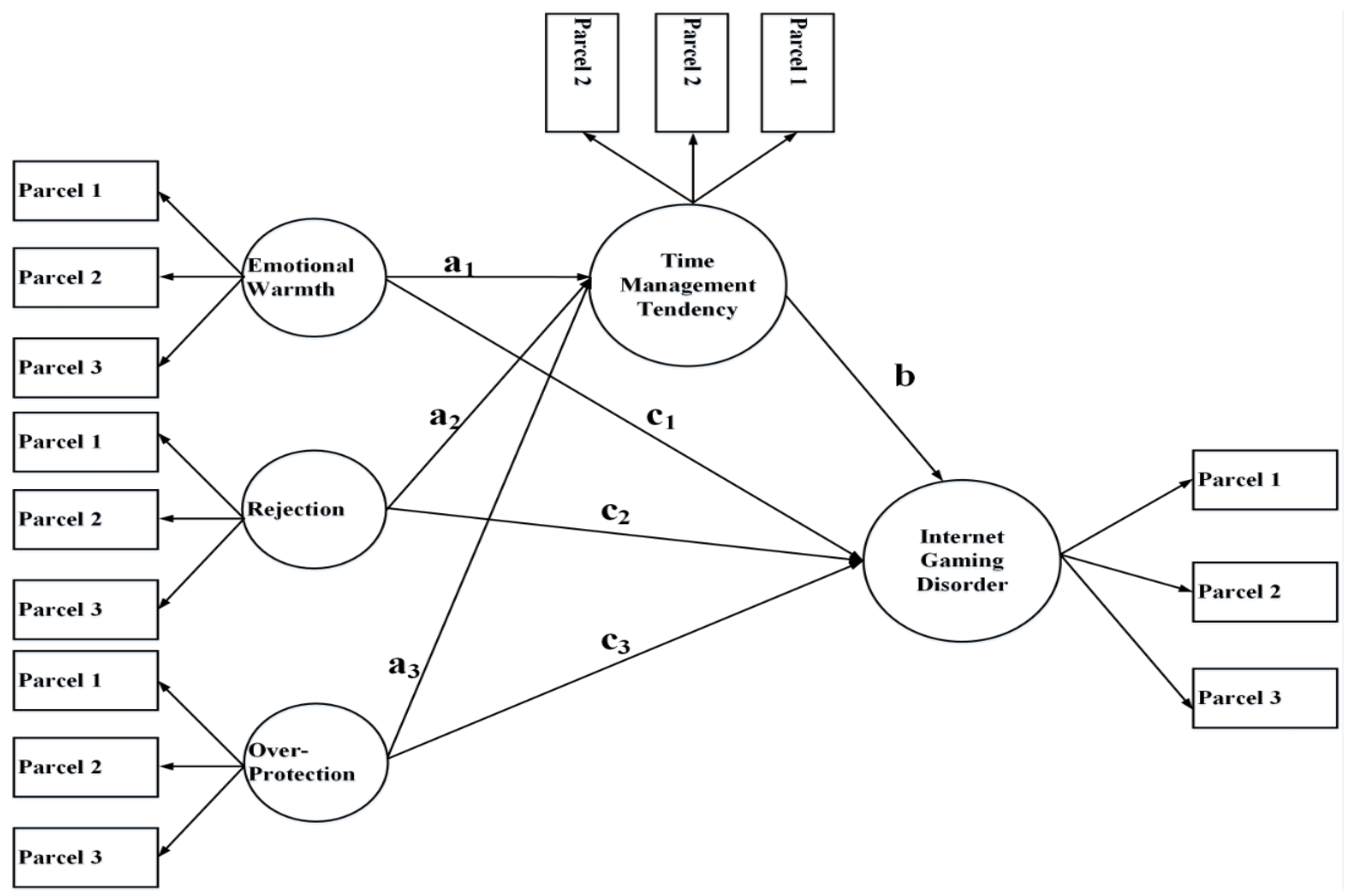
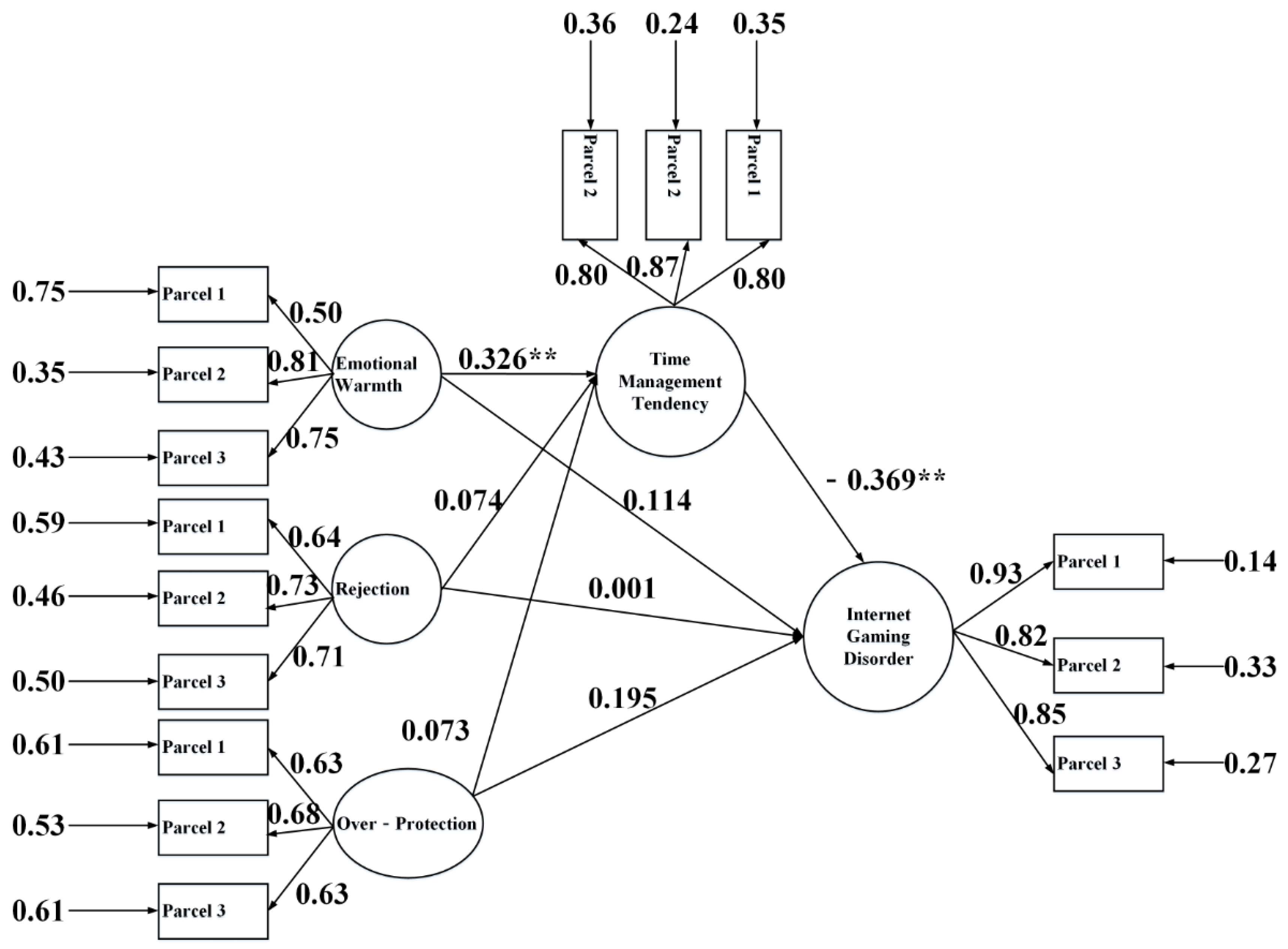
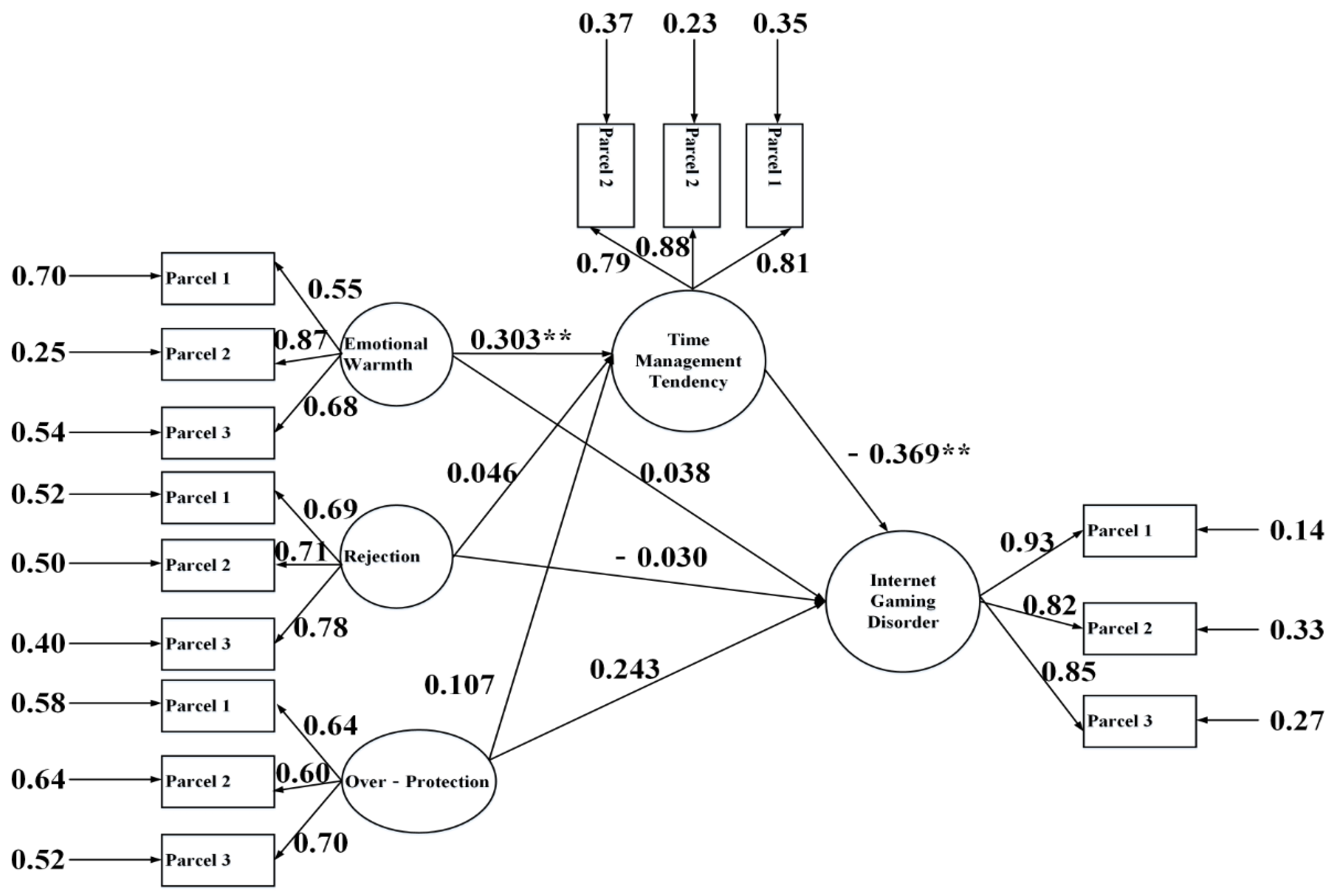
| Variables | M ± SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.41 ± 0.41 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Fathers’ parenting style | ||||||||
| 2.63 ± 0.57 | −0.030 * | 1.00 | |||||
| 3.50 ± 0.51 | 0.173 * | −0.337 * | 1.00 | ||||
| 2.99 ± 0.47 | 0.208 * | −0.034 * | 0.460 * | 1.00 | |||
| Mothers’ parenting style | ||||||||
| 2.72 ± 0.58 | −0.018 * | 0.726 * | −0.154 * | −0.015 * | 1 | ||
| 3.42 ± 0.56 | 0.116 * | −0.151 * | 0.590 * | 0.379 * | −0.187 * | 1 | |
| 2.84 ± 0.49 | 0.154 * | −0.054 * | 0.355 * | 0.725 * | −0.137 * | 0.504 * | 1 |
| 3.28 ± 0.56 | −0.248 * | 0.243 * | −0.065 * | −0.084 * | 0.223 * | −0.013 * | −0.119 * |
| Demographic Variable | Addicts (n = 44) | Non-Addicts (n = 313) | χ2 (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | |||
| Boys (n = 157) | 32 (20.39%) | 125 (79.61%) | 16.84 (p < 0.01) ** |
| Girls (n = 200) | 12 (6.00%) | 188 (94.00%) | |
| Grade | |||
| 10th (n = 286) | 36 (12.58%) | 250 (87.41%) | 0.09 (p = 0.76) |
| 11th (n = 71) | 8 (11.27%) | 63 (88.73%) | |
| Lives in school dormitory | |||
| Yes (n = 253) | 33 (13.04%) | 220 (86.96%) | 0.42 (p = 0.52) |
| No (n = 104) | 11 (10.58%) | 93 (89.42%) |
| Fit Index | Fathers | Mothers |
|---|---|---|
| χ2 (df) | 364.138 (110) | 356.764 (110) |
| CFI | 0.913 | 0.920 |
| NNFI | 0.896 | 0.899 |
| IFI | 0.914 | 0.921 |
| RMSEA (90% CI) | 0.081 (0.071–0.089) | 0.079 (0.070–0.088) |
| SRMR | 0.064 | 0.067 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, I.-H.; Lee, Z.-H.; Dong, X.-Y.; Gamble, J.H.; Feng, H.-W. The Influence of Parenting Style and Time Management Tendency on Internet Gaming Disorder among Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239120
Chen I-H, Lee Z-H, Dong X-Y, Gamble JH, Feng H-W. The Influence of Parenting Style and Time Management Tendency on Internet Gaming Disorder among Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):9120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239120
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, I-Hua, Zeng-Han Lee, Xiao-Yu Dong, Jeffrey Hugh Gamble, and Hung-Wei Feng. 2020. "The Influence of Parenting Style and Time Management Tendency on Internet Gaming Disorder among Adolescents" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 9120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239120
APA StyleChen, I.-H., Lee, Z.-H., Dong, X.-Y., Gamble, J. H., & Feng, H.-W. (2020). The Influence of Parenting Style and Time Management Tendency on Internet Gaming Disorder among Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 9120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239120







