Evaluation of Priming Efficiency of Forskolin in Tissue-Specific Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Dopaminergic Neurons: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Culture: Revival and Expansion of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BM-MSC), Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (AD-MSC) and Dental Pulp-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (DP-MSC)
2.2. Neuronal Differentiation
2.3. Neurites’ Length Analysis
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Transcriptional Characterization of MSC Induced into Neuronal Cells: Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.7. Immunocytochemistry
2.8. Intracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry
2.9. Immunoblotting
2.10. Dopamine Release Estimation by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.11. Calcium Ion Imaging
2.12. Data Interpretation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dose and Duration Titration of FGF2 and Forskolin to Obtain Desired Neuronal Differentiation Effect Upon Inducing hMSCs
3.2. Change in the Cellular Morphology of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Was Observed upon Treatment with FGF2 and Forskolin
3.3. Forskolin Leads to Increase in the Neurites’ Length, Axonal Development, Appearance of Distinct Nucleus and Marked Change in the Morphology of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
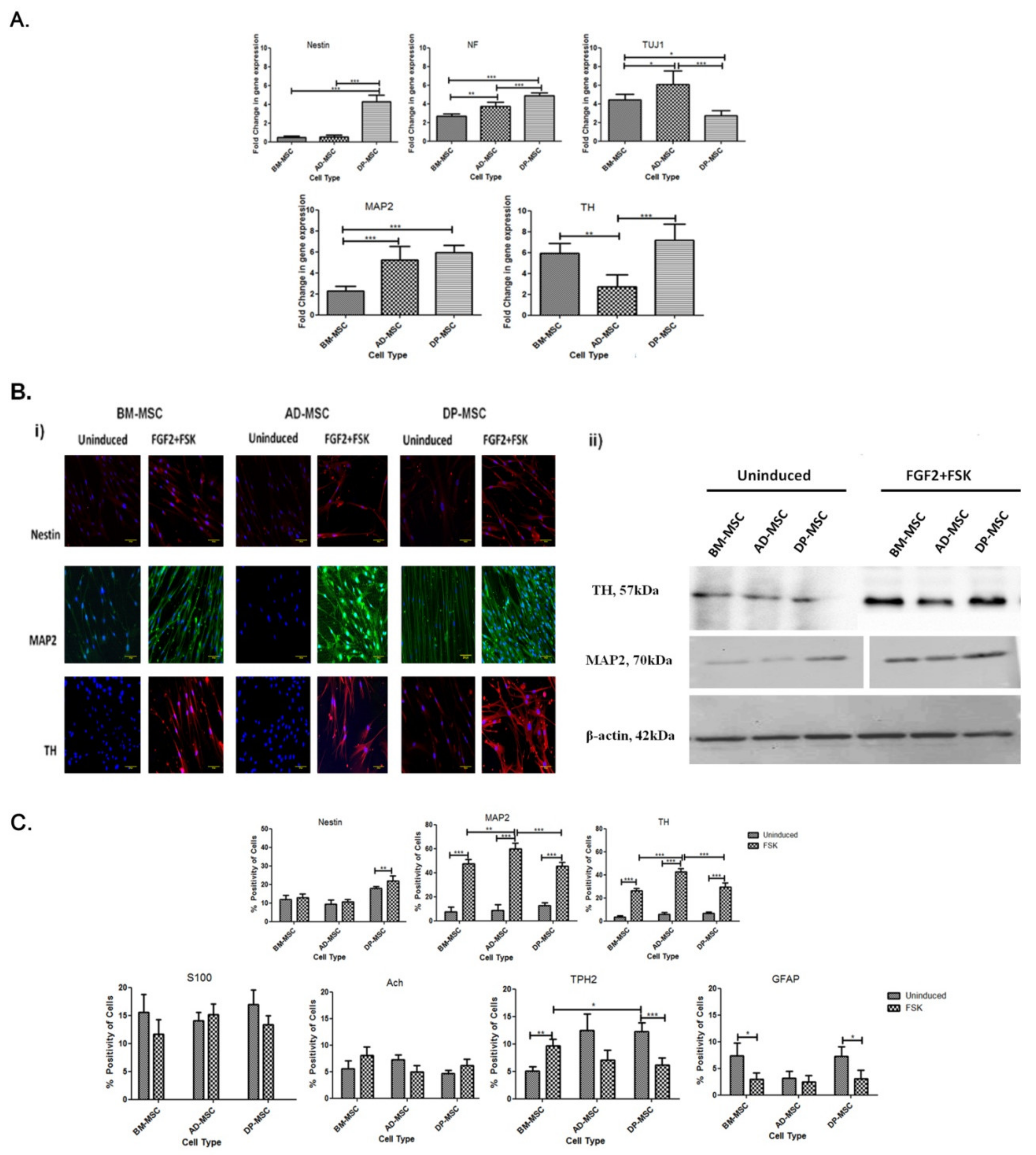
3.4. Treatment of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells with FGF2 and Forskolin Is Marked by an Increased Expression of Neuronal and DAergic Neuronal Genes
3.5. An Upsurge in the Expression of Proteins Followed the Upregulation of Neuronal and DAergic Neuronal Genes
3.6. Flow Cytometric Enumeration Reveals an Increase in the Percentage of Cells Positive for Neuronal and Dopaminergic Neuronal Proteins Post-Differentiation hMSCs
3.7. Infinitesimal Percentage of Cells Positive for Non-Dopaminergic Markers Were Observed Post-Induction
3.8. Increase in the Genes and Proteins Expression, Responsible for Functionality of Neuronal and Dopaminergic Neuronal Cells
3.8.1. mRNA Expression of Transcription Factors Responsible for Survival and Maintenance of DAergic Neuronal Cells
3.8.2. FSK Improves Functional Dopaminergic Specifications at Both Gene and Protein Level
3.8.3. Neuronal Differentiation Led to Changes in the Cells at Ultra-Structural Level
3.9. Induced Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Release Higher Concentration of Dopamine in the Medium
3.10. Significantly Higher Change in the Calcium Ion Efflux Was Observed in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Post-Induction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seamon, K.B.; Padgett, W.; Daly, J.W. Forskolin: Unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 3363–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.L.; Zang, T.; Zou, Y.; Chang, J.C.; Gibson, J.R.; Huber, K.M.; Zhang, C.L. Small molecules enable neurogenin 2 to efficiently convert human fibroblasts into cholinergic neurons. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fimia, G.M.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Cyclic AMP signalling. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 1971–1972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Ji, Z.; Tsalkova, T.; Mei, F. Epac and PKA: A tale of two intracellular cAMP receptors. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2008, 40, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taran, R.; Mamidi, M.K.; Singh, G.; Dutta, S.; Parhar, I.S.; John, J.P.; Bhonde, R.; Pal, R.; Das, A.K. In vitro and in vivo neurogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from different sources. J. Biosci. 2014, 39, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Discher, D.E.; Péault, B.M.; Phinney, D.G.; Hare, J.M.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: Cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen. Med. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rendra, E.; Scaccia, E.; Bieback, K. Recent advances in understanding mesenchymal stromal cells. F1000Research 2020, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgaz, S.; Kuçi, Z.; Kuçi, S.; Bönig, H.; Bader, P. Clinical Use of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in the Treatment of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2019, 46, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.S.; Bahat-Stroomza, M.; Barzilay, R.; Burshtein, A.; Bulvik, S.; Barhum, Y.; Panet, H.; Melamed, E.; Offen, D. Regenerative effect of neural-induced human mesenchymal stromal cells in rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Cytotherapy 2008, 10, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, G.E.; Howard, L.; O’Brien, T.; Windebank, A.J.; Barry, F.P. Elevation of cAMP in mesenchymal stem cells transiently upregulates neural markers rather than inducing neural differentiation. Stem Cells Dev. 2009, 18, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedenstein, A.J.; Piatetzky, S., II; Petrakova, K.V. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1966, 16, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedenstein, A.J.; Petrakova, K.V.; Kurolesova, A.I.; Frolova, G.P. Heterotopic of bone marrow: Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation 1968, 6, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedenstein, A.J.; Chailakhjan, R.K.; Lalykina, K.S. The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1970, 3, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedvika, D.; Xiufang, G.; Stephen, L.; Maria, S.; James, J.H. Small molecule induction of human umbilical stem cells into myelin basic protein positive oligodendrocytes in a defined three-dimensional environment. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 3, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sujeong, J.; Hyong-Ho, C.; Yong-Bum, C.; Jong-Seong, P.; Han- Seong, J. Functional neural differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells using bFGF and forskolin. BMC Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Kakkar, A.; Sharma, R.; Kharbanda, O.P.; Monga, N.; Kumar, M.; Chowdhary, S.; Airan, B.; Mohanty, S. Synergistic Effect of BDNF and FGF2 in Efficient Generation of Functional Dopaminergic Neurons from human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, K.G.; Mohanty, S.; Ray, A.R.; Malhotra, R.; Airan, B. Culture & differentiation of mesenchymal stem cell into osteoblast on degradable biomedical composite scaffold: In vitro study. Indian J. Med. Res. 2015, 142, 747–758. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, S.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, N.; Singh, H.; Roychoudhury, A.; Mohanty, S.; Sen, S.; Nag, T.C.; Tandon, R. Molecular characterization of explant cultured human oral mucosal epithelial cells. IOVS 2011, 52, 9548–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunghoi, H.; Sangmi, C.; Kaka, L.; Insik, H.; Jisook, M.; Kwang-Soo, K. Functional Roles of Nurr1, Pitx3, and Lmx1a in Neurogenesis and Phenotype Specification of Dopamine Neurons During In Vitro Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 23, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agostini, M.; Romeo, F.; Inoue, S.; Niklison-Chirou, M.V.; Elia, A.J.; Dinsdale, D.; Morone, N.; Knight, R.A.; Mak, T.W.; Melino, G. Metabolic reprogramming during neuronal differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1502–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malosio, M.L.; Giordano, T.; Laslop, A.; Meldolesi, J. Dense-core granules: A specific hallmark of the neuronal/neurosecretory cell phenotype. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yumei, W.; Christina, W.C.; Shan, X.; Hayworth, J.; Kenneth, W.; Richard, J.; Hess, F.; Harald, F.; Camilli, P.D. Contacts between the endoplasmic reticulum and other membranes in neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4859–E4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Compagnucci, C.; Piemonte, F.; Sferra, A.; Piermarini, E.; Bertini, E. The cytoskeletal arrangements necessary to neurogenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patton, R.G.; Simons, K.; Dotti, C.G. Axonal and Dendritic Endocytic Pathways in Cultured Neurons. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 119, 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hass, R.; Kasper, C.; Böhm, S.; Jacobs, R. Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): A comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2011, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giai Via, A.; Frizziero, A.; Oliva, F. Biological properties of mesenchymal Stem Cells from different sources. Musclesligaments Tendons J. 2012, 2, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ledesma-Martínez, E.; Mendoza-Núñez, V.M.; Santiago-Osorio, E. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Dental Pulp: A Review. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 4709572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paldino, E.; Cenciarelli, C.; Giampaolo, A.; Milazzo, L.; Pescatori, M.; Hassan, H.J.; Casalbore, P. Induction of dopaminergic neurons from human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell by forskolin. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, A.; Safa, M.; Alikaram, F.; Kargozar, S.; Asadi, H.M.; Joghataei, T.; Soleimani, M. Rapid Induction of Neural Differentiation in Human Umbilical Cord Matrix Mesenchymal Stem Cells by cAMP-elevating Agents. Int. J. Mol. Cell Med. Summer 2016, 5, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Tio, M.; Kia, H.W.; Wendy, L.; Wang, T.T.; Udolph, G. Roles of db-cAMP, IBMX and RA in aspects of neural differentiation of cord blood derived mesenchymal like stem cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trzaska, K.A.; King, C.C.; Li, K.Y.; Kuzhikandathil, E.V.; Nowycky, M.C.; Ye, J.H.; Rameshwar, P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor facilitates maturation of mesenchymal stem cell-derived dopamine progenitors to functional neurons. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzaska, K.A.; Kuzhikandathil, E.V.; Rameshwar, P. Specification of a dopaminergic phenotype from adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.; Casali, C.; Chan, C. Forskolin and IBMX Induce Neural Transdifferentiation of MSCs Through Down regulation of the NRSF. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachetti, P.; Sousa, K.M.; Hall, A.C.; Liste, I.; Steffensen, K.R.; Theofilopoulos, S.; Parish, C.L.; Hazenberg, C.; Richter, L.A.; Hovatt, O.A.; et al. Liver X Receptors and oxysterols promote ventral midbrain neurogenesis in vivo and in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nandy, B.S.; Mohanty, S.; Singh, M.; Behari, M.; Airan, B. Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 alone as an efficient inducer for differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into dopaminergic neurons. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Chang, K.C.; Tsai, S.J.; Chang, H.H.; Lin, C.P. Neurogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells to neuron-like cells in dopaminergic and motor neuronal inductive media. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briolay, A.; Lencel, P.; Bessueille, L.; Caverzasio, J.; Buchet, R.; Magne, D. Autocrine stimulation of osteoblast activity by Wnt5a in response to TNF-alpha in human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Song, G.S.; Jung, J.S. Increase in proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor cells isolated from postnatal and adult mice brain by Wnt-3a and Wnt-5a. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 288, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farías, G.G.; Alfaro, I.E.; Cerpa, W.; Grabowski, C.P.; Godoy, J.A.; Bonansco, C.; Inestrosa, N.C. Wnt-5a/JNK signalling promotes the clustering of PSD-95 in hippocampal neurons. JBC 2009, 284, 15857–15866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nusse, R. Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosso, S.B.; Inestrosa, N.C. WNT signalling in neuronal maturation and synaptogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W. Wnt/β-catenin signalling regulates neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Razanau, A.; Feng, D.; Lobo, V.G.; Xie, J. Control of alternative splicing by forskolin through hnRNP K during neuronal differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 8059–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, M.; Vaishnav, P.K.; Dinda, A.K.; Mohanty, S. Evaluation of Priming Efficiency of Forskolin in Tissue-Specific Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Dopaminergic Neurons: An In Vitro Comparative Study. Cells 2020, 9, 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092058
Singh M, Vaishnav PK, Dinda AK, Mohanty S. Evaluation of Priming Efficiency of Forskolin in Tissue-Specific Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Dopaminergic Neurons: An In Vitro Comparative Study. Cells. 2020; 9(9):2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092058
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Manisha, Pardeep Kumar Vaishnav, Amit Kumar Dinda, and Sujata Mohanty. 2020. "Evaluation of Priming Efficiency of Forskolin in Tissue-Specific Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Dopaminergic Neurons: An In Vitro Comparative Study" Cells 9, no. 9: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092058
APA StyleSingh, M., Vaishnav, P. K., Dinda, A. K., & Mohanty, S. (2020). Evaluation of Priming Efficiency of Forskolin in Tissue-Specific Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Dopaminergic Neurons: An In Vitro Comparative Study. Cells, 9(9), 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092058




