Identification and Expression Analysis of Cold Shock Protein 3 (BcCSP3) in Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Material and Stresses
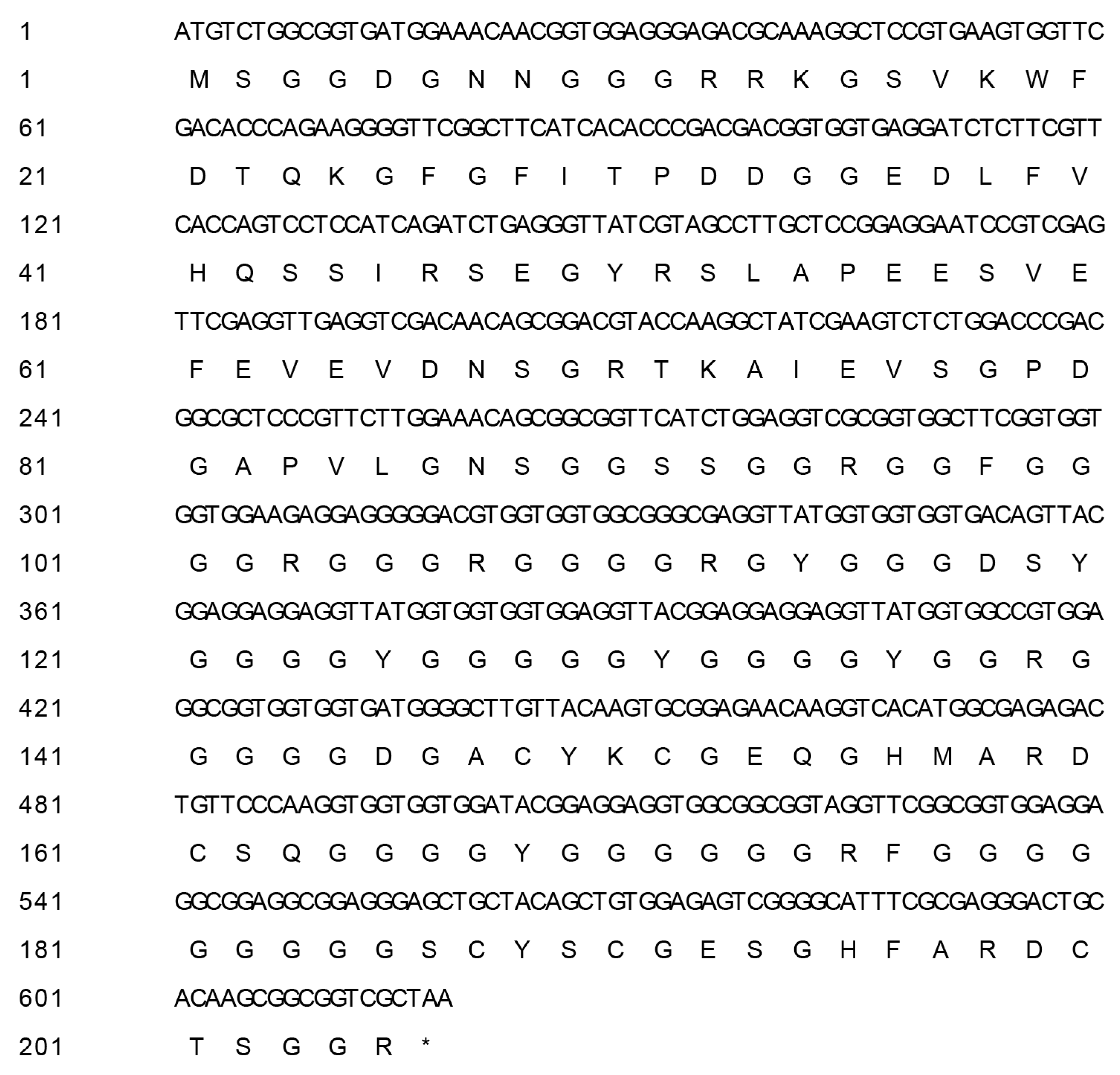
2.2. Identification and Isolation of BcCSP3
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis of BcCSP3 Protein
2.4. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree
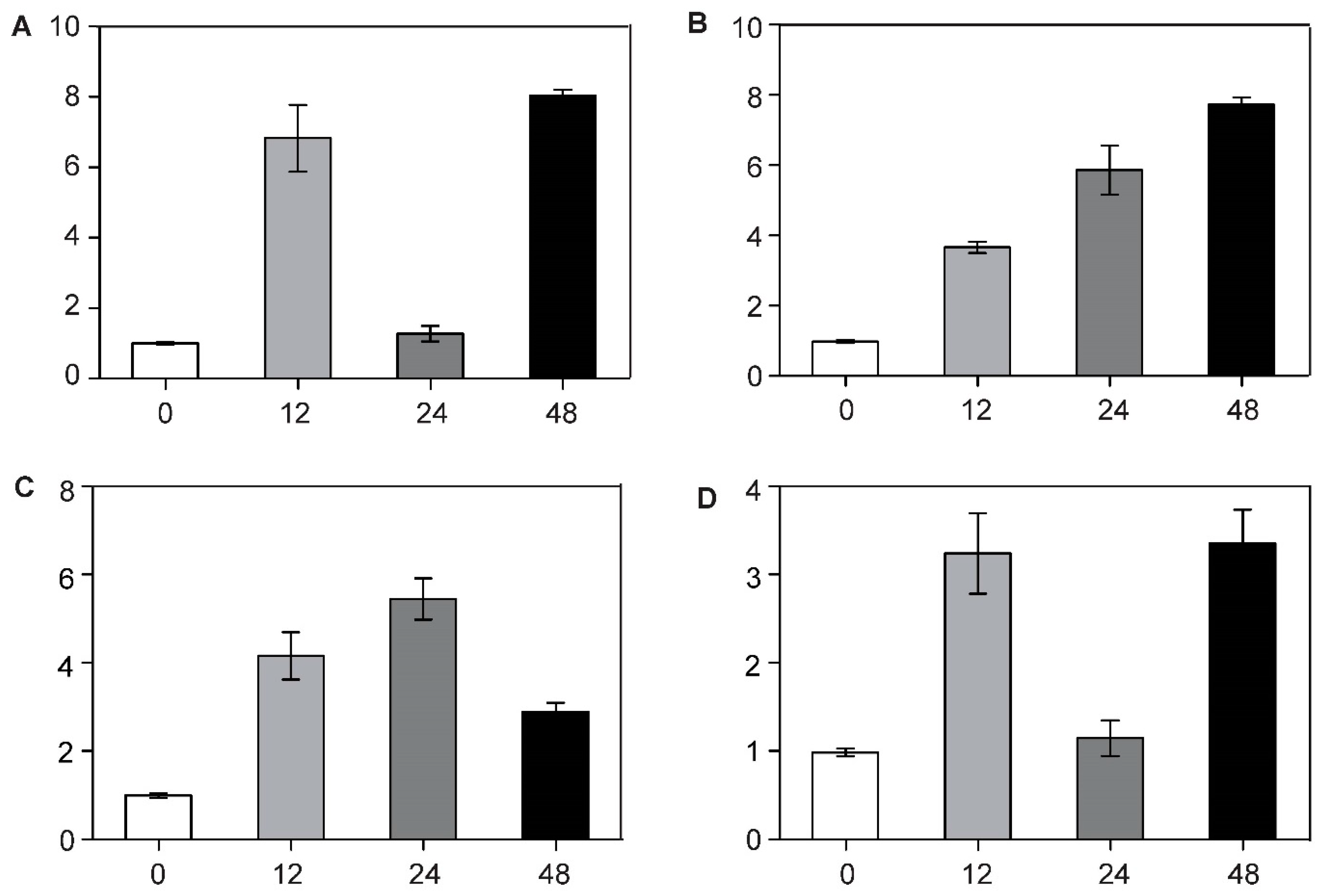
2.5. Analysis of BcCSP3 under Stress Treatments
2.6. Subcellular Localization of BcCSP3 Protein
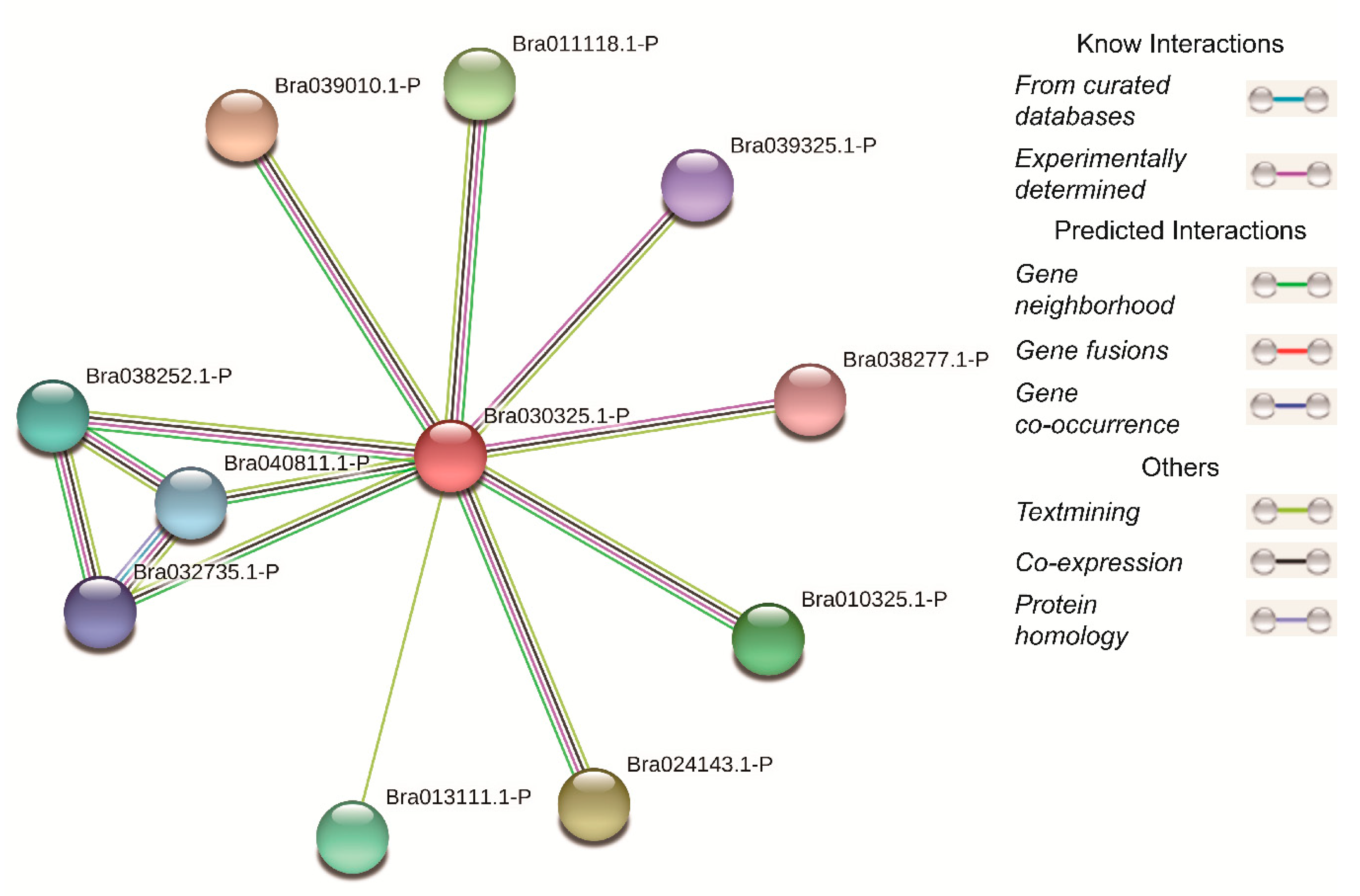
2.7. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Cloning of BcCSP3
3.2. Analysis of Proteins
3.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. BcCSP3 Expression Pattern under Various Abiotic Stresses
3.5. Subcellular Localization Analysis
3.6. Protein–Protein Interaction Network
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Jansen, P.; Westphal, E.; Siemonsma, J.; Piluek, K. Plant Resources of South-East Asia 8; Vegetables. Pudoc: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, F.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Hu, J.; Hou, X. Components of the Arabidopsis CBF cold-response pathway are conserved in non-heading Chinese cabbage. Plant Mol. Biol. Report 2011, 29, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; Qi, L.; Guo, H.; Li, J.; Yang, S. PIF3 is a negative regulator of the CBF pathway and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6695–E6702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.R.; Hodges, H.F.; McKinion, J.M. A comparison of scenarios for the effect of global climate change on cotton growth and yield. Funct. Plant Biol. 1997, 24, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.; Patterson, B.D. Responses of plants to low, nonfreezing temperatures: Proteins, metabolism, and acclimation. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1982, 33, 347–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.K. Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, D.; Imai, R. Conservation of the cold shock domain protein family in plants. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Imai, R. Pleiotropic roles of cold shock domain proteins in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 2, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, D.; Nakaminami, K.; Toyomasu, T.; Imai, R. A cold-regulated nucleic acid-binding protein of winter wheat shares a domain with bacterial cold shock proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35248–35256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaminami, K.; Sasaki, K.; Kajita, S.; Takeda, H.; Karlson, D.; Ohgi, K.; Imai, R. Heat stable ssDNA/RNA-binding activity of a wheat cold shock domain protein. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 4887–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaminami, K.; Karlson, D.T.; Imai, R. Functional conservation of cold shock domains in bacteria and higher plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10122–10127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Park, S.J.; Kwak, K.J.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, J.Y.; Song, J.; Jang, B.; Jung, C.H.; Kang, H. Cold shock domain proteins and glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana can promote the cold adaptation process in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 35, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Sasaki, K.; Imai, R. Cold shock domain protein 3 regulates freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23454–23460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Kim, M.H.; Imai, R. Arabidopsis cold shock domain protein 2 is a negative regulator of cold acclimation. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, A.F.; Bocca, S.N.; Ramos, R.L.B.; Barrôco, R.M.; Magioli, C.; Jorge, V.C.; Coutinho, T.C.; Rangel-Lima, C.M.; De Rycke, R.; Inzé, D.; et al. AtGRP2, a cold-induced nucleo-cytoplasmic RNA-binding protein, has a role in flower and seed development. Planta 2007, 225, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kwak, K.J.; Oh, T.R.; Kim, Y.O.; Kang, H. Cold shock domain proteins affect seed germination and growth of Arabidopsis thaliana under abiotic stress conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Xiong, A.; Hou, X. Characterization and co-expression analysis of WRKY orthologs involved in responses to multiple abiotic stresses in Pak-choi (Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis). BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Hou, X. Identification, evolution and functional inference on the cold-shock domain protein family in Pak-choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis) and Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). J. Plant Interact. 2019, 14, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geourjon, C.; Deleage, G. SOPMA: Significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Bioinformatics 1995, 11, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteros, J.J.A.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Sønderby, C.K.; Petersen, T.N.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, K. TMbase-A database of membrane spanning proteins segments. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1993, 374, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D. ProtScale Tool: Amino acid scale: Refractivity. J. Theor. Biol 1975, 50, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Higgins, D.G. Multiple sequence alignment using ClustalW and ClustalX. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2003, 1, 2.3.1–2.3.22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, K.; Van Poucke, M.; Van Soom, A.; Vandesompele, J.; Van Zeveren, A.; Peelman, L.J. Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in bovine preimplantation embryos. BMC Dev. Biol. 2005, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhu, W.; Yu, K.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H. Predicting protein-protein interactions based only on sequences information. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4337–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, Z. Functional features, biological pathways, and protein interaction networks of addiction-related genes. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graumann, P.L.; Marahiel, M.A. A superfamily of proteins that contain the cold-shock domain. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Sato, S.; Sasaki, K.; Saburi, W.; Matsui, H.; Imai, R. Cold shock domain protein 3 is involved in salt and drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. FEBS Open Biol. 2013, 3, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juntawong, P.; Sorenson, R.; Bailey-Serres, J. Cold shock protein 1 chaperones mRNA s during translation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2013, 74, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Protein Name | ORF (bp) | Amino Acid | WM (kDa) | pI | GRAVY | Instability Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BcCSP3 | 618 | 205 | 19.39 | 5.92 | −0.764 | 59.39 |
| AtCSP1 | 900 | 299 | 30.09 | 8.18 | −0.687 | 33.62 |
| AtCSP2 | 612 | 203 | 19.15 | 5.62 | −0.790 | 55.39 |
| AtCSP3 | 906 | 301 | 29.56 | 7.41 | −0.521 | 53.95 |
| AtCSP4 | 606 | 201 | 19.08 | 6.29 | −0.693 | 63.08 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, F.; Wang, J.; Duan, W.; Hou, X. Identification and Expression Analysis of Cold Shock Protein 3 (BcCSP3) in Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis). Plants 2020, 9, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070890
Huang F, Wang J, Duan W, Hou X. Identification and Expression Analysis of Cold Shock Protein 3 (BcCSP3) in Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis). Plants. 2020; 9(7):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070890
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Feiyi, Jin Wang, Weike Duan, and Xilin Hou. 2020. "Identification and Expression Analysis of Cold Shock Protein 3 (BcCSP3) in Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis)" Plants 9, no. 7: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070890
APA StyleHuang, F., Wang, J., Duan, W., & Hou, X. (2020). Identification and Expression Analysis of Cold Shock Protein 3 (BcCSP3) in Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis). Plants, 9(7), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070890





