Contribution of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1 (CRF1) to Serotonin Receptor 5-HT2CR Function in Amygdala Neurons in a Neuropathic Pain Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
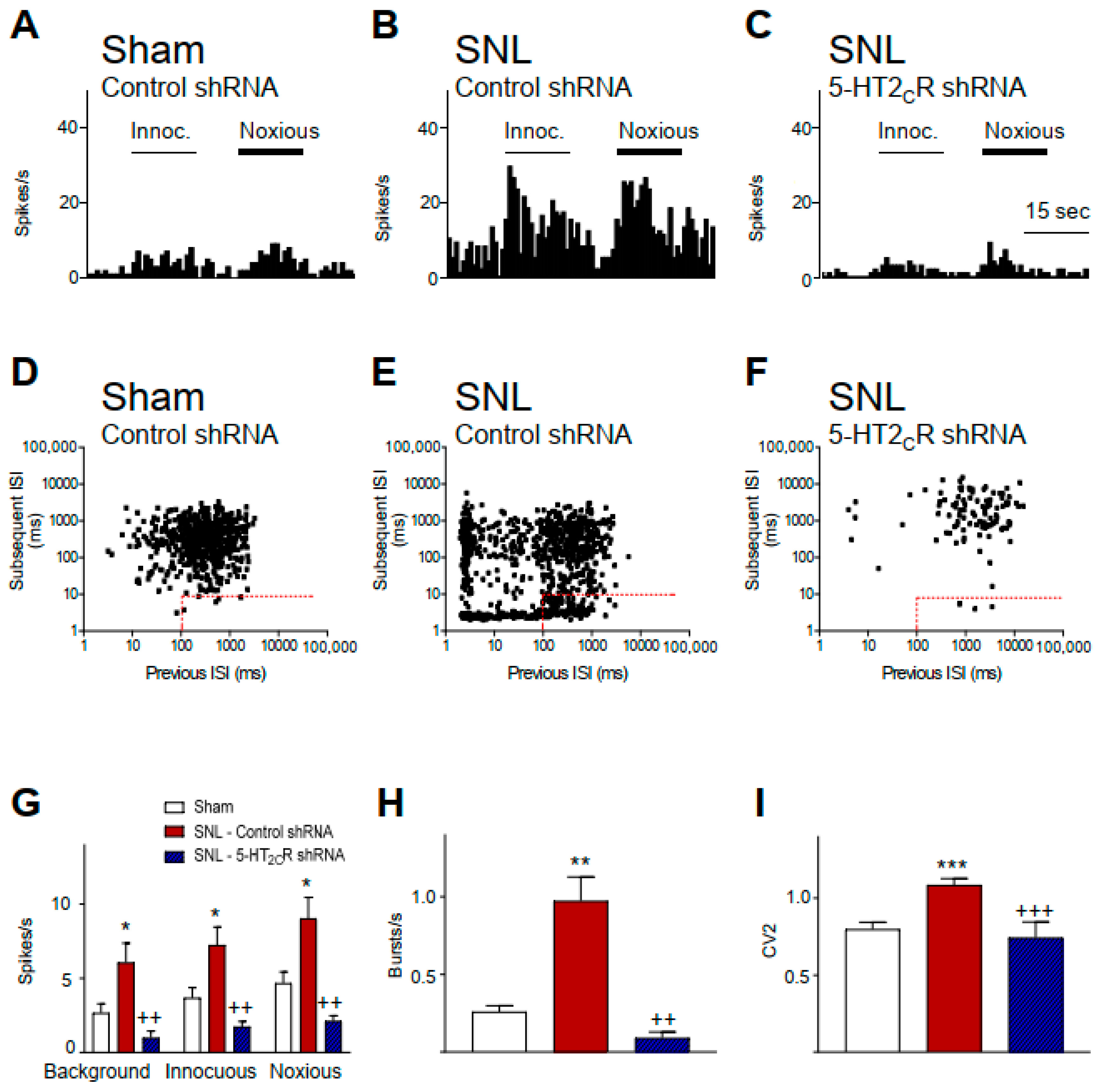
2.1. 5-HT2CR Knockdown in the BLA Inhibits Activity of CeA Neurons in Neuropathic Rats
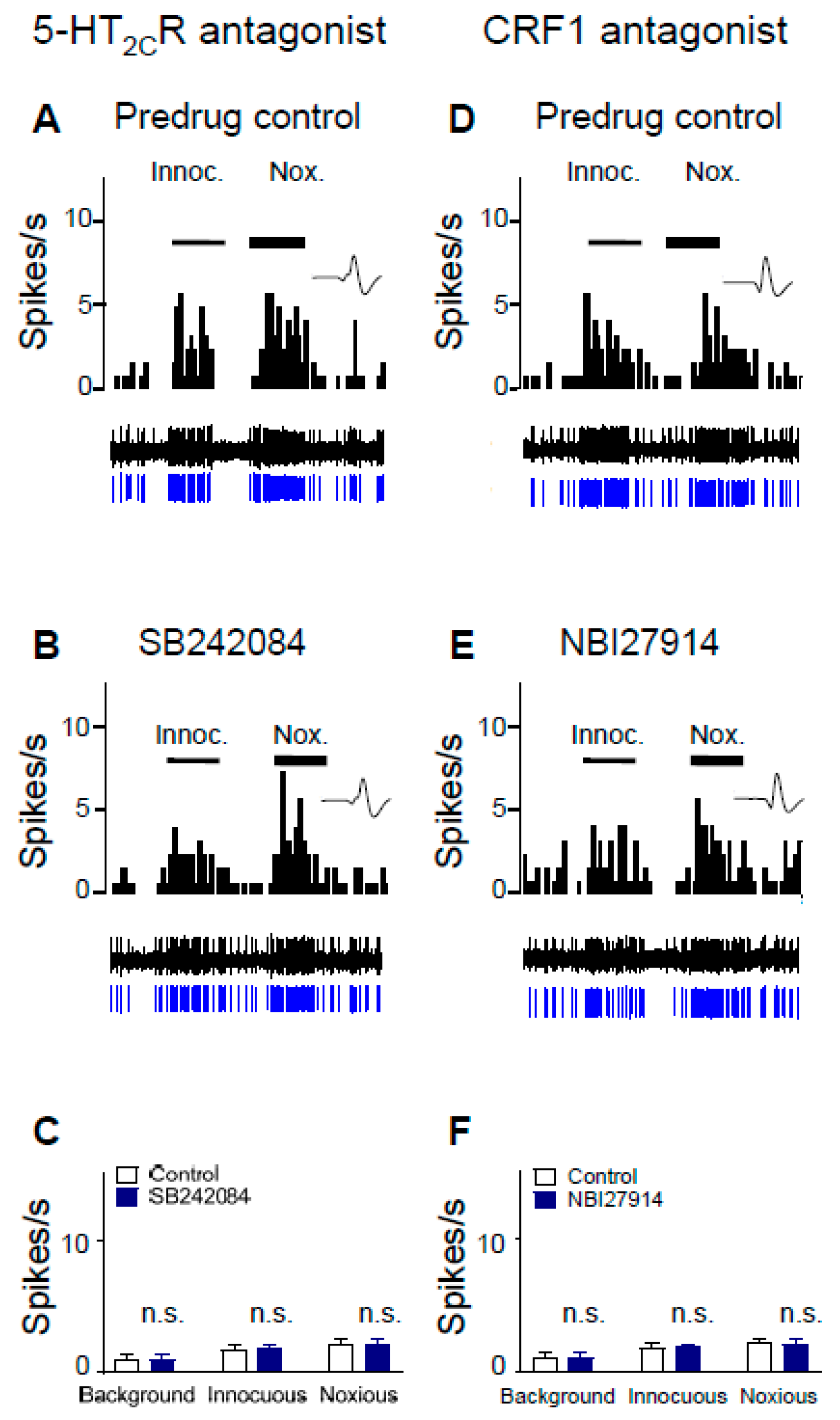
2.2. Inhibitory Effects of Antagonists for 5-HT2CR and CRF1 Receptor on CeA Neurons in Neuropathic Rats
2.3. 5-HT2CR Knockdown Eliminates the Inhibitory Effects of Antagonists for 5-HT2CR and CRF1 Receptor on CeA Neurons in Neuropathic Rats
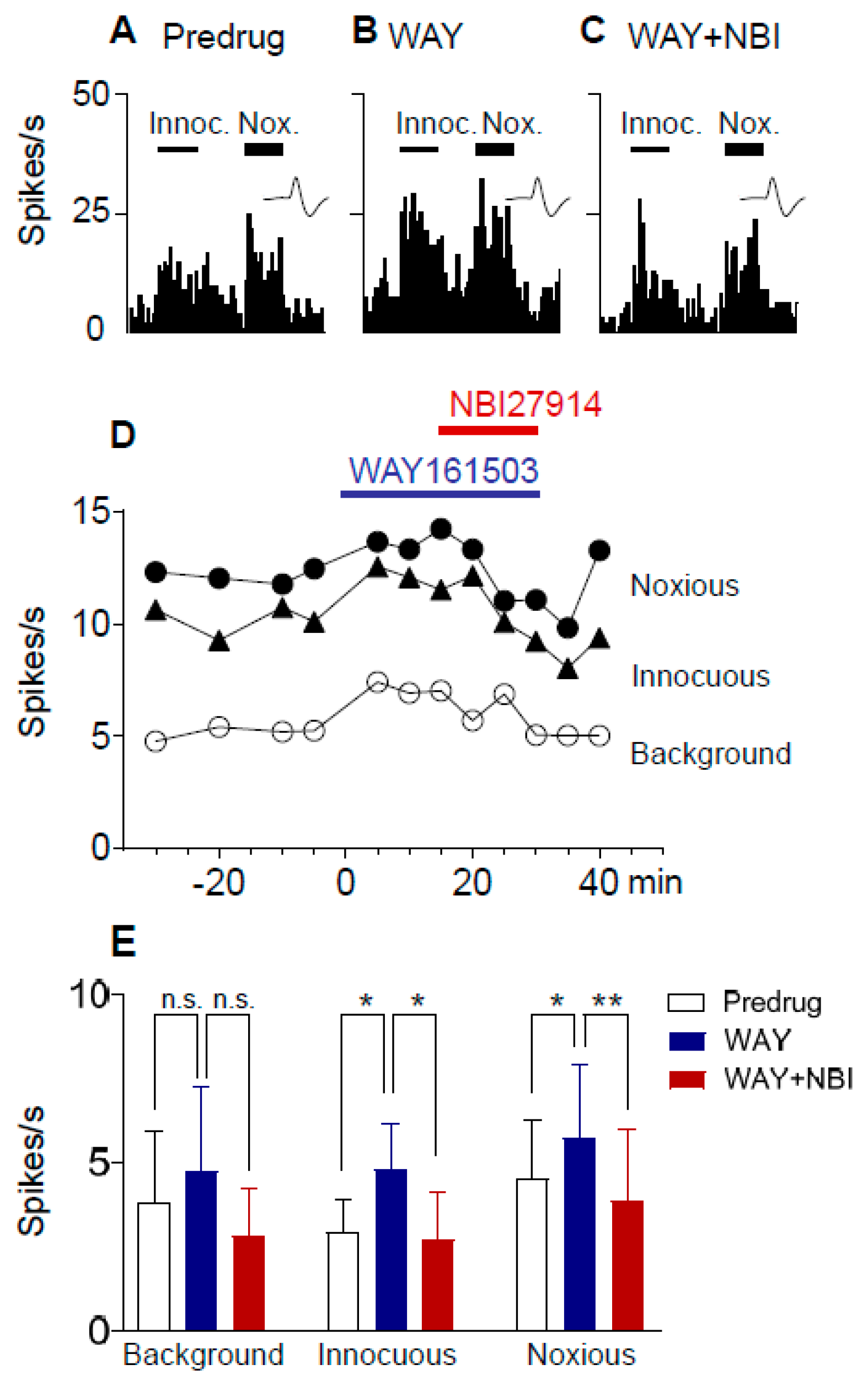
2.4. Excitatory Effects of a 5-HT2CR Agonist (WAY161503) Are Blocked by a CRF1 Receptor Antagonist (NBI27914) in Neuropathic Rats
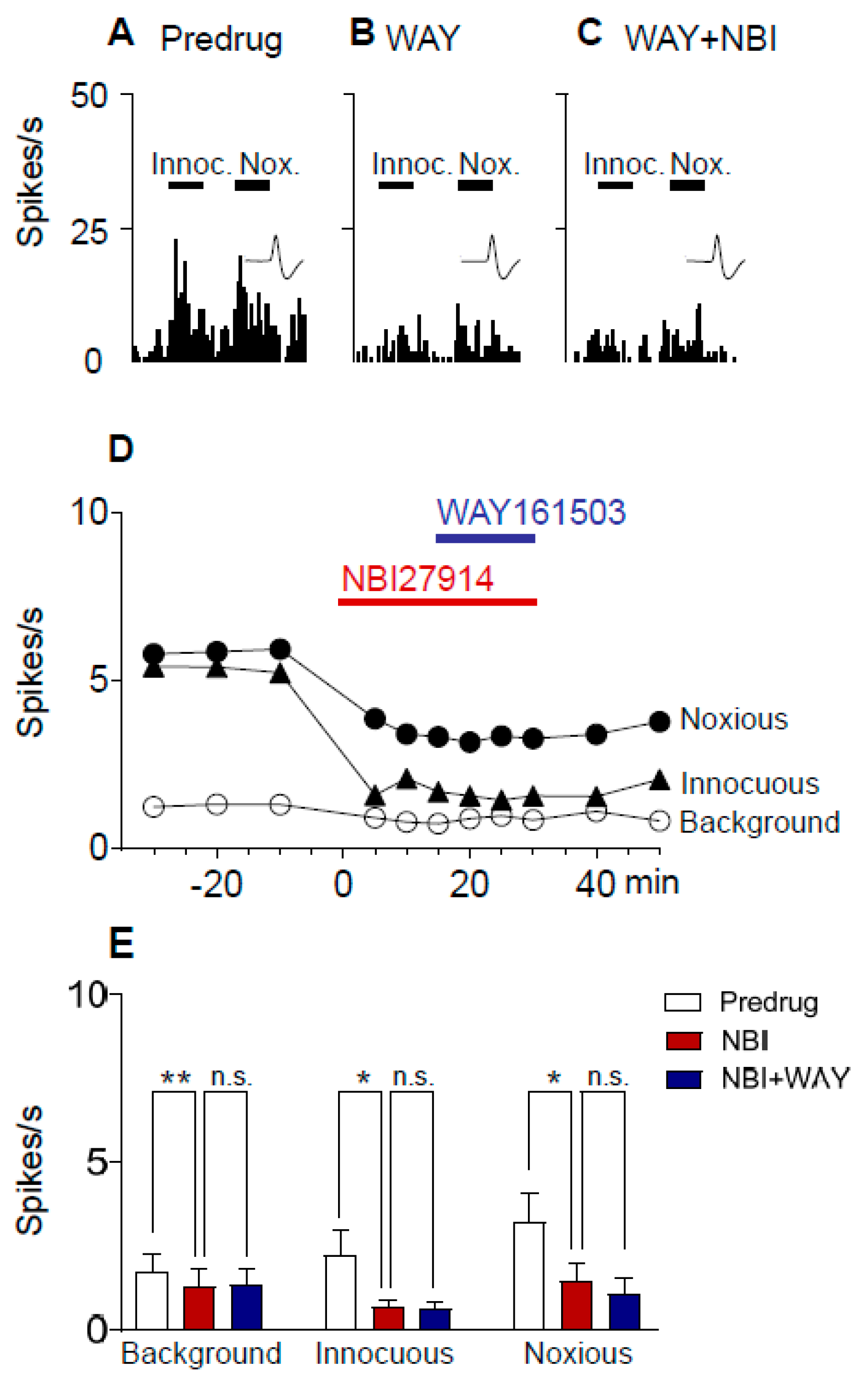
2.5. Excitatory Effects of a 5-HT2CR Agonist (WAY161503) Are Prevented by a CRF1 Receptor Antagonist (NBI27914) in Neuropathic Rats
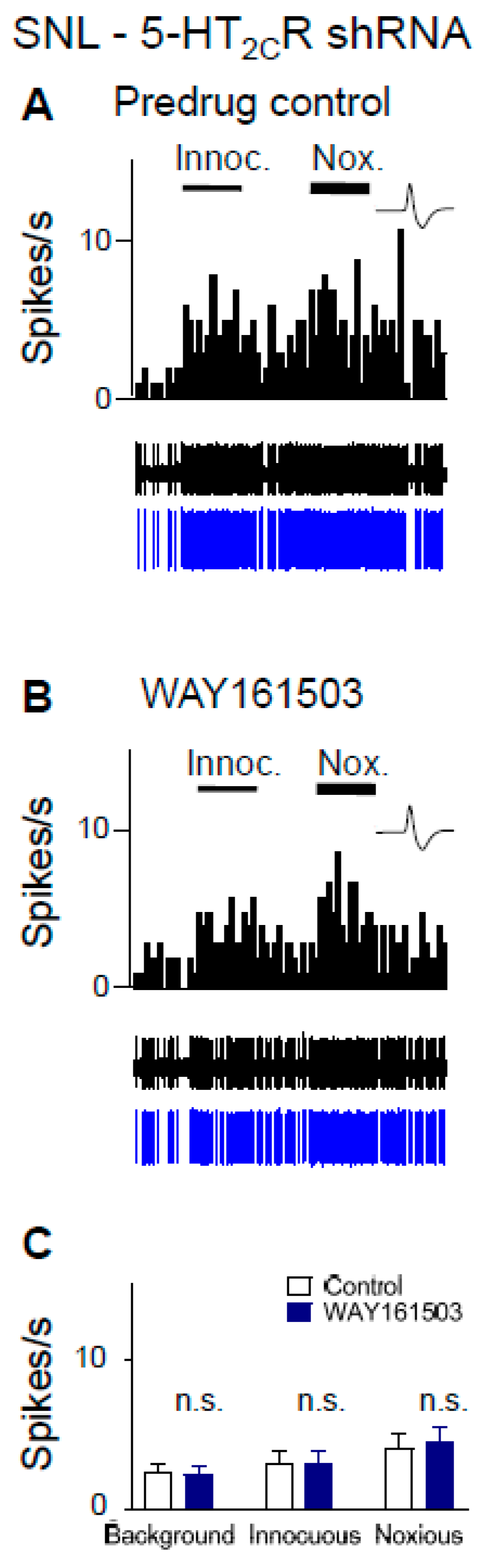
2.6. Excitatory Effects of a 5-HT2CR Agonist (WAY161503) Are Eliminated by 5-HT2CR Knockdown in Neuropathic Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Neuropathic Pain Model
4.3. Viral Vector for 5-HT2CR Knockdown
4.4. Systems Electrophysiology
4.5. Neuronal Activity Analysis
4.6. Drugs and Drug Application by Microdialysis
4.7. Verification of Recording Site
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heinricher, M.M.; Tavares, I.; Leith, J.L.; Lumb, B.M. Descending control of nociception: Specificity, recruitment and plasticity. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossipov, M.H.; Dussor, G.O.; Porreca, F. Central modulation of pain. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, C. Is serotonin hyperalgesic or analgesic? Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2006, 10, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Rygh, L.J.; Dickenson, A.H. Bad news from the brain: Descending 5-HT pathways that control spinal pain processing. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bockaert, J.; Claeysen, S.; Bécamel, C.; Dumuis, A.; Marin, P. Neuronal 5-HT metabotropic receptors: Fine-tuning of their structure, signaling, and roles in synaptic modulation. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 326, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannon, J.; Hoyer, D. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Serotonin Sleep Mol. Funct. Clin. Asp. 2008, 195, 155–182. [Google Scholar]
- Millán, M.; Marin, P.; Bockaert, J.; Mannourylacour, C. Signaling at G-protein-coupled serotonin receptors: Recent advances and future research directions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, R.H.; O’Connor, A.B.; Audette, J.; Baron, R.; Gourlay, G.K.; Haanpää, M.L.; Kent, J.L.; Krane, E.J.; Lebel, A.A.; Levy, R.M.; et al. Recommendations for the Pharmacological Management of Neuropathic Pain: An Overview and Literature Update. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnerup, N.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S. Pharmacotherapy for Neuropathic Pain in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 62, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Chen, P.P. A review of SSRIs and SNRIs in neuropathic pain. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 2813–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoletano, F.; Lionetto, L.; Martelletti, P. Sumatriptan in clinical practice: Effectiveness in migraine and the problem of psychiatric comorbidity. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2014, 15, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negro, A.; Koverech, A.; Martelletti, P. Serotonin receptor agonists in the acute treatment of migraine: A review on their therapeutic potential. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, N.H.; Cremers, T.I.; Sotty, F. Therapeutic Potential of 5-HT2C Receptor Ligands. Sci. World J. 2010, 10, 1870–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasch-Andersen, C.; Møller, M.U.; Christiansen, L.; Thinggaard, M.; Otto, M.; Brosen, K.; Sindrup, S.H. A candidate gene study of serotonergic pathway genes and pain relief during treatment with escitalopram in patients with neuropathic pain shows significant association to serotonin receptor2C (HTR2C). Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, M.A.; Zangrossi, H. Involvement of 5-HT2C and 5-HT1A receptors of the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala in the anxiolytic effect of chronic antidepressant treatment. Neuropharmacology 2014, 79, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelps, E.A.; LeDoux, J.E. Contributions of the Amygdala to Emotion Processing: From Animal Models to Human Behavior. Neuron 2005, 48, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemett, D.A.; Punhani, T.; Duxon, M.S.; Blackburn, T.P.; Fone, K.C. Immunohistochemical localisation of the 5-HT2C receptor protein in the rat CNS. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeiano, M.; Palacios, J.; Mengod, G. Distribution of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptor family mRNAs: Comparison between 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. Mol. Brain Res. 1994, 23, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchio, M.; McHugh, S.B.; Bannerman, D.M.; Sharp, T.; Capogna, M. Serotonin, Amygdala and Fear: Assembling the Puzzle. Front. Neural Circuits 2016, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Yin, G.; Ai, M.; Han, J. Serotonergic projections from the nucleus raphe dorsalis to the amygdala in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1991, 134, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, J.P.; Ragole, T.; Amat, J.; Greenwood, B.N.; Strong, P.V.; Paul, E.D.; Fleshner, M.; Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F. 5-hydroxytryptamine 2C receptors in the basolateral amygdala are involved in the expression of anxiety after uncontrollable traumatic stress. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funada, M.; Hara, C. Differential effects of psychological stress on activation of the 5-hydroxytryptamine- and dopamine-containing neurons in the brain of freely moving rats. Brain Res. 2001, 901, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, C.E.; Martinez, R.C.R.; Silva, M.A.D.S.; Brandão, M.L. Increases in extracellular levels of 5-HT and dopamine in the basolateral, but not in the central, nucleus of amygdala induced by aversive stimulation of the inferior colliculus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Stevenson, P.L.; Carter, R.N.; MacColl, G.; French, K.L.; Simons, J.P.; Al-Shawi, R.; Kelly, V.; Chapman, K.E.; Holmes, M.C. Overexpression of 5-HT2C receptors in forebrain leads to elevated anxiety and hypoactivity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 30, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Luo, T.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J. Anxiolytic effects of 5-HT1A receptors and anxiogenic effects of 5-HT2C receptors in the amygdala of mice. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisler, L.K.; Zhou, L.; Bajwa, P.; Hsu, J.; Tecott, L.H. Serotonin 5-HT(2C) receptors regulate anxiety-like behavior. Genes Brain Behav. 2007, 6, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.M.; Merchant, K.M. Serotonin 2C receptors within the basolateral amygdala induce acute fear-like responses in an open-field environment. Brain Res. 2003, 993, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, M.A.; Zangrossi, H. Serotonin-2C receptors in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala mediate the anxiogenic effect of acute imipramine and fluoxetine administration. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012, 15, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mello Cruz, A.P.; Pinheiro, G.; Alves, S.H.; Ferreira, G.; Mendes, M.; Faria, L.; Macedo, C.E.; Motta, V.; Landeira-Fernandez, J. Behavioral effects of systemically administered MK-212 are prevented by ritanserin microinfusion into the basolateral amygdala of rats exposed to the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology 2005, 182, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, V. Amygdala pain mechanisms. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 227, 261–284. [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer, V.; Li, W.; Bird, G.C.; Han, J.S. The amygdala and persistent pain. Neuroscientist 2004, 10, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.M.; Neugebauer, V. Amygdala Plasticity and Pain. Pain Res. Manag. 2017, 2017, 8296501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedoyin, M.O.; Vicini, S.; Neale, J.H. Endogenous N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) inhibits synaptic plasticity/transmission in the amygdala in a mouse inflammatory pain model. Mol. Pain 2010, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, G.C.; Lash, L.L.; Han, J.S.; Zou, X.; Willis, W.D.; Neugebauer, V. Protein kinase A-dependent enhanced NMDA receptor function in pain-related synaptic plasticity in rat amygdala neurones. J. Physiol. 2005, 564, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.J.; Chen, C.C.; Yang, H.W.; Chang, Y.T.; Bai, S.W.; Chen, C.C.; Yen, C.T.; Min, M.Y. Role of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase in Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity of a Nociceptive Input on Capsular Central Amygdaloid Neurons in Normal and Acid-Induced Muscle Pain Mice. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 2258–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Neugebauer, V. Differential mechanisms of CRF1 and CRF2 receptor functions in the amygdala in pain-related synaptic facilitation and behavior. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3861–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.S.; Li, W.; Neugebauer, V. Critical Role of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide 1 Receptors in the Amygdala in Synaptic Plasticity and Pain Behavior. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10717–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Li, Z.; Neugebauer, V. Reactive oxygen species mediate visceral pain–related amygdala plasticity and behaviors. Pain 2015, 156, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugebauer, V.; Li, W.; Bird, G.C.; Bhave, G.; Gereau, R.W. Synaptic Plasticity in the Amygdala in a Model of Arthritic Pain: Differential Roles of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors 1 and 5. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Kiritoshi, T.; Gregoire, S.; Ji, G.; Guerrini, R.; Calo, G.; Neugebauer, V. Neuropeptide S: A novel regulator of pain-related amygdala plasticity and behaviors. J. Neurophysiol. 2013, 110, 1765–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shinohara, K.; Watabe, A.M.; Nagase, M.; Okutsu, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Kurihara, H.; Kato, F. Essential role of endogenous calcitonin gene-related peptide in pain-associated plasticity in the central amygdala. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 2149–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimura, Y.K.; Takahashi, Y.; Watabe, A.M.; Kato, F. Synaptic and network consequences of monosynaptic nociceptive inputs of parabrachial nucleus origin in the central amygdala. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 115, 2721–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, L.; Silva, R.; Pinto-Ribeiro, F.; Pêgo, J.M.; Bessa, J.M.; Pertovaara, A.; Sousa, N.; Almeida, A. Neuropathic pain is associated with depressive behaviour and induces neuroplasticity in the amygdala of the rat. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 213, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, R.; Takahashi, Y.; Inoue, K.; Kato, F. NMDA receptor-independent synaptic plasticity in the central amygdala in the rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 2007, 127, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Zhang, W.; Mahimainathan, L.; Narasimhan, M.; Kiritoshi, T.; Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Green, T.A.; Neugebauer, V. 5-HT2C Receptor Knockdown in the Amygdala Inhibits Neuropathic-Pain-Related Plasticity and Behaviors. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 1378–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Nagase, M.; Ikeda, R.; Kato, F. Role of capsaicin-sensitive C-fiber afferents in neuropathic pain-induced synaptic potentiation in the nociceptive amygdala. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, L.; Dickenson, A.H. Asymmetric time-dependent activation of right central amygdala neurones in rats with peripheral neuropathy and pregabalin modulation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 36, 3204–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Neugebauer, V. Differential Effects of CRF1 and CRF2 Receptor Antagonists on Pain-Related Sensitization of Neurons in the Central Nucleus of the Amygdala. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 3893–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Neugebauer, V. Hemispheric Lateralization of Pain Processing by Amygdala Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 102, 2253–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Neugebauer, V. Reactive Oxygen Species Are Involved in Group I mGluR-Mediated Facilitation of Nociceptive Processing in Amygdala Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 104, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, W.; Neugebauer, V. Block of NMDA and non-NMDA receptor activation results in reduced background and evoked activity of central amygdala neurons in a model of arthritic pain. Pain 2004, 110, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Neugebauer, V. Differential Roles of mGluR1 and mGluR5 in Brief and Prolonged Nociceptive Processing in Central Amygdala Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 91, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Neugebauer, V. Differential Changes of Group II and Group III mGluR Function in Central Amygdala Neurons in a Model of Arthritic Pain. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, G.; Ji, G.; Grégoire, S.; Neugebauer, V. Nasal Application of Neuropeptide S Inhibits Arthritis Pain-Related Behaviors through an Action in the Amygdala. Mol. Pain 2014, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, V.; Li, W. Differential Sensitization of Amygdala Neurons to Afferent Inputs in a Model of Arthritic Pain. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 89, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Sun, H.; Fu, Y.; Li, Z.; Pais-Vieira, M.; Galhardo, V.; Neugebauer, V. Cognitive impairment in pain through amygdala-driven prefrontal cortical deactivation. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Hough, C.; Li, H. Serotonin type II receptor activation facilitates synaptic plasticity via n-methyl-d-aspartate-mediated mechanism in the rat basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience 2003, 119, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Bocchio, M.; Bannerman, D.M.; Sharp, T.; Capogna, M. Control of Amygdala Circuits by 5-HT Neurons via 5-HT and Glutamate Cotransmission. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.D.; O’Flaherty, B.M.; Rainnie, D.G. Serotonin gating of cortical and thalamic glutamate inputs onto principal neurons of the basolateral amygdala. Neuropharmacology 2017, 126, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainnie, D.G. Serotonergic Modulation of Neurotransmission in the Rat Basolateral Amygdala. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 82, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, S.; Neugebauer, V. 5-HT2CR blockade in the amygdala conveys analgesic efficacy to SSRIs in a rat model of arthritis pain. Mol. Pain 2013, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugebauer, V.; Li, W. Processing of Nociceptive Mechanical and Thermal Information in Central Amygdala Neurons with Knee-Joint Input. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasio, N.C.; Stutz, S.J.; Fink, L.H.; Swinford-Jackson, S.E.; Sears, R.M.; DiLeone, R.J.; Rice, K.C.; Moeller, F.G.; Cunningham, K.A. Serotonin (5-HT) 5-HT2A Receptor (5-HT2AR):5-HT2CR Imbalance in Medial Prefrontal Cortex Associates with Motor Impulsivity. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasio, N.C.; Stutz, S.J.; Fox, R.G.; Sears, R.M.; Emeson, R.B.; DiLeone, R.J.; O’Neil, R.T.; Fink, L.H.; Li, D.; Green, T.A.; et al. Functional status of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor (5-HT2CR) drives interlocked phenotypes that precipitate relapse-like behaviors in cocaine dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, E.A.; Wild, C.T.; Cunningham, K.A.; Zhou, J. Targeting the 5-HT2C Receptor in Biological Context and the Current State of 5-HT2C Receptor Ligand Development. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant’Ana, A.B.; Vilela-Costa, H.H.; Vicente, M.A.; Hernandes, P.M.; De Andrade, T.G.C.S.; Zangrossi, H. Role of 5-HT2C receptors of the dorsal hippocampus in the modulation of anxiety- and panic-related defensive responses in rats. Neuropharmacology 2019, 148, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asan, E.; Yilmazer-Hanke, D.; Eliava, M.; Hantsch, M.; Lesch, K.P.; Schmitt, A. The Corticotropin-Releasing Factor (CRF)-system and monoaminergic afferents in the central amygdala: Investigations in different mouse strains and comparison with the rat. Neuroscience 2005, 131, 953–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, T.L.; Vale, W.W. CRF and CRF receptors: Role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 525–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, T.S. Amygdaloid CRF Pathways: Role in Autonomic, Neuroendocrine, and Behavioral Responses to Stress. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 697, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomrenze, M.B.; Millan, E.Z.; Hopf, F.W.; Keiflin, R.; Maiya, R.; Blasio, A.; Dadgar, J.; Kharazia, V.; De Guglielmo, G.; Crawford, E.; et al. A Transgenic Rat for Investigating the Anatomy and Function of Corticotrophin Releasing Factor Circuits. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, J.M.; Holsboer, F. Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors 1 and 2 in anxiety and depression. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2002, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Brunson, K.L.; Cariaga, W.; Baram, T.Z.; Müller, M.B. Immunocytochemical distribution of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type-1 (CRF1)-like immunoreactivity in the mouse brain: Light microscopy analysis using an antibody directed against the C-terminus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 420, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Johnson, A.C.; Schulkin, J.; Myers, D.A. Long-term expression of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in response to an acute colonic inflammation. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lariviere, W.R.; Melzack, R. The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in pain and analgesia. Pain 2000, 84, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, G.; Akil, H.; McNally, G. Role of corticotropin-releasing hormone in the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the behavioral, pain modulatory, and endocrine consequences of opiate withdrawal. Neuroscience 2002, 112, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinniger, V.; Porcher, C.; Mouchet, P.; Juhem, A.; Bonaz, B. c-fos and CRF receptor gene transcription in the brain of acetic acid-induced somato-visceral pain in rats. Pain 2004, 110, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Xie, W.; Meij, J.T.; Dolgas, C.M.; Yu, L.; Herman, J.P. Limbic and HPA axis function in an animal model of chronic neuropathic pain. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 88, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, S.P.; Cauli, B.; Cabezas, C.; Muzerelle, A.; Poncer, J.C.; Gaspar, P. Multiscale single-cell analysis reveals unique phenotypes of raphe 5-HT neurons projecting to the forebrain. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 4007–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.F.; Mascagni, F.; McDonald, A.J. Serotonin-immunoreactive axon terminals innervate pyramidal cells and interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 505, 314–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, A.; Descarries, L.; Beaudet, A. Organization of ascending serotonin systems in the adult rat brain. A radioautographic study after intraventricular administration of [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuroscience 1981, 6, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pockros-Burgess, L.A.; Pentkowski, N.S.; Der-Ghazarian, T.; Neisewander, J.L. Effects of the 5-HT2C receptor agonist CP809101 in the amygdala on reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior and anxiety-like behavior. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, P.R.; Fox, M.A.; Jensen, C.L.; Laporte, J.L.; French, H.T.; Wendland, J.R.; Murphy, D.L. Altered 5-HT2C receptor agonist-induced responses and 5-HT2C receptor RNA editing in the amygdala of serotonin transporter knockout mice. BMC Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, G.; Ahanonu, B.; Grewe, B.F.; Wang, D.; Schnitzer, M.J.; Scherrer, G. An amygdalar neural ensemble that encodes the unpleasantness of pain. Science 2019, 363, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veinante, P.; Yalcin, I.; Barrot, M. The amygdala between sensation and affect: A role in pain. J. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmin, L.; Rabkin, S.D.; Granato, A.; Boudah, A.; Ohara, P.T. Analgesia and hyperalgesia from GABA-mediated modulation of the cerebral cortex. Nature 2003, 424, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinricher, M.M.; McGaraughty, S. Microinjection of morphine into various amygdaloid nuclei differentially affects nociceptive responsiveness and RVM neuronal activity. Diabetes Nerv. Syst. 2002, 96, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.; Fu, Y.; Adwanikar, H.; Neugebauer, V. Non-pain-related CRF1 activation in the amygdala facilitates synaptic transmission and pain responses. Mol. Pain 2013, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Neugebauer, V. Pro- and Anti-Nociceptive Effects of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor (CRF) in Central Amygdala Neurons Are Mediated Through Different Receptors. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 99, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.J.; Chung, J.M.; Honore, M.; Seltzer, Z. Models of Neuropathic Pain in the Rat. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2003, 9, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.; Yakhnitsa, V.; Kiritoshi, T.; Presto, P.; Neugebauer, V. Fear extinction learning ability predicts neuropathic pain behaviors and amygdala activity in male rats. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918804441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Fu, Y.; Ruppert, K.A.; Neugebauer, V. Pain-related anxiety-like behavior requires CRF1 receptors in the amygdala. Mol. Pain 2007, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neugebauer, V.; Fu, Y.; Ji, G.; Galhardo, V. CRF1 receptors in the basolateral amygdala contribute to pain-related decision-making deficits. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 2007, 37, 723-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, K.A.; Fox, R.G.; Anastasio, N.C.; Bubar, M.J.; Stutz, S.J.; Moeller, F.G.; Gilbertson, S.R.; Rosenzweig-Lipson, S. Selective serotonin 5-HT2C receptor activation suppresses the reinforcing efficacy of cocaine and sucrose but differentially affects the incentive-salience value of cocaine- vs. sucrose-associated cues. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, P.J.; Tampakeras, M.; Sinyard, J.; Slassi, A.; Isaac, M.; Higgins, G.A. Characterizing the effects of 5-HT2C receptor ligands on motor activity and feeding behaviour in 5-HT2C receptor knockout mice. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentkowski, N.S.; Duke, F.D.; Weber, S.M.; APockros, L.; Teer, A.P.; Hamilton, E.C.; Thiel, K.J.; Neisewander, J.L. Stimulation of Medial Prefrontal Cortex Serotonin 2C (5-HT2C) Receptors Attenuates Cocaine-Seeking Behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, G.; Neugebauer, V. Contribution of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1 (CRF1) to Serotonin Receptor 5-HT2CR Function in Amygdala Neurons in a Neuropathic Pain Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184380
Ji G, Neugebauer V. Contribution of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1 (CRF1) to Serotonin Receptor 5-HT2CR Function in Amygdala Neurons in a Neuropathic Pain Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(18):4380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184380
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Guangchen, and Volker Neugebauer. 2019. "Contribution of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1 (CRF1) to Serotonin Receptor 5-HT2CR Function in Amygdala Neurons in a Neuropathic Pain Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 18: 4380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184380
APA StyleJi, G., & Neugebauer, V. (2019). Contribution of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1 (CRF1) to Serotonin Receptor 5-HT2CR Function in Amygdala Neurons in a Neuropathic Pain Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(18), 4380. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184380



