Abstract
New flavonoidal glucosides leufolins A (1) and B (2), have been isolated from the ethyl acetate soluble fraction of the whole plants of Leucas urticifolia. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of extensive analysis of nuclear magnetic resonance (1D and 2D NMR) spectral data. Both of these compounds exhiited significant inhibitory potential against the enzyme butyrylcholinesterase.
Introduction
The genus Leucas, belonging to the family Lamiaceae, comprises about 100 species. In the Indo-Pakistani subcontinent, the genus is represented by 35 species which are mostly herbs or undershrubs found in temperate or hilly regions [1]. L. urticifolia is an annual herb which is commonly found in Karachi and other parts of Sind province of Pakistan. It is astringent, stimulant, haemostatic, anthelmintic and diuretic. The plant is also used for the treatment of diarrhea, dysentery, uterine haemorrhages, dropsy, gravel, cystitis, calculus, bronchial catarrh, skin diseases, fever and various types of mental disorders [2,3]. Our literature survey revealed that no phytochemical work has been carried out on this species so far. An ethanolic extract of L. urticifolia showed strong toxicity in the brine shrimp lethality test. On fractionation of the extract, the major toxicity was located in the EtOAc fraction. This prompted us to undertake bioassay directed isolation studies on this fraction, which resulted in the isolation and structure elucidation of two new bioactive flavonoidal glucosides named as leufolins A (1) and B (2), respectively.
Results and Discussion
The methanolic extract of shade-dried whole plant material of L. urticifolia was evaporated in vacuo, suspended in H2O, and successively partitioned with n-hexane, EtOAc, and n-BuOH. As a result of a series of column chromatographic techniques leufolins A (1) and B (2) were isolated from the EtOAc fraction as described in the Experimental.
Leufolin A (1) was isolated as a light yellow amorphous solid which gave a violet coloration with ferric chloride and was recognized as a flavonoid glucoside from its positive reaction with Molish and Shinoda reagents [4]. The molecular formula was determined to be C30H28O12 by high-resolution FABMS (negative mode), showing a [M-H]- peak at m/z 580.1580 (calc. for C30H27O12: 580.1584). The IR spectrum showed absorption bands at 3400 cm-1 (hydroxyl), 1710 cm-1 (CO), 1690 cm-1 (conjugated ester), 1621, 975 cm-1 (olefinic). The UV absorption bands at λmax 212, 285 and 325 nm suggested it to be flavanone [5]. On addition of AlCl3 and AlCl3/HCl, a bathochromic shift of 40 nm was observed suggesting the presence of a chelated hydroxyl group at C-5 [6].
The 1H-NMR spectra displayed a signal at δ 12.50 for a chelated hydroxyl group and two meta coupled protons on ring A at δ 6.16 (d, J=1.9 Hz) and δ 6.21 (d, J=1.8 Hz). The retro Diels-Alder (RDA) fragment observed in the mass spectrum at m/z 152 was due to ring A with two hydroxyl groups, while that at m/z 428 indicated the presence of a substituted sugar moiety in ring B. The flavanone structure was also indicated by an AMX system with resonances at δ 5.28 (dd, J=12.3, 2.7 Hz), 2.71 (dd, J=17.1, 2.7 Hz, H-3eq) and 3.12 (dd, J=17.1, 12.3 Hz, H-3ax) [7]. The 1H-NMR spectrum showed four further aromatic protons of ring B with AA'BB' system at δ 7.26 (2H, d, J=8.5 Hz) and δ 6.69 (2H, d, J=8.5 Hz) assigned to H-2'/H-6' and H-3'/H-5', respectively. The anomeric proton of the hexose moiety was observed at δ 4.97 (J=7.0 Hz). Its larger coupling constant confirmed the β-glucosidic linkage, and further signals of the hexose moiety were observed at δ 3.33-3.45. The spectrum further showed the presence of a p-hydroxy-trans-cinnamoyl moiety [olefinic protons at δ 7.59 (d, J=15.8 Hz) and δ 6.33 (d, J=15.8 Hz) and aromatic protons at δ 7.37 (d, J=8.5 Hz) and δ 6.77 (d, J=8.5 Hz). This was also supported by the mass fragments in EIMS at m/z 417 due to the loss of p-hydroxycinnamate moiety from the molecular ion peak at m/z 580.
The 13C-NMR (BB and DEPT) spectra of 1 corroborated the presence of two methylene, eighteen methine and ten quaternary carbons. The signals at δ 80.3, 44.0 and 198.4 were typical of C-2, C-3 and C-4 carbons of the flavanone skeleton [7].
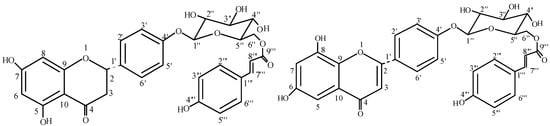
Figure 1.
Structures of leufolins A (1) and B (2).
The signals of sugar moiety appeared at δ 101.1, 74.5, 77.8, 71.8, 75.6 and 64.6, respectively. The 13C-NMR spectrum showed signal of ester carbonyl at δ 169.0; olefinic carbons at δ 146.8 and 114.9; hydroxyl substituted aromatic carbon at δ 161.1 and two other aromatic carbons at δ 131.2 and 116.4, respectively. Acid hydrolysis of 1 provided D-glucose, p-coumaric acid and naringenin. The downfield shift of oxymethylene protons as well as the oxymethylene carbon of the glucosyl moiety, revealed the presence of p-hydroxycinnamate moiety at C-6''.
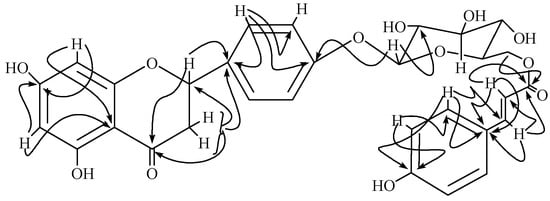
Figure 2.
Important HMBC correlations of 1.
The structure was fully supported by the HMBC correlations illustrated in Figure 2. The anomeric proton at δ 4.97 showed 3J correlation with signal at C-4' (δ 164.3) and 2J correlation with signal at C-2'' (δ 74.5). Similarly, p-hydroxycinnamate moiety was confirmed by 3J correlations of both Ha-6'' and Hb-6'' with carbonyl of the ester moiety at δ 169.0. The absolute configuration at C-2 was assigned S on the basis of CD spectrum which showed similar Cotton effects as reported in the literature for related flavonoids [8,9]. On the basis of these evidences, the structure of 1 could be assigned as {6-[4-(5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl)phenoxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl}methyl-(E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoate. The 1H-1H COSY, HMQC and HMBC correlations were in complete agreement to the assigned structure.
Leufolin B (2) formed a light yellow amorphous solid, which gave same color reactions as those of 1. The molecular formula was established as C30H26O12 by FABMS (positive mode), which showed a [M+H]+ peak at m/z 579.1424 (calc. for C30H27O12: 579.1427). The UV spectrum showed maxima at 315, 275, 273 and 221 nm for a flavone skeleton [10]. It did not display a bathochromic shift upon addition of AlCl3 and AlCl3/HCl, revealing the absence of chelated hydroxyl group at C-5 [6]. The IR spectrum showed the bands at 3390 cm-1(hydroxyl), 1685 cm-1 (ester), 1660 cm-1 (CO) and 1590 cm-1 (C=C).

Table 1.
1H- and 13C-NMR spectral data (CD3OD) for leufolins A (1) and B (2).
| 1 | 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/H | δ H | δ C | δ H | δ C |
| 1 | - | - | ||
| 2 | 5.28 (1H, dd, 12.3, 2.7) | 80.3 | 164.9 | |
| 3 | 3.12 (1H, dd, 17.1, 12.3) 2.71 (1H, dd, 17.1, 2.7) | 44.0 | 6.89 (1H, s) | 104.7 |
| 4 | 198.4 | 182.8 | ||
| 5 | 164.9 | 6.90 (1H, d, 1.8) | 114.7 | |
| 6 | 6.21 (1H, d, 1.8) | 97.9 | - | 162.6 |
| 7 | 166.8 | 6.81 (1H, d, 1.8) | 101.6 | |
| 8 | 6.16 (1H, d, 1.9) | 97.1 | 150.0 | |
| 9 | 158.9 | 144.6 | ||
| 10 | 104.9 | 115.2 | ||
| 1' | 130.8 | 122.0 | ||
| 2' | 7.26 (1H, d, 8.5) | 128.9 | 7.07 (1H, d, 9.7) | 123.1 |
| 3' | 6.69 (1H, d, 8.5) | 115.7 | 7.25 (1H, d, 9.7) | 116.7 |
| 4' | 164.3 | 163.8 | ||
| 5' | 6.69 (1H, d, 8.5) | 115.7 | 7.25 (1H, d, 9.7) | 116.7 |
| 6' | 7.26 (1H, d, 8.5) | 128.9 | 7.07 (1H, d, 9.7) | 123.1 |
| 1'' | 4.97 (1H, d, 7.0) | 101.1 | 5.78 (1H, d, 7.3) | 101.7 |
| 2'' | 3.33 (1H, m) | 74.5 | 3.66 (1H, m) | 74.6 |
| 3'' | 3.45 (1H, m) | 77.8 | 3.94 (1H, m) | 78.3 |
| 4'' | 3.39 (1H, m) | 71.8 | 4.15 (1H, m) | 71.8 |
| 5'' | 3.75 (1H, t, 7.7) | 75.6 | 4.17 (1H, m) | 75.7 |
| 6'' | 4.55 (1H, d, 11.7) 4.28 (1H, dd, 11.7, 7.2) | 64.6 | 4.85-4.89 (2H, m) | 64.8 |
| 1''' | 127.2 | 134.0 | ||
| 2''' | 7.37 (1H, d, 8.5) | 131.2 | 7.45 (1H, d, 8.4) | 130.6 |
| 3''' | 6.77 (1H, d, 8.5) | 116.4 | 7.23 (1H, d, 8.4) | 116.9 |
| 4''' | - | 161.1 | 162.8 | |
| 5''' | 6.77 (1H, d, 8.5) | 116.4 | 7.23 (1H, d, 8.4) | 116.9 |
| 6''' | 7.37 (1H, d, 8.5) | 131.2 | 7.45 (1H, d, 8.4) | 130.6 |
| 7''' | 7.59 (1H, d, 15.8) | 146.8 | 6.75 (1H, d, 12.9) | 144.6 |
| 8''' | 6.33 (1H, d, 15.8) | 114.9 | 6.09 (1H, d, 12.9) | 115.6 |
| 9''' | 169.0 | 166.6 | ||
The 1H-NMR spectrum was similar to that of compound 1, except now the presence of a trisubstituted double bond of the flavone moiety at δ 6.89 (1H, s) and a variation in the chemical shifts of meta coupled protons of the ring A was noted (Table 1). In the 13C-NMR spectrum olefinic carbons appeared at δ 164.9 and 104.7, which were characteristic for C-2 and C-3 of flavones. On the basis of this evidence, coupled with HMQC and HMBC correlations, the structure of leufolin B (2) could be assigned as {6-[4-(6,8-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-2-yl)phenoxy]-3,5-dihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl}methyl-(E)-3(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoate. It is the positional isomer of the acylated flavonoidal glucoside earlier reported from Thymus serpyllum [11] and Palhinhaea cernua [10], respectively.
Biological Activity
Cholinesterases are enzymes that share extensive sequence homology and distinct substrate specificity and inhibition sensitivity. Cholinesterases are potent target for the symptomatic treatment of Alzheimers disease and related dementia. It has been found that butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibition is an effective tool for the treatment of AD and related dementias [12]. It has been found that BChE is found in significantly higher quantities in Alzheimer plaques than in plaques of normal age-related non-demented brains. It is general viewed as a back up for the homologus acetylcholinesterase and to act as a scavenger for anticholinesterase compounds [13].
Eserine was used as positive control in BChE inhibitory assay for 1 and 2. From the results (Table 2) it is obvious that both leufolins A (1) and B (2) are potent inhibitors of BChE enzyme. On the other hand, very weak activity was observed against acetylcholinestrase (IC50 values 74.5 and 72.3 µM, respectively, compared to eserine (IC50 0.04)

Table 2.
Steady-state inhibition of BChE enzyme by compounds 1 and 2.
| Compounds | IC50 ± SEM[μM] |
|---|---|
| Leufolin A (1) | 1.6±0.98 |
| Leufolin B (2) | 3.6±1.7 |
| Eserine * | 0.93±0.3 |
*Standard inhibitor of BChE
Experimental
General
UV and IR spectra were recorded on Hitachi UV-3200 and JASCO 302-A spectrophotometers, respectively. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded at 400 MHz and 100 MHz, respectively, on a Bruker AM-400 spectrometer with tetramethylsilane (TMS) as a standard. The 2D-NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AMX-500 NMR spectrometer. Optical rotations were measured on a JASCO DIP-360 digital polarimeter using a 10 cm tube. Mass spectra (EI, FAB and HREIMS) were measured on Finnigan MAT 12 and MAT 312 spectrometers and ions are given in m/z (%). TLC was performed on precoated silica gel F254 plates; the detection was done at 254 nm and by spraying with ceric sulphate reagent. Silica gel (E-Merck, 230-400 mesh) was used for column chromatography. Melting points were determined on a Gallenkamp apparatus and are uncorrected. For enzyme inhibition assay all the chemicals were purchased from Sigma Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO, U.S.A.).
Plant Material
The whole plant of Leucas urticifolia Vahl. was collected from Karachi, Pakistan in July 2003 and identified by Dr. Javed Zaki, Plant Taxonomist, Department of Botany, University of Karachi, where a voucher specimen (BKU 101) has been deposited.
Extraction and Isolation
The air dried whole plant material (10 kg) was extracted with methanol (3 × 30 L) at room temperature. The extract was evaporated to yield the residue (500 g), which was divided into n-hexane (80 g), chloroform (30 g), ethyl acetate (8 g), n-butanol (270 g) and water (100 g) soluble fractions. The ethyl acetate soluble fraction, which showed major toxicity in a brine shrimp lethality test, was subjected to column chromatography over silica gel eluting with mixtures of dichloromethane and methanol in increasing order of polarity to obtain three major fractions A, B and C. The fraction B obtained from CHCl3-MeOH (5:5) was again chromatographed over silica gel using CHCl3-MeOH (9:1) as eluent to afford two successive fractions BA and BB. Column chromatography of subfraction BB and elution with CHCl3-MeOH (4:6) afforded leufolin A (1, 15 mg). On the other hand, the fraction C, obtained from CHCl3-MeOH (3:7), yielded leufolin B (2, 13 mg).
{6-[4-(5, 7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-3, 4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl) phenoxy]-3, 4, 5-trihydroxy tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl} methyl (E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoate (Leufolin A, 1): C30H27O12; light yellow amorphous powder; mp 110-112 °C (EtOH); [α]D +43° (c. 0.12, MeOH); CD curve [θ]333 +6848 (max), [θ]298 -3201 (min), [θ]249 +3600 (max), [θ]242 +2021 (min); UV (MeOH) λmax 325, 285, 212 nm; IR νmax (KBr): 3400, 1710, 1690, 1621, 975 cm-1; EIMS, m/z 428 [M]+, 417, 272, 178, 163, 152, 147, 91, 77; Negative HRFABMS: 580.1580 (calcd 580.1584 for C30H27O12); 1H- and 13C-NMR spectral data are shown in Table 1; important HMBC correlations are illustrated in Figure 2.
{6-[4-(6, 8-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-2-yl) phenoxy]-3, 5-dihydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl} methyl(E)-3(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propenoate (Leufolin B, 2): light yellow amorphous powder; mp 140-142 °C (EtOH); [α]D +16° (c. 0.12 MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax 315, 275, 273, 221 nm; IR νmax (KBr): 3390, 1685, 1660, 1590 cm-1; EIMS, m/z 427 [M]+, 416, 270, 178, 163, 152, 147, 91, 77; Positive HRFABMS: 579.1424 (calcd 579.1427 for C30H27O12); 1H-and 13C-NMR spectral data are shown in Table 1.
Acid Hydrolysis
Compound 1 (15 mg) was refluxed in 10 % HCl for 40 minutes. The cooled reaction mixture was neutralized with 10 % NaOH. The resulting aqueous mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate. The aqueous phase was concentrated and D-glucose was identified by Co-TLC using an 11:2:2:2 EtOAc-MeOH-H2O-HOAc solvent system and by the sign of its optical rotation ([α]D = +52.2). It was further confirmed by comparing the retention time of its TMS ether with a standard sample by GC. The residue recovered from the organic phase was a binary mixture of two components which could be separated through preparative TLC using a 1:3 EtOAc-n-hexanesolvent system and identified as naringenin [14] (needles, mp 255-256 °C) and p-coumaric acid (amorphous solid, mp 210-213 °C).
In vitro Butyrylcholinesterase inhibition assay
Butyrylcholinesterase inhibiting activity was measured by the spectrophotometric method previously reported in the literature [15]. Butyrylthiocholine chloride was used as substrate to assay butyrylcholinesterase. The reaction mixture containing 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 8, 150 µL), DTNB (10 µL), test compound solution (10 µL) and butyrylcholinesterase solution (20 µL) was mixed and incubated for 15 minutes (25 °C). The reaction was then initiated by the addition of butyrylthiocholine (10 µL). The hydrolysis of butyrylthiocholine was monitored by the formation of yellow 5-thio-2-nitrobenzoate anions as the result of the reaction of DTNB with thiocholine, released by the enzymatic hydrolysis of butyrylthiocholine at a wavelength of 412 nm (15 min.). Test compounds and the positive control (eserine) were dissolved in EtOH. All the reactions were performed in triplicate in 96-well micro-titre plates in SpectraMax 340 (Molecular Devices, U.S.A.). The percentage (%) inhibition was calculated as follows (E – S)/E × 100, where E is the activity of the enzyme without test compound and S is the activity of enzyme with test compound.
Determination of IC50 values
The concentrations of test compound and positive control that inhibited the hydrolysis of substrate (butyrylthiocholine) by 50 % (IC50) were determined by monitoring the effect of various concentrations of these compounds in the inhibition value assays. The IC50 values were then calculated as standard mean error of five assays using the EZ-Fit Enzyme Kinetics program (Perrella Scientific Inc., Amherst, MA, U.S.A.).
References
- Jafri, S. M. H. Flora of Karachi; The Book Corporation Karachi: Karachi, Pakistan, 1966; p. 391. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, G. Dictionary of the Economic Products of India; Cosmo Publications: Delhi, India, 1890; Vol. 6, p. 632. [Google Scholar]
- Mhaskar, K. S.; Blatter, E.; Caius, J. F. Indian Medicinal Plants; SriSatguru Publications: Delhi, India, 1935; Vol. 9, p. 2778. [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda, J. A new biologically active flavone glycoside from the roots of Cassia fistula Linn. J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1928, 48, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Davidson, R. S.; Howarth, W. O. Isolation and structure of clemantine, A new flavanone glycoside from Clematis armandii Franch. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 5169–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabry, T. J.; Markham, K. R.; Thomas, M. B. The systematic identification of flavonoids; Springer-Verlag: New York, 1970; p. 271. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Anis, I.; Malik, A.; Nawaz, S. A.; Choudhary, M. I. Cholinesterase inhibitory constituents from Onosma hispida. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iinuma, M.; Ohyama, M.; Tanaka, T.; Mizuno, M.; Hong, S. K. Three 2', 4', 6'- Trioxygenated flavanones in roots of Echinosophora koreensis. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdev, K.; Kulshrestha, D. K. Aliarin, a new flavonoid from Dodonaea viscose Linn. Indian J. Chem. B. 1982, 21, 798–799. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, R. H.; Ge, H. M.; Shi, D. H.; Tan, R. X. An apigenin-derived xanthine oxidase inhibitor from Palhinhaea cernua. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washington, J. S.; Saxena, V. K. A new acylated apigenin 4'-O-β-D-glucoside from the stems of Thymus serpyllum Linn. J. Inst. Chem. (India) 1985, 57, 153–154. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S. Q.; Holloway, H. W.; Utsuki, T.; Brossi, A.; Greig, N. H. Synthesis of novel phenserine-based-selective inhibitors of butyrylcholinesterase for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, M.; Glick, D.; Loewensten, Y.; Soreq, H. Engineering of human cholinesterase explains and predict diverse consequences of administration of various drugs and poisons. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 67, 283–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, L. J.; Borradaile, N. M.; Huff, M. W. Antiatherogenic properties of naringenin, a citrus flavonoid. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 1999, 17, 160–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G. L.; Courtney, K. D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R. M. A New and rapid calorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Contact the authors.
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.