Alleviating Health Risks for Water Safety: A Systematic Review on Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Modelling of Proximity-Dependent Emerging Pollutants in Aquatic Systems †
Abstract
1. Introduction
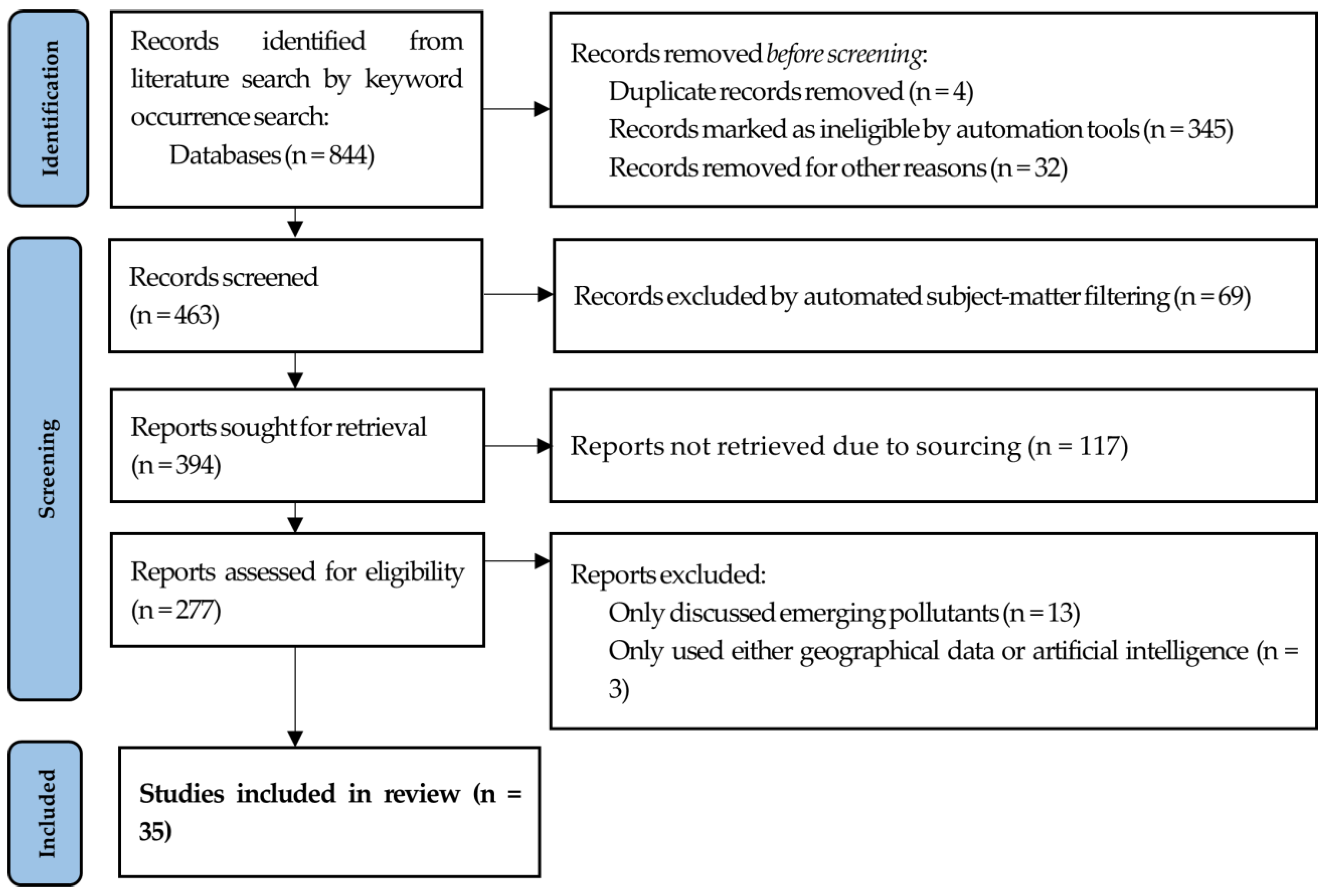
2. Method
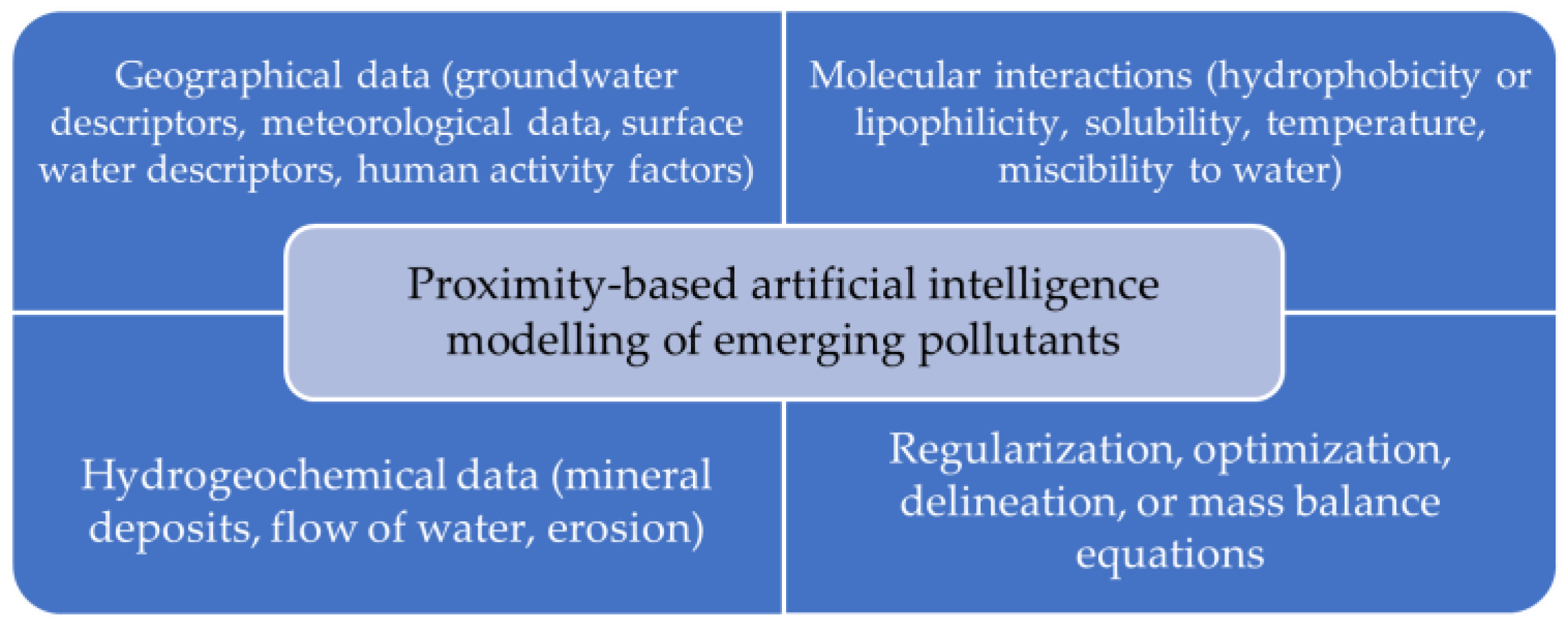
3. Proximity-Based Machine Learning for Emerging Pollutants in Water Resource Management
3.1. Pesticides and Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
3.2. Heavy Metals
3.3. Pharmaceuticals, Hormone-Distrupting Compounds, Fragrances, and Personal Care Products
3.4. Microplastics
3.5. Summary
4. Current State and Future Outlook for Modelled and Simulated Water Resources
4.1. Ongoing Research on Water Resources and Artificial Intelligence
4.2. Future Research and Trajectory of Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauptman, B.H.; Naughton, C.C.; Harmon, T.C. Using Machine Learning to Predict 1,2,3-Trichloropropane Contamination from Legacy Non-Point Source Pollution of Groundwater in California’s Central Valley. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 22, 100955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh Motlagh, Z.; Derakhshani, R.; Sayadi, M.H. Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment in Central Iran: Integration of GIS-Based DRASTIC Model and a Machine Learning Approach. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivan, E.L.; Bashir, F.M.; Eziashi, A.C.; Gammoudi, T.; Dodo, Y.A. Ground Water Quality Evaluation Using Hydrogeochemical Characterization and Novel Machine Learning in the Chikun Local Government Area of Kaduna State, Nigeria. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 1875–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Pastor, I.; Lopez-Granado, O.M.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; Hernández, E.I.; Jordán Vidal, M.M.; Gómez Lucas, I. Environmental Factors Influencing DDT–DDE Spatial Distribution in an Agricultural Drainage System Determined by Using Machine Learning Techniques. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 9067–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeka, M.E. Evaluation and Prediction of Irrigation Water Quality of an Agricultural District, SE Nigeria: An Integrated Heuristic GIS-Based and Machine Learning Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 54178–54203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salele, B.; Dodo, Y.A.; Sani, D.A.; Abuhussain, M.A.; Sayfutdinovna Abdullaeva, B.; Brysiewicz, A. Run-off Modelling of Pervious and Impervious Areas Using Couple SWAT and a Novel Machine Learning Model in Cross-Rivers State Nigeria. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Jones, D.K.; Blazer, V.S.; Iwanowicz, L.; Williams, B.; Smalling, K. Modeling Estrogenic Activity in Streams throughout the Potomac and Chesapeake Bay Watersheds. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojtahedi, A.; Dadashzadeh, M.; Azizkhani, M.; Mohammadian, A.; Almasi, R. Assessing Climate and Human Activity Effects on Lake Characteristics Using Spatio-Temporal Satellite Data and an Emotional Neural Network. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeka, M.E.; Igwe, O.; Onwuka, O.S.; Nwodo, O.M.; Ugar, S.I.; Undiandeye, P.A.; Anyanwu, I.E. Efficacy of GIS-Based AHP and Data-Driven Intelligent Machine Learning Algorithms for Irrigation Water Quality Prediction in an Agricultural-Mine District within the Lower Benue Trough, Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 54204–54233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Rahim, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Asif, M.R.; Dey, H.C.; Khurram, D.; Al, M.A.; Islam, M.; Idris, A.M. Utilizing Machine Learning to Evaluate Heavy Metal Pollution in the World’s Largest Mangrove Forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Mohammadi, A.; Khosravi, R.; Zarei, A. Distribution, Exposure, and Human Health Risk Analysis of Heavy Metals in Drinking Groundwater of Ghayen County, Iran. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 13127–13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, D.; Słowik, J.; Chilicka, K. Heavy Metals and Human Health: Possible Exposure Pathways and the Competition for Protein Binding Sites. Molecules 2021, 26, 6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Ullah, M.I.; Sajjad, A.; Shakeel, Q.; Hussain, A. Environmental and Health Effects of Pesticide Residues. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 48: Pesticide Occurrence, Analysis and Remediation Vol. 2 Analysis; Inamuddin, Ahamed, M.I., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 311–336. ISBN 978-3-030-54719-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran; Bharti, R.; Sharma, R. Effect of Heavy Metals: An Overview. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaynab, M.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Ameen, A.; Sharif, Y.; Ali, L.; Fatima, M.; Khan, K.A.; Li, S. Health and Environmental Effects of Heavy Metals. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, N.H.A.; Yaacob, W.F.W.; Nasir, S.A.M.; Shaadan, N. The Effect of Chemical Parameters on Water Quality Index in Machine Learning Studies: A Meta-Analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2084, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, D.; Ma, L.; Lu, X.; Song, J.; Lei, M. Using Big Data Searching and Machine Learning to Predict Human Health Risk Probability from Pesticide Site Soils in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Wahba, M.; Fathi, H.; Alshehri, F.; Abdalla, F.; El Attar, R.M. Assessment of Groundwater Quality in Arid Regions Utilizing Principal Component Analysis, GIS, and Machine Learning Techniques. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 205, 116645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangcao, Z.; Su, C.; Xianjun, X.; Ge, W.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, L.; Pan, H. Employing Machine Learning to Predict the Occurrence and Spatial Variability of High Fluoride Groundwater in Intensively Irrigated Areas. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 167, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, K.; Ayoubi, S.; Nabiollahi, K.; Garosi, Y.; Gislum, R. Predicting Heavy Metal Contents by Applying Machine Learning Approaches and Environmental Covariates in West of Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 233, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, S. ANN-Based Integrated Risk Ranking Approach: A Case Study of Contaminants of Emerging Concern of Fish and Seafood in Europe. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijlil, S.; Essahlaoui, A.; Mohajane, M.; Essahlaoui, N.; Mili, E.M.; Van Rompaey, A. Machine Learning Algorithms for Modeling and Mapping of Groundwater Pollution Risk: A Study to Reach Water Security and Sustainable Development (Sdg) Goals in a Mediterranean Aquifer System. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kim, J.-H.; Li, M.-H. Predicting Stream Water Quality under Different Urban Development Pattern Scenarios with an Interpretable Machine Learning Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, R.M.; Seibert, D.; Quesada, H.B.; de Jesus Bassetti, F.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Bergamasco, R. Occurrence, Impacts and General Aspects of Pesticides in Surface Water: A Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 135, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafrudin, M.; Kristanti, R.A.; Yuniarto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Rhee, J.; Al-onazi, W.A.; Algarni, T.S.; Almarri, A.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Pesticides in Drinking Water—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfikrie, N.; Bin Ho, Y.; Zaidon, S.Z.; Juahir, H.; Tan, E.S.S. Occurrence of Pesticides in Surface Water, Pesticides Removal Efficiency in Drinking Water Treatment Plant and Potential Health Risk to Consumers in Tengi River Basin, Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, J.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, M.; Lohmann, R.; Vojta, S.; Katz, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Identification of Key Anthropogenic and Land Use Factors and Ecological Risk Assessment of Dissolved Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Organochlorine Pesticides (OCPs) in an Urbanized Estuary in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 207, 116876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, K.E.; Anthamatten, P.J.; Adgate, J.L.; McKenzie, L.M.; Starling, A.P.; Berg, K.; Murphy, R.C.; Richardson, K. A Data-Driven Approach to Identifying PFAS Water Sampling Priorities in Colorado, United States. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, D.; Abbas, A.; Jeon, J.; Ligaray, M.; Baek, S.-S.; Cho, K.H. Developing a Deep Learning Model for the Simulation of Micro-Pollutants in a Watershed. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 300, 126858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.C.; Mills, G.A.; Gravell, A.; Kerwick, M.; Fones, G.R. Pesticide Fate during Drinking Water Treatment Determined through Passive Sampling Combined with Suspect Screening and Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendell, A.-K.; Guse, B.; Bieger, K.; Wagner, P.D.; Kiesel, J.; Ulrich, U.; Fohrer, N. A Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Environmental Fate and Transport Processes of Pesticides and Their Transformation Products in Agricultural Landscapes Dominated by Subsurface Drainage with SWAT+. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 173629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mahmood, A.; Shao, Y.; Jarosiewicz, P.; Gonsior, G.; Cuellar-Bermudez, S.P.; Chen, Z.; Stibany, F.; Schäffer, A. Combined Simulation on Pesticides Fate, Toxicities and Ecological Risk in Rice Paddies for Sustainable Development Goals Achievements. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, M.; Al-jabery, K.; Wunsch, D.; Burken, J.G. Examining Plant Uptake and Translocation of Emerging Contaminants Using Machine Learning: Implications to Food Security. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 133999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obasi, P.N.; Akudinobi, B.B. Potential Health Risk and Levels of Heavy Metals in Water Resources of Lead–Zinc Mining Communities of Abakaliki, Southeast Nigeria. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Gaagai, A.; Eid, M.H.; Szűcs, P.; Hussein, H.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elsayed, S.; Khalifa, M.M.; Moghanm, F.S.; Moustapha, M.E.; et al. Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment Using Indexing Approaches, Multivariate Statistical Analysis, Artificial Neural Networks, and GIS Techniques in El Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarawy, A.; El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Use of Hyperspectral Reflectance and Water Quality Indices to Assess Groundwater Quality for Drinking in Arid Regions, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Morabet, R.; Barhazi, L.; Bouhafa, S.; Dahim, M.A.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, N.A. Geospatial Distribution and Machine Learning Algorithms for Assessing Water Quality in Surface Water Bodies of Morocco. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, P.-L.; Moldovanu, S.; Iticescu, C.; Calmuc, M.; Calmuc, V.; Topa, C.; Moraru, L. Assessing and Forecasting Water Quality in the Danube River by Using Neural Network Approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 162998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama Aziz, K.H.; Mustafa, F.S.; Omer, K.M.; Hama, S.; Hamarawf, R.F.; Rahman, K.O. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment: Efficient and Low-Cost Removal Approaches to Eliminate Their Toxicity: A Review. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 17595–17610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agbasi, J.C.; Egbueri, J.C. Assessment of PTEs in Water Resources by Integrating HHRISK Code, Water Quality Indices, Multivariate Statistics, and ANNs. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 10407–10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Xue, F.; Han, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Jiang, J. Assessment of the Spatial Association between Multiple Pollutants of Surface Water and Digestive Cancer Incidence in China: A Novel Application of Spatial Machine Learning. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Maurya, B.M.; Chettri, D.; Pooja; Pulwani, C.; Jajula, M.; kanda, S.S.; babu, H.W.S.; Elangovan, A.; Velusamy, P.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Heavy Metals Detection: Methodological and Ethical Challenges. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2023, 7, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavianpour, B.; Piadeh, F.; Gheibi, M.; Ardakanian, A.; Behzadian, K.; Campos, L.C. Applications of Artificial Intelligence for Chemical Analysis and Monitoring of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products in Water and Wastewater: A Review. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Gallagher, D.L.; Dietrich, A.M.; Su, M.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; An, W.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Data Analytics Determines Co-Occurrence of Odorants in Raw Water and Evaluates Drinking Water Treatment Removal Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16770–16782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büngener, L.; Postila, H.; Löder, M.G.J.; Laforsch, C.; Ronkanen, A.-K.; Heiderscheidt, E. The Fate of Microplastics from Municipal Wastewater in a Surface Flow Treatment Wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkajit, P.; Sukkuea, A.; Thongnonghin, B. Comparative Analysis of Five Convolutional Neural Networks and Transfer Learning Classification Approach for Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 78, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tang, D.W.S. Modeling Microplastic Transport through Porous Media: Challenges Arising from Dynamic Transport Behavior. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 484, 136728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyadh, A.; Peleato, N.M. Exploring Spatial and Temporal Importance of Input Features and the Explainability of Machine Learning-Based Modelling of Water Distribution Systems. Digit. Chem. Eng. 2025, 14, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, Y.; Wang, D.; Gong, Z.; Chen, J.; Shen, L.; Fan, M.; Li, Z. Industrial Wastewater Source Tracing: The Initiative of SERS Spectral Signature Aided by a One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network. Water Res. 2023, 232, 119662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpe, O.D.; Choo, G.; Kang, J.-K.; Yun, S.-T.; Oh, J.-E. Identification of Organic Chemical Indicators for Tracking Pollution Sources in Groundwater by Machine Learning from GC-HRMS-Based Suspect and Non-Target Screening Data. Water Res. 2024, 252, 121130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Rahman, M.S.; Nice, M.S.; Netema, B.N.; Islam, K.R.; Debnath, P.C.; Chowdhury, P.; Halder, M.; Zaman, S.; Ghosh, G.C.; et al. Application of Machine Learning and Multivariate Approaches for Assessing Microplastic Pollution and Its Associated Risks in the Urban Outdoor Environment of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Emerging Pollutants of Interest | Study | Models Used | Performance Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDT-DDE | [4] | Random Forest (Mutual Information) | Accuracy = 0.815 (0.852) |
| TCP | [1] | Classification and Regression Tree, Random Forest, Boosted Regression Trees | R2 = 0.020, 0.44, 0.41 |
| PFOS, PFOA | [28] | Random Forest | Accuracy = 86% (low risk), 80% (medium risk), 90% (high risk) |
| Acetamiprid, aldicarb sulfone, azoxystrobin, bentazon, hexaconazole, metalaxyl | [29] | Long-term Short Memory (LSTM), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) | For bentazon, LSTM: Training (R2 = 0.99), Validation (R2 = 0.93) |
| Water quality index, mercury, iron, lead | [3] | Emotional Artificial Neural Network | R2 = 0.89 (Training) and 0.83 (Validation) |
| Heavy metal pollution index | [37] | Artificial Neural Network, Support Vector Machines | Zn (R2 = 0.98–0.99), Cd (R2 = 0.89–0.96), Pb (R2 = 0.999–0.998) |
| Estrogenic activity | [7] | Random Forests with Principal Component Analysis | R2 = 0.00–0.05 (Non-Potomac/Chesapeake Bay Watersheds), 0.02–0.11 (Potomac Temporal Comparison Sites) |
| Microplastics | [46] | Convolutional Neural Network with Transfer Learning | R2 = 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rupin, M.D.J.V.; Mendoza, K.G.C.; Rubi, R.V. Alleviating Health Risks for Water Safety: A Systematic Review on Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Modelling of Proximity-Dependent Emerging Pollutants in Aquatic Systems. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 32, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032007
Rupin MDJV, Mendoza KGC, Rubi RV. Alleviating Health Risks for Water Safety: A Systematic Review on Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Modelling of Proximity-Dependent Emerging Pollutants in Aquatic Systems. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 32(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032007
Chicago/Turabian StyleRupin, Marc Deo Jeremiah Victorio, Kylle Gabriel Cruz Mendoza, and Rugi Vicente Rubi. 2025. "Alleviating Health Risks for Water Safety: A Systematic Review on Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Modelling of Proximity-Dependent Emerging Pollutants in Aquatic Systems" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 32, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032007
APA StyleRupin, M. D. J. V., Mendoza, K. G. C., & Rubi, R. V. (2025). Alleviating Health Risks for Water Safety: A Systematic Review on Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Modelling of Proximity-Dependent Emerging Pollutants in Aquatic Systems. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 32(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032007








