Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease accounts for approximately 50% to 80% of all causes of dementia. Co-existence of AD with other diseases causing dementia poses a diagnostic challenge, as we are still far from diagnosing AD accurately in order to manage it appropriately. Neuroimaging techniques, not only help diagnose AD but also consistently feature in diagnostic and research criteria for AD as biomarkers. Molecular biomarkers including positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and structural biomarkers including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), have been used in various therapeutic and prognostic studies in AD. This review highlights the recent advances in neuroimaging biomarkers, including molecular biomarkers (PET and SPECT tracers) and structural biomarkers (MRI), for AD. For the purpose of this review, molecular biomarkers have been further subcategorized into non-specific radiotracers (FDG-PET and blood flow SPECT) and specific amyloid- and tau-related radiotracers. The aim of this review is to discuss the recent advances and evidence of molecular and structural biomarkers of AD.
1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s dementia (AD) is the most common cause of dementia accounting for approximately 50–80% of all causes of dementia [1]. AD is characterised by cognitive decline especially memory impairment followed by impairment in other cognitive domains, with histopathological features of amyloid deposition and intra-neuronal tau deposition in senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, respectively [2]. The incidence of AD increases with age and doubles every five years after the age of 60 [3]. With increasing life expectancy worldwide, the prevalence of AD is expected to increase exponentially, increasing the urgency of accurate diagnosis in order to initiate management strategies early to help prevent progression of cognitive decline and reduce morbidity [4,5]. AD often co-exist with other diseases that cause dementia, and despite advances in diagnostic techniques, we are still far from accurately diagnosing and managing AD appropriately. Neuroimaging not only supports diagnosis of AD as the cause of dementia but also consistently features in the diagnostic criteria for probable AD [6].
The currently available therapeutic strategies can alleviate behavioural disturbances in AD, but drugs to halt disease progression comprehensively are still elusive [7]. Recently, drugs targeting Aβ protein have emerged with the promise of slowing cognitive impairment in AD, but the clinical relevance and long-term side effects require further longitudinal observation [8]. The complex aetiology and pathology of AD may be responsible for unsuccessful attempts at disease-modifying therapy [9]. Imaging biomarkers play an important role not only in visualising the typical abnormalities of AD for diagnosis and monitoring disease progression but also in therapeutics of AD by predicting response to novel AD drugs [10] (Figure 1). The National Institute of Ageing and Alzheimer’s Association (NIA-AA) in 2011 incorporated biomarkers in the diagnostic criteria of AD [11,12]. Further, the International Working Group (IWG) in 2014 categorised biomarkers for AD into diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, focussing on MRI and PET biomarkers [13].
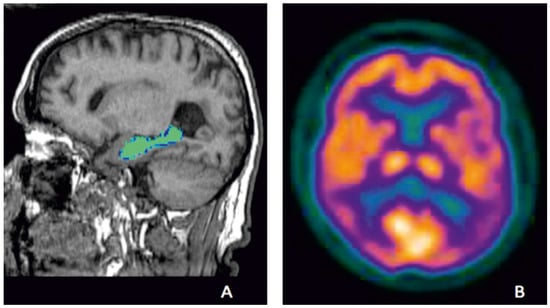
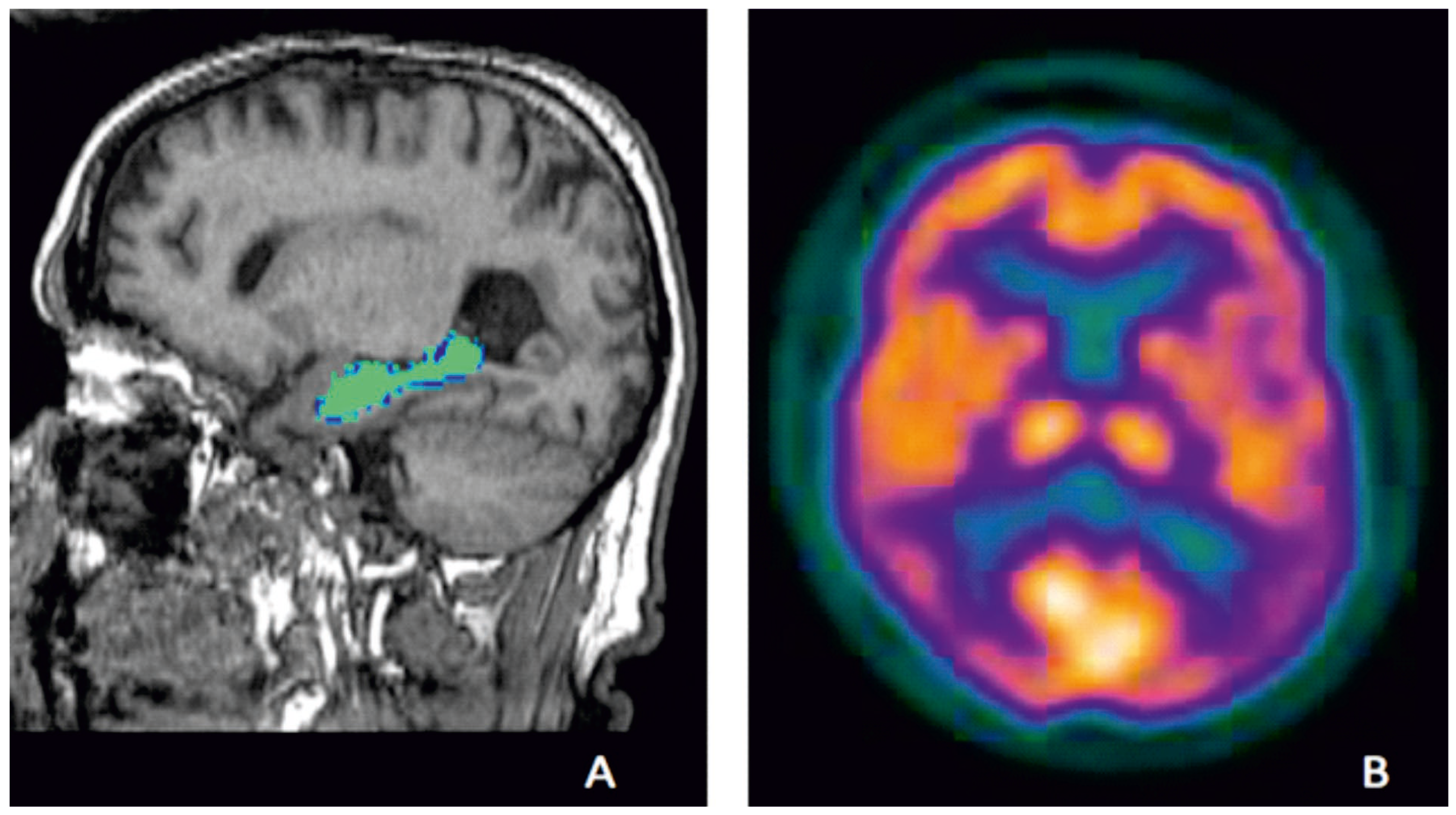
Figure 1.
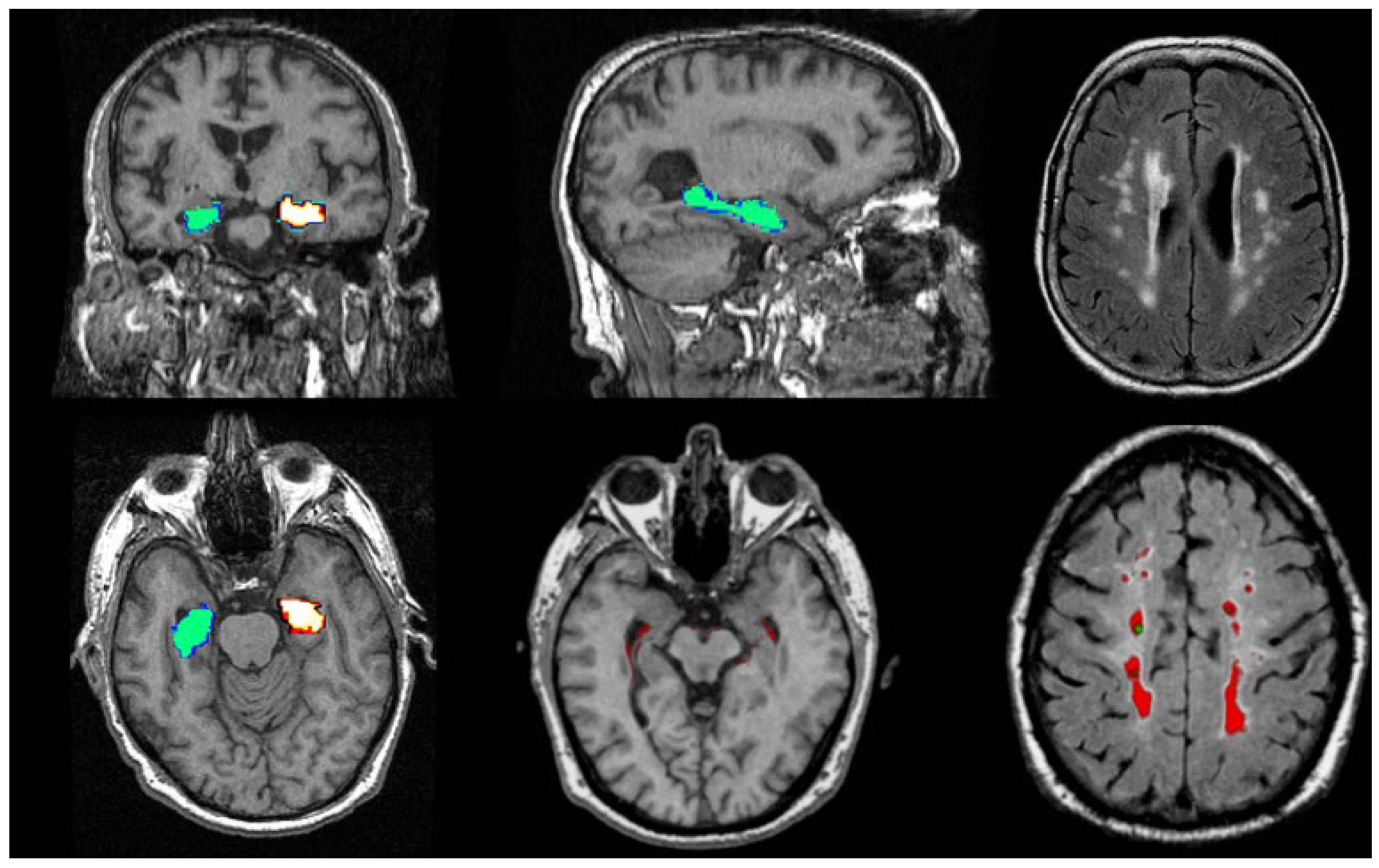
Examples of established biomarkers in AD; hippocampal volumes on MRI of a participant from Aberdeen Birth Cohort 1936 study, illustrating hippocampal volume measurement which is highlighted in green (A) and temporo-parietal defects (violet) on FDG-PET showing hypo-metabolism in temporo-parietal region of a participant from an Alzheimer’s disease clinical trial who met research criteria for probable AD (B) (Courtesy—Alison D. Murray, University of Aberdeen).
Recently, NIA-AA, has updated the recommendations for pre-clinical, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and AD diagnosis, and categorised neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers into AT(N) groups. The A denotes amyloid deposition (A), T denotes pathological fibrillary tau, and N signifies neurodegeneration [6,14].
The recent shift towards different imaging biomarkers in AD research has made it necessary for us to review imaging biomarkers in AD, which not only include molecular biomarkers but also MRI biomarkers. This review highlights the recent advances and evidence in the imaging biomarkers, including molecular biomarkers (PET and SPECT tracers) and structural biomarkers (MRI), for AD.
2. Molecular Biomarkers
The molecular biomarkers which are commonly used for diagnostic, prognostic, or therapeutic purposes in AD can be further subcategorized into non-specific radiotracers, such as FDG-PET, blood flow SPECT, and dopamine transporter scan (DaT scan), and specific radiotracers including amyloid and tau radiotracers. Recent PET imaging approaches targeting neuroinflammation include mitochondrial translocator protein (TSPO), which provides evidence of microglial involvement in AD pathogenesis, and synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A), a glycoprotein located on the membrane of synaptic vesicles, which may contribute to understanding AD pathophysiology and developing interventional strategies targeting inflammatory pathways [15]. However, PET imaging tracers targeting neuroinflammation are outwith the scope of this review.
2.1. Molecular Biomarkers with Non-Specific Radiotracers
Radioactive tracers such as 18F fluoro-deoxy glucose and 99m Tc-labelled tracer HMPAO (d, 1, hexamethylpropylene amine oxime) are used for brain FDG-PET and cerebral blood flow SPECT, respectively. These techniques are useful for differentiating dementia subtypes in clinical and research settings. In research settings, these techniques provide details of molecular and pathophysiology of the diseases causing dementia. Details of non-specific radiotracers in AD are provided below.
2.1.1. FDG-PET
FDG-PET is a well-established and extensively used neuroimaging tool to aid in clinical diagnosis of neurodegenerative conditions, including AD, as hypo-metabolism in certain brain regions corresponds to neuronal loss and functional impairment [16,17,18]. Reduced cerebral blood glucose uptake on FDG-PET in the areas of neurodegeneration, can help distinguish AD from other causes of dementia [19,20,21] and is considered a molecular imaging biomarker for AD [16,22]. Hypo-metabolism on FDG-PET precedes the detectible atrophy on structural MRI in AD and is a more sensitive technique for detecting early neurodegenerative disease [23,24,25]. Moreover, characteristic temporo-parietal hypo-metabolism can be seen on FDG-PET even before structural changes in people with AD [26,27] (Figure 2). With advancement in AD pathology, FDG-PET can detect extension of cortical hypo-metabolism to the frontal lobes, especially the prefrontal association cortex and anterior cingulate gyrus [28]. Moreover, it has been established that hippocampal, posterior cingulate cortex, and precuneus hypo-metabolism is seen in the early stage of AD [29,30]. Other neocortical areas are involved via brain networks, and the disease progresses in a stereotypical pattern [31].
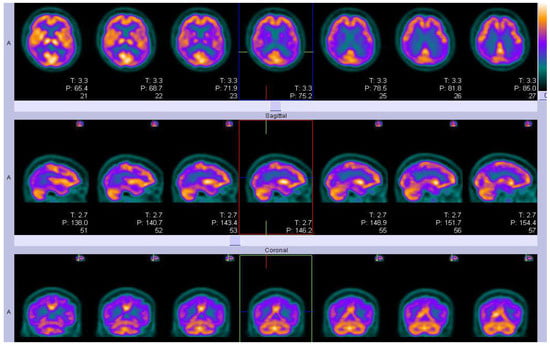
Figure 2.
An example of FDG-PET imaging in a participant from an Alzheimer’s disease clinical trial who met research criteria for probable AD, showing temporo-parietal hypo-metabolism(violet diagonal band) and normal areas of metabolism(golden). T is the thickness (2.2 mm) and P is the position relative to the isocentre of the field of view(FoV).(Courtesy—Alison D. Murray, University of Aberdeen).
Sensitivity and specificity of 99% and 98%, respectively, have been reported for FDG-PET to distinguish people with AD from normal subjects [32]. However, the specificity of FDG-PET to distinguish AD from other causes of dementia, including dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) were reported to be 71% and 65%, respectively, while sensitivity remains at 99% [32,33]. Recently, FDG-PET has been included as an independent biomarker in the ATN framework for AD diagnosis, as hypo-metabolism on FDG-PET predicts greater atrophy, poorer cognitive function, and a higher conversion to AD from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) [16]. Notably, conversion to AD from MCI can be predicted from a similar glucose uptake pattern as AD on FDG-PET [30]. Moreover, a higher rate of progression and associated cognitive decline can be predicted from the severity and progression of hypo-metabolism on FDG-PET in MCI patients. Thus, FDG-PET not only has diagnostic value but also prognostic value in people with AD [34,35,36,37].
Various clinical trials have used FDG-PET for treatment response evaluation in people with AD [38,39] and as an imaging biomarker for measurement of outcome and participant selection in AD and other dementia-related therapeutic trials [40,41].
2.1.2. SPECT
SPECT is a molecular imaging modality using gamma-emitting radiotracers; their distribution in the body is detected using a gamma camera [42]. SPECT highlights blood flow in different brain regions to evaluate brain and neurological conditions. The radiotracer 133Xe was the first to be used for brain perfusion in 1990, followed by the use of various other radiotracers such as HMPAO (hexamethyl propylene amine oxime) and ECD (ethylcysteinate dimer), which are static radiotracers in contrast to 133Xe, which is a diffusible radiotracer. However, SPECT should only be used as an aid to the diagnosis of a dementia subtype. The exceptions are Parkinson’s disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies, where dopamine transporter imaging (DaT) with DaTscanTM (Ioflupane 123-I SPECT) has been found to be useful for confirming an underlying pre-synaptic dopaminergic deficit [43]. These radiotracers are manuctured by GEHealthcare and Siemens.
2.1.3. ECD and HMPAO-SPECT
SPECT is being widely used for cerebral blood flow (CBF) studies and helps identify functional abnormalities relevant to Alzheimer’s disease [44]. 99mTc-ECD and 99mTc-HMPAO are the two most commonly used static radiotracers [45], having several technical, economic, and logistical advantages over other radiotracers [46]. 99mTc-ECD has in vitro chemical stability lasting several hours after reconstitution, faster blood clearance, and a high signal-to-noise ratio, making it an efficient technique to elucidate brain functions in various neurological disorders including cerebrovascular disease [47] and Alzheimer’s disease [48]. In addition, 99mTc-HMPAO, in which 99mTc is attached to the chelating agent HMPAO, is useful for the detection of regional blood flow in the brain and hence is used in diagnostic evaluation of dementias. It has greater specificity in comparison to the clinical criteria in differentiating AD from other dementias and can help in differential diagnosis of AD [49,50,51].
Notably, SPECT radiotracers are relatively less expensive and having a longer half-life than PET radiotracers, enabling more flexibility in tracer provision, administration, and imaging time. SPECT has been widely studied and may be used for the diagnostic workup of people with diseases causing dementia. Earlier, concerns were raised regarding SPECT use due to image quality, artefacts, and difficulty in quantifying blood flow, but emerging technology has addressed these shortcomings. The technological advancements include both the hardware and software techniques that help improve image quality and subsequent image analysis [52]. Data from large cross-sectional studies have been used to make inter-subject comparisons using t- or z-statistics, in order to eliminate individual variations in position, shape, and size [53]. The sensitivity and specificity of rCBF SPECT in differentiating AD from VaD are 74.5% and 72.4%, AD from FTD are 79.7% and 79.9%, AD from DLB are 70.2% and 76.2%, and AD from healthy controls are 76.1% and 85.4%, respectively [54].
Hypoperfusion on SPECT has been well correlated with the onset, the severity, clinical features, and prognosis of AD [55]. Parietal hypoperfusion is the most commonly seen in early-onset AD [56], while late-onset AD is characterised by medial temporal lobes hypoperfusion [57]. Some studies have found hypoperfusion in temporo-parietal regions to correlate with mini mental state examination (MMSE) scores in people with AD [58]. Notably, frontal lobe hypoperfusion has been negatively correlated with cognitive functions and positively correlated with rate of progression of the disease [59]. However, median survival time for people with AD has been negatively correlated with left temporal lobe hypoperfusion [60]. Thus, blood flow SPECT can be considered as a biomarker in AD [61,62], depicting the disease much earlier than the clinical manifestation [63].
2.1.4. Dopamine Transporter SPECT
SPECT for investigating the striatal dopamine transporter (DAT) status has been widely used in uncertain parkinsonian syndromes [64] (Figure 3). Despite no changes on ioflupane SPECT in AD in comparison to controls, it is helpful in differentiating AD from DLB. In DLB, there is 40–70% loss of striatal dopamine and dopaminergic cells, resulting in loss of dopamine transporter [65]. Dopamine transporter SPECT can thus be useful in differentiating neurodegenerative parkinsonian syndromes (PS) from non-dopamine-deficiency aetiologies, including drug-induced parkinsonism and essential tremor [66,67], with sensitivity and specificity of over 90% [68].
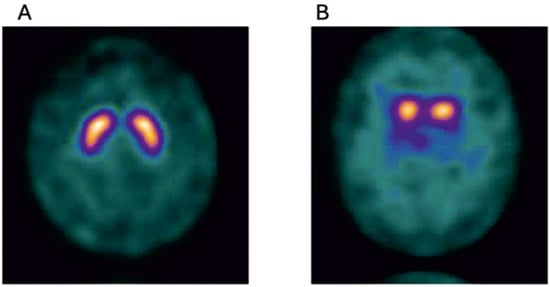
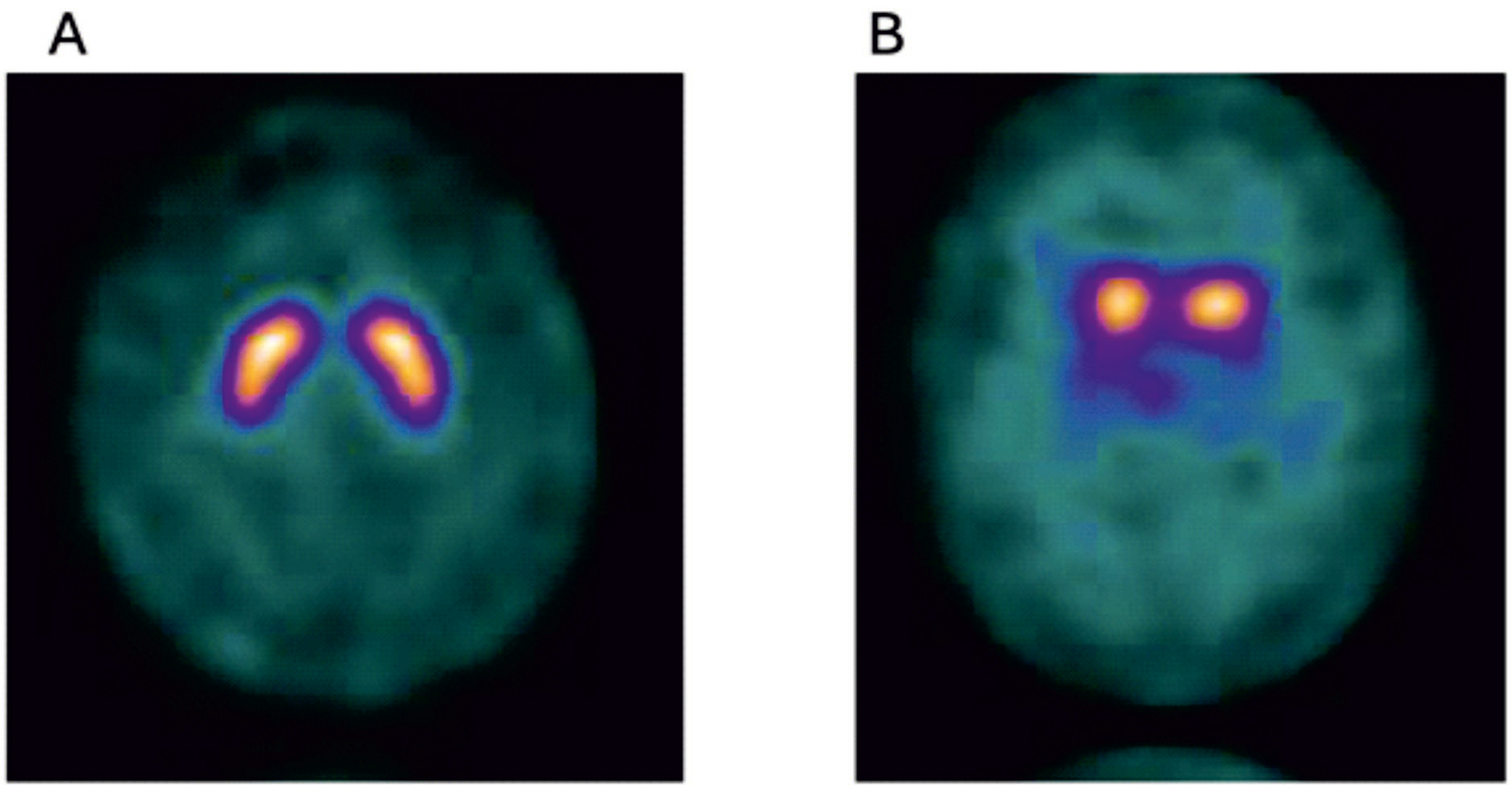
Figure 3.
Normal I 123 ioflupane SPECT image (DAT scan) (A), and for comparison an abnormal 123 ioflupane SPECT image from a participant of the Parkinsonism Incidence in North-East Scotland (PINE) study (B), showing lack of tracer uptake in the putamen bilaterally(Golden) (Courtesy—Alison D. Murray, University of Aberdeen).
2.2. Molecular Biomarkers with Specific Radiotracers
A growing class of radiotracers targeting specific protein aggregates, amyloid-β (Aβ), and tau, are providing new avenues for research in AD diagnosis, as these radiotracers directly label the underlying disease pathologies. Amongst the two specific type of tracers, tau tracers are emerging as preferable to researchers for therapeutic and prognostic evaluation in AD clinical trials, due to the failure of agents targeting amyloid pathology. Thus, in this review, we provide a brief summary of amyloid PET and greater detail about tau PET.
2.2.1. Amyloid PET
Pittsburg Compound B (PIB), a 11-C labelled PET tracer was first to be used as an amyloid-specific radiotracer [69], and demonstrated that amyloid deposition precedes clinical manifestation of AD by 15 years [70,71]. However, this has been recently refuted, with proposals that cognitive decline precedes amyloid deposition [72], thus opening a new avenue in research to look beyond our understanding of amyloid in AD. The Amyloid Imaging Task Force [73] has clearly stated that amyloid PET should only be used if there is diagnostic ambiguity and that tracers can improve diagnostic accuracy. However, recently, it has been reported that initiation and discontinuation of medications in the management of AD can be influenced by the use of amyloid PET imaging in clinical practice [39,74].
PiB binds specifically with insoluble fibrillary Aβ, and cortical binding of PiB has been seen in more than 90% of people with AD [75]. Following PIB, several other 18F-labelled PET tracers such as [18F]Flutemetamol, [18F]Florbetaben, and [18F]Florbetapir have emerged as potential tools to aid in AD diagnosis and are widely used for research purposes [76,77]. The 18F-labelled PET tracers have a half-life of 110 min, overcoming the disadvantage of PIB, as PIB has a shorter half-life of 20 min, resulting in practical difficulties for clinical and research use. The U.S. FDA has provided its approval for use of [18F]Florbetapir in 2012 for exploring AD or other causes of cognitive impairment, followed by approval of [18F]Flutemetamol and [18F]Florbetaben in 2013 and 2014, respectively [77]. Amyloid PET has been found to be more sensitive but less specific than FDG-PET in distinguishing AD from other causes of dementia such as FTD [78]. Despite the association of amyloid deposition with AD, it has also been consistently found in cognitively healthy people [79], raising the question of whether amyloid deposition is a pathognomonic or necessary feature for the diagnosis of AD.
Although, it is difficult to ascertain the timing of amyloid deposition, it is believed to begin at the preclinical stage [71]. Amyloid PET has shown cortical uptake of amyloid tracers in the cingulum, precuneus, and frontal, parietal, and lateral temporal cortices in people with AD [80,81]. Moreover, amyloid PET has prognostic value, as people with MCI with positive findings on amyloid PET have a higher chance of conversion to AD, while those who are negative on amyloid PET have higher negative predictive value for conversion to AD from MCI [82,83,84]. It has also been noted that the rate of cognitive decline is directly proportional to amyloid deposition in people with MCI [85], and amyloid PET may help identify people at risk of cognitive decline and disease progression [86].
Amyloid tracers have also been used recently to monitor the therapeutic response of the amyloid-based drugs. Primary endpoints in these trials are usually measures of cognitive function such as the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale—Cognitive Subscale (ADAS-cog) [87] or the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR) [88]. However, due to cognitive reserve and ceiling and floor effects of psychometric tests, clinical presentations usually differ between people with AD [89,90]. Recently, 18-Florbetapir PET has been used in the PRIME study to evaluate treatment response of human monoclonal antibody on participants with prodromal or mild AD participants, which depicted a dose- and time-dependent reduction of Aβ plaques [91]. For the last few decades, most research has slavishly focused on Aβ as a target for the treatment of AD. However, most of the novel therapeutic agents targeting Aβ have failed to improve cognitive function or slow cognitive decline [92,93].
2.2.2. Tau PET
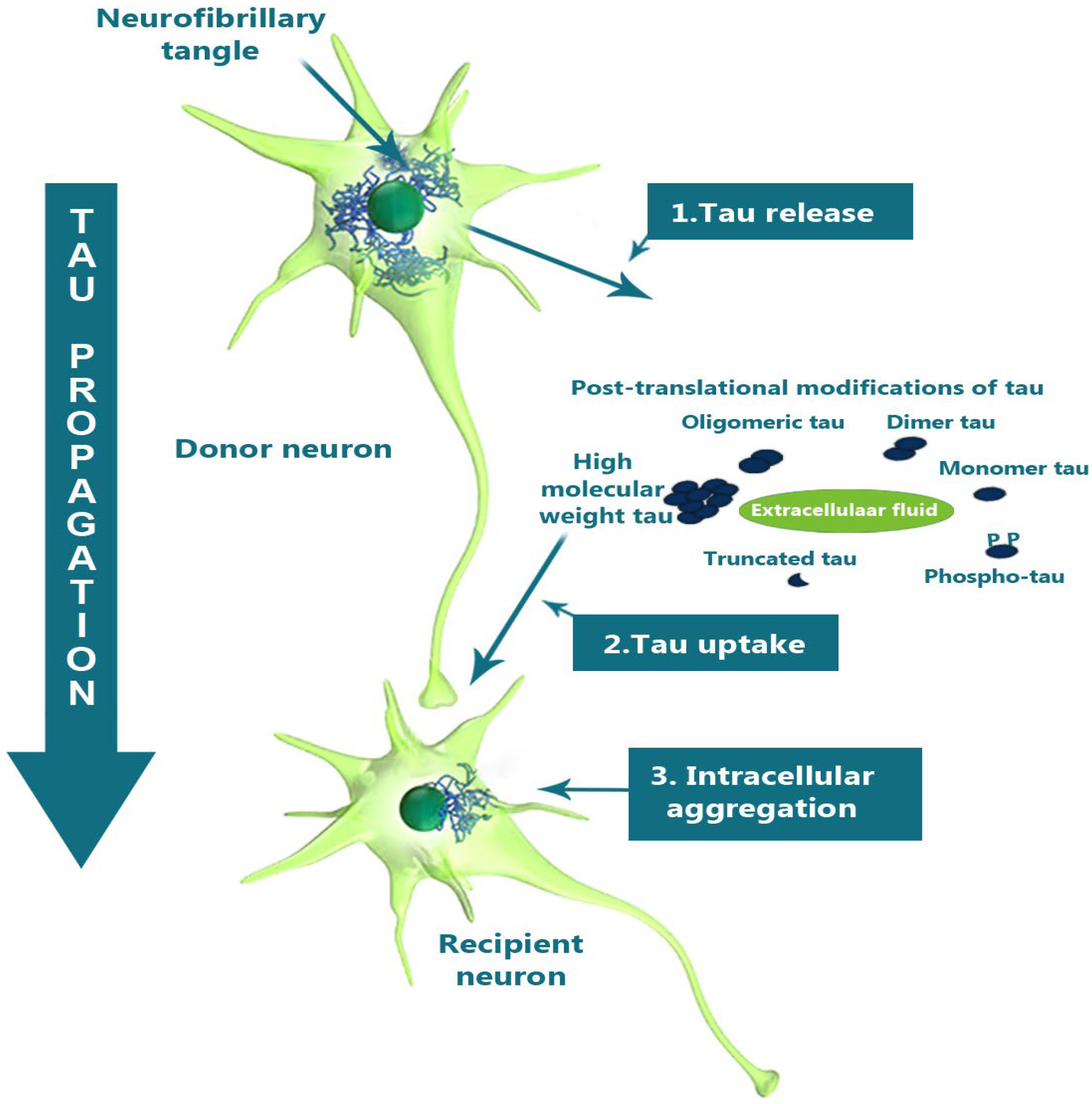
Tau protein helps stabilise the microtubules, which are essential for intracellular transport and cytoskeletal support. In its pathological state, tau becomes hyper-phosphorylated and accumulates intra-neuronally as neuro-fibrillary tangles (NFTs). Tau propagates intra-neuronally by releasing intracellular pathological tau into extracellular space, where it is taken up by recipient neurons and subsequently forms intracellular aggregates [94] (Figure 4).
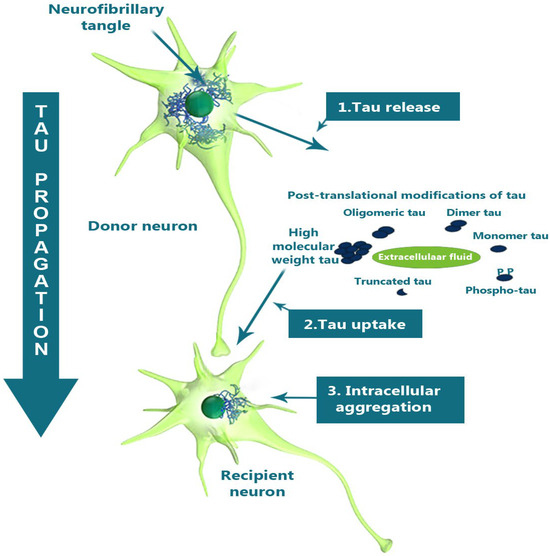
Figure 4.
A schematic diagram illustrating the tau propagation hypothesis. Neuron-to-neuron transmission of tau in AD is shown, with the release of pathological tau into the extracellular space from a donor neuron, followed by uptake by a recipient neuron after post-translational modifications, leading to the formation of intracellular aggregates. Adapted with permission from [94].
Moreover, the clinical severity of dementia is closely associated with tau deposition in comparison to amyloid deposition [95,96]. Notably, Braak’s pathologic staging of AD corresponds with the distribution of NFTs, which correlates with cognitive impairment [97]. The distribution of NFTs and its correlation with brain atrophy further justify close association of tau protein with neurodegenerative conditions like AD [98]. Furthermore, clinico-pathological studies reveals a close association of tau pathology with loss of neurons and synaptic activity, the key correlates of cognition [99]. Recently, tau pathology was reported to be present much earlier than amyloid pathology in younger AD subjects, pointing to a role of tau in the initial stages of AD and in the initiation of the disease process [100,101]. After the onset of cognitive impairment in AD, tau pathology progresses at a faster rate [97]; thus, PET imaging could have an important role in evaluating prognosis of the disease.
Following the failure of anti-amyloid therapies, a paradigm shift has been observed in the last decade toward tau as a therapeutic target, with the development of several PET tracers to target tau pathology [100]. A variety of PET ligands have the ability to detect tau aggregates formed in AD with high affinity [102,103]. The retention pattern of tau PET overlaps with regions of brain atrophy [104] and predicts cognitive performance [105]. 2-(1-{6-[(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)(methyl)amino]-2-naphthyl}ethylidene)malononitrile ([18F]FDDNP) was the first PET tau tracer to accomplish imaging in humans, and a high density of NFTs was observed in the hippocampus [106,107]. However, FDDNP was reported to bind senile plaques and NFTs equally [107], leading to a search for a more selective tau tracer. A tracer which specifically binds tau should have high affinity towards paired helical filaments (PHF) to produce enough signal to be detected in vivo. Further, the tracer should be more selective towards tau rather than Aβ, as tau is found to be less frequently distributed in the neocortex in comparison to Aβ [108]. Furthermore, (18)F-labelled THK-523 or ((18)F-6-(2-fluoroethoxy)-2-(4-aminophenyl)quinoline) was the earliest tau-specific tracer to target tau in vivo, but its use in research or clinical trials was precluded due to high retention rate in the white matter [109,110]. Several other 18F-labelled arylquinoline derivative tau PET radiotracers, such as (18)F-THK-5105 and (18)F-THK-5117, were developed [111,112]. but the more recently developed 18F-THK-5351 has better imaging characteristics, with higher tau binding affinity and lower white matter retention [113].
Furthermore, radiotracers 18F-AV-1451 (also known as T807 and 18F-flortaucipir) and 18-F-AV-680 (also known as T808), both benzimidazole pyrimidine derivatives, were developed [37,114] with higher affinity for tau aggregates and lower white matter retention. Recently, it has been concluded that 18F-flortaucipir has better sensitivity than amyloid PET and can help detect preclinical cognitive changes in people with AD [105]. Further, region-based analysis of 18F-flortaucipir depicted that the spread of tau pathology is consistent with Braak staging [115,116] (Figure 5). Recently, FDA has approved the first tau PET tracer, 18F-AV-1451(18F-flortaucipir), for the estimation of NFTs in people who are being evaluated for AD [117].
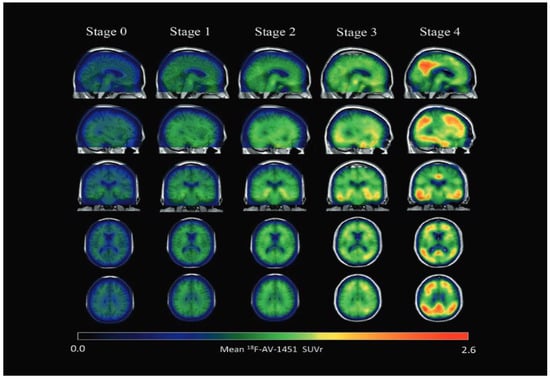
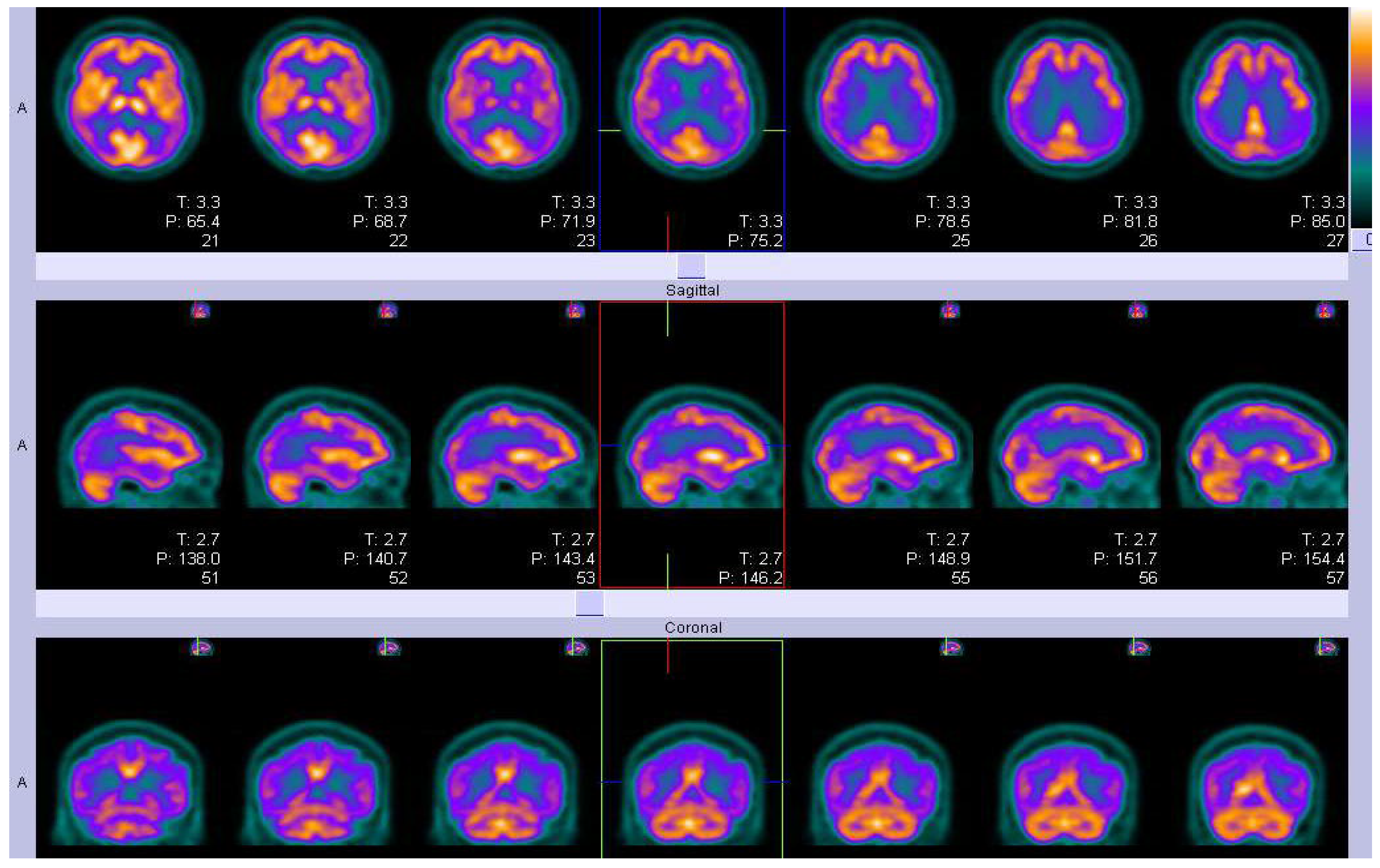
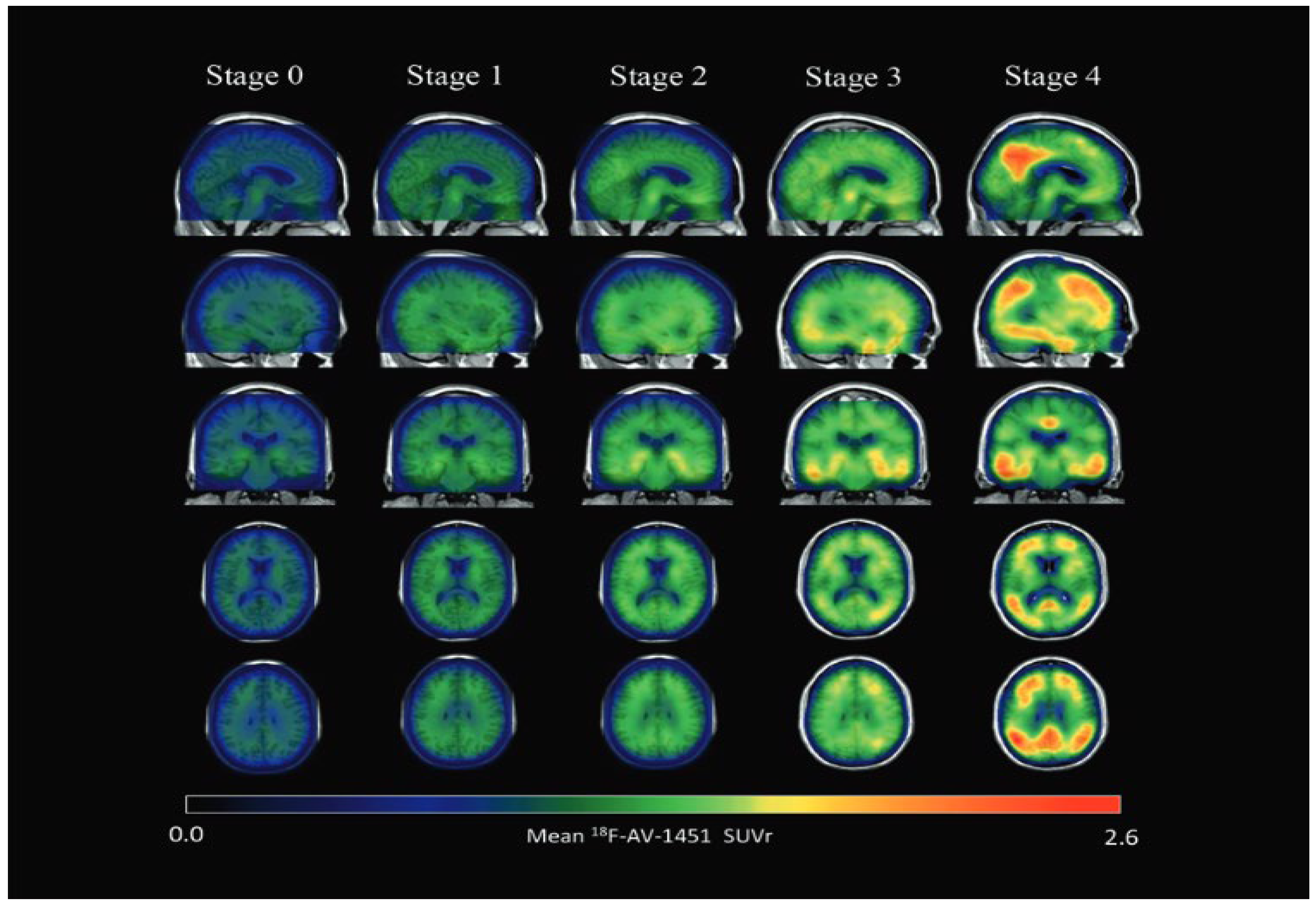
Figure 5.
Parametric 18 F-AV-1451 images across stages. In general, 18 F-AV-1451 SUVr increased throughout the cortex and subcortex from stage 0 to stage 4. Participants in stage 0 had tau levels corresponding to those of normal young adults. A dominating tau elevation in medial temporal regions (Braak I/II ROIs) was shown in stage 1. While stage 2 presented increased SUVrs in extramedial temporal regions, stage 3 showed greater SUVrs increase in Braak III/IV ROIs, including the inferior and lateral temporal lobes. Stage 4 had significantly elevated 18F-AV-1451 SUVr extending into the neocortex. ROI, region of interest; SUVr, standard uptake value ratio. Reproduced with permission [118].
In addition, tau PET tracers, such as the pyridinyl-butadienyl-benzothiazole derivative 11-C-PBB3, show higher sensitivity for tau [119] and MK-6240, a pyrrolo-pyridine-isoquinolone amine, has significant tau binding capacity without affinity for normal brain tissue [120]. Notably, 11-C-PBB3 can be quantified using cortical grey matter as a reference region for AD and other non-AD tauopathies to enhance its use in research [121]. Further, newer tau radiotracers such as [18F]RO-948 and [18F]JNJ64349311 [103,122,123,124] have been used to detect tau pathology, and it has been established that the tau pathology is deposited independently of Aβ deposition in the brain and is related to age [125,126,127]. Moreover, [18F]RO-948 is also claimed to be promising radiotracer for quantitative imaging in people with AD [128].
A recent study suggests that tau PET is better than amyloid PET and MRI in predicting cognitive change and has a role as a prognostic biomarker in preclinical and prodromal stages of AD [129]. However, tau PET tracer’s propensity for off-target binding to amyloid deposits and monoamine oxidase B may hamper their specificity in detecting tau pathology [130].
3. Structural Biomarkers
Computed tomography (CT) and MRI are two widely used structural imaging techniques, and CT is less expensive, faster, and more widely available than MRI, even in underprivileged nations [131]. However, CT is mostly used to rule out other reversible causes of dementia, such as tumour or subdural haematomas, and to help elucidate cortical atrophy and ventricular enlargement in AD [132]. Cortical atrophy and ventricular enlargement detected on CT scans are very late structural changes in AD and hence limit the use of CT as a biomarker for AD. MRI, another structural imaging technique, can readily detect characteristic structural changes in AD, such as medial temporal lobe in brain, quite early and hence qualifies as a neuroimaging biomarker for AD [133,134,135].
MRI Biomarkers in AD
It is imperative to discuss MRI biomarkers amongst the neuroimaging biomarkers, as structural MRI is an accessible neuroimaging technique for the evaluation of people with AD and is recommended in various diagnostic guidelines [136]. Hippocampus and medial temporal lobe volume measures on MRI are the most validated MRI biomarkers for AD, but structural and functional connectivity analyses using diffusion tensor imaging and resting state fMRI, respectively, can depict network disruption in AD.
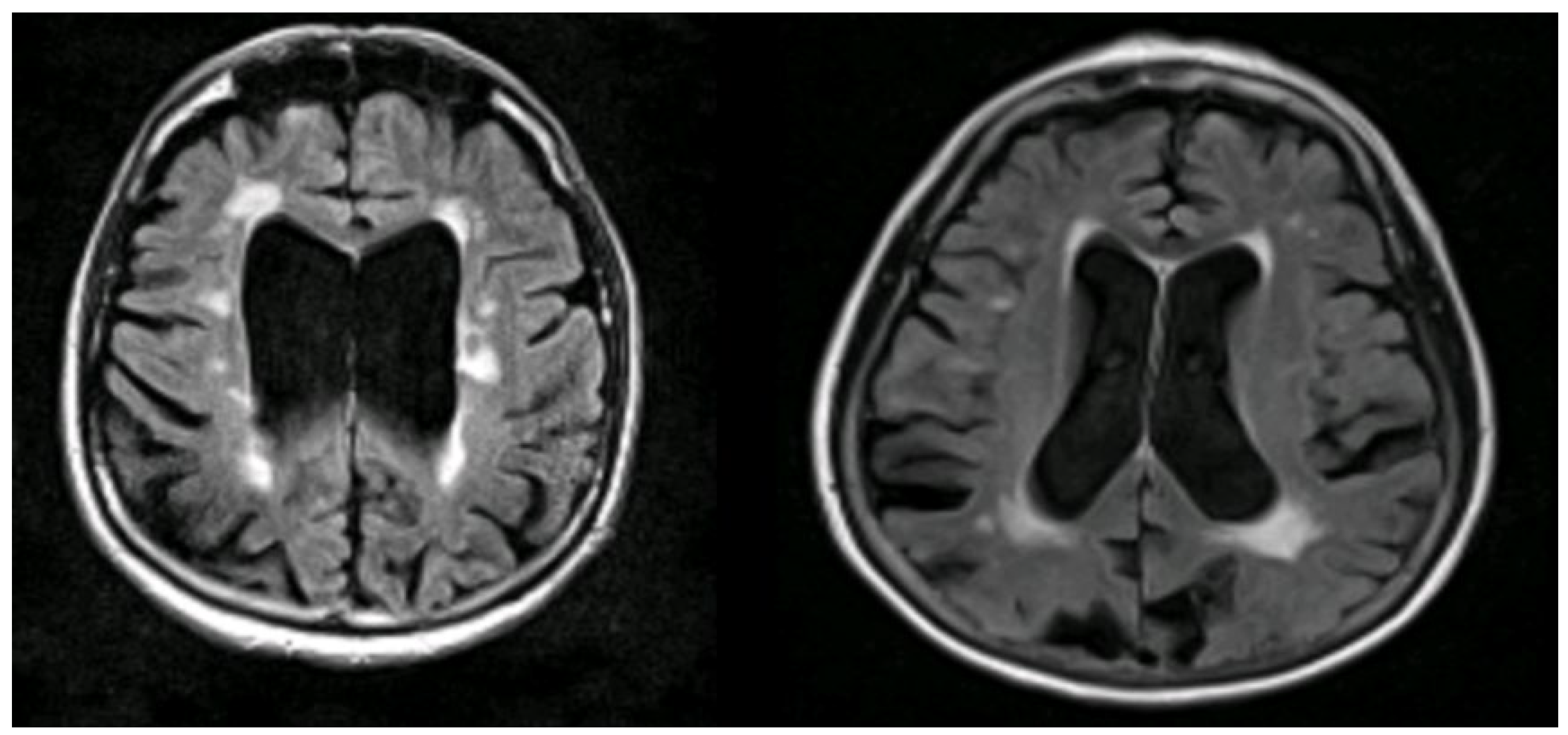
For more than a decade, a characteristic atrophy pattern on 3DT1weighted MRI has been used to distinguish AD from other causes of dementia [137] (Figure 6 and Figure 7). MRI is not only used for visual- and voxel-wise analysis of atrophy pattern to predict different causes of dementia from AD [138], but also the location of WMHs in deep and periventricular brain regions is characteristic of cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD), secondary to hypertension. Microbleeds in cortical area are characteristic of Aβ pathology [139] and also of amyloid-related imaging abnormalities seen as a complication of anti-amyloid therapy.
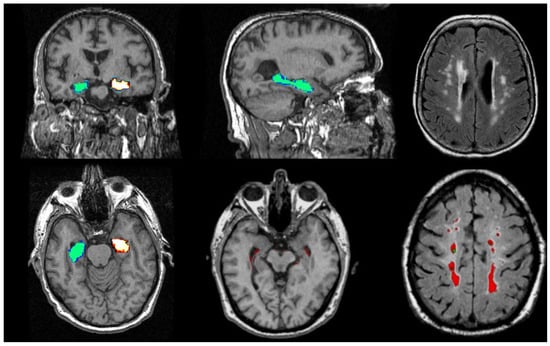
Figure 6.
Illustrations of MRI biomarkers in AD showing hippocampal volume (green and golden) in participants from the Aberdeen Birth Cohort 1936 study, illustrating hippocampal volume measurement (top row: left and centre; bottom row: left and centre), and white matter hyperintensities (top row: right, bottom row: right) in white and red. (Courtesy—Alison D. Murray, University of Aberdeen).
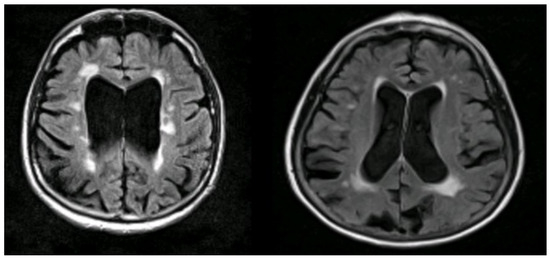
Figure 7.
Illustrations to show co-existing WMHs on MRI in people with AD. The WMH are seen as white areas around the ventricles (Courtesy—Jennifer Waymont, University of Aberdeen).
With advancement in voxel-based morphometry to extract intracranial volumes, including brain volume, hippocampal volume, ventricular volume, cortical thickness, and cortical surface area, these have been recognised as biomarkers in AD. Shape and volume analysis of substructural changes in the hippocampus can distinguish AD from other causes of dementia [140]. Furthermore, for targeting pre-dementia stages in drug trials, hippocampal volume has been validated as a neuroimaging biomarker [141]. The pattern of cortical thinning can detect presymptomatic AD subjects, for example, in those at genetic risk of AD, and can predict severity of symptoms [142,143]. Furthermore, ventricular volume can also help differentiate AD from healthy controls [144].
Resting-state fMRI has been assessed as a biomarker to distinguish AD from other causes of dementia [145]. However, task-based fMRI did not show consistent findings [146,147]. Resting-state fMRI uses measures based on graph theory [148] or functional connectivity [149]. Resting-state fMRI in AD shows changes in the default mode network for interacting brain regions such as hippocampal co-activation [150] and increased activation in the medial temporal lobe [151].
AD has traditionally been considered as a cortical dementia, but some have demonstrated white matter (WM) abnormalities in AD, such as gliosis and demyelination, and considered WM damage to be independent of cortical damage [152,153]. WM damage and axonal deposition of tau may precede the cortical damage [154,155,156], suggesting not only a link between tau pathology and white matter damage but also the implication of tau in the initiation of AD pathogenesis. This WM damage can be quantified using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), an MRI-based neuroimaging technique, which maps the WM microstructure changes in the brain [157]. Recently, diffuse microstructural changes have been observed in AD on DTI [152]. A summary of biomarkers used in AD has been provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Biomarkers Used in Alzheimer’s Disease: Relevance, Strengths, and Limitations.
4. Future Directions
Machine learning techniques offer opportunities to analyse the value of imaging and other biomarkers in AD [158].With regard to the algorithms used for identifying AD from healthy controls, research has been conducted using machine learning, deep learning, or a combination of both approaches, and some studies even combine other modalities such as PET and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) with MRI to differentiate AD from healthy controls and other type of dementias [159]. Machine learning approaches can classify AD from healthy controls using hippocampal volume, with area under tAddedhe curve (AUC) of 0.912 [160]. Exploring areas beyond the hippocampus, researchers have achieved an AUC of 0.97 using temporal lobe structures, including hippocampus, para-hippocampal gyri, entorhinal cortex, and perirhinal cortex [161]; hippocampal features had the highest contribution in classification decisions (approx. 25–45%), temporal features stood second in classification decision (approx. 13%), followed by cingulate and frontal regions (approx. 8–13% each) [162]. In order to distinguish AD from other dementias, machine learning approach achieved an AUC of 0.948 and 0.731 with DLB for testing and training datasets, respectively [163]. Moreover, an AUC of 0.93 has been achieved in differentiating AD from FTD by developing frontotemporal dementia index, which is a ratio of the weighted sum of volumetric indexes of FTD-dominant and AD-dominant structures on MRI [164]. Moreover, machine learning algorithms can not only help identify the best treatment options but also predict the effectiveness of specific interventions in AD [165]. Hence, it can be concluded that machine learning seems to be widely used for classification of AD to differentiate it from either healthy controls or other causes of dementia.
5. Conclusions
Imaging biomarkers are of proven utility in supporting the clinical diagnosis of AD in a person with dementia, in selecting those to participate in clinical trials, in monitoring progression, and in measuring responses to treatment. The combination of biomarkers along with other personalised variables and genetic variables in convolutional neural network artificial intelligence algorithms, trained and validated using real-world data, is likely to be the most valuable in defining who, when, and with what to treat in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.D.M. and S.M.T.; data curation, S.M.T. and P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.T.; writing—review and editing, A.D.M., S.M.T. and P.C.; supervision, A.D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kanekar, S.; Poot, J.D. Neuroimaging of Vascular Dementia. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 52, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humpel, C. Identifying and Validating Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrada, M.M.; Brookmeyer, R.; Paganini-Hill, A.; Berlau, D.; Kawas, C.H. Dementia Incidence Continues to Increase with Age in the Oldest Old The 90+ Study. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.; Langerman, H. Alzheimer’s Disease—Why We Need Early Diagnosis. Degener. Neurol. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2019, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattamwar, P.R.; Mathuranath, P.S. An Overview of Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2010, 13, S116–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a Biological Definition of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachurin, S.O.; Bovina, E.V.; Ustyugov, A.A. Drugs in Clinical Trials for Alzheimer’s Disease: The Major Trends. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 1186–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beshir, S.A.; Hussain, N.; Menon, V.B.; Al Haddad, A.H.I.; Al Zeer, R.A.K.; Elnour, A.A. Advancements and Challenges in Antiamyloid Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2024, 2024, 2052142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, N.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dean, R.A.; Devous, M.D.; Nikolcheva, T.; Pesini, P.; Salter, H.; Potter, W.Z.; Sperling, R.S.; Bateman, R.J.; et al. Revolutionizing Alzheimer’s Disease and Clinical Trials through Biomarkers. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 1, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Durrleman, S.; Younesi, E.; Rojkova, K.; Escott-Price, V.; Corvol, J.-C.; Broich, K.; Dubois, B.; Lista, S.; et al. A Precision Medicine Initiative for Alzheimer’s Disease: The Road Ahead to Biomarker-Guided Integrative Disease Modeling. Climacteric 2017, 20, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The Diagnosis of Dementia Due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.; Luo, Y.; Mok, V.C.; Shi, L. Advances in Computerized MRI-based Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; Hampel, H.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Blennow, K.; DeKosky, S.T.; Gauthier, S.; Selkoe, D.; Bateman, R.; et al. Advancing Research Diagnostic Criteria for Alzheimer’s Disease: The IWG-2 Criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Feldman, H.H.; Frisoni, G.B.; Hampel, H.; Jagust, W.J.; Johnson, K.A.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. A/T/N: An Unbiased Descriptive Classification Scheme for Alzheimer Disease Biomarkers. Neurology 2016, 87, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, P.; Guo, Y.; Yu, J. Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease: Emerging Trends and Clinical Implications. Chin. Med. J. 2025, 138, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.-N.; Xu, W.; Li, J.-Q.; Guo, Y.; Cui, M.; Chen, K.-L.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Dong, Q.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.-T.; et al. FDG-PET as an Independent Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Biological Diagnosis: A Longitudinal Study. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward Defining the Preclinical Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoshima, S.; Mosci, K.; Cross, D.; Thientunyakit, T. Brain [F-18]FDG PET for Clinical Dementia Workup: Differential Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Types of Dementing Disorders. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, A.; Hansen, N.; Downey, R.; Johnson, C. FDG-PET Imaging of Dementia and Neurodegenerative Disease. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2020, 41, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosconi, L. Glucose Metabolism in Normal Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: Methodological and Physiological Considerations for PET Studies. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2013, 1, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Tripathi, M.; Damle, N.; Kushwaha, S.; Jaimini, A.; D’Souza, M.M.; Sharma, R.; Saw, S.; Mondal, A. Differential Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Dementias Using Metabolic Phenotypes on F-18 FDG PET/CT. Neuroradiol. J. 2014, 27, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouter, C.; Henniges, P.; Franke, T.N.; Irwin, C.; Sahlmann, C.O.; Sichler, M.E.; Beindorff, N.; Bayer, T.A.; Bouter, Y. 18F-FDG-PET Detects Drastic Changes in Brain Metabolism in the Tg4-42 Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kljajevic, V.; Grothe, M.J.; Ewers, M.; Teipel, S. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Distinct Pattern of Hypometabolism and Atrophy in Preclinical and Predementia Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunari, I.; Samuraki, M.; Chen, W.-P.; Yanase, D.; Takeda, N.; Ono, K.; Yoshita, M.; Matsuda, H.; Yamada, M.; Kinuya, S. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET and Optimized Voxel-Based Morphometry for Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease: Aging Effect on Diagnostic Performance. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, E.; Collette, F.; Bastin, C. Cerebral Glucose Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cortex 2024, 179, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Macintosh, E.L.; Broski, S.M.; Johnson, G.B.; Hunt, C.H.; Cullen, E.L.; Peller, P.J. Multimodality Imaging of Neurodegenerative Processes: Part 1, The Basics and Common Dementias. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 207, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.M.; Murray, A.D. Alzheimer’s Dementia: The Emerging Role of Positron Emission Tomography. Neuroscientist 2021, 28, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.K.J.; Bohnen, N.I.; Wong, K.K.; Minoshima, S.; Frey, K.A. Brain PET in Suspected Dementia: Patterns of Altered FDG Metabolism. RadioGraphics 2014, 34, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, M.; Destrieux, C.; Hommet, C.; Mondon, K.; Cottier, J.-P.; Beaufils, E.; Vierron, E.; Vercouillie, J.; Ibazizene, M.; Voisin, T.; et al. Precuneus and Cingulate Cortex Atrophy and Hypometabolism in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: MRI and 18F-FDG PET Quantitative Analysis Using FreeSurfer. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 583931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Imamura, T.; Sasaki, M.; Yamaji, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Kitagaki, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Hirono, N.; Shimomura, T.; Mori, E. Regional Cerebral Glucose Metabolism in Dementia with Lewy Bodies and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1998, 51, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.A.; Deng, J.; Neuhaus, J.; Sible, I.J.; Sias, A.C.; Lee, S.E.; Kornak, J.; Marx, G.A.; Karydas, A.M.; Spina, S.; et al. Patient-Tailored, Connectivity-Based Forecasts of Spreading Brain Atrophy. Neuron 2019, 104, 856–868.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosconi, L.; Tsui, W.H.; Herholz, K.; Pupi, A.; Drzezga, A.; Lucignani, G.; Reiman, E.M.; Holthoff, V.; Kalbe, E.; Sorbi, S.; et al. Multicenter Standardized 18F-FDG PET Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Other Dementias. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.; Mena, E.; Subramaniam, R.M. Brain PET in the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 39, e413–e426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; von Arnim, C.A.F.; Burnie, N.; Bozeat, S.; Cummings, J. Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease: Role in Early and Differential Diagnosis and Recognition of Atypical Variants. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyer, S.; Simon, M.; Doyen, M.; Mortada, A.; Roch, V.; Jeanbert, E.; Thilly, N.; Malaplate, C.; Kearney-Schwartz, A.; Jonveaux, T.; et al. 18F-FDG PET Can Effectively Rule out Conversion to Dementia and the Presence of CSF Biomarker of Neurodegeneration: A Real-World Data Analysis. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, S.M.; Harvey, D.; Madison, C.M.; Koeppe, R.A.; Reiman, E.M.; Foster, N.L.; Weiner, M.W.; Jagust, W.J. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Associations between Cognitive, Functional, and FDG-PET Measures of Decline in AD and MCI. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Arteaga, J.; Cashion, D.K.; Chen, G.; Gangadharmath, U.; Gomez, L.F.; Kasi, D.; Lam, C.; Liang, Q.; Liu, C.; et al. A Highly Selective and Specific PET Tracer for Imaging of Tau Pathologies. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 31, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Langbaum, J.B.S.; Fleisher, A.S.; Ayutyanont, N.; Reschke, C.; Lee, W.; Liu, X.; Bandy, D.; Alexander, G.E.; Thompson, P.M.; et al. Twelve-Month Metabolic Declines in Probable Alzheimer’s Disease and Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment Assessed Using an Empirically Pre-Defined Statistical Region-of-Interest: Findings from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høilund-Carlsen, P.F.; Revheim, M.-E.; Costa, T.; Kepp, K.P.; Castellani, R.J.; Perry, G.; Alavi, A.; Barrio, J.R. FDG-PET versus Amyloid-PET Imaging for Diagnosis and Response Evaluation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Benefits and Pitfalls. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, T.W.; Fam, D.; Graff-Guerrero, A.; Verhoeff, N.P.G.; Tang-Wai, D.F.; Masellis, M.; Black, S.E.; Wilson, A.A.; Houle, S.; Pollock, B.G. Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography in Semantic Dementia after 6 Months of Memantine: An Open-Label Pilot Study. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 28, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potkin, S.G.; Anand, R.; Fleming, K.; Alva, G.; Keator, D.; Carreon, D.; Messina, J.; Wu, J.C.; Hartman, R.; Fallon, J.H. Brain Metabolic and Clinical Effects of Rivastigmine in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2001, 4, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.F.; Gemmell, H.G.; Murray, A.D. (Eds.) Practical Nuclear Medicine, 3rd ed.; Springer: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-1-85233-875-6. [Google Scholar]
- Antonini, A.; Leenders, K.L.; Vontobel, P.; Maguire, R.P.; Missimer, J.; Psylla, M.; Günther, I. Complementary PET Studies of Striatal Neuronal Function in the Differential Diagnosis between Multiple System Atrophy and Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 1997, 120, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, B.L.; Johnson, K.A.; Gerada, B.; Carvalho, P.A.; Satlin, A. The Scintigraphic Appearance of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Prospective Study Using Technetium-99m-HMPAO SPECT. J. Nucl. Med. 1992, 33, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Catafau, A.M. Brain SPECT in Clinical Practice. Part I: Perfusion. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 259–271. [Google Scholar]
- Devous, M.D. Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography in Neurotherapeutics. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brass, L.M.; Walovitch, R.C.; Joseph, J.L.; Léveillé, J.; Marchand, L.; Hellman, R.S.; Tikofsky, R.S.; Masdeu, J.C.; Hall, K.M.; Van Heertum, R.L. The Role of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Brain Imaging with 99mTc-Bicisate in the Localization and Definition of Mechanism of Ischemic Stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 1994, 14 (Suppl. S1), S91–S98. [Google Scholar]
- Waldemar, G.; Walovitch, R.C.; Andersen, A.R.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Bigelow, R.; Joseph, J.L.; Paulson, O.B.; Lassen, N.A. 99mTc-Bicisate (Neurolite) SPECT Brain Imaging and Cognitive Impairment in Dementia of the Alzheimer Type: A Blinded Read of Image Sets from a Multicenter SPECT Trial. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 1994, 14 (Suppl. S1), S99–S105. [Google Scholar]
- Dougall, N.J.; Bruggink, S.; Ebmeier, K.P. Systematic Review of the Diagnostic Accuracy of 99mTc-HMPAO-SPECT in Dementia. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2004, 12, 554–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Takahashi, K.; Oyama, J.; Tsuchiya, J.; Sanjo, N.; Tateishi, U. Brain Perfusion SPECT in Dementia: What Radiologists Should Know. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2024, 42, 1215–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, P.R.; Lloyd, J.J.; Snowden, J.S.; Neary, D.; Testa, H.J. A Clinical Role for 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT in the Investigation of Dementia? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 64, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchareb, Y.; AlSaadi, A.; Zabah, J.; Jain, A.; Al-Jabri, A.; Phiri, P.; Shi, J.Q.; Delanerolle, G.; Sirasanagandla, S.R. Technological Advances in SPECT and SPECT/CT Imaging. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Mizumura, S.; Nagao, T.; Ota, T.; Iizuka, T.; Nemoto, K.; Takemura, N.; Arai, H.; Homma, A. Automated Discrimination between Very Early Alzheimer Disease and Controls Using an Easy Z-Score Imaging System for Multicenter Brain Perfusion Single-Photon Emission Tomography. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2007, 28, 731–736. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, J.-W.; Kim, S.; Na, H.Y.; Ahn, S.; Lee, S.J.; Kwak, K.-H.; Lee, M.-A.; Hsiung, G.-Y.R.; Choi, B.-S.; Youn, Y.C. Effect of White Matter Hyperintensity on Medial Temporal Lobe Atrophy in Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. Neurol. 2013, 69, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valotassiou, V.; Sifakis, N.; Papatriantafyllou, J.; Angelidis, G.; Georgoulias, P. The Clinical Use of SPECT and PET Molecular Imaging in Alzheimer’s Disease; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-993-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nitrini, R.; Buchpiguel, C.A.; Caramelli, P.; Bahia, V.S.; Mathias, S.C.; Nascimento, C.M.; Degenszajn, J.; Caixeta, L. SPECT in Alzheimer’s Disease: Features Associated with Bilateral Parietotemporal Hypoperfusion. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2000, 101, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, P.M.; Holmes, C.; Hoffmann, S.M.A.; Bolt, L.; Holmes, R.; Rowden, J.; Fleming, J.S. Alzheimer’s Disease: Differences in Technetium-99m HMPAO SPECT Scan Findings between Early Onset and Late Onset Dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, G.; Nobili, F.; Copello, F.; Vitali, P.; Gianelli, M.V.; Taddei, G.; Catsafados, E.; Mariani, G. 99mTc-HMPAO Regional Cerebral Blood Flow and Quantitative Electroencephalography in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Correlative Study. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 40, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Hashikawa, K.; Fukuyama, H.; Kubota, T.; Kitamura, S.; Matsuda, H.; Hanyu, H.; Nabatame, H.; Oku, N.; Tanabe, H.; et al. Decreased Cerebral Blood Flow and Prognosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Multicenter HMPAO-SPECT Study. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2007, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, J.J.; Walstra, G.J.; Hijdra, A.; Van Royen, E.A.; Verbeeten, B.; van Gool, W.A. Measurement of Temporal Regional Cerebral Perfusion with Single-Photon Emission Tomography Predicts Rate of Decline in Language Function and Survival in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 26, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, S.; Aizawa, Y.; Sugashi, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Rodrigues, P.P. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease in the Current State: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Inui, Y.; Kizawa, T.; Kimura, Y.; Kato, T. Current and future prospects of nuclear medicine in dementia. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2017, 57, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valotassiou, V.; Malamitsi, J.; Papatriantafyllou, J.; Dardiotis, E.; Tsougos, I.; Psimadas, D.; Alexiou, S.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; Georgoulias, P. SPECT and PET Imaging in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherfler, C.; Nocker, M. Dopamine Transporter SPECT: How to Remove Subjectivity? Mov. Disord. 2009, 24 (Suppl. S2), S721–S724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaamonde-Gamo, J.; Flores-Barragán, J.M.; Ibáñez, R.; Gudín, M.; Hernández, A. DaT-SCAN SPECT in the differential diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease. Rev. Neurol. 2005, 41, 276–279. [Google Scholar]
- Akdemir, Ü.Ö.; Bora Tokçaer, A.; Atay, L.Ö. Dopamine Transporter SPECT Imaging in Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonian Disorders. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 51, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, M.; Amthauer, H.; Klaffke, S.; Kühn, A.; Lüdemann, L.; Arnold, G.; Wernecke, K.-D.; Kupsch, A.; Felix, R.; Venz, S. Combined 123I-FP-CIT and 123I-IBZM SPECT for the Diagnosis of Parkinsonian Syndromes: Study on 72 Patients. J. Neural Transm. 2005, 112, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigo, F.; Matinella, A.; Erro, R.; Tinazzi, M. [123I]FP-CIT SPECT (DaTSCAN) May Be a Useful Tool to Differentiate between Parkinson’s Disease and Vascular or Drug-Induced Parkinsonisms: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 1369-e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klunk, W.E.; Engler, H.; Nordberg, A.; Wang, Y.; Blomqvist, G.; Holt, D.P.; Bergström, M.; Savitcheva, I.; Huang, G.; Estrada, S.; et al. Imaging Brain Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Burnham, S.; Bourgeat, P.; Brown, B.; Ellis, K.A.; Salvado, O.; Szoeke, C.; Macaulay, S.L.; Martins, R.; Maruff, P.; et al. Amyloid β Deposition, Neurodegeneration, and Cognitive Decline in Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Knopman, D.S.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Weiner, M.W.; Aisen, P.S.; Shaw, L.M.; Vemuri, P.; Wiste, H.J.; Weigand, S.D.; et al. Tracking Pathophysiological Processes in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Updated Hypothetical Model of Dynamic Biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, J.A.; Panizzon, M.S.; Gustavson, D.E.; Franz, C.E.; Sanderson-Cimino, M.E.; Lyons, M.J.; Kremen, W.S. Amyloid-β Positivity Predicts Cognitive Decline but Cognition Predicts Progression to Amyloid-β Positivity. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.A.; Minoshima, S.; Bohnen, N.I.; Donohoe, K.J.; Foster, N.L.; Herscovitch, P.; Karlawish, J.H.; Rowe, C.C.; Carrillo, M.C.; Hartley, D.M.; et al. Appropriate Use Criteria for Amyloid PET: A Report of the Amyloid Imaging Task Force, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, and the Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimers Dement. 2013, 9, E1–E16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Rosenberg, P.; Oh, E. A Review of Diagnostic Impact of Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography Imaging in Clinical Practice. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2018, 46, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovici, G.D.; Jagust, W.J. Amyloid Imaging in Aging and Dementia: Testing the Amyloid Hypothesis in Vivo. Behav. Neurol. 2009, 21, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.M.; Schneider, J.A.; Bedell, B.J.; Beach, T.G.; Bilker, W.B.; Mintun, M.A.; Pontecorvo, M.J.; Hefti, F.; Carpenter, A.P.; Flitter, M.L.; et al. Use of Florbetapir-PET for Imaging Beta-Amyloid Pathology. JAMA 2011, 305, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Bagni, O.; Schillaci, O. 18F-Labeled Radiopharmaceuticals for the Molecular Neuroimaging of Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 8, 268–281. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovici, G.D.; Rosen, H.J.; Alkalay, A.; Kornak, J.; Furst, A.J.; Agarwal, N.; Mormino, E.C.; O’Neil, J.P.; Janabi, M.; Karydas, A.; et al. Amyloid vs FDG-PET in the Differential Diagnosis of AD and FTLD. Neurology 2011, 77, 2034–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, W.J.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Knol, D.L.; Tijms, B.M.; Scheltens, P.; Verhey, F.R.J.; Visser, P.J.; Amyloid Biomarker Study Group; Aalten, P.; Aarsland, D.; et al. Prevalence of Cerebral Amyloid Pathology in Persons without Dementia: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2015, 313, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogal, P.; Mahoney, C.; Graeme-Baker, S.; Roy, A.; Shah, S.; Fraioli, F.; Cowley, P.; Jäger, H.R. The Common Dementias: A Pictorial Review. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 3405–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolk, D.A.; Klunk, W.E. Update on Amyloid Imaging: From Healthy Aging to Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2009, 9, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeveste, B.; Prieto, E.; Guillén, E.F.; Jimenez, A.; Montoya, G.; Villino, R.; Riverol, M.; Arbizu, J. Combination of Amyloid and FDG PET for the Prediction of Short-Term Conversion from MCI to Alzheimer´s Disease in the Clinical Practice. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025, 52, 3567–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, A.; Carter, S.F.; Rinne, J.; Drzezga, A.; Brooks, D.J.; Vandenberghe, R.; Perani, D.; Forsberg, A.; Långström, B.; Scheinin, N.; et al. A European Multicentre PET Study of Fibrillar Amyloid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, A.; Koivunen, J.; Edison, P.; Archer, H.A.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Någren, K.; Bullock, R.; Walker, Z.; Kennedy, A.; Fox, N.C.; et al. Conversion of Amyloid Positive and Negative MCI to AD over 3 Years. Neurology 2009, 73, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijbers, W.; Mormino, E.C.; Schultz, A.P.; Wigman, S.; Ward, A.M.; Larvie, M.; Amariglio, R.E.; Marshall, G.A.; Rentz, D.M.; Johnson, K.A.; et al. Amyloid-β Deposition in Mild Cognitive Impairment Is Associated with Increased Hippocampal Activity, Atrophy and Clinical Progression. Brain 2015, 138, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlster, P.; Niederländer, C.; Kriza, C.; Schaller, S.; Kolominsky-Rabas, P.L. Clinical Assessment of Amyloid Imaging in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 36, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, W.G.; Mohs, R.C.; Davis, K.L. A New Rating Scale for Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Psychiatry 1984, 141, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.C.; Ernesto, C.; Schafer, K.; Coats, M.; Leon, S.; Sano, M.; Thal, L.J.; Woodbury, P. Clinical Dementia Rating Training and Reliability in Multicenter Studies: The Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Experience. Neurology 1997, 48, 1508–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhorna, J.; Krahnke, T.; Shear, M.; Harrison, J.E.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale Variants in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Alzheimer’s Disease: Change over Time and the Effect of Enrichment Strategies. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2016, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, Y. Cognitive Reserve in Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; et al. The Antibody Aducanumab Reduces Aβ Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxford, A.E.; Stewart, E.S.; Rohn, T.T. Clinical Trials in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Hurdle in the Path of Remedy. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 2020, 5380346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, R.; Sterling, K.; Song, W. Amyloid β-Based Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: Challenges, Successes and Future. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S. Tau Propagation as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target for Dementia: Potentials and Unanswered Questions. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriagada, P.V.; Growdon, J.H.; Hedley-Whyte, E.T.; Hyman, B.T. Neurofibrillary Tangles but Not Senile Plaques Parallel Duration and Severity of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1992, 42, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierer, L.M.; Hof, P.R.; Purohit, D.P.; Carlin, L.; Schmeidler, J.; Davis, K.L.; Perl, D.P. Neocortical Neurofibrillary Tangles Correlate with Dementia Severity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Arch. Neurol. 1995, 52, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological Stageing of Alzheimer-Related Changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitwell, J.L.; Josephs, K.A.; Murray, M.E.; Kantarci, K.; Przybelski, S.A.; Weigand, S.D.; Vemuri, P.; Senjem, M.L.; Parisi, J.E.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. MRI Correlates of Neurofibrillary Tangle Pathology at Autopsy: A Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. Neurology 2008, 71, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.T.; Alafuzoff, I.; Bigio, E.H.; Bouras, C.; Braak, H.; Cairns, N.J.; Castellani, R.J.; Crain, B.J.; Davies, P.; Del Tredici, K.; et al. Correlation of Alzheimer Disease Neuropathologic Changes with Cognitive Status: A Review of the Literature. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhi, W.; Wang, L. Role of Tau Protein in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Development of Its Targeted Drugs: A Literature Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Hata, Y.; Ichimata, S.; Nishida, N. Tau and Amyloid-β Pathology in Japanese Forensic Autopsy Series Under 40 Years of Age: Prevalence and Association with APOE Genotype and Suicide Risk. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 72, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleisher, A.S.; Pontecorvo, M.J.; Devous, M.D.; Lu, M.; Arora, A.K.; Truocchio, S.P.; Aldea, P.; Flitter, M.; Locascio, T.; Devine, M.; et al. Positron Emission Tomography Imaging with [18F]Flortaucipir and Postmortem Assessment of Alzheimer Disease Neuropathologic Changes. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzy, A.; Chiotis, K.; Lemoine, L.; Gillberg, P.-G.; Almkvist, O.; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.; Nordberg, A. Tau PET Imaging in Neurodegenerative Tauopathies—Still a Challenge. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1112–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, T.M.; Du, R.; Klencklen, G.; Baker, S.L.; Jagust, W.J. Distinct Effects of Beta-Amyloid and Tau on Cortical Thickness in Cognitively Healthy Older Adults. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Smith, R.; Ohlsson, T.; Strandberg, O.; Mattsson, N.; Insel, P.S.; Palmqvist, S.; Hansson, O. Associations between Tau, Aβ, and Cortical Thickness with Cognition in Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2019, 92, e601–e612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agdeppa, E.D.; Kepe, V.; Liu, J.; Flores-Torres, S.; Satyamurthy, N.; Petric, A.; Cole, G.M.; Small, G.W.; Huang, S.C.; Barrio, J.R. Binding Characteristics of Radiofluorinated 6-Dialkylamino-2-Naphthylethylidene Derivatives as Positron Emission Tomography Imaging Probes for Beta-Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, RC189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoghi-Jadid, K.; Small, G.W.; Agdeppa, E.D.; Kepe, V.; Ercoli, L.M.; Siddarth, P.; Read, S.; Satyamurthy, N.; Petric, A.; Huang, S.-C.; et al. Localization of Neurofibrillary Tangles and Beta-Amyloid Plaques in the Brains of Living Patients with Alzheimer Disease. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2002, 10, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Furumoto, S.; Fodero-Tavoletti, M.; Harada, R.; Mulligan, R.S.; Kudo, Y.; Masters, C.L.; Yanai, K.; Rowe, C.C.; Okamura, N. The Challenges of Tau Imaging. Future Neurol. 2012, 7, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodero-Tavoletti, M.T.; Okamura, N.; Furumoto, S.; Mulligan, R.S.; Connor, A.R.; McLean, C.A.; Cao, D.; Rigopoulos, A.; Cartwright, G.A.; O’Keefe, G.; et al. 18F-THK523: A Novel in Vivo Tau Imaging Ligand for Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain 2011, 134, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Furumoto, S.; Fodero-Tavoletti, M.T.; Mulligan, R.S.; Hodges, J.; Harada, R.; Yates, P.; Piguet, O.; Pejoska, S.; Doré, V.; et al. In Vivo Evaluation of a Novel Tau Imaging Tracer for Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, N.; Furumoto, S.; Fodero-Tavoletti, M.T.; Mulligan, R.S.; Harada, R.; Yates, P.; Pejoska, S.; Kudo, Y.; Masters, C.L.; Yanai, K.; et al. Non-Invasive Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease Neurofibrillary Pathology Using 18F-THK5105 PET. Brain 2014, 137, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, R.; Okamura, N.; Furumoto, S.; Furukawa, K.; Ishiki, A.; Tomita, N.; Hiraoka, K.; Watanuki, S.; Shidahara, M.; Miyake, M.; et al. [(18)F]THK-5117 PET for Assessing Neurofibrillary Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, R.; Okamura, N.; Furumoto, S.; Furukawa, K.; Ishiki, A.; Tomita, N.; Tago, T.; Hiraoka, K.; Watanuki, S.; Shidahara, M.; et al. 18F-THK5351: A Novel PET Radiotracer for Imaging Neurofibrillary Pathology in Alzheimer Disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, D.T.; Bahri, S.; Szardenings, A.K.; Walsh, J.C.; Mu, F.; Su, M.-Y.; Shankle, W.R.; Elizarov, A.; Kolb, H.C. Early Clinical PET Imaging Results with the Novel PHF-Tau Radioligand [F-18]-T807. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 34, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquié, M.; Chong, M.S.T.; Antón-Fernández, A.; Verwer, E.E.; Sáez-Calveras, N.; Meltzer, A.C.; Ramanan, P.; Amaral, A.C.; Gonzalez, J.; Normandin, M.D.; et al. [F-18]-AV-1451 Binding Correlates with Postmortem Neurofibrillary Tangle Braak Staging. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Hwang, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.M.; Lyoo, C.H.; Ryu, Y.H.; Lee, M.S. Tau PET in Alzheimer Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neurology 2016, 87, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthel, H. First Tau PET Tracer Approved: Toward Accurate In Vivo Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1409–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-D.; Lu, J.-Y.; Li, H.-Q.; Yang, Y.-X.; Jiang, J.-H.; Cui, M.; Zuo, C.-T.; Tan, L.; Dong, Q.; Yu, J.-T.; et al. Staging Tau Pathology with Tau PET in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Longitudinal Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, M.; Shimada, H.; Suhara, T.; Shinotoh, H.; Ji, B.; Maeda, J.; Zhang, M.-R.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Ono, M.; et al. Imaging of Tau Pathology in a Tauopathy Mouse Model and in Alzheimer Patients Compared to Normal Controls. Neuron 2013, 79, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostetler, E.D.; Walji, A.M.; Zeng, Z.; Miller, P.; Bennacef, I.; Salinas, C.; Connolly, B.; Gantert, L.; Haley, H.; Holahan, M.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of 18F-MK-6240, a Promising PET Tracer for In Vivo Quantification of Human Neurofibrillary Tangles. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Endo, H.; Ichise, M.; Shimada, H.; Seki, C.; Ikoma, Y.; Shinotoh, H.; Yamada, M.; Higuchi, M.; Zhang, M.-R.; et al. A New Method to Quantify Tau Pathologies with (11)C-PBB3 PET Using Reference Tissue Voxels Extracted from Brain Cortical Gray Matter. EJNMMI Res. 2016, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbi, L.C.; Knust, H.; Körner, M.; Honer, M.; Czech, C.; Belli, S.; Muri, D.; Edelmann, M.R.; Hartung, T.; Erbsmehl, I.; et al. Identification of Three Novel Radiotracers for Imaging Aggregated Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease with Positron Emission Tomography. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7350–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria Bohórquez, S.; Marik, J.; Ogasawara, A.; Tinianow, J.N.; Gill, H.S.; Barret, O.; Tamagnan, G.; Alagille, D.; Ayalon, G.; Manser, P.; et al. [18F]GTP1 (Genentech Tau Probe 1), a Radioligand for Detecting Neurofibrillary Tangle Tau Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Declercq, L.; Rombouts, F.; Koole, M.; Fierens, K.; Mariën, J.; Langlois, X.; Andrés, J.I.; Schmidt, M.; Macdonald, G.; Moechars, D.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of 18F-JNJ64349311, a Novel PET Tracer for Tau Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, S.N.; Schöll, M.; Baker, S.L.; Ayakta, N.; Swinnerton, K.N.; Bell, R.K.; Mellinger, T.J.; Shah, V.D.; O’Neil, J.P.; Janabi, M.; et al. Amyloid and Tau PET Demonstrate Region-Specific Associations in Normal Older People. Neuroimage 2017, 150, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontecorvo, M.J.; Devous, M.D.; Navitsky, M.; Lu, M.; Salloway, S.; Schaerf, F.W.; Jennings, D.; Arora, A.K.; McGeehan, A.; Lim, N.C.; et al. Relationships between Flortaucipir PET Tau Binding and Amyloid Burden, Clinical Diagnosis, Age and Cognition. Brain 2017, 140, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuestefeld, A.; Pichet Binette, A.; Berron, D.; Spotorno, N.; van Westen, D.; Stomrud, E.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Strandberg, O.; Smith, R.; Palmqvist, S.; et al. Age-Related and Amyloid-Beta-Independent Tau Deposition and Its Downstream Effects. Brain 2023, 146, 3192–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara, H.; Comley, R.A.; Borroni, E.; Honer, M.; Kitmiller, K.; Roberts, J.; Gapasin, L.; Mathur, A.; Klein, G.; Wong, D.F. Evaluation of 18F-RO-948 PET for Quantitative Assessment of Tau Accumulation in the Human Brain. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Smith, R.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Groot, C.; Leuzy, A.; Strandberg, O.; Palmqvist, S.; Olsson, T.; Jögi, J.; Stormrud, E.; et al. Accuracy of Tau Positron Emission Tomography as a Prognostic Marker in Preclinical and Prodromal Alzheimer Disease: A Head-to-Head Comparison Against Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, C.; Villeneuve, S.; Smith, R.; Hansson, O.; Ossenkoppele, R. Tau PET Imaging in Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 20S–26S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, S.; Caroli, A.; Geroldi, C.; Barillot, C.; Frisoni, G.B.; Collins, D.L. MRI-Based Automated Computer Classification of Probable AD versus Normal Controls. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2008, 27, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, T.; Sheelakumari, R.; James, J.S.; Mathuranath, P. A Review of Neuroimaging Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurol. Asia 2013, 18, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Stoub, T.R.; Shah, R.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Killiany, R.J.; Albert, M.S.; Hyman, B.T.; Blacker, D.; Detoledo-Morrell, L. Alzheimer-Signature MRI Biomarker Predicts AD Dementia in Cognitively Normal Adults. Neurology 2011, 76, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakas, J.E.; Howe, M.D.; Thompson, L.I.; Riera, N.M.; Riddle, M.C. Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease: Past, Present and Future Clinical Use. Biomark. Neuropsychiatry 2023, 8, 100063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.A.; Fox, N.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Klunk, W.E. Brain Imaging in Alzheimer Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK). Dementia: Assessment, Management and Support for People Living with Dementia and Their Carers; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: Clinical Guidelines; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (UK): London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-4731-2978-8. [Google Scholar]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Pievani, M.; Testa, C.; Sabattoli, F.; Bresciani, L.; Bonetti, M.; Beltramello, A.; Hayashi, K.M.; Toga, A.W.; Thompson, P.M. The Topography of Grey Matter Involvement in Early and Late Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain 2007, 130, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.; Bouwman, F.; Burton, E.J.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; O’Brien, J.T.; Fox, N.C.; Ridgway, G.R.; Schott, J.M. Patterns of Atrophy in Pathologically Confirmed Dementias: A Voxelwise Analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, S.; Vernooij, M.W.; Kuijer, J.P.A.; Larsson, E.-M.; Jäger, H.R.; Barkhof, F. Cerebral Microbleeds: Imaging and Clinical Significance. Radiology 2018, 287, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kälin, A.M.; Park, M.T.M.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Lerch, J.P.; Michels, L.; Schroeder, C.; Broicher, S.D.; Kollias, S.; Nitsch, R.M.; Gietl, A.F.; et al. Subcortical Shape Changes, Hippocampal Atrophy and Cortical Thinning in Future Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.L.G.; Schwarz, A.J.; Isaac, M.; Pani, L.; Vamvakas, S.; Hemmings, R.; Carrillo, M.C.; Yu, P.; Sun, J.; Beckett, L.; et al. Coalition Against Major Diseases/European Medicines Agency Biomarker Qualification of Hippocampal Volume for Enrichment of Clinical Trials in Predementia Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014, 10, 421–429.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Bakkour, A.; Salat, D.H.; Feczko, E.; Pacheco, J.; Greve, D.N.; Grodstein, F.; Wright, C.I.; Blacker, D.; Rosas, H.D.; et al. The Cortical Signature of Alzheimer’s Disease: Regionally Specific Cortical Thinning Relates to Symptom Severity in Very Mild to Mild AD Dementia and Is Detectable in Asymptomatic Amyloid-Positive Individuals. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keuss, S.E.; Coath, W.; Cash, D.M.; Barnes, J.; Nicholas, J.M.; Lane, C.A.; Parker, T.D.; Keshavan, A.; Buchanan, S.M.; Wagen, A.Z.; et al. Rates of Cortical Thinning in Alzheimer’s Disease Signature Regions Associate with Vascular Burden but Not with β-Amyloid Status in Cognitively Normal Adults at Age 70. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ekin, A.; de Haan, G. Shape Analysis of Brain Ventricles for Improved Classification of Alzheimer’s Patients. In Proceedings of the 2008 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 October 2008; IEEE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 2252–2255. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenfeld, C.; Werner, C.J.; Reetz, K. Resting-State Connectivity in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Is There Potential for an Imaging Biomarker? Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 18, 849–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A.; Albert, M.S.; Krauss, G.; Speck, C.L.; Gallagher, M. Response of the Medial Temporal Lobe Network in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment to Therapeutic Intervention Assessed by fMRI and Memory Task Performance. Neuroimage Clin. 2015, 7, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, B.; Suppiah, S.; Ibrahim, N.; Mohamad, M.; Hassan, H.A.; Nasser, N.S.; Saripan, M.I. Diagnostic Power of Resting-state fMRI for Detection of Network Connectivity in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 2941–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaee, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, A.; Babajani-Feremi, A. Identifying Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Using Resting-State fMRI and Graph Theory. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ward, B.D.; Xie, C.; Li, W.; Wu, Z.; Jones, J.L.; Franczak, M.; Antuono, P.; Li, S.-J. Classification of Alzheimer Disease, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Normal Cognitive Status with Large-Scale Network Analysis Based on Resting-State Functional MR Imaging. Radiology 2011, 259, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greicius, M.D.; Srivastava, G.; Reiss, A.L.; Menon, V. Default-Mode Network Activity Distinguishes Alzheimer’s Disease from Healthy Aging: Evidence from Functional MRI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4637–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Salat, D.H.; Bates, J.F.; Atiya, M.; Killiany, R.J.; Greve, D.N.; Dale, A.M.; Stern, C.E.; Blacker, D.; Albert, M.S.; et al. Medial Temporal Lobe Function and Structure in Mild Cognitive Impairment. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esrael, S.M.A.M.; Hamed, A.M.M.; Khedr, E.M.; Soliman, R.K. Application of Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Alzheimer’s Disease: Quantification of White Matter Microstructural Changes. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; MacFall, J.R.; Payne, M.E. Classification of White Matter Lesions on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Elderly Persons. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendlin, B.B.; Carlsson, C.M.; Johnson, S.C.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Willette, A.A.; Okonkwo, O.C.; Sodhi, A.; Ries, M.L.; Birdsill, A.C.; et al. CSF T-Tau/Aβ42 Predicts White Matter Microstructure in Healthy Adults at Risk for Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.; Przybelski, S.A.; Reid, R.I.; Lesnick, T.G.; Ramanan, V.K.; Botha, H.; Matchett, B.J.; Murray, M.E.; Reichard, R.R.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. White Matter Damage Due to Vascular, Tau, and TDP-43 Pathologies and Its Relevance to Cognition. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siger, M.; Schuff, N.; Zhu, X.; Miller, B.L.; Weiner, M.W. Regional Myo-Inositol Concentration in Mild Cognitive Impairment Using 1H Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2009, 23, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croall, I.D.; Lohner, V.; Moynihan, B.; Khan, U.; Hassan, A.; O’Brien, J.T.; Morris, R.G.; Tozer, D.J.; Cambridge, V.C.; Harkness, K.; et al. Using DTI to Assess White Matter Microstructure in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease (SVD) in Multicentre Studies. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehoe, E.G.; McNulty, J.P.; Mullins, P.G.; Bokde, A.L.W. Advances in MRI Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomark. Med. 2014, 8, 1151–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Kowshik, S.S.; Lteif, D.; Puducheri, S.; Jasodanand, V.H.; Zhou, O.T.; Walia, A.S.; Guney, O.B.; Zhang, J.D.; Poésy, S.; et al. AI-Based Differential Diagnosis of Dementia Etiologies on Multimodal Data. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2977–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, L.; Igel, C.; Liv Hansen, N.; Osler, M.; Lauritzen, M.; Rostrup, E.; Nielsen, M.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative and the Australian Imaging Biomarkers and Lifestyle Flagship Study of Ageing. Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Using MRI Hippocampal Texture. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2016, 37, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chincarini, A.; Bosco, P.; Calvini, P.; Gemme, G.; Esposito, M.; Olivieri, C.; Rei, L.; Squarcia, S.; Rodriguez, G.; Bellotti, R.; et al. Local MRI Analysis Approach in the Diagnosis of Early and Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroimage 2011, 58, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diogo, V.S.; Ferreira, H.A.; Prata, D.; for the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Machine Learning: A Multi-Diagnostic, Generalizable Approach. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.V.; Westman, E.; Beyer, M.K.; Kramberger, M.G.; Aguilar, C.; Pirtosek, Z.; Aarsland, D. Multivariate Classification of Patients with Alzheimer’s and Dementia with Lewy Bodies Using High-Dimensional Cortical Thickness Measurements: An MRI Surface-Based Morphometric Study. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Mai, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Fang, W.; Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Liao, W.; Xiao, S.; et al. An MRI-Based Strategy for Differentiation of Frontotemporal Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, K.; Salcidua, S.; Orellana, P.; Sauma-Pérez, T.; León, T.; Steinmetz, L.C.L.; Ibañez, A.; Duran-Aniotz, C.; de la Cruz, R. Systematic Review: Fluid Biomarkers and Machine Learning Methods to Improve the Diagnosis from Mild Cognitive Impairment to Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).