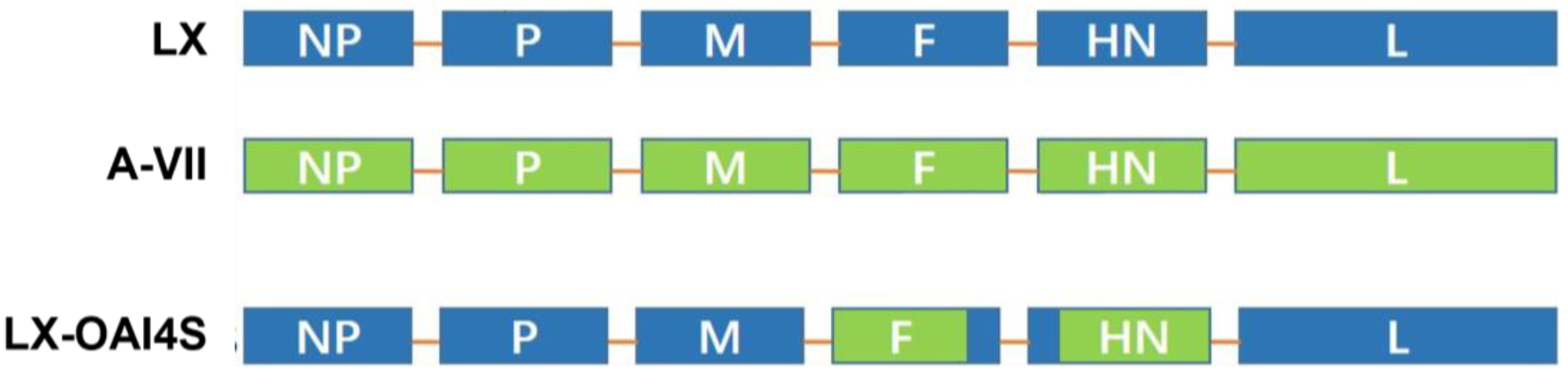
Figure 1.
Schematic description of the structure of the LX-OAI4S. The ectodomain of the F and HN gene of the NDV LX strain was replaced by that of the vaccine strain A-VII. Blue color represents genes derived from the LX strain; green color represents genes derived from the A-VII strain.
Figure 1.
Schematic description of the structure of the LX-OAI4S. The ectodomain of the F and HN gene of the NDV LX strain was replaced by that of the vaccine strain A-VII. Blue color represents genes derived from the LX strain; green color represents genes derived from the A-VII strain.
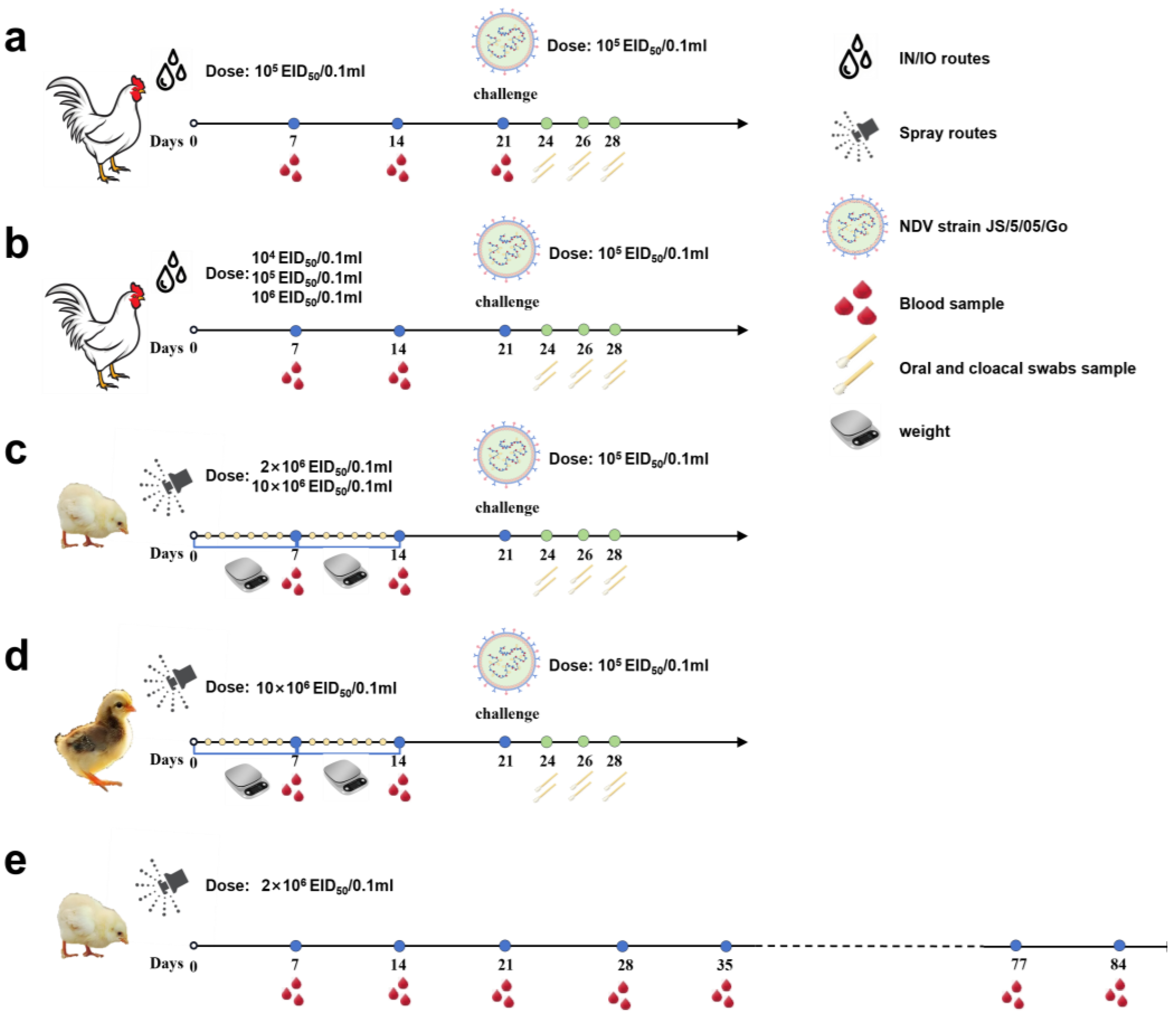
Figure 2.
Flow chart of animal experiment implementation. (a) Three-week-old specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, vaccine strain La Sota, VG/GA, and PBS, respectively, via the intranasal and intraocular (IN/IO) routes with a dosage of 106 EID50/0.1 mL. Blood samples were collected on 7, 14, and 21 dpv to separate serum. Chickens were challenged with 105 EID50/0.1 mL of NDV strain JS2/06 via the IN/IO route at 21 dpv. Oral and cloacal swabs were collected from birds to evaluate viral shedding at 3, 5, and 7 dpc. (b) Three-week-old SPF chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S via the IN/IO routes with a dosage of 104 EID50/0.1 mL, 105 EID50/0.1 mL, and 106 EID50/0.1 mL, respectively. Blood samples were collected on 7, 14, and 21 dpv to separate serum. Chickens were challenged with 105 EID50/0.1 mL of NDV strain JS2/06 via the IN/IO route at 21 dpv. Oral and cloacal swabs were collected from birds to evaluate viral shedding at 3, 5, and 7 dpc. (c) One-day-old SPF chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, strain LX-OAI4S, La Sota, and VG/GA, respectively, via the spray routes with a dosage of 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL and 10 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL, respectively. The weight of chickens was continuously detected for 14 days after vaccination. Blood samples were collected on 7 and 14 dpv to separate serum. Chickens were challenged with 105 EID50/0.1 mL of NDV strain JS2/06 via the IN/IO route at 21 dpv. Oral and cloacal swabs were collected from birds to evaluate viral shedding at 3, 5, and 7 dpc. (d) One-day-old commercial chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, La Sota, and VG/GA, respectively, via the spray routes with a dosage of 10 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL. The weight of the chickens was continuously detected for 14 days after vaccination. Blood samples were collected on 7 and 14 dpv to separate serum. Chickens were challenged with 105 EID50/0.1 mL of NDV strain JS2/06 via the IN/IO route at 21 dpv. Oral and cloacal swabs were collected from birds to evaluate viral shedding at 3, 5, and 7 dpc. (e) One-day-old SPF chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S via the spray routes with a dosage of 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL. Blood samples were collected every 7 days until day 84.
Figure 2.
Flow chart of animal experiment implementation. (a) Three-week-old specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, vaccine strain La Sota, VG/GA, and PBS, respectively, via the intranasal and intraocular (IN/IO) routes with a dosage of 106 EID50/0.1 mL. Blood samples were collected on 7, 14, and 21 dpv to separate serum. Chickens were challenged with 105 EID50/0.1 mL of NDV strain JS2/06 via the IN/IO route at 21 dpv. Oral and cloacal swabs were collected from birds to evaluate viral shedding at 3, 5, and 7 dpc. (b) Three-week-old SPF chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S via the IN/IO routes with a dosage of 104 EID50/0.1 mL, 105 EID50/0.1 mL, and 106 EID50/0.1 mL, respectively. Blood samples were collected on 7, 14, and 21 dpv to separate serum. Chickens were challenged with 105 EID50/0.1 mL of NDV strain JS2/06 via the IN/IO route at 21 dpv. Oral and cloacal swabs were collected from birds to evaluate viral shedding at 3, 5, and 7 dpc. (c) One-day-old SPF chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, strain LX-OAI4S, La Sota, and VG/GA, respectively, via the spray routes with a dosage of 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL and 10 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL, respectively. The weight of chickens was continuously detected for 14 days after vaccination. Blood samples were collected on 7 and 14 dpv to separate serum. Chickens were challenged with 105 EID50/0.1 mL of NDV strain JS2/06 via the IN/IO route at 21 dpv. Oral and cloacal swabs were collected from birds to evaluate viral shedding at 3, 5, and 7 dpc. (d) One-day-old commercial chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, La Sota, and VG/GA, respectively, via the spray routes with a dosage of 10 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL. The weight of the chickens was continuously detected for 14 days after vaccination. Blood samples were collected on 7 and 14 dpv to separate serum. Chickens were challenged with 105 EID50/0.1 mL of NDV strain JS2/06 via the IN/IO route at 21 dpv. Oral and cloacal swabs were collected from birds to evaluate viral shedding at 3, 5, and 7 dpc. (e) One-day-old SPF chickens were vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S via the spray routes with a dosage of 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL. Blood samples were collected every 7 days until day 84.
![Vetsci 11 00532 g002]()
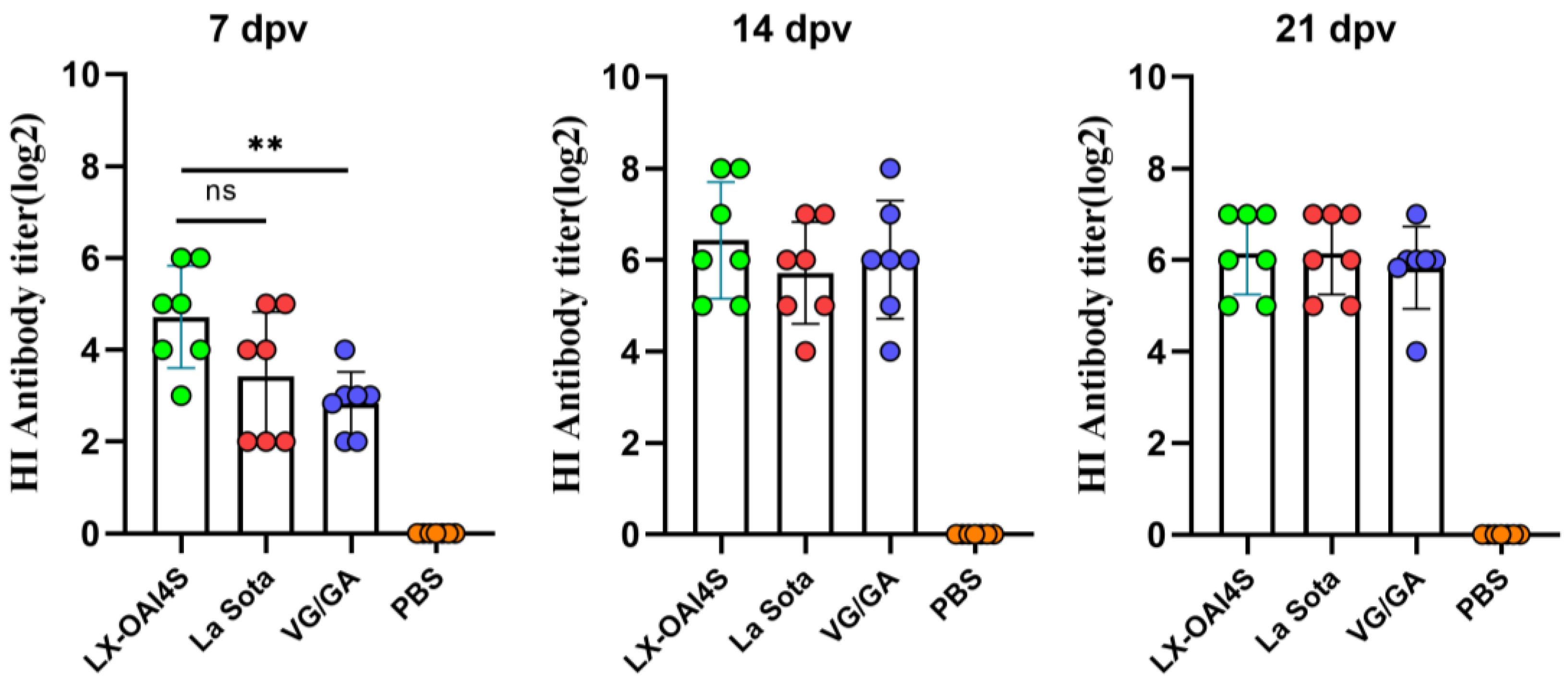
Figure 3.
Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) antibody titers induced in chickens by ND vaccines. Specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 7) and vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, vaccine strain La Sota, VG/GA, and PBS, respectively. Each chicken was vaccinated via the intranasal and intraocular (IN/IO) routes with a dosage of 106 EID50/0.1 mL. The PBS control group was also established. The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected on 7, 14, and 21 dpv to separate serum. Green, red, blue, and orange colors represent the HI potency of the LX-OAI4S, La Sota, VG/GA, and PBS groups, respectively. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA. ** p < 0.01; ns, not significant.
Figure 3.
Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) antibody titers induced in chickens by ND vaccines. Specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 7) and vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, vaccine strain La Sota, VG/GA, and PBS, respectively. Each chicken was vaccinated via the intranasal and intraocular (IN/IO) routes with a dosage of 106 EID50/0.1 mL. The PBS control group was also established. The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected on 7, 14, and 21 dpv to separate serum. Green, red, blue, and orange colors represent the HI potency of the LX-OAI4S, La Sota, VG/GA, and PBS groups, respectively. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA. ** p < 0.01; ns, not significant.
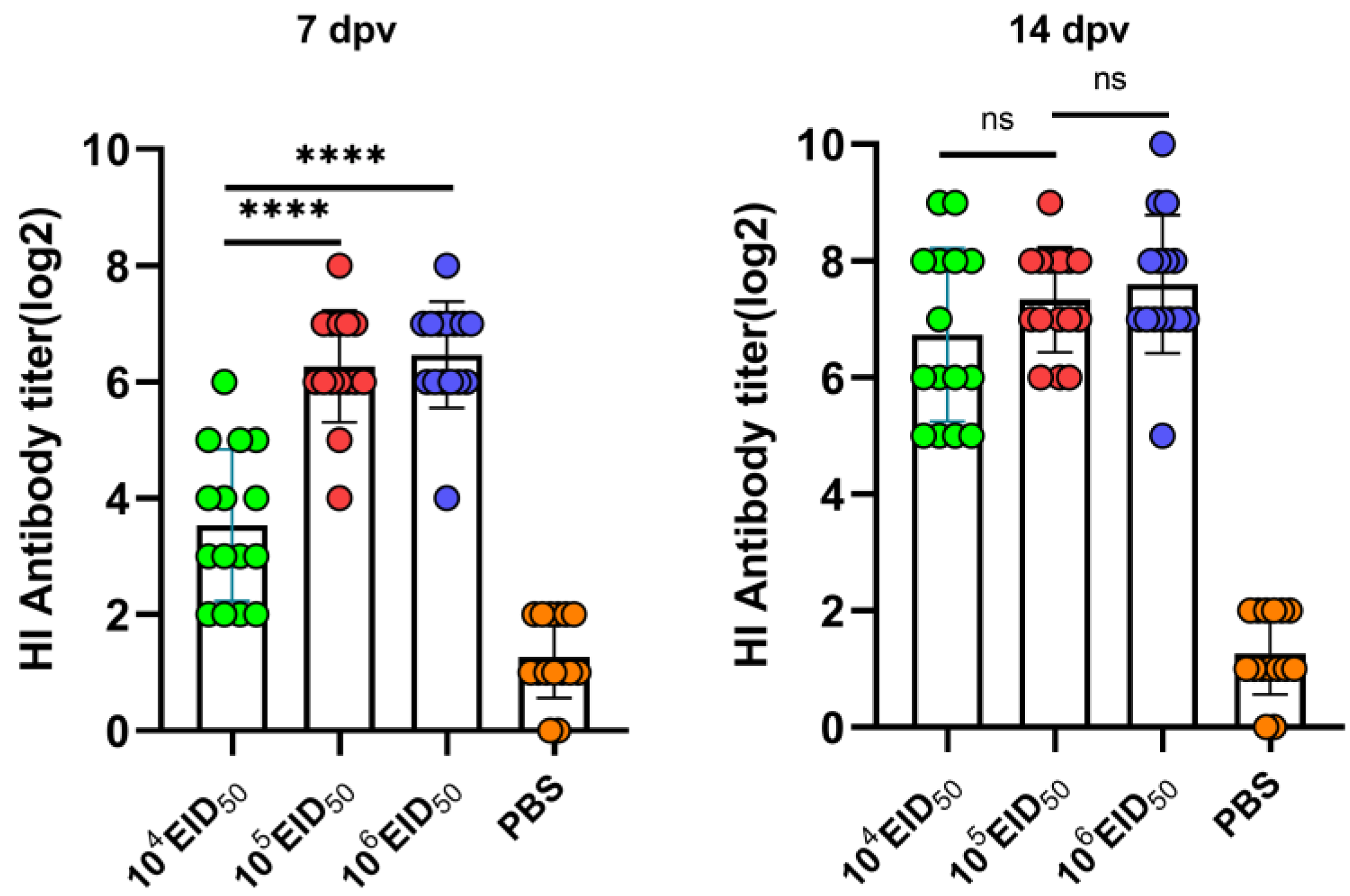
Figure 4.
Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) antibody titers induced in chickens by LX-OAI4S with different doses. Specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 15) and vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S via the IN/IO routes with dosages of 104 EID50/0.1 mL, 105 EID50/0.1 mL, and 106 EID50/0.1 mL, respectively. The PBS control group was also established. The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected on 7, 14, and 21 dpv to separate serum. Green, red, blue, and orange colors represent the HI potency of the LX-OAI4S, La Sota, VG/GA, and PBS groups, respectively. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA. **** p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.
Figure 4.
Hemagglutination inhibition (HI) antibody titers induced in chickens by LX-OAI4S with different doses. Specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 15) and vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S via the IN/IO routes with dosages of 104 EID50/0.1 mL, 105 EID50/0.1 mL, and 106 EID50/0.1 mL, respectively. The PBS control group was also established. The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected on 7, 14, and 21 dpv to separate serum. Green, red, blue, and orange colors represent the HI potency of the LX-OAI4S, La Sota, VG/GA, and PBS groups, respectively. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA. **** p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.
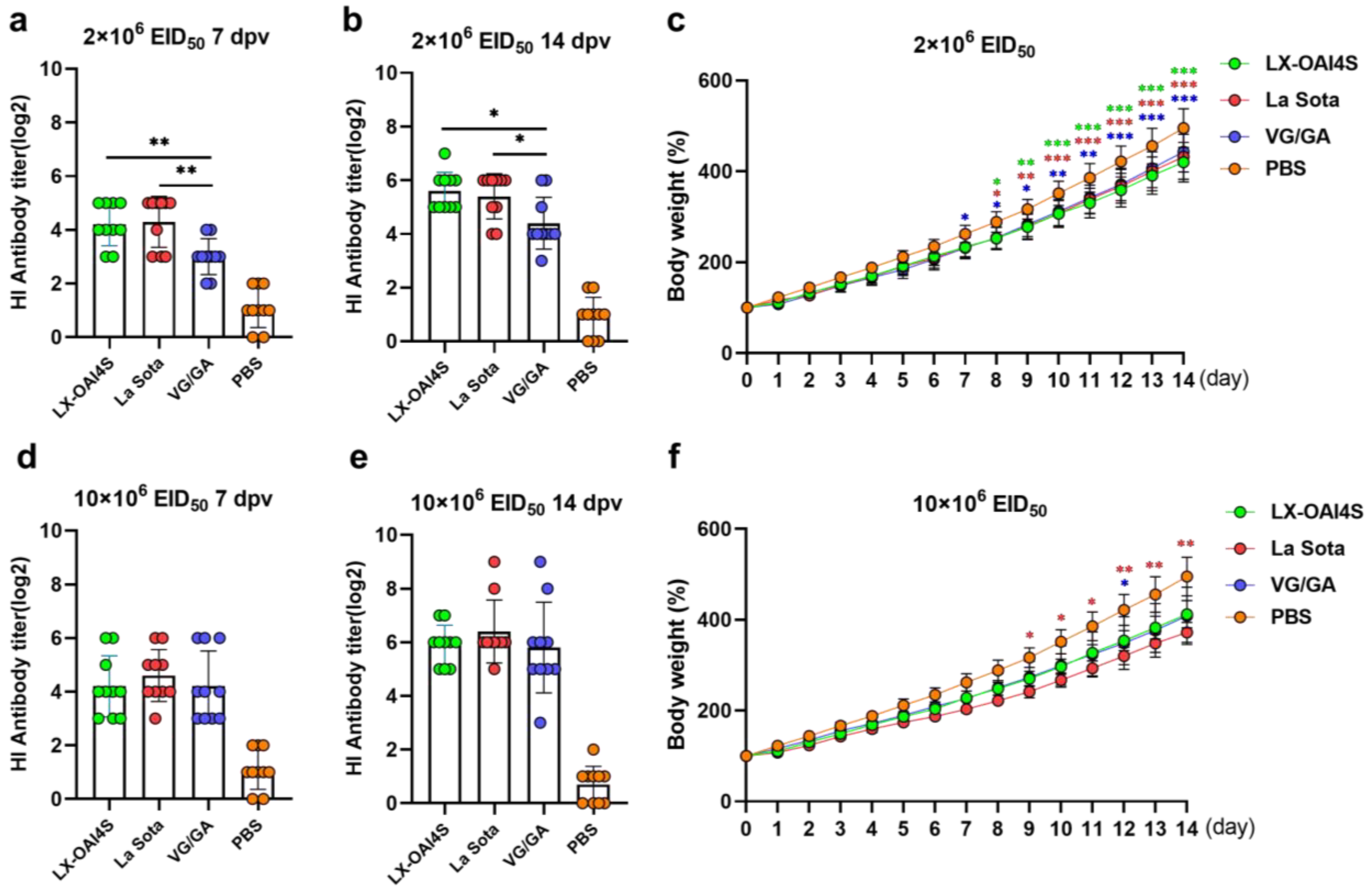
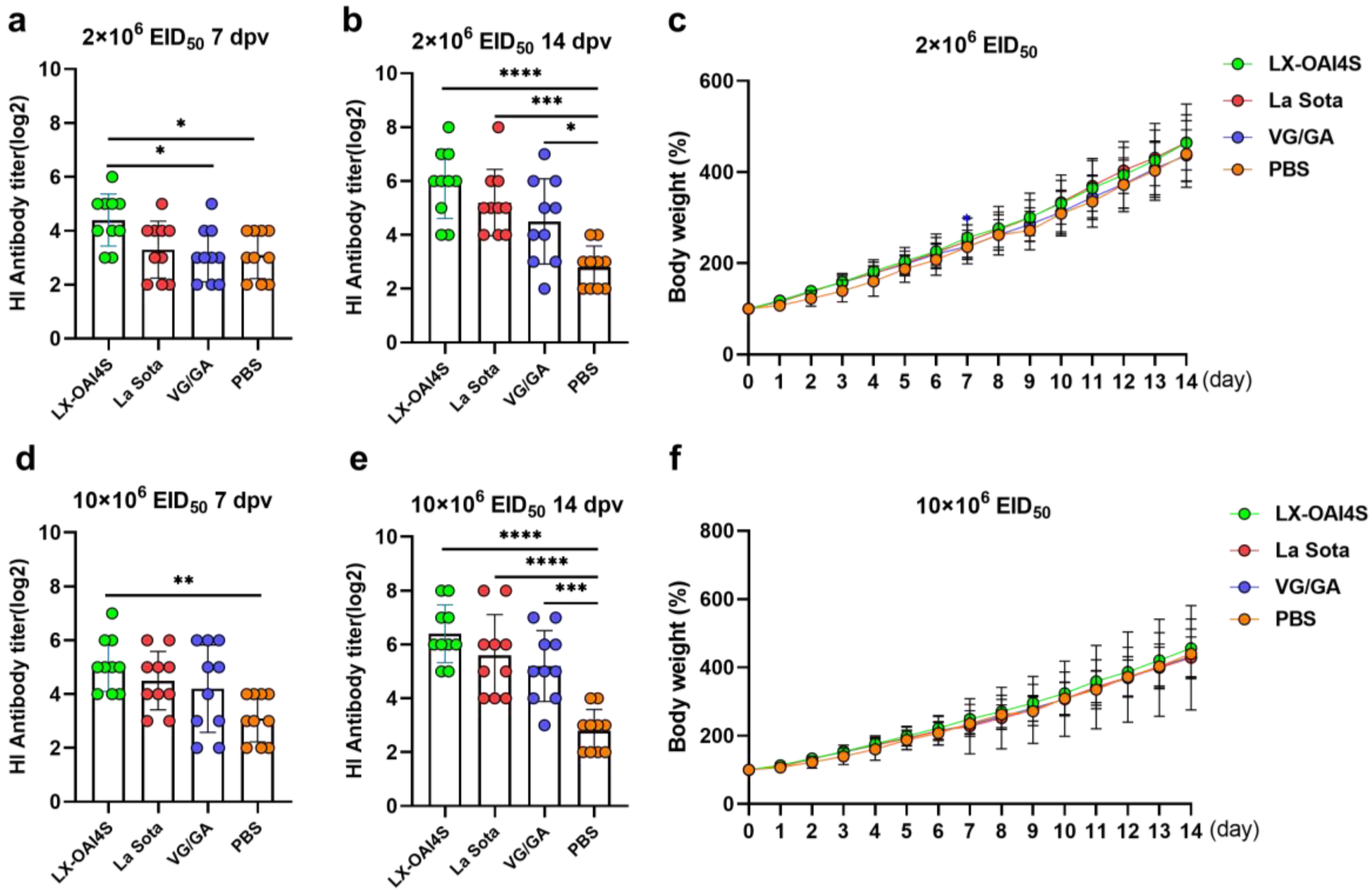
Figure 5.
The HI antibody response and body weight changes in SPF chickens vaccinated with ND vaccine via the spray route. One-day-old specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) and vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, La Sota, and VG/GA via the spray route, respectively. The PBS control group was also established. Two vaccination doses of the vaccines were used, 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL (a,b) and 10 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL (d,e). The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected on 7 and 14 dpv to separate serum. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. The weight of chickens was continuously detected for 14 days after vaccination (c,f). The p-values shown for the comparison between the vaccinated group and the PBS group (c). The p-values shown for the comparison between the LX-OAI4S group and the La Sota or VG/GA group (f). Statistical analyses were performed by multiple t-tests. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
Figure 5.
The HI antibody response and body weight changes in SPF chickens vaccinated with ND vaccine via the spray route. One-day-old specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) and vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, La Sota, and VG/GA via the spray route, respectively. The PBS control group was also established. Two vaccination doses of the vaccines were used, 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL (a,b) and 10 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL (d,e). The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected on 7 and 14 dpv to separate serum. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. The weight of chickens was continuously detected for 14 days after vaccination (c,f). The p-values shown for the comparison between the vaccinated group and the PBS group (c). The p-values shown for the comparison between the LX-OAI4S group and the La Sota or VG/GA group (f). Statistical analyses were performed by multiple t-tests. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
![Vetsci 11 00532 g005]()
Figure 6.
The HI antibody response and body weight changes in commercial chickens vaccinated with the ND vaccine via the spray route. One-day-old commercial chickens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) and vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, La Sota, and the VG/GA via spray route, respectively. The PBS control group was also established. Two vaccination doses of the vaccines were used, 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL (a,b) and 10 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL (d,e). The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected on 7 and 14 days post-vaccination (dpv) to separate serum. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001. The weight of chickens was continuously detected for 14 days after vaccination (c,f). The p-values shown for the comparison between the vaccinated group and the PBS group. Statistical analyses were performed by multiple t-tests. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.
Figure 6.
The HI antibody response and body weight changes in commercial chickens vaccinated with the ND vaccine via the spray route. One-day-old commercial chickens were randomly divided into four groups (n = 10) and vaccinated with recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S, La Sota, and the VG/GA via spray route, respectively. The PBS control group was also established. Two vaccination doses of the vaccines were used, 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL (a,b) and 10 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL (d,e). The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected on 7 and 14 days post-vaccination (dpv) to separate serum. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001. The weight of chickens was continuously detected for 14 days after vaccination (c,f). The p-values shown for the comparison between the vaccinated group and the PBS group. Statistical analyses were performed by multiple t-tests. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001.
![Vetsci 11 00532 g006]()
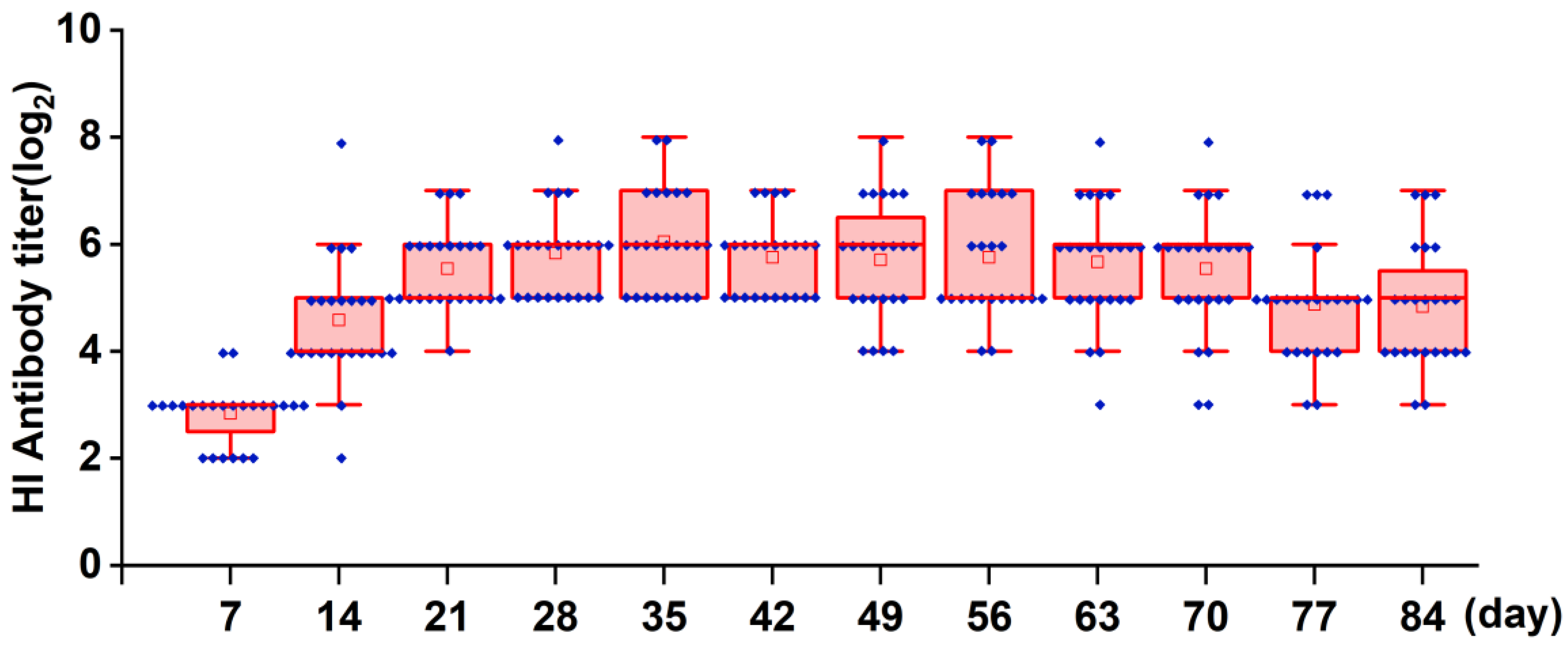
Figure 7.
The sustained HI antibody response in chickens vaccinated with the ND vaccine via the spray route. One-day-old specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens (n = 24) were vaccinated with the recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S via the spray route at doses of 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL. The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected every 7 days until day 84 to separate serum. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains.
Figure 7.
The sustained HI antibody response in chickens vaccinated with the ND vaccine via the spray route. One-day-old specific pathogen-free (SPF) chickens (n = 24) were vaccinated with the recombinant virus strain LX-OAI4S via the spray route at doses of 2 × 106 EID50/0.1 mL. The status of each chicken was observed after vaccination, and blood samples were collected every 7 days until day 84 to separate serum. The HI antibodies were then measured using the corresponding vaccine strains.
Table 1.
Biological characteristics of LX-OAI4S virus.
Table 1.
Biological characteristics of LX-OAI4S virus.
| | HAU | EID50 | TCID50 (DF-1) | MDT | ICPI |
|---|
| P1 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 7.0 | >120 | 0 |
| P2 | 9.0 | – | – | – | – |
| P3 | 9.0 | – | – | – | – |
| P4 | 9.0 | – | – | – | – |
| P5 | 9.0 | 8.83 | 7.5 | >120 | 0 |
| P6 | 9.0 | – | – | – | – |
| P7 | 9.0 | – | – | – | – |
| P8 | 9.0 | – | – | – | – |
| P9 | 9.0 | – | – | – | – |
| P10 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 7.5 | >120 | 0 |
Table 2.
Virus shedding in swabs from vaccinated groups.
Table 2.
Virus shedding in swabs from vaccinated groups.
| Vaccine Strain | 3 dpc | 5 dpc | 7 dpc |
|---|
| O | C | O | C | O | C |
|---|
| LX-OAI4S | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 |
| La Sota | 2/7 | 2/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 |
| VG/GA | 3/7 | 1/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 | 0/7 |
| PBS | 4/5 | 3/5 | - | - | - | - |
Table 3.
Virus shedding in swabs from LX-OAI4S vaccinated groups with different doses.
Table 3.
Virus shedding in swabs from LX-OAI4S vaccinated groups with different doses.
| Vaccine Dose | 3 dpc | 5 dpc | 7 dpc |
|---|
| O | C | O | C | O | C |
|---|
| 104 EID50/0.1 mL | 1/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 |
| 105 EID50/0.1 mL, | 1/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 |
| 106 EID50/0.1 mL | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 | 0/15 |
| PBS | 13/15 | 11/15 | - | - | - | - |
Table 4.
Clinical signs and histological change in vaccinated SPF chickens at a dose of 10×106 EID50.
Table 4.
Clinical signs and histological change in vaccinated SPF chickens at a dose of 10×106 EID50.
| Chicken Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Total |
|---|
| LX-OAI4S | clinical signs | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| oral | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | 4/10 |
| proventriculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| duodenum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| La Sota | clinical signs | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | 5/10 |
| oral | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | - | + | + | ++ | - | 8/10 |
| proventriculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| duodenum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| VG/GA | clinical signs | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| oral | ++ | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | 4/10 |
| proventriculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| duodenum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
Table 5.
Virus shedding in SPF chickens from different vaccinated groups at a dose of 2 × 106 EID50.
Table 5.
Virus shedding in SPF chickens from different vaccinated groups at a dose of 2 × 106 EID50.
| Vaccination Strain | 3 dpc | 5 dpc | 7 dpc |
|---|
| O | C | O | C | O | C |
|---|
| LX-OAI4S | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| La Sota | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 1/10 | 0/10 | 1/10 |
| VG/GA | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| PBS | 8/10 | 8/10 | - | - | - | - |
Table 6.
Clinical signs and histological change in vaccinated commercial chickens at a dose of 10×106 EID50.
Table 6.
Clinical signs and histological change in vaccinated commercial chickens at a dose of 10×106 EID50.
| Chicken Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Total | Mortality |
|---|
| LX-OAI4S | clinical signs | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 | 0 |
| oral | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | - | 2/10 |
| proventriculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| duodenum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| La Sota | clinical signs | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | 1/10 | 10% |
| oral | + | + | - | ++ | - | death | - | + | + | + | 6/9 |
| proventriculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/9 |
| duodenum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/9 |
| VG/GA | clinical signs | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 | 0 |
| oral | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | 3/10 |
| proventriculus | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
| duodenum | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/10 |
Table 7.
Virus shedding in commercial chickens from different vaccinated groups at a dose of 2 × 106 EID50.
Table 7.
Virus shedding in commercial chickens from different vaccinated groups at a dose of 2 × 106 EID50.
| Vaccination Strain | 3 dpc | 5 dpc | 7 dpc |
|---|
| O | C | O | C | O | C |
|---|
| LX-OAI4S | 2/10 | 0/10 | 1/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| La Sota | 5/10 | 2/10 | 0/10 | 1/10 | 0/10 | 1/10 |
| VG/GA | 4/10 | 1/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 |
| PBS | 9/10 | 6/10 | 8/8 | 4/8 | 2/2 | 2/2 |