Development of Chitosan Polysaccharide-Based Magnetic Gel for Direct Red 83:1 Removal from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
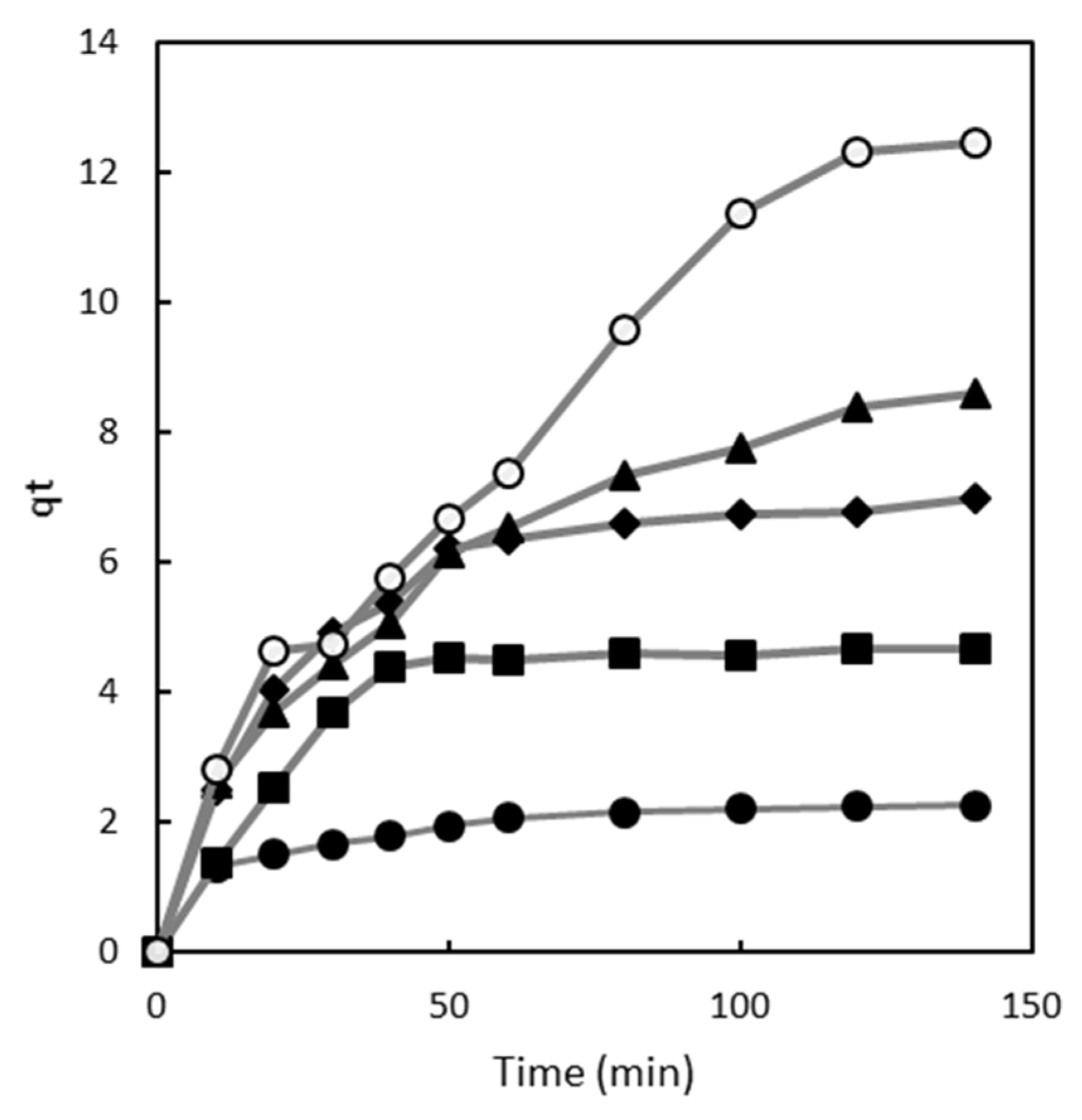
2.1. Effect of Contact Time
2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
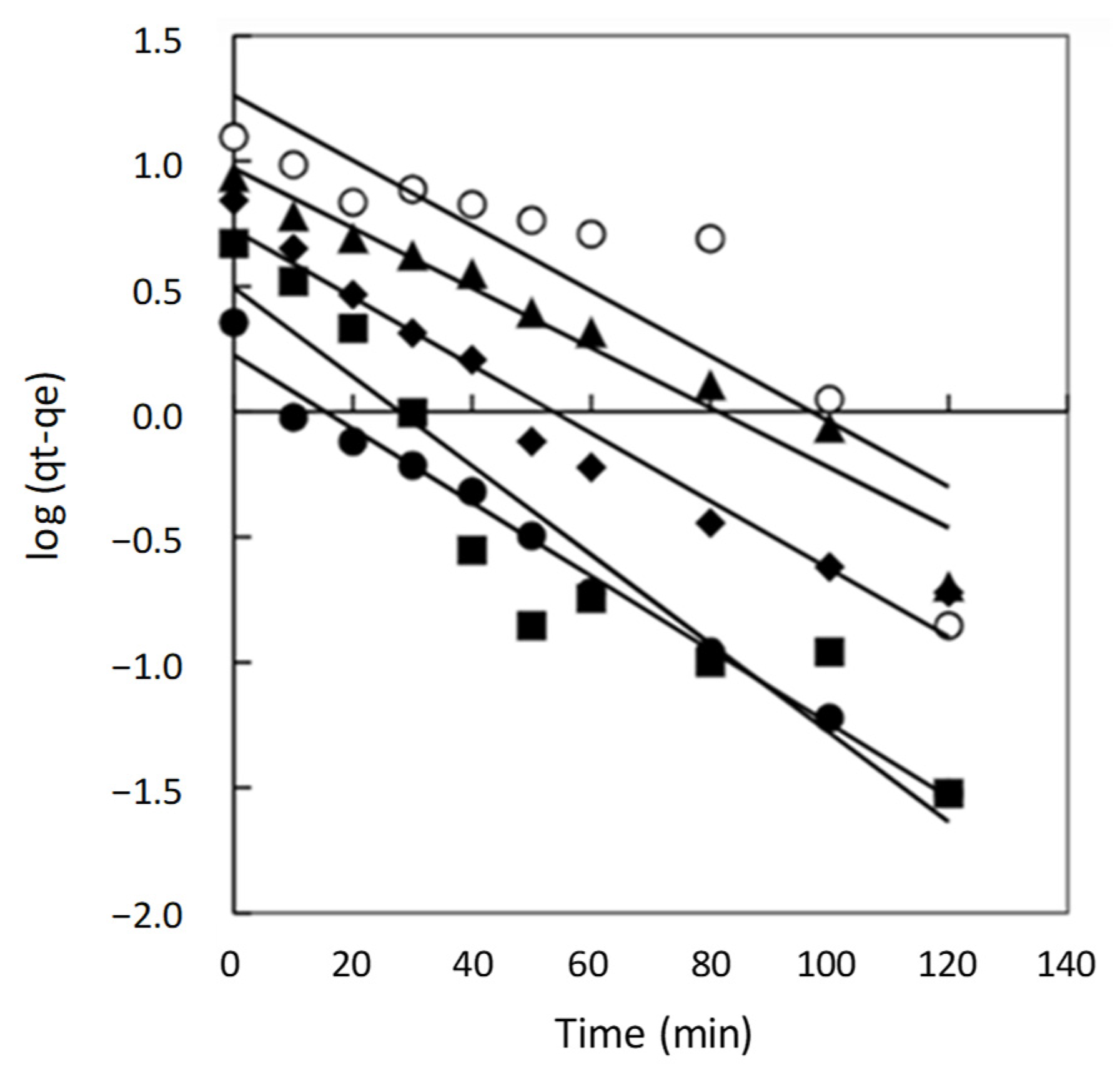
2.2.1. Pseudo First Order Model
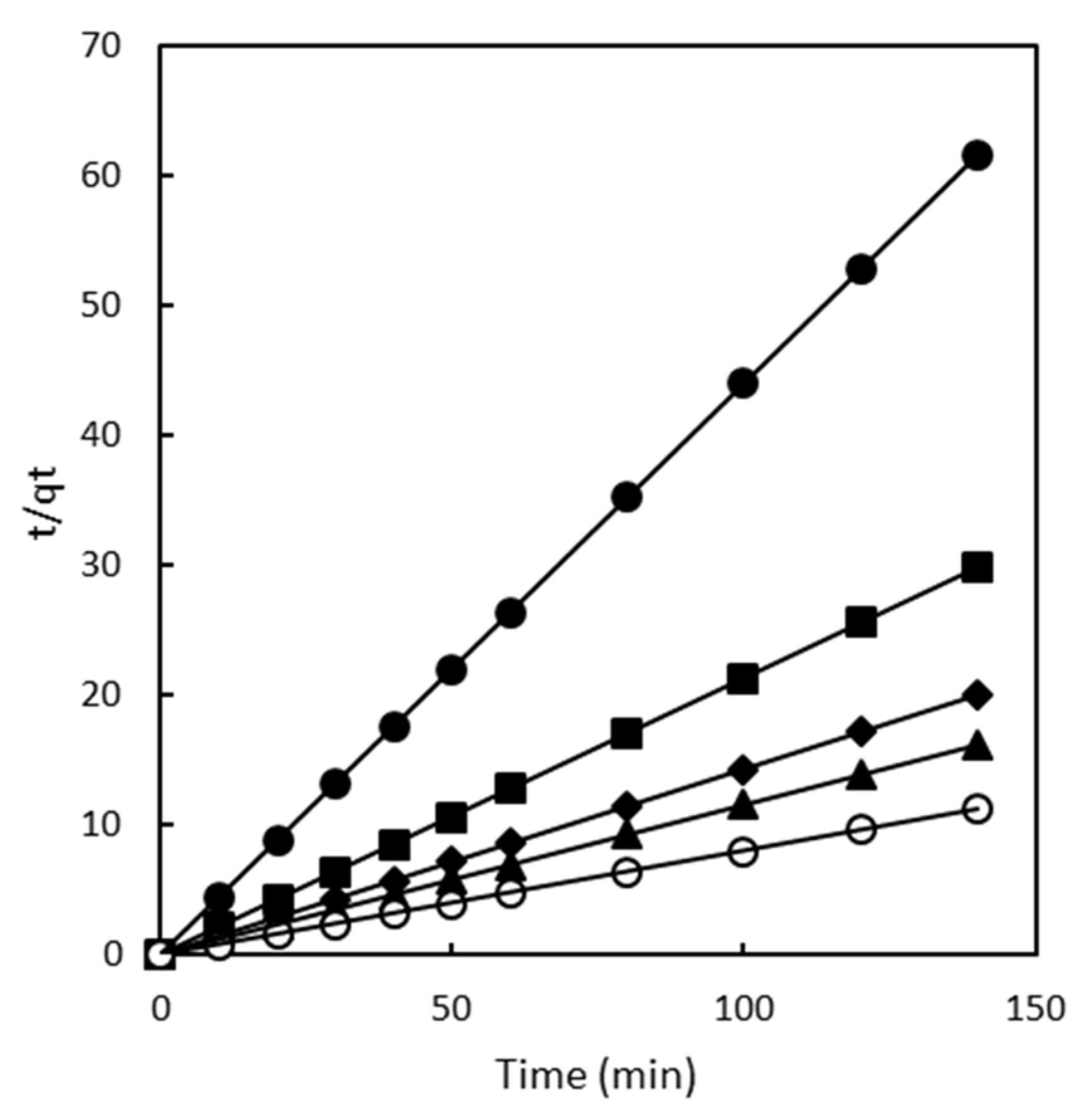
2.2.2. Pseudo Second Order Model
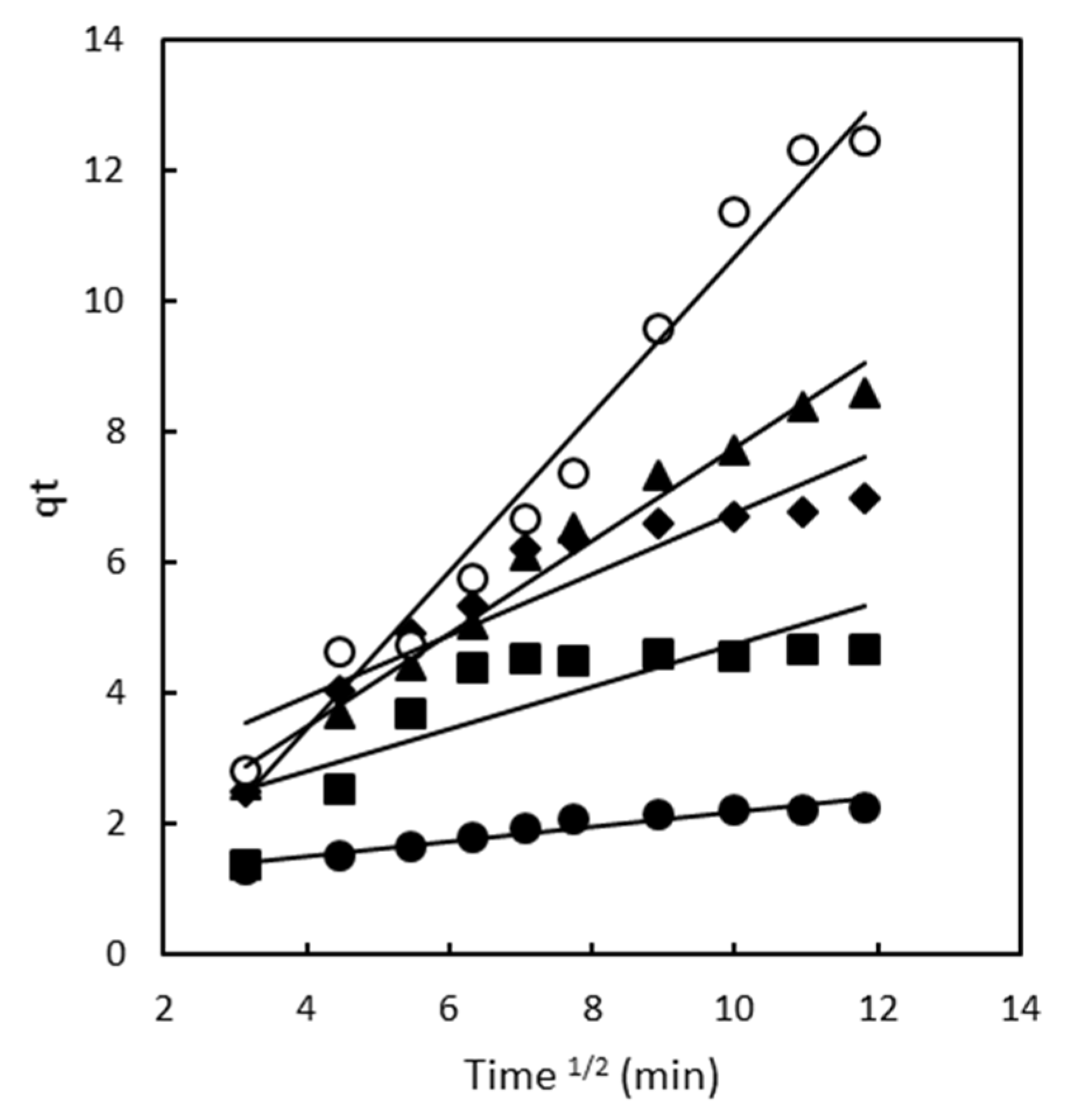
2.2.3. Intraparticle Diffusion Model
2.3. Adsorption Isotherms
2.3.1. Freundlich Isotherm
2.3.2. Langmuir Isotherm
2.3.3. Temkin Isotherm
2.4. Chitosan Magnetic Polymer Characterization
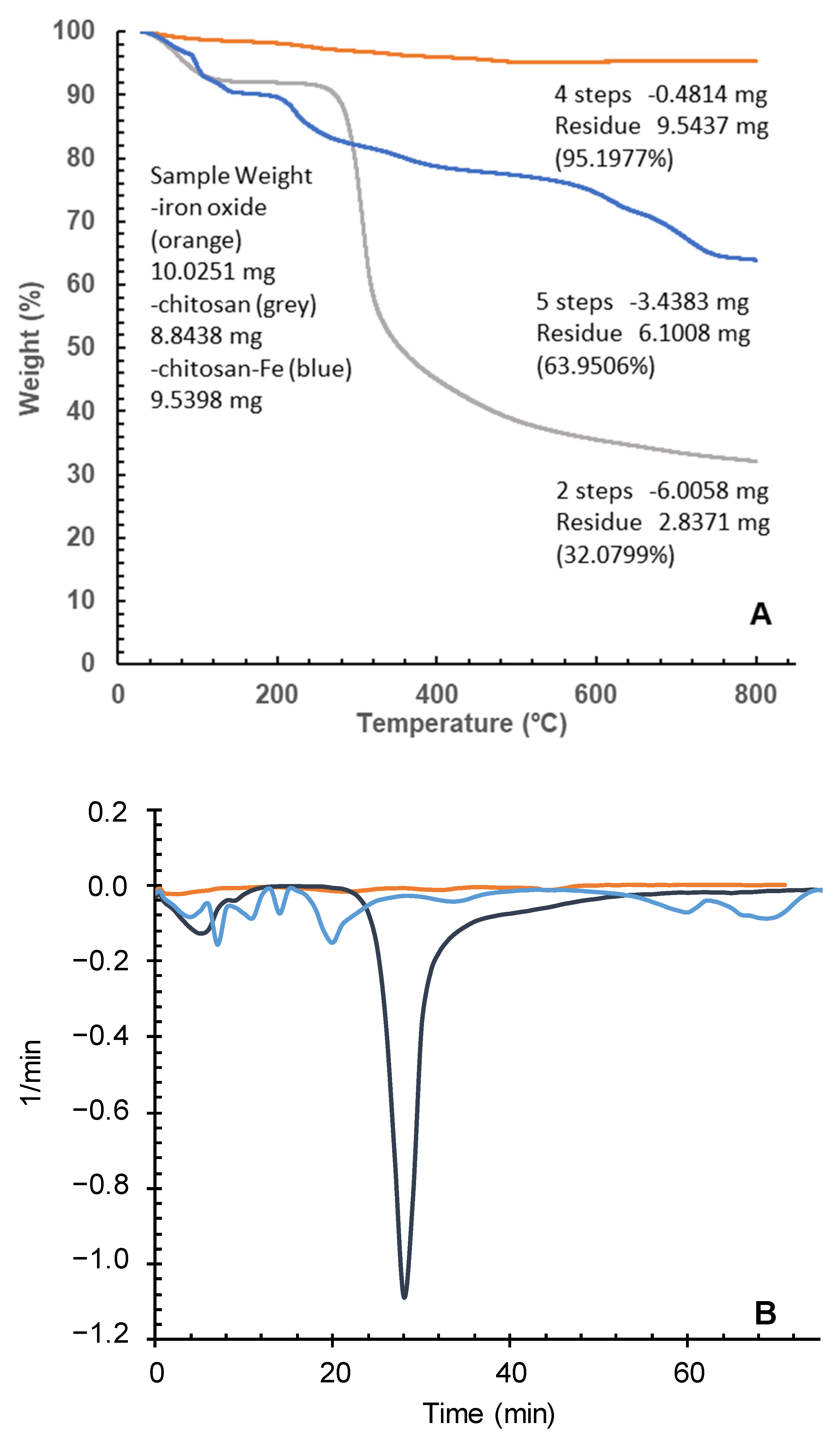
2.4.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.4.2. DRX Powder X-ray Diffraction
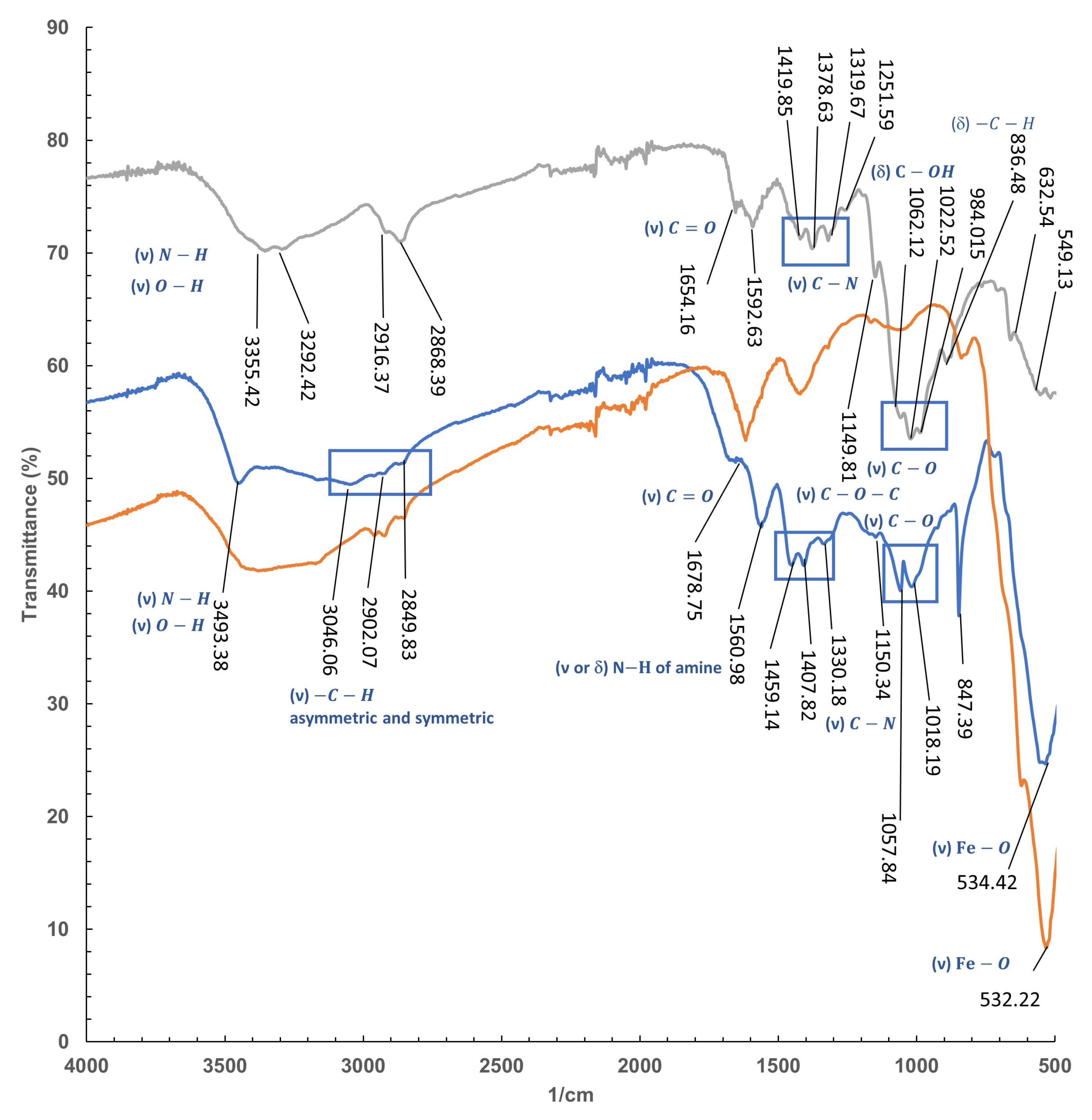
2.4.3. FT-IR
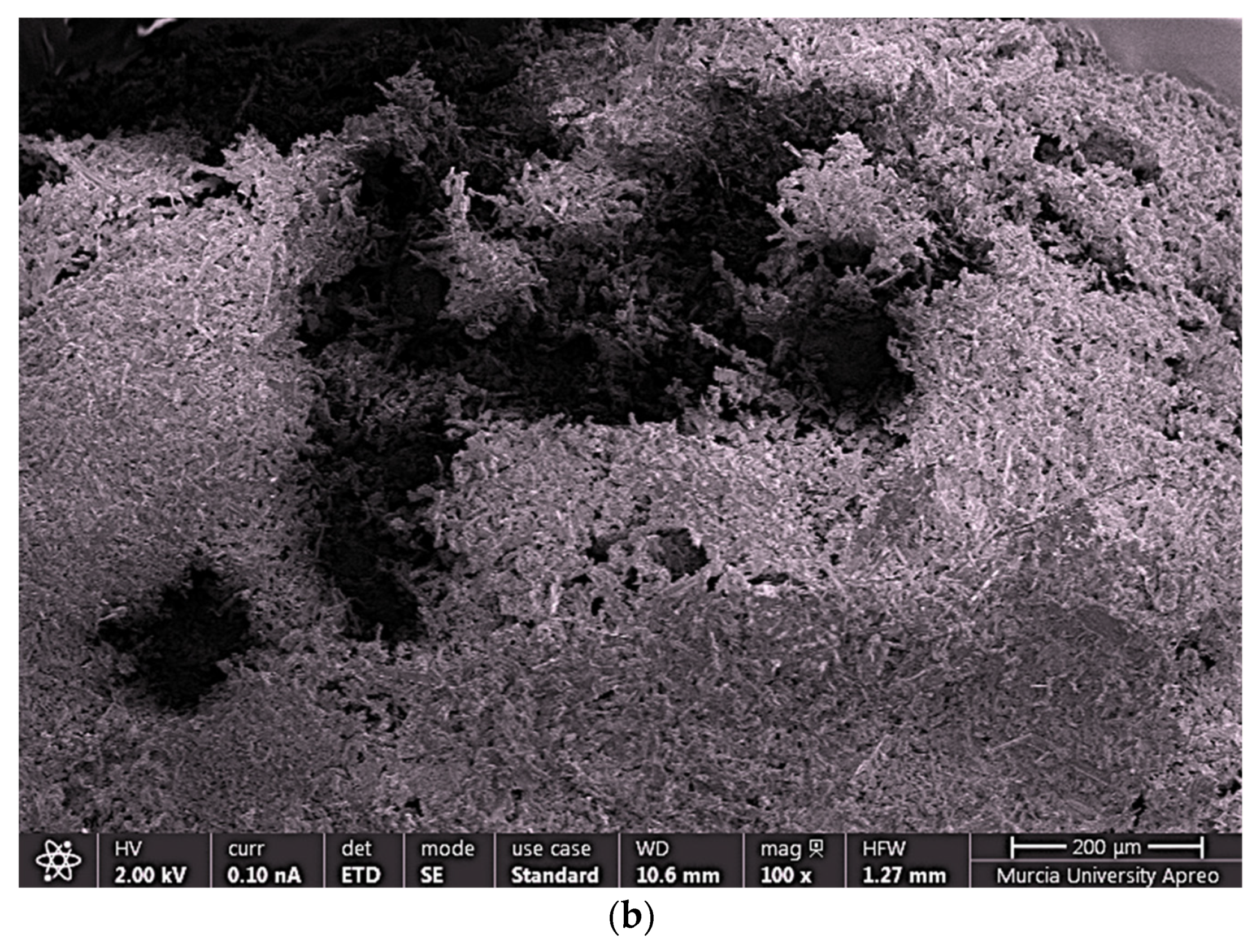
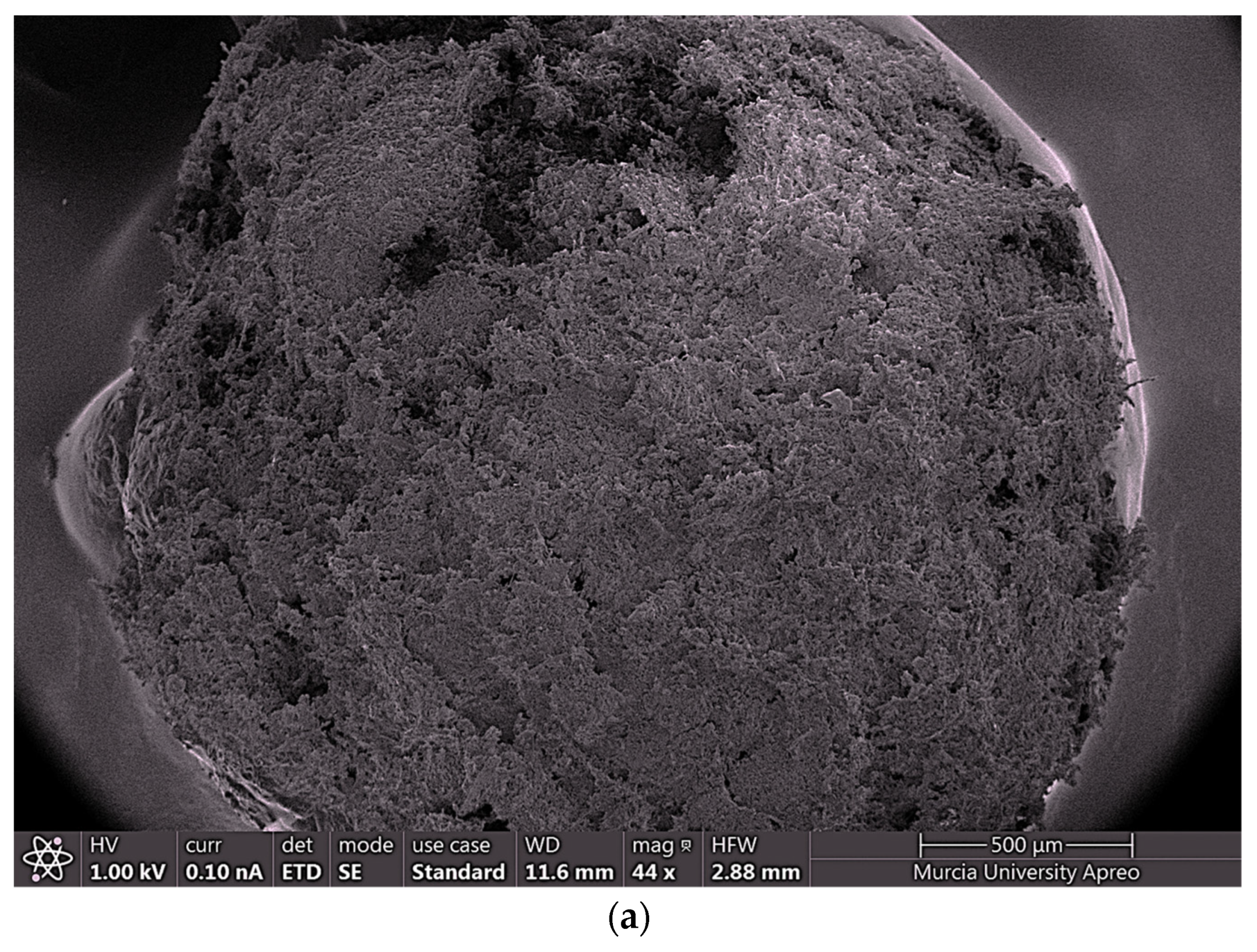
2.4.4. FESEM and EDX
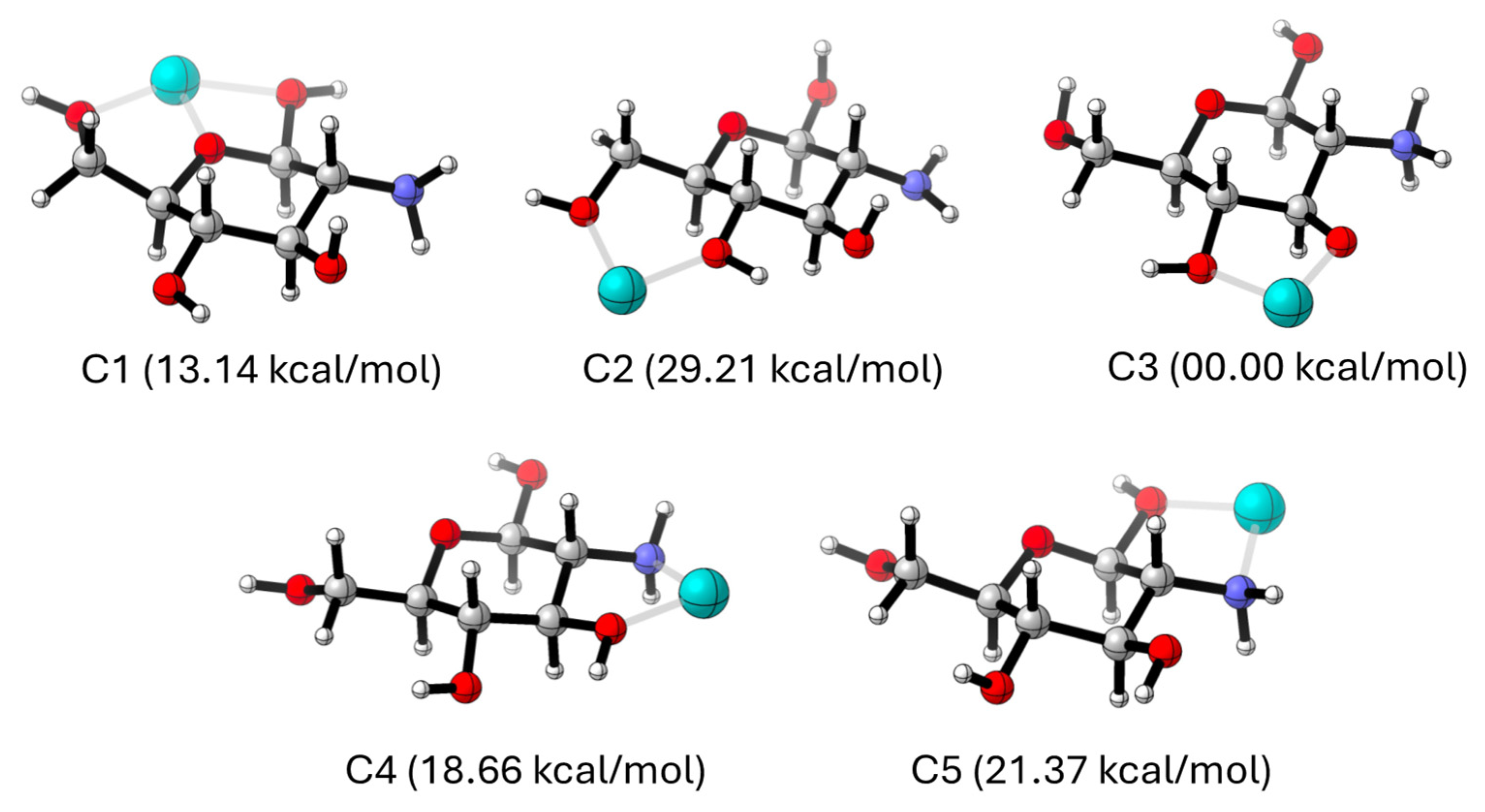
2.4.5. Molecular Models
2.5. Engineering and Economic Feasibilities
- -
- Simplicity of Synthesis: The co-precipitation method used for incorporating Fe nanoparticles into the chitosan gel is simple and cost-effective, making it suitable for large-scale production.
- -
- Operational Conditions: The adsorption process is effective under a wide range of pH and temperature conditions, which aligns well with the varying conditions of industrial wastewater streams.
- -
- Regeneration and Reusability: The magnetic gel beads can be regenerated using organic solvents, enabling multiple cycles of adsorption and desorption without significant loss of efficiency. This reduces the overall operational costs and enhances the sustainability of the process.
- -
- Ease of Separation: The magnetic properties of the gel beads facilitate easy separation from treated water using an external magnetic field. This non-invasive separation technique simplifies the operational procedure and minimizes the need for complex filtration systems.
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Chitosan-Fe Polymer Preparation
4.3. Dye Solution Preparation
4.4. Analyses and Data Evaluation
4.5. Adsorption Experiments
- qt is the amount of dye adsorbed on the polymer at time t (mg/g).
- Co is the initial concentration of dye in the solution (mg/L).
- Ct is the concentration of dye in the solution at time t (mg/L).
- V is the volume of the dye solution used (L).
- m is the mass of the polymer used (g)
4.6. Adsorption Kinetics
4.7. Isotherm Analysis
4.8. Chitosan Magnetic Polymer Characterization
4.9. Computational Calculations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, J.; Thakur, A.; Goyal, A. Industrial Wastewater and Its Toxic Effects. In Biological Treatment of Industrial Wastewater; Shah, M.P., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2021; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandeya; Mohan, D.; Shukla, S.P. Hazardous Consequences of Textile Mill Effluents on Soil and Their Remediation Approaches. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 7, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azanaw, A.; Birlie, B.; Teshome, B.; Jemberie, M. Textile Effluent Treatment Methods and Eco-Friendly Resolution of Textile Wastewater. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara, N.; Siddiqui, S.I.; Rathi, G.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Inamuddin; Asiri, A.M. Nano-Engineered Adsorbent for the Removal of Dyes from Water: A Review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2020, 16, 14–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rápó, E.; Tonk, S. Factors Affecting Synthetic Dye Adsorption; Desorption Studies: A Review of Results from the Last Five Years (2017–2021). Molecules 2021, 26, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Pellicer, J.A.; Gómez-Morte, T.; Auñón, D.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Yáñez-Gascón, M.J.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á.; Cerón-Carrasco, J.P.; Crini, G.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; et al. Removal of an Azo Dye from Wastewater through the Use of Two Technologies: Magnetic Cyclodextrin Polymers and Pulsed Light. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sakkaf, B.M.; Nasreen, S.; Ejaz, N. Degradation Pattern of Textile Effluent by Using Bio and Sono Chemical Reactor. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8965627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Fourmentin, M.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Mapelli, F.; Fenyvesi, É.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; et al. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Using Advanced Treatments. A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1333–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheed, I.O.; Oh, W.D.; Suah, F.B.M. Chitosan Modifications for Adsorption of Pollutants—A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshvardoostchokami, M.; Majidi, M.; Zamani, A.; Liu, B. A Review on the Use of Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives as the Bio-Adsorbents for the Water Treatment: Removal of Nitrogen-Containing Pollutants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Mitropoulos, A.C. Chitosan Adsorbents for Dye Removal: A Review: Chitosan Adsorbents for Dye Removal. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1800–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, S.; Oliveri, I.P.; Lo Presti, F.; Oliveri, V.; Giannakis, S.; Tuccitto, N.; Spampinato, V.; Auditore, A. An Innovative “Up-and-Down” Adsorption Processes for Pyrene Removal from Acid Wastewater as New Approach in Water Remediation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 348, 127516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Alves, D.C.; Healy, B.; Pinto, L.A.D.A.; Cadaval, T.R.S.; Breslin, C.B. Recent Developments in Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Pollutants from Aqueous Environments. Molecules 2021, 26, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanciu, M.-C.; Teacă, C.-A. Natural Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels Used for Dye Removal. Gels 2024, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Lou, T. Preparation of Fibrous Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Composite Foams for the Adsorption of Cationic and Anionic Dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkaboyana, S.K.; Soontarapa, K.; Vinaykumar; Marella, R.K.; Kannan, K. Preparation of Novel Chitosan Polymeric Nanocomposite as an Efficient Material for the Removal of Acid Blue 25 from Aqueous Environment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Zhong, C.; Wang, N.; Meng, J. Facile Fabrication of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Effective Removal of Cationic and Anionic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2805–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raval, N.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Shah, N.K.; Gikas, P.; Kumar, M. Hexametaphosphate Cross-Linked Chitosan Beads for the Eco-Efficient Removal of Organic Dyes: Tackling Water Quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Cai, T.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R. Flocculation of Both Anionic and Cationic Dyes in Aqueous Solutions by the Amphoteric Grafting Flocculant Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Graft-Polyacrylamide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254–255, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, H.; Al Alili, A.; Morajkar, P.P.; Alhassan, S.M. GO Crosslinked Hydrogel Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Carboxymethyl Cellulose—A Versatile Adsorbent for the Treatment of Dyes Contaminated Wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1248–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanajaree, R.; Sriuttha, M.; Lee, V.S.; Wittayanarakul, K. Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Cationic/Anionic Dyes Adsorption on Cross-Linked Chitosan. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 322, 114507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M.; Akbari, A. Facile Fabrication of Magnetic Chitosan Hydrogel Beads and Modified by Interfacial Polymerization Method and Study of Adsorption of Cationic/Anionic Dyes from Aqueous Solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Riyajuddin, S.; Ghosh, K.; Mehta, S.K.; Dan, A. Chitosan-Graphene Oxide Hydrogels with Embedded Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Dye Removal. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 7379–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingrajiya, R.D.; Patel, M.P. Fe3O4 Modified Chitosan Based Co-Polymeric Magnetic Composite Hydrogel: Synthesis, Characterization and Evaluation for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frachini, E.; Petri, D. Magneto-Responsive Hydrogels: Preparation, Characterization, Biotechnological and Environmental Applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 2010–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamin, M.E.; Kitamoto, Y. Influence of pH on Dynamic Magnetic Susceptibility of Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles in a Chitosan Hydrogel Matrix. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, R.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.; Sathya, A.B.; Sivashankar, R. Magnetic Materials and Magnetic Separation of Dyes from Aqueous Solutions: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1275–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer, J.; Rodríguez-López, M.; Fortea, M.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Mercader-Ros, M.; López-Miranda, S.; Gómez-López, V.; Semeraro, P.; Cosma, P.; Fini, P.; et al. Adsorption Properties of β- and Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrins Cross-Linked with Epichlorohydrin in Aqueous Solution. A Sustainable Recycling Strategy in Textile Dyeing Process. Polymers 2019, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botleng, J.; Patel, T.; Lata, R.; Chang, R.; Rohindra, D. Adsorption of Azo Dyes onto Environmentally Friendly Bacterial Cellulose/Kappa-Carrageenan Hydrogel: Isotherm and Kinetic Studies. Adsorption 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.G.; Amalan, A.J.; Subasini, S.; Pius, A. Adsorption and Desorption of Dyes. In Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Composites as Adsorbents; Tharini, J., Thomas, S., Eds.; Carbon Nanostructures; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Jiang, X.; Yu, J.; Chen, X. Adsorption and Removal of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solution Using Magnetic β-Cyclodextrin-Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites as Adsorbents. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Long, F.; Pan, X. A Versatile β-Cyclodextrin and Polyethyleneimine Bi-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoadsorbent for Simultaneous Capture of Methyl Orange and Pb(II) from Complex Wastewater. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, S.; Xu, J. Fabrication of Fe3O4@ Cyclodextrin Magnetic Composite for the High-Efficient Removal of Eu (III). J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 206, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Sun, P.; Yu, T.; Zhou, L. Novel Porous Magnetic Nanospheres Functionalized by β-Cyclodextrin Polymer and Its Application in Organic Pollutants from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber Jr, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Peindy, H.N.; Gimbert, F.; Robert, C. Removal of CI Basic Green 4 (Malachite Green) from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption Using Cyclodextrin-Based Adsorbent: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 53, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia-Salvador, A.; Pellicer, J.A.; Fortea, M.I.; Gómez-López, V.M.; Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Gabaldón, J.A. Adsorption of Direct Blue 78 Using Chitosan and Cyclodextrins as Adsorbents. Polymers 2019, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicer, J.A.; Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Fortea, M.I.; Gabaldón Hernández, J.A.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Mercader-Ros, M.T.; Serrano-Martínez, A.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Cosma, P.; Fini, P.; et al. Removing of Direct Red 83:1 Using α- and HP-α-CDs Polymerized with Epichlorohydrin: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies. Dye. Pigment. 2018, 149, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensalah, H.; Younssi, S.A.; Ouammou, M.; Gurlo, A.; Bekheet, M.F. Azo Dye Adsorption on an Industrial Waste-Transformed Hydroxyapatite Adsorbent: Kinetics, Isotherms, Mechanism and Regeneration Studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafari, J.; Barzanouni, H.; Mazloomi, S.; Amir Abadi Farahani, N.; Sharafi, K.; Soleimani, P.; Haghighat, G.A. Effective Adsorptive Removal of Reactive Dyes by Magnetic Chitosan Nanoparticles: Kinetic, Isothermal Studies and Response Surface Methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Sharma, V.; Mishra, P.K.; Ekielski, A. A Review on Polyacrylonitrile as an Effective and Economic Constituent of Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. Molecules 2022, 27, 8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Lan, R.; He, L.; Liu, H.; Pei, X. A Critical Review of Adsorption Isotherm Models for Aqueous Contaminants: Curve Characteristics, Site Energy Distribution and Common Controversies. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Sun, H.; Chi, G.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y. Control Synthesis of Magnetic Fe3O4–Chitosan Nanoparticles under UV Irradiation in Aqueous System. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Centre for Diffraction Data. Powder Diffraction FileTM (PDF®), Muestra Estándar PDF 04-006-6551 [Base de Datos]; ICDD: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Otake, T.; Wesolowski, D.J.; Anovitz, L.M.; Allard, L.F.; Ohmoto, H. Mechanisms of Iron Oxide Transformations in Hydrothermal Systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 6141–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Queiroz, M.; Melo, K.; Sabry, D.; Sassaki, G.; Rocha, H. Does the Use of Chitosan Contribute to Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation? Mar. Drugs 2014, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, P. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy: Principles and Spectral Interpretation, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen Da Silva Lucas, A.; Quadro Oreste, E.; Leão Gouveia Costa, H.; Martín López, H.; Dias Medeiros Saad, C.; Prentice, C. Extraction, Physicochemical Characterization, and Morphological Properties of Chitin and Chitosan from Cuticles of Edible Insects. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, L.-F.; Cánepa, J.; Kim, S.; Nakamatsu, J. A Simple Approach to Produce Tailor-Made Chitosans with Specific Degrees of Acetylation and Molecular Weights. Polymers 2021, 13, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.; Yin, J.-Y.; Nie, S.-P.; Xie, M.-Y. Applications of Infrared Spectroscopy in Polysaccharide Structural Analysis: Progress, Challenge and Perspective. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, Y.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Choa, Y.-H.; Kim, J.; Nam, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, K.H. Synthesis and Characterizations of Surface-Coated Superparamagentic Magnetite Nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.R.B.; Jorge, M.; Gomes, P. Interaction of Chitosan and Chitin with Ni, Cu and Zn Ions: A Computational Study. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2014, 73, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, P.; De Marsily, G. Calculating Equivalent Permeability: A Review. Adv. Water Resour. 1997, 20, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S. Review of Second-Order Models for Adsorption Systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaussian 16 A03. Available online: https://gaussian.com/citation_a03/ (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Grimme, S. Density Functional Theory with London Dispersion Corrections. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2011, 1, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. A New Mixing of Hartree–Fock and Local Density-Functional Theories. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataei, S.; Nemati-Kande, E.; Bahrami, A. Quantum DFT Studies on the Drug Delivery of Favipiravir Using Pristine and Functionalized Chitosan Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced Basis Sets of Split Valence, Triple Zeta Valence and Quadruple Zeta Valence Quality for H to Rn: Design and Assessment of Accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F. Accurate Coulomb-Fitting Basis Sets for H to Rn. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Isotherm | Parameter | Chitosan-Fe |
|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | KF | 1.28 |
| nF | 1.68 | |
| R2 | 0.844 | |
| Langmuir | qmax | 17.46 |
| KL | 0.76 | |
| aL | 0.043 | |
| R2 | 0.884 | |
| RL | 0.13–0.024 | |
| Temkin | aT | 0.48 |
| bT | 0.67 | |
| R2 | 0.946 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murcia-Salvador, A.; Rodríguez-López, M.I.; Pellicer, J.A.; Gómez-Morte, T.; Auñón-Calles, D.; Yáñez-Gascón, M.J.; Cerón-Carrasco, J.P.; Gil-Izquierdo, Á.; Núñez-Delicado, E.; Gabaldón, J.A. Development of Chitosan Polysaccharide-Based Magnetic Gel for Direct Red 83:1 Removal from Water. Gels 2024, 10, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10080496
Murcia-Salvador A, Rodríguez-López MI, Pellicer JA, Gómez-Morte T, Auñón-Calles D, Yáñez-Gascón MJ, Cerón-Carrasco JP, Gil-Izquierdo Á, Núñez-Delicado E, Gabaldón JA. Development of Chitosan Polysaccharide-Based Magnetic Gel for Direct Red 83:1 Removal from Water. Gels. 2024; 10(8):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10080496
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurcia-Salvador, Ainoa, María Isabel Rodríguez-López, José Antonio Pellicer, Teresa Gómez-Morte, David Auñón-Calles, María Josefa Yáñez-Gascón, José Pedro Cerón-Carrasco, Ángel Gil-Izquierdo, Estrella Núñez-Delicado, and José Antonio Gabaldón. 2024. "Development of Chitosan Polysaccharide-Based Magnetic Gel for Direct Red 83:1 Removal from Water" Gels 10, no. 8: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10080496
APA StyleMurcia-Salvador, A., Rodríguez-López, M. I., Pellicer, J. A., Gómez-Morte, T., Auñón-Calles, D., Yáñez-Gascón, M. J., Cerón-Carrasco, J. P., Gil-Izquierdo, Á., Núñez-Delicado, E., & Gabaldón, J. A. (2024). Development of Chitosan Polysaccharide-Based Magnetic Gel for Direct Red 83:1 Removal from Water. Gels, 10(8), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10080496













