Preparation of Indomethacin Co-Crystals; Comparison of XRD, THz, and FT-IR Spectral Analyses; and Enhancement of Solubility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Various Indomethacin/Co-Former Co-Crystals by Solvent Evaporation
2.3. Identification of Co-Crystal by Powder X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4. Identification of Co-Crystals by Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy (THz-TDS)
2.5. Identification of Co-Crystals by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.6. Solubility Determination of Various Indomethacin Co-Crystals in Phosphate-Buffered Saline (pH 6.8)
3. Results
3.1. Indomethacin/Saccharin (IND/SAC) Co-Crystal Preparation and Characterization

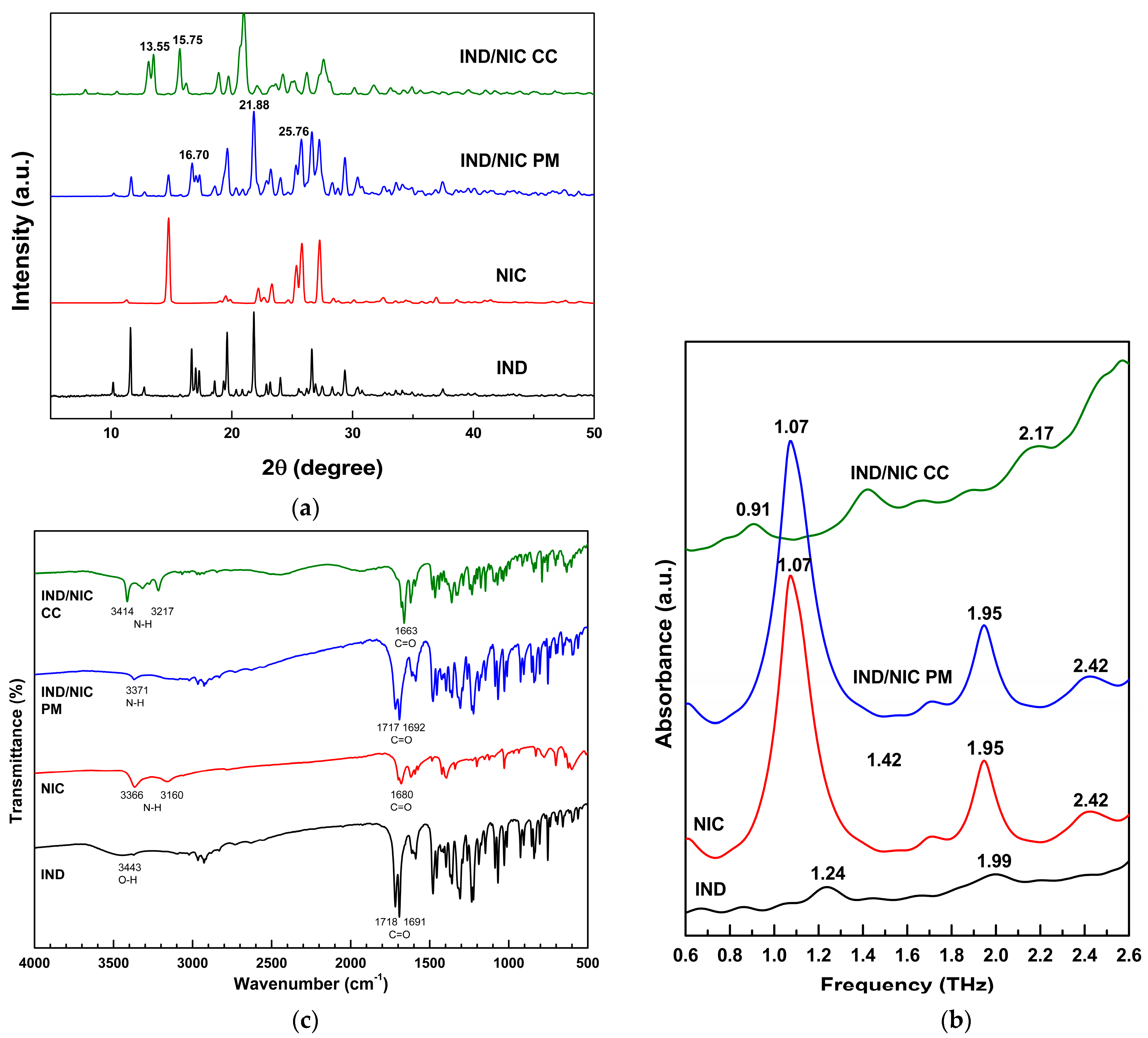
3.2. Indomethacin/Nicotine Amide (IND/NIC) Co-Crystal Preparation and Characterization
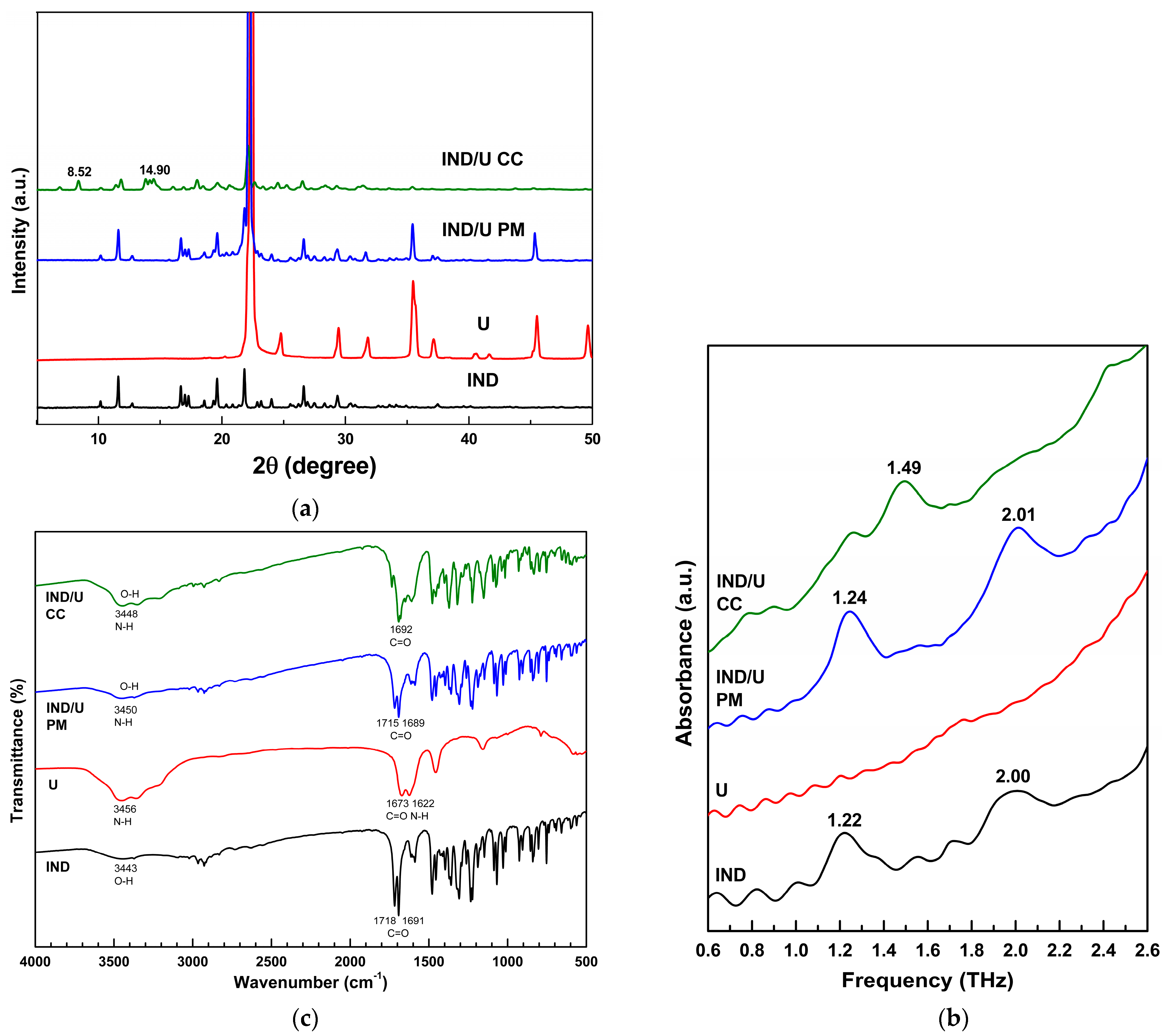
3.3. Indomethacin/Urea (IND/U) Co-Crystal Preparation and Characterization
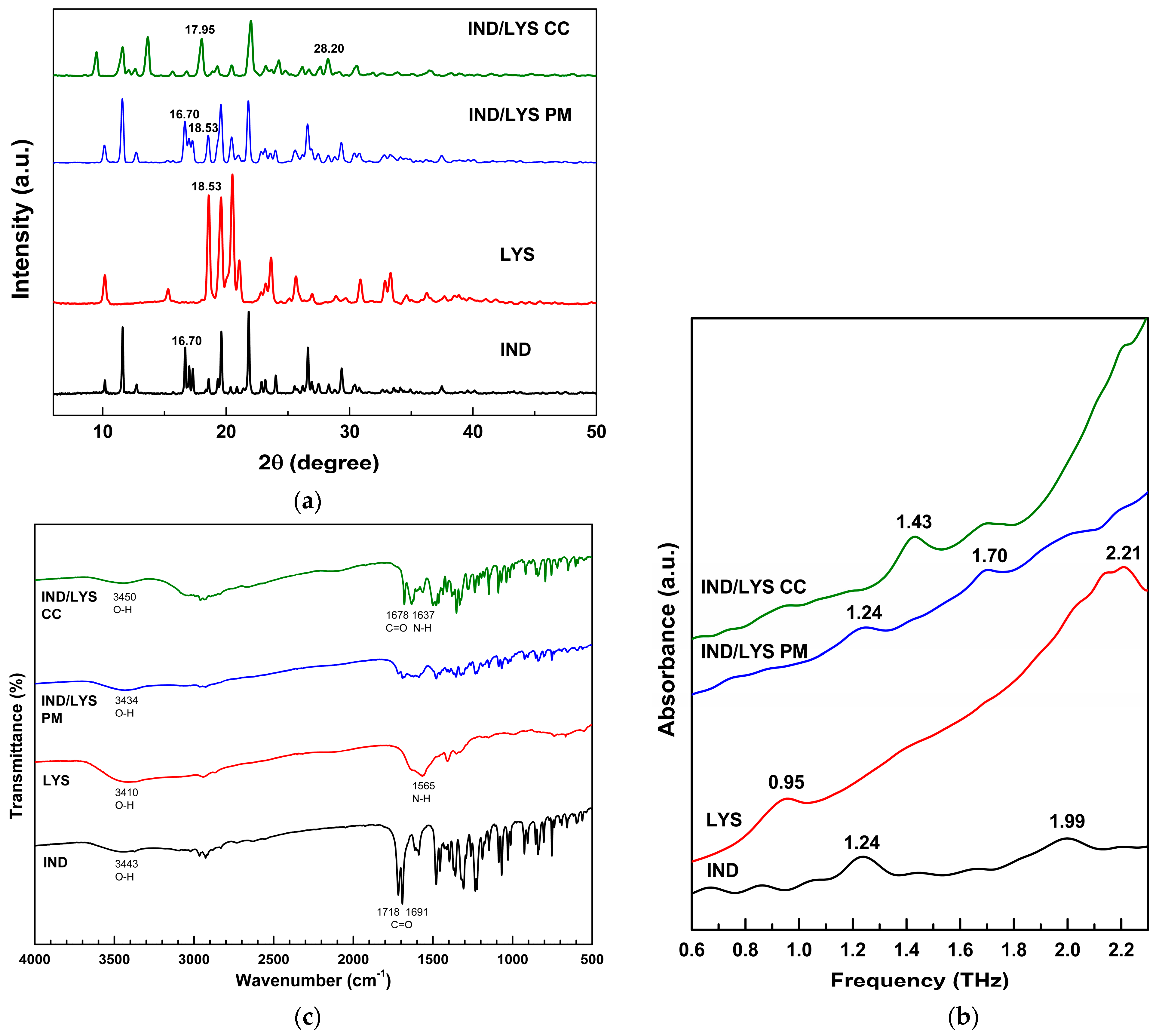
3.4. Indomethacin/Lysine (IND/LYS) Co-Crystal Preparation and Characterization
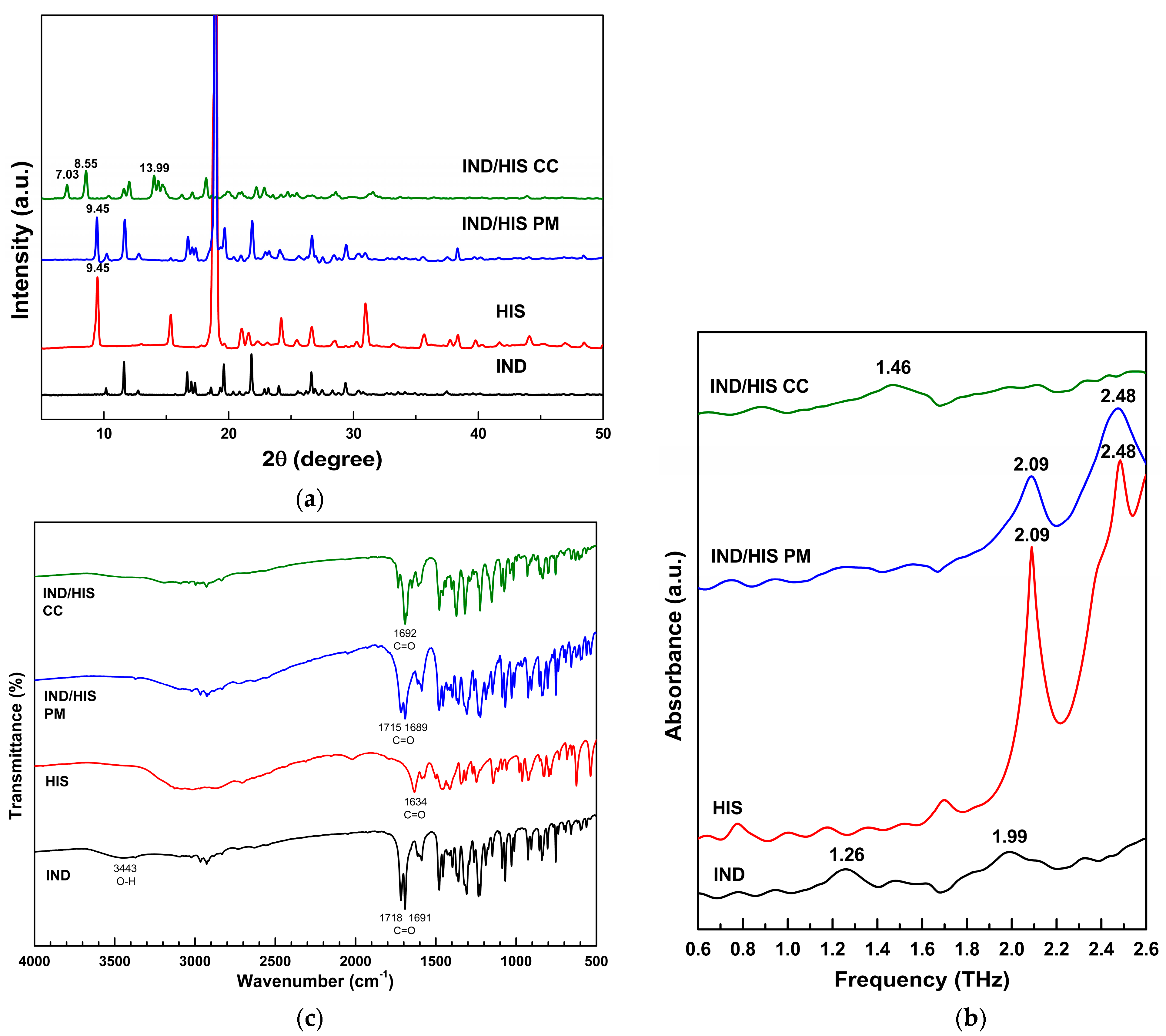
3.5. Indomethacin/Histidine (IND/HIS) Co-Crystal Preparation and Characterization
3.6. Solubility Enhancement by Co-Crystallization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rumondor, A.C.F.; Dhareshwar, S.S.; Kesisoglou, F. Amorphous solid dispersions or prodrugs: Complementary strategies to increase drug absorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug solubility: Importance and enhancement techniques. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serajuddin, A.T.M. Salt formation to improve drug solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, D.P.; Holm, R.; Diego, H.L. Use of pharmaceutical salts and cocrystals to address the issue of poor solubility. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patole, T.; Deshpande, A. Co-crystallization-a technique for solubility enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 3566–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolla, G.; Sarma, B.; Nangia, A.K. Crystal engineering of pharmaceutical cocrystals in the discovery and development of improved drugs. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 11514–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Fatima, Z.; Kaur, C.D.; Mishra, A.; Nashik, S.S.; Rizvi, D.A.; Prasad, R. Glibenclamide–malonic acid cocrystal with an enhanced solubility and bioavailability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2022, 48, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, D.J.; Rodriguez-Hornedo, N. Solubility advantage of pharmaceutical cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2252–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, V.D.; Lankalapalli, S. Rosuvastatin cocrystals: An attempt to modulate physicochemical parameters. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eesam, S.; Bhandaru, J.S.; Akkinepally, R.R.; Bobbala, R.K. Cocrystallization of gliclazide with improved physicochemical properties. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, S.; Zhang, R.; Jia, X.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X. Drug-drug cocrystals: Opportunities and challenges. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavoju, S.; Boström, D.; Velaga, S.P. Indomethacin–saccharin cocrystal: Design, synthesis and preliminary pharmaceutical characterization. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyawan, D.; Sari, R.; Yusuf, H.; Primaharinastiti, R. Preparation and characterization of artesunate-nicotinamide cocrystal by solvent evaporation and slurry method. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2014, 7 (Suppl. S1), 62–65. Available online: https://journals.innovareacademics.in/index.php/ajpcr/article/view/796/547 (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Desiraju, G.R. Supramolecular synthons in crystal engineering—A new organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1995, 34, 2311–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalder, T.K.; Sankolli, R.; Dastidar, P. Homo-or heterosynthon? A crystallographic study on a series of new cocrystals derived from pyrazinecarboxamide and various carboxylic acids equipped with additional hydrogen bonding sites. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 2533–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, P.A.; Sheen, D.B.; Shepherd, E.E.A.; Sherwood, J.N.; Feeder, N.; Docherty, R.; Milojevic, S. Morphological evaluation of the γ-polymorph of indomethacin. J. Cryst. Growth 2002, 237, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalkowsky, S.H.; Dannenfelser, R.M. Aquasol Database of Aqueous Solubility. Version 5; College of Pharmacy, University of Arizona: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1992. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3101 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Pagire, S.K.; Jadav, N.; Vangala, V.R.; Whiteside, B.; Paradkar, A. Thermodynamic investigation of carbamazepine-saccharin co-crystal polymorphs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2009–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, N.; Wang, K.; Schlindwein, W.; Davies, A.; Li, M. In situ monitoring of carbamazepine–nicotinamide cocrystal intrinsic dissolution behaviour. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, M.M.; Haltiwanger, R.C.; Allured, V.S.; Gill, S.C.; Gill, S.J. Peptide-urea interactions as observed in diketopiperazine-urea cocrystal. Biophys. Chem. 1993, 46, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Nangia, A. Curcumin: Pharmaceutical solids as a platform to improve solubility and bioavailability. CrystEngComm. 2018, 20, 3277–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görbitz, C.H.; Husdal, J. Cocrystallizing agents for amino acids. ll. The crystal structures of L-histidine-4,5-imidazoledicarboxylic acid (1:1) and L-lysine-4,5-imidazoledicarboxylic acid (1:1). Acta Chem. Scand. 1998, 52, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzade, P.S.; Shendarkar, G.R. Pharmaceutical cocrystal: A game changing approach for the administration of old drugs in new crystalline form. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Otsuka, M. Characterization of melt-quenched and milled amorphous solids of gatifloxacin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1851–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Jing, P.; Xu, G.; Zhou, Q.; Cai, Y.; Deng, X. Terahertz spectroscopic characterizations and DFT calculations of indomethacin cocrystals with nicotinamide and saccharin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 249, 119309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Lin, H.; Lin, S. Thermal analysis and FTIR spectral curve-fitting investigation of formation mechanism and stability of indomethacin-saccharin cocrystals via solid-state grinding process. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 66, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, M.; Buckton, G.; Rawlinson-Malone, C.F.; Williams, A.C.; Spillman, M.J.; Pidcock, E.; Shankland, K. Application of hydrogen-bond propensity calculations to an indomethacin-nicotinamide (1:1) co-crystal. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 4041–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Lin, S. An investigation of indomethacin–nicotinamide cocrystal formation induced by thermal stress in the solid or liquid state. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2386–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Song, B.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Han, J. Molecular recognition and interaction between uracil and urea in solid-state studied by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 10927–10933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten, G.; Nouri, K.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Löbmann, K. Performance comparison between crystalline and co-amorphous salts of indomethacin-lysine. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, B. Vibrational modes optimization and terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of L-Lysine and L-Lysine hydrate. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1232, 129952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Ren, G.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Qi, W.; Han, J.; Zhao, H. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of L-histidine hydrochloride monohydrate. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1157, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalhi, M.S.; Royall, P.G.; Chan, K.L.A. Mechanistic study of the solubilization effect of basic amino acids on a poorly water-soluble drug. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 19040–19053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavishi, D.D.; Borkhataria, C.H. Spring and parachute: How cocrystals enhance solubility. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2016, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, Y.; Ito, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Sasaki, T.; Tanaka, H. Effects of temperature on terahertz spectra of caffeine/oxalic acid 2:1 cocrystal and its solid-state density functional theory. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Xing, X.; Yang, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhou, L.; Xie, Z.; Han, D. Terahertz spectroscopic characterization and DFT calculations of vanillin cocrystals with nicotinamide and isonicotinamide. CrystEngComm 2023, 25, 2038–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, L.; Abdelkader, A.; Ornik, J.; Castro-Camus, E.; Keck, C.M.; Koch, M. Terahertz spectroscopy for non-destructive solid-state investigation of norfloxacin in paper tablets after wet granulation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, C. Preparation of carbamazepine-nicotinamide cocrystal. Open Access Libr. J. 2021, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Cai, Y.; Deng, X. Terahertz spectroscopic characterizations and DFT calculations of carbamazepine cocrystals with nicotinamide, saccharin and fumaric acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 236, 118346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaru, R.K.; Rout, S.R.; Kenguva, G.; Gorain, B.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Kesharwani, P.; Dandela, R. Recent advances in pharmaceutical cocrystals: From bench to market. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 780582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, J.; Liu, J.; Hong, Z.; Du, Y. Terahertz and Raman spectroscopic investigation of monohydrate cocrystal of antitubercular isoniazid with protocatechuic acid. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, J.; Liu, J.; Qin, J.; Hong, Z. Structural insights into anhydrous and monohydrated forms of 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzoic acid based on Raman and terahertz spectroscopic characterization. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 224, 117436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, J.; Tang, W.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Hong, Z. Vibrational spectroscopic study of polymorphism and polymorphic transformation of the anti-viral drug lamivudine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 137, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.; Pena, M.A.; Bustamante, P. Thermodynamic analysis and enthalpy–entropy compensation for the solubility of indomethacin in aqueous and non-aqueous mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2011, 308, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, D.; Bogner, R.H. Amorphization alone does not account for the enhancement of solubility of drug co-ground with silicate: The case of indomethacin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Substance | Solubility (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| IND | 247 ± 33 |
| IND/SAC CC | 756 ± 34 |
| IND/NIC CC | 696 ± 15 |
| IND/U CC | 575 ± 23 |
| IND/LYS CC | 742 ± 10 |
| IND/HIS CC | 451 ± 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-C.; Hung, C.-T.; Lin, Y.-H.; Tsai, H.-J.; Hu, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-P.; Chen, J.-C.; Hsu, S.-F.; Hsieh, H.-J. Preparation of Indomethacin Co-Crystals; Comparison of XRD, THz, and FT-IR Spectral Analyses; and Enhancement of Solubility. J. Pharm. BioTech Ind. 2024, 1, 2-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi1010002
Hsu C-C, Hung C-T, Lin Y-H, Tsai H-J, Hu P-C, Lin Y-P, Chen J-C, Hsu S-F, Hsieh H-J. Preparation of Indomethacin Co-Crystals; Comparison of XRD, THz, and FT-IR Spectral Analyses; and Enhancement of Solubility. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry. 2024; 1(1):2-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi1010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chih-Chin, Chih-Tse Hung, Ya-Hsuan Lin, Hua-Jeng Tsai, Po-Chih Hu, Yi-Ping Lin, Jyh-Chern Chen, Shen-Fu Hsu, and Hsyue-Jen Hsieh. 2024. "Preparation of Indomethacin Co-Crystals; Comparison of XRD, THz, and FT-IR Spectral Analyses; and Enhancement of Solubility" Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry 1, no. 1: 2-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi1010002
APA StyleHsu, C.-C., Hung, C.-T., Lin, Y.-H., Tsai, H.-J., Hu, P.-C., Lin, Y.-P., Chen, J.-C., Hsu, S.-F., & Hsieh, H.-J. (2024). Preparation of Indomethacin Co-Crystals; Comparison of XRD, THz, and FT-IR Spectral Analyses; and Enhancement of Solubility. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry, 1(1), 2-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi1010002








