Development of a 3D Microfluidic Analytical Device for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Commercial Food Samples with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Food Sample Collection
2.2. Microbiological Tests
2.3. DNA Extraction
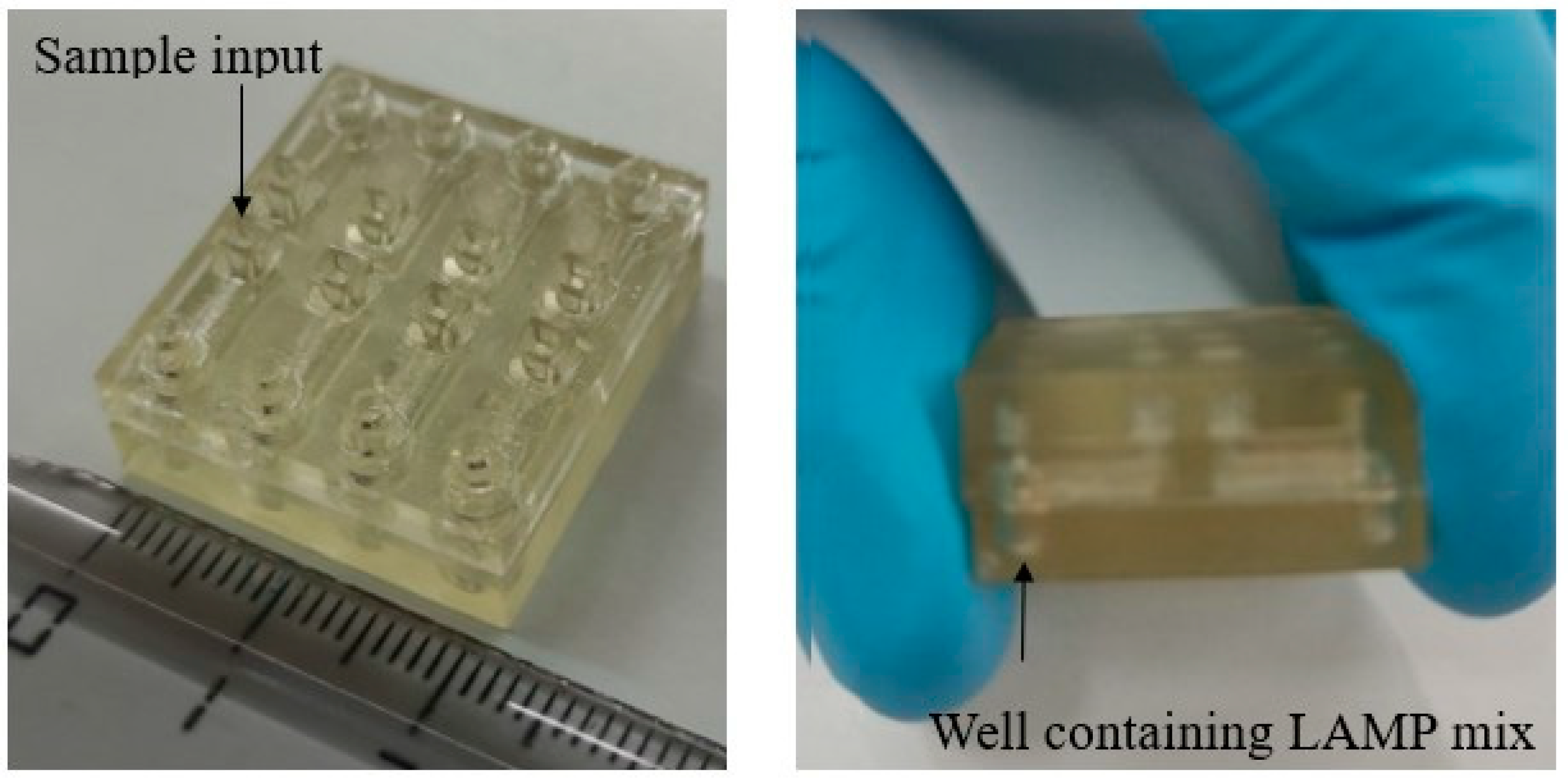
2.4. Fabrication of the Microfluidic Analytical Device
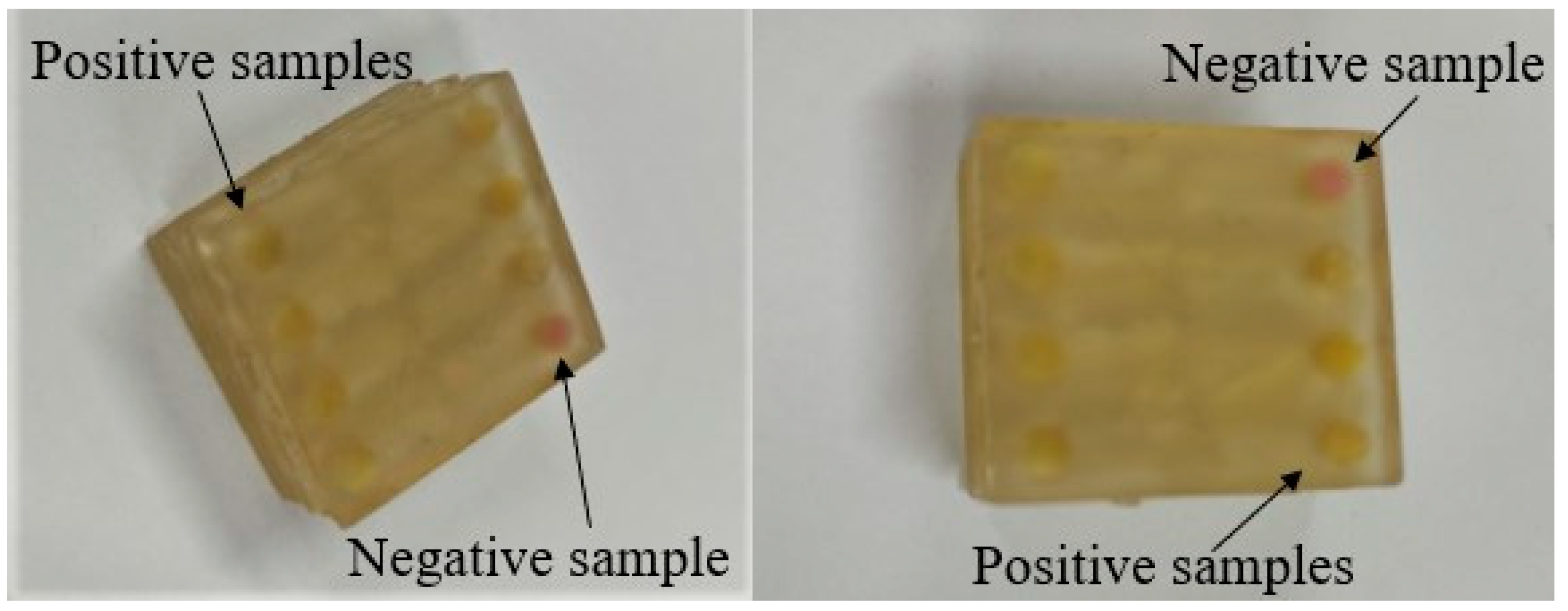
2.5. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method
2.6. Method Standardization
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Programme “Global Salm-Surv” de l’OMS “Global Salm-Surv”. Note D’information INFOSAN No. 6/2005. Available online: http://www.who.int/foodsafety/fs_management/No_06_GSS_Oct05_fr.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The Community Summary Report on Trends and Sources of Zoonoses, Zoonotic Agents, Antimicrobial Resistance and Foodborne Outbreaks in the European Union in 2006. EFSA J. 2007, 5, 130r. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2019 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2023, 19, e06406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Bi, H.; Liu, B.; Qiao, L. Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms by Microfluidics Based Analytical Methods. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5512–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Ye, C.; Xiao, H.; Yin, J.; Liang, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Luo, D.; Gao, D.; Tan, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Optimization of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for robust visualization in SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants diagnosis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 251, 117430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodorou, S.A.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Houhoula, D. A comparison of different DNA extraction methods and molecular techniques for the detection and identification of foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2021, 7, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisawat, M.; Panbangred, W. Efficient and Specific Detection of Salmonella in Food Samples Using a stn-Based Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Method. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 356401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.J.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Pu, J.H.; Ge, Q.L.; Tang, X.J.; Gao, Y.S. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Listeria monocytogenes by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, R.; Parizi, Z.K.; Ghorbanmehr, N.; Mirshafiee, H. Rapid and Simple Detection of Escherichia coli by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay in Urine Specimens. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2018, 10, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, E.B. Probable Inference, the Law of Succession, and Statistical Inference. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1927, 22, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission of the European Communities. White Paper on Food Safety Com (1999) 719 Final. 12.1.2000. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:51999DC0719 (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Papatheodorou, S.A.; Tsironi, T.; Giannakourou, M.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Houhoula, D. Application of microfluidic paperbased analytical devices (μPADs) for food microbial detection. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bai, Y.; You, M.; Hu, J.; Yao, C.; Cao, L.; Xu, F. Fully integrated microfluidic devices for qualitative, quantitative and digital nucleic acids testing at point of care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, A.; Chiu, P.; Qu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C. Integrated Microfluidic-Based Platforms for On-Site Detection and Quantification of Infectious Pathogens: Towards On-Site Medical Translation of SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostic Platforms. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donia, A.; Furqan Shahid, M.; Hassan, S.; Shahid, R.; Ahmad, A.; Javed, A.; Nawaz, M.; Yaqub, T.; Bokhari, H. Integration of RT-LAMP and Microfluidic Technology for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater as an Advanced Point-of-Care Platform. Food Environ. Virol. 2022, 14, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, S.; Huang, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Lin, J. A microfluidic biosensor for rapid and automatic detection of Salmonella using metal-organic framework and Raspberry Pi. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, Y.; Ban, M.; Li, A.; Jin, X.; Du, Y.; Pan, L. A microfluidic colorimetric biosensor for in-field detection of Salmonella in fresh-cut vegetables using thiolated polystyrene microspheres, hose-based microvalve and smartphone imaging APP. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somvanshi, S.B.; Ulloa, A.M.; Zhao, M.; Liang, Q.; Barui, A.K.; Lucas, A.; Jadhav, K.M.; Allebach, J.P.; Stanciu, L.A. Microfluidic paper-based aptasensor devices for multiplexed detection of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 207, 114214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayad, A.; Ibrahim, F.; Mukim Uddin, S.; Cho, J.; Madou, M.; Thong, K.L. A microdevice for rapid, monoplex and colorimetric detection of foodborne pathogens using a centrifugal microfluidic platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokerst, J.C.; Adkins, J.A.; Bisha, B.; Mentele, M.M.; Goodridge, L.D.; Henry, C.S. Development of a Paper-Based Analytical Device for Colorimetric Detection of Select Foodborne Pathogens. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2900–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Huang, Q.; Xie, L.; Xiang, G.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Ma, L.; Luo, X.; Xin, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. A rapid, low-cost, and microfluidic chip-based system for parallel identification of multiple pathogens related to clinical pneumonia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Hejazian, M.; Ooi, C.; Kashaninejad, N. Recent Advances and Future Perspectives on Microfluidic Liquid Handling. Micromachines 2017, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic method for infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2009, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonchamps, P.L.; He, Y.; Wang, K.; Lu, X. Detection of pathogens in foods using microfluidic “lab-on-chip”: A mini review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 10, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Limits of Detection (cfu/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Milk | L. monocytogenes | 102 |
| S. typhimurium | 101 | |
| E. coli | 101 | |
| Chicken | L. monocytogenes | 102 |
| S. typhimurium | 101 | |
| E. coli | 101 | |
| Lettuce | L. monocytogenes | 102 |
| S. typhimurium | 101 | |
| E. coli | 101 |
| S. typhimurium Culture/3D Device | L. monocytogenes Culture/3D Device | E. coli Culture/3D Device | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 0/0 | 2/2 | 4/4 |
| Chicken | 5/5 | 11/11 | 17/17 |
| Lettuce | 2/2 | 15/15 | 14/14 |
| Total | 7/150 | 28/150 | 35/150 |
| S. typhimurium | L. monocytogenes | E. coli | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive predictive value | 65–100% | 88–100% | 90–100% |
| Negative predictive value | 97–100% | 97–100% | 97–100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papatheodorou, S.-A.; Houhoula, D.; Magoulas, S.; Tsantes, A.G.; Tsakali, E.; Akkermans, S.; Van Impe, J.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Tsantes, A.E. Development of a 3D Microfluidic Analytical Device for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Commercial Food Samples with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2024, 69, 41-49. https://doi.org/10.3390/amh69010006
Papatheodorou S-A, Houhoula D, Magoulas S, Tsantes AG, Tsakali E, Akkermans S, Van Impe J, Halvatsiotis P, Tsantes AE. Development of a 3D Microfluidic Analytical Device for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Commercial Food Samples with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Acta Microbiologica Hellenica. 2024; 69(1):41-49. https://doi.org/10.3390/amh69010006
Chicago/Turabian StylePapatheodorou, Spyridon-Andreas, Dimitra Houhoula, Sotirios Magoulas, Andreas G. Tsantes, Efstathia Tsakali, Simen Akkermans, Jan Van Impe, Panagiotis Halvatsiotis, and Argyrios E. Tsantes. 2024. "Development of a 3D Microfluidic Analytical Device for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Commercial Food Samples with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification" Acta Microbiologica Hellenica 69, no. 1: 41-49. https://doi.org/10.3390/amh69010006
APA StylePapatheodorou, S.-A., Houhoula, D., Magoulas, S., Tsantes, A. G., Tsakali, E., Akkermans, S., Van Impe, J., Halvatsiotis, P., & Tsantes, A. E. (2024). Development of a 3D Microfluidic Analytical Device for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Commercial Food Samples with Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. Acta Microbiologica Hellenica, 69(1), 41-49. https://doi.org/10.3390/amh69010006









