Monoclonal Protein Evaluation in the Diagnostic Algorithm for Cardiac Amyloidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Recognizing the ‘Red Flags’ to Suspect CA
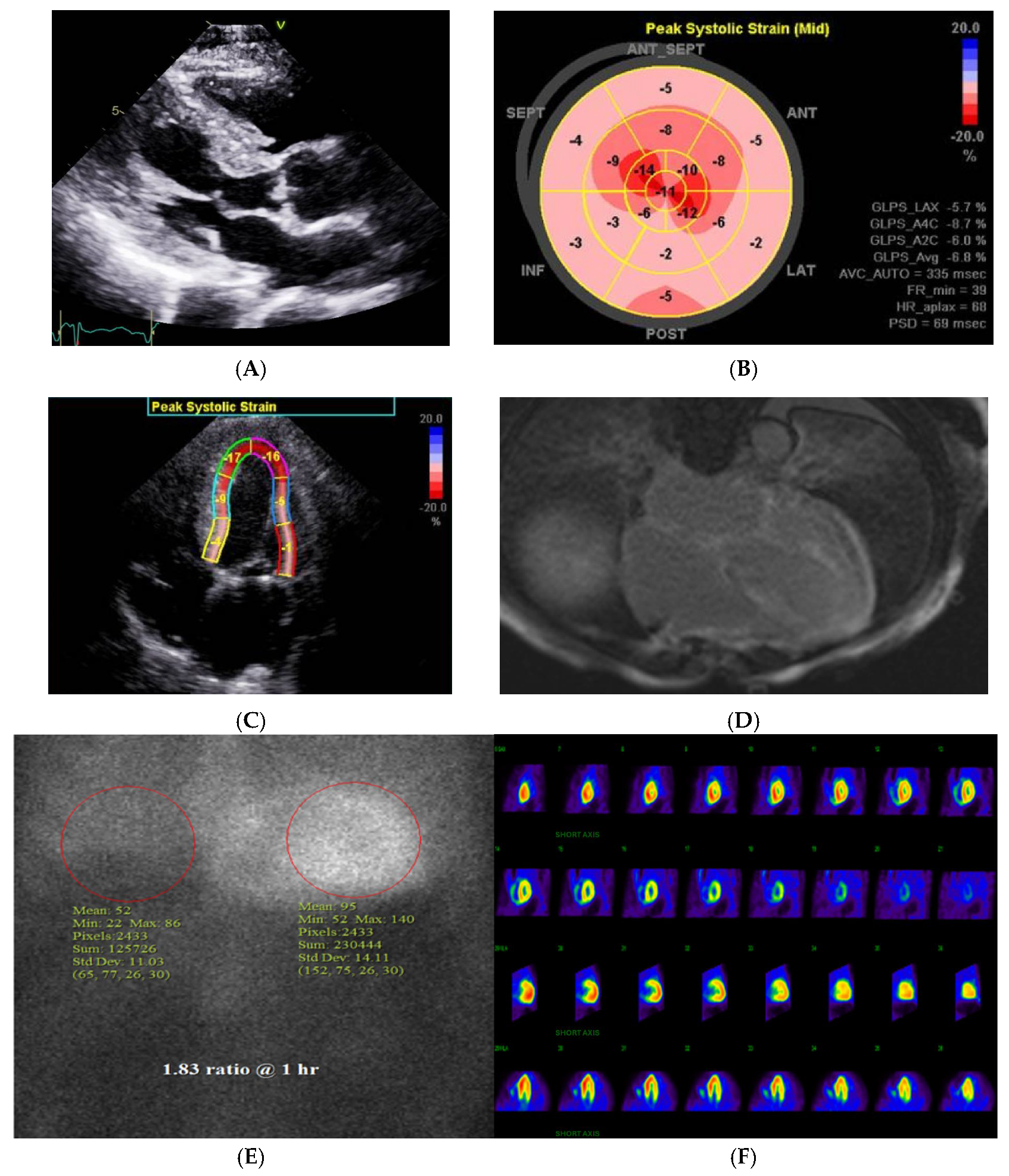
3. Diagnostic Imaging in CA
4. Monoclonal Gammopathy Testing in Suspected CA
5. Pitfalls and Challenges with Monoclonal Gammopathy
6. Advanced Typing Techniques When Non-Invasive Diagnostics Are Inconclusive
7. Advances in Imaging-Role of PET
8. Prognostic Assessment in CA
9. Amyloid-Specific Disease-Modifying Therapies
9.1. Management of ATTR
9.1.1. TTR Silencers
9.1.2. TTR Stabilizers and Degraders
9.2. Management of AL
10. Challenges and Limitations
11. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merlini, G.; Bellotti, V. Molecular mechanisms of amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, A.; Bukhari, S.; Eisele, Y.S.; Soman, P. Molecular Imaging of Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S. Cardiac amyloidosis: State-of-the-art review. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, S.; Lachmann, H.J.; Wechalekar, A.D. Epidemiologic and Survival Trends in Amyloidosis, 1987–2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1567–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Pavia, P.; Rapezzi, C.; Adler, Y.; Arad, M.; Basso, C.; Brucato, A.; Burazor, I.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Damy, T.; Eriksson, U.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of cardiac amyloidosis: A position statement of the ESC Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1554–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, A.; Bukhari, S.; Ahmad, S.; Nieves, R.; Eisele, Y.S.; Follansbee, W.; Brownell, A.; Wong, T.C.; Schelbert, E.; Soman, P. Efficient 1-Hour Technetium-99 m Pyrophosphate Imaging Protocol for the Diagnosis of Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, e010249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oye, M.; Dhruva, P.; Kandah, F.; Oye, M.; Missov, E. Cardiac amyloid presenting as cardiogenic shock: Case series. Eur. Heart J.-Case Rep. 2021, 5, ytab252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, P.S.; Edwards, W.D.; Gertz, M.A. Symptomatic ischemic heart disease resulting from obstructive intramural coronary amyloidosis. Am. J. Med. 2000, 109, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorbala, S.; Vangala, D.; Bruyere, J.; Quarta, C.; Kruger, J.; Padera, R.; Foster, C.; Hanley, M.; Di Carli, M.F.; Falk, R. Coronary microvascular dysfunction is related to abnormalities in myocardial structure and function in cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.; Khan, S.Z.; Ghoweba, M.; Khan, B.; Bashir, Z. Arrhythmias and Device Therapies in Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.; Khan, S.Z.; Bashir, Z. Atrial Fibrillation, Thromboembolic Risk, and Anticoagulation in Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Review. J. Card. Fail. 2023, 29, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.; Barakat, A.F.; Eisele, Y.S.; Nieves, R.; Jain, S.; Saba, S.; Follansbee, W.P.; Brownell, A.; Soman, P. Prevalence of Atrial Fibrillation and Thromboembolic Risk in Wild-Type Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2021, 143, 1335–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.; Oliveros, E.; Parekh, H.; Farmakis, D. Epidemiology, Mechanisms, and Management of Atrial Fibrillation in Cardiac Amyloidosis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.; Kasi, A.; Khan, B. Bradyarrhythmias in Cardiac Amyloidosis and Role of Pacemaker. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.; Khan, B. Prevalence of ventricular arrhythmias and role of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator in cardiac amyloidosis. J. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dember, L.M. Amyloidosis-associated kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 3458–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, Z.; Younus, A.; Dhillon, S.; Kasi, A.; Bukhari, S. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of cardiac amyloidosis. J. Investig. Med. 2024, 72, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milandri, A.; Farioli, A.; Gagliardi, C.; Longhi, S.; Salvi, F.; Curti, S.; Foffi, S.; Caponetti, A.G.; Lorenzini, M.; Ferlini, A.; et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome in cardiac amyloidosis: Implications for early diagnosis and prognostic role across the spectrum of aetiologies. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, B.W.; Reyes, B.A.; Ikram, A.; Donnelly, J.P.; Phelan, D.; Jaber, W.A.; Shapiro, D.; Evans, P.J.; Maschke, S.; Kilpatrick, S.E.; et al. Tenosynovial and Cardiac Amyloidosis in Patients Undergoing Carpal Tunnel Release. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2040–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Smiley, D.; Simsolo, E.; Remotti, F.; Bustamante, A.; Teruya, S.; Helmke, S.; Einstein, A.J.; Lehman, R.; Giles, J.T.; et al. Analysis of lumbar spine stenosis specimens for identification of amyloid. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2022, 70, 3538–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, H.I.; Singh, A.; Alexander, K.M.; Mirto, T.M.; Falk, R.H. Association Between Ruptured Distal Biceps Tendon and Wild-Type Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. JAMA 2017, 318, 962–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, J.; Alvarez, J.; Teruya, S.; Castano, A.; Lehman, R.A.; Weidenbaum, M.; Geller, J.A.; Helmke, S.; Maurer, M.S. Hip and knee arthroplasty are common among patients with transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis, occurring years before cardiac amyloid diagnosis: Can we identify affected patients earlier? Amyloid 2017, 24, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.; Bashir, Z. Diagnostic Modalities in the Detection of Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, Z.; Musharraf, M.; Azam, R.; Bukhari, S. Imaging modalities in cardiac amyloidosis. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.M.; Shpilsky, S.; Nieves, D.; Soman, R. Amyloidosis prediction score: A clinical model for diagnosing Transthy-retin Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Card. Fail. 2020, 26 (Suppl. 10), 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, S.J.; Geske, J.B.; Dispenzieri, A.; Syed, I.S.; Hanson, T.J.; Grogan, M.; Araoz, P.A. LGE Provides Incremental Prognostic Information Over Serum Biomarkers in AL Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamitsos, T.D.; Piechnik, S.K.; Banypersad, S.M.; Fontana, M.; Ntusi, N.B.; Ferreira, V.M.; Whelan, C.J.; Myerson, S.G.; Robson, M.D.; Hawkins, P.N.; et al. Noncontrast T1 mapping for the diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banypersad, S.M.; Fontana, M.; Maestrini, V.; Sado, D.M.; Captur, G.; Petrie, A.; Piechnik, S.K.; Whelan, C.J.; Herrey, A.S.; Gillmore, J.D.; et al. T1 mapping and survival in systemic light-chain amyloidosis. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olausson, E.; Wertz, J.; Fridman, Y.; Bering, P.; Maanja, M.; Niklasson, L.; Wong, T.C.; Fukui, M.; Cavalcante, J.L.; Cater, G.; et al. Diffuse myocardial fibrosis associates with incident ventricular arrhythmia in implantable cardioverter defibrillator recipients. medRxiv 2023. Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.B.; Nieves, A.; Eisele, R.; Follansbee, Y.; Soman, W.P. Clinical Predictors of positive 99mTc-99m pyrophosphate scan in patients hospitalized for decompensated heart failure. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61 (Suppl. 1), 659. [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari, S.; Masri, A.; Ahmad, S.; Eisele, Y.S.; Brownell, A.; Soman, P. Discrepant Tc-99m PYP Planar grade and H/CL ratio: Which correlates better with diffuse tracer uptake on SPECT? J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61 (Suppl. 1), 1633. [Google Scholar]
- Bokhari, S.; Morgenstern, R.; Weinberg, R.; Kinkhabwala, M.; Panagiotou, D.; Castano, A.; DeLuca, A.; Jin, Z.; Maurer, M.S. Standardization of 99mTechnetium pyrophosphate imaging methodology to diagnose TTR cardiac amyloidosis. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Maurer, M.S.; Falk, R.H.; Merlini, G.; Damy, T.; Dispenzieri, A.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Berk, J.L.; Quarta, C.C.; Grogan, M.; et al. Nonbiopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis. Circulation 2016, 133, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, S.; Castaño, A.; Pozniakoff, T.; Deslisle, S.; Latif, F.; Maurer, M.S. (99m)Tc-pyrophosphate scintigraphy for differentiating light-chain cardiac amyloidosis from the transthyretin-related familial and senile cardiac amyloidoses. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 6, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzmann, J.A.; Abraham, R.S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lust, J.A.; Kyle, R.A. Diagnostic performance of quantitative kappa and lamb-da free light chain assays in clinical practice. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gameren, I.I.; Hazenberg, B.P.; Bijzet, J.; van Rijswijk, M.H. Diagnostic accuracy of subcutaneous abdominal fat tissue aspiration for detecting systemic amyloidosis and its utility in clinical practice. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swan, N.; Skinner, M.; O’Hara, C.J. Bone marrow core biopsy specimens in AL (primary) amyloidosis. A morphologic and immunohistochemical study of 100 cases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 120, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbustini, E.; Verga, L.; Concardi, M.; Palladini, G.; Obici, L.; Merlini, G. Electron and immuno-electron microscopy of abdominal fat identifies and characterizes amyloid fibrils in suspected cardiac amyloidosis. Amyloid 2002, 9, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abildgaard, N.; Rojek, A.M.; Møller, H.E.; Palstrøm, N.B.; Nyvold, C.G.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Hansen, C.T.; Beck, H.C.; Marcussen, N. Immunoelectron microscopy and mass spectrometry for classification of amyloid deposits. Amyloid 2020, 27, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leguit, R.J.; Vink, A.; de Jonge, N.; Minnema, M.C.; Oerlemans, M.I. Endomyocardial biopsy with co-localization of a lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma and AL amyloidosis. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2021, 53, 107348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorbala, S.; Kijewski, M.F. Molecular Imaging of Systemic and Cardiac Amyloidosis: Recent Advances and Focus on the Future. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 20S–28S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, M.U.; Hawkins, P.N.; Cappelli, F.; Perfetto, F.; Zampieri, M.; Argiro, A.; Petrie, A.; Law, S.; Porcari, A.; Razvi, Y.; et al. Tc-99m labelled bone scintigraphy in suspected cardiac amyloidosis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, C. Diagnostic performance of CMR, SPECT, and PET imaging for the detection of cardiac amyloidosis: A meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Colby, C.; Laumann, K.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Leung, N.; Dingli, D.; et al. Revised prognostic staging system for light chain amyloidosis incorporating cardiac biomarkers and serum free light chain measurements. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilleness, B.; Ruberg, F.L.; Mussinelli, R.; Doros, G.; Sanchorawala, V. Development and validation of a survival staging system incorporating BNP in patients with light chain amyloidosis. Blood 2019, 133, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmore, J.D.; Damy, T.; Fontana, M.; Hutchinson, M.; Lachmann, H.J.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Quarta, C.C.; Rezk, T.; Whelan, C.J.; Gonzalez-Lopez, E.; et al. A newstaging system for cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2799–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogan, M.; Scott, C.G.; Kyle, R.A.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Gertz, M.A.; Lin, G.; Klarich, K.W.; Miller, W.L.; Maleszewski, J.J.; Dispenzieri, A. Natural History of Wild-Type Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis and Risk Stratification Using a Novel Staging System. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, C.; Ioannou, A.; Patel, R.K.; Razvi, Y.; Porcari, A.; Rauf, M.U.; Bandera, F.; Aimo, A.; Emdin, M.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; et al. Expansion of the National Amyloidosis Centre staging system to detect early mortality in transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2024, 26, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.K.; Levy, W.C.; Vasbinder, A.; Teruya, S.; Santos, J.D.L.; Leedy, D.; Maurer, M.S. Diuretic Dose and NYHA Functional Class are Independent Predictors of Mortality in Patients with Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. JACC CardioOncol. 2020, 2, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, O.C.; Ismael, A.; Pawarova, B.; Manwani, R.; Ravichandran, S.; Law, S.; Foard, D.; Petrie, A.; Ward, S.; Douglas, B.; et al. Longitudinal strain is an independent predictor of survival and response to therapy in patients with systemic AL amyloidosis. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, P.; Dispenzieri, A.; Scott, C.G.; Gertz, M.A.; Perlini, S.; Mussinelli, R.; Lacy, M.Q.; Buadi, F.K.; Kumar, S.; Maurer, M.S.; et al. Independent Prognostic Value of Stroke Volume Index in Patients With Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 11, e006588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, J.; Steidley, D.E.; Carlsson, M.; Ong, M.-L.; Maurer, M.S. Myocardial Contraction Fraction by M-Mode Echocardiography Is Superior to Ejection Fraction in Predicting Mortality in Transthyretin Amyloidosis. J. Card. Fail. 2018, 24, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.; Bashir, Z.; Shpilsky, D.; Eisele, Y.S.; Soman, P. Abstract 16145: Reduced ejection fraction at diagnosis is an independent predictor of mortality in transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2020, 142 (Suppl. 3), A16145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Pica, S.; Reant, P.; Abdel-Gadir, A.; Treibel, T.A.; Banypersad, S.M.; Maestrini, V.; Barcella, W.; Rosmini, S.; Bulluck, H.; et al. Prognostic Value of Late Gadolinium Enhancement Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Cardiac Amyloidosis. Circulation 2015, 132, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Naharro, A.; Kotecha, T.; Norrington, K.; Boldrini, M.; Rezk, T.; Quarta, C.; Treibel, T.A.; Whelan, C.J.; Knight, D.S.; Kellman, P.; et al. Native T1 and Extracellular Volume in Transthyretin Amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-P.; Suh, H.-Y.; Park, S.; Oh, S.; Kwak, S.-G.; Kim, H.-M.; Koh, Y.; Park, J.-B.; Kim, H.-K.; Cho, H.-J.; et al. Pittsburgh B Compound Positron Emission Tomography in Patients With AL Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.; Fatima, S.; Barakat, A.F.; Fogerty, A.E.; Weinberg, I.; Elgendy, I.Y. Venous thromboembolism during pregnancy and postpartum period. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 97, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Yalcin, A.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 411, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.T.; Wang, S.; Vickers, T.A.; Shen, W.; Liang, X.-H. Cellular uptake and trafficking of antisense oligonucleotides. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen Treatment for Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.S.; Schwartz, J.H.; Gundapaneni, B.; Elliott, P.M.; Merlini, G.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Grogan, M.; Witteles, R.; Damy, T.; et al. Tafamidis Treatment for Patients with Transthyretin Amyloid Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, J.L.; Suhr, O.B.; Obici, L.; Sekijima, Y.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Yamashita, T.; Heneghan, M.A.; Gorevic, P.D.; Litchy, W.J.; Wiesman, J.F.; et al. Repurposing diflunisal for familial amyloid polyneuropathy: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 310, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekijima, Y.; Tojo, K.; Morita, H.; Koyama, J.; Ikeda, S.-I. Safety and efficacy of long-term diflunisal administration in hereditary transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis. Amyloid 2015, 22, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pavia, P.; Siepen, F.A.D.; Donal, E.; Lairez, O.; van der Meer, P.; Kristen, A.V.; Mercuri, M.F.; Michalon, A.; Frost, R.J.; Grimm, J.; et al. Phase 1 Trial of Antibody NI006 for Depletion of Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloid. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlstedt, E.; Jimenez-Zepeda, V.; Howlett, J.G.; White, J.A.; Fine, N.M. Clinical Experience With the Use of Doxycycline and Ursodeoxycholic Acid for the Treatment of Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis. J. Card. Fail. 2019, 25, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wixner, J.; Pilebro, B.; Lundgren, H.-E.; Olsson, M.; Anan, I. Effect of doxycycline and ursodeoxycholic acid on transthyretin amyloidosis. Amyloid 2017, 24, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.; Bashir, Z.; Shah, N.; Patel, Y.; Hulten, E. Investigating Cardiac Amyloidosis: A Primer for Clinicians. Rhode Isl. Med. J. 2025, 108, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hasib Sidiqi, M.; Gertz, M.A. Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis diagnosis and treatment algorithm 2021. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenzieri, A.; Buadi, F.; Kumar, S.K.; Reeder, C.B.; Sher, T.; Lacy, M.Q.; Kyle, R.A.; Mikhael, J.R.; Roy, V.; Leung, N.; et al. Treatment of Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis: Mayo Stratification of Myeloma and Risk-Adapted Therapy (mSMART) Consensus Statement. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1054–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bukhari, S. Monoclonal Protein Evaluation in the Diagnostic Algorithm for Cardiac Amyloidosis. LabMed 2025, 2, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2030013
Bukhari S. Monoclonal Protein Evaluation in the Diagnostic Algorithm for Cardiac Amyloidosis. LabMed. 2025; 2(3):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleBukhari, Syed. 2025. "Monoclonal Protein Evaluation in the Diagnostic Algorithm for Cardiac Amyloidosis" LabMed 2, no. 3: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2030013
APA StyleBukhari, S. (2025). Monoclonal Protein Evaluation in the Diagnostic Algorithm for Cardiac Amyloidosis. LabMed, 2(3), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/labmed2030013





