The Hydrodynamics of Ammonoid Swimming: Equations of Motion and Rocking Resonances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Model
2.1. Model Geometry
2.2. Fluid Dynamical Model for Swimming
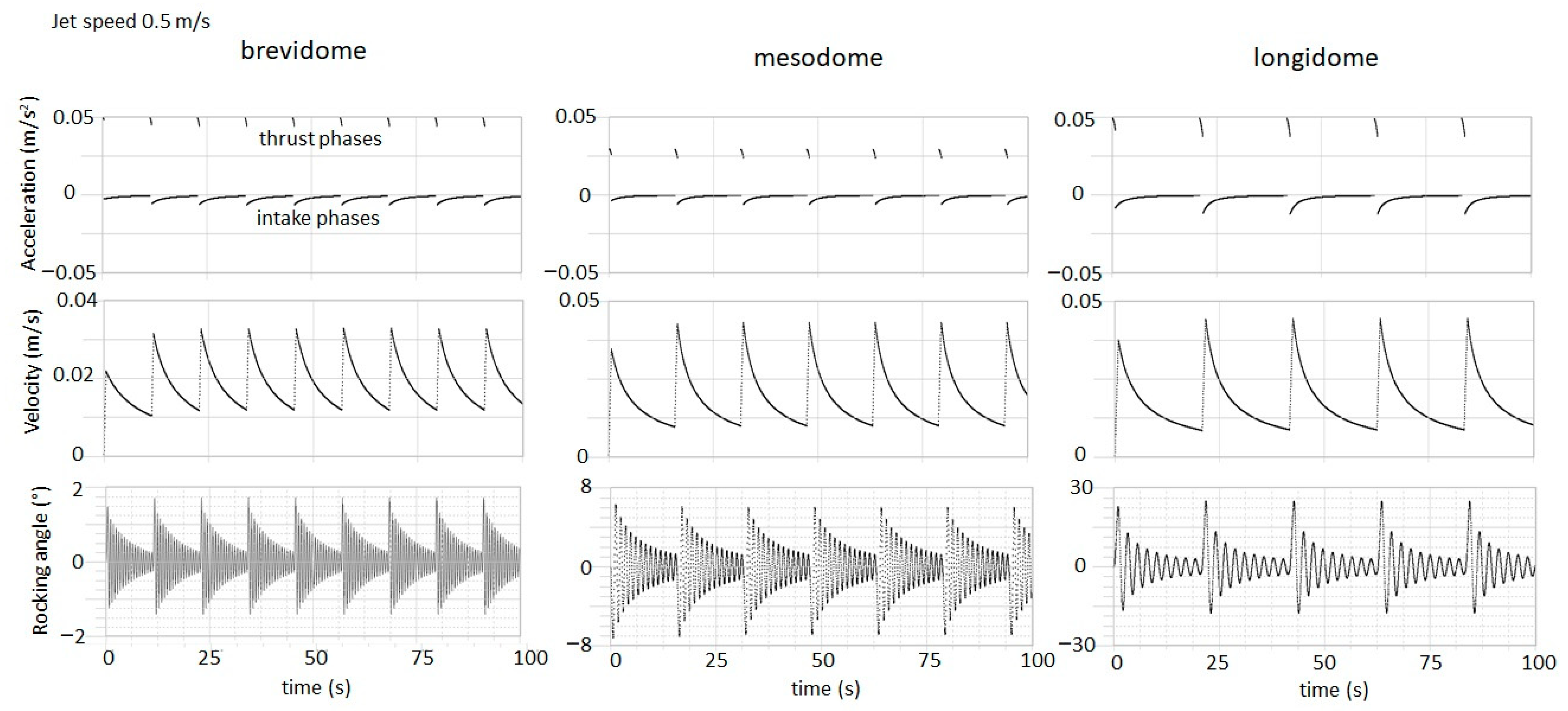
3. Model Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Model Ammonoid
| Type | a (cm) | b (1/rad) | (cm) | (cm) | (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| brevi | 0.4 | 0.09 | 0.003 | 0.16 | 0.0012 |
| meso | 0.4 | 0.09 | 0.0016 | 0.16 | 0.0011 |
| longi | 0.4 | 0.09 | 0.0010 | 0.16 | 0.0010 |
Appendix B. Calculation of the Rotational Drag Term in Equations (4) and (5)
References
- Lehmann, U. The Ammonites: Their Life and Their World; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Landman, N.H.; Tanabe, K.; Davis, R.A. (Eds.) Ammonoid Paleobiology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1996; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Klug, C.; Korn, D.; Landman, N.H.; Tanabe, K.; De Baets, K.; Naglik, C. Describing ammonoid conchs. In Ammonoid Paleobiology: From Anatomy to Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tajika, A.; Naglik, C.; Morimoto, N.; Pascual-Cebrian, E.; Hennhöfer, D.K.; Klug, C. Empirical 3D-model of the conch of the Middle Jurassic ammonite microconch Normannites, its buoyancy, the physical effects of its mature modifications and speculations on their function. Hist. Biol. 2015, 27, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglik, C.; Rikhtegar, F.N.; Klug, C. Buoyancy in Palaeozoic ammonoids from empirical 3D-models and their place in a theoretical morphospace. Lethaia 2016, 49, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, D.K.; Chamberlain, J.A. Buoyancy and hydrodynamics in ammonoids. In Ammonoid Paleobiology; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 169–224. [Google Scholar]
- Klug, C.; Hoffmann, R. Ammonoid septa and sutures. In Ammonoid Paleobiology: From Anatomy to Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 45–90. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, T.L.; Helmuth, B.S.; Saunders, W.B.; Ward, P.D. Septal complexity in ammonoid cephalopods increased mechanical risk and limited depth. Paleobiology 1997, 23, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemanis, R. The ammonite septum is not an adaptation to deep water: Re-evaluating a centuries-old idea. Proc. R. Soc. 2020, B287, 20201919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterman, D.J.; Ritterbush, K.A.; Ciampaglio, C.N.; Johnson, E.H.; Inoue, S.; Mikami, T.; Linn, T.J. Buoyancy control in ammonoid cephalopods refined by complex internal shell architecture. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebdon, N.; Ritterbush, K.; Choi, Y. Assessing the Morphological Impacts of Ammonoid Shell Shape through Systematic Shape Variation. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2020, 60, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebdon, N.; Ritterbush, K.; Choi, Y.; Peterman, D.J. Reevaluating hydrodynamic performance of Late Triassic–Early Jurassic ammonoid shells with a 1D trajectory model. Geobios 2022, 71, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterman, D.J.; Hebdon, N.; Ciampaglio, C.N.; Yacobucci, M.M.; Landman, N.H.; Linn, T. Syn vivo hydrostatic and hydrodynamic properties of scaphitid ammonoids from the US Western Interior. Geobios 2020, 60, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, J.A. Hydromechanical Design of Fossil Cephalopods. In The Ammonoidea: The Evolution, Classification, Mode of Life, and Geological Usefulness of a Major Fossil Group; House, M.R., Senior, J.R., Eds.; Systematics Association, Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981; Volume 18, p. 289. [Google Scholar]
- Klug, C.; Schweigert, G.; Tischlinger, H.; Pochmann, H. Failed prey or peculiar necrolysis? Isolated ammonite soft body from the Late Jurassic of Eichstätt (Germany) with complete digestive tract and male reproductive organs. Swiss J. Palaeontol. 2021, 140, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherns, L.; Spencer, A.R.; Rahman, I.A.; Garwood, R.J.; Reedman, C.; Burca, G.; Turner, M.J.; Hollingworth, N.T.J.; Hilton, J. Correlative tomography of an exceptionally preserved Jurassic ammonite implies hyponome-propelled swimming. Geology 2021, 50, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, C.; Landman, N.H.; Fuchs, D.; Mapes, R.H.; Pohle, A.; Guériau, P.; Reguer, S.; Hoffmann, R. Anatomy and evolution of the first Coleoidea in the Carboniferous. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterman, D.J.; Ritterbush, K.A. Resurrecting extinct cephalopods with biomimetic robots to explore hydrodynamic stability, maneuverability, and physical constraints on life habits. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, W.B.; Shapiro, E.A. Calculation and simulation of ammonoid hydrostatics. Paleobiology 1986, 12, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, D.K.; Landman, N.H. Nautilus—A poor model for the function and behavior of ammonoids? Lethaia 1993, 26, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, T.R.; Askew, G.N. Swimming mechanics and propulsive efficiency in the chambered nautilus. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 170467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.J.; Grosenbaugh, M.A. Jet flow in steadily swimming adult squid. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1125–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raup, D.M.; Chamberlain, J.A. Equations for volume and centre of gravity in ammonoid shells. J. Paleontol. 1967, 41, 566–574. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, D.W. On Growth and Form; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Raup, D.M. Geometric analysis of shell coiling: General problems. J. Paleontol. 1966, 40, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, T. Theoretical modeling of ammonoid morphology. In Ammonoid Paleobiology; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 225–251. [Google Scholar]
- Klug, C.; Korn, D. The origin of ammonoid locomotion. Acta Palaeontol. Pol. 2004, 49, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Westermann, G.E. Ammonoid life and habitat. In Ammonoid Paleobiology; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 607–707. [Google Scholar]
- Naglik, C.; Tajika, A.; Chamberlain, J.; Klug, C. Ammonoid locomotion. In Ammonoid Paleobiology: From Anatomy to Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 649–688. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, P.K.; Cohen, I.M.; Dowling, D.R. Fluid Mechanics, 4th ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting, H. Boundary Layer Theory; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Peterman, D.J.; Ritterbush, K.A. Stability–Maneuverability Tradeoffs Provided Diverse Functional Opportunities to Shelled Cephalopods. Integr. Org. Biol. 2022, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebdon, N.; Polly, P.D.; Peterman, D.J.; Ritterbush, K.A. Detecting mismatch in functional narratives of animal morphology: A test case with fossils. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2022, 62, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, R.; Lemanis, R.; Naglik, C.; Klug, C. Ammonoid buoyancy. In Ammonoid Paleobiology: From Anatomy to Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 613–648. [Google Scholar]
- Parent, H.; Westermann, G.E.; Chamberlain, J.A. Ammonite aptychi: Functions and role in propulsion. Geobios 2014, 47, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, J.A.; Westermann, G.E. Hydrodynamic properties of cephalopod shell ornament. Paleobiology 1976, 2, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
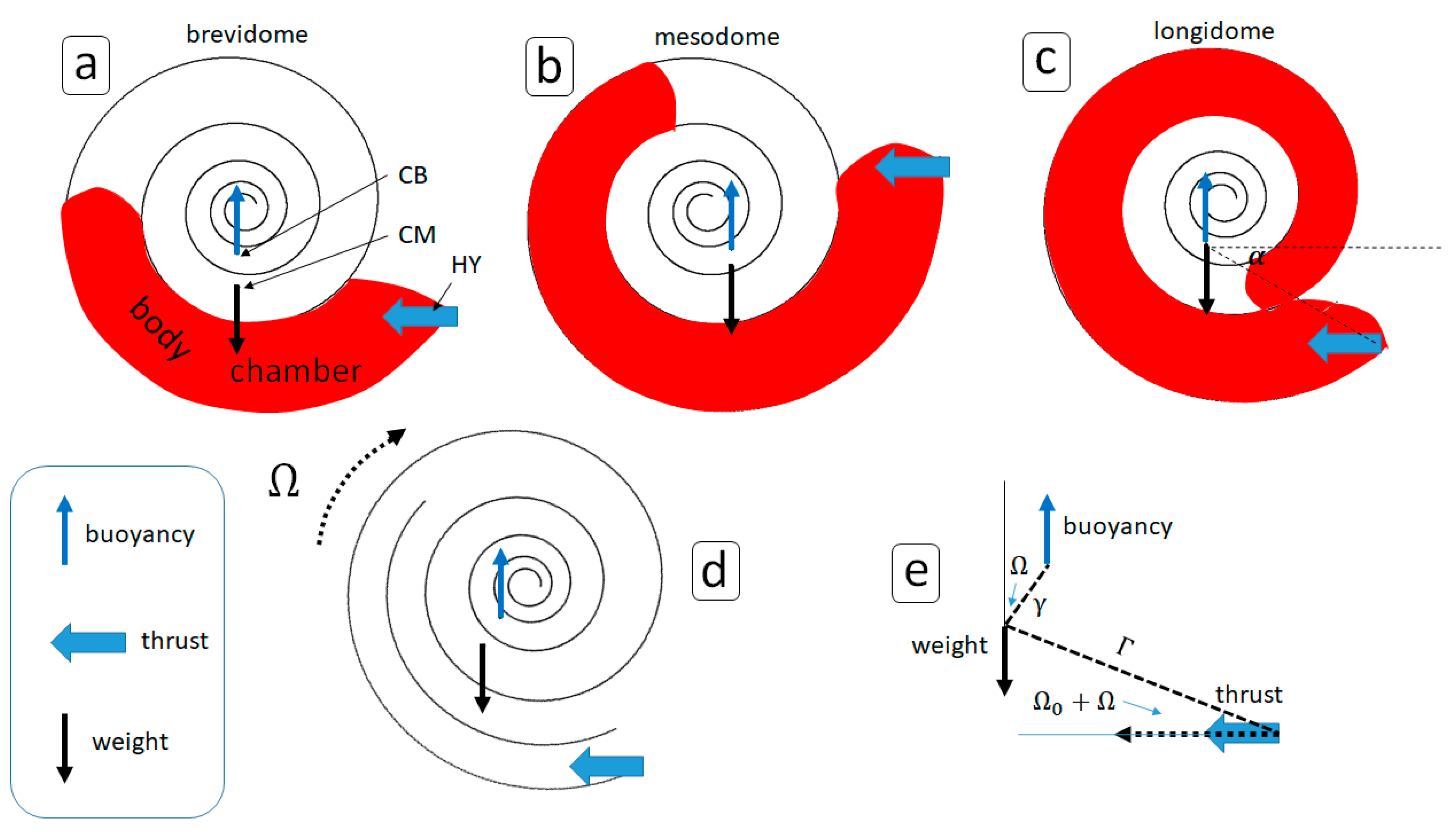

| Type | Angle of Body Length (°) | Umbilical Radius (cm) | Mass of Soft Parts (g) | Mass of Shell (g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| brevi | 116 | 6.48 | 5.53 | 1.100 | 19.15 | 36.60 | 46.30 | 80.6 | |
| meso | 200 | 6.89 | 6.76 | 0.493 | −27.96 | 50.76 | 19.89 | 71.1 | |
| longi | 380 | 6.33 | 5.95 | 0.112 | 30.01 | 67.21 | 16.48 | 79.9 |
| Name | Drag Coefficient, Frontal | Drag Coefficient, Skin Friction | Drag Coefficient, Rotational | Added Mass Coefficient | Jet Speed (cm/s) | Fraction of the Maximum Water Volume Storable in the Mantle Cavity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | |||||||
| Value | 0.5 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.5 | 50 | 0.25 | 0.15 |
| Type | Maximum Rocking Angle (°) | Period of Oscillation (s) | Hydrostatic Qualitative Assessment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| brevi | 3.3 | 1.75 | 0.58 | stable |
| meso | 4.3 | 6.20 | 1.22 | intermediate |
| longi | 4.6 | 22.60 | 2.27 | unstable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Blasio, F.V. The Hydrodynamics of Ammonoid Swimming: Equations of Motion and Rocking Resonances. Foss. Stud. 2023, 1, 34-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/fossils1010004
De Blasio FV. The Hydrodynamics of Ammonoid Swimming: Equations of Motion and Rocking Resonances. Fossil Studies. 2023; 1(1):34-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/fossils1010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Blasio, Fabio Vittorio. 2023. "The Hydrodynamics of Ammonoid Swimming: Equations of Motion and Rocking Resonances" Fossil Studies 1, no. 1: 34-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/fossils1010004
APA StyleDe Blasio, F. V. (2023). The Hydrodynamics of Ammonoid Swimming: Equations of Motion and Rocking Resonances. Fossil Studies, 1(1), 34-46. https://doi.org/10.3390/fossils1010004






