Measuring the Anesthetic Response to Chloroform and Isoflurane in General Anesthesia Mutants in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drosophila Stocks and Culture
2.2. Instrument
2.3. Protocol
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
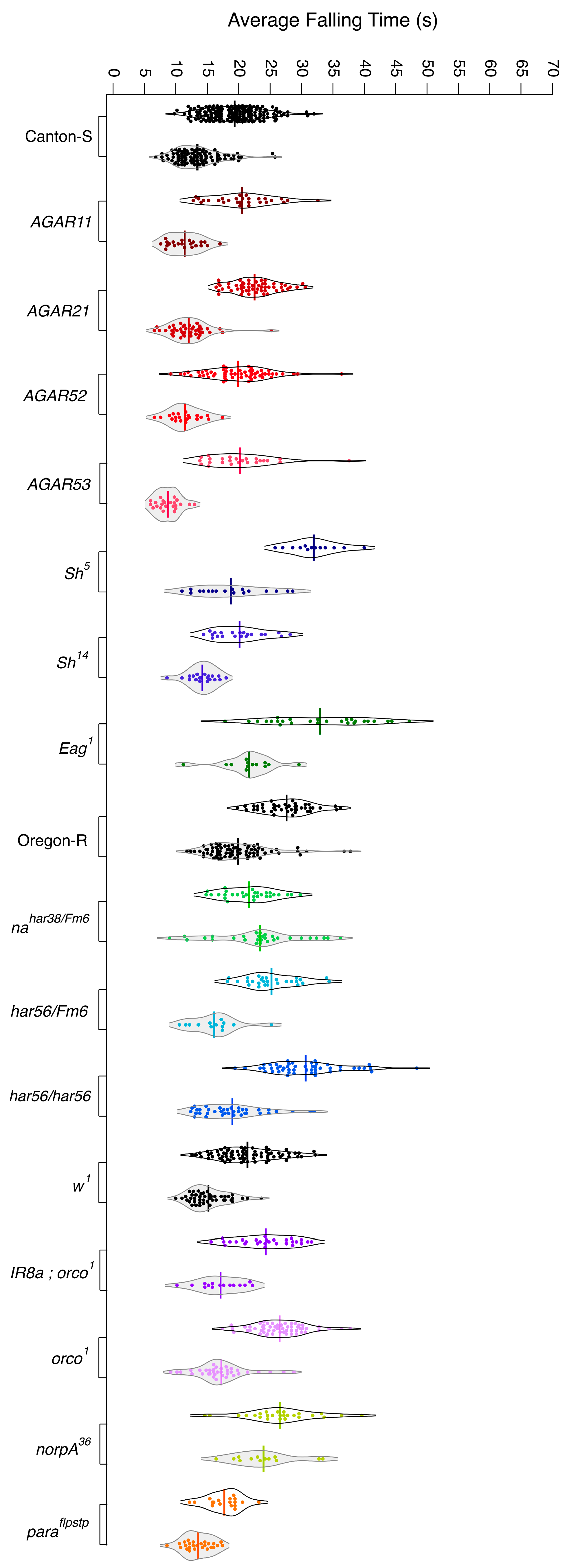
3.1. Wild-Type Flies Present with Differing Levels of Resistance to Anesthetics
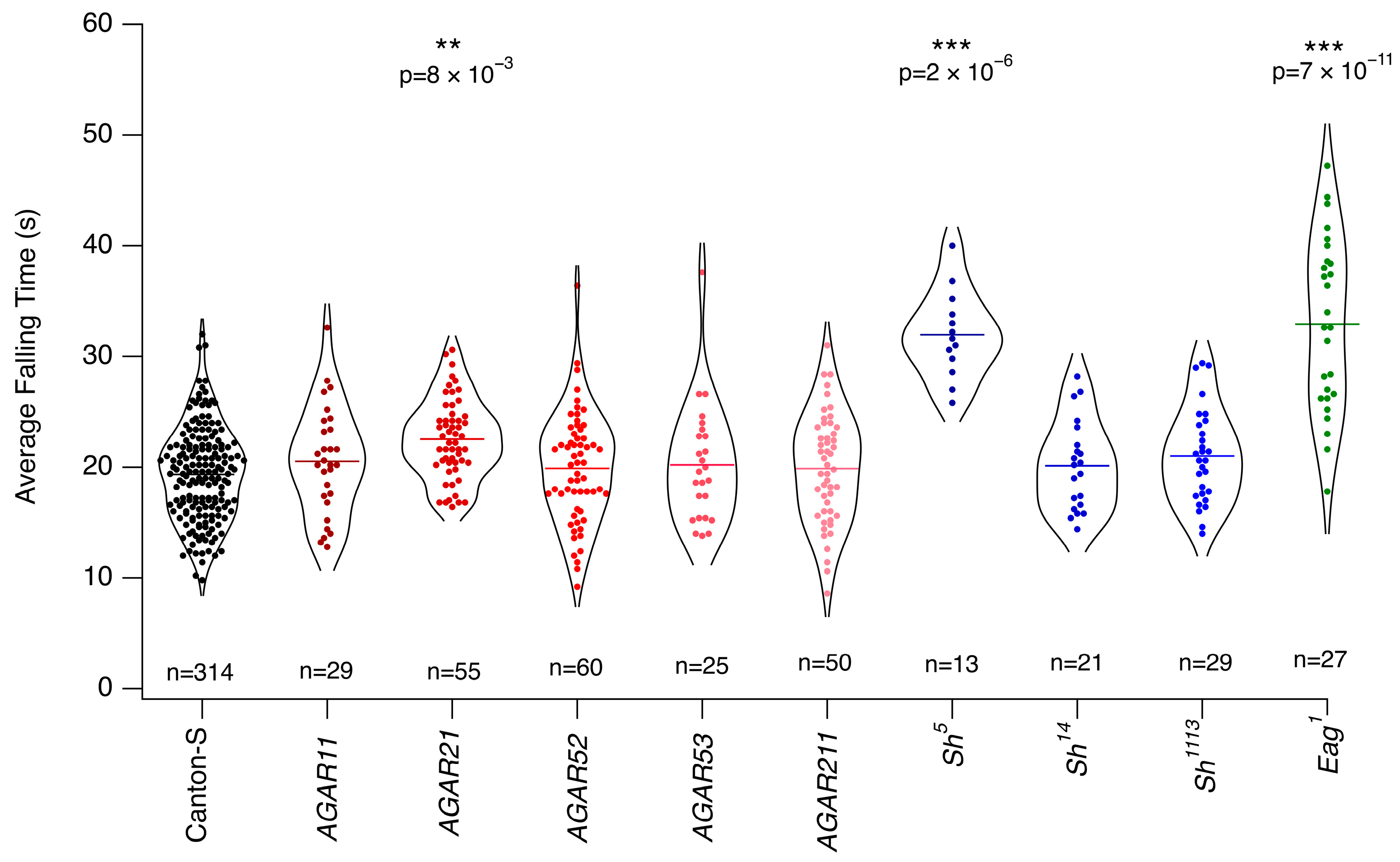
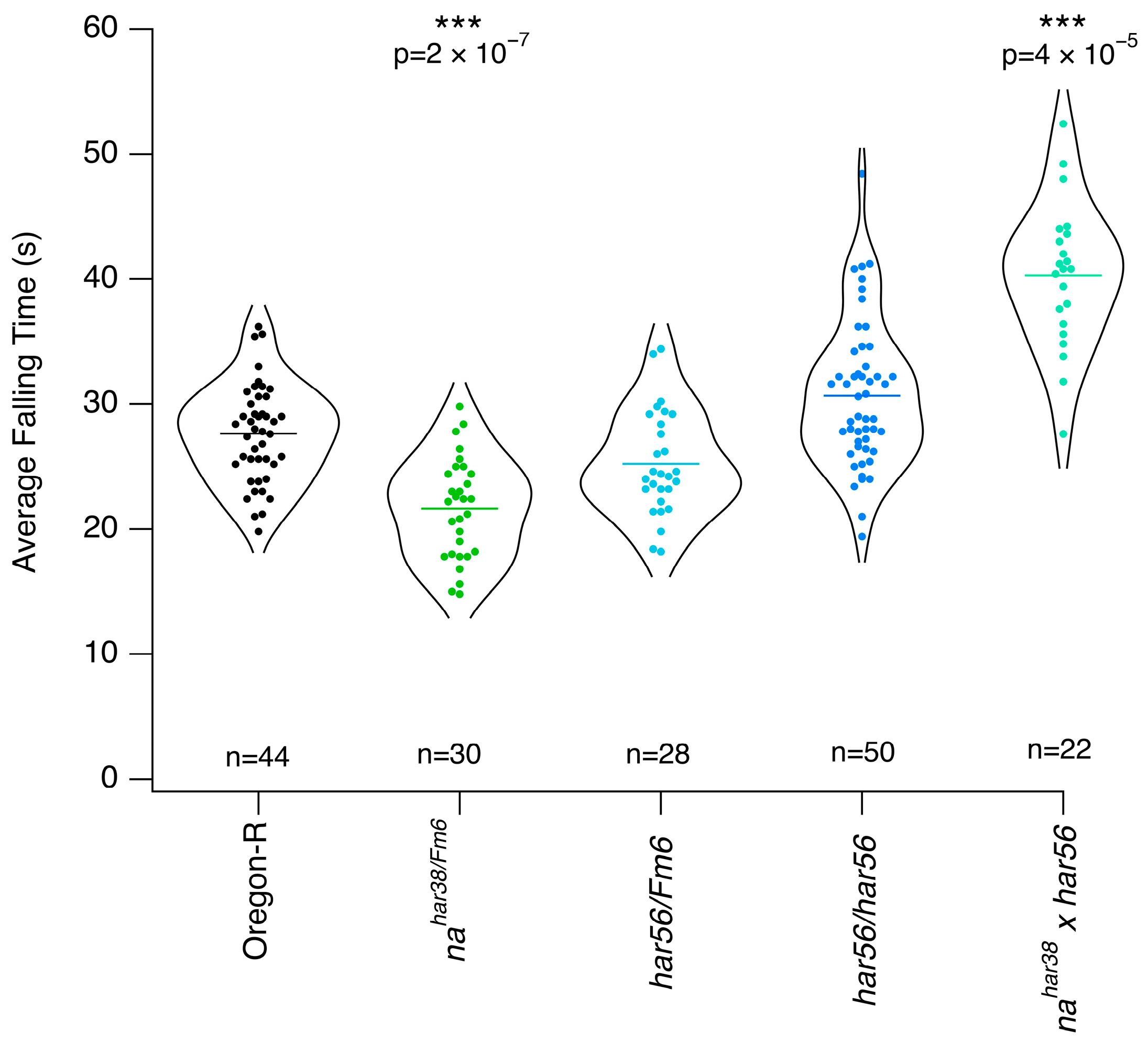
3.2. Mutants with Altered Response to Chloroform
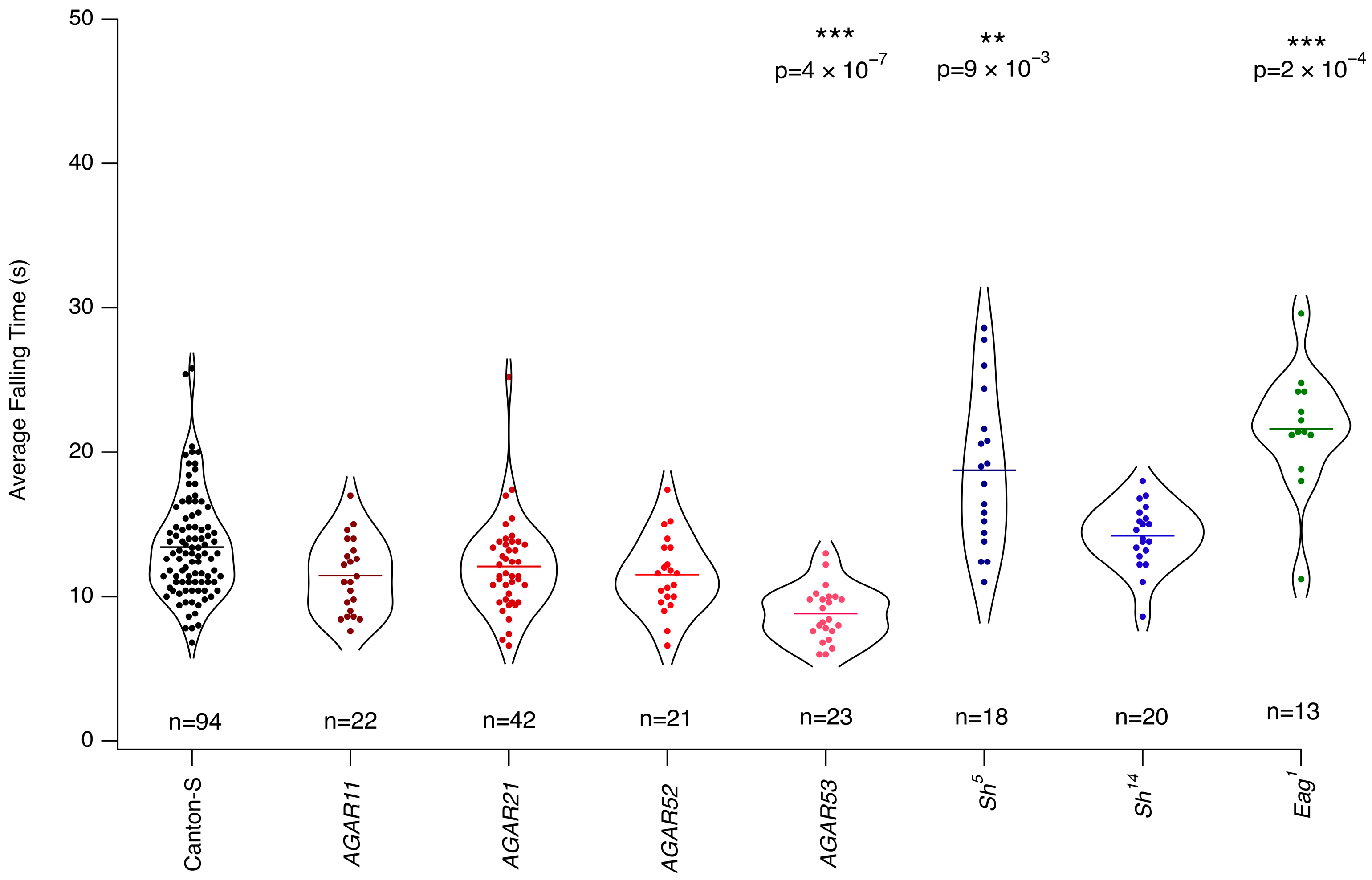
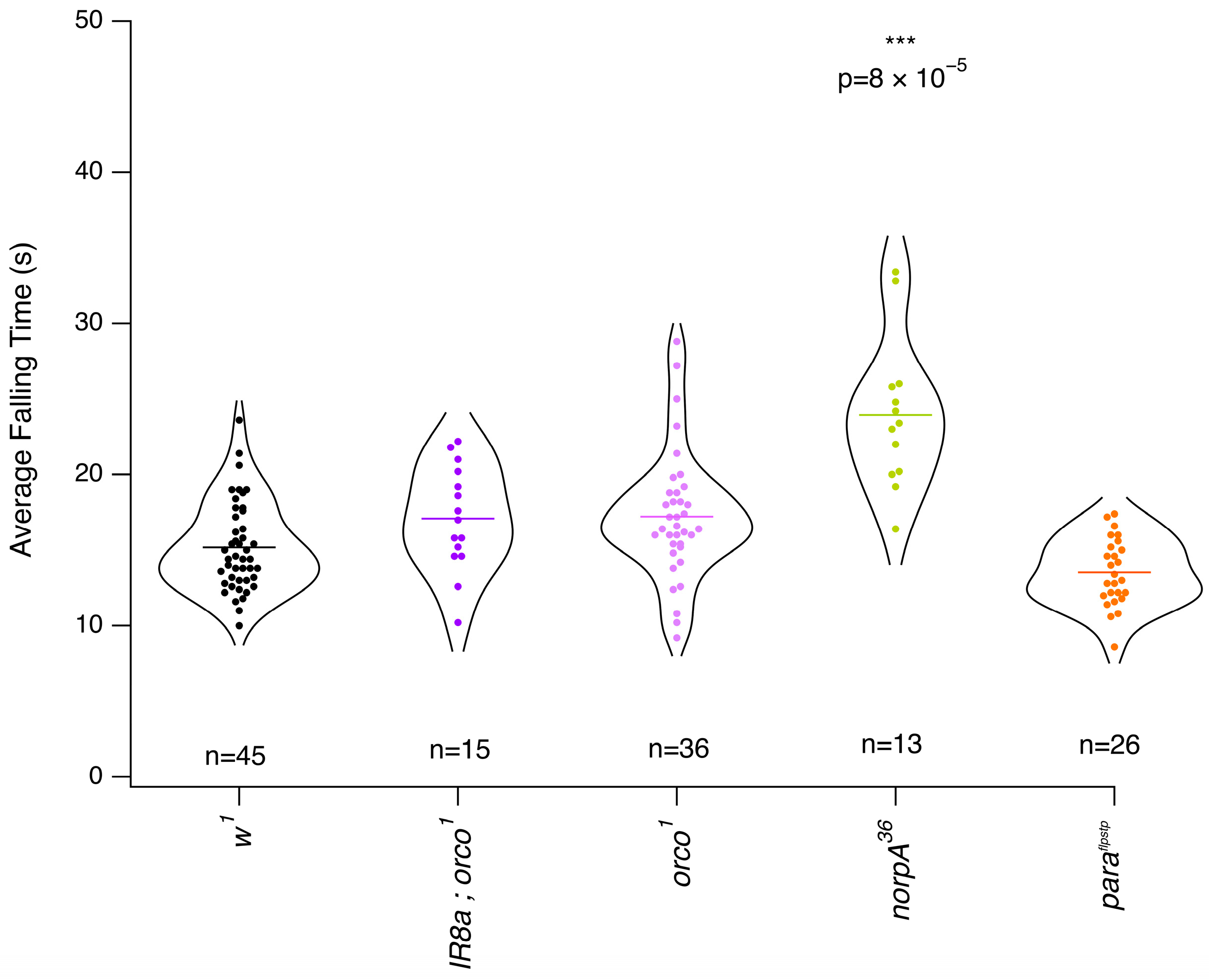
3.3. Mutants with Altered Response to Isoflurane
3.4. Overall Isoflurane Is More Potent than Chloroform
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGAR | Autosomal general anesthesia-resistant |
| har | Halothane-resistant |
| EMS | Ethyl methane sulfonate |
| w1 | w1118 |
| CS | Canton-S |
| OR | Oregon-R |
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
References
- Antognini, J.F.; Carstens, E. In vivo characterization of clinical anaesthesia and its components. Br. J. Anaesth. 2002, 89, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grémiaux, A.; Yokawa, K.; Mancuso, S.; Baluška, F. Plant anesthesia supports similarities between animals and plants: Claude Bernard’s forgotten studies. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014, 9, e27886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, M.; Koutsogiannaki, S.; Schaefers, M.; Babazada, H.; Liu, R.; Yuki, K. The Differential Effects of Anesthetics on Bacterial Behaviors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidman, E.I.E.; Westhorpe, L.J. The Wondrous Story of Anesthesia; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Keating, V. Advances in Anaesthesia. Sci. News 1951, 20, 51–52. [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias, M.; Barber, A.F.; Carnevale, V.; Treptow, W.; Eckenhoff, R.G. Mechanistic insights into the modulation of voltage-gated ion channels by inhalational anesthetics. Biophys. J. 2015, 109, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risks Associated with General Anaesthesia. The Royal College of Anaesthetists. Available online: https://www.rcoa.ac.uk/patients/patient-information-resources/anaesthesia-risk/risks-associated-general-anaesthesia (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Lee, J.J.; Choi, G.J.; Kang, H.; Baek, C.W.; Jung, Y.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Park, Y.H.; Woo, Y.C. Relationship between Surgery under General Anesthesia and the Development of Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3234013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niezgoda, J.; Morgan, P.G. Anesthetic considerations in patients with mitochondrial defects. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2013, 23, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waking Up to Anesthesia, NIH News in Health. 2017. Available online: https://newsinhealth.nih.gov/2011/04/waking-up-anesthesia (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Quinlan, J.J.; Homanics, G.E.; Firestone, L.L. Anesthesia sensitivity in mice that lack the beta3 subunit of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Anesthesiology 1998, 88, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, K.S.; Nash, H.A. A genetic study of the anesthetic response: Mutants of Drosophila melanogaster altered in sensitivity to halothane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8632–8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.G.; Sedensky, M.M. Mutations conferring new patterns of sensitivity to volatile anesthetics in Caenorhabditis elegans. Anesthesiology 1994, 81, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, M.C.; Kumar, R.A.; Krishnan, K.S. Genetics of anesthetic response: Autosomal mutations that render Drosophila resistant to halothane. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 67, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunanithi, S.; Troup, M.; van Swinderen, B. Using Drosophila to understand general anesthesia: From synapses to behavior. Methods Enzymol. 2018, 602, 153–176. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, D.B.; Nash, H.A. Use of Drosophila mutants to distinguish among volatile general anesthetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2135–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, B.; Iyer, S.; Ramaswami, M.; Krishnan, K.S. A genetic and mosaic analysis of a locus involved in the anesthesia response of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1997, 147, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Scott, R.L.; Nash, H.A. A new assay for the genetic study of general anesthesia in Drosophila melanogaster: Use in analysis of mutations in the X-chromosomal 12E region. J. Neurogenet. 2000, 14, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibovitch, B.A.; Campbell, D.B.; Krishnan, K.S.; Nash, H.A. Mutations that affect ion channels change the sensitivity of Drosophila melanogaster to volatile anesthetics. J. Neurogenet. 1995, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Gamo, S. Sensitivity to diethylether anesthesia of fruit flies primarily depends on the genotypes of the sodium channel gene rather than the states of the membranes and the mechanisms might be different from heat-induced paralysis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2001, 22, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.L.; Nash, H.A. Volatile general anesthetics reveal a neurobiological role for the white and brown genes of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurobiol. 2001, 49, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Nash, H.A. Visual mutations reveal opposing effects of illumination on arousal in Drosophila. Genetics 2008, 178, 2413–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Sandstrom, D.J.; Smith, H.E.; High, B.; Marsh, J.W.; Nash, H.A. Drosophila ryanodine receptors mediate general anesthesia by halothane. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalucki, O.H.; Menon, H.; Kottler, B.; Faville, R.; Day, R.; Bademosi, A.T.; Lavidis, N.; Karunanithi, S.; van Swinderen, B. Syntaxin1A-mediated Resistance and Hypersensitivity to Isoflurane in Drosophila melanogaster. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 1060–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troup, M.; Zalucki, O.H.; Kottler, B.D.; Karunanithi, S.; Anggono, V.; van Swinderen, B. Syntaxin1A neomorphic mutations promote rapid recovery from isoflurane anesthesia in Drosophila melanogaster. Anesthesiology 2019, 131, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olufs, Z.P.G.; Loewen, C.A.; Ganetzky, B.; Wassarman, D.A.; Perouansky, M. Genetic variability affects absolute and relative potencies and kinetics of the anesthetics isoflurane and sevoflurane in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamo, S.; Tomida, J.; Dodo, K.; Keyakidani, D.; Matakatsu, H.; Yamamoto, D.; Tanaka, Y. Calreticulin mediates anesthetic sensitivity in Drosophila melanogaster. Anesthesiology 2003, 99, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamo, S. Studies on target genes of general anesthetics. Curr. Drug Targets 2002, 3, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J.A.; Hamming, K.S.; Thacker, C.M.; Scott, R.L.; Sedensky, M.M.; Snutch, T.P.; Morgan, P.G.; Nash, H.A. A putative cation channel and its novel regulator: Cross-species conservation of effects on general anesthesia. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, W.J.; Friedman, E.B.; Hung, H.-T.; Koh, K.; Sowcik, M.; Sehgal, A.; Kelz, M.B. Genetic and anatomical basis of the barrier separating wakefulness and anesthetic-induced unresponsiveness. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalucki, O.; Day, R.; Kottler, B.; Karunanithi, S.; van Swinderen, B. Behavioral and electrophysiological analysis of general anesthesia in 3 background strains of Drosophila melanogaster. Fly 2015, 9, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malacrida, S.; De Lazzari, F.; Mrakic-Sposta, S.; Vezzoli, A.; Zordan, M.A.; Bisaglia, M.; Menti, G.M.; Meda, N.; Frighetto, G.; Bosco, G.; et al. Lifespan and ROS levels in different Drosophila melanogaster strains after 24 h hypoxia exposure. Biol. Open 2022, 11, bio059386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Peng, B.; Lane, N. Anaesthetics disrupt complex I-linked respiration and reverse the ATP synthase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2025, 1866, 149511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turin, L.; Skoulakis, E.M.C.; Horsfield, A.P. Electron spin changes during general anesthesia in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3524–E3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turin, L.; Skoulakis, E.M.C. Electron Spin Resonance (EPR) in Drosophila and General Anesthesia. Methods Enzymol. 2018, 603, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zalucki, O.; van Swinderen, B. What is unconsciousness in a fly or a worm? A review of general anesthesia in different animal models. Conscious. Cogn. 2016, 44, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Mutants | General Anesthetics | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | Gene | Chromosome | Function | Diethyl Ether | Chloroform | Trichloroethylene | Halothane | Enflurane | Isoflurane | Sevoflurane | Desflurane | Methoxyflurane |
| nahar85 | Narrow abdomen | X | Na+ leak channel | [16] | [16] | [16] | [12,16,17,18] | [16] | [16] | [16] | [16] | |
| nahar38 | Narrow abdomen | X | Na+ leak channel | [16] | [16] | [16] | [12,16,17,18] | [16] | [16] | [16] | [16] | |
| har56 | Unknown | X | Unknown | [16] | [16] | [16] | [12,16] | [16] | [16] | [16] | [16] | |
| har63 | Unknown | X | Unknown | [16] | [16] | [16] | [12,16,17,18] | [16] | [16] | [16] | [16] | |
| ShKS133 | Shaker | X | Voltage-gated K+ channel | [19] | [19] | [19] | ||||||
| Sh5 | Shaker | X | Voltage-gated K+ channel | [19] | [19] | [19] | ||||||
| ShKO120 | Shaker | X | Voltage-gated K+ channel | [19] | [19] | [19] | ||||||
| Slo1 | Slowpoke | 3 | Voltage-gated K+ channel | [19] | [19] | [19] | ||||||
| Slo4 | Slowpoke | 3 | Voltage-gated K+ channel | [19] | [19] | (19) | ||||||
| Eag1 | Ether-a-go-go | X | Voltage-gated K+ channel | [19] | [19] | [19] | ||||||
| Eaghd14 | Ether-a-go-go | X | Voltage-gated K+ channel | [19] | [19] | [19] | ||||||
| Eaghd15 | Ether-a-go-go | X | Voltage-gated K+ channel | [19] | [19] | [19] | ||||||
| Parats1 | paralytic | X | Voltage-gated Na+ channel | [20] | [19] | [19] | [19] | |||||
| Parahd839 | Paralytic | X | Voltage-gated Na+ channel | [20] | ||||||||
| Parats3 | Paralytic | X | Voltage-gated Na+ channel | [20] | ||||||||
| mlenap-ts1 | Maleless | 2 | [19] | [19] | [19] | |||||||
| bw1 | Brown | 2 | ABC transporters | [21] | [21] | |||||||
| w1 | White | X | ABC transporters | [21] | [21] | |||||||
| trp | Transient receptor potential | 3 | Non-selective cation channel | [22] | ||||||||
| RyR | Ryanodine receptor | 2 | Intracellular calcium channel | [23] | [23] | [23] | [23] | |||||
| Syx1AH3-C | Syntaxin 1A | 3 | Neurotransmitter release | [24,25] | ||||||||
| Syx1AKARRAA | Syntaxin 1A | 3 | Neurotransmitter release | [24] | ||||||||
| ND2360114 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit | 3 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit | [26] | [26] | |||||||
| Calreth-as311 | Calreticulin | 3 | [27] | [27] | [27] | |||||||
| ScbVol | Scab | 2 | Encodes the α-S3 integrin | [28] | ||||||||
| rutabaga | Adenylate cyclase 1 | X | Adenylate cyclase 1 | [28] | ||||||||
| amn | Amnesiac | X | Neuropeptide precursor | [28] | ||||||||
| Unc79 | Uncoordinated 79 | 3 | Locomotor rhythms | [29] | [30] | |||||||
| AGAR | Resistance to halothane | [14] | ||||||||||
| Genotype | Background | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Canton-S | ||
| w1 | ||
| Oregon-R | ||
| AGAR11 | Canton-S | BDSC 27588 |
| AGAR21 | Canton-S | BDSC 27329 |
| AGAR52 | Canton-S | BDSC 27589 |
| AGAR53 | Canton-S | BDSC 26703 |
| AGAR211 | Canton-S | BDSC 27330 |
| Sh5 | Canton-S | BDSC 111 |
| Sh14 | Canton-S | BDSC 4741 |
| Sh1113 | Canton-S | |
| Eag1 | Canton-S | BDSC 3661 |
| har56 | Oregon-R | BDSC 26699 |
| har56/har56 | Oregon-R | |
| nahar38 | Oregon-R | BDSC 26704 |
| Orco1 | w1 | BDSC 23129 |
| IR8a; Orco1 | w1 | |
| Paraflpstp | w1 | BDSC 67680 |
| NorpA36 | w1 | BDSC 9048 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daplan, E.; Turin, L.; Skoulakis, E.M.C. Measuring the Anesthetic Response to Chloroform and Isoflurane in General Anesthesia Mutants in Drosophila melanogaster. Anesth. Res. 2025, 2, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/anesthres2020012
Daplan E, Turin L, Skoulakis EMC. Measuring the Anesthetic Response to Chloroform and Isoflurane in General Anesthesia Mutants in Drosophila melanogaster. Anesthesia Research. 2025; 2(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/anesthres2020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaplan, Ekin, Luca Turin, and Efthimios M. C. Skoulakis. 2025. "Measuring the Anesthetic Response to Chloroform and Isoflurane in General Anesthesia Mutants in Drosophila melanogaster" Anesthesia Research 2, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/anesthres2020012
APA StyleDaplan, E., Turin, L., & Skoulakis, E. M. C. (2025). Measuring the Anesthetic Response to Chloroform and Isoflurane in General Anesthesia Mutants in Drosophila melanogaster. Anesthesia Research, 2(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/anesthres2020012







