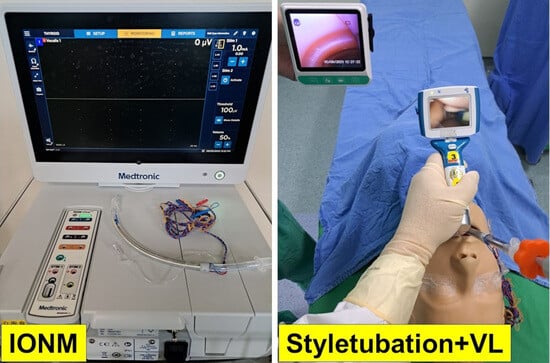
Combined Styletubation with Videolaryngoscopy for Tracheal Intubation in Patients Undergoing Thyroidectomy with Intraoperative Neuromonitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Discussion
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiang, F.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Lu, I.C.; Kuo, W.R.; Hsieh, M.C.; Wu, C.W. Standardization of intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerve in thyroid operation. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, G.W.; Dralle, H.; International Intraoperative Monitoring Study Group; Abdullah, H.; Barczynski, M.; Bellantone, R.; Brauckhoff, M.; Carnaille, B.; Cherenko, S.; Chiang, F.Y.; et al. Electrophysiologic recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring during thyroid and parathyroid surgery: International standards guideline statement. Laryngoscope 2011, 121 (Suppl. S1), S1–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiadis, I.; Karatzas, T.; Charitoudis, G.; Karakostas, E.; Tseleni-Balafouta, S.; Kouraklis, G. Association of intraoperative neuromonitoring with reduced recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in patients undergoing total thyroidectomy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 142, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirocchi, R.; Arezzo, A.; D’Andrea, V.; Abraha, I.; Popivanov, G.I.; Avenia, N.; Gerardi, C.; Henry, B.M.; Randolph, J.; Barczyñski, M. Intraoperative neuromonitoring versus visual nerve identification for prevention of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in adults undergoing thyroid surgery. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 1, CD012483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Hu, M. The value of intraoperative nerve monitoring against recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroid reoperations. Medicine 2021, 100, e28233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qurayshi, Z.; Randolph, G.W.; Alshehri, M.; Kandil, E. Analysis of variations in the use of intraoperative nerve monitoring in thyroid surgery. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 142, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanu, A.; Porceddu, G.; Podda, M.; Cois, A.; Uccheddu, A. Systematic review with meta-analysis of studies comparing intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerves versus visualization alone during thyroidectomy. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 188, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffe, A.M.; Aziz, M.F.; Posner, K.L.; Duggan, L.V.; Mincer, S.L.; Domino, K.B. Management of difficult tracheal intubation: A closed claims analysis. Anesthesiology 2019, 131, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.K.; Cohen, M.M. The incidence of airway problems depends on the definition used. Can. J. Anaesth. 1996, 43, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnet, F.; Racine, S.X.; Borron, S.W.; Clemessy, J.L.; Fournier, J.L.; Lapostolle, F.; Cupa, M. A survey of tracheal intubation difficulty in the operating room: A prospective observational study. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2001, 45, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, T.; Wajima, Z.; Inoue, T.; Sakamoto, A. Predicting difficult intubation in apparently normal patients: A meta-analysis of bedside screening test performance. Anesthesiology 2005, 103, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørskov, A.K.; Wetterslev, J.; Rosenstock, C.V.; Afshari, A.; Astrup, G.; Jakobsen, J.C.; Thomsen, J.L.; Bøttger, M.; Ellekvist, M.; Schousboe, B.M.; et al. Effects of using the simplified airway risk index vs usual airway assessment on unanticipated difficult tracheal intubation—A cluster randomized trial with 64,273 participants. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 116, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, R.A.; Pollard, R.; Dhakal, I.; Cooter, M.; Aronson, S.; Grichnik, K.; Buhrman, W.; Kertai, M.D.; Mathew, J.P.; Stafford-Smith, M. Temporal trends in difficult and failed tracheal intubation in a regional community anesthetic practice. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaggad, A.; Nejmi, S.E.; Bouderka, M.A.; Abbassi, O. Prediction of difficult tracheal intubation in thyroid surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2004, 99, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalezić, N.; Milosavljević, R.; Paunović, I.; Zivaljević, V.; Diklić, A.; Matić, D.; Ivanović, B.; Nesković, V. The incidence of difficult intubation in 2000 patients undergoing thyroid surgery—A single center expirience. Vojnosanit. Pregl. 2009, 66, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutuncu, A.C.; Erbabacan, E.; Teksoz, S.; Ekici, B.; Koksal, G.; Altintas, F.; Kaya, G.; Ozcan, M. The assessment of risk factors for difficult intubation in thyroid patients. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 1748–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyagis, G.S.; Kyriakos, K.P. The effect of goiter on endotracheal intubation. Anesth. Analg. 1997, 84, 611–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cassai, A.; Papaccio, F.; Betteto, G.; Schiavolin, C.; Iacobone, M.; Carron, M. Prediction of difficult tracheal intubations in thyroid surgery. Predictive value of neck circumference to thyromental distance ratio. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amathieu, R.; Smail, N.; Catineau, J.; Poloujadoff, M.P.; Samii, K.; Adnet, F. Difficult intubation in thyroid surgery: Myth or reality? Anesth. Analg. 2006, 103, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yue, H.; Li, J. Comparison of three tracheal intubation techniques in thyroid tumor patients with a difficult airway: A randomized controlled trial. Med. Princ. Pract. 2014, 23, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, G.A.; Snell, J.A.; Coathup, R.; Jones, T.M. Anaesthesia for massive retrosternal thyroidectomy in a tertiary referral centre. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, N.; Ball, C.M.; Myles, P.S.; Serpell, J.; Johnson, W.R.; Paul, E. A cohort and database study of airway management in patients undergoing thyroidectomy for retrosternal goitre. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2014, 42, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, C.; Yu, L.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, Y. Airway management of retrosternal goiters in 22 cases in a tertiary referral center. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2020, 16, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, E.; Quan, T.; Nguyen, H.; Pla, R. Intubation of a patient with a large goiter: The advantageous role of videolaryngoscopy. Case Rep. Anesthesiol. 2019, 2019, 1327482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, S.; Kalpan, J.; Kolli, V. Case report of the use of videolaryngoscopy in thyroid goiter masses: An airway challenge. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2016, 27, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.C.; Esa, N. Anesthesia for massive retrosternal goiter with severe intrathoracic tracheal narrowing: The challenges imposed—A case report. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2012, 62, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, G.; Ning, M.; Zhang, X. Awake fiberoptic intubation in a patient with a large thyroid tumor invading the trachea: A case report. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 2497–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.; Zhang, X. Awake fiberoptic nasotracheal intubation and anesthetic management of a patient with a compressed and deviated airway from a massive thyroid goiter: A case report. Cureus 2023, 15, e35278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.J. Successful advancement of endotracheal tube with combined fiberoptic bronchoscopy and videolaryngoscopy in a patient with a huge goiter. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2050313X20923232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, C.; Zhou, R.; Chen, G.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, T. Anesthesia and airway management in a patient with acromegaly and tracheal compression caused by a giant retrosternal goiter: A case report. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 300060521999541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohn, A.; Kauliņš, T.; Hinkelbein, J.; Kauliņa, K.; Kopp, A.; Russo, S.G.; Kohlen, S.; Schröder, S. Awake tracheotomy in a patient with stridor and dyspnoea caused by a sizeable malignant thyroid tumor: A case report and short review of the literature. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 1891–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, J.Y.; Chow, L.H.; Chan, K.H.; Tsou, M.Y. Successful anesthetic management of a patient with thyroid carcinoma invading the trachea with tracheal obstruction, scheduled for total thyroidectomy. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2014, 77, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeong, Y.I.; Jun, I.G.; Ha, S.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, Y.M. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for the anesthetic management of a patient with a massive intrathoracic goiter causing severe tracheal obstruction with positional symptoms: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e17650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, F.C.; Song, Y.Q.; Li, W.Q.; Yu, W.K. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation would provide a new approach to anesthesia for giant thyroid tumor resection: A case report. Asian J. Surg. 2020, 43, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Saito, Y.; Kadomura, T.; Yamada, R.; Shibuya, S.; Itoh, H.; Ishiwa, D.; Tsuji, K.; Nagashima, Z.; Segawa, S. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for the anesthetic management of a patient with severe airway stenosis caused by thyroid carcinoma invasion. Surg. Today 2021, 51, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.C.; Chu, K.S.; Tsai, C.J.; Wu, C.W.; Kuo, W.R.; Chen, H.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Chiang, F.Y. Optimal depth of NIM EMG endotracheal tube for intraoperative neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy. World J. Surg. 2008, 32, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Tseng, K.Y.; Wang, F.Y.; Lu, I.C.; Wang, H.M.; Wu, C.W.; Chiang, H.C.; Chiang, F.Y. Electromyographic endotracheal tube placement during thyroid surgery in neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerve. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2011, 27, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, G.; Lee, M. The neural integrity monitor electromyogram tracheal tube: Anesthetic considerations. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 29, 403–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Iskandar, F.F.; Nik Lah, N.A.S.; Ismail, A.J.; Yeap, T.B. Challenges in electromyographic endotracheal tube (EMG ETT) placement via awake fibreoptic intubation during emergency thyroidectomy. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e242286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkow, L.; Dackiw, A.P.; Tufano, R.P. Use of the GlideScope for placement of a recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring endotracheal tube. J. Clin. Anesth. 2011, 23, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.M.; Hsu, C.D.; Wu, S.H.; Kuo, Y.W.; Huang, T.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Lu, I.C. Optimization of electromyographic endotracheal tube electrode position by UEScope for monitored thyroidectomy. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2021, 6, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casano, K.; Cannon, C.R.; Didlake, R.; Replogle, W.R.; Cannon, R. Use of GlideScope in patients undergoing NIM thyroidectomy. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 101, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriege, M.; Hilt, J.A.; Dette, F.; Wittenmeier, E.; Meuser, R.; Staubitz, J.I.; Musholt, T.J. Impact of direct laryngoscopy vs. videolaryngoscopy on signal quality of recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in thyroid surgery: A randomised parallel group trial. Anaesthesia 2023, 78, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.Y.; Hu, P.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Chiang, F.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Dionigi, G.; Lu, I.C. Trachway video intubating stylet allows for optimization of electromyographic endotracheal tube placement for monitored thyroidectomy. Gland Surg. 2017, 6, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Tan, H.; Huang, H.F.; Huang, T.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Chang, P.Y.; Lu, D.V.; Lu, I.C. Optimization of intraoperative neural monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve in thyroid surgery. Medicina 2022, 58, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. Styletubation: The paradigmatic role of video-assisted intubating stylet technique for routine tracheal intubation. Asian J. Anesthesiol. 2023; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, H.N.; Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. A paradigm shift of airway management: The role of video-assisted intubating stylet technique. In Advances in Tracheal Intubation; Lovich-Sapola, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, H.N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. Styletubation for routine tracheal intubation for ear-nose-throat surgical procedures. Ann. Otol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kanotra, S.P.; Kuriloff, D.B.; Lesser, J.; Rest-Flarer, F. GlideScope-assisted nerve integrity monitoring tube placement for intra-operative recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2012, 126, 1271–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.W.; Chen, J.Y.; Lan, K.M.; Hung, K.C. The use of Trachway for electromyographic (EMG) tube placement. Gland Surg. 2018, 7, 244–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.C.; Wu, S.H.; Wu, C.W. Neuromuscular blockade management for intraoperative neural monitoring. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.C.; Hsu, C.D.; Chang, P.Y.; Wu, S.H.; Huang, T.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Ko, H.Y.; Dionigi, G.; Chai, Y.J.; Chiang, F.Y.; et al. A surgeon-centered neuromuscular block protocol improving intraoperative neuromonitoring outcome of thyroid surgery. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 817476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.C.; Wu, C.W.; Chang, P.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Tseng, K.Y.; Randolph, G.W.; Cheng, K.I.; Chiang, F.Y. Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade by sugammadex allows for optimization of neural monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Empis de Vendin, O.; Schmartz, D.; Brunaud, L.; Fuchs-Buder, T. Recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring and rocuronium: A selective sugammadex reversal protocol. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 2298–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.J.; Lee, J.M.; Won, D.; Lee, J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, T.K.; Chang, J.E.; Kim, H.; Yang, H.J.; Min, S.W. Comparison of sugammadex dose for intraoperative neuromonitoring in thyroid surgery: A randomized controlled trial. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 2154–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, I.C.; Tan, H.; Wu, S.H.; Huang, T.Y.; Tseng, H.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Dionigi, G.; Chai, Y.J.; Chiang, F.Y.; Chang, P.Y.; et al. A comparison between cisatracurium and rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block on laryngeal electromyography recovery after neostigmine reversal in a porcine model. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 875597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.Y.; Chai, Y.J.; Huang, T.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Dionigi, G.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, C.; Won, D.; Lee, J.M. Administration of neostigmine after tracheal intubation shortens time to successful intraoperative neuromonitoring during thyroid surgery: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, R.; Hennessy, A.; Mannion, S.; O’Leary, G.; Sheahan, P. Effect of endotracheal tube size on vocal outcomes after thyroidectomy: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.F.; Berkow, L. Pro-con debate: Videolaryngoscopy should be standard of care for tracheal intubation. Anesth. Analg. 2023, 136, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungorer, B.; Findik, M.; Kayipmaz, A.E. USB-endoscope laryngoscope is as effective as video laryngoscope in difficult intubation. Disaster Emerg. Med. J. 2021, 6, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrin, T.; Szarpak, L.; Katipoglu, B.; Mishyna, N.; Kockan, B.S.; Ruetzler, K.; Schläpfer, M. Video-assisted versus macintosh direct laryngoscopy for intubation of obese patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Disaster Emerg. Med. J. 2022, 7, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaczynski, P.; Misiolek, H.; Bialka, S.; Owczarek, A.J.; Gola, W.; Szarpak, L.; Smereka, J. A randomized comparison between the VivaSight double-lumen tube and standard double-lumen tube intubation in thoracic surgery patients. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 3903–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, P.; Szarpak, L.; Dabrowska, A.; Pruc, M.; Navolokina, A.; Raczynski, A.; Smereka, J. A comparison of the bébé VieScope™ and direct laryngoscope for use while wearing PPE-AGP: A randomized crossover simulation trial. Children 2022, 9, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwin, K.; Bialka, S.; Czyzewski, L.; Smereka, J.; Marek Dabrowski, M.; Dabrowska, A.; Ladny, J.R.; Ruetzler, K.; Szarpak, L. Video laryngoscopy for endotracheal intubation of adult patients with suspected/ confirmed COVID-19. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Disaster Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 5, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.B.; Luk, H.-N. Sheet barrier and intubating stylet. Encyclopedia 2021, 1, 1058–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 | Case 6 | Case 7 | Case 8 | Case 9 | Case 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age/Gender | 64/F | 71/F | 45/F | 33/F | 54/F | 70/F | 41/F | 80/F | 54/F | 54/F |
| Height (cm)/weight (kg) | 153/64 | 154/52 | 156/60 | 148/62 | 153/53 | 147/47 | 151/55 | 152/55 | 161/72 | 145/56 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.3 | 21.9 | 24.6 | 28.3 | 22.6 | 21.7 | 24.1 | 23.8 | 27.7 | 26.6 |
| ASA physical status | II | II | I | I | I | II | I | III | III | II |
| Comorbidity | Myocardial ischemia (T-wave inversion) | Hypertension | Nil | Nil | Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, multinodular goiter with tracheal compression and deviation | Hypertension | Nil | Hypertension, chronic kidney disease | Hypertension, cerebral aneurysm | Diabetes |
| Diagnosis | Bilateral mutinodular goiter | Parkinson’s disease | Thyroid cyst, left | Thyroid papillary carcinoma, left | Papillary microcarcinoma of thyroid | Bilateral multinodular goiter with tracheal deviation | Left thyroid goiter | Bilateral multiple nodular goiter, 3 cm lesion of left thyroid lower pole, T | Thyroid nodular goiter | Bilateral multinodular goiter |
| Major surgery | Bilateral total thyroidectomy; left upper parathyroid gland autotransplantation | Total thyroidectomy | Excision of thyroid cyst, left | Total thyroidectomy | Total thyroidectomy | Total thyroidectomy | Left total thyroidectomy | Total thyroidectomy | Lobectomy (right), partial thyroidectomy (left) | Total thyroidectomy |
| Size of resected thyroid mass | 0.8 to 2.7 cm | 70 to 94 gm | 2.8 × 1.3 (cm) | 1.4 × 0.9 (cm) | (Right lobe): 7.0 × 5.0 × 3.8, (left lobe): 4.8 × 4.2 × 2.3 (cm); (tumor size: 0.2 cm). | (Right lobe) 6.2 × 5.5 × 4.0; (left lobe) 5.5 × 4.0 × 2.0 (cm) | 3.5 × 3.0 × 1.8 (cm) nodular goiter with hemorrhagic cyst | (Right lobe) 5.5 × 3.0 × 2.2 cm; (left lobe) 6.0 × 4.5 × 3.6 (cm); (tumor) (right 1 cm) and (left 0.4 cm) | 0.74 × 0.8 (cm) | 6.8 × 5.0 × 3.6 (cm) |
| Induction | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.3 mg/kg), SCh (1.4 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (1.0 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.3 mg/kg), SCh (1.4 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.6 mg/kg), SCh (1.3 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (1 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.4 mg/kg), SCh (2 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.2 mg/kg), SCh (2 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.8 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.7 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.9 mg/kg) |
| Maintenance | Sevoflurane | Desflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane |
| MMT | III | II | III | II | III | II | II | III | II | III |
| ULBT | 1 | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 1 | Class 1 | Class 1 | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 1 | Class 2 |
| Inter-incisor distance | 4 cm | 4 cm | 3.5 cm | 4 cm | 4 cm | 4 cm | 4 cm | 5 cm | 4 cm | 4.5 cm |
| Sternomental distance | 15 cm | 13 cm | 17 cm | 16 cm | 16 cm | 16 cm | 16 cm | 15 cm | 15 cm | 17 cm |
| Neck circumference | 34 cm | 39 cm | 31 cm | 34 cm | 34 cm | 35 cm | 38 cm | 39 cm | 36 cm | 34 cm |
| C-L grading | 2b | 2a | 2b | 2a | 2a | 2a | 2b | 2b | 1 | 3 |
| LQS grading | Grade 1 | Grade 1 | Grade 1 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 1 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 |
| View of glottis (POGO grading) | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 90% | 80% | 90% | 100% | 100 % | 60% |
| Success on first attempt | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Intubation time (VS) | 9 s | 4 s | 33 s | 15 s | 14 s | 8 s | 9 s | 7 s | 5 s | 10 s |
| V1 verification | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Complications | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| Subjective satisfaction | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent | Awkward | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent | East and excellent | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent |
| Supplementary materials | Video S1 | Video S2 | Video S3 | Video S4 | Video S5 | Video S6 | Video S7 | Video S8 | Video S9 | Video S10 |
| Case 11 | Case 12 | Case 13 | Case 14 | Case 15 | ||||||
| Age/gender | 71/F | 55/F | 21F | 25/F | 51/F | |||||
| Height (cm)/weight (kg) | 159/53 | 157/72 | 157/63 | 164/64 | 152/73 | |||||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.9 | 29.2 | 25.5 | 25.5 | 31.5 | |||||
| ASA physical status | II | I | I | I | I | |||||
| Comorbidity | Hypertension | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | |||||
| Diagnosis | Multinodular goiter (left) | Thyroid nodule (right) | Papillary carcinoma, right thyroid; multiple nodular goiter, left | Papillary thyroid carcinoma, right | Bilateral thyroid cysts | |||||
| Major surgery | Hemithyroidectomy (left) | Right hemithyroidectomy, left lobectomy | Total tyroidectomy, neck lymph node dissection | Total thyroidectomy | Bilateral subtotal thyroidectomy | |||||
| Size of resected thyroid mass | 0.8 to 2.7 cm | 1.4 × 1.2 × 1.2 (cm) | 1.78 × 1.3 (cm) | 1.8 cm in length | (Right lobe): 3.0 × 3.2; (left lobe): 2.5 × 3.0 (cm) | |||||
| Induction | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.6 mg/kg), SCh (1.5 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.6 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.8 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.6 mg/kg) | MDZ, FEN, PPF, ROC (0.7 mg/kg) | |||||
| Maintenance | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | Sevoflurane | |||||
| MMT | III | II | II | II | II | |||||
| ULBT | Class 3 | Class 1 | Class 1 | Class 1 | Class 1 | |||||
| Inter-incisor distance | 3.5 cm | 3.5 cm | 5.5 cm | 4 cm | 3.5 cm | |||||
| Sternomental distance | 15 cm | 14 | 15 cm | 15 cm | 19 cm | |||||
| Neck circumference | 31 cm | 38 | 35 cm | 34 cm | 40 cm | |||||
| C-L grading | 1 | 3 | 2a | 1 | 2a | |||||
| LQS grading | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 1 | Grade 1 | Grade 1 | |||||
| View of glottis (POGO grading) | 90% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |||||
| Success on first attempt | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Intubation time (VS) | 6 s | 10 s | 11 s | 10 s | 6 s | |||||
| V1 verification | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Complications | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | Nil | |||||
| Subjective satisfaction | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent | Easy and excellent | |||||
| Supplementary materials | Video S11 | Video S12 | Video S13 | Video S14 | Video S15 | |||||
| DL | VL | FOB | Styletubation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Availability and affordability | +++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| Difficult intubation with IONM tube | 6.5% [44] | - | - | 2.7% [44] 0% (this article) |
| First-pass success rate | 75% [20] 96.4% [44] | 97.5% [20] | - | 90% [20] 99% [44] 100% (this article) |
| Time to intubate | 68.8 s [20] | 29.8 s [20] | - | 42.4 s [20] 4–15 s (this article) |
| Initial successful placement without tube depth adjustment | 94.3% [36] 96.4% and 87.3% [37] 33.5% [42] | 67% [40] 97.5% [41] 100% [49] 44% [42] | 100% [38] | 100% [50] 100% (this article) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, H.-S.; Corey, T.; Luk, H.-N.; Qu, J.Z.; Shikani, A. Combined Styletubation with Videolaryngoscopy for Tracheal Intubation in Patients Undergoing Thyroidectomy with Intraoperative Neuromonitoring. Anesth. Res. 2024, 1, 8-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/anesthres1010003
Pan H-S, Corey T, Luk H-N, Qu JZ, Shikani A. Combined Styletubation with Videolaryngoscopy for Tracheal Intubation in Patients Undergoing Thyroidectomy with Intraoperative Neuromonitoring. Anesthesia Research. 2024; 1(1):8-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/anesthres1010003
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Hui-Shan, Tiffany Corey, Hsiang-Ning Luk, Jason Zhensheng Qu, and Alan Shikani. 2024. "Combined Styletubation with Videolaryngoscopy for Tracheal Intubation in Patients Undergoing Thyroidectomy with Intraoperative Neuromonitoring" Anesthesia Research 1, no. 1: 8-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/anesthres1010003
APA StylePan, H.-S., Corey, T., Luk, H.-N., Qu, J. Z., & Shikani, A. (2024). Combined Styletubation with Videolaryngoscopy for Tracheal Intubation in Patients Undergoing Thyroidectomy with Intraoperative Neuromonitoring. Anesthesia Research, 1(1), 8-23. https://doi.org/10.3390/anesthres1010003