Physicochemical Properties and Aroma Compounds Analysis in Watermelon Soy Sauce
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
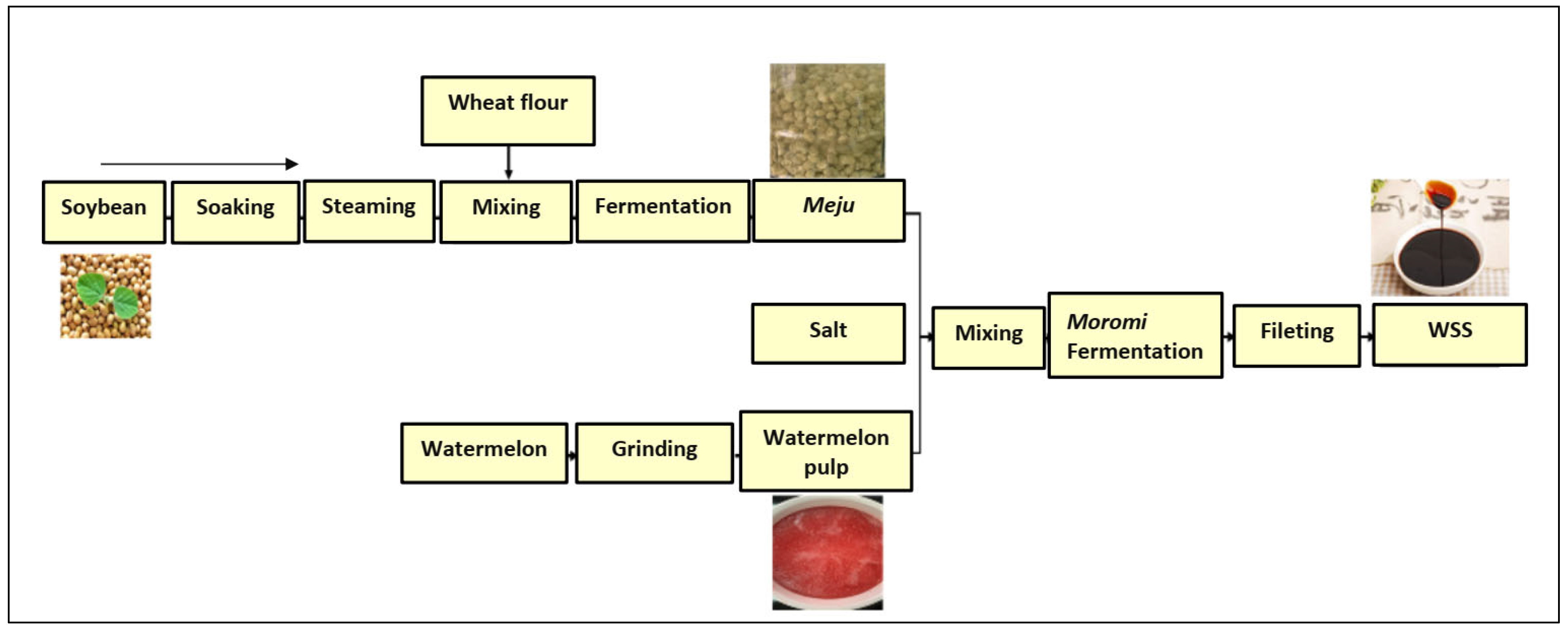
2.1. Sauce Samples
2.2. Physicochemical Properties Analysis
2.3. Amino Acids Composition
2.4. Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction (HS-SPME)
2.5. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Analysis
2.6. E-Nose Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties
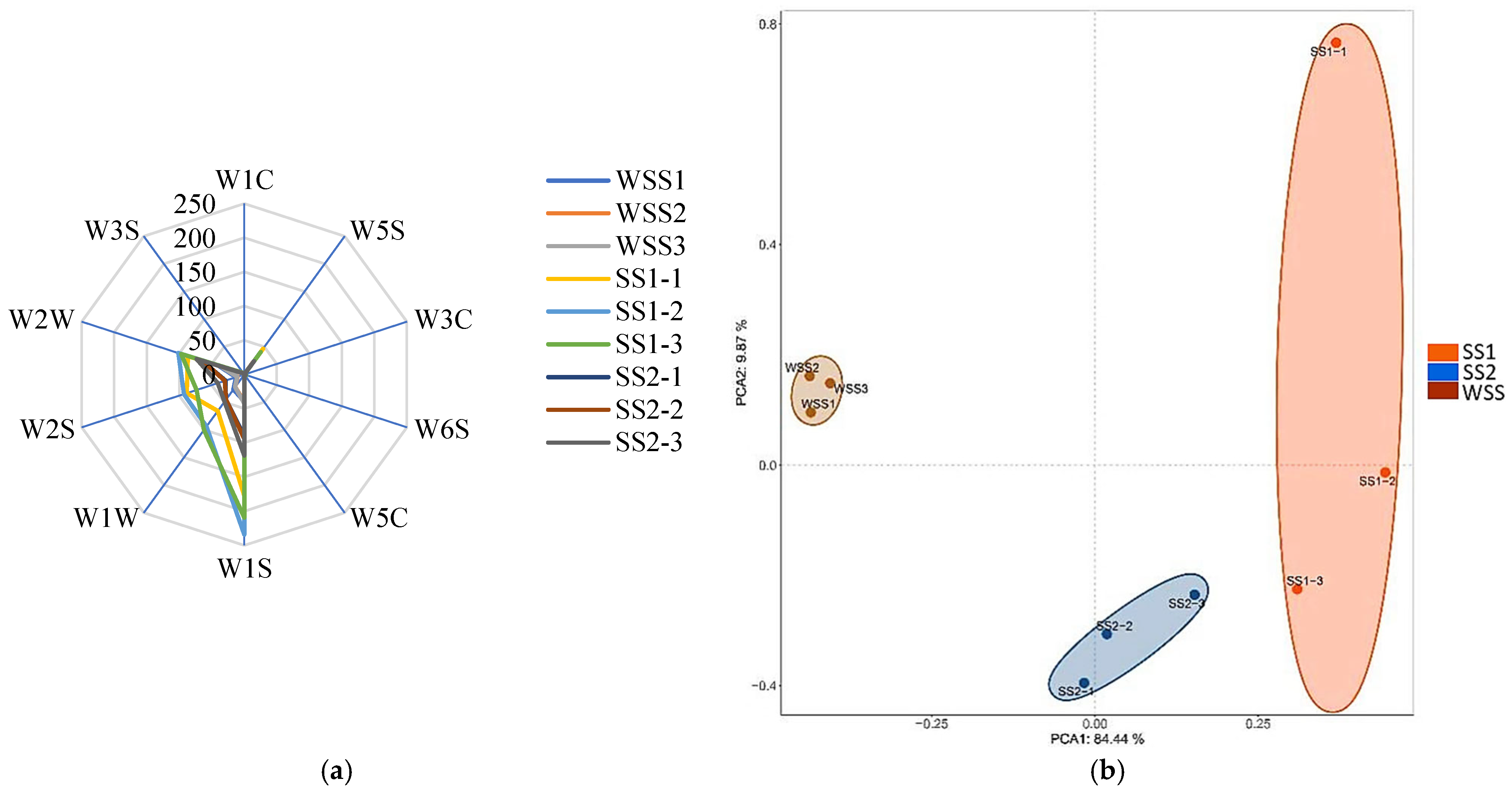
3.2. Volatile Compounds Analysis
3.3. Electronic Nose Analysis
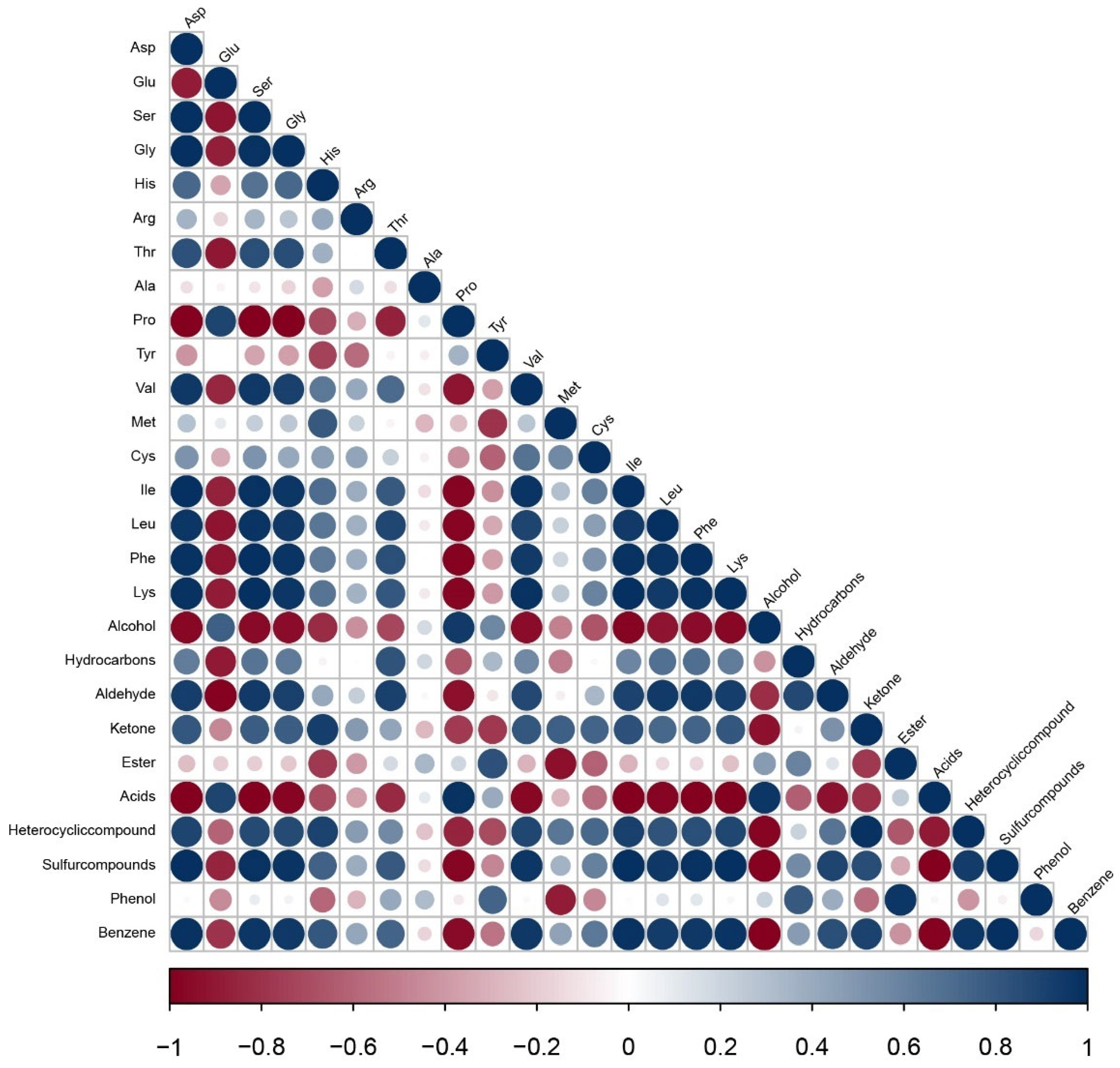
3.4. Correlation of the Predominant Flavor Compounds and Amino Acids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAA | Bitter amino acid |
| DAA | Umami amino acid |
| GC/MS | Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HS-SPME | Headspace solid-phase microextraction |
| HSLS | High-salt liquid-state |
| LSSS | Low salt solid-state |
| MOS | Metal oxide semiconductor |
| ND | Not detected |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| RIs | Retention indices |
| sAA | Salty amino acid |
| SAA | Sweet amino acid |
| TAA | Total free amino acid content |
| WSS | Watermelon soy sauce |
References
- Diez-Simon, C.; Eichelsheim, C.; Mumm, R.; Hall, R.D. Chemical and sensory characteristics of soy sauce: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11612–11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.Z.; Qian, Y.L.; Ji, F.D.; Chen, J.Y.; Han, B.Z. Microbial composition during Chinese soy sauce koji-making based on culture dependent and independent methods. Food Microbiol. 2013, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, M.; Shen, Y.; Qin, X.; Huang, H.; Yang, H.; He, Y.; Bai, W. An high-throughput sequencing approach to the preliminary analysis of bacterial communities associated with changes in amino acid nitrogen, organic acid and reducing sugar contents during soy sauce fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, M.; Su, G.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y. Effect of soy sauce on serum uric acid levels in hyperuricemic rats and identification of flazin as a potent xanthine oxidase inhibitor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4725–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, S. Functional effects of Japanese style fermented soy sauce (shoyu) and its components. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Cai, Y.; Su, G.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, M. Evaluation of aroma differences between high-salt liquid-state fermentation and low-salt solid-state fermentation soy sauces from China. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Peng, D.; Zhang, W.; Duan, M.; Ruan, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhou, S.; Fang, Q. Effect of aroma-producing yeasts in high-salt liquid-state fermentation soy sauce and the biosynthesis pathways of the dominant esters. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanthi, P.V.P.; Linforth, R.; Onyeaka, H.; Gkatzionis, K. Effects of co-inoculation and sequential inoculation of Tetragenococcus halophilus and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii on soy sauce fermentation. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Luo, W.; Wu, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, W.; Suyama, T. Improving RNA content of salt-tolerant Zygosaccharomyces rouxii by atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) mutagenesis and its application in soy sauce brewing. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Hou, L.; Lu, M.; Wang, C.; Zeng, B. Genome shuffling of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii to accelerate and enhance the flavour formation of soy sauce. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Guo, H.L.; Wang, C.L.; Hou, L.H.; Cao, X.H.; Liu, J.F.; Lu, F.P. Comparative study on fermentation performance in the genome shuffled Candida versatilis and wild-type salt tolerant yeast strain. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, I.; Shinohara, Y.; Oguma, T.; Koyama, Y. Survival strategy of the salt-tolerant lactic acid bacterium, Tetragenococcus halophilus, to counteract koji mold, Aspergillus oryzae, in soy sauce brewing. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmeli, Y.; Holyavkin, C.; Topaloglu, A.; Arslan, M.; Kisakesen, H.I.; Cakar, Z.P. Evolutionary engineering and molecular characterization of a caffeine-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, H.; Lv, Z.; Hu, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, F. Search for potential molecular indices for the fermentation progress of soy sauce through dynamic changes of volatile compounds. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, N.; Zhao, H.; Cui, C.; Zhao, M. Changes in fatty acid composition and lipid profile during koji fermentation and their relationships with soy sauce flavour. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherzadeh, M.J.; Gustafsson, L.; Niklasson, C.; Liden, G. Conversion of furfural in aerobic and anaerobic batch fermentation of glucose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 1999, 87, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, D.; Liu, D.; Ye, X. Characterization of aroma-active volatiles in three Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) cultivars using GC–MS–olfactometry and an electronic nose combined with principal component analysis. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Song, J.; Bi, J.; Meng, X.; Wu, X. Characterization of volatile profile from ten different varieties of Chinese jujubes by HS-SPME/GC–MS coupled with E-nose. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liang, W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, H. Identification and analysis of the flavor characteristics of unfermented stinky tofu brine during fermentation using SPME-GC–MS, E-nose, and sensory evaluation. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Deng, Z.; Tie, Y.; Quan, S.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Z.; Pan, Z.; Qin, J.; Wu, R.; Luo, G.; et al. Unveiling the synthesis of aromatic compounds in sauce-flavor Daqu from the functional microorganisms to enzymes. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulia, B.; Anna, R.; Maurizio, G.; Lia, P.; Roberto, L.S. External maturity indicators, carotenoid and sugar compositions and volatile patterns in ‘Cuoredolce’ and ‘Rugby’ mini-watermelon (Citrullus lanatus (Thunb) Matsumura & Nakai) varieties in relation of ripening degree at harvest. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 136, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Feng, Y.; Hadiatullah, H.; Zheng, F.; Yao, Y. Chemical characteristics of three kinds of Japanese soy sauce based on electronic senses and GC-MS analyses. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 579808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.W.; Hong, S.P.; Lim, S.D.; Yi, S.H. Investigation of microbial community of Korean soy sauce (Ganjang) using shotgun metagenomic sequencing and its relationship with sensory characteristics. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, C.; Shan, W.; Zheng, F.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Physicochemical, flavor and microbial dynamic changes during low-salt doubanjiang (broad bean paste) fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 128454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Kwak, H.S.; Kim, M.J. The effect of various salinity levels on metabolomic profiles, antioxidant capacities and sensory attributes of doenjang, a fermented soybean paste. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Tian, T.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Tao, D.; Wu, R.; Yue, X. The dynamic changes of chemical components and microbiota during the natural fermentation process in Da-Jiang, a Chinese popular traditional fermented condiment. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.7-2016; National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Reducing Sugar in Foods. Issued on. AUGUST 31, 2016, Implemented on. MARCH 01, 2017; National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/GB5009.7-2016 (accessed on 3 August 2025).
- Hou, M.F.; Xiang, H.; Hu, X.; Chen, S.J.; Wu, Y.Y.; Xu, J.C.; Yang, X.Q. Novel potential XOD inhibitory peptides derived from Trachinotus ovatus: Isolation, identification and structure-function analysis. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C.; Eun, J.B. Characterization of volatile compounds and physicochemical properties of hongeo using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry during fermentation. Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Yu, J. Comparative analysis of volatile compounds from four radish microgreen cultivars based on ultrasonic cell disruption and HS-SPME/GC–MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.Z.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Kong, B.H. Evaluation of flavor characteristics of bacon smoked with different woodchips by HS-SPME-GC-MS combined with an electronic tongue and electronic nose. Meat Sci. 2021, 182, 108626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.C.; Ling, M.Y. Biochemical changes in soy sauce prepared with extruded and traditional raw materials. Food Res. Int. 1998, 31, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Feng, Y.Z.; Cui, C.; Zhao, H.F.; Zhao, M.M. Effects of koji-making with mixed strains on physicochemical and sensory properties of Chinese-type soy sauce. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C.; Kim, D.W.; Eun, J.B. Physicochemical properties and bacterial community dynamics of hongeo, a Korean traditional fermented skate product, during fermentation at 10 °C. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 104, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Li, J.B.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Q.Q.; Xie, M. Effects of salt concentration on Chinese sauerkraut fermentation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.H.; Kim, K.H.; Sang, E.J.; Che, O.J. The effect of salt concentrations on the fermentation of doenjang, a traditional Korean fermented soybean paste. Food Microbiol. 2016, 86, 103329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Wu, D. Effect of salt concentration on Chinese soy sauce fermentation and characteristics. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jin, F.; Hao, J.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wang, F. Preparation of soy sauce by walnut meal fermentation: Composition, antioxidant properties, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory activities. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, E.; Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Hu, F.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X. Enhancing the taste of raw soy sauce using low intensity ultrasound treatment during moromi fermentation. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lioe, H.N.; Selamat, J.; Yasuda, M. Soy sauce and its umami taste: A link from the past to current situation. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, R71–R76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Yang, L.; Kan, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; He, L.; Fu, J.; Huang, Q.; Ho, C.T.; et al. Chemical profile and sensory evaluation of Cantonese raw soy sauce to reveal the association between taste characteristics and chemical composition. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, A.; Jafri, M.S.; Roper, S.D. In situ Ca2+ imaging reveals neurotransmitter receptors for glutamate in taste receptor cells. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 7978–7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caicedo, A.; Kim, K.N.; Roper, S.D. Glutamate-induced cobalt uptake reveals non-NMDA receptors in rat taste cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 417, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Caicedo, A.; Roper, S.D. Glutamate-induced cobalt uptake reveals non-NMDA receptors in developing rat taste buds. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 1715–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cha, Y.J. Volatile Compounds in seasoning sauce produced from soy sauce residue by reaction flavor technology. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2018, 23, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devanthia, P.V.P.; Konstantinos, G. Soy sauce fermentation: Microorganisms, aroma formation, and process modification. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, A.; Osako, K.; Okamoto, A.; Ohshima, T. Olfactometric characterization of aroma active compounds in fermented fish paste in comparison with fish sauce, fermented soy paste and sauce products. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sluis, C.; Tramper, J.; Wijffels, R.H. Enhancing and accelerating flavour formation by salt-tolerant yeasts in Japanese soy-sauce processes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Hao, L.; Zhang, G.; Jin, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Traditional fermented soybean products: Processing, flavor formation, nutritional and biological activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1971–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.J.; Schilling, M.W.; Mikel, W.B.; Williams, J.B.; Martin, J.M.; Coggins, P.C. Relationships between sensory descriptors, consumer acceptability and volatile flavor compounds of American dry-cured ham. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, T.; An, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Cui, J. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds influencing Chinese-type soy sauces using GC–MS combined with HS-SPME and discrimination with electronic nose. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.A. The aroma of soy sauce. In Science and Brewing Technology of Soy Sauce; Bao, Q.A., Ed.; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 44–73. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Su, G.; Zhao, H.; Cai, Y.; Cui, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, M. Characterisation of aroma profiles of commercial soy sauce by odour activity value and omission test. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y. Comparison of Flavor Profile Relationship of Soy Sauce under Different Storage Conditions. Foods 2023, 12, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhao, S.; Jia, H.; Guo, C.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z.P.; Yue, T.; Yuan, Y. Flavor differences between commercial and traditional soybean paste. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 142, 111052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajanta, K.; Apichartsrangkoon, A.; Chukeatirote, E. Volatile profiles of thua nao, a Thai fermented soy product. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.Y.; Fung, P.K.; Kim, J.S. Aroma impact components in commercial plain sufu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, S.; Kumazawa, K.; Nishimura, O. Studies on the key aroma compounds in raw (uUnheated) and heated Japanese soy sauce. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3396–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.Z.; Cui, C.; Zhao, H.F.; Gao, X.L.; Zhao, M.M.; Sun, W.Z. Effect of koji fermentation on generation of volatile compounds in soy sauce production. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Q.; Cao, L.; He, L.; Wang, P.; Deng, G.; Li, J.; Fu, J.; Huang, Q.; Ho, C.T.; Li, Y.; et al. Tracing the change of the volatile compounds of soy sauce at different fermentation times by PTR-TOF-MS, E-nose and GC-MS. Food Chem. X 2024, 25, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Cui, C.; Zhao, H.F.; Zhao, M.M.; Yang, L.; Ren, J.Y. Changes in volatile aroma compounds of traditional Chinese-type soy sauce during moromi fermentation and heat treatment. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Nian, Y.; Da, D.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, D.; Li, C. Characterization of flavor volatile compounds in sauce spareribs by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and electronic nose. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 124, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tamura, T.; Kyouno, N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Akiyama, Y.; Chen, J.Y. Effect of volatile compounds on the quality of Japanese fermented soy sauce. LWT 2019, 111, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.K. Thermal generation of aroma. In Flavour Development, Analysis and Perception in Food and Beverages; Parker, J.K., Elmore, S., Methven, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 151–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, N.; Wu, X.; Chen, J. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on aroma components, amino acids, and fatty acids of Hami melon (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus naud.) juice. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Leong, S.M.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, F.; Yang, T.; Liu, S. Viscozyme L pretreatment on palm kernels improved the aroma of palm kernel oil after kernel roasting. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| pH | Salinity (%) | Total Acid | Amino Acid Nitrogen Content (g/100 mL) | Total Solids (%) | Reducing Sugar Content (g/100 mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/100 mL) | ||||||
| WSS | 4.37 ± 0.01 a | 9.75 ± 0.19 b | 2.04 ± 0.04 a | 2.02 ± 0.03 a | 24.05 ± 0.48 c | 2.53 ± 0.21 c |
| SS1 | 4.72 ± 0.01 a | 4.68 ± 0.32 c | 1.85 ± 0.11 a | 3.04 ± 0.03 a | 26.13 ± 0.24 b | 10.92 ± 0.17 a |
| SS2 | 4.82 ± 0.01 a | 13.46 ± 0.58 a | 1.76 ± 0.07 a | 2.58 ± 0.07 a | 33.2 ± 0.54 a | 7.65 ± 0.22 b |
| Free Amino Acid | WSS (mg/mL) | SS1 (mg/mL) | SS2 (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | ND | 21.10 ± 0.04 a | 21.07 ± 1.48 a |
| Glu | 74.90 ± 2.78 a | 38.84 ± 2.17 c | 53.54 ± 1.69 b |
| Ser | 1.41 ± 0.004 b | 6.97 ± 0.10 a | 6.65 ± 0.16 a |
| Gly | 0.91 ± 0.14 b | 3.82 ± 0.18 a | 3.61 ± 0.49 a |
| His | ND | 0.87 ± 0.07 a | 2.54 ± 0.71 a |
| Arg | 2.22 ± 1.12 a | 1.80 ± 1.02 a | 3.01 ± 0.16 a |
| Thr | 2.21 ± 0.23 b | 5.16 ± 1.10 a | 3.90 ± 0.17 a |
| Ala | 7.96 ± 1.49 a | 7.78 ± 0.41 a | 7.01 ± 0.34 a |
| Pro | 17.26 ± 0.19 a | 6.58 ± 0.44 b | 7.38 ± 1.35 b |
| Tyr | 2.09 ± 0.76 a | 2.16 ± 0.33 a | 0.73 ± 0.01 b |
| Val | 3.77 ± 0.36 b | 7.86 ± 0.77 a | 8.38 ± 0.57 a |
| Met | 2.55 ± 0.34 b | 2.11 ± 0.40 b | 4.02 ± 0.01 a |
| Cys | 0.98 ± 0.01 b | 1.65 ± 0.39 b | 3.73 ± 1.50 a |
| Ile | 1.43 ± 0.19 b | 5.10 ± 0.07 a | 5.40 ± 0.09 a |
| Leu | 2.12 ± 0.68 c | 9.18 ± 1.35 a | 8.55 ± 0.08 a |
| Phe | 1.60 ± 0.43 c | 6.66 ± 0.11 a | 6.20 ± 0.03 a |
| Lys | 0.95 ± 0.16 c | 5.08 ± 0.33 a | 5.09 ± 0.13 a |
| DAA | 83.77 ± 4.27 a | 71.54 ± 2.69 a | 85.23 ± 4.22 a |
| SAA | 31.97 ± 3.17 a | 32.11 ± 3.25 a | 31.56 ± 2.67 a |
| BAA | 14.51 ± 2.92 c | 39.02 ± 3.43 a | 40.91 ± 1.63 a |
| sAA | 74.9 ± 2.78 a | 59.94 ± 2.21 b | 74.61 ± 3.17 a |
| AAA | 74.9 ± 2.78 a | 60.81 ± 2.28 b | 77.15 ± 3.88 a |
| TAA | 122.36 ± 8.88 a | 132.72 ± 9.28 a | 150.81 ± 8.97 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, S.-R.; Zhao, C.-C.; Defo Deeh, P.B.; Wang, M.-H.; Jin, T.-Y. Physicochemical Properties and Aroma Compounds Analysis in Watermelon Soy Sauce. Gastronomy 2025, 3, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastronomy3040020
Xiong S-R, Zhao C-C, Defo Deeh PB, Wang M-H, Jin T-Y. Physicochemical Properties and Aroma Compounds Analysis in Watermelon Soy Sauce. Gastronomy. 2025; 3(4):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastronomy3040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Si-Rui, Chang-Cheng Zhao, Patrick Brice Defo Deeh, Myeong-Hyeon Wang, and Tie-Yan Jin. 2025. "Physicochemical Properties and Aroma Compounds Analysis in Watermelon Soy Sauce" Gastronomy 3, no. 4: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastronomy3040020
APA StyleXiong, S.-R., Zhao, C.-C., Defo Deeh, P. B., Wang, M.-H., & Jin, T.-Y. (2025). Physicochemical Properties and Aroma Compounds Analysis in Watermelon Soy Sauce. Gastronomy, 3(4), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastronomy3040020






