Sensory and Microbiological Evaluation of Artisanal Garrafa Ice Cream Made with Goat and Cow Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Microbiological Analysis and Phosphatase Test of Goat and Cow Milk
3.2. Microbiological Analysis of Artisanal Ice Creams
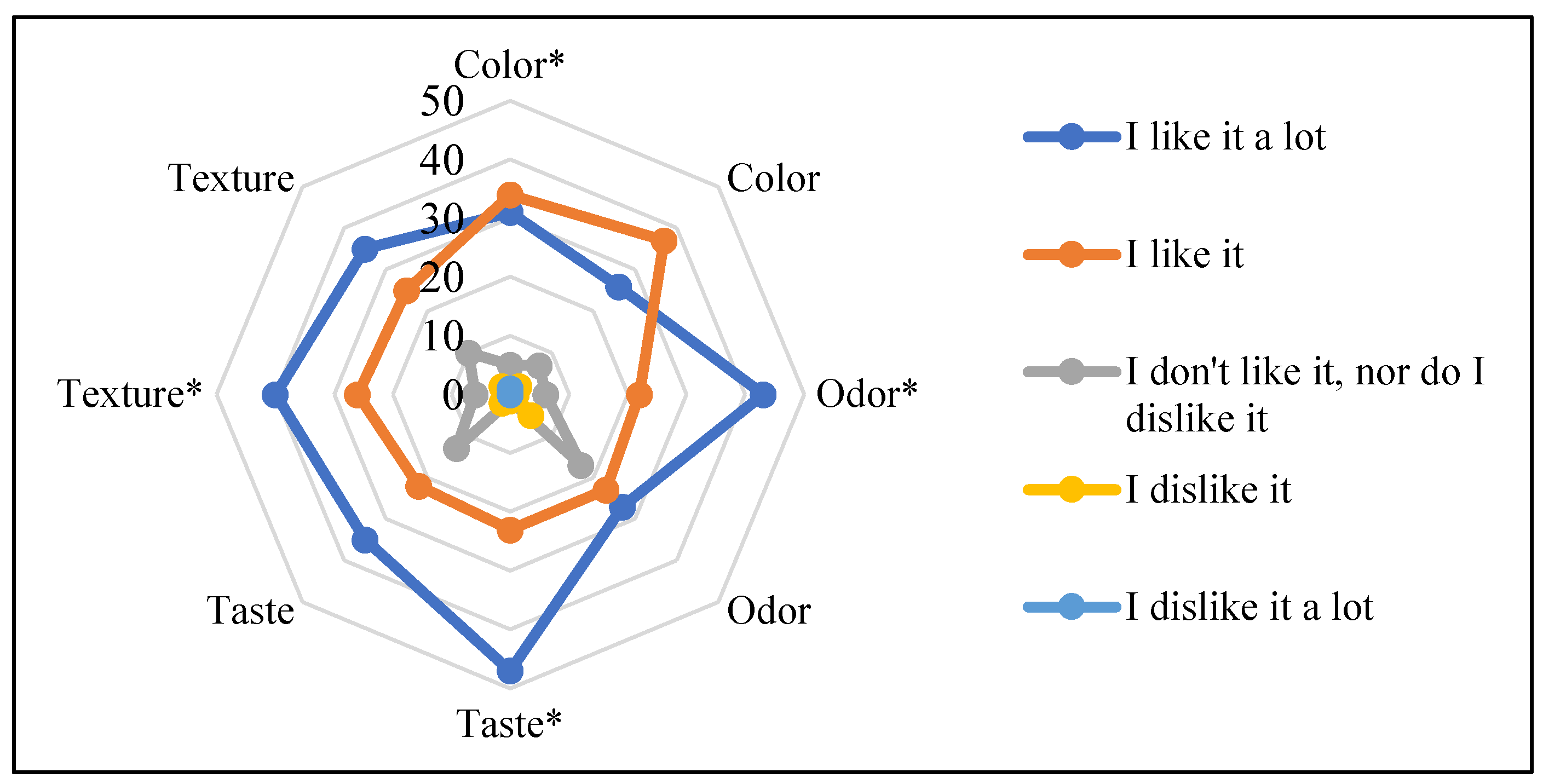
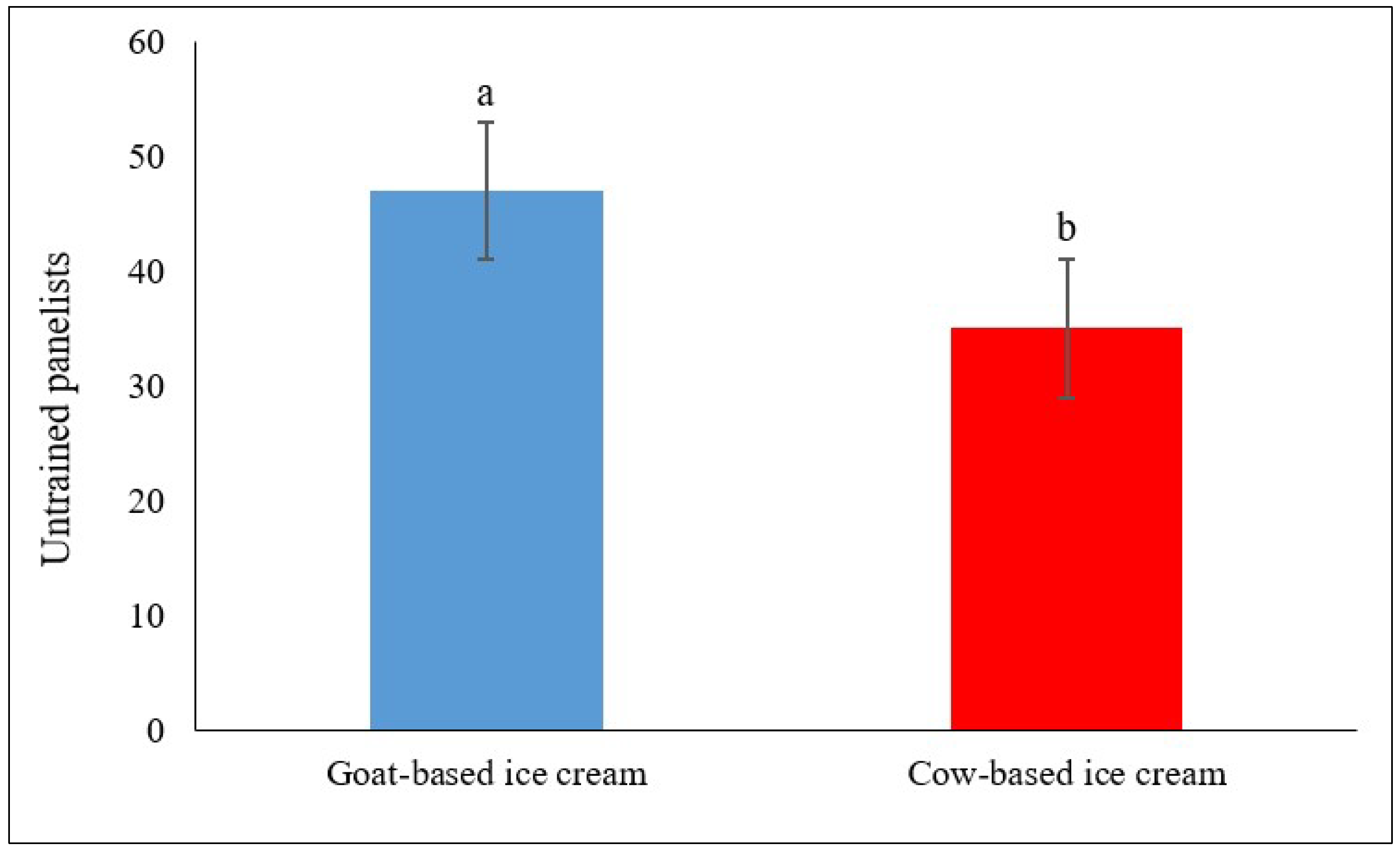
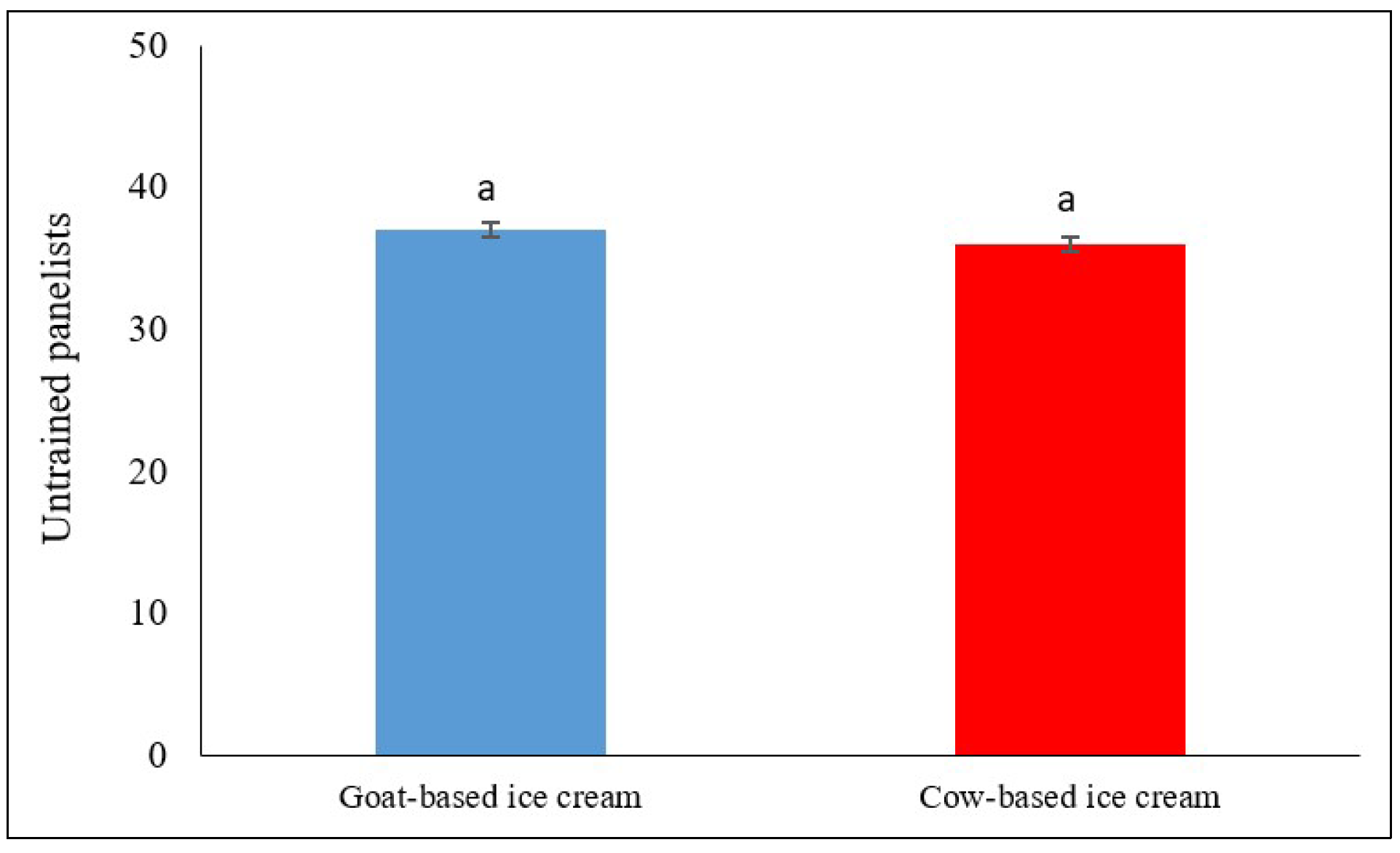
3.3. Acceptance and Sensory Evaluation
3.3.1. Acceptance and Sensory Evaluation of Pecan-Flavored Artisanal Ice Cream Made with Goat and Cow Milk
3.3.2. Acceptance and Sensory Evaluation of Chocolate Cookie-Flavored Artisanal Ice Cream Made with Goat and Cow Milk
3.3.3. Overall Acceptance Between Artisanal Ice Cream Made with Goat and Cow Milk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Training producers in sensory analysis of artisanal garrafa ice cream is essential to enable them to accurately define, identify, and quantify the sensory attributes of different ice cream varieties. This knowledge will enhance production quality, improve marketing strategies, and ultimately increase profitability. Such efforts will strengthen the competitive position of goat milk products among other popular, innovative, and stable dairy offerings.
- It is recommended to continue research on blending goat and cow milk in artisanal ice cream production, exploring diverse flavor profiles and the incorporation of seasonal fruits and functional additives to optimize product quality and consumer acceptance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TC | Total Coliforms |
| FC | Fecal Coliforms |
References
- Escareño, L.; Salinas-González, H.; Wurzinger, M.; Iñiguez, L.; Sölkner, J.; Meza-Herrera, C. Dairy goat production systems: Status quo, perspectives and challenges. Trop. Anim. Health and Prod. 2012, 45, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-González, H.; Echavarría, F.G.; Flores-Najera, M.J.; Flores-Ortiz, M.A.; Gutierrez, R.; Rumayor, A.; Meza-Herrera, C.A.; Pastor, F. Participatory evaluation of goat technologies in semiarid North Central México. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Cienc. For. Ambiente. 2011, 17, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Meza-Herrera, C.; Calderón-Leyva, G.; Soto-Sanchez, M.; Abad-Zavaleta, J.; Serradilla, J.; García-Martinez, A.; Rodríguez-Mártinez, R.; Veliz, F.; Macias-Cruz, U.; Salinas-González, H. The expression of birth weight is modulated by the breeding season in a goat model. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2012, 12, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurzinger, M.; Sölkner, J.; Iñiguez, L. Important aspects and limitations in considering community-based breeding programs for low-input smallholder livestock systems. Small Rumin. Res. 2011, 98, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistema de Información Agroalimentaria y Pesquera (SIAP). Anuario Estadístico de la Producción Agropecuaria en México. 2024. Available online: http://www.gob.mx/siap/acciones-yprogramas/produccion-pecuaria?idiom=es (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Álvarez-Figueroa, M.A.; Pineda-Castro, M.L.; Chacón-Villalobos, A.; Cubero-Castillo, E. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of whole, skimmed and lactose-free goat and bovine milks. Mesoam. Agron. 2022, 33, 47039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidot-Fernández, A. Composition, qualities and benefits of goat milk: Bibliographic review. Rev. Prod. Anim. 2017, 29, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Salinas, F.; Andrade-Montemayor, H.M.; De la Torre-Carbot, K.; Duarte-Vázquez, M.A.; Silva-Jarquin, J.C. Comparative analysis of the protein composition of goat milk from French Alpine, Nubian, and Creole breeds and Holstein Friesian cow milk: Implications for early infant nutrition. Animals 2022, 12, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOM-243-SSA1-2010; Mexican Official Standard. Products and Services. Milk, Milk Formula, Blended Dairy Product, and Dairy Derivatives. Sanitary Provisions And Specifications. Test methods. Official Gazette of the Federation.; Secretaria de Salud: Mexico City, Mexico, 2011; p. 123. Available online: https://dof.gob.mx/normasOficiales/4156/salud2a/salud2a.htm (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Rodríguez-Ordóñez, J.E.; Mejía-Giraldo, L.F.; Serna-Cock, L. Sensory and calorie evaluation of an ice cream mix, where inulin is incorporated as a partial substitute for fat. Rev. Udcaactual. Divulg. Cient. 2019, 22, e1294. [Google Scholar]
- Chacón-Villalobos, A.; Pineda-Castro, M.L.; Jiménez-Goebel, C. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of goat and bovine milk ice creams with vegetable fat. Mesoam. Agron. 2016, 27, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, R.F.; Durán, N.J.; Durán, N.E. Back to the Field. In Food Engineer’s Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Bogota, Colombia, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 95–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M.; Pintado, T.; Delgado-Pando, G. Sensory analysis and consumer research in new meat products development. Foods 2021, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.A. Invited Review: Sensory Analysis of Dairy Foods. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4925–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.A.; Lu, C.D. Current status of global dairy goat production: An overview. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiano, A.N.; Harwood, W.S.; Drake, M.A. A 100-year review: Sensory analysis of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 9966–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidro-Requejo, L.M.; Torres-Hernández, D.; Reyes-González, A. Microbiological Analysis of Strawberry and Coconut Flavored Garrafa Snow Made with Pasteurized Goat Milk. XXX International Agronomy Week, FAZ-UJED. 2018, pp. 855–860. Available online: http://faz.ujed.mx/siafaz/memorias/201830.pdf. (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Peryam, D.R.; Pilgrim, F.J. Hedonic scale method of measuring food preferences. Food Technol. 1957, 11, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Treviño-Garza, M.Z.; Correa-Cerón, R.C.; Ortiz-Lechuga, E.G.; Solís-Arevalo, K.K.; Castillo-Hernández, S.L.; Gallardo-Rivera, C.T.; Arevalo-Niño, K. Effect of Linseed (Linum usitatissimum) Mucilage and chitosan edible coatings on quality and shelf-life of fresh-cut cantaloupe (Cucumis melo). Coatings 2019, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The Dangers of Raw Milk: Unpasteurized Milk Can Pose a Serious Health Risk. 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/buy-store-serve-safe-food/dangers-raw-milk-unpasteurized-milk-can-pose-serious-health-risk (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Isidro-Requejo, L.M.; Pastor-López, F.J.; Maldonado-Jáquez, J.A.; Figueroa-Viramontes, U.; Salinas-Gonzalez, H. Microbiological quality of raw milk under a scheme of good milking and storage practices in a goat production system in the Lagunera Region, Mexico. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2024, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, S.A.; Christiansen, A.; Lee, W.; Banavara, D.S.; López-Hernández, A. Invited review: The application of alkaline phosphatase assays for the validation of milk product pasteurization. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5538–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla-Luque, O.M.; Possas, A.; Cabo, M.L.; Rodríguez-López, P.; Valero, A. Tracking microbial quality, safety and environmental contamination sources in artisanal goat cheesemaking factories. Food Microbiol. 2023, 114, 104301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rola, J.G.; Sosnowski, M. Determination of alkaline phosphatase activity in milk and milk products by fluorometric method. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy. 2010, 54, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- NOM-036-SSA1-1993; Mexican Official Standard. Products and Services. Ice Cream or Snow Cones, Cream, Milk or Vegetable Fat Sorbets and Bases or Mixes for Ice Cream or Snow Cones. Official Gazette of the Federation; Secretaría de Salud: Mexico City, Mexico, 1993; p. 12. Available online: https://salud.gob.mx/unidades/cdi/nom/036ssa13.html (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- Ismail, A.K.; Nawi, N.M.; Ismail, M.M.; Goh, Y.M. Consumers’ preference on goat’s milk based on sensory attributes. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 29, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo-Preko, E.; Niilante, A.J.G.; Blay, A.M.Y. The relevance of the number of categories in the hedonic scale to the Ghanaian consumer in acceptance testing. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 1071216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verruk, S.; Dantas, A.; Prudencio, E.S. Functionally of the components from goat’s milk, recent advances for functional dairy products development and its implications on human health. J. Funct. Foods. 2019, 52, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santi, D.; Giacinti, G.; Chemello, G.; Frangipane, M.T. Improvement of the sensory characteristics of goat milk yogurt. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.D.; Rathaur, A.; Kumar, Y.A.; Shraddha. Nutritional and nutraceutical properties of goat milk for human health: A review. Indian J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal-Pala, C.; Karagul-Yuceer, Y.; Pala, A.; Savas, T. Sensory properties of drinkable yogurt made from milk of different goat breeds. J. Sens. Stud. 2006, 21, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.G.; Beltrão, E.M.; De Sousa, S.; Cruz, G.R.B.; Queiroga, R.C.R.E. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of yogurts made from goat and cow milk. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, G.; Adikari, A.; Nayananjalie, W.; Prasanna, P.; Jayawardena, N.; Wathsala, R. Physicochemical, microbiological and sensory properties of probiotic drinking yogurt developed with goat milk. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kesenkas, H.; Karagözlű, C.; Yerlikaya, O.; Őzer, E.; Akpinar, A.; Akbulut, N. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of winter yogurt produced from mixtures of cow’s and goat’s milk. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 23, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.W.; Drake, M.A. Effect of 3 months frozen-storage on organic acid contents and sensory properties, and their correlations in soft goat milk cheese. Small Rumin. Res. 2005, 58, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresno, M.; Torres, A.; Capote, J.; Álvarez, S. Effect of breed on physicochemical and sensory characteristics of fresh, semihard and hard goat’s milk cheeses. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2020, 48, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Tajonar, K.; Foggi, G.; Mele, M.; Simitzis, P.; Mavrommatis, A.; Tsiplakou, E.; Habib, M.R.; Gonzalez-Ronquillo, M.; Toro-Mujica, P. Consumer attitudes toward dairy products from sheep and goats: A cross-continental perspective. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 8718–8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkaisy, Q.H.; Saadi, A.M.; Al-Ameedee, Z.M.; Kadhim, D.H.; Hamid, R.A. Evaluation of some properties of goat yoghurt ice cream. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2024, 70, 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Akshit, F.N.U.; Deshwal, G.K.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, P.; Maddipatla, D.K.; Singh, M.P.; Goksen, G. Technological challenges in production of goat milk products and strategies to overcome them: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Asim, S.; Raza, A.; Rasul, H.; Ali, M.; Khalid, B.; Shukat, R.; Diantom, A. Effect of lotus seed powder addition on the physical and organoleptic attributes of chocolate flavour frozen yogurt using goat milk. Cogent Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2396952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredient | Pecan Flavor | Chocolate Cookie Flavor |
|---|---|---|
| Milk | 1000 mL | 1000 mL |
| Sugar | 160 g | 160 g |
| Cornstarch (flavored) | Nut-flavored, 18 g | Chocolate-flavored, 18 g |
| Add-ins | Chopped pecans, 5 g | Chopped-chocolate cookies, 5 g |
| Flavoring | Nut flavoring, 1 mL | Cookie flavoring, 1 mL |
| Vanilla extract | 1 mL | 1 mL |
| Milk | TC (CFU/mL) | FC (CFU/mL) | Phosphatase Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw goat milk | 810 | 230 | + |
| Pasteurized goat milk | Absent | Absent | Negative |
| Raw cow milk | 1250 | 480 | + |
| Pasteurized cow milk | Absent | Absent | Negative |
| Permissible limits | ≤20 (CFU/mL) | NA * | 4 (FU/g) |
| Milk | Flavor | Total Coliforms (TC) (CFU/g) | Fecal Coliforms (FC) (CFU/g) | Aerobic Mesophiles (CFU/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goat | Pecan | Absent | Absent | 2550 |
| Goat | Chocolate cookie | Absent | Absent | 1870 |
| Cow | Pecan | Absent | Absent | 2320 |
| Cow | Chocolate cookie | Absent | Absent | 2100 |
| NOM-036-SSA1-1993 Permissible Limits | <100 | * NA | 200,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salinas-González, H.; Isidro-Requejo, L.M.; Pastor-López, F.J.; Hernández-Leal, E. Sensory and Microbiological Evaluation of Artisanal Garrafa Ice Cream Made with Goat and Cow Milk. Gastronomy 2025, 3, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastronomy3030014
Salinas-González H, Isidro-Requejo LM, Pastor-López FJ, Hernández-Leal E. Sensory and Microbiological Evaluation of Artisanal Garrafa Ice Cream Made with Goat and Cow Milk. Gastronomy. 2025; 3(3):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastronomy3030014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalinas-González, Homero, Luis Maconetzín Isidro-Requejo, Francisco Javier Pastor-López, and Enrique Hernández-Leal. 2025. "Sensory and Microbiological Evaluation of Artisanal Garrafa Ice Cream Made with Goat and Cow Milk" Gastronomy 3, no. 3: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastronomy3030014
APA StyleSalinas-González, H., Isidro-Requejo, L. M., Pastor-López, F. J., & Hernández-Leal, E. (2025). Sensory and Microbiological Evaluation of Artisanal Garrafa Ice Cream Made with Goat and Cow Milk. Gastronomy, 3(3), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/gastronomy3030014








