A Hybrid Whale Optimization Approach for Fast-Convergence Global Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Whale Optimization Algorithm
2.2. Nelder–Mead Simplex
2.3. Tabu Search Algorithm
- Memory tiers.
- Tabu list (length k): blocks the last k accepted moves, steering exploration into new regions.
- Elite list (size m): archives the top-m solutions to safeguard global information and guide intensification.
2.4. Levy Flights
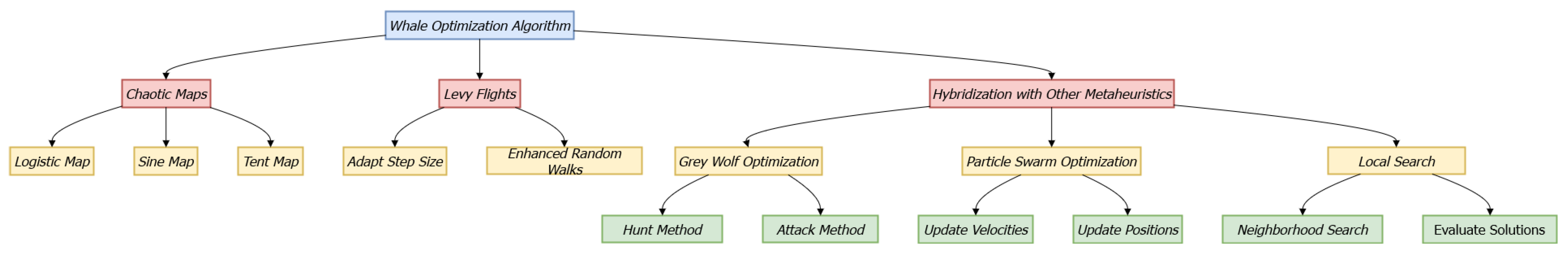
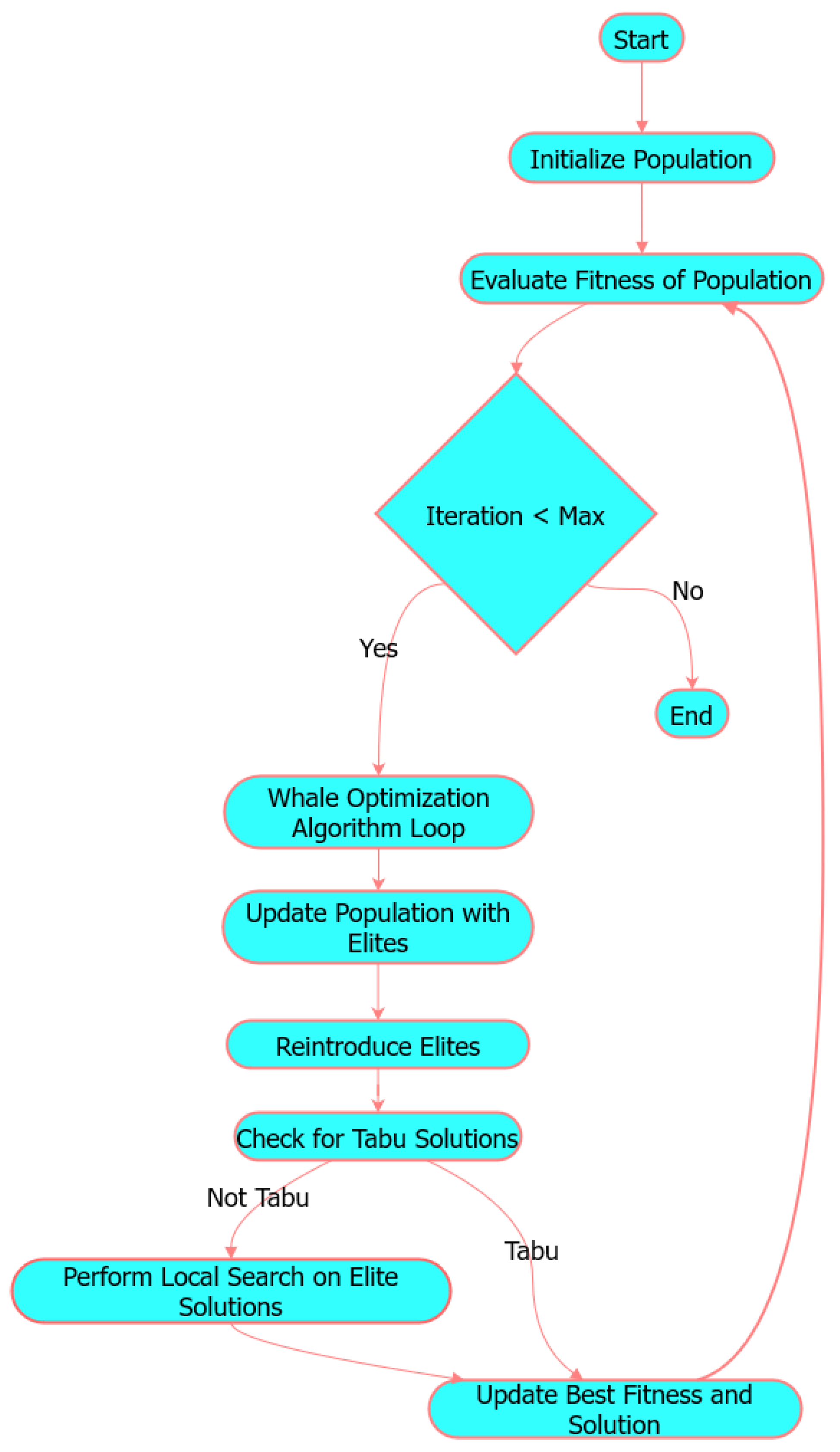
2.5. Enhanced Whale Optimization Algorithm with Levy Flight and Tabu Search Features: LWOATS
| Algorithm 1 LWOATS Optimization Algorithm |
|
1: Initialize the whale population , . 2: Evaluate the fitness value for the initial population 3: for each iteration do 4: Update each agent’s position using WOA (Algorithm A1) enhanced by Levy flights 5: Evaluate the fitness for new solutions 6: Update elite solutions 7: for each elite solution not in tabu list do 8: Apply local search using Nelder–Mead 9: Update best solution if improved 10: Add new solution to tabu list 11: end for 12: Reintroduce elite solutions into the population 13: end for 14: Return the best solution and its fitness |
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparing LWOATS with Known Fundamental Algorithms
Results on Unimodal and Multimodal Functions
3.2. Comparing LWOATS with Advanced DE Variations
3.3. Comparing LWOATS with Other Modified WOA Algorithms
3.4. Performance on F5, F12, and F13
3.5. Influence of Tabu Search and Elite Solutions in Exploitation
3.6. Runtime Complexity
4. LWOATS for Engineering Problems
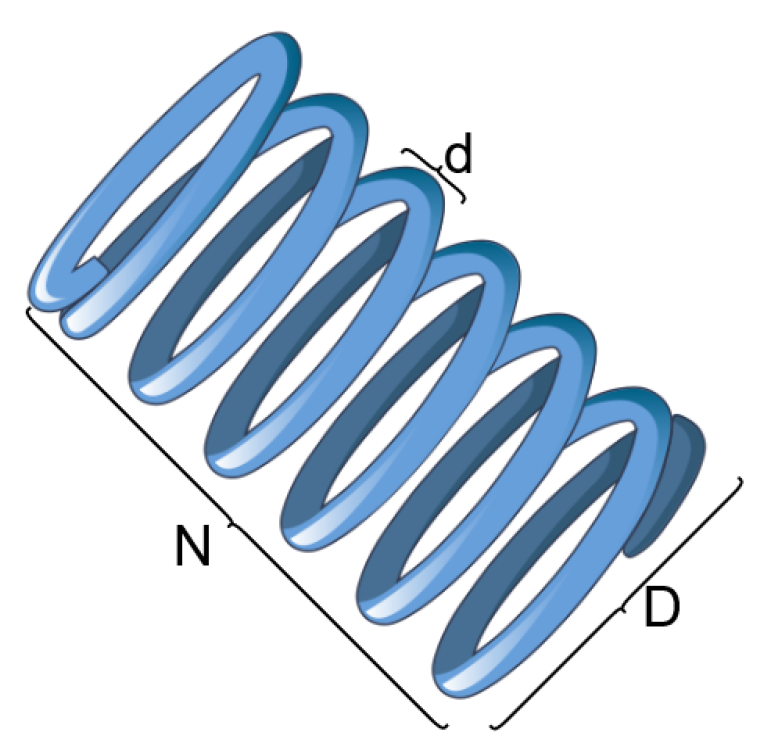
4.1. Tension/Compression Spring Design
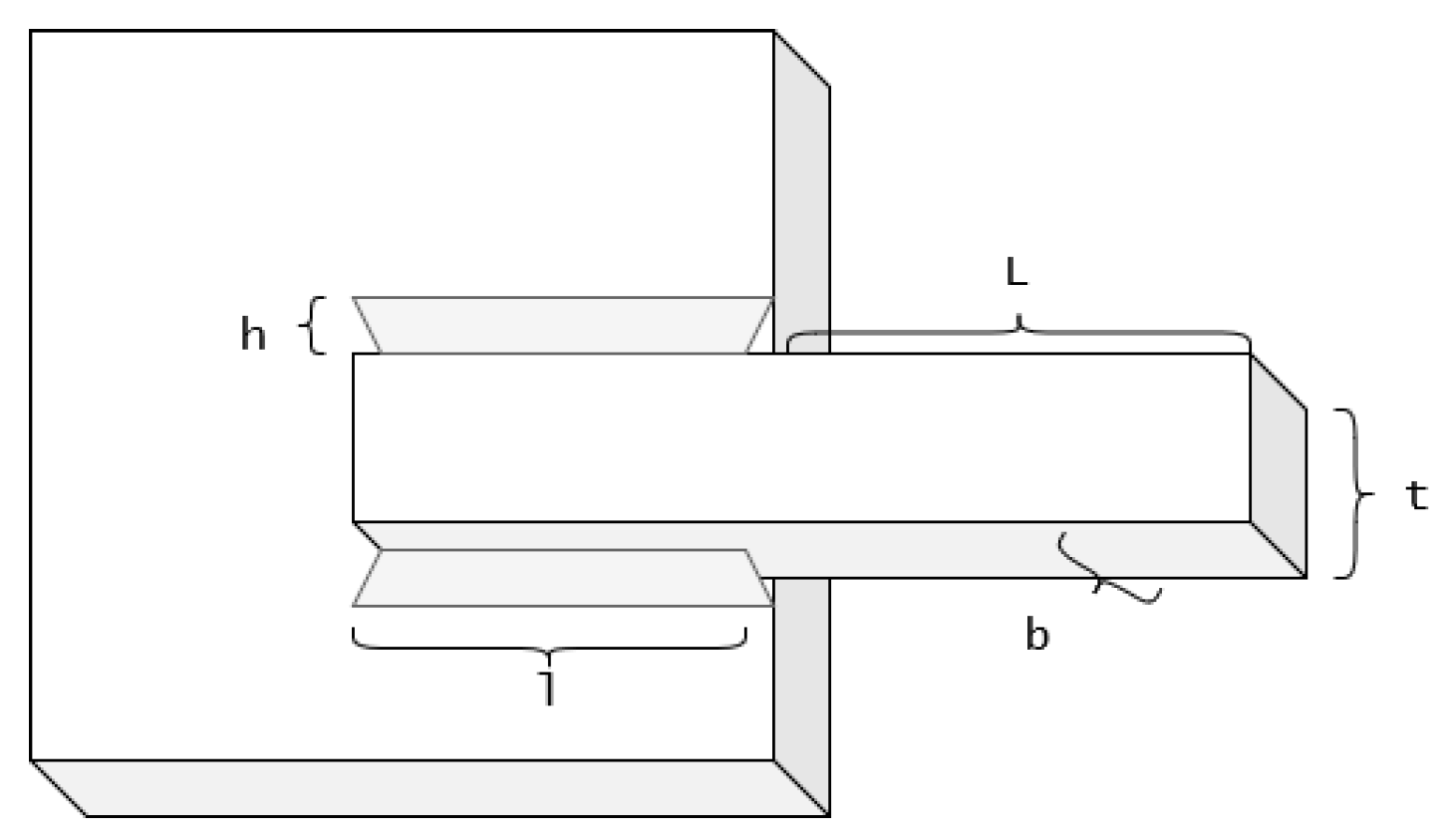
4.2. Welded Beam Design
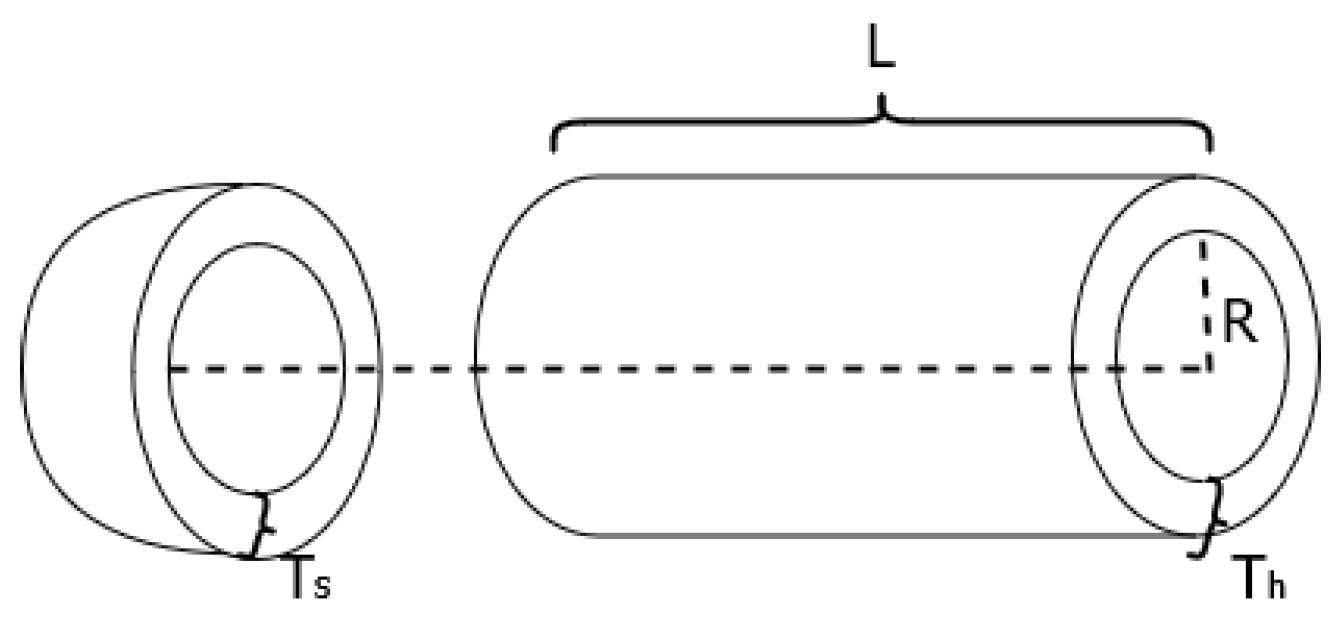
4.3. Pressure Vessel Design
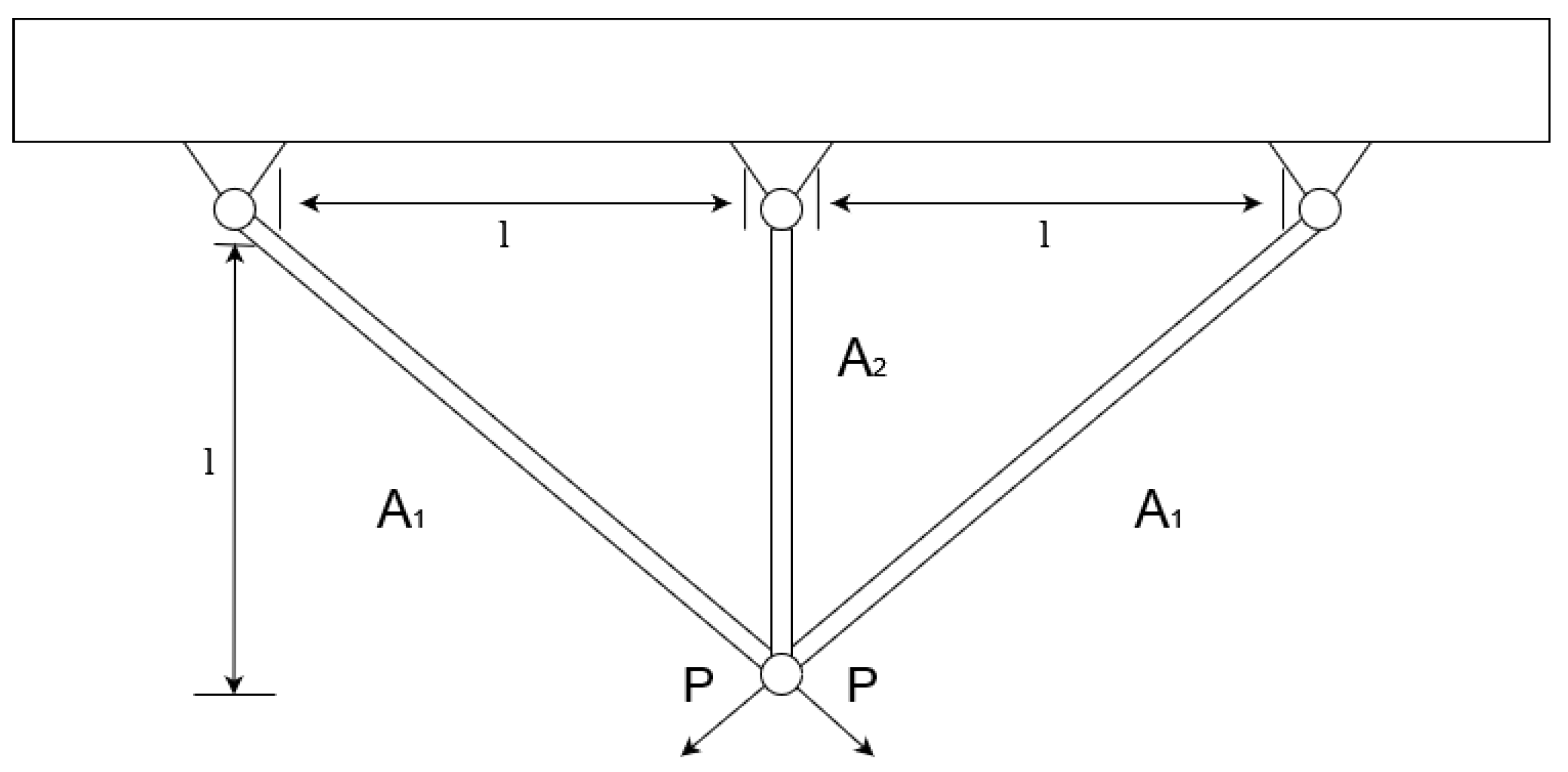
4.4. Three-Bar Truss Design
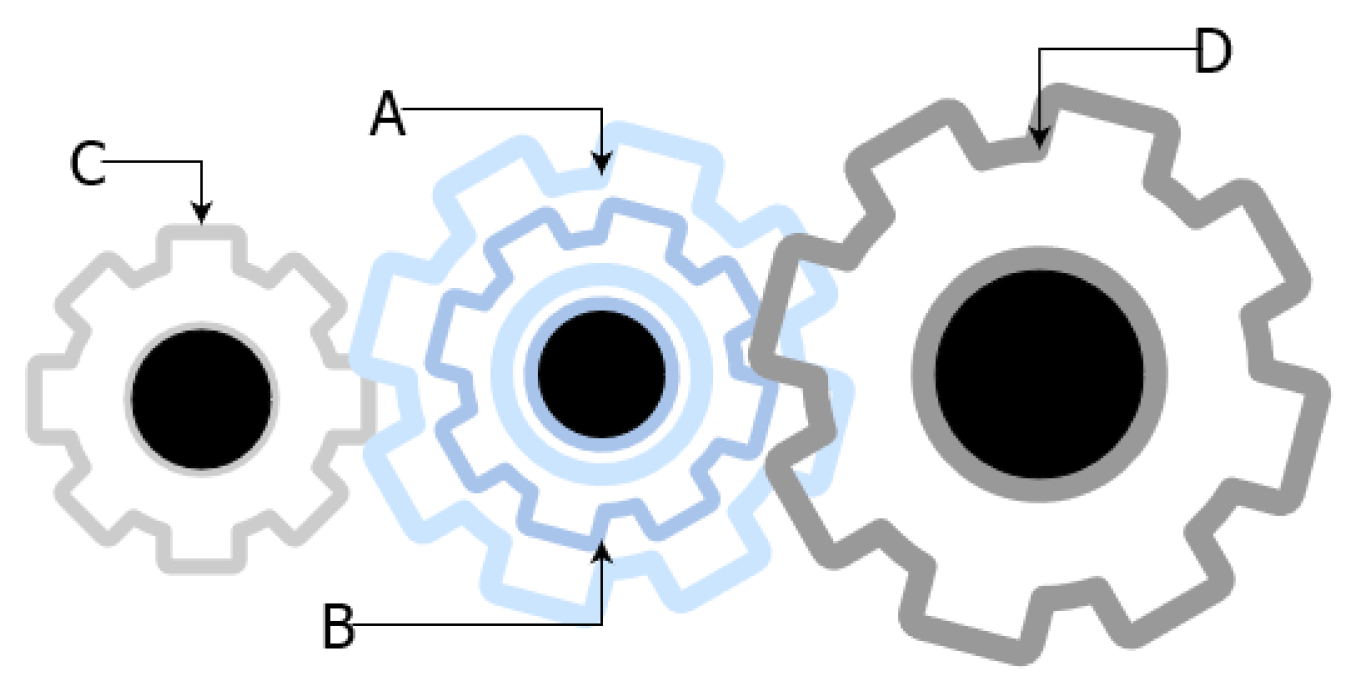
4.5. Gear Train Design
4.6. Speed Reducer
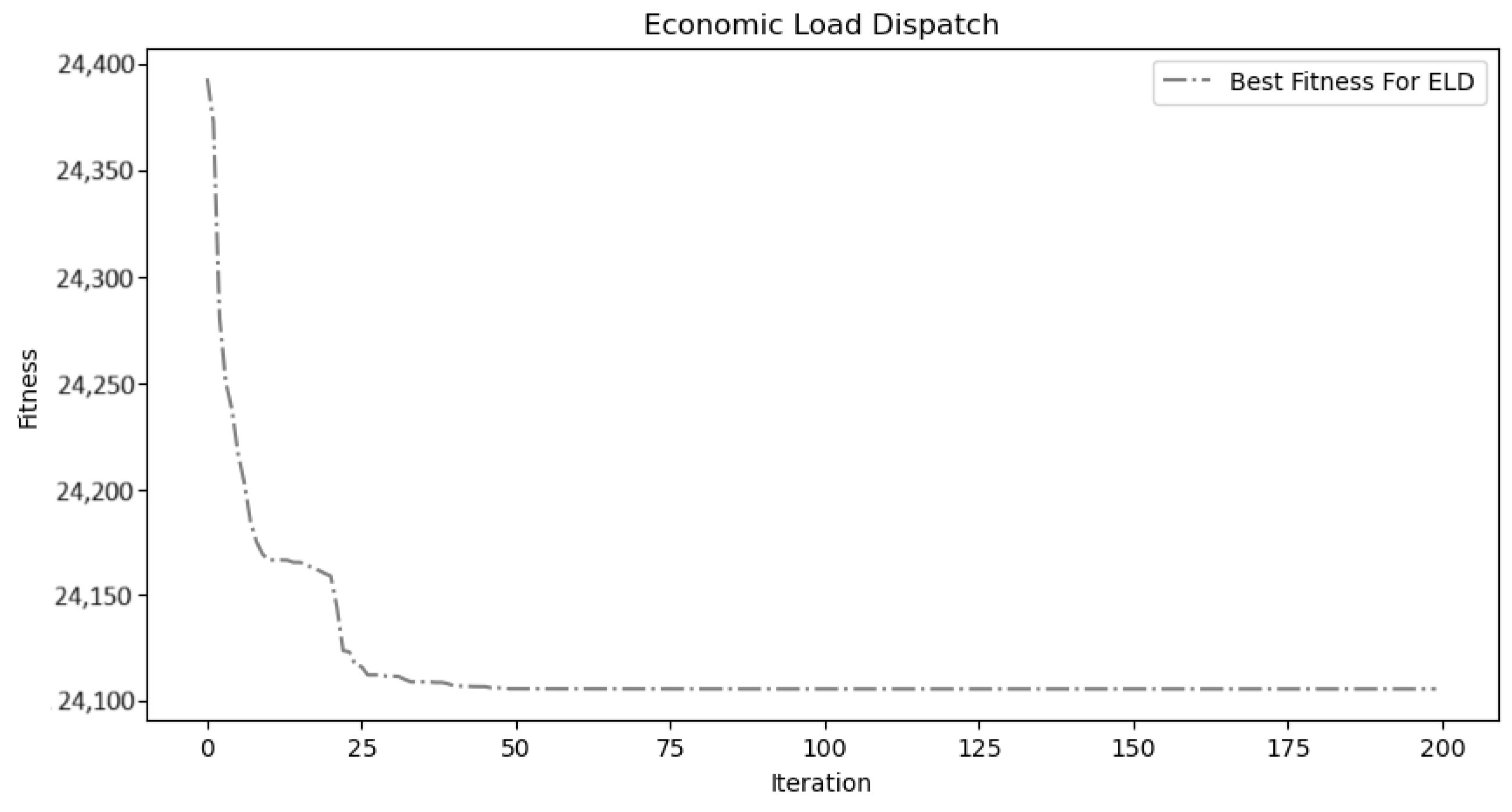
4.7. Economic Load Dispatch
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Appendix A. Standard WOA Update Formulas and Pseudocode
Appendix A.1. Exploration and Encircling Operators
Appendix A.2. Pseudocode
| Algorithm A1 Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) |
|
1: Initialize the whale population , 2: Evaluate the fitness of each whale 3: ← the best solution 4: while t < maximum number of iterations do 5: for each whale do 6: Calculate a, A, C, l, and p 7: if then 8: if then 9: Update the position of the current whale by Equation (A6) 10: else 11: Update the position of the current whale by Equation (A2) 12: end if 13: else 14: Update the position of the current whale by Equation (2) 15: end if 16: Evaluate new solutions 17: if new solution is better then 18: Update 19: end if 20: end for 21: Decrease a 22: t ← t+1 23: end while 24: return ▹ Best solution found |
Appendix B. Nelder–Mead Update Equations
- Reflection: The first attempt to improve the worst point by Nelder–Mead is through a reflection transformation. The process generates a new point by reflecting the worst point through the centroid of the remaining points in the simplex , where is the reflection coefficient, and typically .
- Expansion: in case that the reflection point provides a better solution to the problem, an expansion transformation in the same direction takes place to explore possible better solutions , where is the expansion coefficient, and usually .
- Contraction: If the value of the objective function at the reflected point is not better, the simplex performs a contraction to probe the space between the centroid and the worst point, or between the centroid and the reflection point. The contraction can be outside or inside . is the contraction coefficient, typically .
- Shrink: If none of the above operations yield a point with a better function value than the current best, the algorithm shrinks the simplex toward the best point . This is performed by adjusting each point (except the best one) closer to it: , for all , where is the shrink coefficient and usually .
Appendix C. Benchmark Functions
| Name | Function | Dim | Range | fmin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sphere | 30 | 0 | ||
| Schwefel2.22 | 30 | 0 | ||
| Schwefel1.2 | 30 | 0 | ||
| Schwefel2.21 | 30 | 0 | ||
| Rosenbrock | 30 | 0 | ||
| Step | 30 | 0 | ||
| Quartic | 30 | 0 |
| Name | Function | Dim | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zakharov | 30 | 0 | ||
| Rastrigin | 30 | 0 | ||
| Ackley | 30 | 0 | ||
| Griewank | 30 | 0 | ||
| Penalized 1 | ||||
| where , | 30 | 0 | ||
| Penalized 2 | 30 | 0 |
| Name | Function | Dim | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shekel’s FoxHoles | 2 | 1 | ||
| Kowalik | 4 | 0.00030 | ||
| Six-Hump Camel | 2 | |||
| Drop wave | 2 | −1 | ||
| GoldStein Price | 2 | 3 | ||
| Hartmann 3 | 3 | |||
| Hartmann 6 | 6 | |||
| Shekel 1 | 4 | |||
| Shekel 2 | 4 | |||
| Shekel 3 | 4 |
Appendix D. Tables of Experimental Results
Appendix D.1. LWOATS Compared to Fundamental Algorithms
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | GWO | DE | WOA | LWOATS | ||
| F1 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F2 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F3 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F4 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F5 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F6 | Best | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F7 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Comparison | + | − | = | Decision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS vs. DE | 5871 | 153 | 13 | 0 | 0 | +++++++++++++ |
| LWOATS vs. GWO | 3972 | 1118 | 8 | 2 | 3 | ++++−=++++==− |
| LWOATS vs. PSO | 5657 | 388 | 13 | 0 | 0 | +++++++++++++ |
| LWOATS vs. WOA | 3383 | 1248 | 7 | 2 | 4 | ++++−=++=+==− |
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | GWO | DE | WOA | LWOATS | ||
| F8 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F9 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F10 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F11 | Best | 0 | 0 | |||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F12 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F13 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Function | LWOATS vs. WOA | LWOATS vs. GWO | LWOATS vs. PSO | LWOATS vs. DE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | ||||
| F2 | ||||
| F3 | ||||
| F4 | ||||
| F5 | ||||
| F6 | ||||
| F7 | ||||
| F8 | ||||
| F9 | ||||
| F10 | ||||
| F11 | ||||
| F12 | ||||
| F13 |
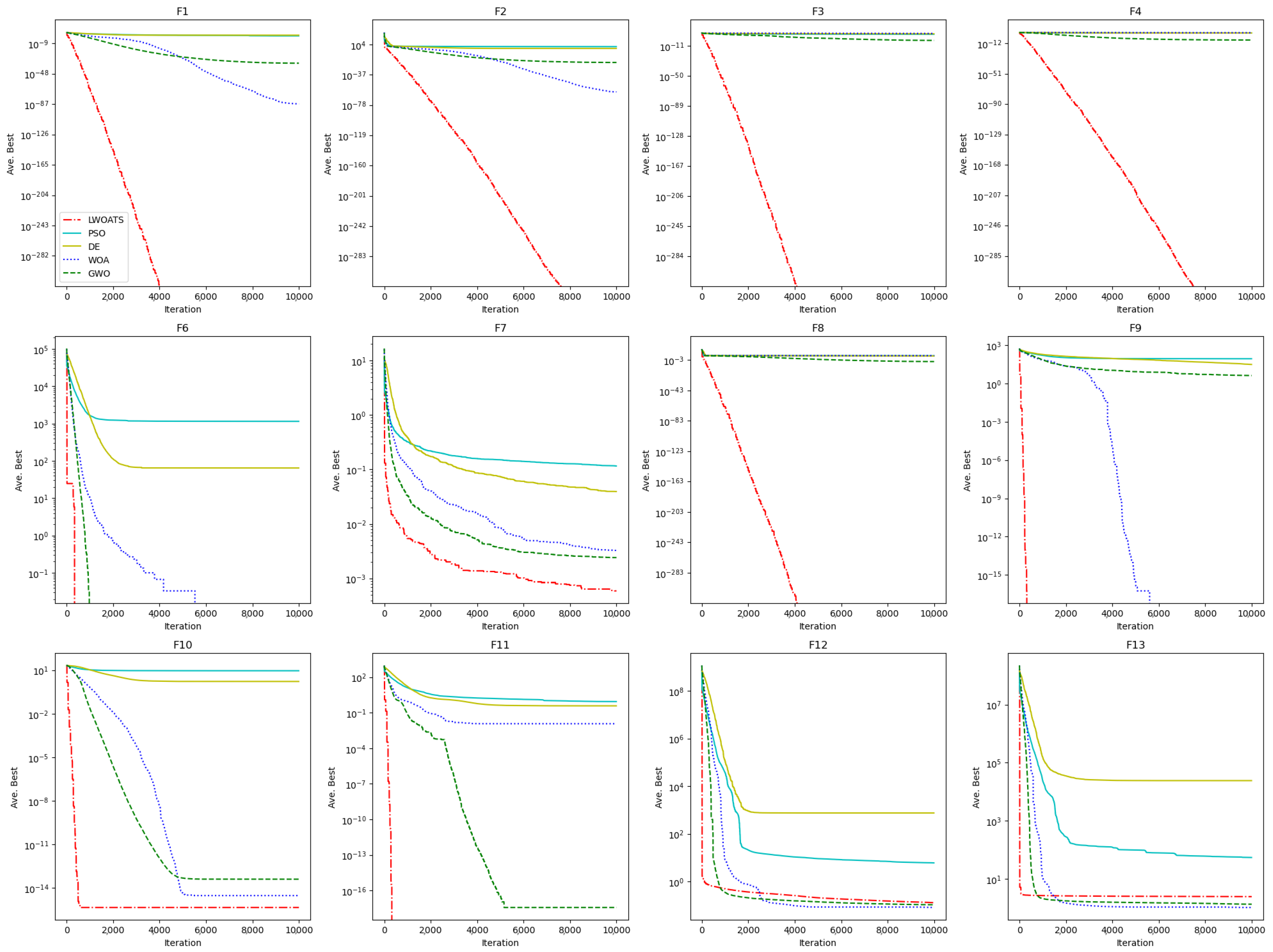
| Comparison | + | − | = | Decision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS vs. DE | 2385 | 870 | 6 | 1 | 3 | −+=+==++++ |
| LWOATS vs. GWO | 3811 | 539 | 9 | 1 | 0 | −++++++++ |
| LWOATS vs. PSO | 2007 | 1237 | 6 | 1 | 3 | −+=+==++++ |
| LWOATS vs. WOA | 3936 | 543 | 9 | 1 | 0 | −+++++++++ |
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | GWO | DE | WOA | LWOATS | ||
| F14 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F15 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F16 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F17 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F18 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F19 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F20 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F21 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F22 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F23 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Function | LWOATS vs. WOA | LWOATS vs. GWO | LWOATS vs. PSO | LWOATS vs. DE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F14 | ||||
| F15 | ||||
| F16 | ||||
| F17 | ||||
| F18 | ||||
| F19 | ||||
| F20 | ||||
| F21 | ||||
| F22 | ||||
| F23 |
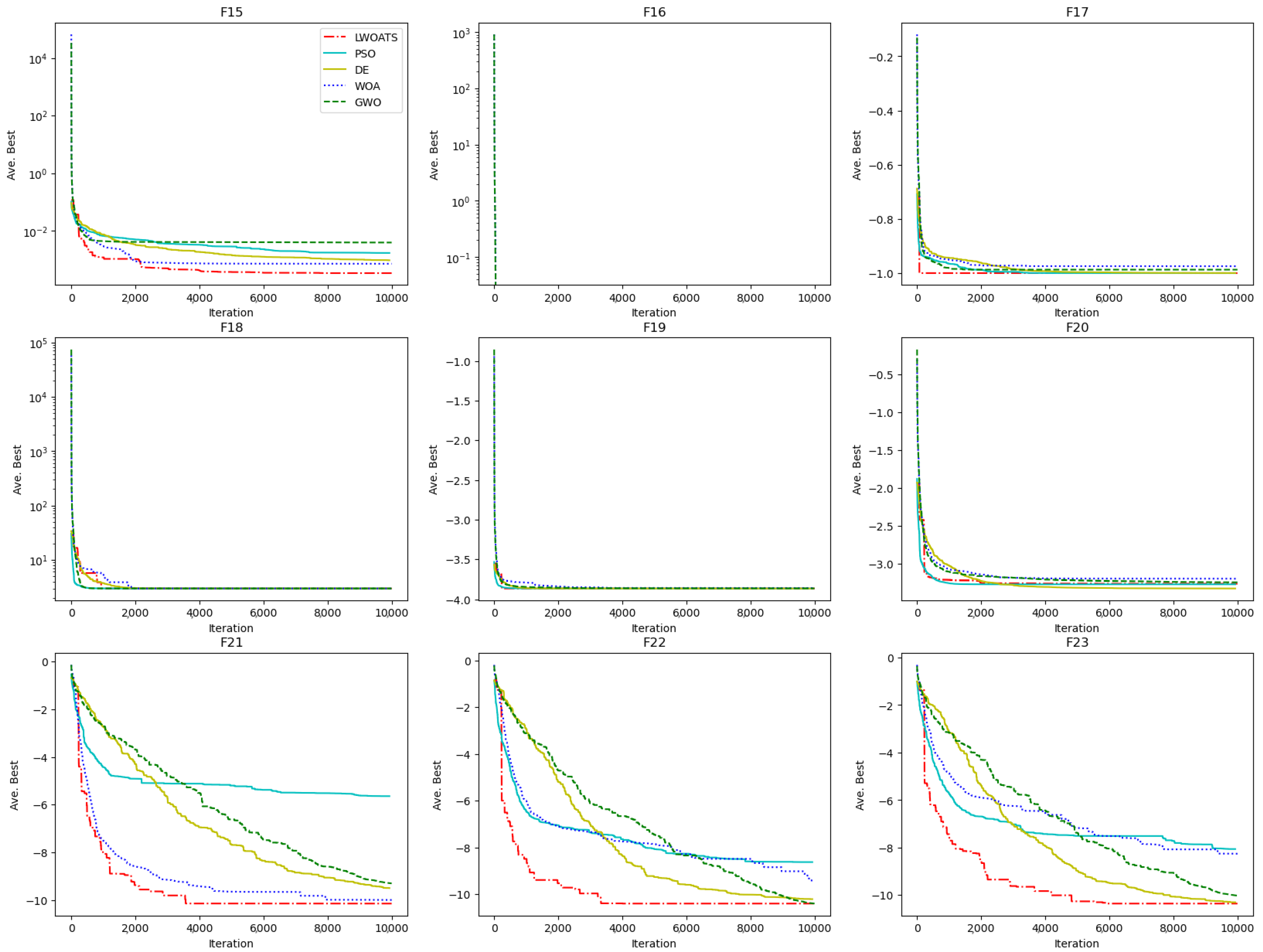
Appendix D.2. LWOATS Compared to Advanced Differential Evolution Variants
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaDE | JADE | iL-SHADE | jSO | LWOATS | ||
| F1 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F2 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F3 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F4 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F5 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F6 | Best | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Worst | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Std | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| F7 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Comparison | + | − | = | Decision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS vs. SaDE | 4981 | 874 | 12 | 1 | 0 | +++++++++++−− |
| LWOATS vs. JADE | 4684 | 926 | 11 | 1 | 1 | +++++=+++++−− |
| LWOATS vs. iL-SHADE | 4216 | 1364 | 9 | 3 | 1 | ++++−=+++++−− |
| LWOATS vs. jSO | 4324 | 1256 | 9 | 3 | 1 | ++++−=+++++−− |
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaDE | JADE | iL-SHADE | jSO | LWOATS | ||
| F8 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F9 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F10 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F11 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F12 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F13 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Function | LWOATS vs. SaDE | LWOATS vs. JADE | LWOATS vs. iL-SHADE | LWOATS vs. jSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | ||||
| F2 | ||||
| F3 | ||||
| F4 | ||||
| F5 | ||||
| F6 | ||||
| F7 | ||||
| F8 | ||||
| F9 | ||||
| F10 | ||||
| F11 | ||||
| F12 | ||||
| F13 |
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaDE | JADE | iL-SHADE | jSO | LWOATS | ||
| F14 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F15 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F16 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F17 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | 0 | 0 | ||||
| F18 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F19 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F20 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F21 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F22 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F23 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Comparison | + | − | = | Decision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS vs. SaDE | 4981 | 874 | 12 | 1 | 0 | +++++++++++−− |
| LWOATS vs. JADE | 4684 | 926 | 11 | 1 | 1 | +++++=+++++−− |
| LWOATS vs. iL-SHADE | 4216 | 1364 | 9 | 3 | 1 | ++++−=+++++−− |
| LWOATS vs. jSO | 4324 | 1256 | 9 | 3 | 1 | ++++−=+++++−− |
| Comparison | + | − | = | Decision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS vs. SaDE | 2875 | 1544 | 7 | 3 | 0 | ++++−−−+++ |
| LWOATS vs. JADE | 2680 | 1505 | 6 | 3 | 1 | +++=−−−+++ |
| LWOATS vs. iL-SHADE | 2707 | 1565 | 6 | 3 | 1 | +++=−−−+++ |
| LWOATS vs. jSO | 2582 | 1603 | 6 | 3 | 1 | +++=−−−+++ |
| Function | LWOATS vs. SaDE | LWOATS vs. JADE | LWOATS vs. iL-SHADE | LWOATS vs. jSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F14 | ||||
| F15 | ||||
| F16 | ||||
| F17 | ||||
| F18 | ||||
| F19 | ||||
| F20 | ||||
| F21 | ||||
| F22 | ||||
| F23 |
Appendix D.3. LWOATS Compared to Other WOA Variations
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSEWOA | NGSWOA | EWOA | WOAmM | LWOATS | ||
| F1 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | 0 | ||||
| F2 | Best | 0 | 0 | |||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F3 | Best | 0 | 0 | |||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | 0 | ||||
| F4 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | |||||
| F5 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F6 | Best | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Worst | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| F7 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSEWOA | NGSWOA | EWOA | WOAmM | LWOATS | ||
| F8 | Best | 0 | 0 | |||
| Worst | 0 | |||||
| Mean | 0 | |||||
| Std | 0 | 0 | ||||
| F9 | Best | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Worst | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| F10 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| F11 | Best | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Worst | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mean | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Std | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| F12 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F13 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Comparison | + | − | = | Decision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS vs. WOAmM | 2683 | 1765 | 5 | 5 | 3 | ++++===+=−=−− |
| LWOATS vs. EWOA | 2771 | 1414 | 6 | 4 | 3 | ++++−=++===−− |
| LWOATS vs. MSEWOA | 2709 | 1476 | 6 | 4 | 3 | ++++−=++===−− |
| LWOATS vs. NGSWOA | 3379 | 806 | 7 | 5 | 1 | +++++==+===+− |
| Function | LWOATS vs. WOAmM | LWOATS vs. EWOA | LWOATS vs. MSEWOA | LWOATS vs. NGSWOA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | ||||
| F2 | ||||
| F3 | ||||
| F4 | ||||
| F5 | ||||
| F6 | ||||
| F7 | ||||
| F8 | ||||
| F9 | ||||
| F10 | ||||
| F11 | ||||
| F12 | ||||
| F13 |
| Function | Result | Algorithms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSEWOA | NGSWOA | EWOA | WOAmM | LWOATS | ||
| F14 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F15 | Best | 0 | ||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F16 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F17 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| F18 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F19 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F20 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F21 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F22 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| F23 | Best | |||||
| Worst | ||||||
| Mean | ||||||
| Std | ||||||
| Comparison | + | − | = | Decision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS vs. WOAmM | 2771 | 1414 | 6 | 3 | 1 | −−+=−+++++ |
| LWOATS vs. EWOA | 3307 | 878 | 7 | 1 | 2 | −++=+++=++ |
| LWOATS vs. MSEWOA | 3060 | 1125 | 6 | 1 | 3 | −++=+++==+ |
| LWOATS vs. NGSWOA | 4101 | 84 | 9 | 0 | 1 | +++=++++++ |
| Function | LWOATS vs. WOAmM | LWOATS vs. EWOA | LWOATS vs. MSEWOA | LWOATS vs. NGSWOA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F14 | ||||
| F15 | ||||
| F16 | ||||
| F17 | ||||
| F18 | ||||
| F19 | ||||
| F20 | ||||
| F21 | ||||
| F22 | ||||
| F23 |
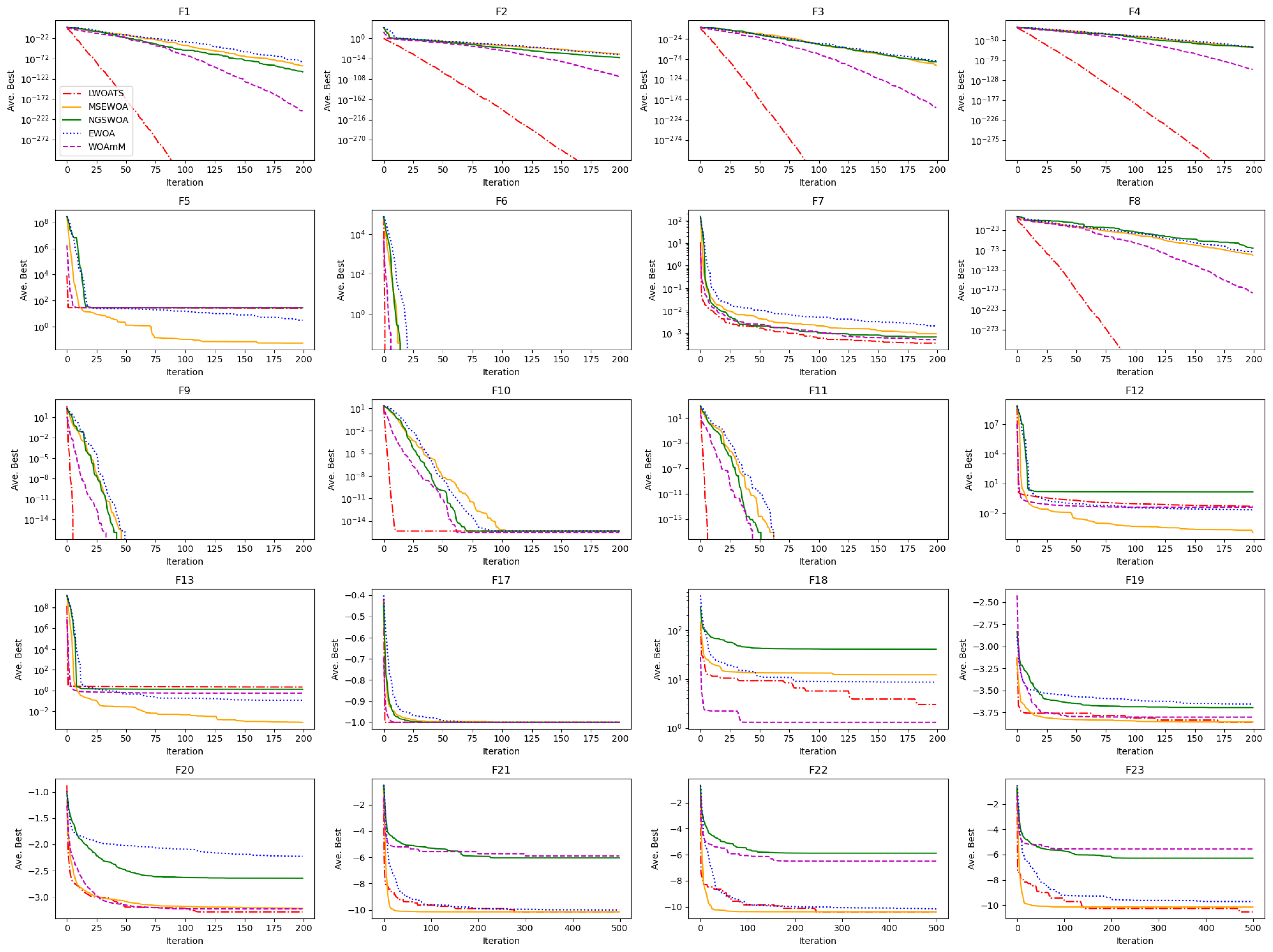
Appendix E. Mathematical Formulation for Engineering Problems
Appendix E.1. Tension/Compression Spring Design
Appendix E.2. Pressure Vessel Design
Appendix E.3. Welded Beam Design
Appendix E.4. Gear Train Design
Appendix E.5. Speed Reducer Design
Appendix E.6. Three-Bar Truss Design
References
- Razmjooy, N.; Ashourian, M.; Foroozandeh, Z. Metaheuristics and Optimization in Computer and Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kaur, P. A comprehensive analysis of nature-inspired meta-heuristic techniques for feature selection problem. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1103–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Sanz, S. Modern meta-heuristics based on nonlinear physics processes: A review of models and design procedures. Phys. Rep. 2016, 655, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O. On the usefulness of non-gradient approaches in topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2011, 43, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokeroglu, T.; Sevinc, E.; Kucukyilmaz, T.; Cosar, A. A survey on new generation metaheuristic algorithms. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 137, 106040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Birattari, M.; Stutzle, T. Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2006, 1, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Genetic algorithms. Sci. Am. 1992, 267, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M. An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.S. A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. In Nature Inspired Cooperative Strategies for Optimization, NICSO; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S. Flower pollination algorithm for global optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Unconventional Computing and Natural Computation, Orléans, France, 3–7 September 2012; pp. 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sanderson, A.C. JADE: Adaptive Differential Evolution With Optional External Archive. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2009, 13, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, R.; Fukunaga, A. Success-history based parameter adaptation for Differential Evolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Cancun, Mexico, 20–23 June 2013; pp. 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, R.; Fukunaga, A.S. Improving the search performance of SHADE using linear population size reduction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014; pp. 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brest, J.; Maučec, M.S.; Bošković, B. iL-SHADE: Improved L-SHADE algorithm for single objective real-parameter optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brest, J.; Maučec, M.S.; Bošković, B. Single objective real-parameter optimization: Algorithm jSO. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Donostia, Spain, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaba, E.; Villar-Rodriguez, E.; Oregi, I.; de Leceta, A.M.F. Focusing on the hybrid quantum computing—Tabu search algorithm: New results on the Asymmetric Salesman Problem. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion (GECCO’21), Lille, France, 10–14 July 2021; pp. 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Duffuaa, S.O. A hybrid algorithm based on tabu search and generalized network algorithm for designing multi-objective supply chain networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 20973–20992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premananda, I.G.A.; Tjahyanto, A.; Mukhlason, A. Efficient iterated local search based metaheuristic approach for solving sports timetabling problems of International Timetabling Competition 2021. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 343, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Dib, O. Application of Metaheuristic Algorithms and Their Combinations to Travelling Salesman Problem. In Intelligent Computing and Optimization, ICO 2023, Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2023; Volume 852, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, A.; Kaveh, A. Sizing optimization of skeletal structures using the enhanced whale optimization algorithm. In Applications of Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms in Civil Engineering; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2017; pp. 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, A.; Ghazaan, M.I. Enhanced whale optimization algorithm for sizing optimization of skeletal structures. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2017, 45, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, M.; Wang, R.; Yu, H.; Wang, S. An image denoising method based on BP neural network optimized by improved whale optimization algorithm. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, R.; Venkataraman, R. Enhancing Whale Optimization Algorithm with Levy Flight for coverage optimization in wireless sensor networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 94, 107359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Houssein, E.H.; Hassanien, A.E.; Taha, A.; Hassanien, E. Maximizing lifetime of wireless sensor networks based on whale optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics 2017; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2018; pp. 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.V.; Mirjalili, S.; Kumar, N.; Alazab, M.; Hwang, W.J. Whale optimization algorithm with applications to resource allocation in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 4285–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenu, K.; Sreelatha, M. W-Scheduler: Whale optimization for task scheduling in cloud computing. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Saha, A.K.; Chhabra, A. Improving whale optimization algorithm with elite strategy and its application to engineering-design and cloud task scheduling problems. Cogn. Comput. 2023, 15, 1497–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Q. Levy flight trajectory-based whale optimization algorithm for global optimization. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 6168–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedabbasi, A. WOASCALF: A new hybrid whale optimization algorithm based on sine cosine algorithm and levy flight to solve global optimization problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2022, 173, 103272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Arora, S. Chaotic whale optimization algorithm. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2018, 5, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, M.; Guo, Q. Modified whale optimization algorithm based on tent chaotic mapping and its application in structural optimization. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 3703–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, I.N.; Jangir, P.; Kumar, A.; Jangir, N.; Totlani, R. A novel hybrid PSO–WOA algorithm for global numerical functions optimization. In Advances in Computer and Computational Sciences: Proceedings of ICCCCS 2016, Volume 2; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, S.; Maadani, M.; Pourmina, M.A. Optimal motion sensor placement in smart homes and intelligent environments using a hybrid WOA-PSO algorithm. J. Reliab. Intell. Environ. 2022, 8, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, H.; Rashid, T. A novel hybrid GWO with WOA for global numerical optimization and solving pressure vessel design. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 14701–14718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Manogaran, G.; El-Shahat, D.; Mirjalili, S. RETRACTED: A hybrid whale optimization algorithm based on local search strategy for the permutation flow shop scheduling problem. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 85, 03–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhan, B.; Zheng, X. A novel whale optimization algorithm of path planning strategy for mobile robots. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 10843–10857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhillar, A.; Choudhary, A. Mobile robot path planning based upon updated whale optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 29–31 January 2020; pp. 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelouah, R.; Siarry, P. Genetic and Nelder–Mead algorithms hybridized for a more accurate global optimization of continuous multiminima functions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 148, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said Solaiman, O.; Sihwail, R.; Shehadeh, H.; Hashim, I.; Alieyan, K. Hybrid Newton–Sperm Swarm Optimization Algorithm for Nonlinear Systems. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihwail, R.; Solaiman, O.S.; Omar, K.; Ariffin, K.A.Z.; Alswaitti, M.; Hashim, I. A Hybrid Approach for Solving Systems of Nonlinear Equations Using Harris Hawks Optimization and Newton’s Method. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 95791–95807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.F.; Tawhid, M.A. A hybrid cuckoo search algorithm with Nelder Mead method for solving global optimization problems. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhouri, H.N.; Hudaib, A.; Sleit, A. Hybrid particle swarm optimization with sine cosine algorithm and Nelder–Mead simplex for solving engineering design problems. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 3091–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.H.; Hsieh, J.G.; Chang, J.Y.; Lin, C.T. Training neural networks via simplified hybrid algorithm mixing Nelder–Mead and particle swarm optimization methods. Soft Comput. 2015, 19, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahara, E.; Kao, Y.T. Hybrid Nelder–Mead simplex search and particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 3880–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, L. Parameter identification of chaotic systems by hybrid Nelder–Mead simplex search and differential evolution algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 3238–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xiao, T.; Fan, W. Hybrid differential evolution and Nelder–Mead algorithm with re-optimization. Soft Comput. 2011, 15, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.F. Hybrid simulated annealing and Nelder-Mead algorithm for solving large-scale global optimization problems. Int. J. Res. Comput. Sci. 2014, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelouah, R.; Siarry, P. A hybrid method combining continuous tabu search and Nelder–Mead simplex algorithms for the global optimization of multiminima functions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2005, 161, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, F. Future paths for integer programming and links to artificial intelligence. Comput. Oper. Res. 1986, 13, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, F. Tabu search: A tutorial. Interfaces 1990, 20, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; WH Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 1, pp. 25–74. [Google Scholar]
- Jensi, R.; Jiji, G.W. An enhanced particle swarm optimization with levy flight for global optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 43, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, S.N.; Bagheri, A.; Najafi, F. PSOSCALF: A new hybrid PSO based on Sine Cosine Algorithm and Levy flight for solving optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 73, 697–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ding, S.; Liang, D.; He, H. A novel particle swarm optimization algorithm with Levy flight and orthogonal learning. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 75, 101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelidari, M.; Hamidzadeh, J. Feature selection by using chaotic cuckoo optimization algorithm with levy flight, opposition-based learning and disruption operator. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 2911–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, B. A novel ant colony optimization algorithm with Levy flight. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 67205–67213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, B.; Li, H. Improving ant colony optimization algorithm with epsilon greedy and Levy flight. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 7, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwah, R.; Kaushik, M.; Chugh, K. A modified whale optimization algorithm to overcome delayed convergence in artificial neural networks. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 10275–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, L. Whale optimization algorithm based on nonlinear convergence factor and chaotic inertial weight. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, N.; Ansari, M.M. Golden jackal optimization: A novel nature-inspired optimizer for engineering applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 198, 116924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Yang, X.S. A literature survey of benchmark functions for global optimisation problems. Int. J. Math. Model. Numer. Optim. 2013, 4, 150–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- xKuZz. PyADE: Python Advanced Differential Evolution Library, version 1.1; GitHub Repository: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm Based on Nonlinear Adaptive Weight and Golden Sine Operator. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 77013–77048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qais, M.; Hasanien, H.; Alghuwainem, S. Enhanced whale optimization algorithm for maximum power point tracking of variable-speed wind generators. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 86, 105937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Miao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, F. Multi-Strategy Ensemble Whale Optimization Algorithm and Its Application to Analog Circuits Intelligent Fault Diagnosis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Saha, A.K.; Sharma, S.; Mirjalili, S.; Chakraborty, R. A novel enhanced whale optimization algorithm for global optimization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 153, 107086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezura-Montes, E.; Coello, C.A. Constraint-handling in nature-inspired numerical optimization: Past, present and future. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2011, 1, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Roy, P.K.; Pal, T. Grey wolf optimization applied to economic load dispatch problems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 83, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Mafarja, M.; Chen, H. Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, L. An effective co-evolutionary particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2007, 20, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomi, A.H.; Yang, X.S.; Alavi, A.H.; Talatahari, S. Bat algorithm for constrained optimization tasks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2013, 22, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 89, 228–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; He, D. A hybrid whale optimization with seagull algorithm for global optimization problems. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Hatamlou, A. Multi-verse optimizer: A nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, A.R. A novel hybrid whale–Nelder–Mead algorithm for optimization of design and manufacturing problems. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 5091–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, E.; Nezamabadi-Pour, H.; Saryazdi, S. GSA: A gravitational search algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2009, 179, 2232–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K. An efficient constraint handling method for genetic algorithms. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2000, 186, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, T.; Liew, K.M. Society and civilization: An optimization algorithm based on the simulation of social behavior. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2003, 7, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. The ant lion optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2015, 83, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadollah, A.; Bahreininejad, A.; Eskandar, H.; Hamdi, M. Mine blast algorithm: A new population based algorithm for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2013, 13, 2592–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. Grasshopper optimization algorithm: Theory and application. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 105, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomi, A.H.; Yang, X.S.; Alavi, A.H. Cuckoo search algorithm: A metaheuristic approach to solve structural optimization problems. Eng. Comput. 2013, 29, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.K.; Pant, M.; Singh, V.P. Improved local search in artificial bee colony using golden section search. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1210.6128. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K.; Goyal, M. A combined genetic adaptive search (GeneAS) for engineering design. Comput. Sci. Inform. 1996, 26, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, B.K.; Kramer, S.N. An augmented Lagrange multiplier based method for mixed integer discrete continuous optimization and its applications to mechanical design. J. Mech. Des. 1994, 116, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Liu, J.; Ni, F.; Zhang, L. Hybrid Strategies Based Seagull Optimization Algorithm for Solving Engineering Design Problems. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, G.; Kumar, V. Spotted hyena optimizer: A novel bio-inspired based metaheuristic technique for engineering applications. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, O.K.; Pauline, O.; Kiong, S.C.; Wahab, H.A.; Jafferi, N. Application of modified flower pollination algorithm on mechanical engineering design problem. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Johor, Malaysia, 18–19 December 2016; Volume 165, p. 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezura-Montes, E.; Coello, C.A.C.; Landa-Becerra, R. Engineering optimization using simple evolutionary algorithm. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, Sacramento, CA, USA, 5 November 2003; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothiya, S.; Ngamroo, I.; Kongprawechnon, W. Ant colony optimisation for economic dispatch problem with non-smooth cost functions. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2010, 32, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Krishan, M.M. A non-convex economic load dispatch problem with valve loading effect using a hybrid grey wolf optimizer. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 12127–12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkoffash, M.S.; Awadallah, M.A.; Alweshah, M.; Zitar, R.A.; Assaleh, K.; Al-Betar, M.A. A non-convex economic load dispatch using hybrid salp swarm algorithm. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 8721–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Khader, A.T.; Bolaji, A.L.A. Tournament-based harmony search algorithm for non-convex economic load dispatch problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 47, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Algorithm | Parameters |
|---|---|
| WOA | , , , |
| DE | , , |
| PSO | , |
| LWOATS | Same parameters with WOA, for Levy flights |
| Source | sum_sq | df | f-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(pop_size) | 7.3 | 4 | 14.7 | |
| C(elite_size_ratio) | 5.4 | 2 | 21.9 | |
| C(local_search_max_iter) | 0.7 | 4 | 1.5 | |
| C(tabu_size_ratio) | 0.05 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Source | sum_sq | df | f-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(pop_size) | 3.5 | 4 | 8.9 | |
| C(elite_size_ratio) | 1.6 | 2 | 8.2 | |
| C(local_search_max_iter) | 0.2 | 4 | 0.5 | |
| C(tabu_size_ratio) | 0.07 | 2 | 0.4 |
| Algorithm | Parameter | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| SaDE | Crossover Probability (), Mutation Factor (F) | , |
| JADE | Proportion of best solutions (p), Parameter control (c) | , |
| iL-SHADE | Memory Size (H) | |
| jSO | Memory Size (H) |
| Algorithm | d | D | N | Best |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS | 0.05168889 | 0.35671364 | 11.28920611 | 0.012665233 |
| HHO [73] | 0.051796393 | 0.359305355 | 11.138859 | 0.012665443 |
| GWO [11] | 0.05169 | 0.356737 | 11.28885 | 0.012666 |
| MFO [76] | 0.051994457 | 0.36410932 | 10.868421862 | 0.0126669 |
| GJO [64] | 0.0515793 | 0.354055 | 11.4484 | 0.01266752 |
| BAT [75] | 0.05169 | 0.35673 | 11.2885 | 0.01267 |
| WSOA [77] | 0.0512 | 0.3441 | 12.0663 | 0.01267 |
| CPSO [74] | 0.051728 | 0.357644 | 11.244543 | 0.0126747 |
| WOA [22] | 0.051207 | 0.345215 | 12.004032 | 0.0126763 |
| MVO [78] | 0.05 | 0.315956 | 14.22623 | 0.0144644 |
| Algorithm | HHO | GWO | MFO | GJO | BAT | WSOA | CPSO | WOA | MVO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0017 | 0.0061 | 0.0132 | 0.0181 | 0.0376 | 0.0376 | 0.0747 | 0.0874 | 14.206 |
| Algorithm | h | l | t | b | Best Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS | 0.20572986 | 3.47048573 | 9.03661999 | 0.20573003 | 1.724854 |
| HWOANM [79] | 0.2057 | 3.4714 | 9.0366 | 0.2057 | 1.72491 |
| MVO [78] | 0.205463 | 3.473193 | 9.044502 | 0.205695 | 1.72645 |
| GWO [11] | 0.205676 | 3.478377 | 9.03681 | 0.205778 | 1.72624 |
| GJO [64] | 0.20562 | 3.4719 | 9.0392 | 0.20572 | 1.72522 |
| WOA [22] | 0.205396 | 3.484293 | 9.037426 | 0.206276 | 1.730499 |
| CPSO [74] | 0.202369 | 3.544214 | 9.048210 | 0.205723 | 1.73148 |
| WSOA [77] | 0.1919 | 3.7633 | 9.1090 | 0.2054 | 1.7519 |
| GSA [80] | 0.182129 | 3.856979 | 10.00000 | 0.202376 | 1.879952 |
| GA [81] | 0.2489 | 6.1730 | 8.1789 | 0.2533 | 2.43312 |
| SCA [82] | 0.2440 | 6.238 | 8.2886 | 0.2446 | 2.3854 |
| Algorithm | HWOANM | GJO | GWO | MVO | WOA | CPSO | WSOA | GSA | SCA | GA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 1.57 | 9.0 | 38.3 | 41.1 |
| Algorithm | R | L | Best Cost | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS | 0.77816867 | 0.38464916 | 40.31961884 | 200 | 5885.3329 |
| GJO [64] | 0.7782955 | 0.3848046 | 40.32187 | 200 | 5887.071123 |
| WSOA [77] | 0.8056 | 0.4081 | 41.7401 | 181.1285 | 5964.6114 |
| HHO [73] | 0.81758383 | 0.4072927 | 42.09174576 | 176.7196352 | 6000.46259 |
| GWO [11] | 0.812500 | 0.434500 | 42.089181 | 176.758731 | 6051.5639 |
| MFO [76] | 0.8125 | 0.4375 | 42.098445 | 176.636596 | 6059.7143 |
| WOA [22] | 0.812500 | 0.437500 | 42.0982699 | 176.638998 | 6059.7410 |
| MVO [78] | 0.8125 | 0.4375 | 42.0907382 | 176.738690 | 6060.8066 |
| CPSO [74] | 0.8125 | 0.4375 | 42.091266 | 176.746500 | 6061.0777 |
| GSA [80] | 1.1250 | 0.6250 | 55.9886598 | 84.4542025 | 8538.8359 |
| Algorithm | GJO | WSOA | HHO | GWO | MFO | WOA | MVO | CPSO | GSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03 | 1.35 | 1.96 | 2.83 | 2.96 | 2.96 | 2.98 | 2.99 | 45.09 |
| Algorithm | Best Cost | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS | 0.78867344 | 0.40825308 | 263.89584339 |
| HHO [73] | 0.788662816 | 0.40828313383 | 263.89584348 |
| ALO [83] | 0.788662816000317 | 0.408283133832901 | 263.895843488 |
| GJO [64] | 0.788657163482708 | 0.408299125193296 | 263.8958439 |
| MVO [78] | 0.78860276 | 0.408453070 | 263.8958499 |
| MBA [84] | 0.7885650 | 0.4085597 | 263.8958522 |
| GOA [85] | 0.788897555578973 | 0.407619570115153 | 263.895881496069 |
| MFO [76] | 0.788244771 | 0.409466905784741 | 263.8959797 |
| SCA [82] | 0.78669 | 0.41426 | 263.9348 |
| CS [86] | 0.78867 | 0.40902 | 263.9716 |
| Algorithm | Best Cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LWOATS | 43 | 19 | 16 | 49 | |
| ALO [83] | 49 | 19 | 16 | 43 | |
| CS [86] | 43 | 16 | 19 | 49 | |
| ABC [87] | 19 | 16 | 44 | 49 | |
| GA [88] | 33 | 14 | 17 | 50 | |
| ALM [89] | 33 | 15 | 13 | 41 |
| Algorithm | Best Cost | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISOA [90] | 3.40385 | 0.7 | 17 | 7.74585 | 7.76495 | 3.32186 | 5.25780 | 2973.9175 |
| LWOATS | 3.50007075 | 0.7 | 17 | 7.30298402 | 7.71628516 | 3.35025427 | 5.28666227 | 2994.5614 |
| GJO [64] | 3.500003 | 0.7 | 17 | 7.321686 | 7.72122 | 3.35025 | 5.28665 | 2994.80495 |
| CS [86] | 3.5015 | 0.7 | 17 | 7.6050 | 7.8181 | 3.3520 | 5.2875 | 3000.981 |
| MFPA [92] | 3.5 | 0.7 | 17 | 7.3 | 7.8005 | 3.35021 | 5.28668 | 2996.219 |
| SHO [91] | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2998.550 |
| EA [93] | 3.506163 | 0.700831 | 17 | 7.46018 | 7.962143 | 3.3629 | 5.3090 | 3025.005 |
| Unit No. | (MW) | (MW) | a | b | c | d | e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 680 | 550 | 8.1000 | 0.00028 | 300 | 0.0350 |
| 2 | 0 | 360 | 309 | 8.1000 | 0.00056 | 200 | 0.0420 |
| 3 | 0 | 360 | 307 | 8.1000 | 0.00056 | 200 | 0.0420 |
| 4 | 60 | 180 | 240 | 7.7400 | 0.00324 | 150 | 0.0630 |
| 5 | 60 | 180 | 240 | 7.7400 | 0.00324 | 150 | 0.0630 |
| 6 | 60 | 180 | 240 | 7.7400 | 0.00324 | 150 | 0.0630 |
| 7 | 60 | 180 | 240 | 7.7400 | 0.00324 | 150 | 0.0630 |
| 8 | 60 | 180 | 240 | 7.7400 | 0.00324 | 150 | 0.0630 |
| 9 | 60 | 180 | 240 | 7.7400 | 0.00324 | 150 | 0.0630 |
| 10 | 40 | 120 | 126 | 8.6000 | 0.00284 | 100 | 0.0840 |
| 11 | 40 | 120 | 126 | 8.6000 | 0.00284 | 100 | 0.0840 |
| 12 | 55 | 120 | 126 | 8.6000 | 0.00284 | 100 | 0.0840 |
| 13 | 55 | 120 | 126 | 8.6000 | 0.00284 | 100 | 0.0840 |
| Unit No. | LWOATS | Unit No. | LWOATS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 680 | 8 | 159.65872993 |
| 2 | 360 | 9 | 109.82395927 |
| 3 | 352.78337842 | 10 | 114.55725804 |
| 4 | 159.66741217 | 11 | 42.55544494 |
| 5 | 109.82971340 | 12 | 55.51997359 |
| 6 | 159.73314659 | 13 | 56.11272851 |
| 7 | 159.75833436 | ||
| Best fuel cost: 24,105.684 USD/h | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koulianos, A.; Litke, A.; Papadakis, N.K. A Hybrid Whale Optimization Approach for Fast-Convergence Global Optimization. J. Exp. Theor. Anal. 2025, 3, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jeta3020017
Koulianos A, Litke A, Papadakis NK. A Hybrid Whale Optimization Approach for Fast-Convergence Global Optimization. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Analyses. 2025; 3(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jeta3020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoulianos, Athanasios, Antonios Litke, and Nikolaos K. Papadakis. 2025. "A Hybrid Whale Optimization Approach for Fast-Convergence Global Optimization" Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Analyses 3, no. 2: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jeta3020017
APA StyleKoulianos, A., Litke, A., & Papadakis, N. K. (2025). A Hybrid Whale Optimization Approach for Fast-Convergence Global Optimization. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Analyses, 3(2), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jeta3020017






