Use of Rituximab to Attempt Recapture of Immune Tolerance to Pegloticase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligible Patients
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Treatment Protocol
2.4. Study Endpoints
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA | Anti-Drug Antibodies |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| MMF | Mycophenolate Mofetil |
| MSU | Monosodium Urate |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| PEG | Pegloticase |
| RTX | Rituximab |
| SU | Serum Urate |
| ULT | Urate-Lowering Therapy |
| XOI | Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor |
References
- Becker, M.A.; Schumacher, H.R.; Benjamin, K.L.; Gorevic, P.; Greenwald, M.; Fessel, J.; Edwards, L.; Kawata, A.K.; Frank, L.; Waltrip, R.; et al. Quality of life and disability in patients with treatment-failure gout. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, V.; Khanna, D.; Singh, J.A.; Forsythe, A.; Edwards, N.L. Improved health-related quality of life and physical function in patients with refractory chronic gout following treatment with pegloticase: Evidence from phase III randomized controlled trials. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundy, J.S.; Baraf, H.S.B.; Yood, R.A.; Edwards, N.L.; Gutierrez-Urena, S.R.; Treadwell, E.L.; Vazquez-Mellado, J.; White, W.B.; Lipsky, P.E.; Horowitz, Z.; et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of Pegloticase for the Treatment of Chronic Gout in Patients Refractory to Conventional Treatment Two Randomized Controlled Trials. JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2011, 306, 711–720. [Google Scholar]
- Botson, J.K.; Tesser, J.R.P.; Bennett, R.; Kenney, H.M.; Peloso, P.M.; Obermeyer, K.; LaMoreaux, B.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Peterson, J. Pegloticase in Combination with Methotrexate in Patients with Uncontrolled Gout: A Multicenter, Open-label Study (MIRROR). J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, P.E.; Calabrese, L.H.; Kavanaugh, A.; Sundy, J.S.; Wright, D.; Wolfson, M.; Becker, M.A. Pegloticase immunogenicity: The relationship between efficacy and antibody development in patients treated for refractory chronic gout. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botson, J.K.; Saag, K.; Peterson, J.; Parikh, N.; Ong, S.; La, D.; LoCicero, K.; Obermeyer, K.; Xin, Y.; Chamberlain, J.; et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of Methotrexate to Increase Response Rates in Patients with Uncontrolled Gout Receiving Pegloticase: Primary Efficacy and Safety Findings. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.P.; Khanna, D.; Cutter, G.; Foster, J.; Melnick, J.; Jaafar, S.; Biggers, S.; Rahman, A.; Kuo, H.C.; Feese, M.; et al. Reducing Immunogenicity of Pegloticase with Concomitant Use of Mycophenolate Mofetil in Patients with Refractory Gout: A Phase II, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troum, O.M.; Botson, J.K.; Obermeyer, K.; Chao, B.; Song, Y.; Zarzoso, J.; Gutierrez, K.; Verma, S.; Padnick-Silver, L.; LaMoreaux, B. Pegloticase and Methotrexate Cotherapy in Patients with Uncontrolled Gout with Prior Pegloticase Monotherapy Failure: Findings of an Open-Label Trial. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2025, 7, e11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklin, P.S.; Morris, P.J.; Knight, S.R. A systematic review of the use of rituximab for the treatment of antibody-mediated renal transplant rejection. Transplant. Rev. 2017, 31, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djamali, A.; Muth, B.L.; Ellis, T.M.; Mohamed, M.; Fernandez, L.A.; Miller, K.M.; Bellingham, J.M.; Odorico, J.S.; Mezrich, J.D.; Pirsch, J.D.; et al. Increased C4d in post-reperfusion biopsies and increased donor specific antibodies at one-week post transplant are risk factors for acute rejection in mild to moderately sensitized kidney transplant recipients. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajuli, S.; Mandelbrot, D.A.; Muth, B.; Mohamed, M.; Garg, N.; Aziz, F.; Redfield, R.R.; Zhong, W.; Astor, B.C.; Djamali, A. Rituximab and Monitoring Strategies for Late Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation. Transplant. Direct 2017, 3, e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, A.A.; Lukovsky, M.; Toyoda, M.; Wang, J.; Reinsmoen, N.L.; Lai, C.H.; Peng, A.; Villicana, R.; Jordan, S.C. Rituximab and intravenous immune globulin for desensitization during renal transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, A.A.; Choi, J.; Cisneros, K.; Reinsmoen, N.; Haas, M.; Ge, S.; Toyoda, M.; Kahwaji, J.; Peng, A.; Villicana, R.; et al. Benefits of rituximab combined with intravenous immunoglobulin for desensitization in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 2014, 98, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Rituxan (rituximab) Injection for Intravenous Use, Package Insert; Federal Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1997.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Krystexxa (pegloticase) Injection for Intravenous Use, Package Insert; Federal Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2010.
- Neogi, T.; Jansen, T.L.; Dalbeth, N.; Fransen, J.; Schumacher, H.R.; Berendsen, D.; Brown, M.; Choi, H.; Edwards, N.L.; Janssens, H.J.; et al. 2015 Gout Classification Criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2557–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershfield, M.S.; Ganson, N.J.; Kelly, S.J.; Scarlett, E.L.; Jaggers, D.A.; Sundy, J.S. Induced and pre-existing anti-polyethylene glycol antibody in a trial of every 3-week dosing of pegloticase for refractory gout, including in organ transplant recipients. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietz, K.; John, R.; Schuster, M.; Ankersmit, J.; Burke, E.; Suciu-Foca, N.; Edwards, N.; Mancini, D.; Itescu, S. Mycophenolate mofetil reduces anti-HLA antibody production and cellular rejection in heart transplant recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2002, 34, 1828–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, M.; Kitade, H.; Mathieu, C.; Waer, M.; Pirenne, J. Inhibitory and stimulatory effects of cyclosporine A on the development of regulatory T cells in vivo. Transplantation 2005, 79, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.Y.; Huh, K.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.I.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, Y.S. Rituximab and hepatitis B reactivation in HBsAg-negative/anti-HBc-positive kidney transplant recipients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2017, 32, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seree-Aphinan, C.; Ratanapokasatit, Y.; Suchonwanit, P.; Rattanakaemakorn, P.; O-Charoen, P.; Pisitkun, P.; Suangtamai, T.; Setthaudom, C.; Chirasuthat, S.; Chanprapaph, K. Optimal time for COVID-19 vaccination in rituximab-treated dermatologic patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1138765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westra, J.; van Assen, S.; Wilting, K.R.; Land, J.; Horst, G.; de Haan, A.; Bijl, M. Rituximab impairs immunoglobulin (Ig)M and IgG (subclass) responses after influenza vaccination in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 178, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safety and Efficacy Study of Intravenous Uricase-PEG 20. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01021241 (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Dang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, G.; Song, W.; Wang, B. Effects of losartan and irbesartan on serum uric acid in hypertensive patients with hyperuricaemia in Chinese population. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2006, 20, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokose, C.; McCormick, N.; Abhishek, A.; Dalbeth, N.; Pascart, T.; Liote, F.; Gaffo, A.; FitzGerald, J.; Terkeltaub, R.; Sise, M.E.; et al. The clinical benefits of sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors in people with gout. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghukasyan, H.; Pedro Navalha, D.D.; Pérez Romero, I.; Prato Wolwacz, M.V.; Ghahramanyan, A.; Tsing Ngan, C.W.; Siqueira Tavares de Melo, M.H.; Serafim Dagostin, C.; Gómez-Lechón Quirós, L. Reducing hyperuricemic events with SGLT2 inhibitors: An updated systematic review with meta-regression. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. (Engl. Ed.) 2025, 72, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Wk −12 | Wk −6 | Wk 0 | Pegloticase 8 mg IV q 2 Weeks | Wk 26 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rituximab 1000 mg IV, twice | Pt 1 | ↓↓ | ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ | ||||||
| Pt 2 | ↓↓ | ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ | |||||||
| Methotrexate 15 mg po weekly | Pt 1 | MTX | |||||||
| Pt 2 | |||||||||
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016–2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023–2024 | 2025 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | ||||||||
| PEG | ↓ ↓ * | |||||||
| MTX-PEG | ↓ ↓ † | |||||||
| RTX-MTX-PEG | ↓ *, † | |||||||
| Patient 2 | ||||||||
| PEG | ↓ ↓ *, † | |||||||
| MMF-PEG | ↓… ↓ ↓ *, † | |||||||
| RTX-MTX-PEG | ↓ ↓ † |
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53 (current), 18 (age at onset) | 43, (current), 20 (age at onset) |
| Prior Urate-Lowering Therapies |
|
|
| Anti-inflammatory therapy | Prednisone 10 mg daily Anakinra 100 mg daily Colchicine 0.6 mg, twice daily | Prednisone 10 mg (up to 20 mg) Anakinra 100 mg daily Colchicine 0.6 mg, twice daily |
| Pre-treatment clinical images | 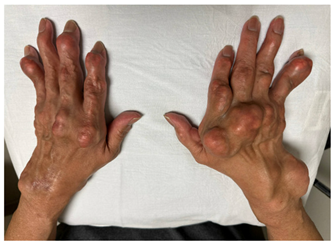 | 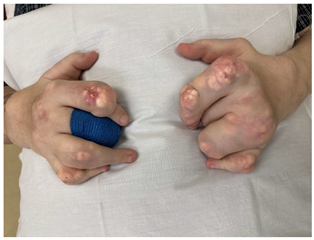 |
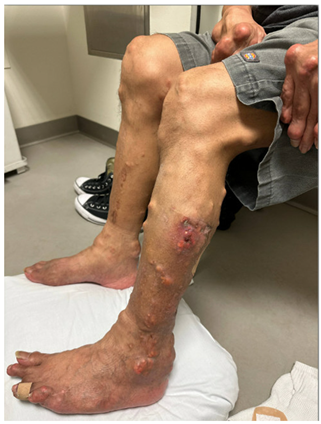 | 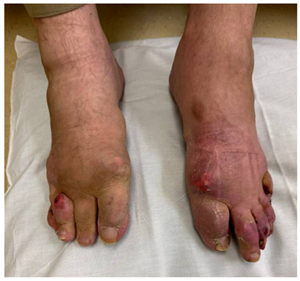 |
| Patient 1 | Date | 2 May 2024 16 May 2024 | 13 June 2024 (Week 6) | 27 June 2024 | ||
| RTX 1000 mg ×2 | PEG #1, 8 mg | |||||
| Methotrexate 15 mg weekly | ||||||
| Urate (mg/dL) | 9.8 | 9.0 | 9.9 | |||
| CD19 | 148 | 0 | ||||
| Patient 2 | Date | 9 August 2024 30 August 2024 | 8 November 2024 (Week 12) | 22 November 2024 | 5 December 2024 | |
| RTX 1000 mg ×2 | PEG #1, 8 mg | PEG #2, 8 mg | ||||
| Methotrexate 15 mg weekly | ||||||
| Urate (mg/dL) | 11.0 | 11.1 | 7.5 | 9.8 | ||
| CD19 | Not Administered | 0 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Gout, Hyperuricemia and Crystal Associated Disease Network. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
FitzGerald, J.D.; Kachru, R.; Xie, C.; Ranganath, V.K. Use of Rituximab to Attempt Recapture of Immune Tolerance to Pegloticase. Gout Urate Cryst. Depos. Dis. 2025, 3, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/gucdd3030018
FitzGerald JD, Kachru R, Xie C, Ranganath VK. Use of Rituximab to Attempt Recapture of Immune Tolerance to Pegloticase. Gout, Urate, and Crystal Deposition Disease. 2025; 3(3):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/gucdd3030018
Chicago/Turabian StyleFitzGerald, John D., Rita Kachru, Chen Xie, and Veena K. Ranganath. 2025. "Use of Rituximab to Attempt Recapture of Immune Tolerance to Pegloticase" Gout, Urate, and Crystal Deposition Disease 3, no. 3: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/gucdd3030018
APA StyleFitzGerald, J. D., Kachru, R., Xie, C., & Ranganath, V. K. (2025). Use of Rituximab to Attempt Recapture of Immune Tolerance to Pegloticase. Gout, Urate, and Crystal Deposition Disease, 3(3), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/gucdd3030018







