Biochemical Properties of the Acid Ectophosphatase Activity of Phytomonas serpens Involved in Cell Proliferation
Abstract
1. Introduction
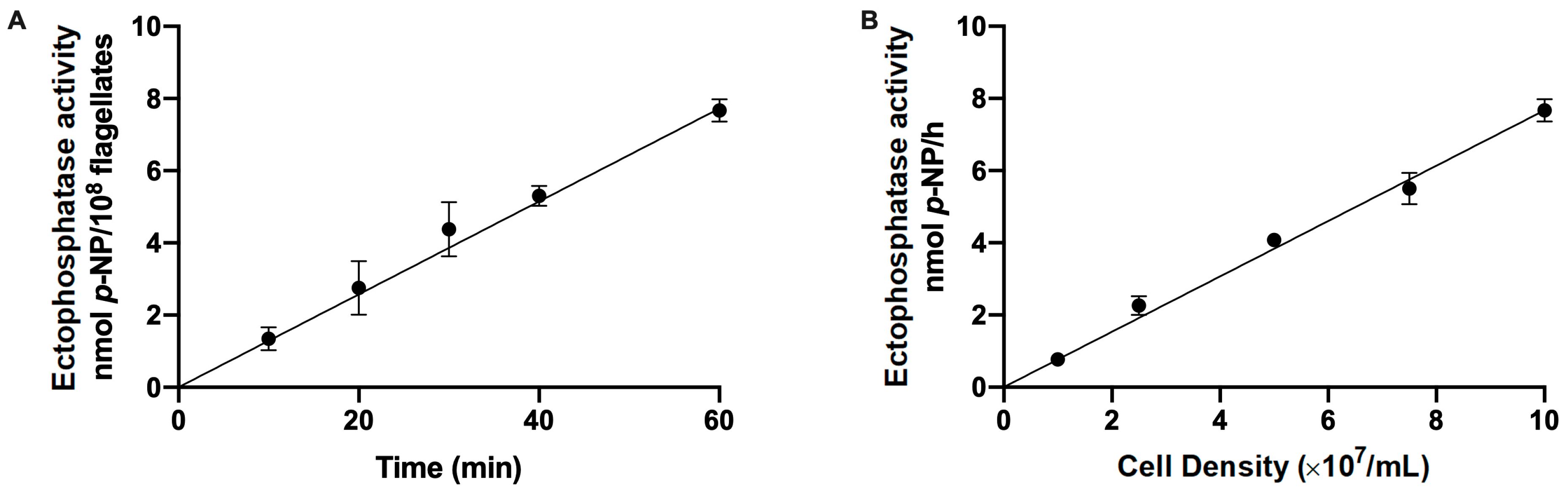
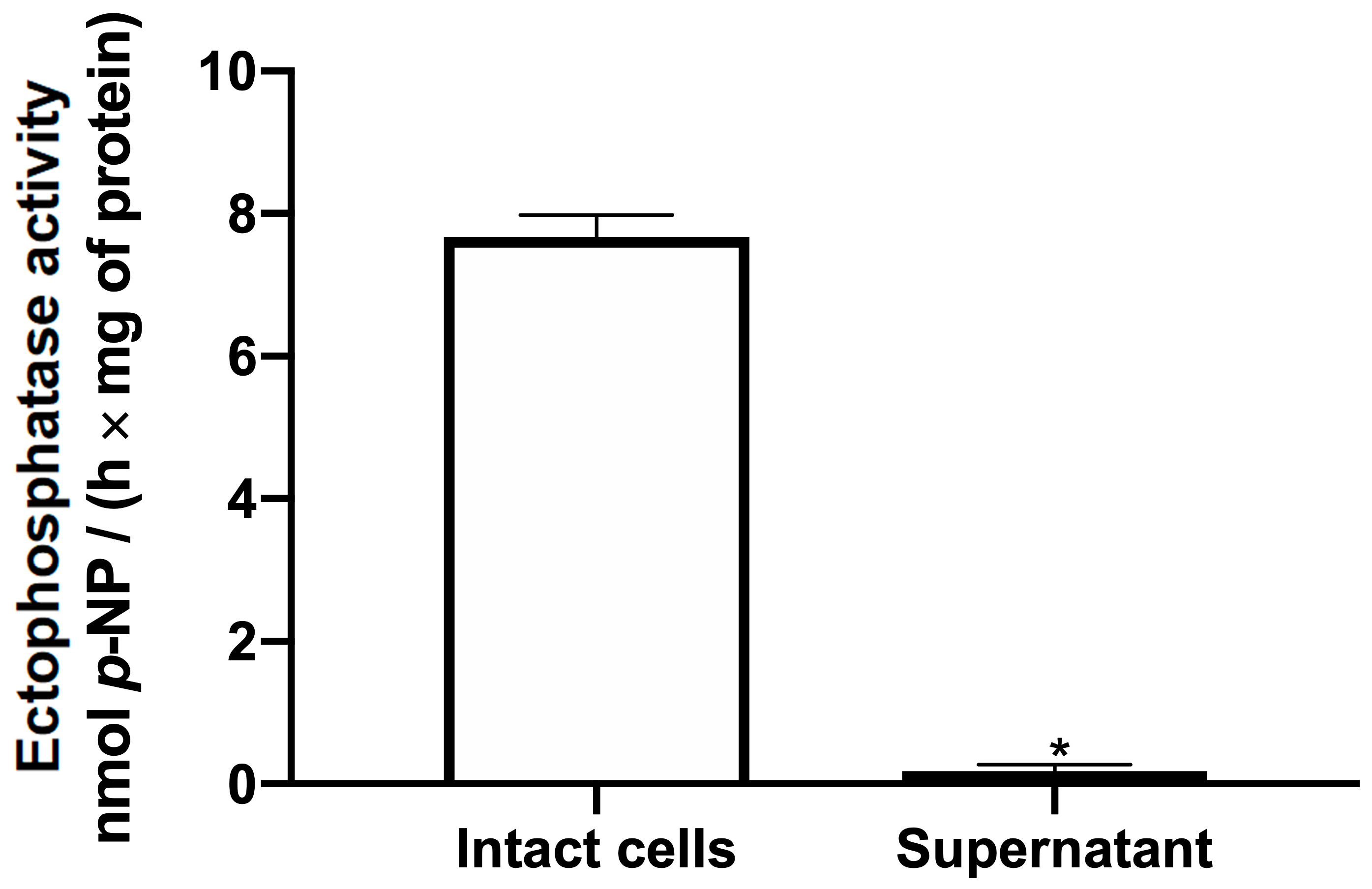
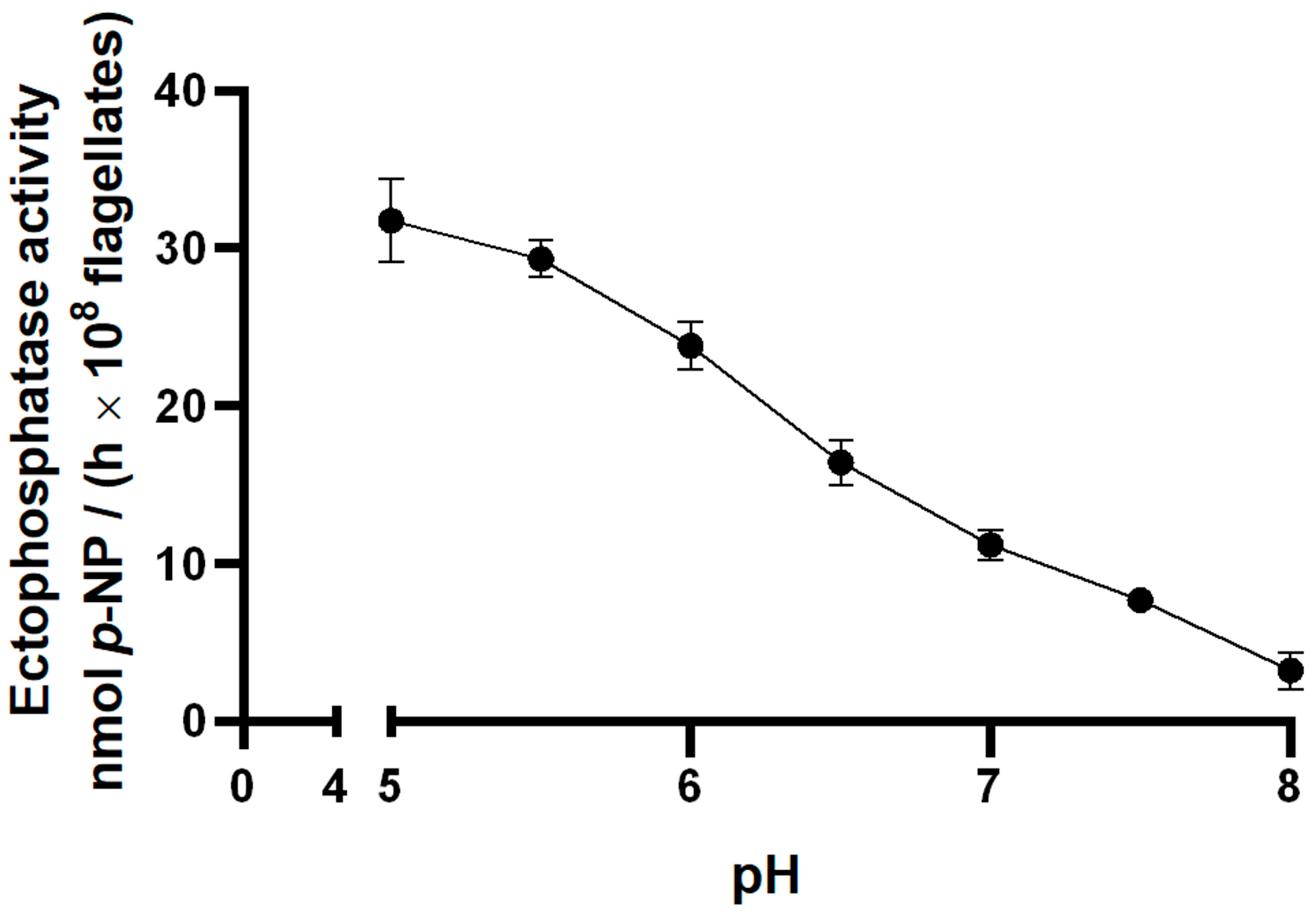
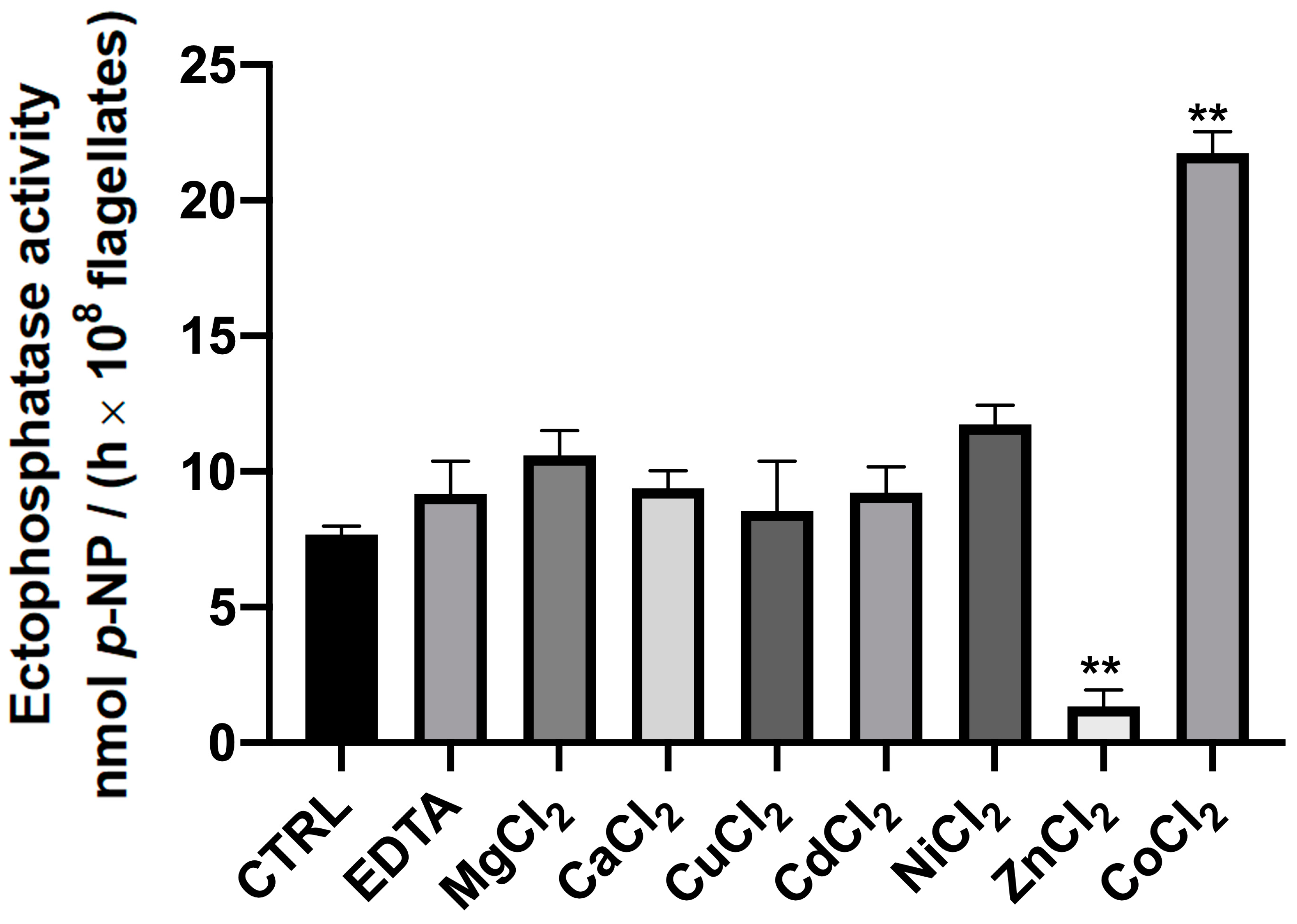
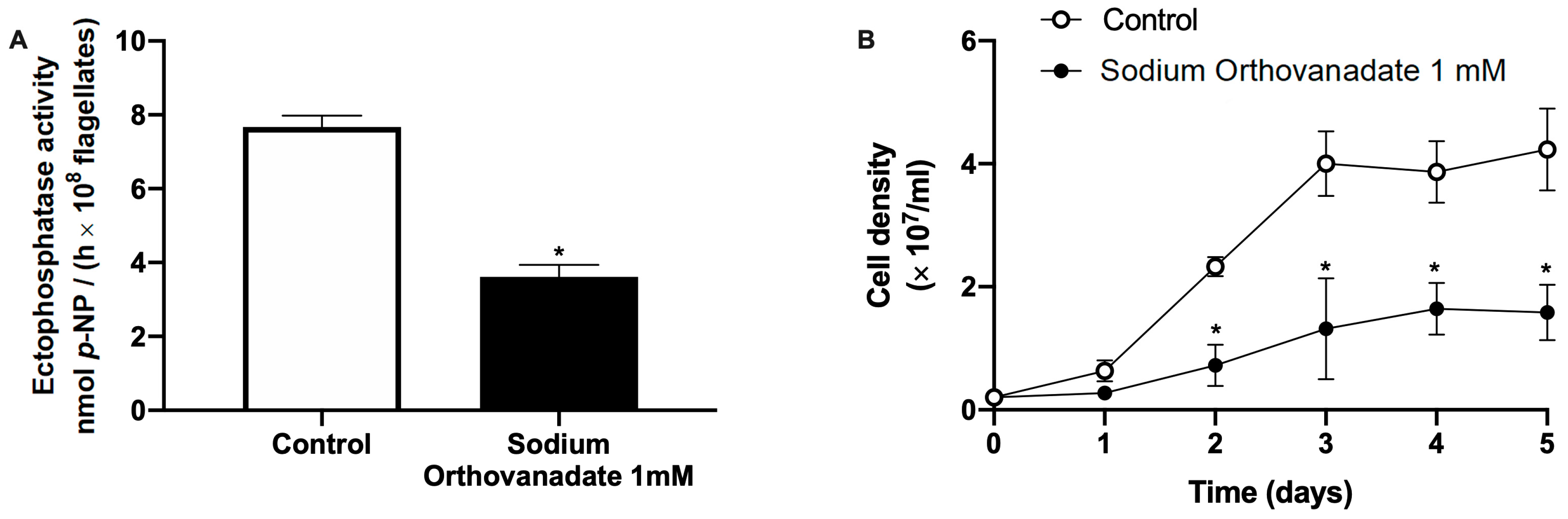
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaskowska, E.; Butler, C.; Preston, G.; Kelly, S. Phytomonas: Trypanosomatids adapted to plant environments. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.A.C.; Silva, K.P.; Souza, G.B.; Alves, P.B.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S.; Scher, R.; Fernandes, R.P.M. Chalcone Derivative Induces Flagellar Disruption and Autophagic Phenotype in Phytomonas serpens In Vitro. Pathogens 2024, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, J.C.A.; Pereira, J.C.R.; Gasparotto, L. Murcha-de-Phytomonas Do Coqueiro No Amazonas. Circ. Técnica 2003, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, E.P. Phytomonas and other trypanosomatid parasites of plants and fruit. Adv. Parasitol. 1999, 42, 29–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwelm, A.; Badstöber, J.; Bulman, S.; Desoignies, N.; Etemadi, M.; Falloon, R.E.; Gachon, C.M.M.; Legreve, A.; Lukeš, J.; Merz, U.; et al. Not in Your Usual Top 10: Protists That Infect Plants and Algae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1029–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.A.; Santos, T.A.C.; de Andrade Nascimento, L.F.; de Jesus, R.A.; Blank, A.F.; Scher, R.; de Souza Moraes, V.R.; Arrigoni-de Fátima Arrigoni-Blank, M.; Fernandes, R.P.M. Anti-Phytomonas activity of the lyophilized residues obtained from the distillation of Lantana camara L. essential oil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 58988–58998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breganó, J.W.; Picão, R.C.; Graça, V.K.; Menolli, R.A.; Jankevicius, S.I.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Jankevicius, J.V. Phytomonas serpens, a tomato parasite, shares antigens with Trypanosoma cruzi that are recognized by human sera and induce protective immunity in mice. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 39, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinge-Filho, P.; Peron, J.P.S.; De Moura, T.R.; Menolli, R.A.; Graça, V.K.; Estevão, D.; Tadokoro, C.E.; Jankevicius, J.V.; Rizzo, L.V. Protective immunity against Trypanosoma cruzi provided by oral immunization with Phytomonas serpens: Role of nitric oxide. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 96, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graça-de-Souza, V.K.; Monteiro-Góes, V.; Manque, P.; Souza, T.A.C.B.; Corrêa, P.R.C.; Buck, G.A.; Ávila, A.R.; Yamauchi, L.M.; Pinge-Filho, P.; Goldenberg, S.; et al. Sera of chagasic patients react with antigens from the tomato parasite Phytomonas serpens. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos-Júnior, A.D.C.M.; Ricart, C.A.O.; Pontes, A.H.; Fontes, W.; Souza, A.R.D.; Castro, M.S.; Lima, B.D. Proteome analysis of Phytomonas serpens, a phytoparasite of medical interest. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.A.; Souza dos Santos, A.L.; Santos Lery, L.M.; Alves e Silva, T.L.; Oliveira, M.M.; Bisch, P.M.; Saraiva, E.M.; Souto-Padrón, T.C.; Lopes, A.H. Evidence that a laminin-like insect protein mediates early events in the interaction of a phytoparasite with its vector’s salivary gland. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Avila-Levy, C.M.; Santos, L.O.; Marinho, F.A.; Dias, F.A.; Lopes, A.H.; Santos, A.L.; Branquinha, M.H. Gp63-like molecules in Phytomonas serpens: Possible role in the insect interaction. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.L.S.; d’Avila-Levy, C.M.; Dias, F.A.; Ribeiro, R.O.; Pereira, F.M.; Elias, C.G.; Souto-Padrón, T.; Lopes, A.H.; Alviano, C.S.; Branquinha, M.H.; et al. Phytomonas serpens: Cysteine peptidase inhibitors interfere with growth, ultrastructure and host adhesion. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos-Santos, A.L.A.; Dick, C.F.; Alves-Bezerra, M.; Silveira, T.S.; Paes, L.S.; Gondim, K.C.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Interaction between Trypanosoma rangeli and the Rhodnius prolixus salivary gland depends on the phosphotyrosine ecto-phosphatase activity of the parasite. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catta-Preta, C.M.C.; Nascimento, M.T.C.; Garcia, M.C.F.; Saraiva, E.M.; Motta, M.C.M.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. The presence of a symbiotic bacterium in Strigomonas culicis is related to differential ecto-phosphatase activity and influences the mosquito–protozoa interaction. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collopy-Junior, I.; Esteves, F.F.; Nimrichter, L.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Alviano, C.S.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. An ectophosphatase activity in Cryptococcus neoformans. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006, 6, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiffer-Moreira, T.; de Sá Pinheiro, A.A.; Alviano, W.S.; Barbosa, F.M.; Souto-Padrón, T.; Nimrichter, L.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Alviano, C.S.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. An ectophosphatase activity in Candida parapsilosis influences the interaction of fungi with epithelial cells. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007, 7, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiffer-Moreira, T.; de Sá Pinheiro, A.A.; Pinto, M.R.; Esteves, F.F.; Souto-Padrón, T.; Barreto-Bergter, E.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Mycelial forms of Pseudallescheria boydii present ectophosphatase activities. Arch Microbiol. 2007, 188, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneipp, L.F.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Holandino, C.; Esteves, F.F.; Souto-Padrón, T.; Alviano, C.S.; Travassos, L.R.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Ectophosphatase activity in conidial forms of Fonsecaea pedrosoi is modulated by exogenous phosphate and influences fungal adhesion to mammalian cells. Microbiology 2004, 150, 3355–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneipp, L.F.; Magalhães, A.S.; Abi-Chacra, E.A.; Souza, L.O.P.; Alviano, C.S.; Santos, A.L.S.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Surface phosphatase in Rhinocladiella aquaspersa: Biochemical properties and its involvement with adhesion. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino-Gomes, D.; Rocco-Machado, N.; Santi, L.; Broetto, L.; Vainstein, M.H.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; Schrank, A.; Beys-da-Silva, W.O. Inhibition of ecto-phosphatase activity in conidia reduces adhesion and virulence of Metarhizium anisopliae on the host insect Dysdercus peruvianus. Curr. Microbiol. 2013, 66, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Vieira, A.L.; Paes-Vieira, L.; Zamboni, D.K.B.B.; Dos-Santos, A.L.A.; Dick, C.F.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Ectophosphatase activity in the early-diverging fungus Blastocladiella emersonii: Biochemical characterization and possible role on cell differentiation. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2018, 117, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, P.M.; Rodrigues, C.O.; Jesus, J.B.; Lopes, A.H.; Souto-Padrón, T.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. A novel ecto-phosphatase activity of Herpetomonas muscarum muscarum inhibited by platelet-activating factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 253, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, P.M.; Rodrigues, C.O.; Romeiro, A.; Grillo, L.A.; Dias, F.A.; Attias, M.; De Souza, W.; Lopes, A.H.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Characterization of ectophosphatase activities in trypanosomatid parasites of plants. Phytopathology 2000, 90, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Passos-Lemos, A.; Fonseca-de-Souza, A.L.; de Sá Pinheiro, A.A.; Berrêdo-Pinho, M.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Ecto-phosphatase activity on the cell surface of Crithidia deanei. Z. Naturforsch C J. Biosci. 2002, 57, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.C.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Aoyama, H.; Fonseca, F.V.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; Vercesi, A.E. A metallo phosphatase activity present on the surface of Trypanosoma brucei procyclic forms. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 118, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida-Amaral, E.E.; Belmont-Firpo, R.; Vannier-Santos, M.A.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Leishmania amazonensis: Characterization of an ecto-phosphatase activity. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 114, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, P.M.L.; Couto, L.C.; Lopes, A.H.C.S.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Characterization of ecto-phosphatase activities of Trypanosoma cruzi: A comparative study between Colombiana and Y strains. Acta Trop. 2006, 100, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.A.O.; Fonseca De Souza, A.L.; Silva, B.A.; Kiffer-Moreira, T.; Santos-Mallet, J.R.; Santos, A.L.S.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Trypanosoma rangeli: Differential expression of cell surface polypeptides and ecto-phosphatase activity in short and long epimastigote forms. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 112, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-de-Souza, A.L.; Dick, C.F.; Dos Santos, A.L.A.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. A Mg2+-dependent ecto-phosphatase activity on the external surface of Trypanosoma rangeli modulated by exogenous inorganic phosphate. Acta Trop. 2008, 107, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jesus, J.B.; Podlyska, T.M.; Hampshire, A.L.C.S.; Vannier-Santos, M.A.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Characterization of an ecto-phosphatase activity in the human parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sá Pinheiro, A.A.; Amazonas, J.N.; de Souza Barros, F.; De Menezes, L.F.; Batista, E.J.O.; Silva, E.F.; De Souza, W.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Entamoeba histolytica: An ecto-phosphatase activity regulated by oxidation–reduction reactions. Exp. Parasitol. 2007, 115, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amazonas, J.N.; Cosentino-Gomes, D.; Werneck-Lacerda, A.; de Sá Pinheiro, A.A.; Lanfredi-Rangel, A.; de Souza, W.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Giardia lamblia: Characterization of ecto-phosphatase activities. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 121, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho-Kelly, L.F.; Freitas-Mesquita, A.L.; Pralon, C.F.; de Souza-Maciel, E.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Identification and characterization of an ectophosphatase activity involved in Acanthamoeba castellanii adhesion to host cells. Eur. J. Protistol. 2023, 91, 126026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Mesquita, A.L.; Carvalho-Kelly, L.F.; Majerowicz, T.S.S.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Euglena gracilis: Biochemical properties of a membrane bound ecto-phosphatase activity modulated by fluoroaluminate complexes and different trophic conditions. Eur. J. Protistol. 2023, 91, 126010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Mesquita, A.L.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Ecto-nucleotidases and ecto-phosphatases from Leishmania and Trypanosoma parasites. Subcell Biochem. 2014, 74, 217–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furuya, T.; Zhong, L.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R.; Lu, H.G.; Moreno, S.N.; Docampo, R. Ecto-protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in Trypanosoma cruzi infective stages. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1998, 92, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyhrman, S. Ectoenzymes in Prorocentrum minimum. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, C.M.; Aoyama, H. Effect of copper on the activation of the acid phosphatase from the green algae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. BioMetals 2010, 23, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, D.; Mayes, M.A.; Wang, G. Kinetic parameters of phosphatase: A quantitative synthesis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiorek, M.; Wyszkowski, M. Effect of cobalt on environment and living organisms—A review. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2019, 17, 11419–11449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Lu, H.G.; Moreno, S.N.J.; Docampo, R. Tyrosine phosphate hydrolysis of host proteins by Trypanosoma cruzi is linked to cell invasion. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 161, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Mesquita, A.L.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Biochemical properties and possible roles of ectophosphatase activities in fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyer, G.; Liu, S.; Kelly, J.; Moffat, J.; Payette, P.; Kennedy, B.; Tsaprailis, G.; Gresser, M.J.; Ramachandran, C. Mechanism of inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatases by vanadate and pervanadate. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-de-Souza, A.L.; Dick, C.F.; Dos Santos, A.L.A.; Fonseca, F.V.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Trypanosoma rangeli: A possible role for ecto-phosphatase activity on cell proliferation. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 122, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, C.F.; Dos Santos, A.L.; Majerowicz, D.; Gondim, K.C.; Caruso-Neves, C.; Silva, I.V.; Vieyra, A.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Na+-dependent and Na+-independent mechanisms for inorganic phosphate uptake in Trypanosoma rangeli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo-Abrahão, T.; Alves-Bezerra, M.; Majerowicz, D.; Freitas-Mesquita, A.L.; Dick, C.F.; Gondim, K.C.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Transport of inorganic phosphate in Leishmania infantum and compensatory regulation at low inorganic phosphate concentration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2683–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, C.F.; Dos Santos, A.L.; Majerowicz, D.; Paes, L.S.; Giarola, N.L.; Gondim, K.C.; Vieyra, A.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Inorganic phosphate uptake in Trypanosoma cruzi is coupled to K(+) cycling and to active Na(+) extrusion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4265–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo-Abrahão, T.; Koeller, C.M.; Steinmann, M.E.; Silva-Rito, S.; Marins-Lucena, T.; Alves-Bezerra, M.; Giarola, N.L.; de Paula, I.F.; Gonzalez-Salgado, A.; Sigel, E.; et al. H+-dependent inorganic phosphate uptake in Trypanosoma brucei is influenced by myo-inositol transporter. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2017, 49, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Kelly, L.F.; Gomes-Vieira, A.L.; Paes-Vieira, L.; da Silva, A.D.Z.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Leishmania amazonensis inorganic phosphate transporter system is increased in the proliferative forms. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2019, 233, 111212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho-de-Araújo, A.D.; Carvalho-Kelly, L.F.; Dick, C.F.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Inorganic phosphate transporter in Giardia duodenalis and its possible role in ATP synthesis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2022, 251, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Kelly, L.F.; Pralon, C.F.; Rocco-Machado, N.; Nascimento, M.T.; Carvalho-de-Araújo, A.D.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Acanthamoeba castellanii phosphate transporter (AcPHS) is important to maintain inorganic phosphate influx and is related to trophozoite metabolic processes. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2020, 52, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho-Kelly, L.F.; Dick, C.F.; Rocco-Machado, N.; Gomes-Vieira, A.L.; Paes-Vieira, L.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Anaerobic ATP synthesis pathways and inorganic phosphate transport and their possible roles in encystment in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Bernardo, R.; Gomes-Vieira, A.L.; Carvalho-Kelly, L.F.; Russo-Abrahão, T.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. The biochemical characterization of two phosphate transport systems in Phytomonas serpens. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 173, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeh, M.; Ahmed, Y.; Quinn, J. Phosphate Acquisition and Virulence in Human Fungal Pathogens. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Fernandes, J.; Vieyra, A. Pyrophosphate formation from acetyl phosphate and orthophosphate: Evidence for heterogeneous catalysis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1988, 266, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microorganism | Optimal pH Range | Km | Vmax | Inhibitory Metals | Stimulant Metals | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phytomonas françai | acid | 0.36 ± 0.06 (mM p-NPP) | 5.34 ± 0.02 nmol Pi/(mg protein × min) | Zn2+ | ND | [24] |
| Phytomonas mcgheei | acid | 1.33 ± 0.27 (mM p-NPP) | 8.54 ± 0.68 nmol Pi/(mg protein × min) | Zn2+ | Cu2+ | [24] |
| Angomonas deanei | ND | 5.35 ± 0.84 (mM p-NPP) | 6.93 ± 0.42 nmol Pi/(h × 108 cells) | Zn2+ | ND | [25] |
| Herpetomonas muscarum | acid | 0.76 ± 0.04 (mM p-NPP) | 4.90 ± 0.46 nmol Pi/(mg protein × min) | Zn2+ | Al3+ | [23] |
| Leishmania amazonensis | ND | 1.78 ± 0.32 (mM p-NPP) | 31.93 ± 3.04 nmol Pi/(h × 107 cells) | Zn2+ | ND | [27] |
| Strigomonas culicis | acid | ND | ND | Zn2+ | Mg2+ | [15] |
| Trypanosoma brucei | acid | 0.66 ± 0.09 (mM p-NPP) | 0.72 ± 0.07 nmol p-NP/(mg protein × min) | Zn2+ | Mg2+ Mn2+ Co2+ Cu2+ | [26] |
| Trypanosoma cruzi (Y strain) | acid | 8.6 (mM p-NPP) | 3.9 nmol p-NP/(mg protein × min) | Zn2+ | ND | [28] |
| Trypanosoma cruzi (Colombiana strain) | acid | 1.6 (mM p-NPP) | 37.0 nmol p-NP/(mg protein × min) | ND | ND | [28] |
| Trypanosoma rangeli (Macias strain) | alkaline | 1.04 ± 0.16 (mM p-NPP) | 8.94 ± 0.36 nmol p-NP/(h × 107 cells) | ND | Mg2+ | [30] |
| Trypanosoma rangeli (H14 strain—short forms) | acid | 3.48 ± 0.62 (mM p-NPP) | 26.27 ± 1.10 nmol p-NP/(h × 107 cells) | Zn2+ | Mg2+ | [29] |
| Trypanosoma rangeli (H14 strain—long forms) | acid | 0.22 ± 0.04 (mM p-NPP) | 17.10 ± 1.07 nmol p-NP/(h × 107 cells) | Zn2+, Ca2+ | Mg2+ Mn2+, Sr2+ | [29] |
| Acanthamoeba castellanii | acid | 2.12 ± 0.54 (mM p-NPP) | 26.12 ± 2.53 nmol Pi/(h × 106 cells) | ND | Mg2+ Co2+ Ni2+ | [34] |
| Euglena gracilis | acid | 2.52 ± 0.12 (mM p-NPP) | 3.62 ± 0.06 nmol Pi/(h × 106 cells) | Zn2+ | Cu2+ | [35] |
| Entamoeba histolytica | acid | 2.68 ± 0.25 (mM p-NPP) | 8.00 ± 0.22 nmol Pi/(h × 105 cells) | Zn2+ | ND | [32] |
| Giardia duodenalis | acid | ND | ND | ND | ND | [33] |
| Trichomonas vaginalis | acid | 0.24 ± 0.02 (mM p-NPP) | 167.2 ± 19.8 nmol Pi/(h × 107 cells) | Zn2+ | ND | [31] |
| Blastocladiella emersonii | alkaline | 1.34 ± 0.18 (mM p-NPP) | 5.29 ± 0.27 nmol Pi/(min × 107 cells) | ND | ND | [22] |
| Candida parapsilosis | acid | 0.47 ± 0.05 (mM p-NPP) | 26.80 ± 1.13 nmol Pi/(h × 107 cells) | Zn2+ | Cu2+ | [17] |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | acid | 29.2 ± 3.3 (mM p-NPP) | 110.9 ± 8.1 nmol p-NP/(h × 108 cells) | Zn2+ | ND | [16] |
| Fonsecae pedrosoi | acid | 15.12 ± 3.55 (mM p-NPP) | 18.07 ± 2.30 nmol p-NP/(h × 107 cells) | ND | Fe3+ | [19] |
| Metarhizium anisopliae | acid | ND | ND | Zn2+, Cu2+, Cd2+ | ND | [21] |
| Pseudallescheria boydii | alkaline | 6.66 ± 1.0 (mM p-NPP) | 103.0 ± 8.6 nmol p-NP/(mg dry weight × min) | Cu2+, Cd2+ | Mg2+, Mn2+, Zn2+ | [18] |
| Rhinocladiella aquaspersa | acid | 3.08 ± 0.38 (mM p-NPP) | 24.46 ± 1.04 nmol p-NP/(h × 107 cells) | ND | Co2+ | [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho-Kelly, L.F.; Freitas-Mesquita, A.L.; Majerowicz, T.S.S.; Meyer-Fernandes, J.R. Biochemical Properties of the Acid Ectophosphatase Activity of Phytomonas serpens Involved in Cell Proliferation. Kinases Phosphatases 2024, 2, 379-390. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2040024
Carvalho-Kelly LF, Freitas-Mesquita AL, Majerowicz TSS, Meyer-Fernandes JR. Biochemical Properties of the Acid Ectophosphatase Activity of Phytomonas serpens Involved in Cell Proliferation. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2024; 2(4):379-390. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho-Kelly, Luiz Fernando, Anita Leocadio Freitas-Mesquita, Thaís Souza Silveira Majerowicz, and José Roberto Meyer-Fernandes. 2024. "Biochemical Properties of the Acid Ectophosphatase Activity of Phytomonas serpens Involved in Cell Proliferation" Kinases and Phosphatases 2, no. 4: 379-390. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2040024
APA StyleCarvalho-Kelly, L. F., Freitas-Mesquita, A. L., Majerowicz, T. S. S., & Meyer-Fernandes, J. R. (2024). Biochemical Properties of the Acid Ectophosphatase Activity of Phytomonas serpens Involved in Cell Proliferation. Kinases and Phosphatases, 2(4), 379-390. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2040024






