Evidence and Modification of Non-Visual Eyestalk Organs in Troglobiont Mysida and Stygiomysida (Crustacea)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
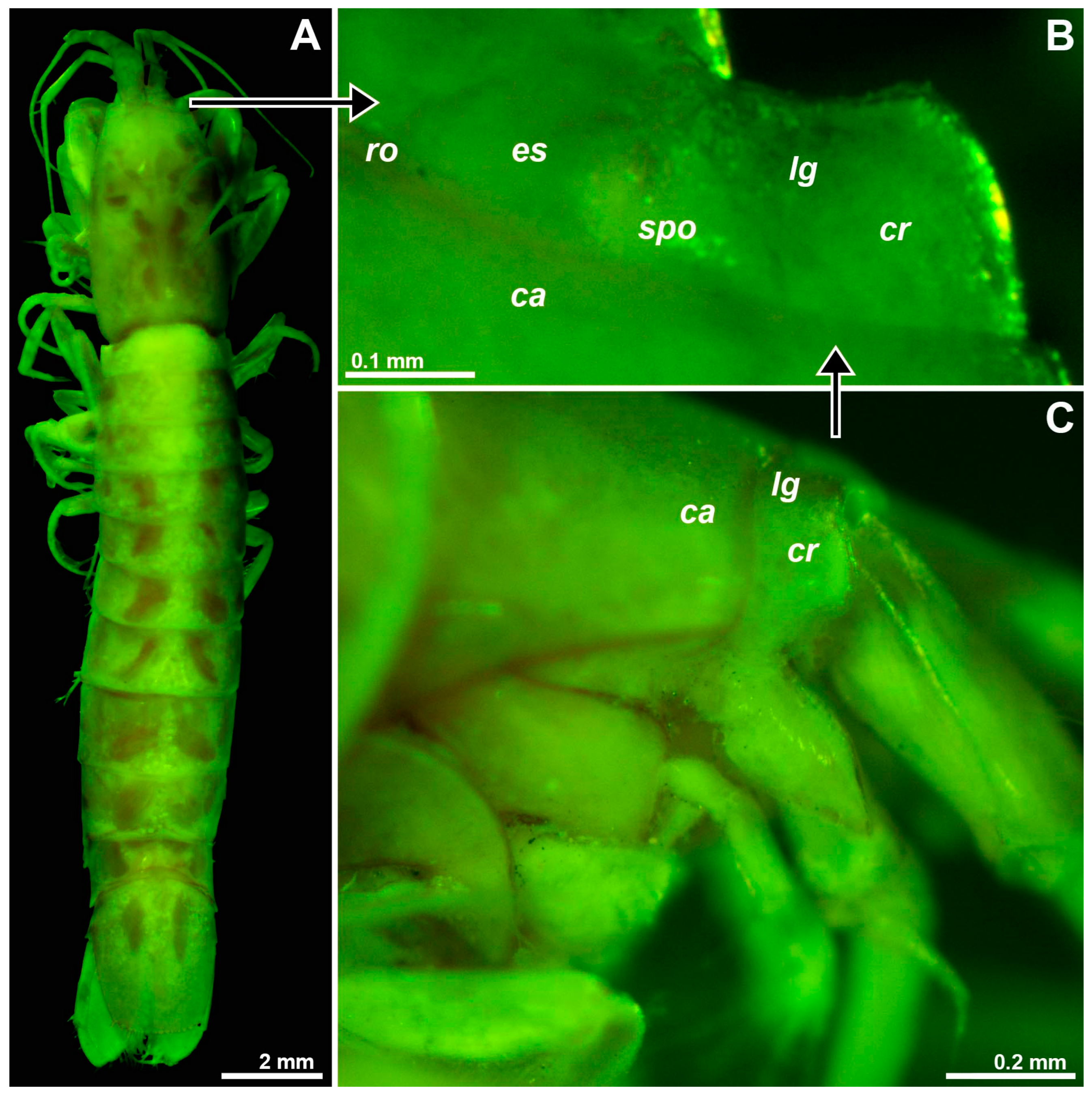
2.1. Terminology and Definitions
2.2. Materials
2.3. Methods
2.4. Abbreviations
- BL = body length (mm)
- DD = decimal degrees of geographic coordinates
- EL = eye length (mm) measured along the midline
- N1–N3 = nauplioid larvae at substages N1 to N3
- OB = Organ of Bellonci
- OBL = length (µm) of OB
- psu = practical salinity unit
- SPO = sensory pore organ
- TR = troglophilia with ‘level’ increasing from the trogloxene to troglophile and troglobiont categories
3. Results
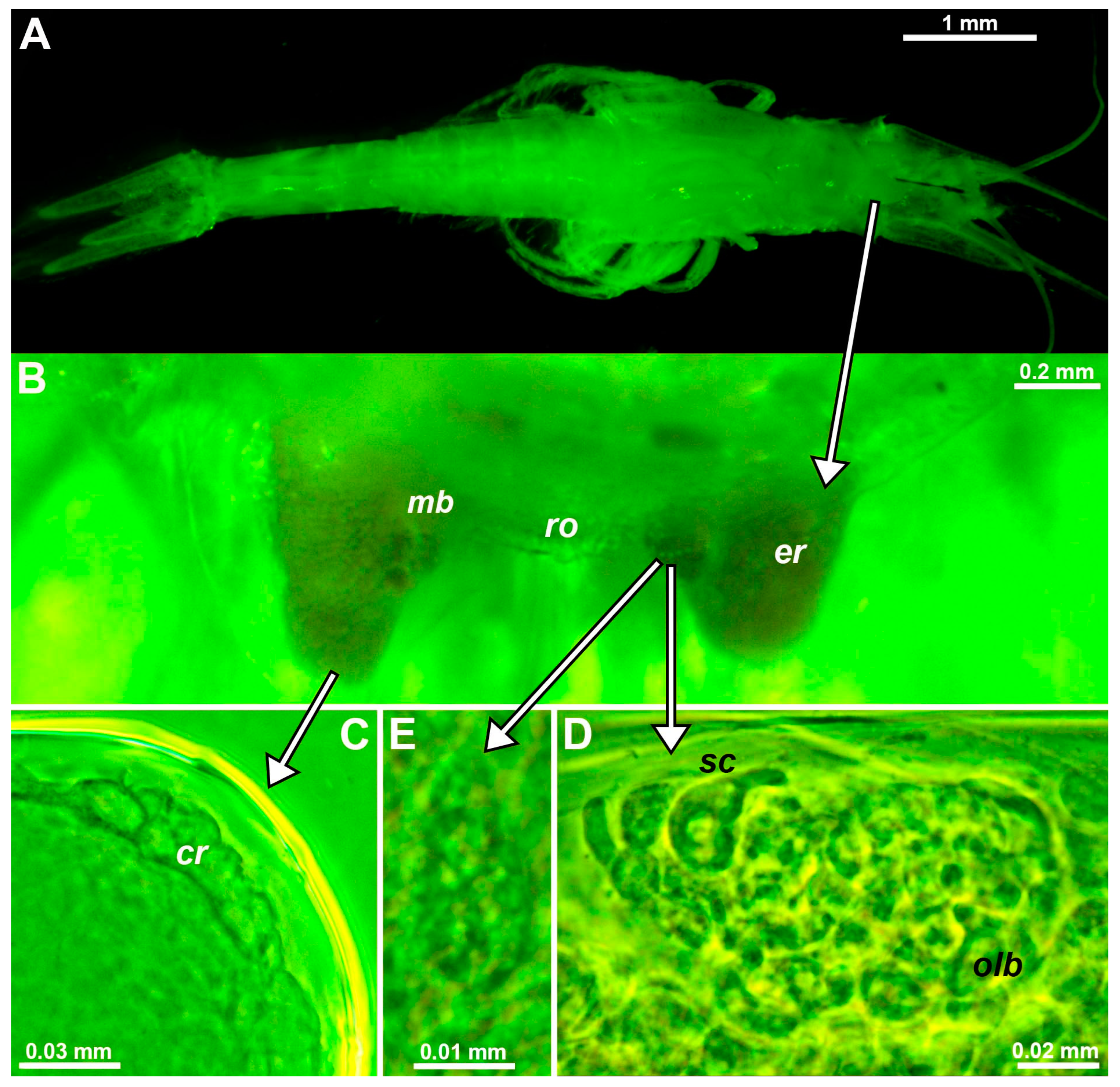
3.1. Eye Structure in Mysida
3.1.1. Structure of Adult Eyes
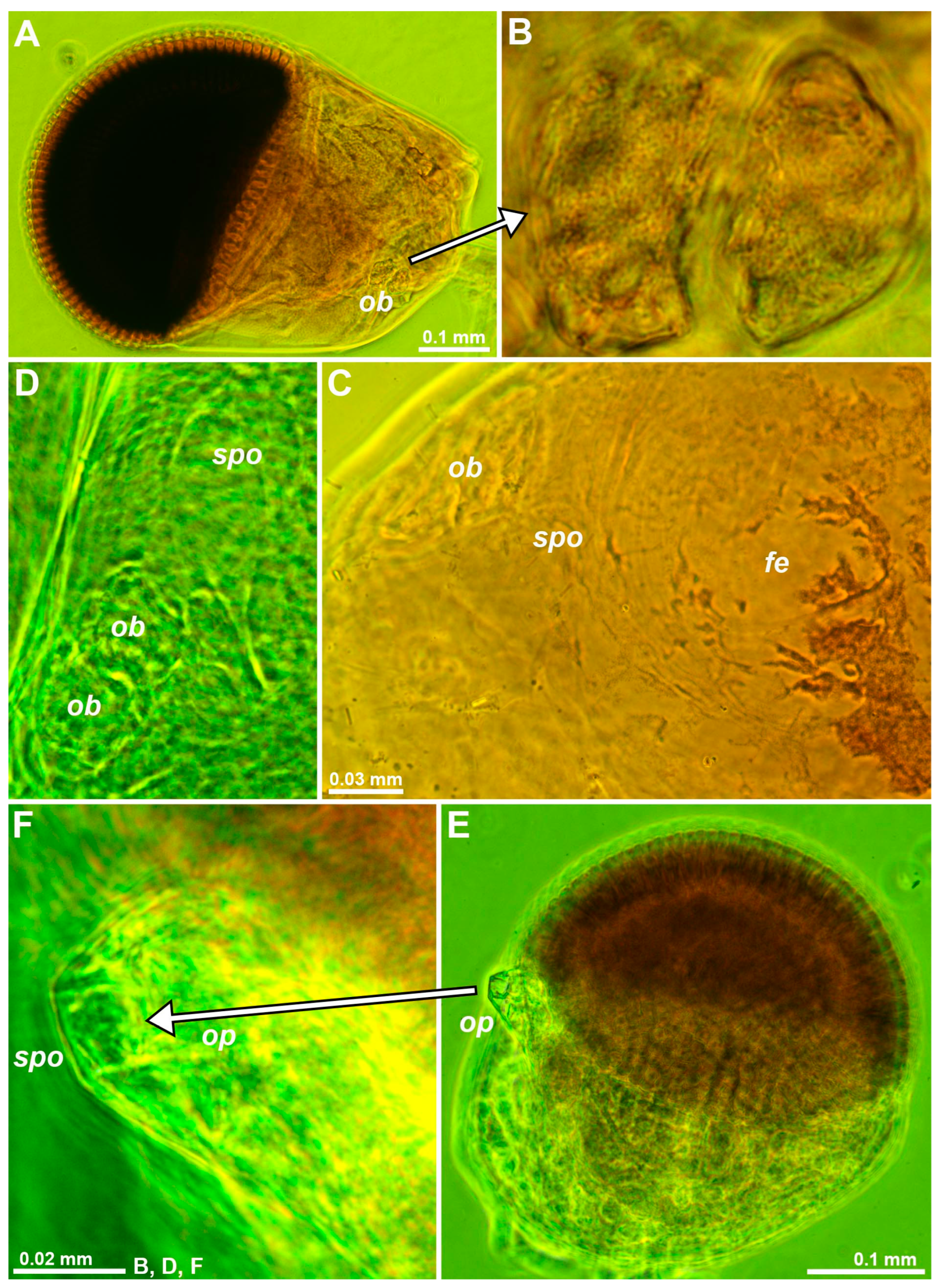
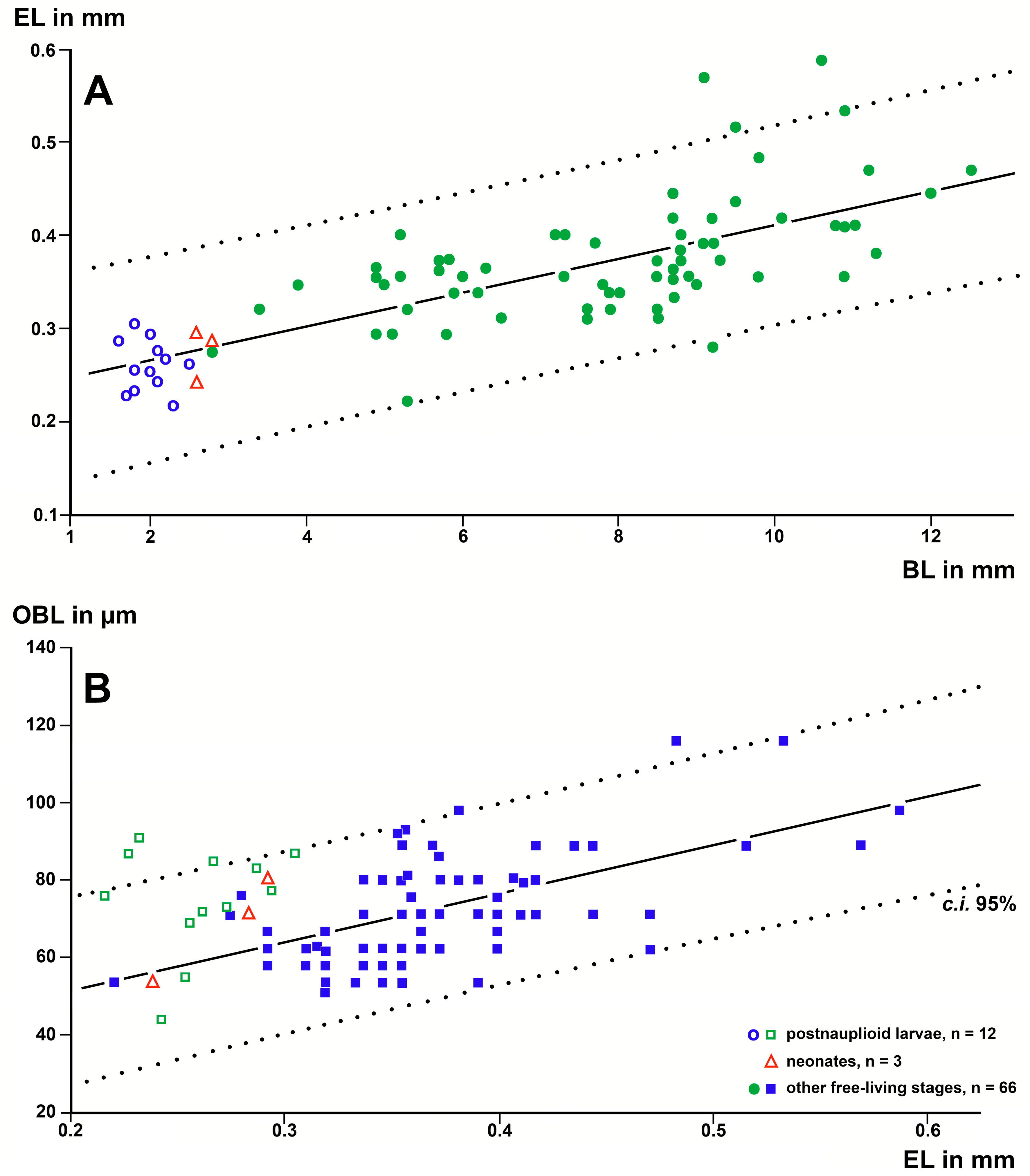
3.1.2. Size and Structure of Larval Eyes
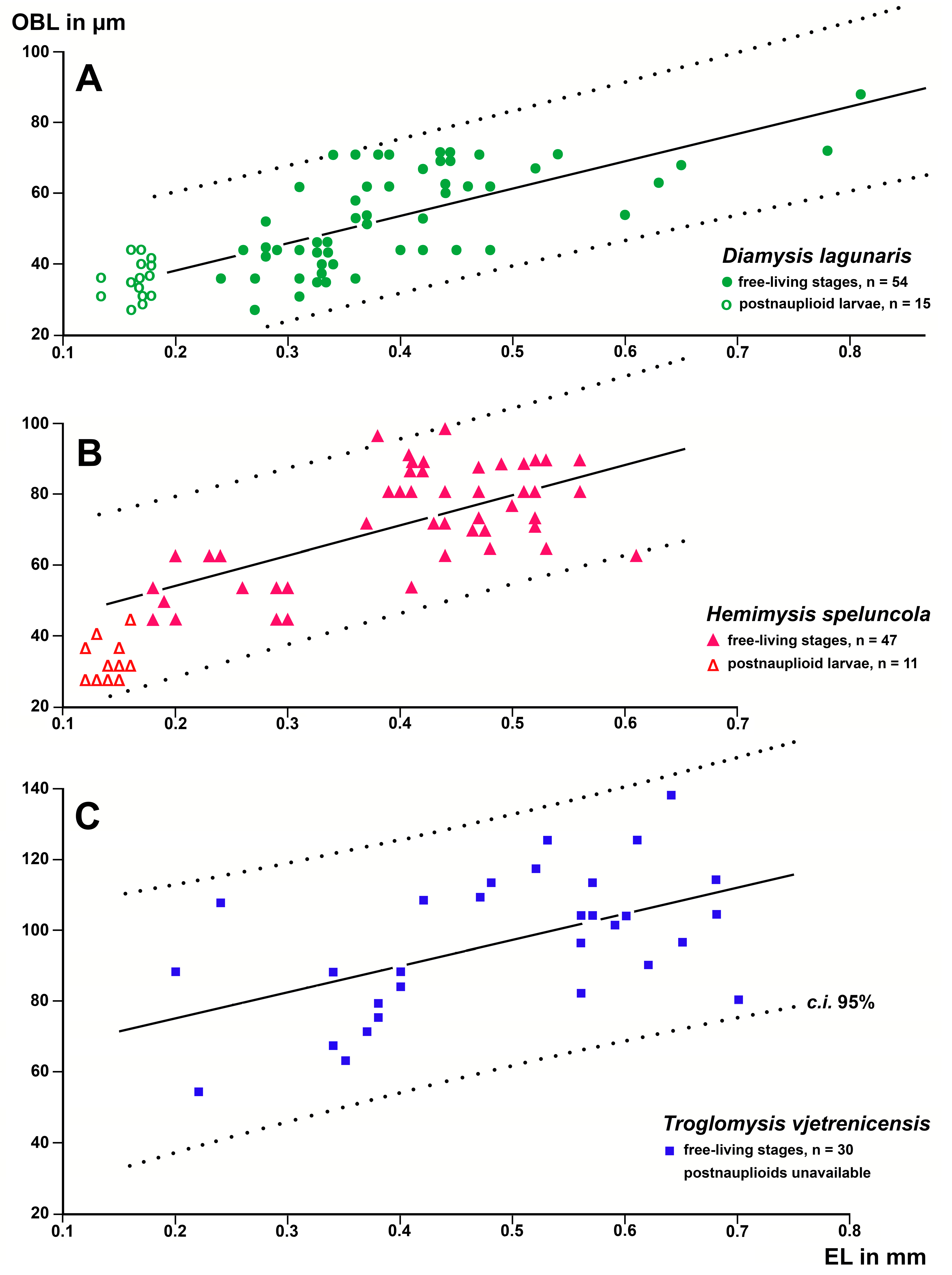
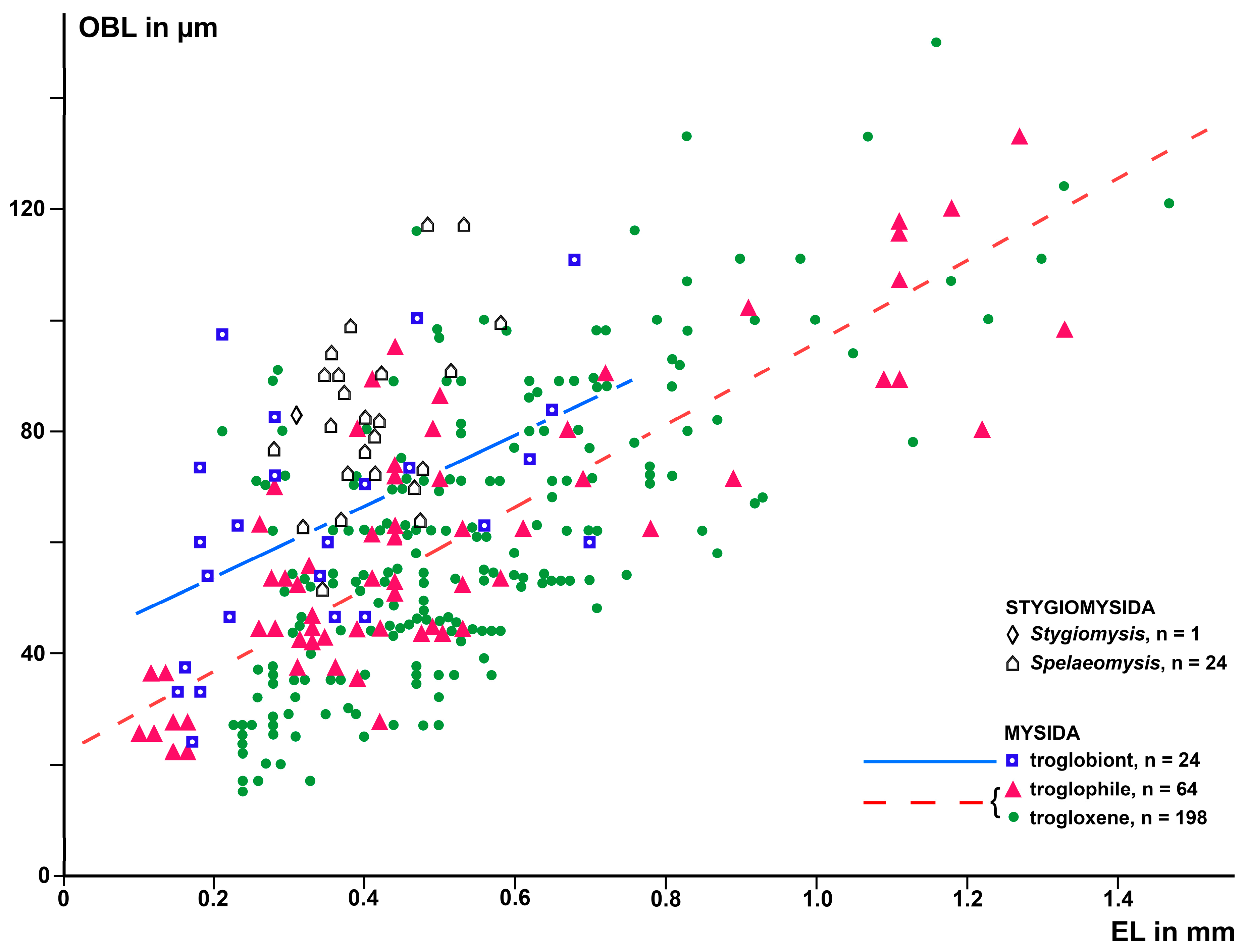
3.1.3. Size of the Organ of Bellonci at Intraspecific Level
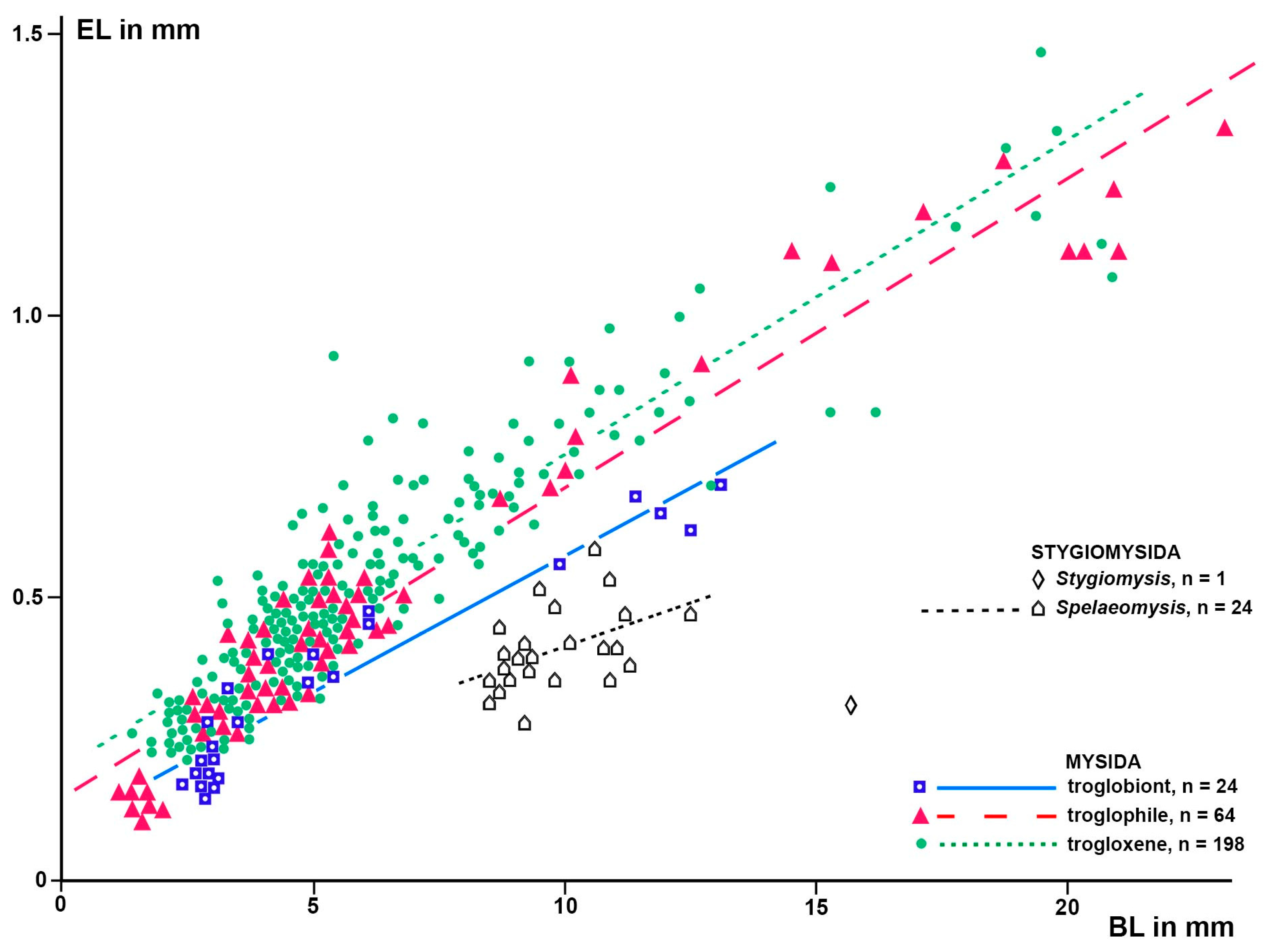
3.1.4. Size of the Organ of Bellonci at Interspecific Level
3.2. Eye structure in Stygiomysida
3.2.1. Eye Rudiments in Spelaeomysis bottazzii
3.2.2. Eye Rudiments in Stygiomysis major
3.2.3. Length of the Organ of Bellonci in Stygiomysida versus Troglobiont Mysida
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayrat, A. Oeil, centres optiques et glandes endocrines de Praunus flexuosus (O.F. Müller). Arch. Zool. Exp. Gén. 1956, 93, 319–366. [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg, E.; Chaigneau, J. The non-visual sense organs. In The Crustacea. Revised and Updated from the Traité de Zoologie; Forest, J., von Vaupel Klein, J.C., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 301–380. [Google Scholar]
- Bellon-Humbert, C. Développement Embryonnaire de Palaemon serratus, Résultats Préliminares; IFREMER: Montpellier, France, 1983; pp. 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Melville, R.; Smith, J.D.D. Official Lists and Indexes of Names and Works in Zoology; International Trust for Zoological Nomenclature: London, UK, 1987; pp. 1–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ariani, A.P.; Wittmann, K.J. The transition from an epigean to a hypogean mode of life: Morphological and bionomical characteristics of Diamysis camassai sp. nov. (Mysidacea, Mysidae) from brackish-water dolinas in Apulia, SE-Italy. Crustaceana 2002, 74, 1241–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariani, A.P.; Wittmann, K.J. Feeding, reproduction, and development of the subterranean peracarid shrimp Spelaeomysis bottazzii (Lepidomysidae) from a brackish well in Apulia (southeastern Italy). J. Crust. Biol. 2010, 30, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura-López, C.; Gómez-Anduro, G.; Arcos, F.G.; Llera-Herrera, R.; Racotta, I.S.; Ibarra, A.M. A novel CHH gene from the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei was characterized and found highly expressed in gut and less in eyestalk and other extra-eyestalk tissues. Gene 2016, 582, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, V.J.; Oshel, P.E. Ultrastructure of the attachment cells of the organ of Bellonci in Gammarus setosus (Crustacea, Amphipoda). J. Morphol. 1989, 200, 93–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.R.; Reddy, P.S. Eyestalk Hormones on Molting and Reproduction. Concepts of Neuropeptide Hormones in Crab; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–172. [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg, E.; Kauri, T. Evidence of non-photoreceptive function of the sensory units of the Organ of Bellonci in Macrobrachium rosenbergii (Decapoda, Caridea). Crustaceana 1992, 62, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, K.J. Comparative biology and morphology of marsupial development in Leptomysis and other Mediterranean Mysidacea (Crustacea). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1981, 52, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, K.J.; Chevaldonné, P. First report of the order Mysida (Crustacea) in Antarctic marine ice caves, with description of a new species of Pseudomma and investigations on the taxonomy, morphology and life habits of Mysidetes species. ZooKeys 2021, 1079, 145–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culver, D.C.; Pipan, T. Ecological and evolutionary classification of subterranean organisms. In Subterranean Biology in the Anthropocene; Reboleira, A.S.P.S., Mendes Gonçalves, F.J., Eds.; ARPHA Conference Abstracts; Pensoft: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2018; Volume 1, p. e29878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, G.L.; Juberthie-Jupeau, L.; Passelaigue, F. Mysidacea. Encyclopaedia Biospeologica; Juberthie, C., Decu, V., Eds.; Société Internationale de Biospéologie: Moulis, France, 1994; Volume 1, pp. 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann, K.J. Untersuchungen zur Lebensweise und Systematik von Leptomysis truncata und zwei verwandten Formen (Crustacea, Mysidacea). Ann. Naturhist. Mus. Wien 1986, 87B, 295–323. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann, K.J.; Chevaldonné, P. Description of Heteromysis (Olivemysis) ekamako sp. nov. (Mysida, Mysidae, Heteromysinae) from a marine cave at Nuku Hiva Island (Marquesas, French Polynesia, Pacific Ocean). Mar. Biodiv. 2016, 47, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariani, A.P.; Wittmann, K.J. Alcuni aspetti della biologia della riproduzione in Spelaeomysis bottazzii Caroli (Mysidacea, Lepidomysidae). Thalassia Salentina 1999, 23, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, E. Grundriss der Biologischen Statistik, 6th ed.; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1967; pp. 1–674. [Google Scholar]
- XLSTAT. Available online: https://www.xlstat.com (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Wittmann, K.J.; Ariani, A.P.; Lagardère, J.-P. Orders Lophogastrida Boas, 1883, Stygiomysida Tchindonova, 1981, and Mysida Boas, 1883 (also known collectively as Mysidacea). In The Crustacea. Revised and Updated from the Traité de Zoologie; von Vaupel Klein, J.C., Charmantier-Daures, M., Schram, F.R., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Cuzin-Roudy, J.; Saleuddin, A.S.M. A study of the neurosecretory centres of the eyestalk in Siriella armata M. Edw. (Crustacea: Mysidacea). Can. J. Zool. 1985, 63, 2783–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariani, A.P.; Wittmann, K.J. Interbreeding versus morphological and ecological differentiation in Mediterranean Diamysis (Crustacea, Mysidacea), with description of four new taxa. Hydrobiologia 2000, 441, 185–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stammer, H.-J. Ein neuer Höhlenschizopode, Troglomysis vjetrenicensis n.g. n.sp. Zugleich eine Übersicht der bisher aus dem Brack- und Süßwasser bekannten Schizopoden, ihrer geographischen Verbreitung und ihrer ökologischen Einteilung—Sowie eine Zusammenstellung der blinden Schizopoden. Zool. Jb. Syst. 1936, 68, 53–104. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann, K.J.; Ariani, A.P.; Daneliya, M. The Mysidae (Crustacea: Peracarida: Mysida) in fresh and oligohaline waters of the Mediterranean. Taxonomy, biogeography, and bioinvasion. Zootaxa 2016, 4142, 1–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanström, B. Über das Organ X, eine inkretorische Gehirndrüse der Crustaceen. Psychiat. Neurol. Bl. Amst. 1934, 38, 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, L.; Grousset, E.; Charmantier, G.; Spanings-Pierrot, C. Occurrence of L—And D-Crustacean Hyperglycemic Hormone Isoforms in the Eyestalk X-Organ/Sinus Gland Complex during the ontogeny of the crayfish Astacus leptodactylus. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 52, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouau, Y. Etude externe de l’équipement sensoriel des antennes 1 et 2 d’un Crustacé Mysidacé souterrain Antromysis juberthiei Bacesco et Orghidan. Arch. Zool. Exp. Gén. 1981, 122, 271–288. [Google Scholar]
- Rotllant, G.; Charmantier-Daures, M.; Trilles, J.P.; Charmantier, G. Ontogeny of the sinus gland and of the organ of Bellonci in larvae and postlarvae of the European lobster Homarus gammarus. Inverteb. Repro. Dev. 1994, 26, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, C.N.; Thampy, D.M.; Pillai, N.K. Optic regression in a subterranean mysid (Crustacea, Mysidacea). Int. J. Speleol. 1972, 4, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Troglobiont vs. Troglophile Mysida | Troglobiont vs. Trogloxene Mysida | Troglophile vs. Trogloxene Mysida | Troglobiont Mysida vs. Stygiomysida | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n species | 5 + 14 | 5 + 49 | 14 + 49 | 5 + 2 | |
| n specimens | 24 + 64 | 24 + 198 | 64 + 198 | 24 + 25 | |
| Effects on EL at given BL | mean ± s.e. | −0.086 ± 0.019 | −0.143 ± 0.020 | −0.057 ± 0.013 | −0.077 ± 0.025 |
| c.i. 95% | −0.123 to −0.049 | −0.182 to −0.103 | −0.084 to −0.031 | −0.127 to −0.028 | |
| P (2-tailed) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.003 | |
| % mean (c.i.) | −17% (76–90%) | −26% (67–81%) | −10% (85–94%) | −19% (69–93%) | |
| Eff. on OBL at given BL | mean ± s.e. | 25.64 ± 3.70 | 24.53 ± 4.05 | −2.63 ± 2.63 | −5.17 ± 4.13 |
| c.i. 95% | 12.29 to 32.99 | 16.56 to 32.50 | −7.80 to +2.54 | −13.48 to +3.14 | |
| P (2-tailed) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.32 (n.s.) | 0.22 (n.s.) | |
| % mean (c.i.) | 42% (120–154%) | 40% (127–153%) | −4% (83–104%) | −6% (84–104%) | |
| Eff. on OBL at given EL | mean ± s.e. | 29.81 ± 3.55 | 32.98 ± 4.00 | 1.67 ± 2.57 | 2.97 ± 3.88 |
| c.i. 95% | 22.76 to 36.86 | 25.11 to 40.85 | −3.31 to +6.82 | −4.83 to +10.78 | |
| P (2-tailed) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.50 (n.s.) | 0.45 (n.s.) | |
| % mean (c.i.) | 49% (137–160%) | 54% (141–166%) | 3% (95–111%) | 4% (94–113%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wittmann, K.J. Evidence and Modification of Non-Visual Eyestalk Organs in Troglobiont Mysida and Stygiomysida (Crustacea). Arthropoda 2023, 1, 432-450. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda1040019
Wittmann KJ. Evidence and Modification of Non-Visual Eyestalk Organs in Troglobiont Mysida and Stygiomysida (Crustacea). Arthropoda. 2023; 1(4):432-450. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda1040019
Chicago/Turabian StyleWittmann, Karl J. 2023. "Evidence and Modification of Non-Visual Eyestalk Organs in Troglobiont Mysida and Stygiomysida (Crustacea)" Arthropoda 1, no. 4: 432-450. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda1040019
APA StyleWittmann, K. J. (2023). Evidence and Modification of Non-Visual Eyestalk Organs in Troglobiont Mysida and Stygiomysida (Crustacea). Arthropoda, 1(4), 432-450. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda1040019





