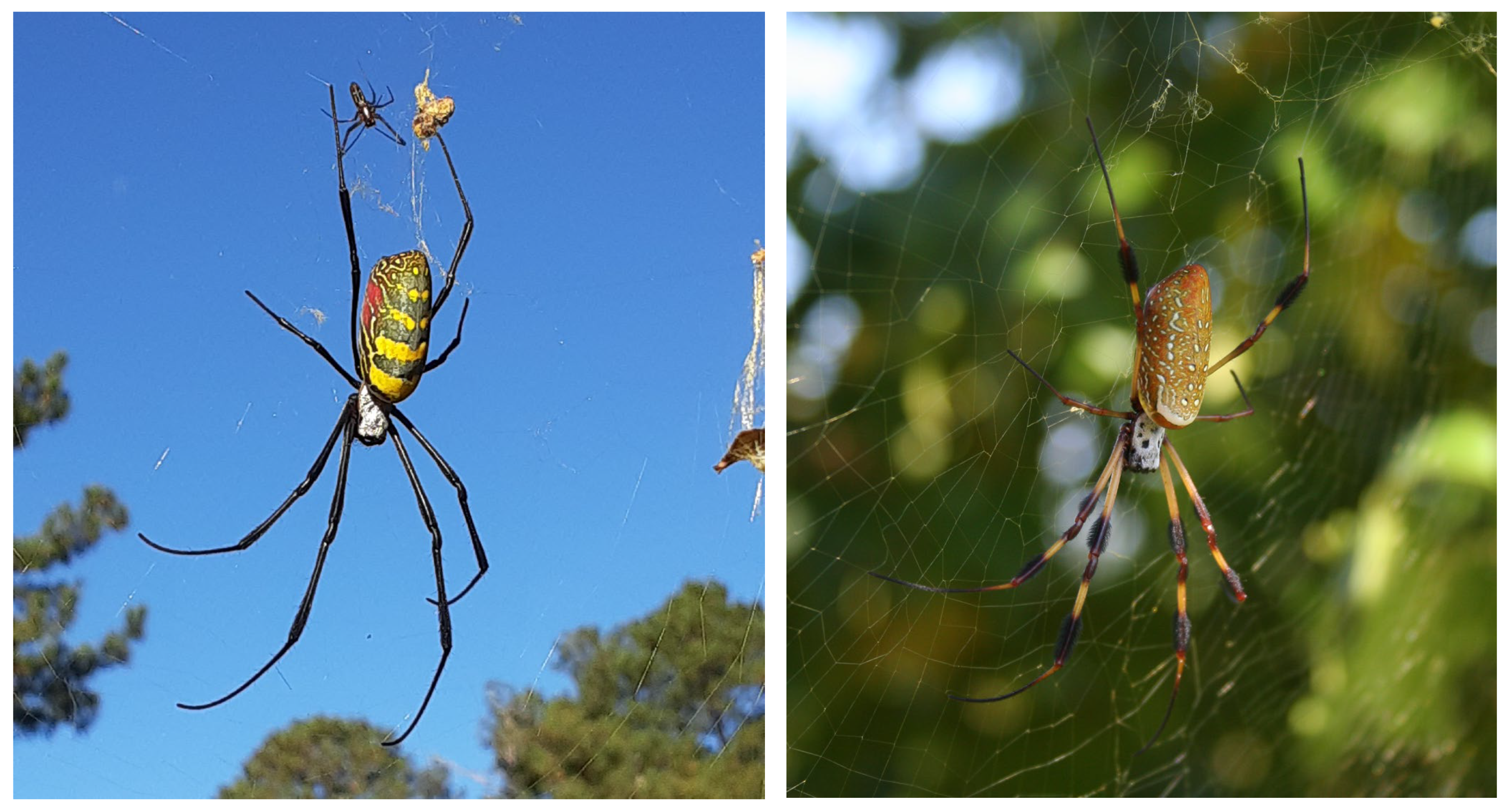
Startle Responses of Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) to Artificial Disturbance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vink, C.J.; Derraik, J.G.B.; Phillips, C.B.; Sirvid, P.J. The invasive Australian redback spider, Latrodectus hasseltii Thorell 1870 (Araneae: Theridiidae): Current and potential distributions, and likely impacts. Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 1003–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarski, J.; Ginsberg, H.; Jakob, E.M. Competitive interactions between a native spider (Frontinella communis, Araneae: Linyphiidae) and an invasive spider (Linyphia triangularis, Araneae: Linyphiidae). Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nentwig, W. Introduction, establishment rate, pathways and impact of spiders alien to Europe. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 2757–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoebeke, E.R.; Huffmaster, W.; Freeman, B.J. Nephila clavata L Koch, the Joro Spider of East Asia, newly recorded from North America (Araneae: Nephilidae). Peerj 2015, 3, e763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, A.; Deitsch, J.F.; Nelsen, D.R.; Sitvarin, M.I.; Coyle, D.R. The Jorō spider (Trichonephila clavata) in the southeastern U.S.: An opportunity for research and a call for reasonable journalism. Biol. Invasions 2023, 25, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ɖậng, V.Ɖ.; Yan, Y.; Kim, K.; Ranjeewa, A. Colonial web building behavior of Nephila clavata L. Koch (Nephilidae) in a forest tea plantation: When to join the crowd. In Proceedings of the Advanced Fieldcourse in Ecology and Conservation—Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden, Yunnan, China, 22 October–3 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.K.; Frick, B.L. Physiological evaluation of newly invasive joro spiders (Trichonephila clavata) in the southeastern USA compared to their naturalized cousin, Trichonephila clavipes. Physiol. Entomol. 2022, 47, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkegard, K.A.; Davenport, L.J. Nephila clavipes (Araneae: Nephilidae): A model species for monitoring climate change in the southeastern United States. Southeast. Nat. 2012, 11, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, M.A.; Uetz, G.W. Antipredator benefits of single-species and mixed-species grouping by Nephila clavipes (L) (Araneae, Tetragnathidae). J. Arachnol. 1992, 20, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, J.A. Social behavior of the golden silk spider, Nephila clavipes (Linnaeus) (Araneae, Araneidae). J. Arachnol. 1976, 4, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Rypstra, A.L. Aggregations of Nephila clavipes (L) (Araneae, Araneidae) in relation to prey availability. J. Arachnol. 1985, 13, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Schronce, A.; Davis, A.K. Novel observation: Northern cardinal (Cardinalis cardinalis) perches on an invasive jorō spider (Trichonephila clavata) web and steals food. Insects 2022, 13, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.C.; Herrig, A.; Allen, W.D.; Jones, T.C. Diel patterns of foraging aggression and antipredator behaviour in the trashline orb-weaving spider, Cyclosa turbinata. Anim. Behav. 2014, 94, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.; Chaves-Campos, J. Contrary to vertebrates, less aggressive and more consistent individuals are common in disturbed habitats in the colonial spider Metabus gravidus (Araneae: Araneidae). Behaviour 2021, 158, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechert, S.E.; Hedrick, A.V. Levels of predation and genetically based antipredator behavior in the spider, Agelenopsis aperta. Anim. Behav. 1990, 40, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, K.; Gadd, R.D.H.; Hess, Z.L.; McDermott, D.R.; MacDonald, L.; Cotter, P.; Armagost, F.; Chen, J.Z.; Berning, A.W.; DiRienzo, N.; et al. Assessing the effects of rearing environment, natural selection, and developmental stage on the emergence of a behavioral syndrome. Ethology 2013, 119, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.; Pruitt, J.N. Are personalities genetically determined? Inferences from subsocial spiders. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 867. [Google Scholar]
- Shearer, T.A.; Pruitt, J.N. Individual differences in boldness positively correlate with heart rate in orb-weaving spiders of genus Larinioides. Curr. Zool. 2014, 60, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.C.; Akoury, T.S.; Hauser, C.K.; Neblett, M.F.; Linville, B.J.; Edge, A.A.; Weber, N.O. Octopamine and serotonin have opposite effects on antipredator behavior in the orb-weaving spider, Larinioides cornutus. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2011, 197, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.C.; Ross, C.R.; Jones, T.C. Diel and life-history characteristics of personality: Consistency versus flexibility in relation to ecological change. Anim. Behav. 2015, 101, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Klomp, D.A.; Norma-Rashid, Y.; Li, D.Q. Consistency in boldness expression varies with ecological context in a jumping spider. Ethology 2019, 125, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Ladd, R.R.E.; Smith, F.; Shattuck, A. Sex-specific effects of a parasite on stress-induced freezing behavior in a natural beetle-nematode system. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.A.; Cardoso, D.G.; Lucia, T.M.C.D.; Guedes, R.N.C. Weevil x insecticide: Does ’personality’ matter? PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, K.; Fuchikawa, T.; Miyatake, T. Decoupling of behavioral trait correlation across life stages in two holometabolous insects. Behav. Genet. 2017, 47, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetz, G.W.; Boyle, J.; Hieber, C.S.; Wilcox, R.S. Antipredator benefits of group living in colonial web-building spiders: The ’early warning’ effect. Anim. Behav. 2002, 63, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.F. Metabolic rates of spiders. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1970, 33, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripp, J.; Eldakar, O.T.; Gallup, A.C.; Arena, P.T. The successful exploitation of urban environments by the golden silk spider, Nephila clavipes (Araneae, Nephilidae). J. Urban Ecol. 2018, 4, juy005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, E.C.; Wilder, S.M.; Hochuli, D.F. Urbanisation at multiple scales is associated with larger size and higher fecundity of an orb-weaving spider. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, E.C.; Wilder, S.M.; Hochuli, D.F. Life history of an urban-tolerant spider shows resilience to anthropogenic habitat disturbance. J. Urban Ecol. 2017, 3, jux004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahirel, M.; De Cock, M.; Vantieghem, P.; Bonte, D. Urbanization-driven changes in web building and body size in an orb web spider. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Clancy, K.M.; Sasaki, T. How to take an ant’s pulse: A procedure for non-destructively monitoring baseline and stimulated heart rate in Formicidae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2021, 169, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Coogler, B.; Johnson, I. The heartrate reaction to acute stress in horned passalus beetles (Odontotaenius disjunctus) is negatively affected by a naturally-occurring nematode parasite. Insects 2017, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Schroeder, H.; Yeager, I.; Pearce, J. Effects of simulated highway noise on heart rates of larval monarch butterflies, Danaus plexippus: Implications for roadside habitat suitability. Biol. Lett. 2018, 14, 20180018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

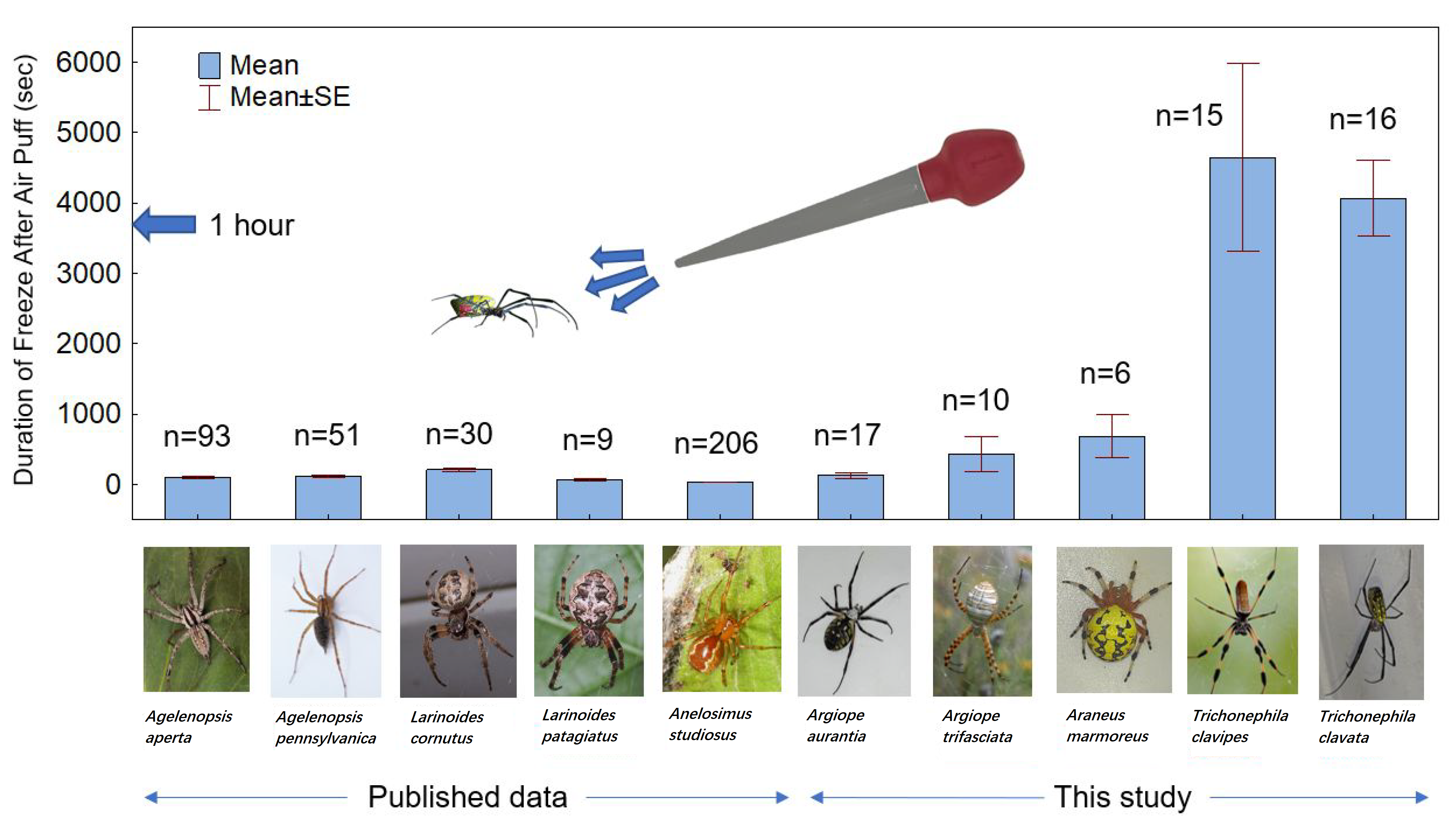
| Spider Species | # Spiders Tested | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Funnel-web spider (Agelenopsis aperta) | 93 | [15] |
| Pennsylvania grass spider (Agelenopsis pennsylvanica) | 51 | [16] |
| Communal spider (Anelosimus studiosus) | 206 | [17] |
| Furrow orb spider (Larinoides cornutus) | 30 | [18] |
| Ornamental orb weaver (Larinoides patagiatus) | 9 | [18] |
| Marbled orb weaver (Araneus marmoreus) | 6 | This study |
| Banded garden spider (Argiope trifasciatus) | 10 | This study |
| Garden spider (Argiope aurantia) | 17 | This study |
| Golden silk spider (Trichonephila clavipes) | 15 | This study |
| Jorō spider (Trichonephila clavata) | 16 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davis, A.K.; Anerao, A.V. Startle Responses of Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) to Artificial Disturbance. Arthropoda 2023, 1, 60-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda1020009
Davis AK, Anerao AV. Startle Responses of Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) to Artificial Disturbance. Arthropoda. 2023; 1(2):60-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda1020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavis, Andrew K., and Amitesh V. Anerao. 2023. "Startle Responses of Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) to Artificial Disturbance" Arthropoda 1, no. 2: 60-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda1020009
APA StyleDavis, A. K., & Anerao, A. V. (2023). Startle Responses of Jorō Spiders (Trichonephila clavata) to Artificial Disturbance. Arthropoda, 1(2), 60-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/arthropoda1020009







