Over the past decade, insect farming has garnered significant scientific and commercial attention due to its potential as a sustainable and efficient alternative nutrient source for both animal feed [] and human consumption []. This interest is well-founded, as insects possess high nutritional value [], can thrive on a wide range of low-cost organic by-products and waste streams [], exhibit exceptional feed-to-biomass conversion efficiency [], and require minimal land and water resources for production while also generating lower greenhouse gas emissions []. The adoption of a favorable legislative framework in the EU further boosted the exploitation of insects for food and feed applications. Regarding feed, the EU Regulation 2017/893 initially authorized the incorporation of insect-derived protein in aquafeeds, whereas more recently, the EU approved the utilization of insect-based proteins in poultry and swine feeds [,]. In parallel, several insect species were approved for human consumption in the EU, paving the way for their inclusion in novel food applications [,].
However, research over these first years of the field’s conception has primarily focused on the nutritional value of insects and their utilization as protein source in food and feed. However, insect production also generates other valuable products and by-products. A prominent by-product of insect farming is insect frass, a material composed of insect feces, exoskeletons, and residual rearing substrate [,]. Notably, the volume and weight of frass can surpass the yield of the insects themselves. Recent studies have highlighted the potential of frass as an effective soil amendment and organic fertilizer, capable of significantly enhancing crop growth [,]. The European Union has recently approved the use of insect frass as a fertilizer, providing specific baseline standards for its production and placing on the market [], a development that is expected to further propel its utilization in crop production and increase the insect frass fertilizer market. Specifically, the insect frass market size was valued at 96 Million US dollars in 2023 and is projected to exceed USD 135 Million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of around 6% from 2024 to 2030 []. It is therefore evident that apart from improving the sustainable profile and the circularity of insect production, the valorization of insect frass is substantial to boost and foster the economic feasibility of the insect sector, providing extra revenue to the insect industry.
1. Frass Effect on Plant Growth
So far, studies have demonstrated the effect of insect frass on the growth and performance of a variety of crops, such as leafy vegetables (e.g., spinach (Spinacia oleracea) [], basil (Ocimum basilicum) [], cabbage (Brassica oleracea) [], lettuce (Lactuca sativa) [,]), and fruity vegetables (e.g., tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) [] or beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) []), as well as arable crops such as barley (Hordeum vulgare) [] and maize (Zea mays) [,]. For instance, the growth of both the above- and below-ground plant biomass of spinach plants was significantly favored by the application of 1% frass of larvae of the yellow mealworm, Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), compared to both the non-treated, negative control, and the positive control treated with inorganic fertilizer []. Similarly, maize yield was improved with the application of frass of larvae of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), when applied at rates of 2.5 t ha−1 []. From the literature available so far, most research works have been conducted using frass of H. illucens and T. molitor larvae (Figure 1). However, more recently, interest has also shifted towards the potential valorization of frass of less studied insect species, such as the lesser mealworm, Alphitobius diaperinus (Panzer) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) [], or the house cricket, Acheta domesticus (L.) (Orthoptera: Gryllidae) [] (Figure 1).
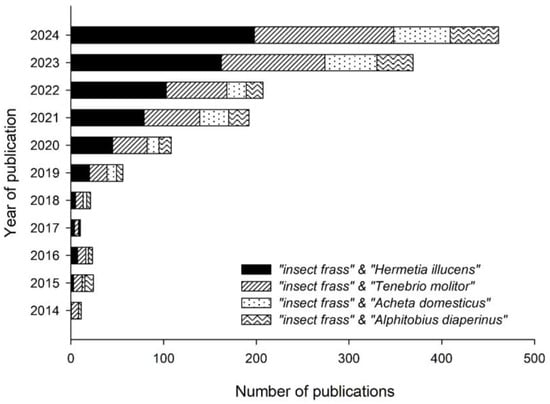
Figure 1.
Number of published articles per year indexed by Google Scholar matching the search queries ‘Hermetia illucens’, Tenebrio molitor, ‘Acheta domesticus’, ‘Alphitobius diaperinus’, and ‘insect frass’, shown per year of publication (2014–2024) (Date of Google Scholar search: 9 January 2025).
2. Frass Composition
Insect frass is rich in both macronutrients (nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K)), as well as secondary nutrients (calcium, magnesium, and sulfur) and micronutrients (manganese, copper, iron, zinc, boron, and sodium). The nutritional composition of insect frass has been recently reviewed by several researchers []. However, it has been shown that its composition varies greatly depending on the insect species. When the nutritional quality of frass from nine insect species was comparatively studied, considerable differences were reported among the different frass fertilizer products evaluated []. Specifically, it was reported that frass from H. illucens and two two-spotted cricket species (Gryllus bimaculatus De Geer and Scapsipedus icipe Hugel and Tanga) were the best in terms of nutrient concentration []. Additionally, the nutrient composition of frass changes depending also on the insect feeding substrate []. In general, when insects are reared on a N-rich substrate, frass is also expected to be rich in nitrogen, and subsequently, its effect on plant growth will be more pronounced []. Moreover, insect frass has been shown to positively influence soil health by enhancing not only soil nutrient availability, but also soil structure.
Apart from a valuable source of nitrogen and other nutrients for plants, the application of insect frass to soil can influence the composition of the soil microbiome by promoting the abundance and/or activity of beneficial soil microorganisms that can facilitate nutrient uptake by plants. Bacteria belonging to Gammaproteobacteria and Bacilli and fungi belonging to Ascomycota have been identified in frass, consistent with microbial communities commonly associated with insect digestive tracts [,,,]. It has been suggested that plant roots can recognize the beneficial microbes and biomolecules present in insect frass, potentially inducing systemic resistance against pests through specific signaling pathways []. For example, frass derived from H. illucens larvae fed on brewer’s spent grain was shown to activate plant defense mechanisms and reduce infestations of Fusarium wilt disease in cowpea plants, an effect attributed to the presence of chitin in H. illucens frass. Microbial isolates associated with frass exhibit various plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) traits, such as phosphate solubilization and siderophore production, which could significantly influence the soil microbial community composition and enhance plant growth [,]. Interestingly, sterilization of frass, which removes microbial activity, resulted in reduced plant yield compared to non-sterilized frass, emphasizing the critical role of these microbes []. The aspects of safety and potential hazards (e.g., microbiological, chemical, etc.) that may arise from frass application should also be given high-priority consideration to ensure these safety risks are minimized in both the crops and the environment [].
3. Concluding Remarks
Without any doubt, insect frass has the potential to play a pivotal role in the ongoing transition towards more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally friendly crop production systems. Fully consistent with the principles of circular economy and zero-waste approaches, this side-stream of insect production is nowadays widely recognized as an effective soil fertilizer, capable of promoting plant growth and enhancing soil properties. However, beyond its agricultural use, insect frass can also be utilized for other applications, such as biogas and biomethane production to be further used for heat and electricity [,]. Additionally, specialized applications of frass, such as its conversion into biochar, have demonstrated significant potential for soil bioremediation, particularly in the remediation of heavy metal and pesticide contamination []. In other words, the best for insect frass is yet to come!
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sogari, G.; Bellezza Oddon, S.; Gasco, L.; van Huis, A.; Spranghers, T.; Mancini, S. Review: Recent Advances in Insect-based Feeds: From Animal Farming to the Acceptance of Consumers and Stakeholders. Animal 2023, 17, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsou, K.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Athanasiadis, V.; Bozinou, E.; Athanassiou, C.G.; Lalas, S.I. Innovative Applications of Tenebrio molitor Larvae in Food Product Development: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2023, 12, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Finke, M.D. Insects as a Complete Nutritional Source. J. Insects Food Feed 2023, 9, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Harahap, I.A.; Osei-Owusu, J.; Saikia, T.; Wu, Y.S.; Fernando, I.; Perestrelo, R.; Câmara, J.S. Bioconversion of Organic Waste by Insects—A Comprehensive Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 187, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B. The Environmental Sustainability of Insects as Food and Feed. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; de Boer, I.J.M. Environmental Impact of the Production of Mealworms as a Protein Source for Humans—A Life Cycle Assessment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Commission Regulation 2017/893 of 24 May 2017 amending Annexes I and IV to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Annexes X, XIV and XV to Commission Regulation (EU) No 142/2011 as regards the provisions on processed animal protein. Off. J. Eur. Union 2017, 138, 92–116. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32017R0893&from=EN (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1372 of 17 August 2021 amending Annex IV to Regulation (EC) No 999/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the prohibition to feed non-ruminant farmed animals, other than fur animals, with protein derived from animals. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, 295, 1–17. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32021R1372 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens); Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods, Food Allergens; Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Scientific opinion on the safety of frozen and freeze-dried formulations of the lesser mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus larva) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hénault-Ethier, L.; Quinche, M.; Reid, B.; Hotte, N.; Fortin, A.; Normandin, É.; de La Rochelle Renaud, G.; Rasooli Zadeh, A.; Deschamps, M.H.; Vandenberg, G. Opportunities and Challenges in Upcycling Agri-food Byproducts to Generate Insect Manure (Frass): A Literature Review. Waste Manag. 2024, 176, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, I.G.; Yong, J.W.; Lalander, C. Frass Derived from Black Soldier Fly Larvae Treatment of Biodegradable Wastes. A Critical Review and Future Perspectives. Waste Manag. 2022, 142, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda, J. Insect Frass in the Development of Sustainable Agriculture. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, H.C.S.; Ashworth, A.J.; Arsi, K.; Guadalupe Rojas, M.; Morales-Ramos, J.A.; Donoghue, A.; Robinson, K. Insect Frass Composition and Potential Use as an Organic Fertilizer in Circular Economies. J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1925 of 5 November 2021 amending certain Annexes to Regulation (EU) No 142/2011 as regards the requirements for placing on the market of certain insect products and the adaptation of a containment method. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, 393, 4–8. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32021R1925 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Global Insect Frass (Biofertilizers) Market By Type (Molitor Larvae, Mealworm), By Application (Seed Treatment, Soil Treatment), By Geographic Scope And Forecast. Available online: https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/product/insect-frass-biofertilisers-market (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Antoniadis, V.; Molla, A.; Grammenou, A.; Apostolidis, V.; Athanassiou, C.G.; Rumbos, C.I.; Levizou, E. Insect Frass as a Novel Organic Soil Fertilizer for the Cultivation of Spinach (Spinacia oleracea): Effects on Soil Properties, Plant Physiological Parameters and Nutrient Status. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5935–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkent, S.; Hodge, S. Glasshouse Evaluation of the Black Soldier Fly Waste Product HexaFrass™ as an Organic Fertilizer. Insects 2021, 12, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawinska, Z.; Radzikowska-Kujawska, D.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Grzanka, M.; Sobiech, Ł.; Skrzypczak, G.; Drożdżyńska, A.; Ślachciński, M.; Świtek, S. Hermetia illucens Frass Fertilization: A Novel Approach for Enhancing Lettuce Resilience and Photosynthetic Efficiency under Drought Stress Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferruzca-Campos, E.A.; Rico-Chavez, A.K.; Guevara-González, R.G.; Urrestarazu, M.; Cunha-Chiamolera, T.P.L.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Guzmán-Cruz, R. Biostimulant and Elicitor Responses to Cricket Frass (Acheta domesticus) in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) under Protected Conditions. Plants 2023, 12, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chepkorir, A.; Beesigamukama, D.; Gitari, H.I.; Chia, S.Y.; Subramanian, S.; Ekesi, S.; Abucheli, B.E.; Rubyogo, J.C.; Zahariadis, T.; Athanasiou, G.; et al. Insect Frass Fertilizer as a Regenerative Input for Improved Biological Nitrogen Fixation and Sustainable Bush Bean Production. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1460599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, D.; Daoulas, G.; Faucon, M.P.; Dulaurent, A.M. Potential Use of Mealworm Frass as a Fertilizer: Impact on Crop Growth and Soil Properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Mochoge, B.; Korir, N.K.; Fiaboe, K.K.M.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Khamis, F.M.; Subramanian, S.; Dubois, T.; Musyoka, M.W.; Ekesi, S.; et al. Exploring Black Soldier Fly Frass as Novel Fertilizer for Improved Growth, Yield, and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Maize Under Field Conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 574592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanga, C.M.; Beesigamukama, D.; Kassie, M.; Egonyu, P.J.; Ghemoh, C.J.; Nkoba, K.; Subramanian, S.; Anyega, A.O.; Ekesi, S. Performance of black soldier fly frass fertiliser on maize (Zea mays L.) growth, yield, nutritional quality, and economic returns. J. Insects Food Feed 2022, 8, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Schlösser, C.; Vögerl, J.; Wichern, F. Excellent excrement? Frass impacts on a soil’s microbial community, processes and metal bioavailability. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 168, 104110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesigamukama, D.; Subramanian, S.; Tanga, C.M. Nutrient Quality and Maturity Status of Frass Fertilizer from Nine Edible Insects. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boiocchi, F.; Porcellato, D.; Limonta, L.; Picozzi, C.; Vigentini, I.; Locatelli, D.P.; Foschino, R. Insect Frass in Stored Cereal Products as a Potential Source of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis for Sourdough Ecosystem. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Jiménez-Gómez, A.; Saati-Santamaría, Z.; Usategui-Martín, R.; Rivas, R.; García-Fraile, P. Mealworm Frass as a Potential Biofertilizer and Abiotic Stress Tolerance-Inductor in Plants. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogouong, J.; Constant, P.; Lavallée, R.; Guertin, C. Gut Microbiome of the Emerald Ash Borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, and its Relationship with Insect Population Density. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratore, M.; Prather, C.; Sun, Y. The Gut Bacterial Communities Across Six Grasshopper Species from a Coastal Tallgrass Prairie. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Zamioudis, C.; Berendsen, R.L.; Weller, D.M.; Van Wees, S.C.M.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Induced Systemic Resistance by Beneficial Microbes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safitri, R.A.; Vandeweyer, D.; Deruytter, D.; Meijer, N.; Coudron, C.L.; Banach, J.L.; Van der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Exploring Potential Uses of Insect Frass for Agricultural Production Considering its Nutrients, and Chemical and Microbiological Safety. J. Insects Food Feed, 2024; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Magro, A.; Lovarelli, D.; Bacenetti, J.; Guarino, M. The Potential of Insect Frass for Sustainable Biogas and Biomethane Production: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 412, 131384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulak, P.; Proc, K.; Pawłowska, M.; Kasprzycka, A.; Berus, W.; Bieganowski, A. Biogas Generation from Insects Breeding Post Production Wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Yan, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.-W. Removal of Neonicotinoid Pesticides by Adsorption on Modified Tenebrio molitor Frass Biochar: Kinetics and Mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).