Nanofertilizers: The Next Generation of Agrochemicals for Long-Term Impact on Sustainability in Farming Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemical Fertilizers and Their Drawbacks
3. Advantages of Nanofertilizers over the Traditional Chemical Fertilizers
4. Need for the Development of Nanofertilizers
5. Types of Nanofertilizers
5.1. Macronutrient-Based Nanofertilizers
5.2. Micronutrient-Based Nanofertilizers
5.3. Polymer-Based Nanofertilizers
5.4. Zeolite-Based Nanofertilizers
5.5. Carbon-Based Nanofertilizers
5.6. Trace Elements Based Nanofertilizers
6. Nano-Biofertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture
7. Nanofertilizers for Improving Biotic and Abiotic Stress Tolerance
8. Large-Scale Production and Commercialization of Nanofertilizers
9. Modes of Nanofertilizers Application
9.1. Soil Application
9.2. Seed Treatment
9.3. Foliar Spray
9.4. Aeroponics Treatment
9.5. Hydroponics Treatment
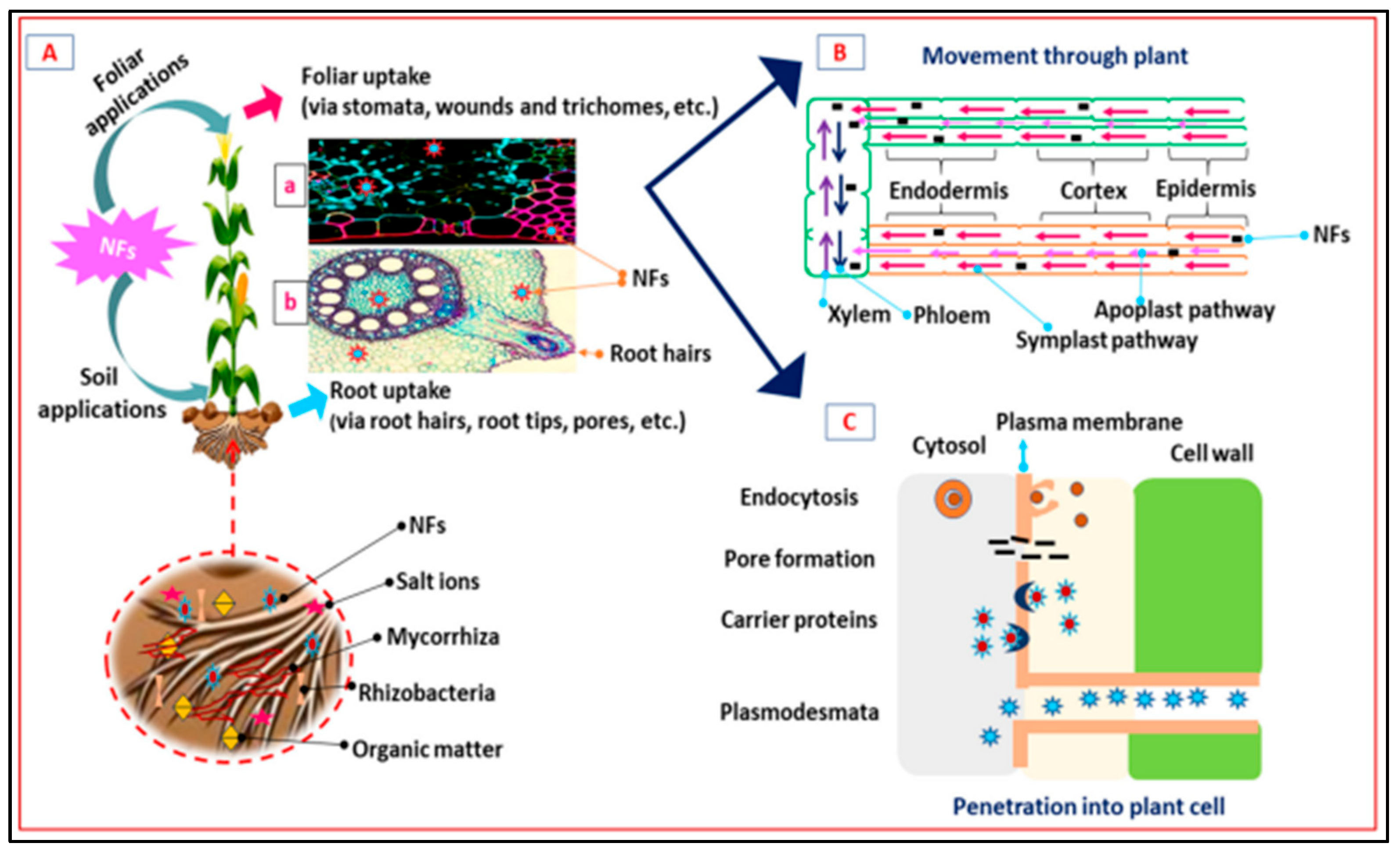
10. Mechanism of Uptake of NFs by Plants
11. Current Status of Nanofertilizers in Crop Production
12. Fabrication of Safe Nanofertilizers
13. Challenges in Nanofertilizers Application
14. Prospects and Future Directions
15. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abobatta, W.F. Over View of Nano-fertilizers. Asian J. Ethnopharma. Med. Foods 2018, 4, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Preetha, P.S.; Balakrishnan, N. A Review of Nano Fertilizers and Their Use and Functions in Soil. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 3117–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, J.C.; Raliya, R. Rapid, Low-Cost, and Ecofriendly Approach for Iron Nanoparticle Synthesis Using Aspergillus oryzae TFR9. J. Nanoparticles 2013, 2013, 141274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Tiwari, K.N.; Nayak, R.K.; Rai, A.; Singh, S.P.; Singh, A.N.; Kumar, Y.; Tomar, H.; Singh, T.; Raliya, R. Nanofertilizers for Increasing Nutrient Use Efficiency, Yield and Economic Returns in Important Winter Season Crops of Uttar Pradesh. Ind. J. Fertil. 2020, 16, 772–786. [Google Scholar]
- Zulfiqar, F.; Navarro, M.; Ashraf, M.; Akram, N.A.; Munné-Bosch, S. Nanofertilizer use for sustainable agriculture: Advantages and limitations. Plant Sci. 2019, 289, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguraj, S.; Wijayathunga, W.M.S.; Gunaratne, G.P.; Amali, R.K.A.; Priyadarshana, G.; Sandaruwan, C.; Karunaratne, V.; Hettiarachchi, L.S.K.; Kottegoda, N. Urea–hydroxyapatite nanohybrid as an efficient nutrient source in Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze (tea). J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 2383–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Darwesh, O.M.; Kornaros, M.; Al-Tohamy, R.; Manni, A.; El-Shanshoury, A.E.R.R.; Metwally, M.A.; Elsamahy, T.; Sun, J. Nano-biofertilizers: Synthesis, advantages, and applications. In Biofertilizers: Advances in Bioinoculants; Rakshit, A., Meena, V.S., Parihar, M., Singh, H.B., Singh, A.K., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, R. Nano-biofertilizers for sustainable agriculture. Just Agric.—Multidiscip. E-Newsl. 2021, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmigid, H.M.; Morsi, M.M.; Hussien, N.A.; Alyamani, A.A.; Alhuthal, N.A.; Albukhaty, S. Green Synthesis of Phosphorous-Containing Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles (nHAP) as a Novel Nano-Fertilizer: Preliminary Assessment on Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savci, S. An Agricultural Pollutant: Chemical Fertilizer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2012, 2012, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.M.A.; Zhang, D. Effects of fertilizer broadcasting on the excessive use of inorganic fertilizers and environmental sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, H. Nanofertilizers and nanopesticides for agriculture. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.K.; Song, X.P.; Joshi, A.; Rajput, V.D.; Singh, M.; Sharma, A.; Singh, R.K.; Li, D.M.; Arora, J.; Minkina, T.; et al. Nanofertilizer Possibilities for Healthy Soil, Water, and Food in Future: An Overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 865048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Mailapalli, D.R. Nanofertilisers, Nanopesticides, Nanosensors of Pest and Nanotoxicity in Agriculture. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews; Lichtfouse, E., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 19, pp. 307–330. [Google Scholar]
- Solanki, P.; Bhargava, A.; Chhipa, H.; Jain, N.; Panwar, J. Nano-fertilizers and their smart delivery system. In Nanotechnologies in Food and Agriculture; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 81–101. [Google Scholar]
- Raliya, R.; Franke, C.; Chavalamane, S.; Nair, R.; Reed, N.; Biswas, P. Quantitative understanding of nanoparticle uptake in watermelon plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernela, M.; Rani, R.; Malik, P.; Mukherjee, T. Nanofertilizers: Applications and Future Prospects. In Nanotechnology; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2020; Volume 9, pp. 287–330. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Dhiman, M.; Sharma, L.; Dadhich, A.; Kaushik, P.; Sharma, M.M. Nanofertilizers: The targeted nutrient supplier and enhance nutrients uptake by pearl millets (Pennisetum glaucum). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 45, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; ALmoshadak, A.S.; Shafi, M.E.; Albaqami, N.M.; Saad, A.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; El-Sayed, M.D.; El-Nahal, A.S.M.; Almakas, A.; El-Mageed, T.A.; et al. Vital roles of sustainable nano-fertilizers in improving plant quality and quantity-an updated review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 7349–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, P.L.; Xiang, X.; Heiden, P. Chitosan nanoparticle based delivery systems for sustainable agriculture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaraswamy, R.V.; Kumari, S.; Choudhary, R.C.; Pal, A.; Raliya, R.; Biswas, P.; Saharan, V. Engineered chitosan based nanomaterials: Bioactivities, mechanisms and perspectives in plant protection and growth. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, P.; Dapkekar, A.; Oak, M.D.; Paknikar, K.M.; Rajwade, J.M. Zinc complexed chitosan/TPP nanoparticles: A promising micronutrient nanocarrier suited for foliar application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, V.; Sharma, G.; Yadav, M.; Choudhary, M.K.; Sharma, S.S.; Pal, A.; Raliya, R.; Biswas, P. Synthesis and in vitro antifungal efficacy of Cu-chitosan nanoparticles against pathogenic fungi of tomato. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saharan, V.; Kumaraswamy, R.V.; Choudhary, R.C.; Kumari, S.; Pal, A.; Raliya, R.; Biswas, P. Cu-Chitosan Nanoparticle Mediated Sustainable Approach to Enhance Seedling Growth in Maize by Mobilizing Reserved Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6148–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanta, N.; Dambale, A.; Rajkhowa, M.; Mahanta, C.; Mahanta, N. Nutrient use efficiency through Nano fertilizers. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 2839–2842. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.Z.H.; Islam, M.R.; Nahar, N.; Al-Mamun, M.R.; Khan, M.A.S.; Matin, M.A. Synthesis and characterization of nanozeolite based composite fertilizer for sustainable release and use efficiency of nutrients. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikndan, A.; Subramanian, K.S. Evaluation of Zeolite Based Nitrogen Nano-fertilizers on Maize Growth, Yield and Quality on Inceptisols and Alfisols. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2015, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Javed, B.; Byrne, H.; Curtin, J.; Tian, F. Zeolites as Carriers of Nano-Fertilizers: From Structures and Principles to Prospects and Challenges. Appl. Nano 2022, 3, 163–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakovskaya, M.; Dervishi, E.; Mahmood, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Watanbe, F.; Biris, A.S. Carbon nanotubes are able to penetrate plant seed coat and dramatically affect seed germination and plant growth. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodakovskaya, M.; Silva, K.D.; Biris, A.S.; Dervishi, E.; Villagarica, H. Carbon nanotubes induce growth enhancement in tobacco cells. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2128–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, R.A.; Hassan, M.M.; Ibrahim, E.A.; Baker, N.H.A.; Shaaban, E.A. Carbon nanotubes impact on date palm in vitro cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2016, 127, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC-National Research Council (US) Committee on Diet and Health. Diet and Health: Implications for Reducing Chronic Disease Risk; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1989; p. 14. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK218751/ (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Piao, J.; Mao, D.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Yang, X. Reference Values of 14 Serum Trace Elements for Pregnant Chinese Women: A Cross-Sectional Study in the China Nutrition and Health Survey 2010–2012. Nutrients 2017, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deditius, A.P.; Utsunomiya, S.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Ewing, R.C.; Hough, R.; Walshe, J. Trace metal nanoparticles in pyrite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 42, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisinin, V.I.; Miroshnikov, S.A.; Sizova, E.A.; Ushakov, A.S.; Miroshnikova, E.P. Metal particles as trace-element sources: Current state and future prospects. World’s Poultry Sci. J. 2018, 74, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Hassan, F.; Rehman, M.S. Nano-particles of Trace Minerals in Poultry Nutrition: Potential Applications and Future Prospects. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 195, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagarová, I.; Nemček, L. Application of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Hybrids as Innovative Sorbents for Separation and Pre-concentration of Trace Elements by Dispersive Micro-Solid Phase Extraction: A Minireview. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 672755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Quezada, G.; Ingle, A.; Golińska, P.; Rai, M. Strategic applications of nano-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Benefits and bottlenecks. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 2123–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Singh, D.P. Nano-biofertilizer: An Emerging Eco-friendly Approach for Sustainable Agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 90, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamun, M.R.; Hasan, M.R.; Ahommed, M.S.; Bacchu, M.S.; Ali, M.R.; Khan, M.Z.H. Nanofertilizers towards sustainable agriculture and environment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhowalla, M. Slow Release Nanofertilizers for Bumper Crops. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 56–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lal, R. Synthetic apatite nanoparticles as a phosphorus fertilizer for soybean (Glycine max). Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani, A.; Akbari, K.; Yousefpour, M.; Ardalani, H. Effects of nano-potassium and nano calcium chelated fertilizers on qualitative and quantitative characteristics of Ocimum basilicum. Int. J. Pharma. Res. Sch. 2014, 3, 00167. [Google Scholar]
- Tarafdar, J.; Raliya, R.; Singh, S.; Gautam, R.; Choudhary, K.; Maurino, V.G.; Saharan, V. MgO nanoparticles biosynthesis and its effect on chlorophyll contents in the leaves of cluster bean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.). Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2014, 6, 538–545. [Google Scholar]
- Tarafdar, J.C.; Raliya, R.; Mahawar, H.; Rathore, I. Development of Zinc Nanofertilizer to Enhance Crop Production in Pearl Millet (Pennisetum americanum). Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, H.; Razmjoo, J. Effect of Foliar Application of Nano-iron Oxidase, Iron Chelate and Iron Sulphate Rates on Yield and Quality of Wheat. Intl. J. Agron. Plant Prod. 2013, 4, 2997–3003. [Google Scholar]
- Giordani, T.; Fabrizi, A.; Guidi, L.; Natali, L.; Giunti, G.; Ravasi, F.; Cavallini, A.; Pardossi, A. Response of tomato plants exposed to treatment with nanoparticles. EQA Int. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 8, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, M.; Ma, C.; Hao, Y.; Guo, J.; Rui, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, T.; et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidoust, D.; Isoda, A. Phytotoxicity assessment of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles on root elongation and growth of rice plant. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 5173–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, G.A.; Saad-Allah, K.M. Green synthesis of sulfur nanoparticles using Ocimum basilicum leaves and its prospective effect on manganese-stressed Helianthus annuus (L.) seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Hong, F.; Lu, S.; Liu, C. Effect of nano-TiO(2) on strength of naturally aged seeds and growth of spinach. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2005, 104, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Patra, P.; Mitra, S.; Dey, K.K.; Jain, S.; Sarkar, S.; Roy, S.; Palit, P.; Goswami, A. Manganese nanoparticles: Impact on non-nodulated plant as a potent enhancer in nitrogen metabolism and toxicity study both In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8777–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotikova, A.P.; Astafurova, T.P.; Burenina, A.; Suchkova, S.; Morgalev, Y.N. Morphophysiological features of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings upon exposure to nickel nanoparticles. Sel’skokhozyaistvennaya Biol. 2018, 53, 578–586. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, N.K.; Al Farttoosi, H.A.K. Response of mung bean to boron nanoparticles and spraying stages (Vigna Radiata L.). Plant Arch. 2019, 19, 712–715. [Google Scholar]
- Taran, N.Y.; Gonchar, O.M.; Lopatko, K.G.; Batsmanova, L.M.; Patyka, M.V.; Volkogon, M.V. The effect of colloidal solution of molybdenum nanoparticles on the microbial composition in rhizosphere of Cicer arietinum L. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.K.; Song, X.P.; Joshi, A.; Tian, D.D.; Rajput, V.D.; Singh, M.; Arora, J.; Minkina, T.; Li, Y.R. Recent Trends in Nano-Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture under Climate Change for Global Food Security. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.H.; Mai, T.T.T.; Phan, K.S.; Nguyen, T.M.; Tran, T.L.A.; Dong, T.N.; Tran, H.C.; Ngo, T.T.H.; Hoang, P.H.; Ha, P.T. Novel Integrated Nanofertilizers for Improving the Growth of Polyscias fruticosa and Asparagus officinalis. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 5791922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, B. Nanotechnology a Potential Tool to Mitigate Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants. In Abiotic and Biotic Stress in Plants; De Oliveira, A.B., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gull, A.; Lone, A.A.; Wani, N.U.I. Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Plants. In Abiotic and Biotic Stress in Plants; De Oliveira, A.B., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahzal, S.; Singh, M.P.; Chaudhary, N.; Singh, N.K. Application of nanoparticles in developing resilience against abiotic stress in rice plant (Oryza sativa L.). In Plant Perspectives to Global Climate Changes Developing Climate-Resilient Plants; Aftab, T., Roychoudhury, A., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; He, C.Q.; Ding, N.Z. Abiotic Stresses: General Defenses of Land Plants and Chances for Engineering Multistress Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, K.F.M.; Alloosh, M.T.; Saleh, M.M.; Alnaddaf, L.; Almuhammady, A.K.; Al-Khayri, J.M. Utilization of Nanofertilizers in Crop Tolerance to Abiotic Stress. In Nanobiotechnology, Mitigation of Abiotic Stress in Plants; Al-Khayri, J.M., Ansari, M.I., Singh, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 261–290. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulhameed, M.F.; Taha, A.A.; Ismail, R.A. Improvement of cabbage growth and yield by nanofertilizers and nanoparticles. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, K.; Jalilian, J.; Pirzad, A. Nano-fertilizers improved drought tolerance in wheat under deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, F.J.; Dal Sasso, G.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, G.B.; Pii, Y.; Delgado-López, J.M.; Guagliardi, A.; Masciocchi, N. Urea functionalized amorphous calcium phosphate nanofertilizers: Optimizing the synthetic strategy towards environmental sustainability and manufacturing costs. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farshchi, H.K.; Azizi, M.; Teymouri, M.; Nikpoor, A.R.; Jaafari, M.R. Synthesis and characterization of nanoliposome containing Fe2+ element: A superior nano-fertilizer for ferrous iron delivery to sweet basil. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 283, 110110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostadi, A.; Javanmard, A.; Machiani, M.A.; Morshedloo, M.R.; Nouraein, M.; Rasouli, F.; Maggi, F. Effect of different fertilizer sources and harvesting time on the growth characteristics, nutrient uptakes, essential oil productivity and composition of Mentha x piperita L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 148, 112290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, T.A.; Bayoumi, Y.; Eid, Y.; Elbasiouny, H.; Elbehiry, F.; Prokisch, J.; El-Ramady, H.; Ling, W. Can Nanofertilizers Mitigate Multiple Environmental Stresses for Higher Crop Productivity? Sustainability 2022, 14, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Menon, S.; Venkat Kumar, S.; Rajeshkumar, S. Mechanistic study on antibacterial action of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using green route. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 286, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Nanoantimicrobials for Plant Pathogens Control: Potential Applications and Mechanistic Aspects. In Nanobiotechnology Applications in Plant Protection-Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences; Abd-Elsalam, K.A., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 111–135. ISBN 978-3-319-91160-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, A.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A.; Kuca, K. Zinc-Based Nanomaterials for Diagnosis and Management of Plant Diseases: Ecological Safety and Future Prospects. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, W.H.; Ma, C.; White, J.C. Nanoparticles for Plant Disease Management. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 6, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lv, L.; Ahmed, T.; Jin, S.; Shahid, M.; Noman, M.; Osman, H.E.H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Li, X.; et al. Effect of the Nanoparticle Exposures on the Tomato Bacterial Wilt Disease Control by Modulating the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Cao, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Ali, A.; Hou, T.; Xiang, Z.; Zhuang, J.; Wu, S.; et al. Potential applications and antifungal activities of engineered nanomaterials against gray mold disease agent Botrytis cinerea on rose petals. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.; Adeel, M.; He, Z.; Umar, M.; Shakoor, N.; Da Silva, W.; Elmer, W.; White, J.C.; Rui, Y. Nanotechnology and Plant Viruses: An Emerging Disease Management Approach for Resistant Pathogens. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6030–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Murmu, G.; Mukherjee, K.; Saha, S.; Maity, D. A comprehensive overview of nanotechnology in sustainable agriculture. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 355, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Bindraban, P.S. Nanofertilizers: New Products for the Industry? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 66, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.V.R. Commercial nanoproducts available in world market and its economic viability. In Advances in Nano-Fertilizers and Nano-Pesticides in Agriculture, A Smart Delivery System for Crop Improvement; Jogaiah, S., Singh, H.B., Fraceto, L.F., De Lema, R., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2021; pp. 561–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Cui, B.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H. Marketing strategy and environmental safety of nano-biopesticides. In Advances in Nano-Fertilizers and Nano-Pesticides in Agriculture, A Smart Delivery System for Crop Improvement; Jogaiah, S., Singh, H.B., Fraceto, L.F., De Lema, R., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2021; pp. 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, R.; Sharma, L.D.; Sen, S.; Karmakar, S.; Banerjee, K.; Baral, K. Enhancing the Productivity of Field Crops through Nano-Fertilizer. In Agricultural Development in Asia: Potential Use of Nano-Materials and Nano-Technology; Asaduzzaman, Afroz, M.M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.bio-fit.eu/q6/lo4-nano-fertilizers-and-genetically-engineered-microbes (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- González-Melendi, P.; Fernández-Pacheco, R.; Coronado, M.J.; Corredor, E.; Testillano, P.S.; Risueño, M.C.; Marquina, C.; Ibarra, M.R.; Rubiales, D.; Pérez-de-Luque, A. Nanoparticles as smart treatment-delivery systems in plants: Assessment of different techniques of microscopy for their visualization in plant tissues. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fageria, N.K.; Filho, M.P.B.; Moreira, A.; Guimarães, C.M. Foliar fertilization of crop plants. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 1044–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.X.; Sun, C.J.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Gu, W. Applications of nanotechnology in agrochemical formulation, perspectives, challenges and strategies. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Nanoagri, Sao Pedro, Brazil, 20–25 June 2010; pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, U.; Barupal, M.; Shekhawat, N.S.; Kataria, V. Aeroponics for propagation of horticultural plants: An approach for vertical farming. Hortic. Int. J. 2018, 2, 443–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, J.C. Nanofertilizers: Future for global food production. In Proceedings of the 2nd Edition of Global Conference on Agriculture and Horticulture, Online, 1–3 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nagula, S.; Ramanjaneyulu, A.V. Nanofertilizers: The Next Generation Fertilizer. Biotica Res. Today 2020, 2, 905–907. [Google Scholar]
- Maluin, F.N.; Hussein, M.Z.; Nik Ibrahim, N.N.L.; Wayayok, A.; Hashim, N. Some Emerging Opportunities of Nanotechnology Development for Soilless and Microgreen Farming. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamir Iqbal, M. Nano-Fertilizers for Sustainable Crop Production under Changing Climate: A Global Perspective; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lombi, E.; Zhao, F.J.; Kopittke, P.M. Nanotechnology: A New Opportunity in Plant Sciences. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.; Varghese, S.H.; Nair, B.G.; Maekawa, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Kumar, D.S. Nanoparticulate material delivery to plants. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurepa, J.; Paunesku, T.; Vogt, S.; Arora, H.; Rabatic, M.; Lu, J.; Wanzer, M.B.; Woloschak, G.E.; Smalle, J.A. Uptake and distribution of ultrasmall anatase TiO2 Alizarin red S nanoconjugates in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2296–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.; Feng, H.; Brown, I.G.; Chu, P.; Yu, Z. Controlling nitrogen migration through micro-nano networks. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Bauer, T.; Chauhan, A.; Jindal, T. Nanoparticles induced stress and toxicity in plants. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 15, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Farooq, M.; Wakeel, A.; Nawaz, A.; Cheema, S.A.; Rehman, H.U.; Ashraf, I.; Sanaullah, M. Nanotechnology in agriculture: Current status, challenges and future opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Singh, A.; Minkina, T.; Rawat, S.; Mandzhieva, S.; Sushkova, S.; Shuvaeva, V.; Nazarenko, O.; Rajput, P.; Komariah Verma, K.K.; et al. Nano-Enabled Products: Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Agriculture. Plants 2021, 10, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Díaz, M.; García-Gonzalo, P.; Mancho, C.; Hernández, L.E.; Alonso, J.; Lobo, M.C. Response of spinach plants to different doses of two commercial nanofertilizers. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 301, 111143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helar, G.; Chavan, A. Synthesis, characterization and stability of gold nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum and its impact on seed. Int. J. Recent Sci. Res. 2015, 6, 3181–3318. [Google Scholar]
- Kandasamy, S.; Prema, R.S. Methods of synthesis of nano particles and its applications. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Yomso, J.; Menon, S. Impact of nanofertilizers on growth and yield parameters of rice crop; A Review. Pharma Innov. J. 2021, 10, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kahlel, A.M.S.; Abdulla, A.A.; Saadalla, H.A.; Hamed, M.H. Effect of Nano Fertilizers and Its Applying Methods on Growth Parameters of Senna (Cassia Angustifolia) Seedling Plant. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 923, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, K.; Verma, P.; Singh, O.; Pawar, A.; Singh, T.; Kumar, Y.; Raliya, R. Effect of nitrogen and zinc nanofertilizer with the organic farming practices on cereal and oil seed crops. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, K.S.; Tarafdar, J.C. Prospects of nanotechnology in Indian farming. Ind. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 81, 887–893. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.K.; Das, S.; Mawlong, L.G. Nanotechnology and its importance in micronutrient fertilization. Int. J. Curr. Micro. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2306–2325. [Google Scholar]
- Meghana, K.T.; Wahiduzzaman, M.D.; Vamsi, G. Nanofertilizers in Agriculture. Acta Sci. Agric. 2021, 5, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, K.S.; Manikandan, A.; Thirunavukkarasu, M.; Rahale, C.S. Nano-fertilizers for Balanced Crop Nutrition. In Nanotechnologies in Food and Agriculture; Rai, M., Ribeiro, C., Mattoso, L., Duran, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Basit, F.; Asghar, S.; Ahmed, T.; Ijaz, U.; Noman, M.; Hu, J.; Liang, X.; Guan, Y. Facile synthesis of nanomaterials as nanofertilizers: A novel way for sustainable crop production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 51281–51297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissue, B.; Yuan, H. Structure, particle size, and annealing of gas phase-condensed Eu3+: Y2O3 nanophosphors. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 171, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, N. Methods of preparation of nanoparticles-a review. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2015, 7, 1806. [Google Scholar]
- Raliya, R.; Tarafdar, J.C. ZnO nanoparticle biosynthesis and its effect on phosphorous-mobilizing enzyme secretion and gum contents in Clusterbean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.). Agric. Res. 2013, 2, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maissel, L.I.; Glang, R. Handbook of Thin Film Technology; Maissel, L.I., Glang, R., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Nieman, G.; Weertman, J.; Siegel, R. Microhardness of nanocrystalline palladium and copper produced by inert-gas condensation. Scr. Metall. 1989, 23, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigue, P.; Delville, M.H.; Labrugère, C.; Cloutet, E.; Kulesza, P.J.; Morand, J.P.; Kuhn, A. Top-down approach for the preparation of colloidal carbon nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2984–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangdi, K. Production of nanofertilizer- a mini review. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, C.C. Nanostructured Materials: Processing, Properties and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, P.; Iannotta, S. Cluster Beam Synthesis of Nanostructured Materials; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nalwa, H.S. Handbook of Nanostructured Materials and Nanotechnology; Five-Volume Set; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.W. Fundamental Principles of Sol—Gel Technology. Inst. Met. 1990, 1990, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Kruis, F.E.; Fissan, H.; Peled, A. Synthesis of nanoparticles in the gas phase for electronic, optical and magnetic applications—A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 1998, 29, 511–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Tang, C.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, H. Photochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles by the sunlight radiation using a seeding approach. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, S.; Sadique, S.; Kazerooni, E.G.; Majeed, U.; Shehzad, M.R. Physical and chemical techniques to produce nano fertilizers. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2019, 15, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, B.; Ahmed, A.I.S.; Omer, A.M.; Agha, M.K.M.; Emam, T.M. Nano-fertilizers: Bio-fabrication, application and biosafety. Novel Res. Microbiol. J. 2020, 4, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toksha, B.; Sonawale, V.A.M.; Vanarase, A.; Bornare, D.; Tonde, S.; Hazra, C.; Kundu, D.; Satdive, A.; Tayde, S.; Chatterjee, A. Nanofertilizers: A review on synthesis and impact of their use on crop yield and environment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghamry, A.M.; Mosa, A.A.; Alshaal, T.A.; El-Ramady, H.R. Nanofertilizers vs. Biofertilizers: New Insights. Environ. Biodiver. Soil Secur. 2018, 2, 51–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kalishwaralal, K.; Deepak, V.; Ramkumarpandian, S.; Nellaiah, H.; Sangiliyandi, G. Extracellular Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by the Culture Supernatant of Bacillus licheniformis. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4411–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Krishnamurthy, R. Antimicrobial efficiency of biologically synthesized nanoparticles using root extract of Plumbago zeylanica as biofertilizer application. Int. J. Bioassays 2015, 4, 4473–4475. [Google Scholar]
- Ndaba, B.; Roopnarain, A.; Rama, H.; Maaza, M. Biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles as fertilizers: An emerging precision agriculture strategy. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 1225–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Eva, O.; Oberdörster, J. An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Persp. J. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachan, R.; Verma, H.; Yadav, A.; Nisha, S. Nanofertilizers: Applications and Future Prospects. Just Agric. 2021, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nongbet, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Mahanta, S.; Ray, M.K.; Khan, M.; Baek, K.-H.; Chakrabartty, I. Nanofertilizers: A Smart and Sustainable Attribute to Modern Agriculture. Plants 2022, 11, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, D.M.; Satapathy, K.C.; Panda, B. Biofertilizers and nanofertilizers for sustainable agriculture: Phycoprospects and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.H.F.; Duran, N.; De Carvalho, H.W.P. Challenges and perspective for the application of nanomaterials as fertilizers. In Advances in Nano-Fertilizers and Nano-Pesticides in Agriculture: A Smart Delivery System for Crop Improvement; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 331–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, J.C. Nanofertilizers: Challenges and Prospects; Scientific Publishers: Jodhpur, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zahra, Z.; Habib, Z.; Hyun, H.; Shahzad, H.M.A. Overview on Recent Developments in the Design, Application, and Impacts of Nanofertilizers in Agriculture. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.; Singh, R.P.; Yadav, D.; Rathore, S.S.; Raj, R.; Avasthe, R.; Yadav, S.K.; Das, A.; Yadav, V.; Yadav, B.; et al. Nanofertilizers for agricultural and environmental sustainability. Chemosphere 2021, 292, 133451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Juthery, H.W.; Lahmoud, N.R.; Alhasan, A.; Al-Jassani, N.; Houria, A. Nano-Fertilizers as a Novel Technique for Maximum Yield in Wheat Biofortification (Article Review). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1060, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

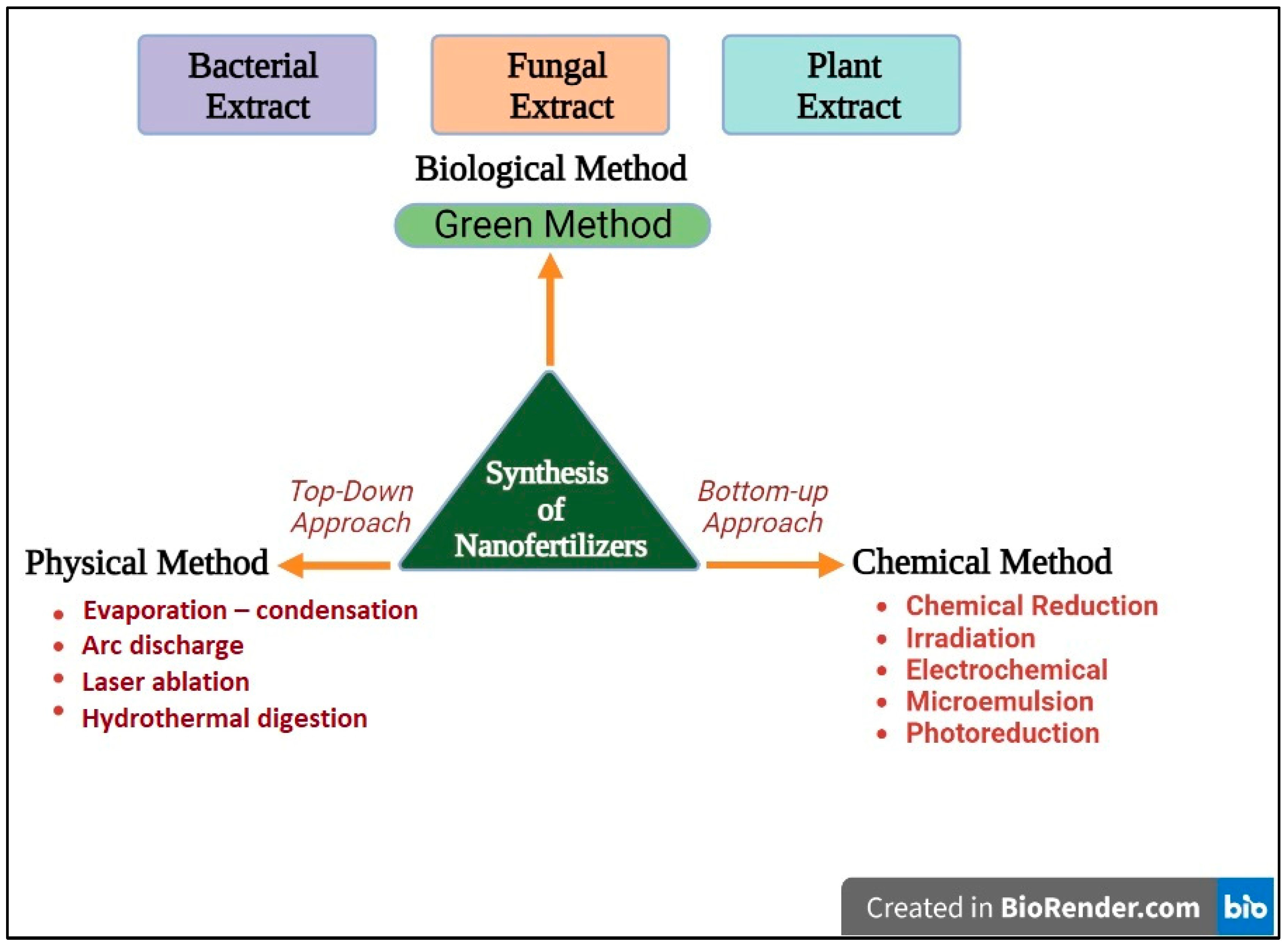


| Properties | Nanofertilizers | Traditional Fertilizers |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility and Dispersion of the mineral nutrients. | Nano-sized advantages the mineral nutrient by improving solubility, dispersion, and can achieve enhanced bioavailability. | Due to large-sized particles, it can show limited solubility and dispersion hence leading to poor bioavailability to the plants. |
| Deprivation rate of Nutrients in Fertilizer. | Nano-sized enables the retention in the soil particle for a prolonged period. | Significantly leached, rain-off, and drifts can occur in the methods. |
| Superintend releasing Mode. | Release rate and pattern of nutrients can be precisely controlled by encapsulating the nanofertilizers in the polymer matrix, supporting sustainable practices. | Direct exposure to fertilizers might be toxic in excess dosage and can also damage the ecosystem associated with the crop field. |
| Nutrient Uptake Efficiency. | Nanostructured Fertilizer can save the excess use and increases the efficiency in uptake ratio during controlled cultivation. | Large-sized Chemical Composite is difficult to uptake by plants hence reducing efficiency and resource utilization. |
| Prolongation of effective nutrient release. | Nanostructured formulation can extend the nutrient supply to the plant for a prolonged time by controlled released efficiency. | Readily available at the time of delivery or foliar leading to the loss of rest nutrients into the soil, forming insoluble salts. |
| Characteristic | Bionanofertilizers | Nanobiofertilizers |
|---|---|---|
| Synthesis of NPs | Biological method | Biological, chemical, or Physical |
| Structure | Biologically synthesized NPs as fertilizer | Nano-encapsulated Organic Molecules as fertilizer |
| Encapsulation | Biomolecules from biological materials | Nanomaterial |
| Core | Micro/macronutrient element | Inorganic and organic |
| Example | MgO [41], ZnO [42], | Phosphorous-hydroxyapatite NPs [9] and Zn-Chitosan NPs [22] |
| Sr. No. | Type of Nanoparticle Used | Mode of Application | Crop Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | N (urea-coated hydroxyapatite) | Soil application | Rice | [41] |
| 2 | P (coated hydroxyapatite) | Foliar spray | Soybean | [42] |
| 3 | K | Foliar spray | Basil | [43] |
| 4 | Ca | Foliar spray | Basil | [43] |
| 5 | Mg (MgO) | Foliar spray | Cluster bean | [44] |
| 6 | Zn (ZnO) | Foliar spray | Pearl Millet | [45] |
| 7 | Zn (Zn-chitosan) | Foliar spray | Wheat | [22] |
| 8 | Fe (Fe2O3) | Foliar spray | Wheat, watermelon, corn, tomato, peanut | [45,46,47,48] |
| 9 | Fe (Fe2O3) | Seed treatment | Rice | [49] |
| 10 | Cu (Cu−chitosan) | Seed treatment | Tomato | [23] |
| 11 | Cu (Cu−chitosan) | Foliar spray | Corn | [24] |
| 12 | S | Seed treatment | Sunflower | [50] |
| 13 | Mn | Seed treatment | Mung bean | [51] |
| 14 | Ti (nanoanatase TiO2) | Soil application | Spinach | [52] |
| 15 | Ni | Seed treatment | Wheat | [53] |
| 16 | B | Foliar spray | Mung bean | [54] |
| 17 | Mo | Foliar spray | Chickpea | [55] |
| 18 | Zn and Mg-doped hydroxyapatite modified with urea | Foliar spray, soil applicant | Wheat | [56] |
| 19 | Urea–hydroxyapatite nanohybrid | Soil applicant | Tea plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) Kuntze) | [6] |
| 20 | Phosphorous-Containing HydroxyapatiteNanoparticles (nHAP) | Foliar spray | Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) | [9] |
| 21 | Integrated Nanofertilizers(N, P, K, Mg, S, Si, Ca, Fe, Cu, Zn, Co, and Ag) | Foliar spray and soil applicant | Polyscias fruticosa and Asparagus officinalis | [57] |
| Commercial Product | Content | Company |
|---|---|---|
| Nano-GroTM | Plant growth regulator and immunity enhancer | Agro Nanotechnology Corp., Miami, FL, USA |
| Nano Green | Extracts of corn, grain, soybeans, potatoes, coconut, and palm | Nano Green Sciences, Inc., Delhi, India |
| Nano-Ag Answer® | Microorganisms, sea kelp, and mineral electrolyte | Urth Agriculture, Monterey, CA, USA |
| Biozar Nano-Fertilizer | Combination of organic materials, micronutrients, and macromolecules | Fanavar Nano-Pazhoohesh Markazi Company, Tehran, Iran |
| Nano Max NPK Fertilizer | Multiple organic acids chelated with major nutrients, amino acids, organic carbon, organic micronutrients/trace elements, vitamins, and probiotics | JU Agri Sciences Pvt. Ltd., Janakpuri, New Delhi, India |
| Master Nano Chitosan Organic Fertilizer | Water soluble liquid chitosan, organic acid, salicylic acids, and phenolic compounds | Pannaraj Intertrade, Bangkok, Thailand |
| TAG NANO (NPK, PhoS, Zinc, Cal, etc.) fertilizers | Proteino-lacto-gluconate chelated with micronutrients, vitamins, probiotics, seaweed extracts, and humic acid | Tropical Agrosystem India (P) Ltd., Karnal, India |
| Nualgi Foliar Spray | Combining 12 essential nutrients loaded in nano-silica (henceforth NF-A) | Nualgi America, Inc., San Marcos, CA, USA [97] |
| NovaLand-Nano | Nano macro- and micro-elements for plant growth (henceforth NF-B) | Land Green & Technology Co., Ltd., Taiwan [97] |
| Titanium dioxide [TiO2]—universal pigment [20 nm] | Titanium dioxide 99% | Land Green & Technology Co., Ltd., Taiwan |
| Silicon dioxide [SiO2]—universal stabilizer agent [20–60 nm] | Silicon dioxide 99% | Land Green & Technology Co., Ltd., Taiwan |
| Manganese dioxide [MnO2]—universal purifier [1–50 nm] | Manganese dioxide 99.9% | Land Green & Technology Co., Ltd., Taiwan |
| Selenium colloid [Se]—universal antioxidant [1–20 nm] | Selenium colloid 99.9% | Land Green & Technology Co., Ltd., Taiwan |
| Nano Urea (Liquid) | Nitrogen supplement for crops | Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative Ltd., New Delhi, India |
| Poly olefin resin-coated urea | N supplement for plants | Japan |
| Neem Coated Urea | N supplement for plants | Aditya Birla Nuvo Ltd., Veraval, India |
| nano-organic compound fertilizer | Plant Growth promoters in vegetables, crops, and flowers | Lazuriton Nano Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Taiwan |
| Hibong biological fulvic acid | Nano fertilizer, humic acid. Chitosan oligosacchairides ≥ 30 g/L, N ≥ 46 g/L, P2O5 ≥ 21 g/L, K2O ≥ 62 g/L, organic matter: 130 g/L | Qingdao Hibong Fertilizer Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China |
| Seaweed nano organic carbon fertilizer | NPK: 2–3–3, seaweed extract ≥ 5%, organic matter: 35%, humic acid ≥ 5%, amino acid ≥ 5% | Qingdao Hibong Fertilizer Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China |
| Supplementary powder (Nano capsule) | N, 0.5%; K2O, 3.9%; Ca, 2.0%; Mg, 0.2%; S, 0.75%; P2O5, 0.7%; Fe, 0.03%; Cu, 0.007%; Zn, 0.004%; Mn, 0.004%; | The Best International Network Co., Ltd., Bangkok, Thailand |
| TAG nano (NPK, Zinc, PhoS, Cal, etc.) fertilizers | Proteino-lacto-gluconate chelated with micronutrients, vitamins, probiotics, seaweed extracts, and humic acid | Tropical Agrosystem India (P) Ltd., New Delhi, India |
| P, K | Fertilizer with a high content of P (30%) and K (20%) | Fosvit K30; Kimitec Group, Spain |
| B | Used as micronutrient | Nano Bor 20%; Alert Biotech, Nashik, India |
| Zn | Growth enhancer | Nano Zinc Chelate Fertilizer; AFME Trading Group, UK |
| Fe, Ca | Plant growth regulator and accelerator | Nano Iron and Calcium, Potassium Chelate Fertilizer; AFME Trading Group, UK |
| Nano micronutrient (EcoStar) (500) g | Zn, 6%; B, 2%; Cu, 1%; Fe, 6%+; EDTA Mo, 0.05%; Mn, 5%+; and AMINOS, 5% | Shan Maw Myae Trading Co., Ltd., Yangon, India |
| Nano ultra-fertilizer (500) g | Organic matter, 5.5%; nitrogen, 10%; P2O5, 9%; K2O, 14%; P2O5, 8%; K2O, 14%; and MgO, 3% | SMTET Eco-technologies Co., Ltd., Taiwan |
| Nano calcium (magic green) (1) kg | CaCO3, 77.9%; MgCO3, 7.4%; SiO2, 7.47%; K, 0.2%; Na, 0.03%; P., 0.02%; Fe-7.4 ppm; Al2O3, 6.3 ppm; Sr, 804 ppm; sulfate, 278 ppm; Ba, 174 ppm; Mn, 172 ppm; and Zn, 10 ppm | AC International Network Co., Ltd., Germany |
| PPC nano (120) mL | M protein, 19.6%; Na2O, 0.3%; K2O, 2.1%; (NH4)2SO4, 1.7%; and diluent, 76% | WAI International Development Co., Ltd., Sungai Buloh, Malaysia |
| Plant nutrition powder (green nano) | N, 0.5%; P2O5, 0.7%; K2O, 3.9%; Ca, 2.0%; Mg, 0.2%; S, 0.8%; Fe, 1.0%; Mn, 49 ppm; Cu, 17 ppm; and Zn, 12 ppm | Green Organic World Co., Ltd., Surin, Thailand |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gade, A.; Ingle, P.; Nimbalkar, U.; Rai, M.; Raut, R.; Vedpathak, M.; Jagtap, P.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Nanofertilizers: The Next Generation of Agrochemicals for Long-Term Impact on Sustainability in Farming Systems. Agrochemicals 2023, 2, 257-278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agrochemicals2020017
Gade A, Ingle P, Nimbalkar U, Rai M, Raut R, Vedpathak M, Jagtap P, Abd-Elsalam KA. Nanofertilizers: The Next Generation of Agrochemicals for Long-Term Impact on Sustainability in Farming Systems. Agrochemicals. 2023; 2(2):257-278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agrochemicals2020017
Chicago/Turabian StyleGade, Aniket, Pramod Ingle, Utkarsha Nimbalkar, Mahendra Rai, Rajesh Raut, Mahesh Vedpathak, Pratik Jagtap, and Kamel A. Abd-Elsalam. 2023. "Nanofertilizers: The Next Generation of Agrochemicals for Long-Term Impact on Sustainability in Farming Systems" Agrochemicals 2, no. 2: 257-278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agrochemicals2020017
APA StyleGade, A., Ingle, P., Nimbalkar, U., Rai, M., Raut, R., Vedpathak, M., Jagtap, P., & Abd-Elsalam, K. A. (2023). Nanofertilizers: The Next Generation of Agrochemicals for Long-Term Impact on Sustainability in Farming Systems. Agrochemicals, 2(2), 257-278. https://doi.org/10.3390/agrochemicals2020017








