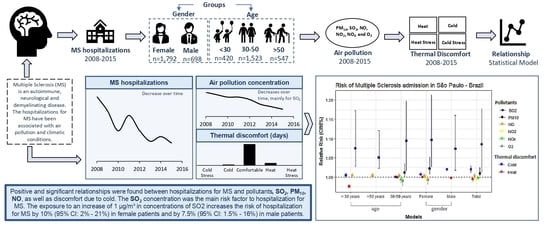
Impacts of Air Pollution and Thermal Discomfort in Hospitalizations for Multiple Sclerosis in Sao Paulo, Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Hospitalizations
2.2.2. Pollutants and Metorological Variables
2.3. Human Thermal Discomfort Index (HDI)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MS Hospitalizations
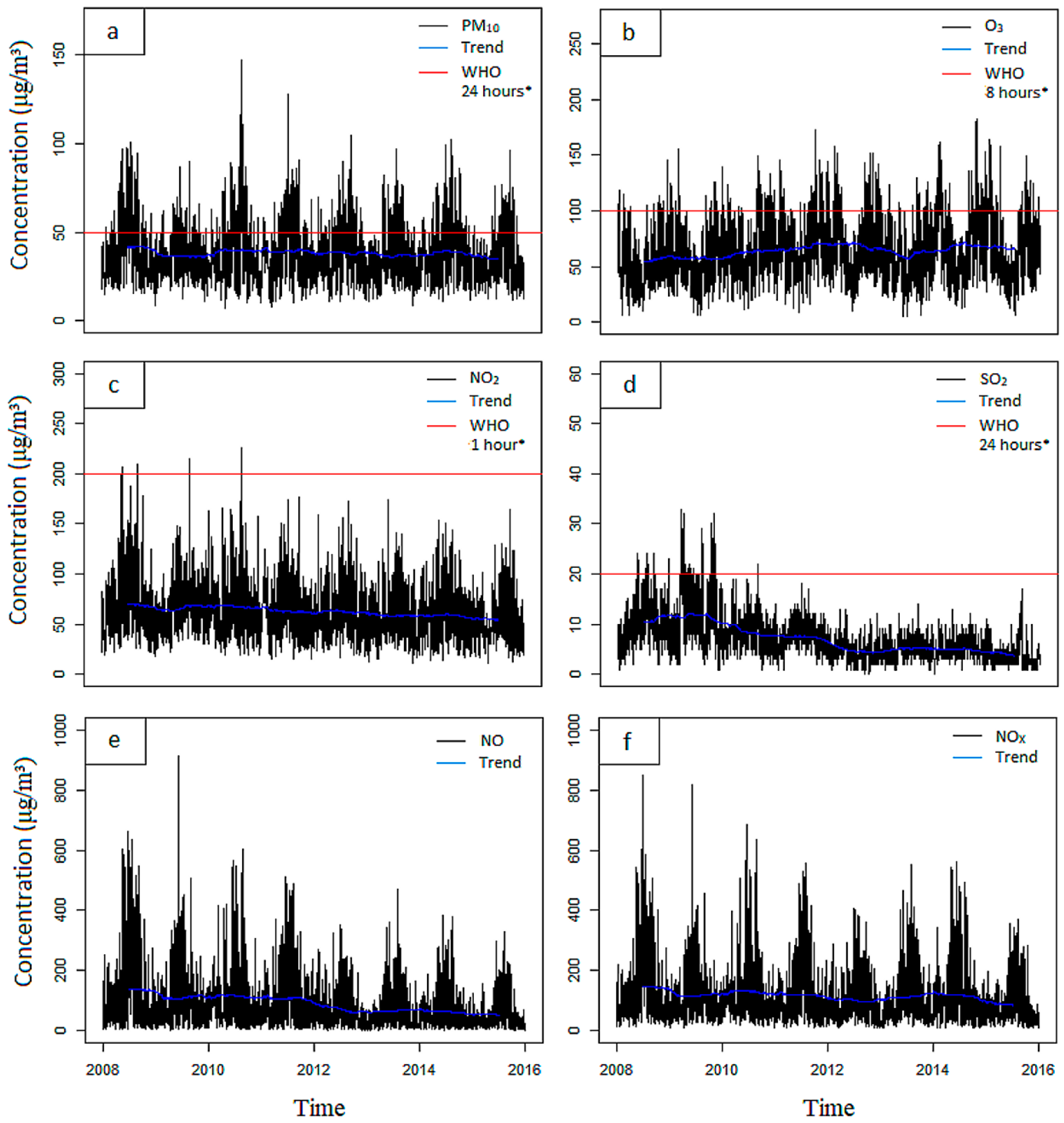
3.2. Pollutants
3.3. Human Thermal Discomfort Index (HDI)
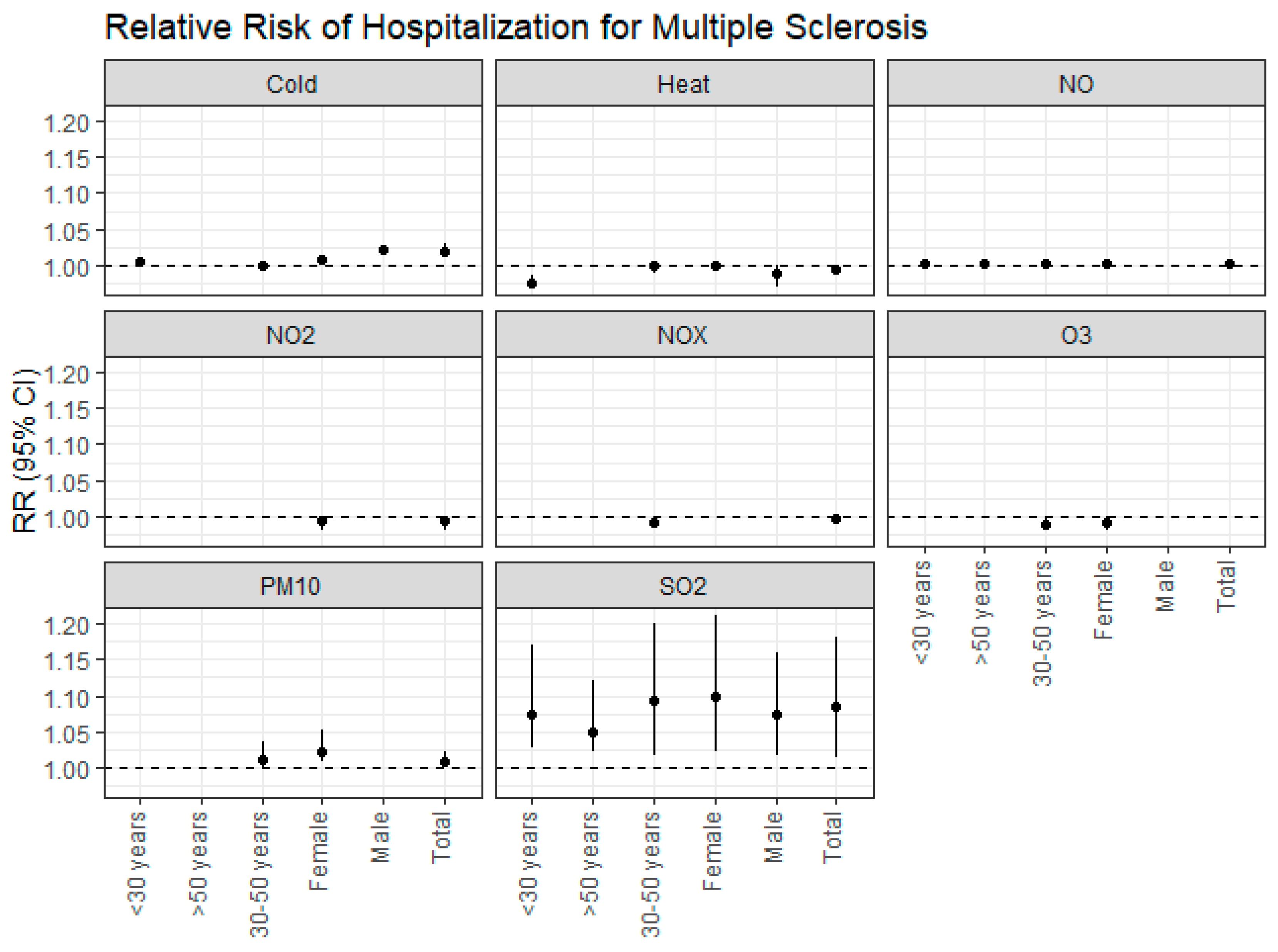
3.4. Relation between Pollutants and HDI with MS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manisalidi, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keswani, A.; Akselrod, H.; Anenberg, S.C. Health and Clinical Impacts of Air Pollution and Linkages with Climate Change. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bălă, G.P.; Râjnoveanu, R.M.; Tudorache, E.; Motișan, R.; Oancea, C. Air pollution exposure—The (in)visible risk factor for respiratory diseases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19615–19628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kindi, S.G.; Brook, R.D.; Biswal, S.; Rajagopalan, S. Environmental determinants of cardiovascular disease: Lessons learned from air pollution. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 656–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, F.R.; Frony-Macedo, A.L.; Piacenti-Silva, M. Influence of particulate matter and meteorological conditions on multiple sclerosis relapse: A preliminary study in São Paulo, Brazil. Arch. Health Investig. 2017, 6, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzano, M.; Schiavetti, I.; Bergamaschi, R.; Pisoni, E.; Bellavia, A.; Mallucci, G.; Carmisciano, L.; Inglese, M.; Cordioli, C.; Marfia, G.A.; et al. The impact of PM2.5, PM10 and NO2 on COVID-19 severity in a sample of patients with multiple sclerosis: A case-control study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 68, 104243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Tabary, M.; Aryannejad, A.; Abolhasani, R.; Araghi, F.; Khaheshi, I.; Azimi, A. Air pollution and multiple sclerosis: A comprehensive review. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 4063–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, A.; Lova, L.; Comoli, P.; Volpe, E.; Villa, S.; Mallucci, G.; La Salvia, S.; Romani, A.; Franciotta, D.; Bollati, V.; et al. Air pollution as a contributor to the inflammatory activity of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanjean, M.; Bind, M.A.; Roux, J.; Ongagna, J.C.; Sèze, J.; Bard, D.; Leray, E. Ozone, NO2 and PM10 are associated with the occurrence of multiple sclerosis relapses. Evidence from seasonal multi-pollutant analyses. Environ. Res. 2018, 163, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.A.; Felipe, E.; Mendes, M.F.; Tilbery, C.P. Esclerose Múltipla: Estudo descritivo de suas formas clínicas em 302 casos. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2000, 58, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegaro, D.; Goldbaum, M.; Morais, L.; Tilbery, M.K.; Moreira, A.; Gabbai, A.A.; Scaff, M. The prevalence of multiple sclerosis in the city of São Paulo, Brazil, 1997. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2001, 104, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, E.; Patrucco, L.; Rojas, J.L. A systematic review of the epidemiology of multiple sclerosis in South America. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydarpour, P.; Amini, H.; Khoshkish, S.; Seidkhani, H.; Sahraian, M.A.; Yunesian, M. Potential Impact of Air Pollution on Multiple Sclerosis in Tehran, Iran. Neuroepidemiology 2014, 43, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelici, L.; Piola, M.; Cavalleri, T.; Randi, G.; Cortini, F.; Bergamaschi, R.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Pesatori, A.C.; Bollati, V. Effects of particulate matter exposure on multiple sclerosis hospital admission in Lombardy region, Italy. Environ. Res. 2016, 145, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petajan, J.H.; White, A.T. Recommendations of physical activity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Sports Med. 1999, 27, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christogianni, A.; O’Garro, J.; Bibb, R.; Filtness, A.; Filingeri, D. Heat and cold sensitivity in multiple sclerosis: A patient-centred perspective on triggers, symptoms, and thermal resilience practices. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 67, 104075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadano, Y.S.; Ugaya, C.M.L.; Franco, A.T. Método de regressão de Poisson: Metodologia para avaliação do impacto da poluição atmosférica na saúde populacional. Ambiente Soc. 2009, 12, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.S.P.; Kawamura, T. Sensible Climates in Monsoon Asia. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1991, 35, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G. The Relationship between Relative Humidity and the Dewpoint Temperature in Moist Air. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparrini, A. Distributed Lag Linear and Non-Linear Models in R: The Package dlnm. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, R.A.; Stasinopoulos, D.M. Generalized additive models for location, scale and shape. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Appl. Stat.) 2005, 54, 507–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, A.M.; Waubant, E.; Casper, T.C.; Roalstad, S.; Candee, M.; Rose, J.W.; Belman, A.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Aaen, G.; Tillema, J.-M.; et al. Urban air quality and associations with pediatric multiple sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, G.; Yue, H.; Yun, Y.; Sang, N. Chronic SO2 inhalation above environmental standard impairs neuronal behavior and represses glutamate receptor gene expression and memory-related kinase activation via neuroinflammation in rats. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Encinas, J.M.; Manganas, L.; Enikolopov, G. Nitric Oxide and Multiple Sclerosis. Curr. Neurol. And Neurosci. Rep. 2005, 5, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disanto, G.; Handel, A.E.; Morahan, J.M.; Deluca, G.C.; Kimball, S.M.; Hypponen, E.; Giovannoni, G.; Ebers, G.C.; Ramagopalan, S.V. Vitamin D and multiple sclerosis hospital admissions in Scotland. QJM Int. J. Med. 2011, 104, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
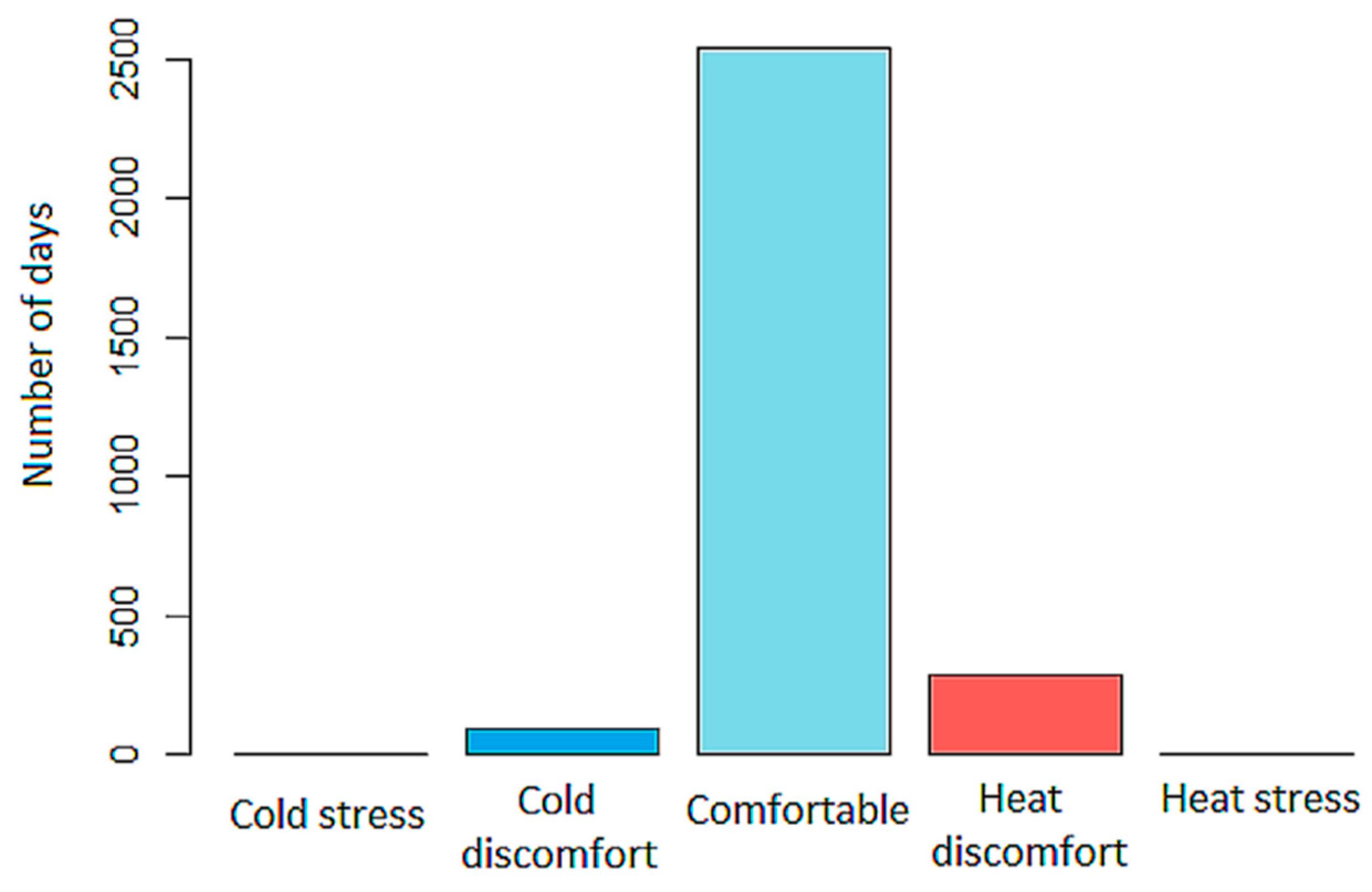
| Relative Humidity (%) | Air Temperature (°C) | HDI | Classification HDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 72.25 | 10.12 | <55 | Cold Stress |
| 77.45 | 13.06 | 55–60 | Cold Discomfort |
| 74.18 | 21.21 | 60–75 | Comfortable |
| 69.02 | 26.82 | 75–80 | Heat Discomfort |
| 67.60 | 32.06 | >80 | Heat Stress |
| Variables | Number of Hospitalizations |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female | 1792 |
| Male | 698 |
| Age | |
| ≤30 years | 420 |
| 30–50 years | 1523 |
| ≥50 years | 547 |
| Year | |
| 2008 | 565 |
| 2009 | 440 |
| 2010 | 266 |
| 2011 | 400 |
| 2012 | 269 |
| 2013 | 175 |
| 2014 | 215 |
| 2015 | 160 |
| Total | 2490 |
| Response Variables | Explanatory Variables | β | Std. Error | T Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitalization: Total | Intercept | 1.0823 | 0.391463 | 2.77 | 0.00573 |
| SO2 | 0.0818 | 0.004617 | 13.49 | 0.00000 | |
| NO | 0.0035 | 0.000601 | 5.98 | 0.00000 | |
| Nox | −0.0020 | 0.002586 | 2.96 | 0.00312 | |
| PM10 | 0.0093 | 0.000699 | −2.21 | 0.02698 | |
| NO2 | −0.0058 | 0.001529 | −3.37 | 0.00076 | |
| Cold | 0.0198 | 0.005562 | −3.53 | 0.00043 | |
| Heat | −0.0050 | 0.009499 | −2.04 | 0.04118 | |
| Hospitalization: Age < 30 years | Intercept | −0.7063667 | 0.924210 | −0.76 | 0.44476 |
| SO2 | 0.0721 | 0.011181 | 5.96 | 0.00000 | |
| NO | 0.0042 | 0.000367 | 11.30 | 0.00000 | |
| Cold | 0.0050 | 0.001849 | −2.03 | 0.04218 | |
| Heat | −0.0240 | 0.002224 | 2.62 | 0.00888 | |
| Hospitalization: Age between 30 and 50 years | Intercept | 1.1536203 | 0.527950 | 2.19 | 0.02896 |
| PM10 | 0.0116 | 0.003080 | 4.51 | 0.00001 | |
| O3 | −0.0095 | 0.002377 | −5.57 | 0.00000 | |
| SO2 | 0.0901 | 0.005656 | 14.36 | 0.00000 | |
| NO | 0.0035 | 0.000805 | 3.14 | 0.00171 | |
| Nox | −0.0063 | 0.000890 | −5.36 | 0.00000 | |
| Cold | 0.0005 | 0.000787 | −2.72 | 0.00649 | |
| Heat | −0.0002 | 0.000110 | −4.68 | 0.00000 | |
| Hospitalization: Age > 50 years | Intercept | −2.2591229 | 0.195089 | −11.58 | 0.00000 |
| SO2 | 0.0488 | 0.009691 | 4.98 | 0.00000 | |
| NO | 0.0038 | 0.000338 | 10.58 | 0.00000 | |
| Hospitalization: Female gender | Intercept | −1.1601294 | 0.658319 | −1.76 | 0.07813 |
| PM10 | 0.0218 | 0.003927 | 5.54 | 0.00000 | |
| SO2 | 0.0925 | 0.006960 | 8.74 | 0.00000 | |
| NO2 | −0.0045 | 0.002200 | −2.69 | 0.00711 | |
| NO | 0.0033 | 0.000413 | 8.08 | 0.00000 | |
| O3 | −0.0069 | 0.001664 | −2.38 | 0.01733 | |
| Cold | 0.0070 | 0.001979 | −1.77 | 0.07645 | |
| Heat | 0.0001 | 0.000021 | 2.04 | 0.04104 | |
| Hospitalization: Male gender | Intercept | −5.6264 | 0.973510 | −5.78 | 0.00000 |
| SO2 | 0.0715 | 0.010040 | 8.65 | 0.00000 | |
| Cold | 0.0198 | 0.001323 | 2.88 | 0.00405 | |
| Heat | −0.0020 | 0.000028 | 3.30 | 0.00098 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diniz, F.R.; Gonçalves, F.L.T.; Zilli Vieira, C.L.; Piacenti-Silva, M. Impacts of Air Pollution and Thermal Discomfort in Hospitalizations for Multiple Sclerosis in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Sclerosis 2023, 1, 113-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis1030012
Diniz FR, Gonçalves FLT, Zilli Vieira CL, Piacenti-Silva M. Impacts of Air Pollution and Thermal Discomfort in Hospitalizations for Multiple Sclerosis in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Sclerosis. 2023; 1(3):113-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis1030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiniz, Fernanda Rodrigues, Fábio L. T. Gonçalves, Carolina Letícia Zilli Vieira, and Marina Piacenti-Silva. 2023. "Impacts of Air Pollution and Thermal Discomfort in Hospitalizations for Multiple Sclerosis in Sao Paulo, Brazil" Sclerosis 1, no. 3: 113-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis1030012
APA StyleDiniz, F. R., Gonçalves, F. L. T., Zilli Vieira, C. L., & Piacenti-Silva, M. (2023). Impacts of Air Pollution and Thermal Discomfort in Hospitalizations for Multiple Sclerosis in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Sclerosis, 1(3), 113-123. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis1030012