Abstract
Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) signaling pathways play a crucial role in a number of biological processes in the eye. Specifically, in the ocular surface, their activity modulates epithelial integrity, inflammation, and generation of pain, while they have a role in visual processing in the retina. The NK1R is broadly expressed in the eye, in both ocular and non-ocular cells, such as leukocytes and neurons. In this review, we will discuss the roles of neurokinin-1 receptors and substance P (SP) in the physiopathology of eye disorders. Finally, we will review and highlight the therapeutic benefits of NK1R antagonists in the treatment of ocular diseases.
1. Introduction
1.1. The Tachykinin Peptide Family and Its Receptors
The tachykinin peptide family is one of the largest peptide families in mammals, which regulates key biological processes, such as wound healing and inflammation. The tachykinin family consists of three genes and multiple neuropeptides. Neurokinin A (NKA), neuropeptide K (NPK), neuropeptide gamma (NPγ), and SP are expressed by the tachykinin precursor 1 (TAC1) gene through alternative splicing. Neurokinin B (NKB) is encoded by TAC3 gene. TAC4 gene expresses both hemokinin-1 (HK-1) and endokinins [,,].
Tachykinin receptors genes (TACR1, TACR2, and TACR3) encode tachykinin 1 (NK1R), 2 (NK2R), and 3 (NK3R), respectively []. SP and HK-1 bind with high affinity to NK1R, NKA to NK2R, and NKB to NK3R. NKA and NKB bind to NK1R with low affinity (almost 100 times lower than SP). NKB and SP have a low affinity for NK2R, while NKA and SP exhibit low affinity for NK3R [,].
The NK1R is widely expressed in the eye, including ocular (corneal and retinal cells) and non-ocular cells (endothelial cells, leukocytes, and neurons) [,].
1.2. NK1R Structure
NK1R is a G-protein coupled receptor with extracellular glycosylation sites. It is located on the cell membrane and it contains 1221 nucleotides and 5 exons. It exists in two isoforms: one which is full length, and the other which is truncated and generated through alternative splicing [,,].
Both the truncated and the full-length NK1R are embedded seven-transmembrane receptors containing extracellular amino-terminal domain with glycosylation sites and an intracellular carboxy-terminal domain. Both receptors share three extracellular (E1, E2, and E3), and three intracellular loops (C1, C2, and C3), whereas the C4 intracellular loop is different. The truncated form lacks the intracellular Ser/Thr residues in the C4 loop. That leads to the absence of interaction with β-arrestin and an impaired interaction with G-proteins [,,,].
The full-length form contains 407 amino acids, whereas the truncated form contains only 311. Specifically, the truncated form lacks 96 amino acids in its C-terminal site, due to the presence of a premature stop codon before exon-5. The two types of NK1R are also different in term of SP affinity, the full-length form being ten times more affine to SP, despite the fact that the SP binding domain is similar in both isoforms [,,]. In fact, nanomolar concentrations of SP are sufficient to activate the full length NK1R, whereas micromolar concentrations of SP are required to activate truncated-NK1R [].
The short carboxyl tail of the truncated form leads to partially active and less efficient SP-mediated NK1R signaling. This is mediated by the interaction with G-proteins and downstream pathways [,]. Specifically, the full-length isoform via SP rapidly activates the downstream RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway and NF-κB. That increases IL-8 mRNA expression and intracellular Ca2+ concentrations. However, the NK1R truncated form is less effective in increasing IL-8 and intracellular calcium levels than the full form. Moreover, the activation of the truncated form has no effect on NF-κB expression. Finally, the truncated NK1R induces protein kinase C (PKC) downregulation and delays the activation of the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling pathway [,,].
In addition to the effects of the carboxyl tail, the presence of glycosylation also impacts NK1R function. Indeed, the glycosylated NK1R is more stable probably because it favors NK1R anchoring to the cell membrane [].
1.3. NK1R Signaling Activity
NK1R, a member of the G protein-coupled receptors superfamily regulates multiple signaling pathways in the eye. Substance P (SP) is a neuropeptide abundantly expressed on the ocular surface, including cornea and the retina [,,], and has the highest affinity for NK1R. Dissociation of SP from NK1R is mediated by metalloproteases [,,,]. SP-NK1R interaction leads to increased cell proliferation and/or migration of corneal epithelial, endothelial cells, keratocytes, and leukocytes. Moreover, it stimulates corneal and retinal neurogenesis [,,]. The binding of SP to the NK1R activates G proteins subunits (G-alpha, G-beta, and G-gamma), and leads to dissociation of the GDP/Gα subunit complex. The dissociated G-beta and G-gamma subunits remain bound to the cell membrane, whereas the GTP/Gα complex further leads to the activation of phospholipase C (PLC) and the production of second messengers [,]. Different active Gα subunits transmit the signals from the NK1R (Gq/11, Gs, G12/13, and Gi) [].
The Gq/11 subunit is involved in the regulation of the MAPK-ERK pathway, leading to proliferation in neural progenitor cells []. The GTP/Gq/11 complex activates PLC, which stimulates the hydrolysis of phospholipids and the production of second messengers, such as DAG (diacylglycerol) and IP3 (inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate) []. DAG activates protein kinase C leading to an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentrations, which is followed by the activation of phosphoinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), Akt serine/threonine kinase, and NF-κB. This leads to the synthesis of cytokines interleukin-1 and -8 (IL-1 and IL-8) [,]. Besides, the increased Ca2+ and DAG concentrations stimulate the phosphorylation of Ras/Raf proteins, which also promote cell proliferation and differentiation [,]. On the other hand, IP3 binds to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3R) on the endoplasmic reticulum leading to increased Ca2+ concentrations in the cytosol (Figure 1) [,].
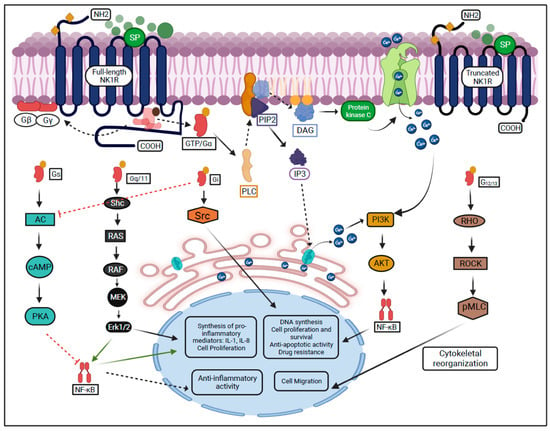
Figure 1.
SP-mediated activation of NK1R and its downstream signaling pathways.
The GTP/G12/13 complex induces cytoskeletal remodeling through the Rock/Rho signaling pathway and leads to cell migration [,]. The G12/13 subunit leads to cell invasion and metastasis and has been described in breast and prostate cancer cell lines through the activation of the RhoA family [,].
The GTP/Gi complex activates the Src, which leads to the transactivation of the tropomyosin receptor kinases and promotes cell proliferation [,]. Previously, the Gi subunit has been reported to suppress cyclic AMP in vitro and activate directly SRC in murine fibroblast cells [,].
The Gs subunit is encoded by GNAS (guanine nucleotide binding protein) abundantly found in neuron precursors [,,]. It has been reported that the Gs suppresses tumor progression in the medulloblastoma cell line and inhibits T lymphocyte proliferation in S49 lymphoma cells [,].
The activation of NK1R by SP is followed by the initiation of a molecular mechanisms ultimately leading to the onset of inflammation. Specifically, the GTP/Gs complex stimulates adenylyl cyclase to promote the synthesis of other second messengers, cAMP, which further induce activation of protein kinases, modulate the function of sodium and calcium channels and inhibit NF-κB [,,,]. The activation of protein kinase C is mediated by arachidonic acids, and favors the onset of neurogenic inflammation. Arachidonic acids are generated through hydrolysis of phospholipids promoted by phospholipase A2 [,,]. Finally, the increased intracellular Ca2+ concentrations lead to the activation of mitogen-activated-protein kinases (MEK/ERK), which promote cell proliferation, migration, leukocyte activation, and the synthesis of IL-1 and IL-8 [,].
1.4. Distribution of NK1R in the Eye
NK1R is broadly expressed in the cornea, iris, retina and choroid, conjunctiva, optic nerve, and lacrimal gland (Figure 2) [,,,].
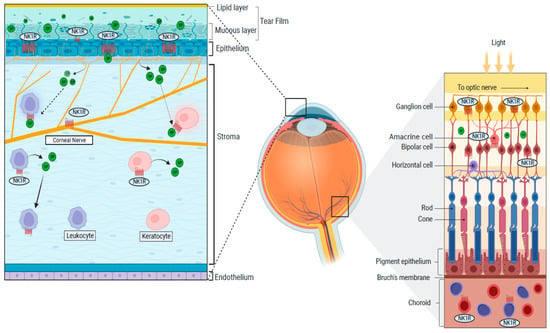
Figure 2.
Distributions of the NK1R in the cornea and the retina.
In the cornea, the epithelium, keratocytes, and corneal nerves express the NK1R [,,]. Moreover, NK1R is expressed on limbal vasculature (on endothelial cells), where it promotes vascular permeability and lymphangiogenesis [,,]. NK1R is also expressed on the iris sphincter smooth muscle fibers and vascular endothelial cells in the choroid [,]. The lacrimal gland also expresses NK1R, while the tear fluid contains large amounts of SP, both in mice and humans [,,,]. Finally, non-neural cells populating the eye, such as immune cells (T-cells, dendritic cells, lymphocytes, and monocytes), also show NK1R expression [,,]. SP-mediated activation of the NK1 receptor induces different effects in different tissues. For instance, it modulates contraction in the iris sphincter muscle [].
Multiple types of retinal cells express the NK1R: specifically, bipolar, amacrine, ganglion cells, and neurons located in the interplexifom layer. Interestingly, the expression profiles and distribution of NK-1 receptors in the retinal subpopulations (cone bipolar, dopaminergic amacrine, and cholinergic cells) display significant differences among mammals [,]. In addition, SP-mediated NK1R activation appears to be specific of certain development stages. For instance, activation of the NK1R in amacrine cholinergic cells lead to increased intracellular Ca2+ in the young rabbit retina, where it also contributes to the development of retinal neurons. In the adult rabbit retina, instead, NK1R activation leads to the modulation of visual signaling in the cone bipolar and dopaminergic amacrine cells. However, it needs further elucidation developmentally in human retinal subpopulations [,].
It should be noted, however, that the expression profiles and distribution of the full-length versus truncated form of NK1R remains unknown in the eye.
1.5. NK1R in Wound Healing, Inflammation, and Pain
Activation of the NK1R has been specifically studied in the pathophysiology of corneal epithelial wound healing, ocular surface inflammation, and pain [,,,,].
1.5.1. NK1R and Corneal Epithelial Wound Healing
The corneal epithelium is frequently exposed to injuries because it is located on the outer surface of the eye, which can result in severe visual impairment [,,]. Moreover, damage and/or activation of corneal nerves—which are distributed on the epithelial surface—result in the release of large amounts of SP. Substance P can then bind to the NK1R abundantly expressed on the corneal epithelium and nerves [,,].
Indeed, it has long been known that NK1R activation is instrumental to the maintenance of an intact corneal epithelium [,,]. For instance, it has been reported that knocking down NK1R in murine models is associated with excessive desquamation and increased epithelial cell proliferation, reduced tear secretion, and corneal nerve and dendritic cell density. Moreover, absence of NK1R appears to be associated with earlier development herpes stromal keratitis (HSV) in experimental models [,]. On the other hand, TAC1KO (i.e., SP-KO) young mice did not show any obvious alteration of the corneal epithelium or nerve density, while it seems that accelerated neuropathy may develop during aging []. Interestingly, administration of a SP-derived peptide was effective in the treatment of neurotrophic keratopathy, a condition where impaired epithelial cell proliferation and migration is well acknowledged [,,,]. Mechanistically, it has been reported that the activation of G-protein subunits and tyrosine kinase pathways are responsible for the increased epithelial cell proliferation/migration following NK1R activation [,,]. On a different note, blocking the NK1R pharmacologically improved epithelial wound healing in an alkali burn model. It should be noted that the apparent discrepancy between these studies could be explained by the different models used, the alkali burn being associated with intense inflammation [,]. It is well possible that while SP is beneficial up to a certain amount, its favorable effects are overcome by massive inflammation associated with its excessive release. Excessively increased SP levels can lead to stem cell exhaustion and acceleration in the senescence of the corneal epithelium. However, it was demonstrated that treatment with NK1R antagonist fosaprepitant significantly ameliorated clinical signs of LSCD [].
The activation of NK1R not only impacts the corneal epithelium, but also the stroma. In fact, it induces migration of keratocytes through activation of the phosphatidylinositol (PI3Ks) and Rac1/RhoA, resulting in improved wound healing [,,].
The role of NK1R and its ligand SP in the maintenance of an intact corneal epithelium is epitomized by diabetic keratopathy, a form of neurotrophic keratopathy associated to sensory neuropathy and epithelial instability and/or disruption. SP levels are reduced in patients with type 1 diabetes, although it is not clear if this is simply a reflection of reduced corneal nerve density, which is commonly observed in these subjects [,,].
1.5.2. NK1R and Ocular Inflammation
Activation of NK1R has a cardinal role in the modulation on multiple layers of the inflammatory response. In the cornea, the inflammatory response can be initiated by the release of the principal NK1R ligand, SP, following damage and/or stimulation of corneal nerves (neurogenic inflammation) (Figure 3) [,,,,]. The NK1R is expressed by virtually all the key players of the inflammatory response: vascular endothelial cells, leukocytes, and nerves. Specifically, proliferation and migration of lymphatic endothelial cells are achieved through regulation of the VEGFR3 expression following SP-mediated NK1R activation and facilitated by the recruitment of neutrophils with angiogenic activity [,,,].
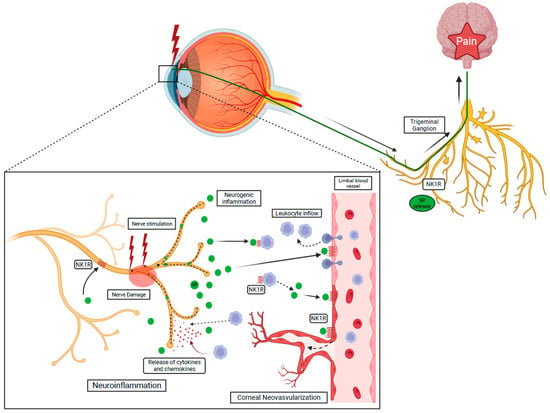
Figure 3.
NK1R activation via SP induces the recruitment of the leukocyte through the breakdown of the blood–tissue barrier and initiates neurogenic inflammation. Activated leukocytes release cytokines and chemokines leading to nerve damage, called neuroinflammation.
Besides promoting leukocyte influx into the cornea, SP also shifts the leukocyte phenotypes towards an “activated” mode. In fact, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, and lymphocytes all express the NK1R. Activation of this receptor promotes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as MIP-1B (macrophage inflammatory protein-1 beta), IL-6, TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α), and IL-8 from macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes [,,]. Those cytokines have been described in ocular inflammation, including uveitis, glaucoma, retinal (macular) edema, and neovascularization. Most of activities of cytokines are mediated by NF-κB [,,].
Recognition of pathogens and their clearance is accomplished by ocular and non-ocular cells including surface epithelia, keratocytes, and antigen-presenting cells (APCs) [,,]. Corneal epithelial cells and keratocytes activate immune cells through the secretion of cytokines, including IL-1α and TNF-α []. Besides, corneal nerves are involved in the protection of the ocular surface through the secretion of SP, which induces neutrophil influx []. On the other hand, APCs residing in the peripheral cornea recognize pathogens through toll-like receptors (TLRs) [,]. For instance, dendritic cells (DC) express the NK1R on their membrane and its activation is associated with prolonged DC survival and type 1 immune response [,].
While the neuroinflammatory response is originally designed to achieve rapid pathogen clearance and wound healing, its derangement/prolonged activation can have a role in highly prevalent ocular disorders, such as dry eye disease [,,] and chronic pain [,].
Corneal neovascularization is a leading cause of blindness worldwide [,,]. It was shown that patients affected with corneal neovascularization express higher levels of SP in the tear fluid [] and that NK1R blockade impairs corneal hem- and lymphangiogenesis in pre-clinical models [,].
Moreover, experimental evidence shows that SP, acting through the NK1R, abolishes the ocular immune privilege through modulation of pro-inflammatory mediators after retinal laser burn (RLB) [], and that pharmacological blockade of NK1R results in reduced corneal graft rejection [,,].
Finally, SP has a role in the progression of pterygium, a form of conjunctival degeneration [,]. Specifically, the NK1R promotes the mobilization of fibroblast and vascular endothelial cells from the bulbar conjunctiva towards the cornea and favors pterygium progression [,].
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a degenerative disorder of the macula that affects elderly people, leading to severe visual impairment. There are two different forms of AMD: dry and neovascular AMD. The role of NK1R in the neovascular form of AMD has been studied in pre-clinical models. Indeed, pharmacological blockade of the NK1R resulted in the reduction of AMD-associated choroidal neovascularization (CNV) [,]. By contrast, it was demonstrated that SP has beneficial effects on retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) through induced migration and proliferation of retinal pigment cells following laser-induced damage in RPE both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, the effect of NK1R on the pathophysiology of AMD could be different depending on the nature and/or stage of AMD [,].
The role of NK1R has also been studied in other retinal diseases. Proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR) is a serious complication of retinal detachment and is characterized by the growth and contraction of subretinal membranes within the vitreous cavity, ultimately leading to visual loss [,]. While the exact pathophysiology of PVR is still incompletely understood, it seems clear that an altered inflammatory response is involved. Interestingly, SP levels are increased in the ocular fluids of PVR patients. On the other hand, a study on mice showed that SP can inhibit the progression of PVR through modulation of cytokines including TNF-α [,]. In conclusion, existing evidence suggest that the exact roles of SP and its receptor NK1 in PVR needs further elucidation.
Retinoblastoma is a rare malignant tumor of childhood that occurs in the retinal subpopulations [,]. It is caused by the inactivation of the RB gene during development. Retinoblastoma cells express the NK1R. Interestingly, it has been shown that nanomolar concentrations of SP induce retinoblastoma cell proliferation []. By contrast, micromolar concentrations of NK1R antagonist (L-733060) and aprepitant prevent retinoblastoma cell proliferation which suggests that the SP/NK1R axis can be therapeutically employed to treat retinoblastoma [,].
The potential role of NK1R antagonists has also been investigated in different inflammatory ocular conditions such as allergic conjunctivitis []. Research on an animal model of allergic conjunctivitis revealed that an NK1R antagonist, L-703606, significantly reduced the ocular redness along with the SP levels in tear fluids. Moreover, a reduction in the number of infiltrating neutrophils and eosinophils was observed. Finally, the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines was decreased by topical administration of L-703606 in the conjunctiva. However, the effect of the NK1R antagonist on corneal epithelium remains elusive in the study [].
Ultraviolet radiation type B (UVR-B) poses a significant risk for the progression of cataract and promotes ocular inflammation. It was shown that fosaprepitant treatment of UVR-B-irradiated animals is associated with reduced NK1R expression in different ocular tissues [,].
Graft versus host disease (GVHD) is an inflammatory condition that occurs following the introduction of donated bone marrow or stem cells with a host. Preclinical models of ocular GVHD (oGVHD) show increased expression of NK1R endothelium and epithelium. This was likely a consequence of CD8+ T lymphocytes activation and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines [].
Herpes Simplex Keratitis (HSK) is associated with increased levels of SP in severe cases []. It was reported that CD8 T cell proliferation was significantly reduced in mice treated with an NK1R antagonist, L-760735, compared to controls, suggesting a key role for SP in herpes-induced corneal inflammation. In conclusion, blocking of SP suppresses the inflammation and infiltrating of immune cells [,,].
1.5.3. NK1R and Ocular Pain
The activation of the NK1R is known to simultaneously promote inflammation and pain []. Corneal pain is normally generated by the activation of transient receptor potential. Trigeminal neurons are responsible for collection of sensory stimuli reaching the cornea and transmit them to the pons via their central branch. From there, the sensory information is further transmitted to the thalamus and cortex, through central neurons [,].
In the human cornea, three subgroups of trigeminal nociceptors have been identified. Mechano-nociceptors (20%) respond to mechanical stimuli, and are involved in acute pain. Polymodal nociceptors (70%) are activated by chemical and mechanical stimuli. Thermo-receptors (10%), instead, respond to temperature fluctuations [,,]. The relevance of the SP-NK1R pathway in humans has been demonstrated before. In fact, the NK1R is expressed in the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis, where activation by SP initiates acute and/or chronic pain responses [,]. It should be noted that while acute pain has beneficial effects on the cornea by inducing eye blinking and tear production, over time, substantial alterations of ion channel expression on corneal nerves and extensive rewiring of the trigeminal neural circuitry occur, which result in chronic neuropathic pain [,]. Chronic pain has a key role in highly prevalent diseases (e.g., dry eye) and can in some cases become a disease by itself [,].
Ocular surface pain is a consequence of most ocular surface diseases, injuries, and surgery []. SP, acting through the NK1R, is involved in conveying corneal pain to the trigeminal ganglion. Specifically, it was shown that large amounts of SP are released in the tear fluid following nerve injury/stimulation [,]. SP can bind to the NK1R expressed on corneal nerves, therefore inducing nerve depolarization and pain [,]. Recently, it was demonstrated that topical application of an NK1R antagonist, fosaprepitant, resulted in a substantial decrease of corneal pain and leukocyte infiltration as a consequence of nerve-released SP blockade [].
1.6. NK1R Antagonists and Their Potential in Eye Diseases
NK1R and/or SP are promising targets to treat a number of ocular diseases and pain [,,].
Different NK1R antagonists, including Fosaprepitant, Lanepitant, Spantide I/II, L-732138 and SR140333, L-733060, and aprepitant have been shown to be effective in ocular graft versus host diseases and pre-clinical models of eye diseases [,,]. One of these medications, Fosaprepitant, has been in clinical use for years, with an excellent safety profile, for the treatment of nausea associated with chemotherapy. Fosaprepitant, applied topically to the ocular surface, effectively reduced ocular surface pain, hem- and lymphangiogenesis, and decreased the level of SP in the tear fluid [,]. Spantide I inhibited the synthesis of IL-8 in corneal epithelial cells, reduced infiltration of inflammatory cells, and decreased hemangiogenesis [,]. Spantide II was able to reinstate the previously abolished immune privilege in the cornea and allowed long-term survival of corneal grafts []. CP-96,345 reduced the SP-mRNA expression and inhibited IL-8 gene expression [].
Finally, L-732138 prevented SP-dependent cell migration in pterygium fibroblast and inhibited migration of pterygium microvascular endothelial cells []. L-732138, L-733060, and aprepitant were effective to inhibit the proliferation of retinoblastoma and induce apoptosis [,,].
Some of these medications have been tested in human clinical trials, although not for eye diseases, but mainly as analgesics, antidepressants, or for the treatment of nausea and cancer [,,,,,].
2. Conclusions
NK-1 receptors activate an intricate molecular machinery that controls key biological responses in the eye. These include modulation of the inflammatory response, wound healing and pain [,]. Emerging evidence suggests that activities mediated by the NK1R could be beneficial or detrimental to wound healing, depending on the amount and timing of activation.
In any case, the expression of the NK1R on multiple populations of ocular and non-ocular cells, and the secretion of its ligand SP in tears, further add complexity to the picture. At the same time, the involvement of NK1R and its principal ligand SP in such basic biological mechanisms makes the manipulation of its activity extremely attractive in terms of treatment.
Author Contributions
I.H.D.: Writing the manuscript, Review and Editing, Visualization; G.F.: Writing the manuscript; Review and Editing; Visualization; contribution to the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the IRCCS San Raffaele Scientific Institute.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by institutional work. The figures in this article were prepared using Biorender.com.
Conflicts of Interest
The other author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Pennefather, J.N.; Lecci, A.; Candenas, M.L.; Patak, E.; Pinto, F.M.; Maggi, C.A. Tachykinins and Tachykinin Receptors: A Growing Family. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Berger, A.; Milne, C.D.; Paige, C.J. Tachykinins in the Immune System. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasagni Vitar, R.M.; Rama, P.; Ferrari, G. The Two-Faced Effects of Nerves and Neuropeptides in Corneal Diseases. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2022, 86, 100974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.M.; Pintado, C.O.; Pennefather, J.N.; Patak, E.; Candenas, L. Ovarian Steroids Regulate Tachykinin and Tachykinin Receptor Gene Expression in the Mouse Uterus. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2009, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, N.P.; Garraway, L.A.; Eddy, R.L.; Shows, T.B.; Iijima, H.; Paquet, J.L.; Gerard, C. Human Substance P Receptor (NK-1): Organization of the Gene, Chromosome Localization, and Functional Expression of CDNA Clones. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 10640–10646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, V.; Pinto, F.M.; González-Ravina, C.; Santamaría-López, E.; Candenas, L.; Fernández-Sánchez, M. Tachykinins and Kisspeptins in the Regulation of Human Male Fertility. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keringer, P.; Rumbus, Z. The Interaction between Neurokinin-1 Receptors and Cyclooxygenase-2 in Fever Genesis. Temp. Austin 2019, 6, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, T.A.; Rojo, J.; Nieto, P.M.; Pinto, F.M.; Hernandez, M.; Martín, J.D.; Candenas, M.L. Tachykinins and Tachykinin Receptors: Structure and Activity Relationships. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2045–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.D.; Leeman, S.E. Neurokinin-1 Receptor: Functional Significance in the Immune System in Reference to Selected Infections and Inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1217, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, C.A. The Mammalian Tachykinin Receptors. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1995, 26, 911–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolorz, J.; Demir, S.; Gottschlich, A.; Beirith, I.; Ilmer, M.; Lüthy, D.; Walz, C.; Dorostkar, M.M.; Magg, T.; Hauck, F.; et al. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is a Target in Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumors. Curr. Oncol. Tor. Ont 2021, 29, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.-P.; Lai, S.; Tuluc, F.; Tansky, M.F.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Leeman, S.E.; Douglas, S.D. Differences in the Length of the Carboxyl Terminus Mediate Functional Properties of Neurokinin-1 Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12605–12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitsin, S.; Pappa, V.; Douglas, S.D. Truncation of Neurokinin-1 Receptor-Negative Regulation of Substance P Signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eapen, P.M.; Rao, C.M.; Nampoothiri, M. Crosstalk between Neurokinin Receptor Signaling and Neuroinflammation in Neurological Disorders. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, D.; Challiss, R.A.J. Alternative Splicing of G Protein-Coupled Receptors: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3337–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansky, M.F.; Pothoulakis, C.; Leeman, S.E. Functional Consequences of Alteration of N-Linked Glycosylation Sites on the Neurokinin 1 Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10691–10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redkiewicz, P. The Regenerative Potential of Substance P. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.B.; Naderi, A.; Cho, W.; Ortiz, G.; Musayeva, A.; Dohlman, T.H.; Chen, Y.; Ferrari, G.; Dana, R. Modulating the Tachykinin: Role of Substance P and Neurokinin Receptor Expression in Ocular Surface Disorders. Ocul. Surf. 2022, 25, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, F.; Rama, P.; Ferrari, G. Substance P and Its Inhibition in Ocular Inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, C.A.; Patacchini, R.; Giachetti, A.; Meli, A. Tachykinin Receptors in the Circular Muscle of the Guinea-Pig Ileum. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 101, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, H.; Kawada, T. Overview of the Primary Structure, Tissue-Distribution, and Functions of Tachykinins and Their Receptors. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, K.L. Tachykinin-Mediated Modulation of the Immune Response. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 3331–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koon, H.-W.; Zhao, D.; Na, X.; Moyer, M.P.; Pothoulakis, C. Metalloproteinases and Transforming Growth Factor-α Mediate Substance P-Induced Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation and Proliferation in Human Colonocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45519–45527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Hirschfeld, J.; Lopez-Briones, L.G.; Belmonte, C. Neurotrophic Influences on Corneal Epithelial Cells. Exp. Eye Res. 1994, 59, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słoniecka, M.; Le Roux, S.; Zhou, Q.; Danielson, P. Substance P Enhances Keratocyte Migration and Neutrophil Recruitment through Interleukin-8. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, A.E.; Sumpter, T.L.; Rojas-Canales, D.M.; Bandyopadhyay, M.; Chen, Z.; Tkacheva, O.; Shufesky, W.J.; Wallace, C.T.; Watkins, S.C.; Berger, A.; et al. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Signaling Is Required for Efficient Ca2+ Flux in T-Cell-Receptor-Activated T Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3448–3465.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Aranda, M.; Téllez, T.; McKenna, L.; Redondo, M. Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists as a New Strategy to Overcome Cancer Resistance. Cancers 2022, 14, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hayre, M.; Degese, M.S.; Gutkind, J.S. Novel Insights into G Protein and G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling in Cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 27, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, R.; Ueda, H.; Ito, H.; Takasaki, J.; Nagata, K.-I.; Asano, T. Involvement of Gq/11 in Both Integrin Signal-Dependent and -Independent Pathways Regulating Endothelin-Induced Neural Progenitor Proliferation. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 59, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guard, S.; Watson, S.P. Tachykinin Receptor Types: Classification and Membrane Signalling Mechanisms. Neurochem. Int. 1991, 18, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.D. Regulation of Nuclear Factor KappaB Activation by G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 70, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsybko, A.S.; Ilchibaeva, T.V.; Popova, N.K. Role of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Mood Disorders. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 28, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwindinger, W.F.; Robishaw, J.D. Heterotrimeric G-Protein Βγ-Dimers in Growth and Differentiation. Oncogene 2001, 20, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raddatz, R.; Crankshaw, C.L.; Snider, R.M.; Krause, J.E. Similar Rates of Phosphatidylinositol Hydrolysis Following Activation of Wild-Type and Truncated Rat Neurokinin-1 Receptors. J. Neurochem. 2002, 64, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, Y.; Daguet De Montety, M.C.; el Etr, M.; Beaujouan, J.C.; Glowinski, J. Tachykinin Receptors of the NK1 Type (Substance P) Coupled Positively to Phospholipase C on Cortical Astrocytes from the Newborn Mouse in Primary Culture. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yu, F.; Ullah, A.; Hubrack, S.; Daalis, A.; Jung, P.; Machaca, K. Endoplasmic Reticulum Remodeling Tunes IP3-Dependent Ca2+ Release Sensitivity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshki, J.; Douglas, S.D.; Lai, J.-P.; Schwartz, L.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Tuluc, F. Neurokinin 1 Receptor Mediates Membrane Blebbing in HEK293 Cells through a Rho/Rho-Associated Coiled-Coil Kinase-Dependent Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9280–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; Moeller, B.J.; Juneja, J.; Booden, M.A.; Der, C.J.; Daaka, Y.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Fields, T.A.; Casey, P.J. The G12 Family of Heterotrimeric G Proteins Promotes Breast Cancer Invasion and Metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8173–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; Stemmle, L.N.; Madden, J.F.; Fields, T.A.; Daaka, Y.; Casey, P.J. A Role for the G12 Family of Heterotrimeric G Proteins in Prostate Cancer Invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26483–26490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Recio, S.; Gascón, P. Biological and Pharmacological Aspects of the NK1-Receptor. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 495704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Kugimiya, T.; Miyazaki, T. Substance P Receptor in U373 MG Human Astrocytoma Cells Activates Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases ERK1/2 through Src. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2005, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.H.; Federman, A.; Pace, A.M.; Zachary, I.; Evans, T.; Pouysségur, J.; Bourne, H.R. Mutant Alpha Subunits of Gi2 Inhibit Cyclic AMP Accumulation. Nature 1991, 351, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.C.; Huang, J.; Ali, S.; Lowry, W.; Huang, X.Y. Src Tyrosine Kinase Is a Novel Direct Effector of G Proteins. Cell 2000, 102, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Jia, C.; Dai, C. GNAS Promotes Inflammation-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Promoting STAT3 Activation. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2020, 25, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.N.; Druey, K.M. Heterotrimeric G Protein Signaling: Role in Asthma and Allergic Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Remke, M.; Shih, D.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xia, Y.; et al. The G Protein α Subunit Gαs Is a Tumor Suppressor in Sonic Hedgehog-Driven Medulloblastoma. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Herrmann, V.; Hofer, J.K.; Insel, P.A. Beta-Adrenergic Receptor/CAMP-Mediated Signaling and Apoptosis of S49 Lymphoma Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2000, 279, C1665–C1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khawaja, A.M.; Rogers, D.F. Tachykinins: Receptor to Effector. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 28, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, Y.; Tsuchida, K.; Negishi, M.; Ito, S.; Nakanishi, S. Direct Linkage of Three Tachykinin Receptors to Stimulation of Both Phosphatidylinositol Hydrolysis and Cyclic AMP Cascades in Transfected Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 2437–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.Y.; Kannan, S.; Chen, Y.J.; Tan, F.C.K.; Ong, W.Y.; Go, M.L.; Verma, C.S.; Low, C.-M.; Lam, Y. A New Generation of Arachidonic Acid Analogues as Potential Neurological Agent Targeting Cytosolic Phospholipase A2. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, A.; Boscoboinik, D.; Hensey, C. The Protein Kinase C Family. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 208, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaechter, J.; Benowitz, L. Activation of Protein Kinase C by Arachidonic Acid Selectively Enhances the Phosphorylation of GAP-43 in Nerve Terminal Membranes. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonelli, F.; Lasagni Vitar, R.M.; Merlo Pich, F.G.; Fonteyne, P.; Rama, P.; Mondino, A.; Ferrari, G. Corneal Endothelial Cell Reduction and Increased Neurokinin-1 Receptor Expression in a Graft-versus-Host Disease Preclinical Model. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 220, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, S.L.; Borbely, G.; Słoniecka, M.; Backman, L.J.; Danielson, P. Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 Modulates the Functional Expression of the Neurokinin-1 Receptor in Human Keratocytes. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 41, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddipati, S.; Rao, P.; Jerome, A.D.; Burugula, B.B.; Gerard, N.P.; Suvas, S. Loss of Neurokinin-1 Receptor Alters Ocular Surface Homeostasis and Promotes an Early Development of Herpes Stromal Keratitis. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4021–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvinsson, J.C.; Reducha, P.V.; Sheykhzade, M.; Warfvinge, K.; Haanes, K.A.; Edvinsson, L. Neurokinins and Their Receptors in the Rat Trigeminal System: Differential Localization and Release with Implications for Migraine Pain. Mol. Pain 2021, 17, 17448069211059400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Im, S.-T.; Wu, J.; Cho, C.S.; Jo, D.H.; Chen, Y.; Dana, R.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.-M. Corneal Lymphangiogenesis in Dry Eye Disease Is Regulated by Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor System through Controlling Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 3. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 22, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasagni Vitar, R.M.; Bonelli, F.; Atay, A.; Triani, F.; Fonteyne, P.; Di Simone, E.; Rama, P.; Mondino, A.; Ferrari, G. Topical Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Fosaprepitant Ameliorates Ocular Graft-versus-Host Disease in a Preclinical Mouse Model. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 212, 108825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Ogata, M.; Kawai, M.; Mashima, Y.; Nishida, T. Substance P in Human Tears. Cornea 2003, 22, S48–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Ogata, M.; Kawai, M.; Mashima, Y.; Nishida, T. Substance P and Its Metabolites in Normal Human Tears. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 2622–2625. [Google Scholar]
- Suvas, S. Role of Substance P Neuropeptide in Inflammation, Wound Healing, and Tissue Homeostasis. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Lal, G. Neurokinin Receptors and Their Implications in Various Autoimmune Diseases. Curr. Res. Immunol. 2021, 2, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Wakita, D.; Nishimura, T. Neuropeptide Signaling Activates Dendritic Cell-Mediated Type 1 Immune Responses through Neurokinin-2 Receptor. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2012, 188, 4200–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.M.; Mitchell, D.; Morton, I.K.M. Typical and Atypical NK1 Tachykinin Receptor Characteristics in the Rabbit Isolated Iris Sphincter. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 112, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Catalani, E.; Gangitano, C.; Bosco, L.; Casini, G. Expression of the Neurokinin 1 Receptor in the Mouse Retina. Neuroscience 2004, 128, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, G.; Rickman, D.W.; Sternini, C.; Brecha, N.C. Neurokinin 1 Receptor Expression in the Rat Retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 389, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, G.; Dal Monte, M.; Fornai, F.; Bosco, L.; Willems, D.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Z.J.; Bagnoli, P. Neurokinin 1 Receptor Expression and Substance P Physiological Actions Are Developmentally Regulated in the Rabbit Retina. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.D.-J.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-M. The Role of Neuropeptides in Pathogenesis of Dry Dye. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, H.; Amouzegar, A.; Nakao, T.; Chen, Y.; Dana, R. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonism Ameliorates Dry Eye Disease by Inhibiting Antigen-Presenting Cell Maturation and T Helper 17 Cell Activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dana, R.; Yin, J. Sensory Neurons Directly Promote Angiogenesis in Response to Inflammation via Substance P Signaling. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2020, 34, 6229–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, F.; Giacomini, C.; Lorusso, A.; Aramini, A.; Rama, P.; Ferrari, G. NK1 Receptor Antagonists as a New Treatment for Corneal Neovascularization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6783–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubimov, A.V.; Saghizadeh, M. Progress in Corneal Wound Healing. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 49, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labetoulle, M.; Baudouin, C.; Calonge, M.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Boboridis, K.G.; Akova, Y.A.; Aragona, P.; Geerling, G.; Messmer, E.M.; Benítez-del-Castillo, J. Role of Corneal Nerves in Ocular Surface Homeostasis and Disease. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoukhri, D. Effect of Inflammation on Lacrimal Gland Function. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasagni Vitar, R.M.; Barbariga, M.; Fonteyne, P.; Bignami, F.; Rama, P.; Ferrari, G. Modulating Ocular Surface Pain Through Neurokinin-1 Receptor Blockade. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, T.; Chikama, T.-I.; Morishige, N.; Yanai, R.; Yamada, N.; Saito, J. Persistent Epithelial Defects Due to Neurotrophic Keratopathy Treated with a Substance P-Derived Peptide and Insulin-like Growth Factor 1. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 51, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, T.; Inui, M.; Nomizu, M. Peptide Therapies for Ocular Surface Disturbances Based on Fibronectin–Integrin Interactions. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 47, 38–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, S.; Rama, P.; Olzi, D.; Lambiase, A. Neurotrophic Keratitis. Eye 2003, 17, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, H.S.; Said, D.G.; Messmer, E.M.; Rolando, M.; Benitez-Del-Castillo, J.M.; Hossain, P.N.; Shortt, A.J.; Geerling, G.; Nubile, M.; Figueiredo, F.C.; et al. Neurotrophic Keratopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 66, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Nagano, T.; Chikama, T.; Nishida, T. Up-Regulation of Phosphorylation of Focal Adhesion Kinase and Paxillin by Combination of Substance P and IGF-1 in SV-40 Transformed Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 242, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, T.; Nakamura, M.; Ofuji, K.; Reid, T.W.; Mannis, M.J.; Murphy, C.J. Synergistic Effects of Substance P with Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 on Epithelial Migration of the Cornea. J. Cell. Physiol. 1996, 169, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmade, F.; Sechoy-Chambon, O.; Coquelet, C.; Bonne, C. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) Specifically Binds to Bovine Lens Epithelial Cells and Increases the Number of Fibronectin Receptor Sites. Curr. Eye Res. 1994, 13, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasagni Vitar, R.; Triani, F.; Barbariga, M.; Fonteyne, P.; Rama, P.; Ferrari, G. Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor Pathway Blockade Ameliorates Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency by Modulating MTOR Pathway and Preventing Cell Senescence. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 849–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Nakayasu, K.; Iwatsu, M.; Kanai, A. Endogenous Substance P in Corneal Epithelial Cells and Keratocytes. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 46, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, H.; Tan, H.C.; Lin, M.T.-Y.; Mehta, J.S.; Liu, Y.-C. Diabetic Corneal Neuropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lee, A.; Lo, A.C.Y.; Kwok, J.S.W.J. Diabetic Corneal Neuropathy: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 816062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogru, M.; Katakami, C.; Inoue, M. Tear Function and Ocular Surface Changes in Noninsulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Ophthalmology 2001, 108, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Di Nardo, A. Skin Neurogenic Inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrigan, F.; Vink, R.; Turner, R.J. Inflammation in Acute CNS Injury: A Focus on the Role of Substance P: Neurogenic Inflammation in Acute CNS Injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbariga, M.; Fonteyne, P.; Ostadreza, M.; Bignami, F.; Rama, P.; Ferrari, G. Substance P Modulation of Human and Murine Corneal Neovascularization. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziche, M.; Morbidelli, L.; Pacini, M.; Geppetti, P.; Alessandri, G.; Maggi, C.A. Substance P Stimulates Neovascularization in Vivo and Proliferation of Cultured Endothelial Cells. Microvasc. Res. 1990, 40, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeno, E.W.; Mantyh, P.; Vercellotti, G.M.; Moldow, C.F. Functional Neurokinin 1 Receptors for Substance P Are Expressed by Human Vascular Endothelium. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohara, H.; Tajima, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Tabata, Y. Angiogenesis Induced by Controlled Release of Neuropeptide Substance P. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8617–8625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez, B.G.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Villa-Collar, C.; Alvarez-Peregrina, C.; Sánchez-Tena, M.Á. Influence of Cytokines on Inflammatory Eye Diseases: A Citation Network Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakefield, D.; Lloyd, A. The Role of Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Eye Disease. Cytokine 1992, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.M.; O’Connell, J.; O’Brien, D.I.; Goode, T.; Bredin, C.P.; Shanahan, F. The Role of Substance P in Inflammatory Disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004, 201, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashaghi, A.; Marmalidou, A.; Tehrani, M.; Grace, P.M.; Pothoulakis, C.; Dana, R. Neuropeptide Substance P and the Immune Response. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2016, 73, 4249–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Yi, S.; Wei, L. Ocular Microbiota and Intraocular Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 609765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yu, F.-S.X. Toll-like Receptors and Corneal Innate Immunity. Curr. Mol. Med. 2006, 6, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akpek, E.K.; Gottsch, J.D. Immune Defense at the Ocular Surface. Eye 2003, 17, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.T.; Lausch, R.N.; Oakes, J.E. Substance P Differentially Stimulates IL-8 Synthesis in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 3871–3877. [Google Scholar]
- Hamrah, P.; Huq, S.O.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Dana, M.R. Corneal Immunity Is Mediated by Heterogeneous Population of Antigen-Presenting Cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelsins, B.M.; Sumpter, T.L.; Tkacheva, O.A.; Rojas-Canales, D.M.; Erdos, G.; Mathers, A.R.; Shufesky, W.J.; Storkus, W.J.; Falo, L.D.; Morelli, A.E.; et al. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Agonists Bias Therapeutic Dendritic Cells to Induce Type 1 Immunity by Licensing Host Dendritic Cells to Produce IL-12. Blood 2013, 121, 2923–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taketani, Y.; Marmalidou, A.; Dohlman, T.H.; Singh, R.B.; Amouzegar, A.; Chauhan, S.K.; Chen, Y.; Dana, R. Restoration of Regulatory T-Cell Function in Dry Eye Disease by Antagonizing Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruzat, A.; Qazi, Y.; Hamrah, P. In Vivo Confocal Microscopy of Corneal Nerves in Health and Disease. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 15–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.W.; Lee, J.L.; Kang, H.G.; Gu, N.; Byun, H.; Yeo, A.; Noh, H.; Kim, S.; Choi, E.Y.; Song, J.S.; et al. Corneal Lymphangiogenesis Facilitates Ocular Surface Inflammation and Cell Trafficking in Dry Eye Disease. Ocul. Surf. 2018, 16, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih, D.; Zhao, Z.; Nicolle, P.; Reboussin, E.; Joubert, F.; Luzu, J.; Labbé, A.; Rostène, W.; Baudouin, C.; Mélik Parsadaniantz, S.; et al. Chronic Dry Eye Induced Corneal Hypersensitivity, Neuroinflammatory Responses, and Synaptic Plasticity in the Mouse Trigeminal Brainstem. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, P.-S.; Reboussin, E.; Liang, H.; Kessal, K.; Godefroy, D.; Rostene, W.; Sahel, J.-A.; Baudouin, C.; Melik Parsadaniantz, S.; Reaux Le Goazigo, A. Ocular Inflammation Induces Trigeminal Pain, Peripheral and Central Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 88, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.L.; Dana, R. Inflammatory Corneal Neovascularization: Etiopathogenesis. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2011, 26, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasagni Vitar, R.M.; Triolo, G.; Fonteyne, P.; Acuti Martellucci, C.; Manzoli, L.; Rama, P.; Ferrari, G. Epidemiology of Corneal Neovascularization and Its Impact on Visual Acuity and Sensitivity: A 14-Year Retrospective Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 733538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, M.R.; Schaumberg, D.A.; Kowal, V.O.; Goren, M.B.; Rapuano, C.J.; Laibson, P.R.; Cohen, E.J. Corneal Neovascularization after Penetrating Keratoplasty. Cornea 1995, 14, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, K.; Karamichos, D.; Mathew, R.; Zieske, J.D.; Stein-Streilein, J. Retinal Laser Burn-Induced Neuropathy Leads to Substance P-Dependent Loss of Ocular Immune Privilege. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunicka, K.J.; Mellon, J.; Robertson, D.; Petroll, M.; Brown, J.R.; Niederkorn, J.Y. Severing Corneal Nerves in One Eye Induces Sympathetic Loss of Immune Privilege and Promotes Rejection of Future Corneal Allografts Placed in Either Eye: Corneal Nerves and Corneal Graft Rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, S.; Kenyon, B.M.; Hamrah, P. Immunomodulatory Role of Neuropeptides in the Cornea. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam, S.; Niederkorn, J.Y. Corneal Nerve Ablation Abolishes Ocular Immune Privilege by Downregulating CD103 on T Regulatory Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, J.; Di Girolamo, N.; Coroneo, M.T.; Wakefield, D. The Role of Substance P in the Pathogenesis of Pterygia. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 4482–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Girolamo, N.; Coroneo, M.; Wakefield, D. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Is Partially Responsible for the Increased Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Expression in Ocular Epithelial Cells after UVB Radiation. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nowosielski, Y.; Haas, G.; Seifarth, C.; Wohlfarter, W.; Tasan, R.; Verius, M.; Troger, J.; Bechrakis, N. The Involvement of NK1 and Y2 Receptor in the Development of Laser-Induced CNVs in C57Bl/6N Mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 177, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, A.; Mahdi, L.; Musat, O. AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 59, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.H.; Jin, Y.; Son, Y. Substance-P Blocks Degeneration of Retina by Stimulating Migration and Proliferation of Retinal Pigmented Epithelial Cells. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 12, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.S.; Kim, S.; Nam, S.; Um, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Son, Y. Effect of Substance P on Recovery from Laser-Induced Retinal Degeneration. Wound Repair Regen. 2015, 23, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troger, J.; Kremser, B.; Irschick, E.; Göttinger, W.; Kieselbach, G. Substance P in Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy: The Significance of Aqueous Humor Levels for Evolution of the Disease. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1998, 236, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasaki, H.; Shinagawa, K.; Mochizuki, M. Risk Factors for Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1998, 17, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.; Son, B.K.; Kim, S.; Son, Y.; Yu, S.-Y.; Hong, H.S. Substance P Prevents Development of Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy in Mice by Modulating TNF-α. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 933–943. [Google Scholar]
- Idrees, S.; Sridhar, J.; Kuriyan, A.E. Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy: A Review. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2019, 59, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R.; Montero, I.; González-Moles, M.A.; Robles, M.J. Neurokinin-1 Receptors Located in Human Retinoblastoma Cell Lines: Antitumor Action of Its Antagonist, L-732,138. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, M.A.; Bremner, R. The Search for the Retinoblastoma Cell of Origin. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R. A New Frontier in the Treatment of Cancer: NK-1 Receptor Antagonists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Pérez, A.; Coveñas, R.; Rosso, R.; Zamarriego, C.; Soult, J.A.; Montero, I. Antitumoral Action of the Neurokinin-1-Receptor Antagonist L-733,060 and Mitogenic Action of Substance P on Human Retinoblastoma Cell Lines. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 2567–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M. The NK-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant as a Broad Spectrum Antitumor Drug. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 28, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groneberg, D.A.; Bielory, L.; Fischer, A.; Bonini, S.; Wahn, U. Animal Models of Allergic and Inflammatory Conjunctivitis. Allergy 2003, 58, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Blanco, T.; Ge, H.; Xia, Y.; Pang, K.; Chen, Y.; Dana, R. Therapeutic Efficacy of Topical Blockade of Substance P in Experimental Allergic Red Eye. Ocul. Surf. 2022, 26, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollows, F.; Moran, D. Cataract--the Ultraviolet Risk Factor. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1981, 2, 1249–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.; Wegener, A.R.; Kronschläger, M.; Schönfeld, C.-L.; Holz, F.G.; Meyer, L.M. UVR-B-Induced NKR-1 Expression in Ocular Tissues Is Blocked by Substance P Receptor Antagonist Fosaprepitant in the Exposed as Well as Unexposed Partner Eye. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2021, 29, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, B.; Kate, A.; Joseph, J.; Dave, V.P. Herpes Simplex Infection of the Eye: An Introduction. Community Eye Health 2020, 33, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jerome, A.; Suvas, S. Discrepancy between Neurokinin 1 Receptor Antagonist Treatment and Neurokinin 1 Receptor Knockout Mice in the CD8 T Cell Response to Corneal HSV-1 Infection. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 126.16. [Google Scholar]
- Poccardi, N.; Rousseau, A.; Haigh, O.; Takissian, J.; Naas, T.; Deback, C.; Trouillaud, L.; Issa, M.; Roubille, S.; Juillard, F.; et al. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Replication, Ocular Disease, and Reactivations from Latency Are Restricted Unilaterally after Inoculation of Virus into the Lip. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01586-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, T.B.; Seyed-Razavi, Y.; Ghezzi, C.E.; Dieckmann, G.; Nieland, T.J.F.; Cairns, D.M.; Pollard, R.E.; Hamrah, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Corneal Pain and Experimental Model Development. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019, 71, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puja, G.; Sonkodi, B.; Bardoni, R. Mechanisms of Peripheral and Central Pain Sensitization: Focus on Ocular Pain. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 764396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcourt, A.; Gorham, L.; Dhandapani, R.; Prato, V.; Taberner, F.J.; Wende, H.; Gangadharan, V.; Birchmeier, C.; Heppenstall, P.A.; Lechner, S.G. Touch Receptor-Derived Sensory Information Alleviates Acute Pain Signaling and Fine-Tunes Nociceptive Reflex Coordination. Neuron 2017, 93, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julius, D.; Basbaum, A.I. Molecular Mechanisms of Nociception. Nature 2001, 413, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galor, A.; Moein, H.-R.; Lee, C.; Rodriguez, A.; Felix, E.R.; Sarantopoulos, K.D.; Levitt, R.C. Neuropathic Pain and Dry Eye. Ocul. Surf. 2018, 16, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Giusti, P. Mast Cells, Glia and Neuroinflammation: Partners in Crime? Immunology 2014, 141, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Hehn, C.A.; Baron, R.; Woolf, C.J. Deconstructing the Neuropathic Pain Phenotype to Reveal Neural Mechanisms. Neuron 2012, 73, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, M.; Jokić-Begić, N. Psychological Contribution to Understanding the Nature of Dry Eye Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study of Anxiety Sensitivity and Dry Eyes. Health Psychol. Behav. Med. 2020, 8, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, M.H.; Dana, R. Corneal Nerve Alterations in Dry Eye-Associated Ocular Surface Disease. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2009, 49, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, D.; Cohen, N.K.; Galor, A. Ocular Surface Pain: A Narrative Review. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2020, 9, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, S.; Martin, E.; Enríquez-de-Salamanca, A. Tear Fluid Biomarkers in Ocular and Systemic Disease: Potential Use for Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine. EPMA J. 2016, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galor, A.; Hamrah, P.; Haque, S.; Attal, N.; Labetoulle, M. Understanding Chronic Ocular Surface Pain: An Unmet Need for Targeted Drug Therapy. Ocul. Surf. 2022, 26, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, F.; Lorusso, A.; Rama, P.; Ferrari, G. Growth Inhibition of Formed Corneal Neovascularization Following Fosaprepitant Treatment. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, e641–e648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.B.; Young, A.D.; Marriott, I. The Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Substance P/NK-1R Interactions in Inflammatory CNS Disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.-P.; Ho, W.-Z.; Yang, J.-H.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Douglas, S.D. A Non-Peptide Substance P Antagonist down-Regulates SP MRNA Expression in Human Mononuclear Phagocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 128, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharun, K.; Jambagi, K.; Arya, M.; Aakanksha, C.S.; Patel, P.K.; Dixit, S.K.; Dhama, K. Clinical Applications of Substance P (Neurokinin-1 Receptor) Antagonist in Canine Medicine. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 76, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Tang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, M.; Zhan, X. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Can Prevent the Delayed Phase in Patients: A Single Center Retrospect Study. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, W.; Kang, S.; Luo, Y.; Sheng, J.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Huang, Y.; et al. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist-Based Triple Regimens in Preventing Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: A Network Meta-Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Deng, S.; Sherchan, P.; Cui, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, G.; Lian, L.; Xie, S.; Lenahan, C.; Travis, Z.D.; et al. Neurokinin Receptor 1 (NK1R) Antagonist Aprepitant Enhances Hematoma Clearance by Regulating Microglial Polarization via PKC/P38MAPK/NFκB Pathway After Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Mice. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2021, 18, 1922–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.E.; Mohan, R.R.; Mohan, R.R.; Ambrósio, R.; Hong, J.; Lee, J. The Corneal Wound Healing Response: Cytokine-Mediated Interaction of the Epithelium, Stroma, and Inflammatory Cells. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2001, 20, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto, M.V.; Mohan, R.R.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Hutcheon, A.E.K.; Zieske, J.D.; Wilson, S.E. Wound Healing in the Cornea: A Review of Refractive Surgery Complications and New Prospects for Therapy. Cornea 2005, 24, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).