Hemodynamic Implications of Aortic Stenosis on Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Progression: A Patient-Specific CFD Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
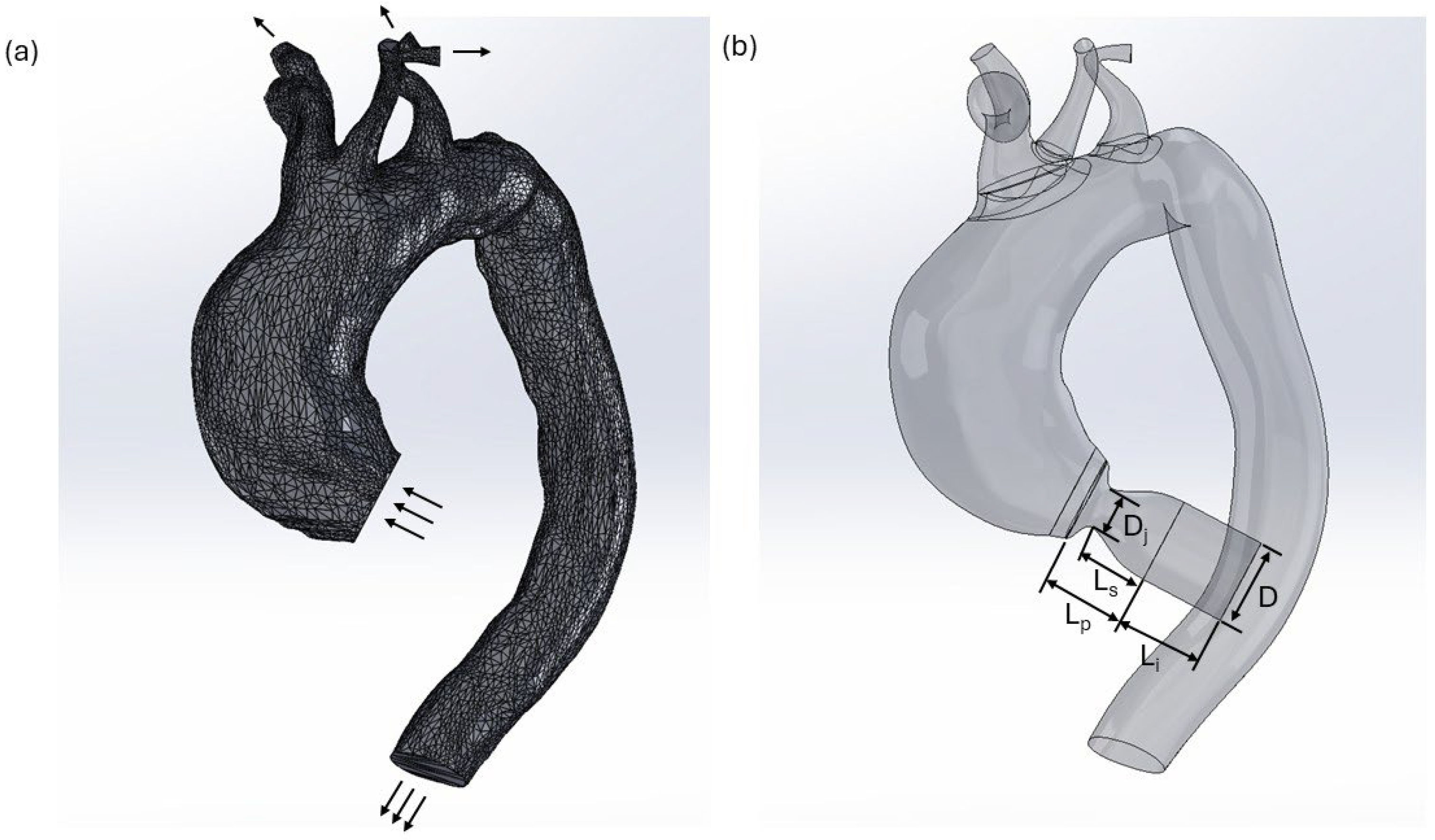
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Configuration and Boundary Conditions
2.2. Governing Equations
2.3. Mesh Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
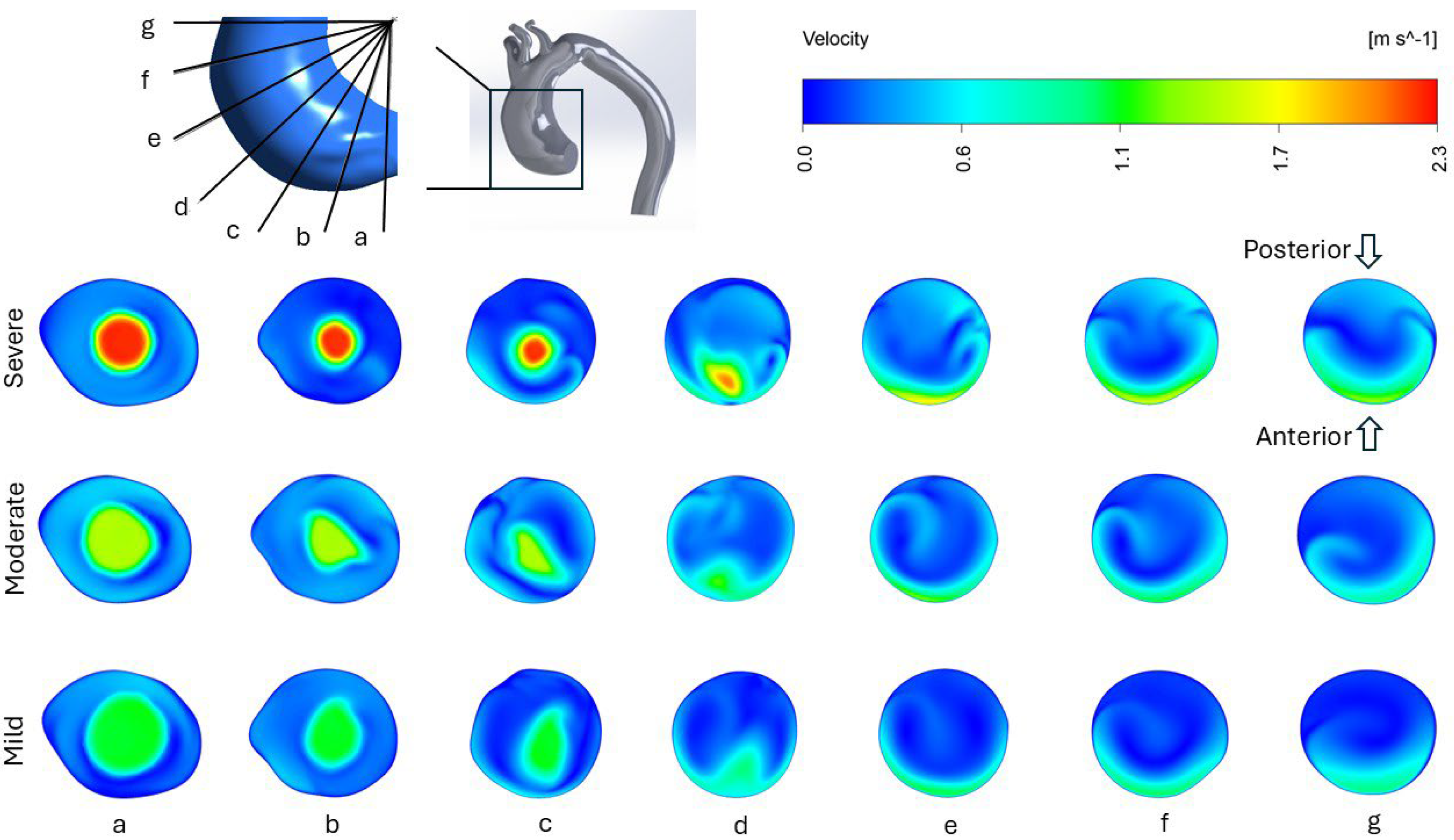
3.1. Velocity Profile and Flow Structure
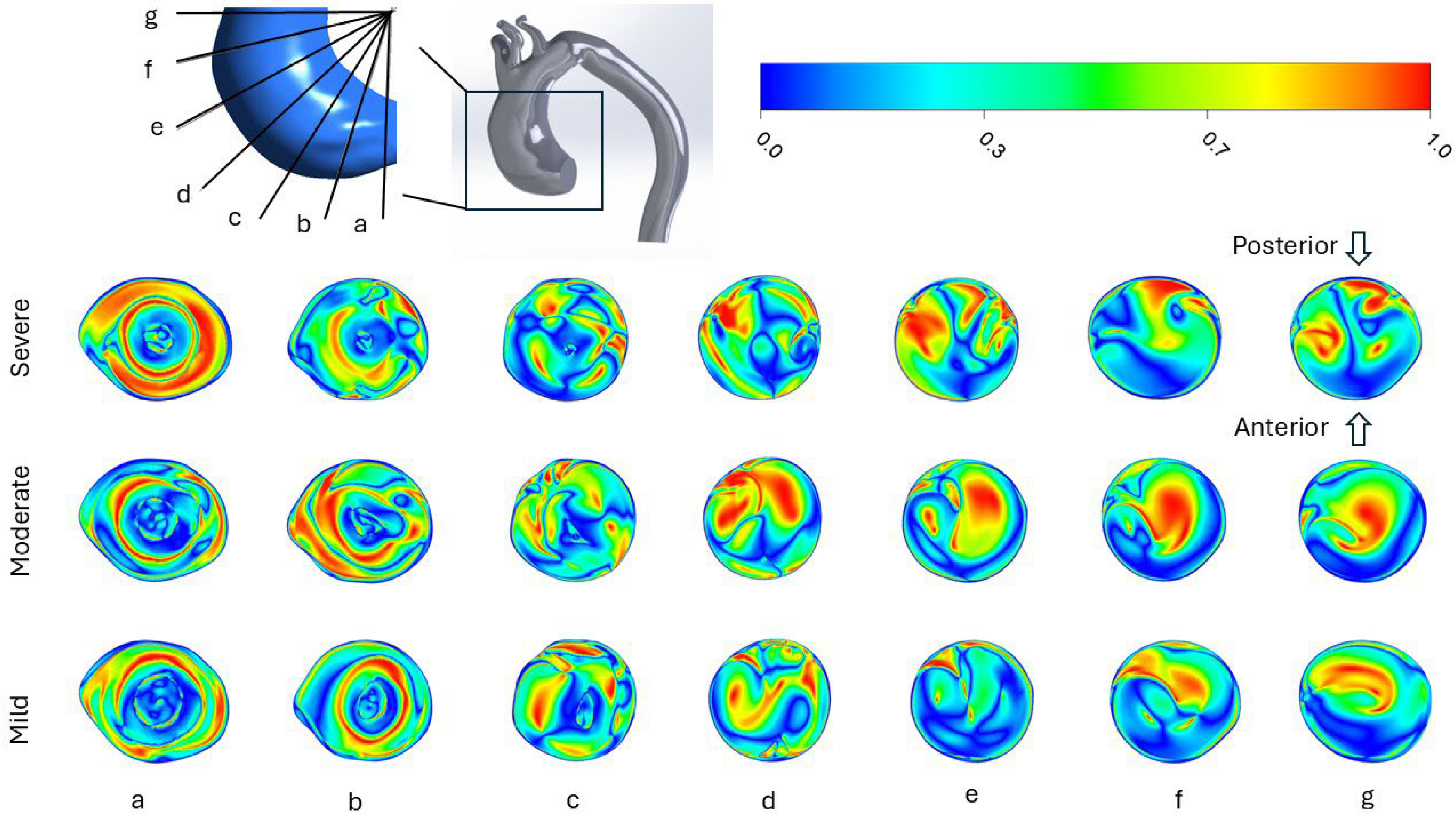
3.2. Helicity
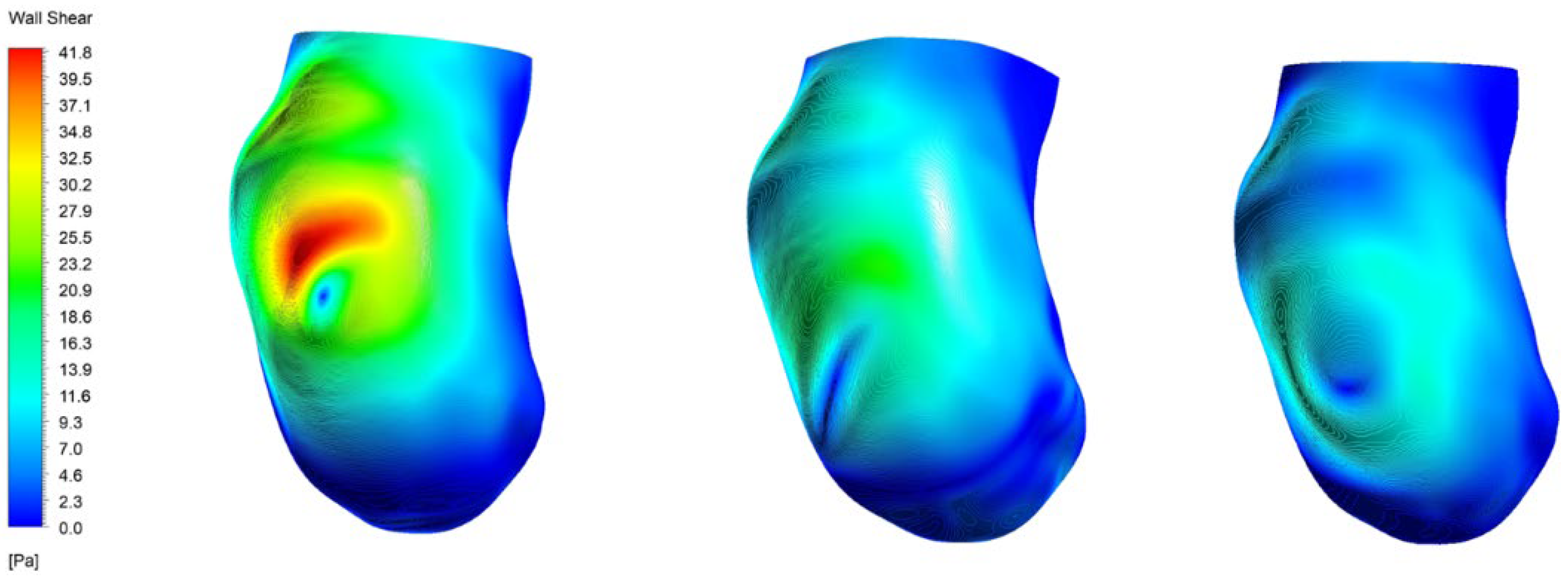
3.3. Wall Shear Stress
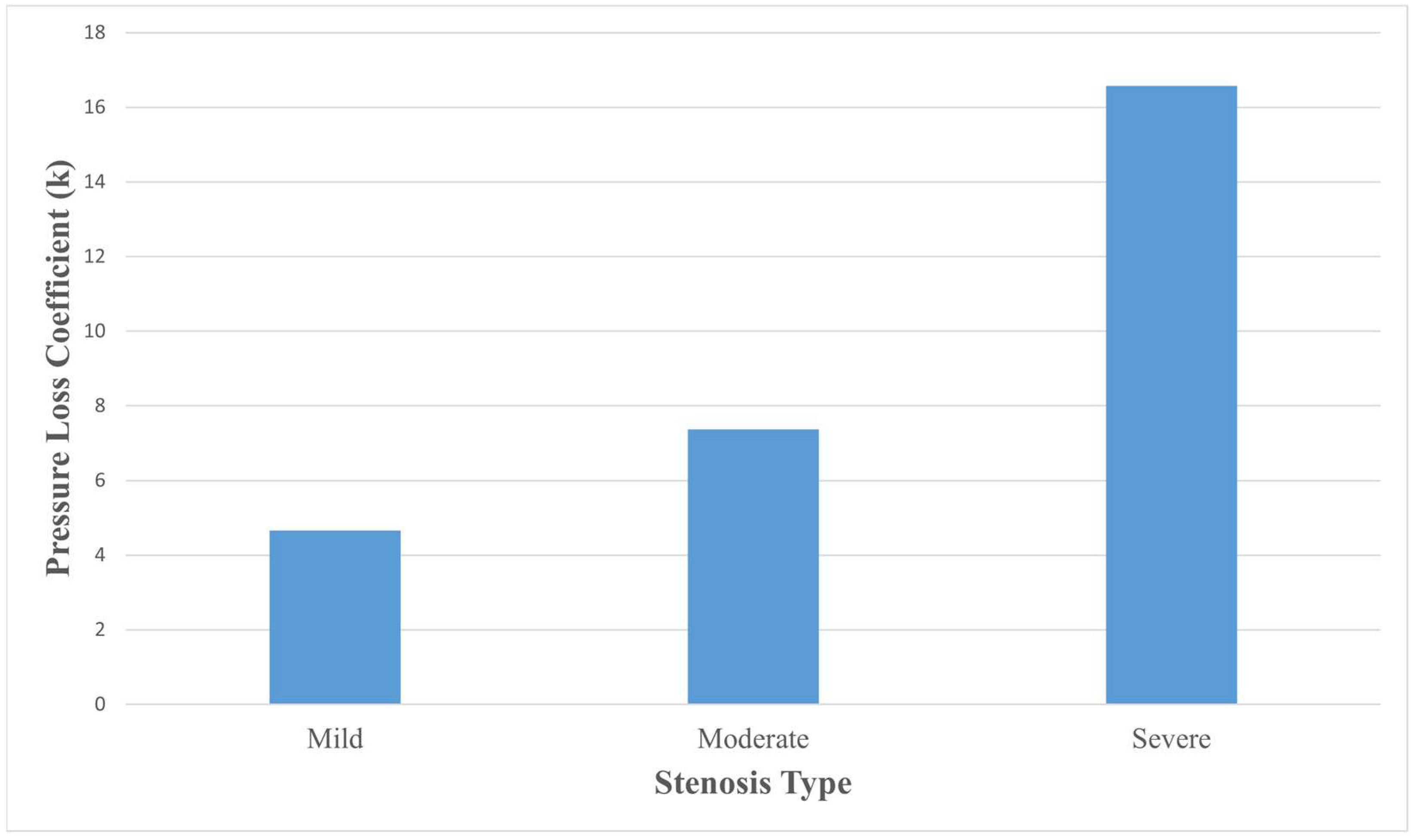
3.4. Pressure Loss Coefficient
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| WSS | Wall shear stress |
| AS | Aortic stenosis |
| AAA | Abdominal aortic aneurysm |
| CTA | Computed Tomography Angiography |
References
- Standring, S.; Ellis, H.; Healy, J.; Johnson, D.; Williams, A.; Collins, P.; Wigley, C. Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2005, 26, 2703. [Google Scholar]
- Juang, D.; Braverman, A.C.; Eagle, K. Aortic Dissection. Circulation 2008, 118, e507–e510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deplano, V.; Boufi, M.; Gariboldi, V.; Loundou, A.D.; D’Journo, X.B.; Cautela, J.; Djemli, A.; Alimi, Y.S. Mechanical Characterisation of Human Ascending Aorta Dissection. J. Biomech. 2019, 94, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonow, R.O.; Mann, D.L.; Zipes, D.P.; Libby, P. Braunwald’s Heart Disease e-Book: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 1437727700. [Google Scholar]
- Pape, L.A.; Tsai, T.T.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Oh, J.K.; O’Gara, P.T.; Evangelista, A.; Fattori, R.; Meinhardt, G.; Trimarchi, S.; Bossone, E.; et al. Aortic Diameter ≥5.5 cm Is Not a Good Predictor of Type A Aortic Dissection: Observations from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Circulation 2007, 116, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbel, R.; Eggebrecht, H. Aortic Dimensions and the Risk of Dissection. Heart 2006, 92, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condemi, F.; Campisi, S.; Viallon, M.; Troalen, T.; Xuexin, G.; Barker, A.J.; Markl, M.; Croisille, P.; Trabelsi, O.; Cavinato, C.; et al. Fluid- and Biomechanical Analysis of Ascending Thoracic Aorta Aneurysm with Concomitant Aortic Insufficiency. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 2921–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin, J.P.; Cibotti-Sun, M.; Elma, M.A. 2022 Aortic Disease Guideline-at-a-Glance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2348–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.H.; Elefteriades, J.A. Natural History of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms: Size Matters, plus Moving beyond Size. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 56, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzi, P.; Gunga, Z.; Niclauss, L.; Delay, D.; Roumy, A.; Pfister, R.; Colombier, S.; Patella, F.; Qanadli, S.D.; Kirsch, M. Type A Aortic Dissection in Aneurysms Having Modelled Pre-Dissection Maximum Diameter below 45 mm: Should We Implement Current Guidelines to Improve the Survival Benefit of Prophylactic Surgery? Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2021, 59, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliathamby, D.; Gutierrez, M.; Liu, A.; Ouzounian, M.; Forbes, T.L.; Tan, K.T.; Chung, J. Ascending Aortic Length and Its Association with Type A Aortic Dissection. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, X.; Wang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Chi, H.; Cao, H.; Ma, W.; Yan, Z.; Liu, G. Relationship Between Length and Curvature of Ascending Aorta and Type a Dissection. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 927105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliathamby, D.; Keshishi, M.; Ouzounian, M.; Forbes, T.L.; Tan, K.; Simmons, C.A.; Chung, J. Ascending Aortic Geometry and Its Relationship to the Biomechanical Properties of Aortic Tissue. JTCVS Open 2023, 13, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanath, V.S.; Oh, J.K.; Sundt III, T.M.; Eagle, K.A. Acute Aortic Syndromes and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2009, 84, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goody, P.R.; Hosen, M.R.; Christmann, D.; Niepmann, S.T.; Zietzer, A.; Adam, M.; Bönner, F.; Zimmer, S.; Nickenig, G.; Jansen, F. Aortic Valve Stenosis: From Basic Mechanisms to Novel Therapeutic Targets. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabello, B.A.; Paulus, W.J. Aortic Stenosis. Lancet 2009, 373, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García–Herrera, C.M.; Celentano, D.J.; Herrera, E.A. Modelling and Numerical Simulation of the in Vivo Mechanical Response of the Ascending Aortic Aneurysm in Marfan Syndrome. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2017, 55, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y. An Experimental Study of Pulsatile Flow in a Compliant Aortic Root Model under Varied Cardiac Outputs. Fluids 2018, 3, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Thomas, N.; Ullah, A.H.; Eichholz, B.; Estevadeordal, J.; Suzen, Y.B. Experimental and Computational Study of Pulsatile Flow Characteristics in Romanesque and Gothic Aortic Arch Models. Med. Eng. Phys. 2022, 102, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campobasso, R.; Condemi, F.; Viallon, M.; Croisille, P.; Campisi, S.; Avril, S. Evaluation of Peak Wall Stress in an Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm Using FSI Simulations: Effects of Aortic Stiffness and Peripheral Resistance. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2018, 9, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simao, M.; Ferreira, J.M.; Tomas, A.C.; Fragata, J.; Ramos, H.M. Aorta Ascending Aneurysm Analysis Using CFD Models towards Possible Anomalies. Fluids 2017, 2, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petuchova, A.; Maknickas, A. Computational Analysis of Aortic Haemodynamics in the Presence of Ascending Aortic Aneurysm. Technol. Health Care 2022, 30, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo, F.S.; Almeida, G.d.C.; Alvares de Azevedo, B.; Ibanez Aguilar, I.F.; Azevedo, B.N.; Teixeira, P.S.; Camargo, G.C.; Correia, M.G.; Nieckele, A.O.; Oliveira, G.M.M. Stress Load and Ascending Aortic Aneurysms: An Observational, Longitudinal, Single-Center Study Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radl, L.; Jin, Y.; Pepe, A.; Li, J.; Gsaxner, C.; Zhao, F.H.; Egger, J. AVT: Multicenter aortic vessel tree CTA dataset collection with ground truth segmentation masks. Data Brief. 2022, 40, 107801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassanova, R.A.; Giddens, D.P. Disorder Distal to Modeled Stenoses in Steady and Pulsatile Flow. J. Biomech. 1978, 11, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Seo, J.H.; Mittal, R. Computational Modelling and Analysis of Haemodynamics in a Simple Model of Aortic Stenosis. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 851, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.S.; Frankel, S.H.; Fischer, P.F. Direct Numerical Simulation of Stenotic Flows. Part 1. Steady Flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 582, 253–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Chu, W.; Lee, L.; Yu, H. Numerical Evaluation of Curvature Effects on Shear Stresses Across Arterial Stenoses. Biomed. Eng. Appl. Basis Commun. 2002, 14, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhun, C.-S.; Newswanger, R.; Cysyk, J.P.; Ponnaluri, S.; Good, B.; Manning, K.B.; Rosenberg, G. Dynamics of Blood Flows in Aortic Stenosis: Mild, Moderate, and Severe. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, S.B. Turbulent Flows. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 2020–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyverfeldt, P.; Trenti, C.; Ziegler, M.; Bjarnegård, N.; Lindenberger, M. Helical Flow in Tortuous Aortas and Its Relationship to Turbulence: A Whole-Aorta 4D Flow MRI Study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1124604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglino, G.; Cosentino, D.; Steeden, J.A.; De Nova, L.; Castelli, M.; Ntsinjana, H.; Pennati, G.; Taylor, A.M.; Schievano, S. Using 4D Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Validate Computational Fluid Dynamics: A Case Study. Front. Pediatr. 2015, 3, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Batista, M.D.; Ferretti, N.M. State-of-the-Art Review on Measurement of Pressure Losses of Fluid Flow Through Pipe Fittings; NIST Technical Note 2206; National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Commerce: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bappoo, N.; Syed, M.B.J.; Khinsoe, G.; Kelsey, L.J.; Forsythe, R.O.; Powell, J.T.; Hoskins, P.R.; McBride, O.M.B.; Norman, P.E.; Jansen, S.; et al. Low Shear Stress at Baseline Predicts Expansion and Aneurysm-Related Events in Patients with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2021, 14, e013160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.J.; Kuhn, D.C.S.; Lozowy, R.J.; Kulbisky, G.P. Low Wall Shear Stress Predominates at Sites of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 63, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, L.P.; Powell, J.T.; Kelsey, L.J.; Lim, B.; Ashleigh, R.; Venermo, M.; Koncar, I.; Norman, P.E.; Doyle, B.J. Morphology and Hemodynamics in Isolated Common Iliac Artery Aneurysms Impacts Proximal Aortic Remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Duprey, A.; Zainal, M.; Schlicht, M.; Williams, D.; Berguer, R. Determination of the Elastic Modulus of Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm at Different Ranges of Pressure Using Uniaxial Tensile Testing. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 142, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, D.C.; Deveja, R.P.; Kritharis, E.P.; Perrea, D.; Sionis, G.D.; Toutouzas, K.; Stefanadis, C.; Sokolis, D.P. Regional and Directional Variations in the Mechanical Properties of Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, E.; Nishigami, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Sakamoto, T.; Nakao, K. Impact of Shear Stress and Atherosclerosis on Entrance-Tear Formation in Patients with Acute Aortic Syndromes. Heart Vessel. 2014, 29, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W.C. Aortic Dissection: Anatomy, Consequences, and Causes. Am. Heart J. 1981, 101, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, T.; Sica, G.; Bocchini, G.; Romano, F.; Lassandro, F.; Rea, G.; Muto, E.; Pinto, A.; Iacobellis, F.; Crivelli, P.; et al. MDCT Imaging of Non-Traumatic Thoracic Aortic Emergencies and Its Impact on Diagnosis and Management—A Reappraisal. Tomography 2022, 8, 200–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gara, P.T.; DeSanctis, R.W. Acute Aortic Dissection and Its Variants. Circulation 1995, 92, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.; Sharma, S.; Farci, F.; Le, J. Aortic Dissection; StatPearls: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gülan, U.; Calen, C.; Duru, F.; Holzner, M. Blood Flow Patterns and Pressure Loss in the Ascending Aorta: A Comparative Study on Physiological and Aneurysmal Conditions. J. Biomech. 2018, 76, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Lachapelle, K.; Wener, E.; Cartier, R.; De Varennes, B.; Fraser, R.; Leask, R.L. Energy Loss, a Novel Biomechanical Parameter, Correlates with Aortic Aneurysm Size and Histopathologic Findings. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isselbacher, E.M. Thoracic and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Circulation 2005, 111, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, H.; Lee, S.J. Effect of Pulsatile Swirling Flow on Stenosed Arterial Blood Flow. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cell Count (Millions) | WSS (Pa) | Changes (% Difference) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.553 | 5.65 | 1.48 |
| 1.01 | 5.566 | 0.32 |
| 1.76 | 5.548 | 0.25 |
| 3.3 | 5.534 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nahid, A.B.M.N.S.; Nuhash, M.M.; Zhang, R. Hemodynamic Implications of Aortic Stenosis on Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Progression: A Patient-Specific CFD Study. J. Vasc. Dis. 2025, 4, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4040038
Nahid ABMNS, Nuhash MM, Zhang R. Hemodynamic Implications of Aortic Stenosis on Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Progression: A Patient-Specific CFD Study. Journal of Vascular Diseases. 2025; 4(4):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleNahid, A B M Nazmus Salehin, Mashrur Muntasir Nuhash, and Ruihang Zhang. 2025. "Hemodynamic Implications of Aortic Stenosis on Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Progression: A Patient-Specific CFD Study" Journal of Vascular Diseases 4, no. 4: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4040038
APA StyleNahid, A. B. M. N. S., Nuhash, M. M., & Zhang, R. (2025). Hemodynamic Implications of Aortic Stenosis on Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Progression: A Patient-Specific CFD Study. Journal of Vascular Diseases, 4(4), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4040038