Intracranial Aneurysms: Relevance of Superposed Blood Pulse Waves and Tobacco Smoke?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence and Rupture Risk of IAs
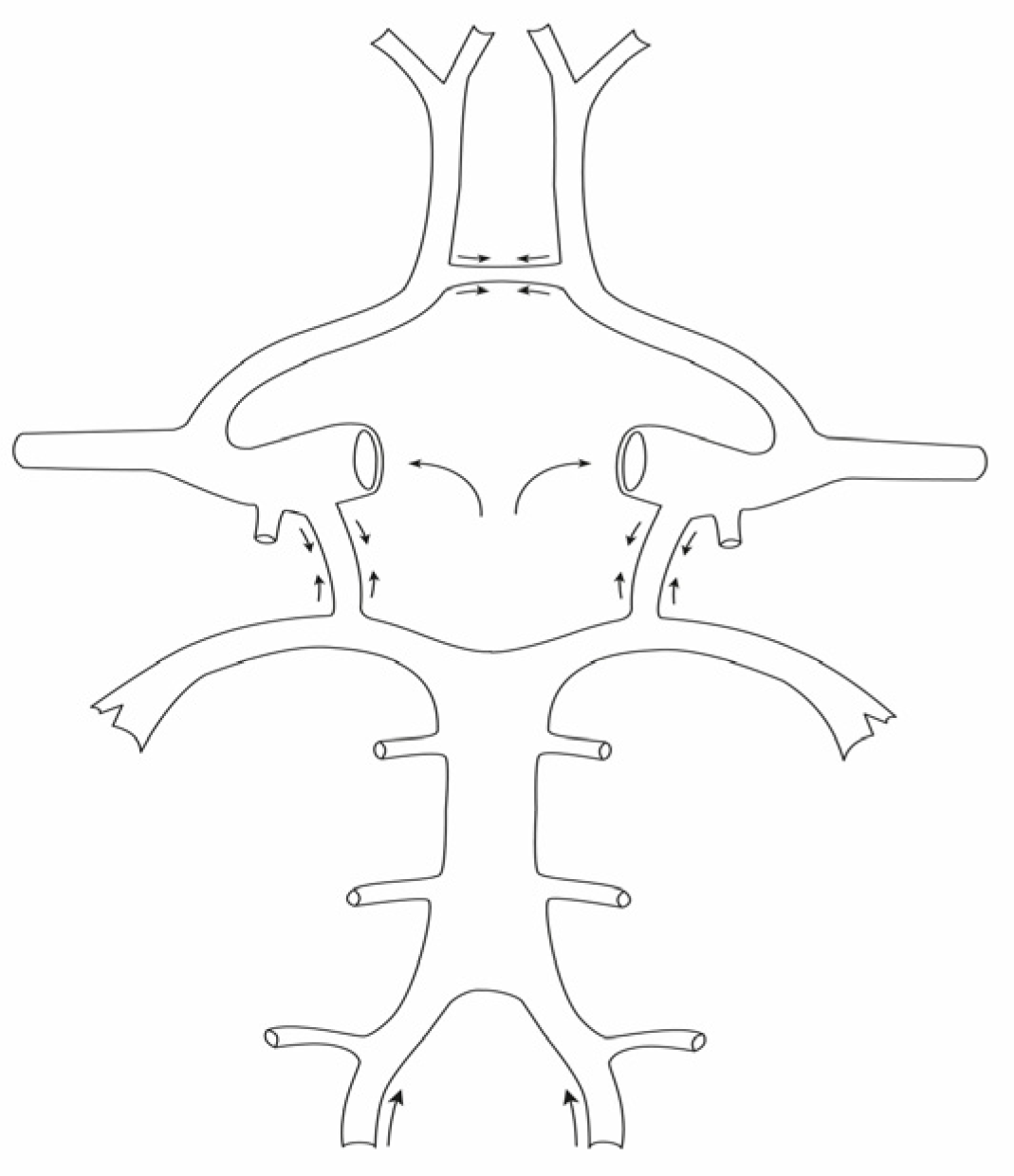
3.2. Superposed Blood Pulse Waves Can Promote the Development of Aneurysms
3.3. Different Frequency of IAs on the Left and Right Side of the Brain Base
3.4. Possible Explanation for the Predominance of Left-Sided IAs
3.5. Frequency of IAs in Women and Men
| Women n | Men n | Women IA | Men IA | IA Women % | IA Men % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harada [19] | 3253 | 5341 | 144 | 133 | 4.4 | 2.5 |
| Imaizumi [27] | 1707 | 2363 | 106 | 70 | 6.2 | 3.0 |
| Li [20] | 2445 | 2368 | 206 | 130 | 8.6 | 5.5 |
| Horikoshi [28] | 2454 | 2064 | 84 | 43 | 3.4 | 2.1 |
| Total | 9859 | 12,136 | 540 | 376 | 5.3 | 3.1 |
| Ratio | 1.7 | 1 |
3.6. Unusually High Prevalence of IAs in Anterior Cerebral Arteries in Men
3.7. Tobacco Smoke: A Toxic Factor at the Anterior Cerebral Arteries?
4. Conclusions
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Clinical Impact
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Etminan, N.; Buchholz, B.A.; Dreier, R.; Dreier, R.; Bruckner, P.; Torner, J.C.; Steiger, H.-J.; Hanggi, D.; Macdonald, R.L. Cerebral aneurysms: Formation, progression and developmental chronology. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, B.; Guo, E.; Wang, L.; Liu, P.; Wen, X.; Xu, W.; Jiang, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Number of cigarettes smoked per day, smoking index, and intracranial aneurysm rupture: A case-control study. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongable, G.L.; Lanzino, G.; Germanson, T.P.; Truskowski, L.L.; Torner, J.C.; Kassel, N.F. Gender-related differences in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 84, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Nelson, L.M.; Koepsell, T.D.; van Belle, G. Cigarette smoking, alcohol use, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 1992, 23, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebral, J.R.; Raschi, M. Suggested connections between risk factors of intracranial aneurysms: A review. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 1366–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etminan, N.; Dörfler, A.; Steinmetz, H. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms-pathogenesis and individualized management. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2020, 117, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieteling, E.W.; Rinkel, G.J. Characteristics of intracranial aneurysms and subarachnoid haemorrhage in patients with polycystic kidney disease. J. Neurol. 2003, 250, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, E.; Gibson, W.T. A review of the genetics of intracranial berry aneurysms and implications for genetic counseling. J. Genet. Counsel. 2017, 26, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutard, M. Experimental cerebral aneurysms in the female heterozygous Blotchy mouse. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1999, 80, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, N.; Handa, H.; Hazama, F. Experimentally induced cerebral aneurysms in rats: Part II. Surg. Neurol. 1979, 11, 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, M.; Miyamoto, S.; Mizoguchi, A.; Kume, N.; Kita, T.; Hashimoto, N. Mouse model of cerebral aneurysm. Experimental induction by renal hypertension and local hemodynamic changes. Stroke 2002, 33, 1911–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brutto, V.; Ortiz, J.G.; Biller, J. Intracraial arterial Dolichoectasia. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatomi, H.; Segawa, H.; Kurata, A.; Shiokawa, Y.; Nagata, K.; Kamiyama, H.; Ueki, K.; Kirino, T. Clinicopathological study of intracranial fusiform and dolichoectatic aneurysms. Insight on the mechanism of growth. Stroke 2000, 31, 896–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghods, A.J.; Lopes, D.; Chen, M. Gender differences in cerebral aneurysm location. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Tian, L.; Wang, Y.X.J. An analysis of 1256 cases of sporadic ruptured cerebral aneurysm in a single Chinese Institution. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlak, M.H.; Algra, A.; Brandenburg, R.; Rinkel, G.J. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.G.; Jung, Y.T.; Kim, M.S.; Eun, C.K.; Jang, S.H. Size and location of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2009, 45, 11–15. Available online: www.jkns.or.kr0.3340/jkns.2009.45.1.11 (accessed on 12 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igase, K.; Matsubara, I.; Igase, M.; Miyazaki, H.; Sadamoto, K. Initial experience in evaluating the prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms detected on 3-tesla MRI. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 33, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Fukuyama, K.; Shirouzu, T.; Ichinose, M.; Fujimura, H.; Kakumoto, K.; Yamanaga, Y. Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in healthy asymptomatic Japanese adults: Differences in gender and age. Acta Neurochir. 2013, 155, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Chen, S.W.; Li, Y.D.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y.S.; Hu, D.J.; Tan, H.Q.; Wu, Q.; Wang, W.; Sun, Z.K.; et al. Prevalence of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in Chinese adults aged 35 to 75 years. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingall, T.; Asplund, K.; Mähönen, M.; Bonita, R. A multinational comparison of subarachnoid hemorrhage epidemiology in the WHO MONICA stroke study. Stroke 2000, 31, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, R. Macrocirculation. Pulse waves. In Human Physiology and Pathophysiology (Translated from German), 32nd ed.; Brandes, R., Lang, F., Schmidt, R.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.P.; Cheng, K.M.; Yu, S.-C.H.; Au Yeung, K.M.; Cheung, Y.L.; Chan, C.M.; Lui, W.M. Size, location, and multiplicity of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in the Hong Kong Chinese population with subarachnoid haemorrhage. Hong Kong Med. J. 2009, 15, 262–266. Available online: www.hkmj.org (accessed on 13 October 2021).
- Aarhus, M.; Helland, C.A.; Wester, K. Differences in anatomical distribution, gender, and sidedness between ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms in a defined patient population. Acta Neurochir. 2009, 151, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, T.; Jiao, S.; Li, B.; Guan, J.; Wang, Y.X.J. Epidemiological investigation of 264 sporadic cases of ruptured cerebral aneurysm at a single institution in southwest China. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyziewski, R.M.; Klis, K.M.; Kucala, R.; Polak, J.; Kwinta, B.M.; Starowicz-Filip, A.; Stachura, K.; Piszczek, K.; Moskala, M.; Tomaszewski, K.A. Intracranial aneurysm distribution and characteristics according to gender. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 32, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, Y.; Mizutani, T.; Shimizu, K.; Sato, Y.; Taguchi, J. Detection rates and sites of unruptured intracranial aneurysms according to sex and age: An analysis of MR angiography-based brain examinations of 4070 healthy Japanese adults. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikoshi, T.; Akiyama, I.; Yamagata, Z.; Nukui, H. Retrospective analysis of the prevalence of asymptomatic cerebral aneurysm in 4518 patients undergoing magnetic resonance angiography-when does cerebral aneurysm develop? Neurol. Med. Chir. 2002, 42, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdan, A.; Barnes, J.; Mitchell, P. Subarachnoid hemorrhage and the female sex: Analysis of risk factors, aneurysm characteristics, and outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csordas, A.; Kreutmayer, S.; Ploner, C.; Braun, P.R.; Karlas, A.; Backovic, A.; Wick, G.; Bernhard, D. Cigarette smoke extract induces prolonged endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagic cell death in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 92, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, A.; Castro, V.M.; Ozdemir, Y.H.; Dagen, S.; Yu, S.; Dligach, D.; Finan, S.; Gainer, V.; Shadick, N.A.; Murphy, S.; et al. Association of intracranial aneurysm rupture with smoking duration, intensity, and cessation. Neurology 2017, 89, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katotomichelakis, M.; Balatsouras, D.; Tripsianis, G.; Davris, S.; Maroudias, N.; Danielides, V.; Simopoulos, C. The effect of smoking on the olfactory function. Rhinology 2007, 45, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.W.; Lee, S.I.; Noh, S.J.; Jeong, Y.G.; Kim, M.S.; Jeong, Y.T. What is the significance of a large number of ruptured aneurysms smaller than 7 mm in diameter? J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2009, 45, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, Y.; Horikoshi, T.; Sugita, M.; Yagishita, T.; Nukui, H. Size of cerebral aneurysms and related factores in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg. Neurol. 2004, 61, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Kyung-Do, H.; Park, Y.M.; Bae, J.M.; Kim, S.U.; Jeun, S.S.; Yang, S.H. Cigarette smoking is associated with increased risk of malignant gliomas: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Cancers 2020, 12, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvera, S.A.N.; Miller, A.B.; Rohan, T.E. Cigarette smoking and risk of glioma: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1848–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Jiang, J.; Liu, B.; Han, W.; Wu, Y.; Zou, X.; Nasca, P.C.; Xue, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. Smoking and adult glioma: A population-based case-control study in China. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, A.; Juarez, J.J.; Incontri, D.; Ibarra, A.; Cazares, H.G. Sex-specific differences in glioblastoma. Cells 2021, 10, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Sun, C.R.; He, M.; Yin, L.C.; Du, H.G.; Zhangh, J.M. Correlation between tumor location and clinical properties of glioblastomas in frontal and temporal lobes. World Neurosurg. 2018, 115, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| n | Artery | Left Side | Right Side | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aarhus [24] | 17 | vertebrobasilar | 15 | 2 | <0.0001 |
| Liu et al. [25] | 69 | anterior cerebral | 53 | 16 | <0.001 |
| Krzyzewski [26] | 99 | internal carotid | 64 | 35 | <0.01 |
| Imaizumi [27] | 148 | internal carotid | 82 | 66 |
| n (IA) ACA + AcoA | Men % | Women % | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kongable [3] | 301 | 46.1 | 26.6 | <0.001 |
| Ghods [14] | 97 | 29.0 | 15.0 | <0.001 |
| Hamdan [29] | 216 | 44.8 | 26.3 | <0.001 |
| Aarhus [24] | 130 | 47.7 | 25.7 | <0.0001 |
| Krzyzewski [26] | 79 | 31.0 | 17.0 | <0.015 |
| Harada [19] | 57 | 18.0 | 8.9 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barz, U.; Schreiber, A.; Barz, H. Intracranial Aneurysms: Relevance of Superposed Blood Pulse Waves and Tobacco Smoke? J. Vasc. Dis. 2023, 2, 222-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd2020016
Barz U, Schreiber A, Barz H. Intracranial Aneurysms: Relevance of Superposed Blood Pulse Waves and Tobacco Smoke? Journal of Vascular Diseases. 2023; 2(2):222-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd2020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarz, Ulrich, Almut Schreiber, and Helmut Barz. 2023. "Intracranial Aneurysms: Relevance of Superposed Blood Pulse Waves and Tobacco Smoke?" Journal of Vascular Diseases 2, no. 2: 222-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd2020016
APA StyleBarz, U., Schreiber, A., & Barz, H. (2023). Intracranial Aneurysms: Relevance of Superposed Blood Pulse Waves and Tobacco Smoke? Journal of Vascular Diseases, 2(2), 222-229. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd2020016







