Profound Opioid and Medetomidine Withdrawal: A Case Series and Narrative Review of Available Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Case Series Review
2.3. Medication Usage
2.4. Narrative Literature Review
3. Results
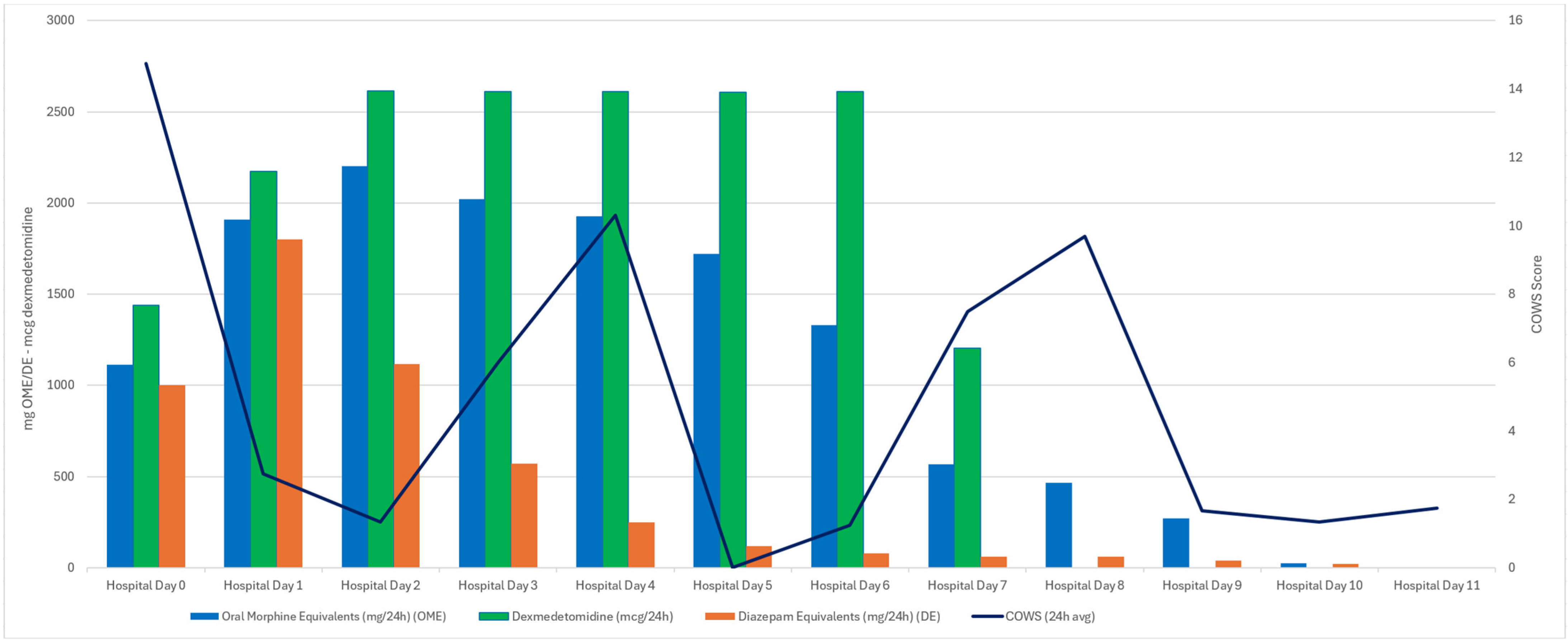
3.1. Case One
3.2. Case Two
3.3. Case Three
3.4. Case Four
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary
4.2. Introduction to Narrative Review
4.3. Pharmacology and Comparison to Xylazine
4.4. Dexmedetomidine Withdrawal Syndrome
4.5. Timeline and Epidemiology
4.6. Concepts in Clinical Management
4.7. High Dose Oral Alpha-2 Agonist Therapy
4.8. Combination Alpha-2 Agonist Therapy
4.9. Low Dose Dexmedetomidine Infusion Outside the ICU
4.10. High Dose Dexmedetomidine
4.11. Transdermal Clonidine
4.12. Public Health Implications and Future Directions
4.13. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Term |
| MICU | Medical Intensive Care Unit |
| ED | Emergency Department |
| α2 | Alpha-2 (adrenergic receptor) |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| HR | Heart Rate |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| RR | Respiratory Rate |
| SPO2 | Pulse Oximetry |
| COWS | Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale |
| PHA | Public Health Alert |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| PO | Per Os (by mouth/oral) |
| IVF | Intravenous Fluid |
| ODT | Oral Dissolving Table |
| IVP | Intravenous Push |
| QTc | Corrected QT Interval |
| SANRA | Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles |
| CARE | CAse REport guidelines |
| GABA | Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| AV | Atrioventricular |
References
- Quijano, T.; Crowell, J.; Eggert, K.; Clark, K.; Alexander, M.; Grau, L.; Heimer, R. Xylazine in the drug supply: Emerging threats and lessons learned in areas with high levels of adulteration. Int. J. Drug Policy 2023, 120, 104154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.K.; Camacho, T.E.; Olson, R.; Grover, Z.; Rapoza, T.; Larson, M.J. Xylazine’s impacts on the community in Philadelphia: Perspectives of people who use opioids and harm reduction workers. Subst. Use Misuse 2024, 60, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, R.; Agwuncha, C.; Wilson, C.; Schrecker, J.; Holt, A.; Heltsley, R. Withdrawal signs and symptoms among patients positive for fentanyl with and without xylazine. J. Addict. Med. 2025, 19, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, K.; Li, Y.; Kahoud, J.L.; Cho, D.; Mulholland, J.; Roque, S.; Stugart, L.; Gillingham, J.; Borne, E.; Slovis, B. Tranq dope: Characterization of an ED cohort treated with a novel opioid withdrawal protocol in the era of fentanyl/xylazine. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 85, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; London, K.; Murphy, L.; Casey, E.; Durney, P.; Arora, M.; McKeever, R.; Tasillo, A.; Goodstein, D.; Hart, B.; et al. Notes from the Field: Suspected Medetomidine Withdrawal Syndrome among Fentanyl-Exposed Patients—Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, September 2024–January 2025. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2025, 74, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philadelphia Department of Public Health. Health Alert: Drug Checking Findings: January–June 2025. 11 September 2025. Available online: https://www.substanceusephilly.com/q1q22025 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Bryant, C.E.; England, G.C.W.; Clarke, K.W. A comparison of the sedative effects of medetomidine and xylazine in the horse. J. Vet. Anaesth. 1991, 18, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyner, C.L.; Woody, B.J.; Reid, J.S.; Chafetz, E.P.; Lederer, H.A.; Norton, J.F.; Jöchle, W. Multicenter clinical comparison of sedative and analgesic effects of medetomidine and xylazine in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1997, 211, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, K.S.; Durney, P.; Warrick-Stone, T.; Alexander, K.; Kahoud, J.L. Decreased effectiveness of a novel opioid withdrawal protocol following the emergence of medetomidine as a fentanyl adulterant. Biomedicines 2025, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesson, D.R.; Ling, W. The clinical opiate withdrawal scale (COWS). J. Psychoact. Drugs 2003, 35, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, C.H. Benzodiazepines: How They Work and How to Withdraw (The Ashton Manual); Institute of Neuroscience, Newcastle University: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, M.L. Demystifying Opioid Conversion Calculations: A Guide for Effective Dosing, 2nd ed.; American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Ed.; American Society of Health-System Pharmacists: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Kienle, G.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; Sox, H.; Riley, D.; CARE Group. The CARE guidelines: Consensus-based clinical case reporting guideline development. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, G.M. Dexmedetomidine: A review of its use for sedation in the intensive care setting. Drugs 2015, 75, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukry, M.; Miller, J.A. Update on dexmedetomidine: Use in nonintubated patients requiring sedation for surgical procedures. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2010, 6, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maze, M.; Tranquilli, W. Alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists: Defining the role in clinical anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1991, 74, 581–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, R.; Brown, H.C.; Mitchell, D.H.; Silvius, E.N. Dexmedetomidine: A novel sedative-analgesic agent. Bayl. Univ. Med. Cent. Proc. 2001, 14, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karol, M.D.; Maze, M. Pharmacokinetics and interaction pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine in humans. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2000, 14, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll-Weng, E.; Manecke, G.R., Jr.; Thistlethwaite, P.A. Dexmedetomidine and cardiac arrest. Anesthesiology 2004, 100, 738–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheinin, H.; Karhuvaara, S.; Olkkola, K.T.; Kallio, A.; Anttila, M.; Vuorilehto, L.; Scheinin, M. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of intramuscular dexmedetomidine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1992, 52, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, A.; Salonen, M.; Forssell, H.; Scheinin, H.; Scheinin, M.; Tuominen, J. Medetomidine premedication in dental surgery: A double-blind cross-over study with a new alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1990, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yuen, V.M.; Goulay-Dufay, S.; Kwok, P.C. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, R.; Savola, J.M.; Saano, V.; Nyman, L. Characterization of the selectivity, specificity and potency of medetomidine as an α2-adrenoceptor agonist. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 150, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaygıngül, R.; Belge, A. The comparison of clinical and cardiopulmonary effects of xylazine, medetomidine and detomidine in dogs. Ankara Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2018, 65, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, P.M.; Bartkowski, R.R. Drug interactions of clinical significance with opioid analgesics. Drug Saf. 1993, 8, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.B.; Mariani, J.J.; Levin, F.R. New directions in the treatment of opioid withdrawal. Lancet 2020, 395, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, G.; Walsh, J.; Plawman, A.; Gianutsos, P.; Alto, W.; Mancl, L.; Rudolf, V. A novel non-opioid protocol for medically supervised opioid withdrawal and transition to antagonist treatment. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2018, 44, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrman-Dupre, R.; Kaigh, C.; Salzman, M.; Haroz, R.; Peterson, L.K.; Schmidt, R. Management of xylazine withdrawal in a hospitalized patient: A case report. J. Addict. Med. 2022, 16, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayub, S.; Parnia, S.; Poddar, K.; Bachu, A.K.; Sullivan, A.; Khan, A.M.; Ahmed, S.; Jain, L. Xylazine in the opioid epidemic: A systematic review of case reports and clinical implications. Cureus 2023, 15, e36864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukoyi, A.T.; Coker, S.A.; Lewis, L.D.; Nierenberg, D.W. Two cases of acute dexmedetomidine withdrawal syndrome following prolonged infusion in the intensive care unit: Report of cases and review of the literature. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, S.; Kaplan, J.B.; Adamczyk, K.; Chiu, S.H.; Shah, C.V. Evaluation of dexmedetomidine withdrawal in critically ill adults. J. Crit. Care 2021, 62, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouajram, R.H.; Bhatt, K.; Croci, R.; Baumgartner, L.; Puntillo, K.; Ramsay, J.; Thompson, A. Incidence of dexmedetomidine withdrawal in adult critically ill patients: A pilot study. Crit. Care Explor. 2019, 1, e0035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieller, L.A.; Alaniz, C.; Pleva, M.R.; Miller, J.T. Incidence of rebound hypertension after discontinuation of dexmedetomidine. Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, L.; Hooper, S. Dexmedetomidine withdrawal syndrome and opioid sensitivity. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 2023, 13 (Suppl. 1), e105–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.; Hoehn, K.; Brouillette, G. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome as a Result of Withdrawal from Prolonged Dexmedetomidine. J. Pediatr. Intensive Care 2015, 4, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, K.P.; Quan, A.P.T.; Baumgartner, L.P.; Jia, S.; Croci, R.B.; Puntillo, K.R.; Ramsay, J.; Bouajram, R.H.P. Effects of a clonidine taper on dexmedetomidine use and withdrawal in adult critically ill patients—A pilot study. Crit. Care Explor. 2020, 2, e0245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; McLaughlin, K.C.; Romero, N.; Crowley, K.E. Evaluation of dexmedetomidine withdrawal and management after prolonged infusion. Clin. Ther. 2024, 46, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philadelphia Department of Public Health, Division of Substance Use Prevention and Harm Reduction. Health Alert: In Philadelphia, Medetomidine, a Potent Non-Opioid Veterinary Sedative, Has Been Detected in the Illicit Drug Supply [Health Alert PDPH-HAN-0441A]. Philadelphia Department of Public Health; 13 May 2024. Available online: https://hip.phila.gov/document/4421/PDPH-HAN-0441A-05-13-24.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2025).
- Murphy, L.; Krotulski, A.; Hart, B.; Wong, M.; Overton, R.; McKeever, R. Clinical characteristics of patients exposed to medetomidine in the illicit opioid drug supply in Philadelphia: A case series. Clin. Toxicol. 2025, 63, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nham, A.; Le, J.N.; Thomas, S.A.; Gressick, K.; Ussery, E.N.; Ko, J.Y.; Gladden, R.M.; Mikosz, C.A.; Schier, J.G.; Vivolo-Kantor, A.; et al. Overdoses involving medetomidine mixed with opioids—Chicago, Illinois, May 2024. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2025, 74, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowski, S.J.; Tamama, K.; Trautman, W.J.; Stratton, D.L.; Lynch, M.J. Notes from the Field: Severe Medetomidine Withdrawal Syndrome in Patients Using Illegally Manufactured Opioids—Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, October 2024–March 2025. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2025, 74, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durney, P.; Kahoud, J.L.; Warrick-Stone, T.; Montesi, M.; Carter, M.; Butt, S.; Mencia, A.M.; Omoregie, L.; Shah, M.; Bloomfield, M.; et al. Biochemical identification and clinical description of medetomidine exposure in people who use fentanyl in Philadelphia, PA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.J.; Casey, E.R.; Zwiebel, S.J. Diagnosis and management of medetomidine withdrawal: Clinical implications of the shifting illicit opioid landscape. J. Acad. Consult. Liaison Psychiatry 2025, 66, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, K.S.; Huo, S.; Murphy, L.; Warrick-Stone, T.; Goodstein, D.; Montesi, M.; Carter, M.; Butt, S.; Alexander, K.; Satz, W.; et al. Severe fentanyl withdrawal associated with medetomidine adulteration: A multicenter study from Philadelphia, PA. J. Addict. Med. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennsylvania Coordinated Medication-Assisted Treatment Program (PENNCAMP). Medetomidine. Available online: https://penncamp.org/medetomidine/ (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Fairbanks, C.A.; Kitto, K.F.; Nguyen, H.O.; Stone, L.S.; Wilcox, G.L. Clonidine and dexmedetomidine produce antinociceptive synergy in mouse spinal cord. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.; Elliott, J. Alpha2 receptors and agonists in pain management. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2001, 14, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.K.M.; Cheung, C.W.; Chong, Y.K. Alpha-2 agonists in acute pain management. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 2849–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Mishima, A.; Ono, S.; Fukuda, H.; Vasko, M.R. Inhibitory effects of clonidine and tizanidine on release of substance P from slices of rat spinal cord and antagonism by α adrenergic receptor antagonists. Neuropharmacology 1991, 30, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Smithburger, P.L.; Kane-Gill, S.L. Review of adjunctive dexmedetomidine in the management of severe acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2015, 41, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association of Critical Care Nurses (AACN). Dexmedetomidine (Precedex) in the Progressive Care Unit. Available online: https://www.aacn.org/education/ce-activities/nti23330/dexmedetomidine-precedex-in-the-progressive-care-unit (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Patch, R.K.; Eldrige, J.S.; Moeschler, S.M.; Pingree, M.J. Dexmedetomidine as part of a multimodal analgesic treatment regimen for opioid induced hyperalgesia in a patient with significant opioid tolerance. Case Rep. Anesthesiol. 2017, 2017, 9876306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durney, P.; Carter, M.; London, K.; Goodstein, D.C.; Montesi, M.; Butt, S.; Warrick-Stone, T.; Fiore, J. Low-Dose Dexmedetomidine: Repurposing an Intravenous Agent for Opioid & Alpha-2 Withdrawal. In Proceedings of the American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) Annual Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 24–27 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hospira, Inc. Dexmedetomidine Hydrochloride Injection [package insert]. revised 2021 (21 038/S 017). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/206628s017lbl.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Rodriguez, K.; Anderson, R.L.; Keriazes, G.; Meyers, B. A Retrospective Review of High versus Standard Dose Dexmedetomidine for Sedation in Critically Ill Patients. J. Intensive Crit. Care 2016, 02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bajwa, B.S. Role of dexmedetomidine in anesthesia and critical care. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2014, 3, 10711–10722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iirola, T.; Aantaa, R.; Laitio, R.; Kentala, E.; Lahtinen, M.; Wighton, A.; Garratt, C.; Ahtola-Sätilä, T.; Olkkola, K.T. Pharmacokinetics of prolonged infusion of high-dose dexmedetomidine in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voscopoulos, C.; Kirk, F.L.; Lovrincevic, M.; Lema, M. The use of “high dose” dexmedetomidine in a patient with critical tracheal stenosis and anterior mediastinal mass. Open Anesth. J. 2011, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, M.S.; Heel, R.C. Transdermal Clonidine. Drugs 1988, 35, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaess, S.S.; Attridge, R.L.; Gutierrez, G.C. Clonidine as a strategy for discontinuing dexmedetomidine sedation in critically ill patients: A narrative review. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2020, 77, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lardieri, A.B.; Fusco, N.M.; Simone, S.; Walker, L.K.; Morgan, J.A.; Parbuoni, K.A. Effects of clonidine on withdrawal from long-term dexmedetomidine in the pediatric patient. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, L.; Gregory, M. Clonidine transdermal patches for use in outpatient opiate withdrawal. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 1989, 6, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sica, D.A.; Grubbs, R. Transdermal clonidine: Therapeutic considerations. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2005, 7, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, A.B.; Hartman, C.F.; Flaherty, C.P.; E Ebeling-Koning, N.; A Beauchamp, G.; Katz, K.D. Novel use of clonidine patch to treat tizanidine withdrawal. Cureus 2024, 16, e54831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, N. Rise of illicit medetomidine use: A worrisome trend. Am. J. Addict. 2025, 34, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Durney, P.; Paquin, E.; Fitzpatrick, G.; Lockstein, D.; Warrick-Stone, T.; Montesi, M.; Patel-Francis, S.H.; Rashid, J.; Vaughan-Ogunlusi, O.; Goodsell, K.; et al. Profound Opioid and Medetomidine Withdrawal: A Case Series and Narrative Review of Available Literature. Psychoactives 2025, 4, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040037
Durney P, Paquin E, Fitzpatrick G, Lockstein D, Warrick-Stone T, Montesi M, Patel-Francis SH, Rashid J, Vaughan-Ogunlusi O, Goodsell K, et al. Profound Opioid and Medetomidine Withdrawal: A Case Series and Narrative Review of Available Literature. Psychoactives. 2025; 4(4):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040037
Chicago/Turabian StyleDurney, Phil, Elise Paquin, Gamal Fitzpatrick, Drew Lockstein, TaReva Warrick-Stone, Maeve Montesi, Sejal H. Patel-Francis, Jamal Rashid, Oluwarotimi Vaughan-Ogunlusi, Kelly Goodsell, and et al. 2025. "Profound Opioid and Medetomidine Withdrawal: A Case Series and Narrative Review of Available Literature" Psychoactives 4, no. 4: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040037
APA StyleDurney, P., Paquin, E., Fitzpatrick, G., Lockstein, D., Warrick-Stone, T., Montesi, M., Patel-Francis, S. H., Rashid, J., Vaughan-Ogunlusi, O., Goodsell, K., Kahoud, J. L., Martin, C., Chism, K., Goebel, P., Alexander, K., Goodstein, D., & London, K. S. (2025). Profound Opioid and Medetomidine Withdrawal: A Case Series and Narrative Review of Available Literature. Psychoactives, 4(4), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040037





