Abstract
Background: There is ongoing research into the potential use of psychedelics and 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (MDMA) as alternatives to commonly used medications for treating major depressive and anxiety disorders. Aims: We aimed to assess the efficacy of psychedelics and MDMA in managing depressive and anxiety symptoms and evaluate their safety profiles. Methods: We searched five databases for randomized controlled trials of psychedelics and MDMA targeting depressive and anxiety symptoms and conducted a meta-analysis using a random effects model when possible. The review protocol is registered in PROSPERO under CRD42022341325. Results: Psilocybin induced a rapid and sustained reduction in depressive and anxiety symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder and in patients with life-threatening cancer. MDMA induced a decrease in depressive symptoms in patients with life-threatening cancer, autism spectrum disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder. MDMA’s effect size was either negligible or negative in reducing generalized anxiety symptoms, but MDMA reduced social anxiety symptoms. Ayahuasca induced a reduction in depressive symptoms in individuals with treatment-resistant major depressive and personality disorders. Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) induced a decrease in anxiety symptoms in individuals with life-threatening cancer. Psilocybin’s adverse effects were noticeable for elevated blood pressure, headaches, and panic attacks. For MDMA, elevated blood pressure, headaches, panic attacks, and feeling cold were noticeable. Conclusions: Psychedelics (psilocybin, ayahuasca, and LSD) and MDMA have the potential to induce a reduction in depressive and anxiety symptoms. Adverse effects are noticed. Rigorous randomized controlled studies with larger sample sizes utilizing instruments with better reliability and validity are warranted.
1. Introduction
Major depressive and anxiety disorders are psychiatric disorders that can cause severe impairment in functioning. The current pharmacological interventions take time to produce a clinical response, and many patients either do not respond well to these treatments or develop treatment resistance. Recent advancements in understanding faulty brain circuits and neuroplasticity have led to the development of new strategies for finding more effective pharmacological agents for these disorders. These new agents may shorten the time patients need to respond to treatment and may provide longer-lasting benefits. Psychedelics and 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (MDMA) are among the apparent targets, likely because of their possible immediate and long-lasting efficacy. Esketamine, the enantiomer of ketamine, is accessible for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD) in the United States of America (USA). However, its use is restricted due to its potential for abuse and misuse. Around 51% of 6381 people who reported past-year psychedelic use in the 2016–2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health abused lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), psilocybin (mushroom), or MDMA [1]. The documentation of psychedelics and MDMA risks for addiction is scant, and their adverse profile pictures mostly use the following term: no serious adverse effects.
Psychedelics (LSD, mescaline, ayahuasca, and psilocybin), dissociatives (phencyclidine) (PCP), dextromethorphan (DMX), ketamine, deliriants (atropine and scopolamine), and kappa-opioid agonists (Salvinorin A) and entactogens are notable hallucinogens [2,3] that alter behavior, mood, thought, and perception [2]. Psilocybin, ayahuasca, and LSD have been the subjects of study for the management of depressive and anxiety symptoms [3,4,5], as has the entactogen MDMA for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and life-threatening illness-related anxiety [6,7].
Psilocybin activates 5HT2A-R and 5HT1A-R [8,9] within default-mode network DMN-associated brain regions, inhibits the activity of adenylate cyclase, decreases protein kinase A-mediated extracellular Ca2+ influx [10] and stimulates glutamate in contrast to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) release [11]. Psilocybin, consumed as mushrooms, is sometimes sold on the street as PCP. In addition, 10 mg (about the weight of a grain of table salt) of psilocybin per gram of mushroom is said to cause agitation, hallucinations, dizziness, weakness, and anxiety [12].
The median lethal dose (LD50) for psilocybin in rats and mice is 280–285 mg (about the weight of ten grains of rice)/kg, while in rabbits, it is 12.5 mg (about half the weight of a grain of rice)/kg [13]. It is presumed that psilocybin use and harm are low compared to illicit substances [14].
LSD interacts directly with 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, D2, and α2 receptors and indirectly with glutamate through N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors [15]. LSD (also known as acid on the street) can cause panic attacks, horrific hallucinations and illusions, long-term psychosis, and post-hallucinogen perception disorder [16,17]. LSD LD50 values range from 0.3 mg/kg intravenously (i.v.) in rabbits to 16.5 mg/kg i.v. in rats and 46–60 mg/kg i.v. in mice [18]. Between 2002 and 2018, the National Survey on Drug Use and Health found a rise in LSD use among those with a bachelor’s degree, single status, antisocial behavior, and co-occurring mental health and drug abuse disorders [19].
Ayahuasca interacts with dopamine, serotonin (5HT2A, 5HT1A, and 5HT2C), and norepinephrine through its monoamine oxidase inhibitors activity [20,21,22,23], respectively. Ayahuasca has hormonal effects, specifically elevating prolactin levels, cortisol, and growth hormone [24]. There have been reports of toxicity in humans and animals [25]. Wiltshire and colleagues reported the death of a man who consumed ayahuasca, psilocybin, cannabis, and papaver seeds [26]. Lima and colleagues noted that administering ayahuasca to rats at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg caused a reduction in locomotion by 44% and a decrease in vertical exploration by 62% [27]. According to Pitol and colleagues, providing Wistar rats with 4 mL/kg over 14 days led to arterial hypertrophy [28]. The abuse of ayahuasca was evaluated using the Addiction Severity Index by Fábregas and colleagues, and the researchers concluded that ayahuasca does not have negative psychosocial repercussions consistent with other addictive drugs [29].
MDMA releases serotonin [30], dopamine, and norepinephrine [31], as well as oxytocin, vasopressin, and cortisol [32]. The LD50 of MDMA in animals ranges from about 100 to 300 mg/kg. Most fatalities involving MDMA are attributable to dehydration and concurrent drug intoxication [33,34,35]. MDMA is frequently abused for recreational purposes [36]. It is reported that MDMA has a less intense reinforcing effect than other substances used for recreational purposes but still carries the risk of addiction [37].
Findings from open-label and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) signaled that psychedelics and MDMA can manage depressive and anxiety symptoms and are well tolerated. Literature reviews on psychedelics’ benefits focused on psilocybin, and most reviews clustered different psychedelics in one group. Also, literature reviews showed less or no emphasis on psychedelics’ possible long-term benefits. Li and colleagues focused on psilocybin for depressive symptoms [38]. Romeo and colleagues evaluated the combined effects of psychedelics (psilocybin, ayahuasca, and LSD) on depressive symptoms [39]. Leger and colleagues assessed the methodological differences in outcomes in using psychedelics for anxiety and depressive symptoms [40]. Goldberg and colleagues focused on the antianxiety and antidepressant effects of psilocybin before administration and before follow-up [41]. Vargas and colleagues examined psilocybin only for depressive and anxiety symptoms [42]. Galvo-Coelho and colleagues investigated the acute, medium-term, and long-term antidepressant effects of psilocybin and ayahuasca [43]. No previous review focused on MDMA benefits in managing depressive and anxiety symptoms.
In this review, we focused on several critical issues not addressed in prior reviews:
- Pharmacological differences exist among psychedelics overall, and each one of them may have a different clinical response when used to treat MDD or anxiety disorders. Thus, we investigated the benefits of each psychedelic individually.
- We assessed whether psychedelics produce a long-lasting effect beyond a quick relief of depressive or anxiety symptoms.
- We based our analysis on core instruments: clinician-reported or self-reported outcome measures to quantify hallucinogens’ clinical responses to mitigate discrepancies between outcome measures.
- We investigated the potential benefits of MDMA in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- We investigated psychedelics and MDMA safety profiles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Criteria for Considering Studies
2.1.1. Types of Studies
We included relevant RCTs in our investigation regardless of the publication date, country of origin, language, or outcomes. We excluded open-label trials.
2.1.2. Types of Participants
Adults 18 years old or older with or without any psychiatric history and with or without a medical illness.
2.2. Types of Interventions
2.2.1. Experimental Intervention
Any psychedelics that alleviate depressive or anxiety symptoms.
2.2.2. Control Intervention
The control intervention can be a placebo or any active pharmacological agent as a comparator.
2.3. Types of Outcome Measures
2.3.1. Clinical Response
A reduction in clinician-rated depressive and anxiety symptoms or a self-reported reduction in symptoms.
2.3.2. Adverse Events
Any medical or neuropsychiatric incident related to psychedelics.
2.4. Types of Settings
The settings were not limited and included medical centers, outpatient clinics, academic universities, or hospitals.
2.5. Search Methods for Identification of Studies
Electronic Searches
The review was based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) criteria [44]. It is listed on the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD42022341325). Articles published from inception to June 2022 were searched in the following databases: Academic Search Complete (1976–2022), Scopus (1998–2022), Embase, PubMed (1975–2022), and Google Scholar (2018–2022). Search terms were, for example, psychedelics + and + depression + and + randomized + controlled + trials.
2.6. Data Collection and Analysis
Two authors (DF and VK) independently screened the titles of all studies obtained by the search strategy, excluded all irrelevant articles, and then retained potentially relevant studies. NR solved disagreements between DF and VK.
The following data were extracted:
- Publication status, title, authors’ names, source, country, and year of publication.
- Trial characteristics: design and setting.
- Interventions: type of pharmacological and control intervention, dose, and duration.
- Number of participants, age, gender, loss to follow-up, and race.
- Outcomes.
2.7. Evaluation of the Methodological Quality of Randomized Controlled Trials, Bias Risk, and Heterogeneity
Methodological and risk of bias considerations are based on the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions guidelines [45]. The JADAD scale analyzed the methodological quality of clinical trials independently, and each trial was assigned a JADAD score. The JADAD scale ranges from 0 to 5, with trials scoring 3 or above regarded to be of high quality [46]. The I2 statistic evaluated statistical heterogeneity between studies [47].
- I2 = 0% to 40%: might not be important.
- I2 = 30% to 60%: may represent moderate heterogeneity.
- I2 = 50% to 90%: may represent substantial heterogeneity.
- I2 = 75% to 100%: considerable heterogeneity.
2.8. Data Synthesis
A pooled effect size analysis was performed when the combined studies reached at least two. In such cases, data were synthesized by using random-effects frequentist meta-analysis. Results were quantified and interpreted by the standardized mean difference (Cohen’s d) and 95% confidence interval. A Cohen’s d = 0.2 was interpreted as a small effect size, 0.5 as moderate, and 0.8 as large [48]. The results yielded a p-value of 0.05, and values below this were considered statistically significant. Meta-analyses were conducted in Jeffreys’s Amazing Statistics Program, JASP Team (2020). JASP (Version 0.14.1) [Computer software] (the University of Amsterdam Nieuwe Achtergracht 129B Amsterdam, The Netherlands and Open-source, Cross-platform Software for Ecological and Evolutionary Meta-analysis (OpenMEE). We performed a qualitative summary when a meta-analysis was not feasible and provided the effect size result.
A meta-regression analysis was conducted when there were two or more studies on a particular hallucinogen utilizing moderators such as age, psychedelics dosage, sample size, gender, dropout rate, adverse effects, and race. Lastly, a table summary of the selected variables was presented, comprising demographics, setting, study design, and outcomes.
No ethical approval or written informed consent was required for this review, as no patient-specific information was gathered or evaluated.
3. Results
3.1. Description of Studies
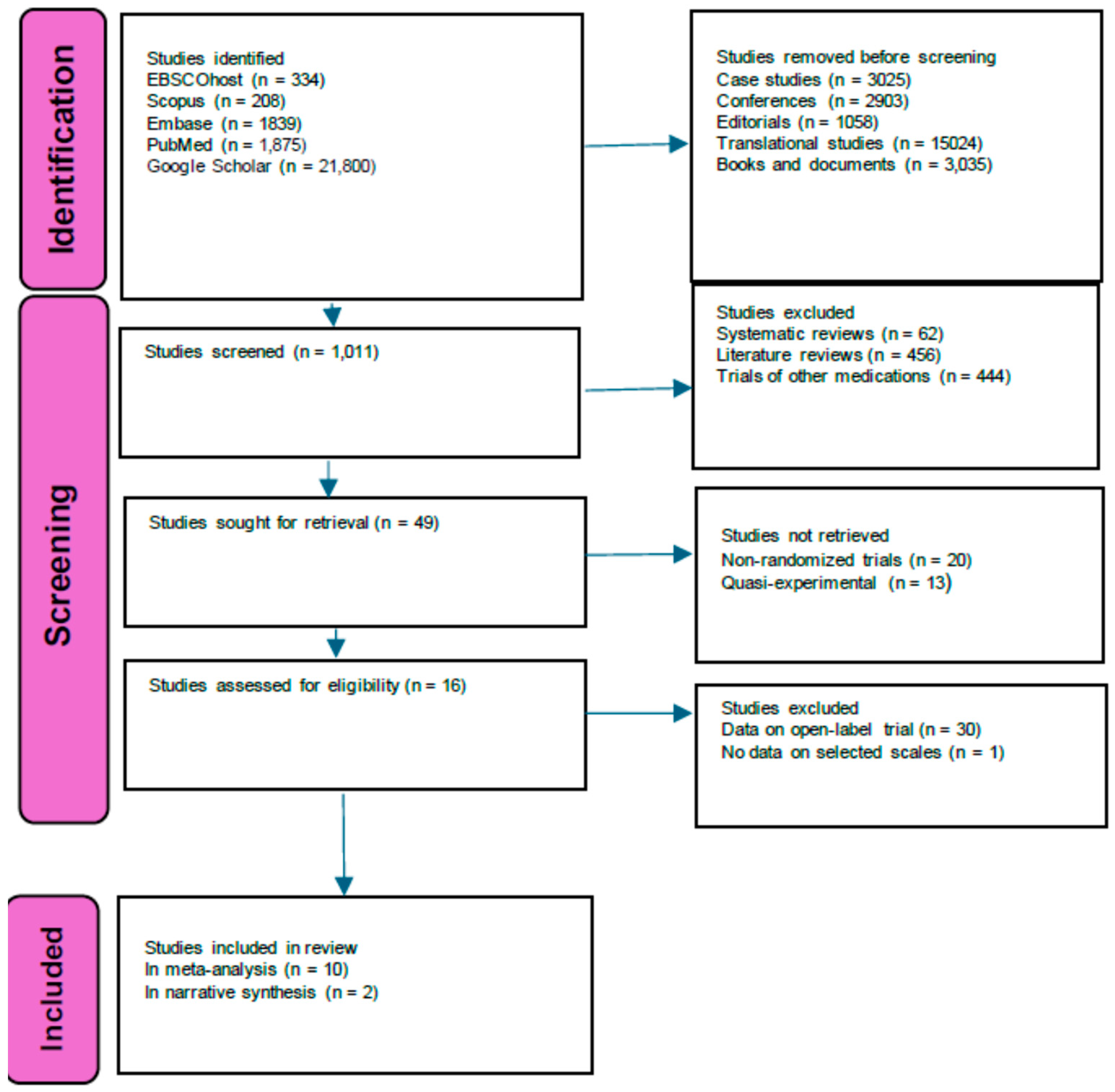
After screening, the search strategy yielded 49 studies (Figure 1). Sixteen of them qualified for inclusion in the investigation. We excluded three trials in which results were completed on the open-label design [49,50,51] and one trial conducted in a naturalistic setting [52]. We included 12 trials [7,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63], 10 of which provided data, allowing us to conduct a meta-analysis. Table 1 summarizes the individual characteristics of the studies included. More than half of the twelve trials took place in the United States of America (USA). Half of them were cross-over trials. Psychotherapy was provided in nine of the twelve studies. The study locations varied, but there was a trend toward academic/university and outpatient settings. Trial participants were diagnosed with life-threatening cancer, moderate to severe MDD, treatment-resistant MDD, PTSD, and autism spectrum disorder. For all the studies, the mean (μ) sample size was 32.75 with a standard deviation (σ) of 22.24, a μ age of 38.75, σ 13.43, psilocybin dosages μ 25.25 mg, σ 3.19 per 70 kg, MDMA dosages μ116 mg, σ 10.55, LSD dosage 200 μg, and ayahuasca 25 mg/70 kg. Five studies involved psilocybin, and among them, the study of Davis and colleagues [53] included a waiting list period for which data were analyzed in the long-term and were based on Gukasyan and colleagues’ analysis [64]. Psilocybin’s long-term benefit from Ross and colleagues 52 was investigated through data from Agin-Liebes and colleagues [65].
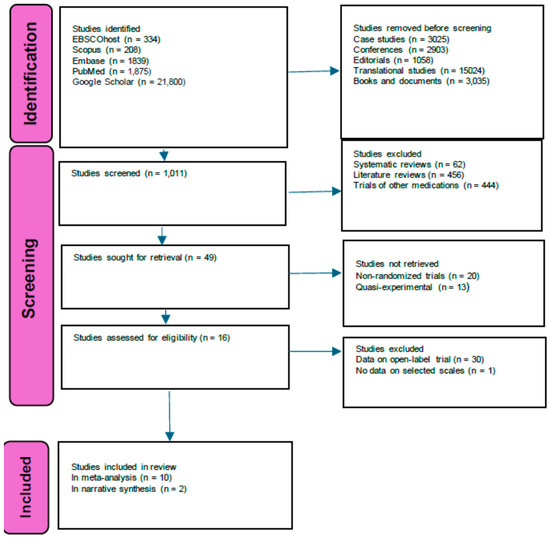
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the study selection process.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the included studies.
3.2. Risk of Bias in Included Studies
A description of the methodological quality of randomized trials and biases is provided in Supplementary Table S1. The average JADAD score for all studies was 4.18.
3.3. Synthesis of Results
3.3.1. Depressive Symptoms—Clinician-Rated Measures
Psilocybin: Pooled data at six months in patients with moderate and severe depressive symptoms and life-threatening cancer showed that psilocybin (20–30 mg/70 kg) significantly reduced Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) scores (d = 2.814, 95% CI = 2.210 to 3.418, p = 0.001, I2 = 0%). At week six, psilocybin (25 mg) outperformed escitalopram in reducing HAM-D scores in individuals with moderate to severe depressive symptoms (not corrected for multiple comparisons) (d = 2.395, 95% CI = 1.726 to 3.064). A pooled analysis was not feasible.
Ayahuasca: When ayahuasca (0.36 mg/kg) was compared to a placebo, the HAM-D (d = 0.849, 95% CI = 0.210 to 1.750) and the Montgomery–Asberg Scale for Depression (MADRS) scores (d = 1.490, 95% CI = 0.670 to 2.320) dropped rapidly at week one in individuals with treatment-resistant MDD with a high level of personality disorder. A pooled analysis was not feasible.
3.3.2. Depressive Symptoms—Self-Rated Measures
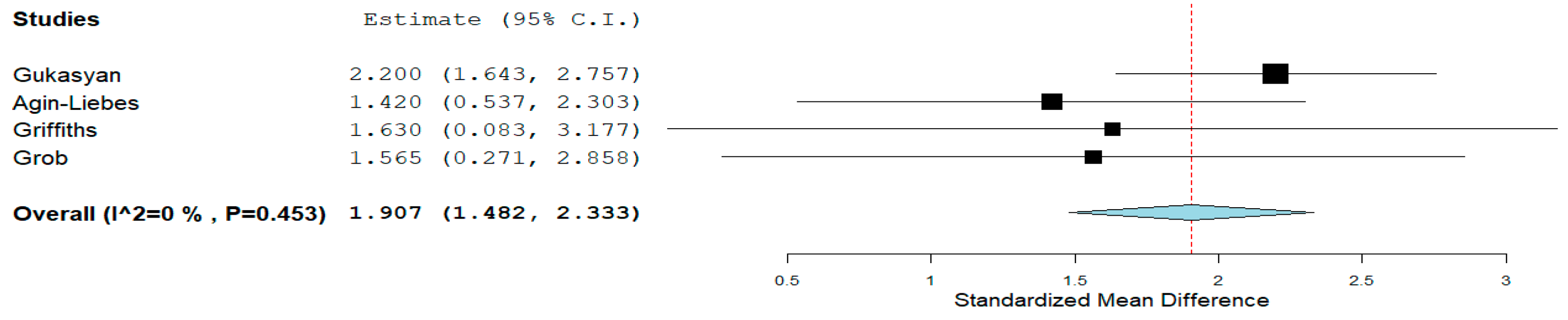
Psilocybin: In individuals with life-threatening cancer, a pooled analysis indicated that psilocybin (20–30 mg/70 kg) decreased the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) score significantly in two weeks compared to a placebo (d = 1.023, 95% CI = 0.424 to 1.622, p = 0.001, I2 = 0%). At week six, in individuals with moderate to severe depressive symptoms, as a secondary outcome, psilocybin (25 mg) fared better than escitalopram in reducing the BDI score (d = 1.043, 95% CI = 0.494 to 1.543) (not corrected for multiple comparisons). In individuals with moderate to severe depressive symptoms with life-threatening cancer, a pooled analysis indicated that the BDI score reduction was maintained at six months (d = 1.907, 95% CI = 1.482 to 2.333, p = 0.001, I2 = 0%) (Figure 2). At six months in individuals with life-threatening cancer, a decrease in the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS depression) was seen (d = 2.311, 95% CI = 0.987 to 3.634, p = 0.001). However, the real effect may differ due to high heterogeneity (I2 = 78.47%).
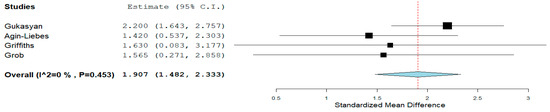
Figure 2.
Psilocybin BDI score reduction. The diamond shape represents the pooled estimate.
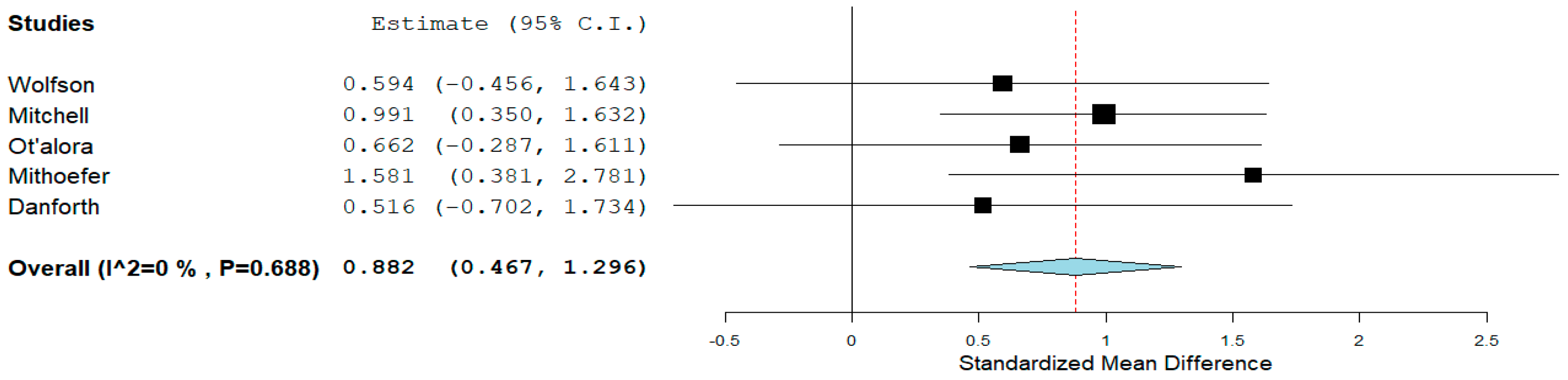
MDMA: Data extracted from MDMA originated from individuals with life-threatening cancer, autistic adults, and PTSD. A pooled analysis suggested that MDMA (75–180 mg) could lower the BDI score (d = 0.882, 95% CI = 0.467 to 1.296, p = 0.001, I2 = 0%) (Figure 3) from two months to twelve months compared to treatment at baseline.
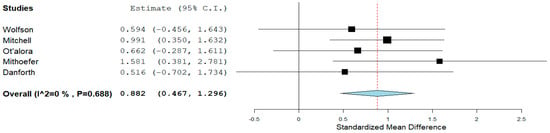
Figure 3.
MDMA BDI score reduction. The diamond shape represents the pooled estimate.
3.3.3. Anxiety Symptoms—Clinician-Rated Measures
Psilocybin: The pooled analysis in individuals with life-threatening cancer, who stayed in treatment for up to six months, indicated that psilocybin significantly reduced the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) score (d = 2.853, 95% CI = 1.638 to 4.068, p < 0.001). The actual effect may differ due to high heterogeneity (I2 = 68.76%).
MDMA: In autistic adults, at 6-month follow-up, MDMA (75–125 mg) appeared to induce a decline in Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale total scores (d = 1.482, 95% CI = 0.143 to 2.821). A pooled analysis was not viable.
3.3.4. Anxiety Symptoms—Self-Rated Measures
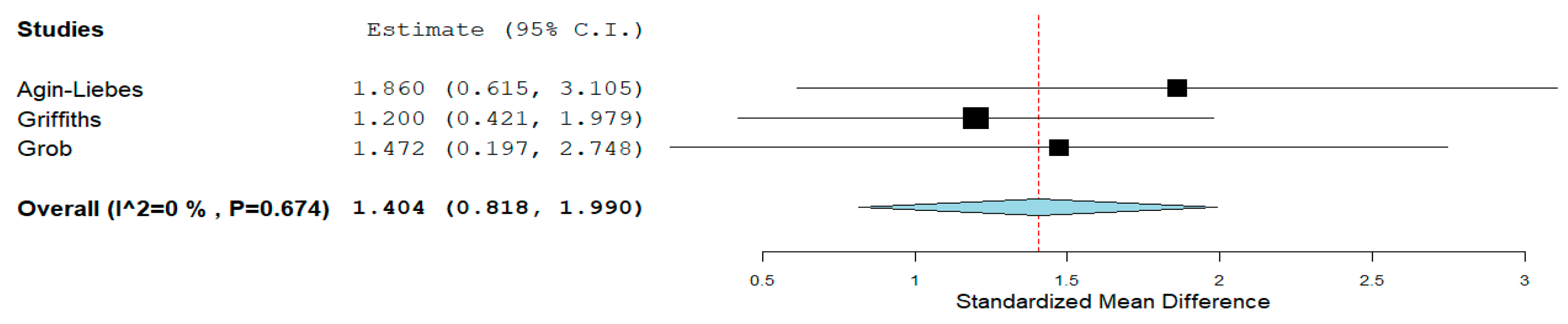
Psilocybin: In life-threatening cancer from baseline to week two, psilocybin (20–30 mg/70 kg) compared to a placebo significantly reduced State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) (d = 1.158, 95% CI = 0.538 to 1.778, p < 0.001, I2 = 0%) and STAI-State scores (d = 1.066, 95% CI = 0.330 to 1.798, p < 0.004, I2 = 33.75%). At six months, in individuals with life-threatening cancer, psilocybin (21–30 mg/70 kg) significantly reduced both STAI-Trait (d = 1.404, 95% CI = 0.818 to 1.990, p < 0.001, I2 = 0%) (Figure 4) and STAI-State scores (d = 1.310, 95% CI = 0.654 to 1.965, p < 0.001, I2 = 0%). However, psilocybin’s effect size reduction on the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS anxiety) was small and non-statistically significant (d = 0.219, 95% CI = −0.400 to 0.838, p = 0.488) with moderate heterogeneity (I2 = 47.67%).
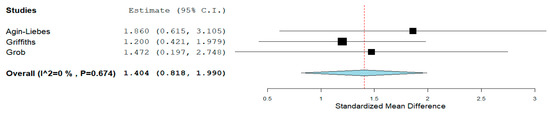
Figure 4.
Psilocybin STAI–Trait score reduction. The diamond shape represents the pooled estimate.
MDMA: At six months, in autistic adults and in individuals with life-threatening cancer MDMA (75–125 mg)’s reduction in both STAI-Trait (d = 0.462, 95% CI = −0.737 to 1.662, p = 0.450) and STAI-State scores (d = −0.139, 95% CI = −1.416 to 1.138, p = 0.831) was not statistically significant and had substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 54.49% and I2 = 59.70%, respectively).
LSD: In individuals with life-threatening cancer who received LSD (200 μg) over two months compared to a placebo, there was an indication that LSD could reduce STAI-Trait (d = 1.100, 95% CI= 0.860 to 3.060) and STAI-State scores (d = 1.200, 95% CI = 0.760 to 3.160).
3.3.5. Meta-Regression
Potential moderators of psilocybin and MDMA’s therapeutic effects, including age, dosage, sample size, gender, dropout rate, adverse effects, and race, had no meta-effect on the results.
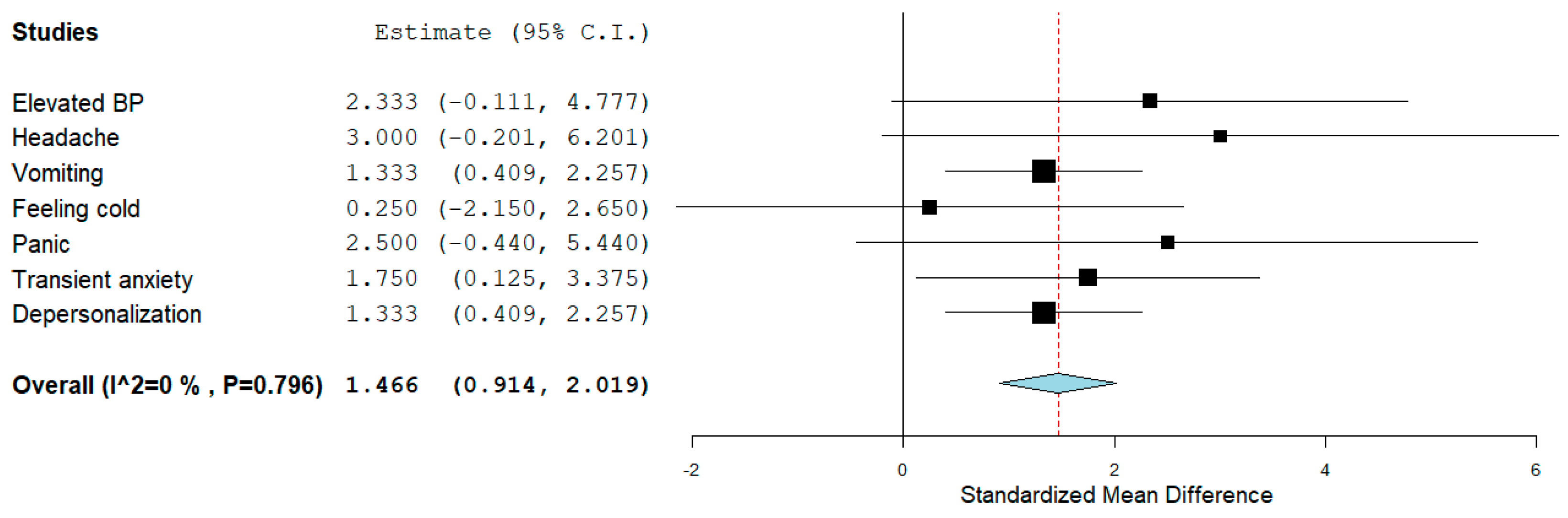
3.3.6. Adverse Effects
Several types of adverse effects were surveyed (Supplementary Table S2 and Figure S1). On average, 38.88% of the complaints were documented on psilocybin, 33.33% on MDMA, 18.51% on LSD, and 9.25% on ayahuasca (Supplementary Table S3). Up to 80% of the thirty-two adverse effects that occurred during a period spanning from week two up to twelve months included elevated blood pressure, headache, vomiting, feeling cold, panic attacks, transient anxiety, and depersonalization. Except for feeling cold, all of them had a large effect size (Figure 5). According to the one-sample t-test, psychedelics and MDMA had a sizable effect size of reported adverse effects that was statistically significant (Table 2). The effect size based on the paired sample t-test yielded statistical significance for psilocybin (elevated blood pressure, headache, and panic attacks) (d = 3.739, 95% CI = 1.697 to 5.763, p < 0.001) and MDMA (elevated BP, headache, panic attacks, and feeling cold) (d = 0.878, 95% CI = 0.160 to 1.565, p = 0.016) but not for ayahuasca (headache) (d = 0.087, 95% CI = –0.902 to 1.063, p = 0.873) or LSD (elevated BP and feeling cold) (d = 0.619, 95% CI = −0.218 to 1.415, p = 0.153).
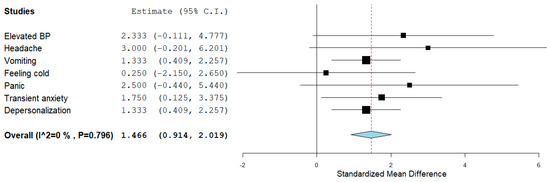
Figure 5.
Up to 80% of the adverse effects and their effect size. The diamond shape represents the pooled estimate.

Table 2.
One sample t-test for psychedelics and MDMA.
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Main Results
Psilocybin induced a rapid and sustained reduction in depressive and anxiety symptoms in patients with severe depressive symptoms and life-threatening cancer. Ayahuasca reduced depressive symptoms, and LSD reduced anxiety symptoms in individuals with life-threatening cancer. A decrease in depressive symptoms was noted with MDMA, primarily in the long-term in patients with life-threatening cancer, autism spectrum disorder in adults, and in patients with PTSD. The effect size of MDMA on anxiety symptoms was either negligible or negative for generalized anxiety symptoms but positive for social anxiety symptoms.
The results on psilocybin agree with those of Li and colleagues [38] and Goldberg and colleagues [41], indicating its benefits in reducing depressive symptoms in contrast to Galvo-Coelho and colleagues [43], who found no statistical significance of a benefit of psilocybin on depressive symptoms. For MDMA, ayahuasca, or LSD, no prior studies were found, permitting us to contrast our analysis.
There are few reports of adverse effects in the selected trials, and data about dropout rates were scant. The paired sample t-test yielded statistical significance for psilocybin regarding elevated blood pressure, headaches, and panic attacks, as well as for MDMA regarding elevated blood pressure, headaches, panic attacks, and feeling cold.
4.2. Overall Completeness and Applicability of Evidence
Psychedelics and MDMA modulate 5-HT 1A, 5-HT 1C, 5-HT 2, and 5-HT3 to generate anxiolytic effects; 5-HT 1A and 5-HT2 to generate antidepressant effects, and 5-HT3 to generate reward and cognition improvement effects [66,67]. Psychedelics and MDMA’s pharmacological properties may be beyond serotonin. Indeed, psilocybin releases GABA and glutamate; LSD binds to D1 and D3 receptors; ayahuasca increases monoamine oxidase inhibitory (MAOI) characteristics; and MDMA releases oxytocin, vasopressin, and cortisol. Dopamine, NMDA, and rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) mediate ketamine’s therapeutic effects [15,68]. Therefore, the basic pharmacology of psilocybin, ayahuasca, LSD, and MDMA for anxiety disorder and MDD merits additional study. This brings together the importance of the validity of the depression–anxiety–serotonin paradigm.
The DMN connects brain areas associated with introspective activities, thinking, and autobiographical memory [69,70]. Posner and colleagues suggested that people with a high familial risk for MDD had more DMN connectivity and less negative DMN–central executive network (CEN) connectivity than individuals with a low familial risk [71]. Schultz and colleagues suggested that decreased connectivity between the frontoparietal cognitive control network (FPN) and the rest of the brain is associated with depressive symptoms in the general population [72]. Psilocybin reduces DMN connectivity [73], acute LSD administration reduces functional connectivity in the visual, sensorimotor, and auditory networks and DMN connectivity [74], and ayahuasca lessens DMN brain activity [63]. MDMA interferes with fear memory, resulting in various affiliative and prosocial behaviors [75]. Psilocybin, ayahuasca, LSD, and MDMA may differ from commonly used medications to treat MDD and anxiety disorder by influencing the DMN and suppressing fear and negative emotions, which could explain the possible large effect size.
Johnson and colleagues emphasized in a summary of psychedelic studies and preventive measures that certain psychedelics are not known to cause organ damage or neuropsychological deficiencies and that their toxicity is low. Despite being portrayed as physically safe and not a substance of dependence, psychedelics can have psychological consequences like prolonged psychoses [76].
Dropout in RCTs is frequent and poses a risk to the validity of the data because completers and non-completers may have distinct characteristics [77]. There is a great likelihood that individuals in experimental research will drop out if they experience unpleasant adverse effects. Psychological and physiological adverse effects were observed for psilocybin and MDMA. Clinical case reports on ayahuasca and LSD revealed troubling psychological effects. About 1–1.5 h after ingesting ayahuasca, Rocha and colleagues [78] reported temporary disorientation (20–30 min), fear, anxiety, dissociation, depersonalization, agitation, confusion, anxiety, and visual hallucinations. Goldman and his colleagues wrote about a case of LSD flashback syndrome treated with an SSRI twenty-five years after the individual stopped using LSD [79]. Despite the lack of significant adverse effects typically recorded, there is still reason for concern regarding the safety and tolerance of psychedelics and MDMA. Because of insufficient documentation on attrition, there is room to continue interrogating psychedelics and MDMA’s tolerability and safety.
4.3. Abuse and Misuse Concerns
Psilocybin-containing mushrooms with varying concentrations are widely used illegally. Unprepared and unsupervised users may engage in harmful behavior, and individuals who already have a psychiatric disorder or are at risk of developing psychotic disorders may see their condition worsen [76]. MDMA has the potential to cause physical dependency. Ecstasy use reflects “compulsive usage” and “escalating use” [37]. LSD may accumulate in the body over time, resulting in user tolerance. LSD dependency can cause prolonged psychosis [80]. Using the Addiction Severity Index (ASI) (ASI Alcohol Use and Psychiatric Status subscales) on currently active ayahuasca users, Fábregas and colleagues found that ritual ayahuasca use did not seem to be linked to the significant psychosocial effects that are often caused by other drugs of abuse [29]. Therefore, research on its potential for addiction merits further investigation.
4.4. Legal Aspects
Psilocybin, LSD, MDMA, and ayahuasca are considered controlled substances in many countries in the world, restricting their potential applications for trials. Many trials have small sample sizes. Monitoring psychedelics and MDMA safety and tolerability seems primordial. Approval for controlled trials benefits of these substances may need to weigh their effort in that context. The setting of studies can also be a barrier to exploration. Uthaug and colleagues [52] found that ayahuasca’s non-pharmacological factors may influence improvements in participants’ mental health via a placebo effect, though a pharmacological response from the substances may not be ruled out. Psychedelics trials run in safe and comfortable environments, with clinicians knowledgeable about their use, may be necessary [81].
4.5. Limitations
Pre-selected standard measures were selected to gauge the efficacy of psychedelics and MDMA. Nevertheless, despite the extensive use of standardized scales in research, they may have limited therapeutic utility. Self-rating yielded more information than clinician-rating measures, which restricts the generalizability of this review’s findings.
While addressing the long-term effects of psychedelics and MDMA on depressive and anxiety symptoms, there was no control group. The absence of control groups can either inflate or deflate results. Psychedelics and MDMA were mainly used to facilitate psychotherapy. The use of psychedelics and MDMA as psychotherapy adjuncts in most studies limits the interpretation of their actual benefits. Most trials enrolled a limited number of participants, and several were more experimental than clinical.
Not all patients being compared have the same condition. Furthermore, some of the compounds included in this review have very different mechanisms of action. Drawing valuable conclusions from combining different conditions seems complicated. Clustering the analysis by a specific disease could have helped reduce confounders and generate a more accurate effect size. MDMA acts as both a stimulant and a hallucinogen [82]; therefore, its effects may be more related to increased tenderness and contentment rather than changing perceptions. Most of the rating scale results were based on secondary analysis, which can significantly hinder the interpretation of the analysis.
Overall, the trials included in this review were limited by small sample sizes, making it difficult to confidently employ the results in the broader population. In addition, the mixed results with MDMA and its limited effectiveness in treating generalized anxiety raise concerns regarding when and how MDMA should be used. While this review scrutinizes side effects, the long-term risks of psilocybin, LSD, ayahuasca, and MDMA remain unclear; this could potentially translate to significant risks for patients. A call for more robust trials underlines that the existing evidence is not strong enough to fully endorse psilocybin, LSD, ayahuasca, and MDMA for widespread clinical use.
5. Conclusions
5.1. Implications for Practice and Policy
This review offers insights into the potential of psychedelics and MDMA for treating depression and anxiety. The findings, especially for psilocybin, are promising. However, significant concerns regarding the small sample sizes, inconsistent effectiveness, and long-term safety need to be addressed. The study rightly calls for more rigorous research before psychedelics and MDMA can be widely recommended as treatments.
5.2. Implications for Research
Psychedelics and MDMA affect vital brain areas related to MDD and anxiety disorder. It seems that their pharmacological roots are beyond serotonin, and this warrants further investigations. Much needs to be known about the long-term effects of psilocybin, ayahuasca, LSD, and MDMA on individuals with MDD and anxiety disorder. Psychedelics’ psychological consequences, such as prolonged psychoses, compared to their potential benefits for managing depressive and anxiety symptoms, warrant further investigations. Characteristics of completers and non-completers in the context of dropout rates in RCTs involving psychedelics and how they might affect the validity of the results also warrant further investigations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/psychoactives3040029/s1, Figure S1: Adverse effects. Table S1: Assessment of methodological quality of randomized trials and biases; Table S2: Adverse effects surveyed. Table S3: Adverse effect complaints (number of individuals, mean and standard error).
Author Contributions
The study was conceived and designed by D.F., D.F., V.K.K. and N.R. evaluated bibliographies, extracted data, analyzed the methodological quality of clinical trials, and then assigned JADAD scores. D.F. conducted the meta-analysis and drafted the initial version of the manuscript. D.F., V.K.K. and N.R. contributed to the writing of the manuscript and approved its final form. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data availability criterion does not apply to this article because no new data were generated or analyzed for this investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Salas-Wright, C.P.; Hodges, J.C.; Hai, A.H.; Alsolami, A.; Vaughn, M.G. Toward a typology of hallucinogen users in the United States. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 229, 109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volgin, A.D.; Yakovlev, O.A.; Demin, K.A.; Alekseeva, P.A.; Kyzar, E.J.; Collins, C.; Nichols, D.E.; Kalueff, A.V. Understanding Central Nervous System Effects of Deliriant Hallucinogenic Drugs through Experimental Animal Models. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollenweider, F.X. Brain Mechanisms of Hallucinogens and Entactogens. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2001, 3, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, D.; Barnes, G.; Giaroli, G.; Tracy, D. Classical Hallucinogens as Antidepressants? A Review of Pharmacodynamics and Putative Clinical Roles. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 4, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, N.M.; Gibbs, D.; Bird, C.I.V.; Daniel, A.; Jelen, L.A.; Knight, G.; Goldsmith, D.; Young, A.H.; Rucker, J.J. Historic Psychedelic Drug Trials and the Treatment of Anxiety Disorders. Depress. Anxiety 2020, 37, 1261–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, B.; Higbed, L.; Nutt, D. A Review of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA)-Assisted Psychotherapy. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfson, P.E.; Andries, J.; Feduccia, A.A.; Jerome, L.; Wang, J.B.; Williams, E.; Carlin, S.C.; Sola, E.; Hamilton, S.; Yazar-Klosinski, B.; et al. MDMA-Assisted Psychotherapy for Treatment of Anxiety and Other Psychological Distress Related to Life-Threatening Illnesses: A Randomized Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smausz, R.; Neill, J.; Gigg, J. Neural Mechanisms Underlying Psilocybin’s Therapeutic Potential—The Need for Preclinical In Vivo Electrophysiology. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, J.K. Psilocybin. In Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs; Aronson, J.K., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1048–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Halberstadt, A.L.; Geyer, M.A. Multiple Receptors Contribute to the Behavioral Effects of Indoleamine Hallucinogens. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 364–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R. Serotonergic Regulation of Neuronal Excitability in the Prefrontal Cortex. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A.J.; Gates, M.J. Hallucinogens and Psychedelics. In Principles of Forensic Toxicology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 467–489. [Google Scholar]
- Tylš, F.; Páleníček, T.; Horáček, J. Psilocybin—Summary of Knowledge and New Perspectives. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.W.; Griffiths, R.R.; Hendricks, P.S.; Henningfield, J.E. The Abuse Potential of Medical Psilocybin According to the 8 Factors of the Controlled Substances Act. Neuropharmacology 2018, 142, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gregorio, D.; Aguilar-Valles, A.; Preller, K.H.; Heifets, B.D.; Hibicke, M.; Mitchell, J.; Gobbi, G. Hallucinogens in Mental Health: Preclinical and Clinical Studies on LSD, Psilocybin, MDMA, and Ketamine. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.E.; Rose, A.J. LSD: Its Use, Abuse, and Suggested Treatment (Observations by the Haight-Ashbury Medical Clinic). J. Psychedelic Drugs 1968, 1, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, M.J. Flashbacks: Recurrent Intrusive Images after the Use of LSD. Am. J. Psychiatry 1969, 126, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passie, T.; Halpern, J.H.; Stichtenoth, D.O.; Emrich, H.M.; Hintzen, A. The Pharmacology of Lysergic Acid Diethylamide: A Review. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2008, 14, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killion, B.; Hai, A.H.; Alsolami, A.; Vaughn, M.G.; Sehun Oh, P.; Salas-Wright, C.P. LSD Use in the United States: Trends, Correlates, and a Typology of Us. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 223, 108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frecska, E.; Bokor, P.; Winkelman, M. The Therapeutic Potentials of Ayahuasca: Possible Effects against Various Diseases of Civilization. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.S.; Presti, D.E. Endogenous Psychoactive Tryptamines Reconsidered: An Anxiolytic Role for Dimethyltryptamine. Med. Hypotheses 2005, 64, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liester, M.B.; Prickett, J.I. Hypotheses Regarding the Mechanisms of Ayahuasca in the Treatment of Addictions. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2012, 44, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffell, S.; Netzband, N.; Bird, C.; Young, A.H.; Juruena, M.F. The Pharmacological Interaction of Compounds in Ayahuasca: A Systematic Review. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2020, 42, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, R.G.; Valle, M.; Bouso, J.C.; Nomdedéu, J.F.; Rodríguez-Espinosa, J.; McIlhenny, E.H.; Barker, S.A.; Barbanoj, M.J.; Riba, J. Autonomic, Neuroendocrine, and Immunological Effects of Ayahuasca: A Comparative Study with d-Amphetamine. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 31, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrella-Parra, E.A.; Almanza-Pérez, J.C.; Alarcón-Aguilar, F.J. Ayahuasca: Uses, Phytochemical and Biological Activities. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2019, 9, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiltshire, P.E.J.; Hawksworth, D.L.; Edwards, K.J. Light Microscopy Can Reveal the Consumption of a Mixture of Psychotropic Plant and Fungal Material in Suspicious Death. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2015, 34, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.-M.; Ferreira, S.M.; Ávila, A.-A.L.; Perazzo, F.F.; Schneedorf, J.M.; Hinsberger, A.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Les effets de l’ayahuasca sur le système nerveux central: Étude comportementale. Phytothérapie 2007, 5, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitol, D.L.; Siéssere, S.; Dos Santos, R.G.; Rosa, M.L.N.M.; Hallak, J.E.C.; Scalize, P.H.; Pereira, B.F.; Iyomasa, M.M.; Semprini, M.; Riba, J.; et al. Ayahuasca Alters Structural Parameters of the Rat Aorta. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fábregas, J.M.; González, D.; Fondevila, S.; Cutchet, M.; Fernández, X.; Barbosa, P.C.R.; Alcázar-Córcoles, M.Á.; Barbanoj, M.J.; Riba, J.; Bouso, J.C. Assessment of Addiction Severity among Ritual Users of Ayahuasca. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010, 111, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalant, H. The Pharmacology and Toxicology of “Ecstasy” (MDMA) and Related Drugs. CMAJ 2001, 165, 917–928. [Google Scholar]
- Green, A.R.; Mechan, A.O.; Elliott, J.M.; O’Shea, E.; Colado, M.I. The Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “Ecstasy”). Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 463–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamilar-Britt, P.; Bedi, G. The Prosocial Effects of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA): Controlled Studies in Humans and Laboratory Animals. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 57, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, O.G.; Halm, S.; Seifritz, E. Psychedelics in the Treatment of Unipolar and Bipolar Depression. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2022, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmler, L.D.; Liechti, M.E. Pharmacology of MDMA- and Amphetamine-like New Psychoactive Substances. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2018, 252, 143–164. [Google Scholar]
- Holze, F.; Vizeli, P.; Müller, F.; Ley, L.; Duerig, R.; Varghese, N.; Eckert, A.; Borgwardt, S.; Liechti, M.E. Distinct Acute Effects of LSD, MDMA, and D-Amphetamine in Healthy Subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA): Current Perspectives. Subst. Abus. Rehabil. 2013, 4, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenhardt, L.; Bruno, R.; Topp, L. Is Ecstasy a Drug of Dependence? Drug Alcohol Depend. 2010, 107, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.-X.; Hu, Y.-R.; Chen, W.-N.; Zhang, B. Dose Effect of Psilocybin on Primary and Secondary Depression: A Preliminary Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, B.; Karila, L.; Martelli, C.; Benyamina, A. Efficacy of Psychedelic Treatments on Depressive Symptoms: A Meta-Analysis. J. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 34, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, R.F.; Unterwald, E.M. Assessing the Effects of Methodological Differences on Outcomes in the Use of Psychedelics in the Treatment of Anxiety and Depressive Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.B.; Pace, B.T.; Nicholas, C.R.; Raison, C.L.; Hutson, P.R. The Experimental Effects of Psilocybin on Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 284, 112749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.S.; Luís, Â.; Barroso, M.; Gallardo, E.; Pereira, L. Psilocybin as a New Approach to Treat Depression and Anxiety in the Context of Life-Threatening Diseases-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão-Coelho, N.L.; Marx, W.; Gonzalez, M.; Sinclair, J.; De Manincor, M.; Perkins, D.; Sarris, J. Classic Serotonergic Psychedelics for Mood and Depressive Symptoms: A Metaanalysis of Mood Disorder Patients and Healthy Participants. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Chandler, J.; Welch, V.A.; Higgins, J.P.; Thomas, J. Updated Guidance for Trusted Systematic Reviews: A New Edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, ED000142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadad, A.R.; Moore, R.A.; Carroll, D.; Jenkinson, C.; Reynolds, D.J.; Gavaghan, D.J.; Mcquay, H.J. Assessing the Quality of Reports of Randomized Clinical Trials: Is Blinding Necessary? Control. Clin. Trials 1996, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring Inconsistency in Metaanalyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Daws, R.E.; Timmermann, C.; Giribaldi, B.; Sexton, J.D.; Wall, M.B.; Erritzoe, D.; Roseman, L.; Nutt, D.; Carhart-Harris, R. Increased Global Integration in the Brain after Psilocybin Therapy for Depression. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithoefer, M.C.; Wagner, M.T.; Mithoefer, A.T.; Jerome, L.; Martin, S.F.; Yazar-Klosinski, B.; Michel, Y.; Brewerton, T.D.; Doblin, R. Durability of Improvement in Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms and Absence of Harmful Effects or Drug Dependency after 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine-Assisted Psychotherapy: A Prospective Long-Term Follow-up Study. J. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 27, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, L.; Feduccia, A.A.; Wang, J.B.; Hamilton, S.; Yazar-Klosinski, B.; Emerson, A.; Mithoefer, M.C.; Doblin, R. Long-Term Follow-up Outcomes of MDMA-Assisted Psychotherapy for Treatment of PTSD: A Longitudinal Pooled Analysis of Six Phase 2 Trials. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 2485–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthaug, M.V.; Mason, N.L.; Toennes, S.W.; Reckweg, J.T.; de Sousa Fernandes Perna, E.B.; Kuypers, K.P.C.; van Oorsouw, K.; Riba, J.; Ramaekers, J.G. A Placebo-Controlled Study of the Effects of Ayahuasca, Set and Setting on Mental Health of Participants in Ayahuasca Group Retreats. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Barrett, F.S.; May, D.G.; Cosimano, M.P.; Sepeda, N.D.; Johnson, M.W.; Finan, P.H.; Griffiths, R.R. Effects of Psilocybin-Assisted Therapy on Major Depressive Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.; Bossis, A.; Guss, J.; Agin-Liebes, G.; Malone, T.; Cohen, B.; Mennenga, S.E.; Belser, A.; Kalliontzi, K.; Babb, J.; et al. Rapid and Sustained Symptom Reduction Following Psilocybin Treatment for Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Life-Threatening Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, R.R.; Johnson, M.W.; Carducci, M.A.; Umbricht, A.; Richards, W.A.; Richards, B.D.; Cosimano, M.P.; Klinedinst, M.A. Psilocybin Produces Substantial and Sustained Decreases in Depression and Anxiety in Patients with Life-Threatening Cancer: A Randomized Double-Blind Trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grob, C.S.; Danforth, A.L.; Chopra, G.S.; Hagerty, M.; McKay, C.R.; Halberstadt, A.L.; Greer, G.R. Pilot Study of Psilocybin Treatment for Anxiety in Patients with Advanced-Stage Cancer. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carhart-Harris, R.; Giribaldi, B.; Watts, R.; Baker-Jones, M.; Murphy-Beiner, A.; Murphy, R.; Martell, J.; Blemings, A.; Erritzoe, D.; Nutt, D.J. Trial of Psilocybin versus Escitalopram for Depression. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.M.; Bogenschutz, M.; Lilienstein, A.; Harrison, C.; Kleiman, S.; Parker-Guilbert, K.; Ot’alora, G.M.; Garas, W.; Paleos, C.; Gorman, I.; et al. MDMA-Assisted Therapy for Severe PTSD: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Study. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ot’alora, G.M.; Grigsby, J.; Poulter, B.; Van Derveer, J.W., 3rd; Giron, S.G.; Jerome, L.; Feduccia, A.A.; Hamilton, S.; Yazar-Klosinski, B.; Emerson, A.; et al. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine-Assisted Psychotherapy for Treatment of Chronic Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Randomized Phase 2 Controlled Trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithoefer, M.C.; Mithoefer, A.T.; Feduccia, A.A.; Jerome, L.; Wagner, M.; Wymer, J.; Holland, J.; Hamilton, S.; Yazar-Klosinski, B.; Emerson, A.; et al. 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA)-Assisted Psychotherapy for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Military Veterans, Firefighters, and Police Officers: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Dose-Response, Phase 2 Clinical Trial. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danforth, A.L.; Grob, C.S.; Struble, C.; Feduccia, A.A.; Walker, N.; Jerome, L.; Yazar-Klosinski, B.; Emerson, A. Reduction in Social Anxiety after MDMA-Assisted Psychotherapy with Autistic Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 3137–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, P.; Holstein, D.; Michel, Y.; Doblin, R.; Yazar-Klosinski, B.; Passie, T.; Brenneisen, R. Safety and Efficacy of Lysergic Acid Diethylamide-Assisted Psychotherapy for Anxiety Associated with Life-Threatening Diseases. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2014, 202, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palhano-Fontes, F.; Barreto, D.; Onias, H.; Andrade, K.C.; Novaes, M.M.; Pessoa, J.A.; Mota-Rolim, S.A.; Osório, F.L.; Sanches, R.; Dos Santos, R.G.; et al. Rapid Antidepressant Effects of the Psychedelic Ayahuasca in Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Psychol. Med. 2019, 49, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gukasyan, N.; Davis, A.K.; Barrett, F.S.; Cosimano, M.P.; Sepeda, N.D.; Johnson, M.W.; Griffiths, R.R. Efficacy and Safety of Psilocybin-Assisted Treatment for Major Depressive Disorder: Prospective 12-Month Follow-Up. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agin-Liebes, G.I.; Malone, T.; Yalch, M.M.; Mennenga, S.E.; Ponté, K.L.; Guss, J.; Bossis, A.P.; Grigsby, J.; Fischer, S.; Ross, S. Long-Term Follow-up of Psilocybin-Assisted Psychotherapy for Psychiatric and Existential Distress in Patients with Life-Threatening Cancer. J. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 34, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, P.J. Serotonin Receptor Subtypes: Implications for Psychopharmacology. Br. J. Psychiatry 1991, 159, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieff, J.; Cooper, R.E.; Stockmann, T.; Amendola, S.; Hengartner, M.P.; Horowitz, M.A. The Serotonin Theory of Depression: A Systematic Umbrella Review of the Evidence. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 3243–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, D.; Enns, D.; Nuñez, J.P.; Posa, N.A.; Gobbi, L. D-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide, Psilocybin, and Other Classic Hallucinogens: Mechanism of Action and Potential Therapeutic Applications in Mood Disorders. Prog. Brain Res. 2018, 242, 69–96. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, L.E.; Minuzzi, L.; MacQueen, G.; Hall, G.; Kennedy, S.H.; Milev, R. The Default Mode Network in Healthy Individuals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Connect. 2017, 7, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieder, M.; Wang, D.J.J.; Dierks, T.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Jann, K. Default Mode Network Complexity and Cognitive Decline in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, J.; Cha, J.; Wang, Z.; Talati, A.; Warner, V.; Gerber, A.; Peterson, B.S.; Weissman, M. Increased Default Mode Network Connectivity in Individuals at High Familial Risk for Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, D.H.; Ito, T.; Solomyak, L.I.; Chen, R.H.; Mill, R.D.; Anticevic, A.; Cole, M.W. Global Connectivity of the Fronto-Parietal Cognitive Control Network Is Related to Depression Symptoms in the General Population. Netw. Neurosci. 2019, 3, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, F.S.; Krimmel, S.R.; Griffiths, R.R.; Seminowicz, D.A.; Mathur, B.N. Psilocybin Acutely Alters the Functional Connectivity of the Claustrum with Brain Networks That Support Perception, Memory, and Attention. Neuroimage 2020, 218, 116980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Liechti, M.E.; Lang, U.E.; Borgwardt, S. Advances and Challenges in Neuroimaging Studies on the Effects of Serotonergic Hallucinogens: Contributions of the Resting Brain. Prog. Brain Res. 2018, 242, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, M.B.; Norrholm, S.D.; Khoury, L.M.; Jovanovic, T.; Rauch, S.A.; Reiff, C.M.; Dunlop, B.W.; Rothbaum, B.O.; Howell, L.L. Inhibition of Serotonin Transporters Disrupts the Enhancement of Fear Memory Extinction by 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 2883–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Richards, W.; Griffiths, R. Human Hallucinogen Research: Guidelines for Safety. J. Psychopharmacol. 2008, 22, 603–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L.; Kenward, M.G.; Fairclough, D.L.; Horton, N.J. Differential Dropout and Bias in Randomised Controlled Trials: When It Matters and When It May Not. BMJ 2013, 346, e8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.M.; Rossi, G.N.; Osório, F.L.; Hallak, J.E.C.; Dos Santos, R.G. Adverse Effects after Ayahuasca Administration in the Clinical Setting. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 42, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.; Galarneau, D.; Friedman, R. New Onset LSD Flashback Syndrome Triggered by the Initiation of SSRIs. Ochsner J. 2007, 7, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Barnwal, P.; Ramasamy, A.; Sen, S.; Mondal, S. Lysergic Acid Diethylamide: A Drug of “Use”? Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 6, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucker, J.J.H.; Iliff, J.; Nutt, D.J. Psychiatry & the Psychedelic Drugs. Past, Present & Future. Neuropharmacology 2018, 142, 200–218. [Google Scholar]
- United States Drug Enforcement Administration. Ecstasy or MDMA (Also Known as Molly). Available online: https://www.dea.gov/factsheets/ecstasy-or-mdma-also-known-molly (accessed on 14 June 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).