Abstract
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) represents major public and socioeconomic issues. Alcohol exerts its pharmacological effects by altering different neurotransmitter systems, such as g-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glutamate, opioids, etc. Recent evidence suggests that the dynorphin (DYN)/kappa opioid receptor (KOR) system mediates the negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal. This system is also involved in stress-mediated alcohol intake in alcohol-dependent subjects. The DYN/KOR system probably exerts its action in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) to mediate the negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal. This article aims to review the current literature regarding the role of the DYN/KOR system in the actions of alcohol. We first review the literature regarding the effect of alcohol on the level of the peptide and its receptor, and the role of the endogenous DYN/KOR system in alcohol reward and negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal is then discussed. We also review the literature regarding the effects of KOR ligands on these processes.
1. Introduction
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a major public health problem in the United States and around the globe. It is marked by the lack of control to stop or reduce alcohol intake. People who drink excessively over a long time may suffer from the long-term effects of alcohol, such as unsafe behaviors, hepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis [1]. Moreover, alcoholism can cause cancers and cardiovascular problems [2]. Alcohol use and abuse are the seventh-leading cause of premature death and disability worldwide. In the United States, alcohol is considered the third-leading preventable cause of death [3]. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH, 2019) (https://www.samhsa.gov/data/report/2019-nsduh-annual-national-report, accessed on 3 October 2022) reports that 14.5 million people aged 12 and older have AUD. This number includes 9.0 million men and 5.5 million women.
The socioeconomic impact of AUD is also tremendous. The annual social expenses of AUD are estimated to be at least USD 148 billion [4]. Therefore, more research is needed to characterize new targets to develop medications to treat AUD effectively and safely. Any advancement in this field would be highly desirable to help those suffering from AUD and decrease the cost to society.
The effects of alcohol differ from person to person, based on various factors such as how much and how frequently a person drinks alcohol. Additionally, it depends on age, gender, health status, and family history of alcoholism [5]. Binge drinking, defined as increased alcohol consumption over a relatively short time, is a regular pattern of alcohol consumption in the United States and has negative public health and socioeconomic and behavioral consequences (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, https://search.cdc.gov/search/?query=Alcohol&dpage=1, accessed on 3 October 2022). However, while not all people who binge drink are addicted to alcohol, binge drinking is a significant element in the progression of AUD. Chronic alcohol use has been shown to rewire the reward and anti-reward neurocircuitries, leading to negative affective states, which then serve as a negative reinforcer and result in relapse (for reviews, see [6,7,8,9]).
Withdrawal symptoms are one of the distinguishing signs of alcoholism, and it is frequently characterized by a decrease in physiological responses and increased negative affective states [10,11,12]. Withdrawal signs are categorized into somatic and affective signs. Given that the somatic signs of withdrawal last for shorter periods than the motivational, affective, and cognitive deficits associated with alcohol withdrawal, a single pharmacotherapy that reduces alcohol consumption during both acute withdrawal and protracted abstinence would be an ideal goal for the treatment of AUD [13,14]. Increasing evidence suggests that the dynorphin (DYN)/kappa opioid receptor (KOR) system is involved in the action of alcohol and negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal, particularly in subjects dependent on alcohol and undergoing stressful conditions.
DYN is derived from a precursor known as prodynorphin (pDYN), encoded by the preprodynorphin (ppDYN) gene. DYN exists in many forms, including DYN A and DYN B (for a review, see [15]). DYN possesses a high affinity toward the KOR. The peptide and its corresponding receptor are found in the cortex, amygdala, striatum, thalamus, hypothalamus, midbrain, hippocampus, pons, and medulla ([16,17]; for a review, see [18]). Other studies show that the highest expression of KORs lies on the mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons, projecting from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) to the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Indeed, DYN is known to regulate dopaminergic tone and to produce aversion and dysphoria ([19,20,21]; for a review, see [22]).
Changes in the level of DYN have been reported following treatment with addictive drugs. For example, the DYN level increases in response to alcohol administration and following withdrawal from alcohol [23,24], which is thought to mediate the negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal ([10,11,12]; for a review, see [15]). This article reviews the literature regarding the role of the DYN/KOR system in the acute and chronic actions of alcohol. We first provide evidence for the action of alcohol on the DYN/KOR system and then describe the results of the studies showing that this system regulates the actions of alcohol.
2. Materials and Methods
A PubMed search was conducted using the keywords: Alcohol, Opioids, Alcohol Use Disorders, Dynorphin, Kappa Opioid Receptor, DYN/KOR, Anxiety, Depression, Negative Affective States, Withdrawal, Consumption, Elevated Plus Maze, Forced Swim Test, Microdialysis, Dynorphin-immunoreactivity (DYN-IR). We selected a total of 96 peer-reviewed articles related to the role of the DYN/KOR system in the action of alcohol, reviewed 74 (referenced here), and summarized 35 of those (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of articles reviewed and included in this article.
3. Results
The review of the current literature revealed that alcohol affects the endogenous DYN/KOR system, and this system plays a functional role in the actions of alcohol, particularly in affective signs of alcohol withdrawal in subjects dependent on alcohol and exposed to stress. We first discuss the effect of alcohol on the level of DYN and KORs in different brain areas. We then discuss the involvement of the DYN/KOR system in the action of alcohol, followed by the neuroanatomical sites of action of the endogenous DYN. We also discuss the impact of gender/sex and age on the role of this system in the action of alcohol.
3.1. Effects of Alcohol on the DYN/KOR System
Initial work by Jamensky and Gianoulakis sought to determine whether there were variations in KOR density and the level of pDYN mRNA and DYN in different brain areas of alcohol-preferring C57BL/6J mice and alcohol-avoiding DBA/2 mice [32]. It was reported that C57BL/6J mice exhibited increased alcohol consumption and had more KOR binding sites and DYN A (1–13) in the amygdala and DYN A (1–8) in the VTA. In contrast, the DBA/2 mice that consume less alcohol expressed considerably higher KOR binding sites, pDYN mRNA, as well as DYN A (1–13), and DYN A (1–8) in the NAc and septum [32]. Furthermore, DBA/2 mice had higher levels of KOR in the periaqueductal gray (PAG) and DYN A (1-13), and DYN A (1-8) in the caudate putamen. The authors concluded that as the increased stimulation of accumbal KOR is linked to decreased dopamine release and aversive states, the higher levels of KOR, pDYN mRNA, and DYN peptides in the limbic regions of the DBA/2 mice may explain why these mice consume less alcohol than C57BL/6J mice [32]. However, further studies are needed to prove this concept, as mice lacking DYN or KOR self-administer less alcohol than their wild-type controls [27,38].
Ploj and colleagues (2000) conducted a similar study and assessed the basal levels of DYN B as well as nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) and met-enkephalin-Arg6 Phe7 (MEAP) in C57BL/6J mice and DBA/2J mice. In addition, the effects of prolonged alcohol self-administration on the level of these peptides were investigated in these mouse lines. They showed that C57BL/6J mice had reduced immunoreactivity (IR) levels of DYN B and MEAP in the NAc, hippocampus, and substantia nigra, decreased DYN B-IR levels in the striatum, and lower MEAP-IR levels in the frontal cortex than DBA/2J mice. C57BL/6J mice, compared to DBA/2J mice, had higher DYN B-IR levels in the pituitary gland and the PAG and higher N/OFQ-IR levels in the frontal cortex and the hippocampus. It was suggested that these strain-related differences between C57BL/6J mice and DBA/2J mice might lead to diverse alcohol-taking behavior [43]. Although these studies showed changes in the level of DYN or KOR between the two mouse lines, further studies are needed to establish a causal relationship between the changes in the DYN/KOR system observed in these studies [32,43] and the difference in alcohol preference/avoidance between the two mouse lines.
Another study observed the impact of repeated episodic ethanol exposure on the tissue contents of endogenous opioid peptides in adolescent Wistar rats. β-endorphin (beta-END) levels in the alcohol-intoxicated state were lower than in the controls; however, this effect was not observed in rats tested three weeks after the last ethanol exposure, showing changes in beta-END levels are due to alcohol administration and does not occur after alcohol administration is ceased for three weeks. A trend toward increased DYN B levels was observed in the pituitary of rats intoxicated with alcohol. At three weeks, there was a higher DYN B level in the substantia nigra of the ethanol-treated group. The effects of ethanol exposure persisted in various brain areas three weeks after exposure to ethanol. In the amygdala, ethanol exposure reduced MEAP levels. In the VTA and substantia nigra, the MEAP levels were higher in ethanol-exposed rats compared to the control group. These changes may play a significant role in the behavioral and molecular actions of alcohol. However, further research is needed to define the exact role of these alterations in different actions of alcohol. For example, whether these changes mediate the rewarding actions of alcohol, its sedative, or other actions.
In another study, Nylander’s research team measured changes in the level of opioid peptides following a twice-daily injection of alcohol for 13 days in male Sprague-Dawley rats [23]. They discovered that DYN B levels were significantly elevated in the NAc 30 min and 21 days after the last alcohol injection. The peptide level was decreased in the cingulate cortex 30 min following the last dose of alcohol given on day 13. The authors suggested that repeated exposure to ethanol may lead to short- and long-lasting alterations in the turnover of DYN in a site-specific manner [23]. However, further studies are needed to define the relationship between these changes and the effects of alcohol.
Subsequent studies using in vivo microdialysis in combination with solid-phase radioimmunoassay were performed to assess the dose–response and time course of the effect of alcohol on the release of opioid peptides, including DYN A 1–8 in different brain regions [33,35,40]. Marinelli and colleagues first measured changes in DYN (1–8) levels in response to different doses of alcohol in the rat NAc shell [40]. Alcohol at a moderate dose (1.6 g/kg, i.p.) only transiently (at 30 min) increased the DYN level in the NAc, but a robust rise in the peptide level was observed after the higher dose of alcohol (3.2 g/kg). The authors concluded that the rise in DYN may mediate the aversive effect of alcohol. However, alcohol at both doses also induces sedation, a response observed following KOR activation [50]. Thus, whether the rise in DYN level mediates the aversive effects of alcohol or its sedative effects needs further investigation.
The same laboratory then assessed the effect of alcohol on the level of DYN A (1–8) in the CeA [35]. A microdialysis probe was lowered unilaterally in this brain region and assessed the effect of different doses of ethanol on the level of opioid peptides. While there was no effect of ethanol on the level of met-enkephalin (ME), the level of beta-END and DYN (1–8) was significantly increased following moderate to high doses of ethanol. However, these changes in DYN (1–8) occurred in a delayed manner. Jarjour and colleagues also reported similar delayed changes in the level of DYN (1–8) in the VTA in response to ethanol administration [33]. These authors showed that ethanol had a biphasic effect on the release of beta-END, with low to moderate, but not high, doses of ethanol causing increases in beta-END release in the midbrain/VTA [33]. The ethanol-induced increase in beta-END release in the VTA area of the midbrain is proposed to play a key role in the ethanol-induced stimulation of the mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons and the associated rewarding and reinforcing effects of alcohol [33]. Given that the rise in DYN occurred later than the rise in beta-END, it is unclear what role the rise in DYN A (1–8) would play in this region. Is the rise in DYN level a result of alcohol administration or a compensatory response due to the rise in beta-END and the stimulated dopamine release in the NAc to reduce dopamine back to basal level or even lower?
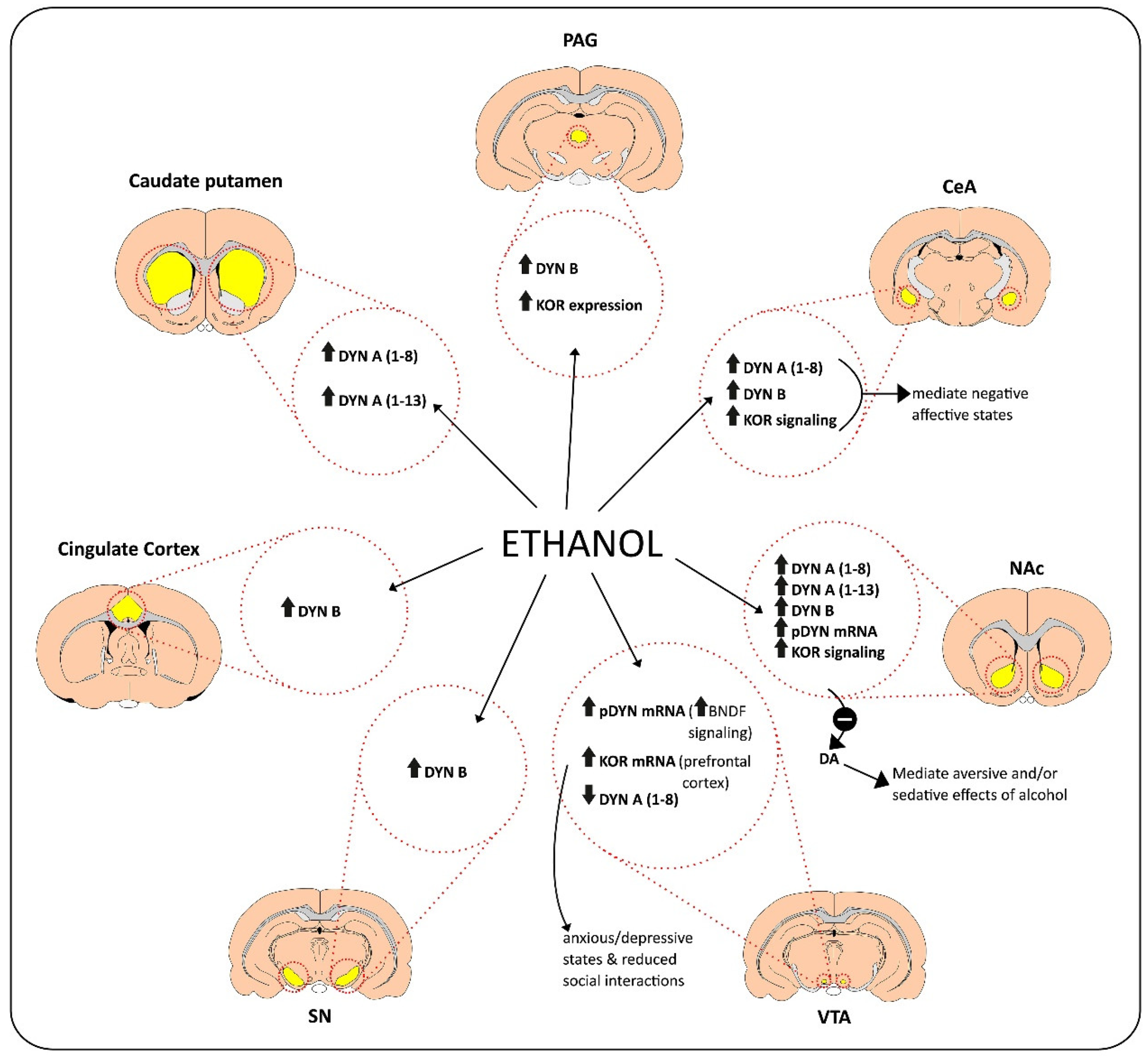
Bazov and colleagues analyzed post-mortem NAc samples of humans with AUD to assess changes in pDYN and KOR (OPRK1) gene expression and co-expression [26]. No significant differences were observed in pDYN and OPRK1 gene expression levels of post-mortem human NAc samples between those with AUD and controls. A downregulation of dopamine D1 but not D2 receptor expression was seen in individuals with AUDs, suggesting that this dysregulation of dopaminergic pathways may create negative affective states. The expression of D1 and D2 receptors was also strongly correlated with that of pDYN and OPRK1 genes, raising the possibility that there may be co-regulated patterns among these gene clusters [26]. Overall, these findings reveal that alcohol induces changes in the level of DYN and KOR expression in different brain areas (Figure 1).
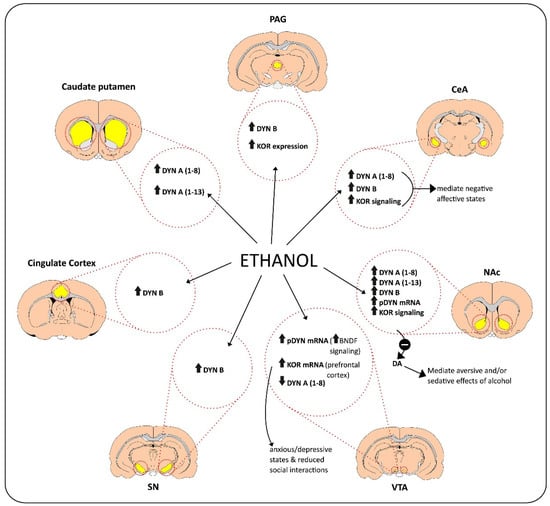
Figure 1.
The action of alcohol on the release of dynorphins (DYN) in different brain regions.
Logrip and colleagues have shown that alcohol increases ppDYN expression via the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). They also found that the blockade of KOR decreases BDNF-induced reduction in ethanol intake [29]. However, the behavioral and molecular changes associated with the peptide release have not been established. Nevertheless, some of these studies show a connection between alterations in the DYN/KOR system and behavioral changes associated with alcohol withdrawal in some brain areas (see Section 3.5).
3.2. The Role of the DYN/KOR System in the Actions of Alcohol
Increasing literature suggests that the DYN/KOR system plays a functional role in the positive and negative reinforcing actions of alcohol, as well as in stress-mediated increases in alcohol consumption in subjects dependent on alcohol (for reviews, see [6,7,8,9]). Activation of the DYN/KOR system would be predicted to limit ethanol consumption, whereas pharmacological inhibition of KOR would be expected to increase ethanol consumption. Consistent with this notion, Lindholm and colleagues have shown that U50,488H administration reduced alcohol consumption in rats [39]. Logrip and colleagues examined the effect of U50,488H on alcohol reward using the place conditioning paradigm. They found that the KOR agonist decreases alcohol-induced place preference and the accompanying conditioned locomotor sensitization [30]. These authors concluded that activation of the KOR system decreases alcohol intake due to reduced alcohol reward. However, a decrease in locomotor activity due to KOR activation may be an alternative explanation for the reduced alcohol intake in subjects treated with a KOR agonist, although, in this study, they used lower doses of U50,488H, which did not suppress locomotion. Furthermore, studies have investigated the effects of KOR antagonists on ethanol consumption, and self-administration yielded a mixed result, with both enhancing and suppressing effects of the DYN/KOR system on ethanol intake [41,47]. Nevertheless, the controversy may stem from whether animals had prior alcohol experience and a history of dependence (see Section 3.5).
It is expected that activation of the DYN/KOR system decreases alcohol consumption [41]. However, once the animals are exposed to alcohol chronically, the system is upregulated and may mediate the negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal. In the absence of alcohol, this enhanced DYN/KOR signaling leads to the development of negative affective states associated with increased alcohol consumption. This response can be blocked by the KOR antagonist [47]. For example, nor-BNI, a long-acting KOR antagonist, has been reported to decrease ethanol self-administration in subjects with alcohol dependence while having no effects on non-dependent subjects [48]. However, this result was not recapitulated using a short-acting KOR antagonist, zyklophin. The KOR antagonist, at doses that blocked KOR-mediated actions, did not affect alcohol self-administration in alcohol-vapor-exposed animals compared to air-exposed controls [44]. Together, these data raise concerns about the use of these antagonists (at least the short-acting KOR antagonists) because it may be that sustained inhibition of the DYN/KOR system is needed, as obtained following nor-BNI treatment, to reduce the negative affective states that develop in chronically alcohol-treated subjects to reduce alcohol craving.
3.3. Alcohol Self-Administration/Consumption Studies
The DYN/KOR system has been linked to alcohol self-administration. Blednov and colleagues used the two-bottle choice (TBC) paradigm and studied the role of endogenous DYN in alcohol consumption. They discovered that female but not male mice with the deletion of the ppDYN gene consumed significantly lesser alcohol than their wild-type controls [27]. Mice lacking the ppDYN gene also exhibited reduced saccharine consumption, showing that this system may regulate the intake of both alcohol and natural rewarding agents. However, ppDYN knockout and wild-type mice both displayed comparable conditioned taste aversion to alcohol, showing that this system may not mediate the taste-aversive effect of alcohol. Additionally, the deletion of ppDYN did not change the motivational valence of the context when associated with ethanol in the place conditioning paradigm [42]. These knockout mice also did not differ from wild-type mice in signs of acute ethanol-induced withdrawal [27]. However, the rewarding action of ethanol was enhanced in the absence of DYN when mice were tested for state-dependent place preference, i.e., under a drugged state [42]. This effect was recapitulated in the presence of nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI), a KOR antagonist [42]. Overall, the latter finding suggests that the endogenous DYN regulates the rewarding action of alcohol but not the motivational valence of context [42]. This enhanced state-dependent CPP may also explain why knockout mice consume less alcohol than wild-type mice, i.e., animals may find alcohol too rewarding and thus reduce their intake.
Another study used KOR knockout and their wild-type controls in the TBC paradigm to examine the role of the DYN/KOR system in oral alcohol self-administration. Mice with the targeted disruption of KOR showed a decreased preference for alcohol and saccharin but an increased preference for quinine [38]. These authors suggested that the disruption of the DYN/KOR system affects orosensory reward through central mechanisms, which, in turn, reduces alcohol palatability [38]. Interestingly, KOR knockout mice displayed enhanced evoked-dopamine levels in the NAc in response to alcohol administration [49]. The ability of the KOR blockade to regulate the ethanol-evoked dopamine release in the NAc led to the conclusion that a decrease in the activity of the DYN/KOR system might enhance the reinforcing effect of ethanol [49]. Thus, it may be that the rewarding action of alcohol is enhanced in knockout mice, which may experience reward at a lesser volume of alcohol than wild-type mice. An alternative explanation is enhanced taste aversion in null mice. However, as stated above, Blednov and colleagues found no difference in alcohol taste aversion between mice of the two genotypes [27].
One study proposed that the DYN/KOR system is activated following chronic alcohol administration, and the increased activity of this system following withdrawal results in increased alcohol self-administration. Therefore, KOR antagonists should reduce the negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal [36]. Additional evidence shows that DYN plays a functional role in the transition to alcohol dependence and not in the acute reinforcing effects of alcohol [36]. The authors concluded that KOR is a mediator of the negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal and repeated stress and plays an important role in subjects dependent on alcohol. Thus, the DYN/KOR system may be a potential target for treating AUD in subjects undergoing abstinence, particularly those experiencing stress in their lives [48].
3.4. Kappa Opioid Alterations in Anxious and Depressive States
The DYN/KOR system plays a part in regulating negative affective states due to alcohol withdrawal (for a review, see [48]). Various models are available to investigate anxiety- and depressive-like behavior following alcohol administration and withdrawal in rodents. Many studies sought to observe how alcohol consumption induces or relates to anxiety or depression. One study used a light–dark box (LDB), shelter-seeking and risk-taking behaviors in the concentric square field test, and locomotion in the open field to assess the impact of prenatal ethanol exposure (PEE) on anxiety- and depression-like behaviors later in life. They also investigated whether this treatment would induce any DYN or KOR gene expression changes later in life. PEE-induced alterations in gene transcription were associated with an anxiety-prone phenotype, as rats showed increased avoidance of the undesirable areas of the LDB and concentric square field, increased shelter-seeking in the concentric square field, and a decrease in exploration in all behavioral tasks. Additionally, it was found that animals exposed to ethanol prenatally had a selective upregulation of pDYN mRNA in the VTA and KOR mRNA in the prefrontal cortex. This study provides evidence suggesting that the PEE-induced anxiety-prone phenotype correlates with alterations in DYN and KOR gene expression [46]. However, further studies are warranted to confirm the causal relationship of such gene expression alterations to behavioral changes.
Another study aimed to determine the role of the DYN/KOR system in regulating anxious behavior during acute withdrawal from ethanol [12]. An elevated plus maze (EPM) was used to record anxious behaviors during ethanol withdrawal. nor-BNI was administered to some rats to assess how KOR blockade affects ethanol self-administration under this condition. Results showed that chronic ethanol liquid diet exposure caused an increase in anxiety-like behaviors, as evidenced by a reduction in open-arm exploration. Additionally, the rats experiencing ethanol withdrawal had a significant decrease in the number of total arm entries. Anxiety-like behaviors associated with ethanol withdrawal were blocked by the KOR antagonist. These results suggest that the DYN/KOR system may mediate the anxiety-like behaviors associated with alcohol withdrawal [12].
The involvement of the DYN/KOR system in anxiety-related behaviors during prolonged ethanol abstinence was also explored. These authors used the EPM to investigate the effect of nor-BNI on anxiety-like behaviors induced by a mild stressor in abstinent rats. Stress exposure decreased the amount of time that alcohol-withdrawn animals spent in the open arms, showing signs of anxiety-like behaviors in these animals compared to their controls. The KOR antagonist reduced these behaviors, indicating that the DYN/KOR system is a critical mediator of stress-induced anxiety associated with alcohol withdrawal and that while KOR antagonism may be sufficient to reduce the heightened stress response found after long-term ethanol withdrawal, direct activation of the DYN/KOR system may not be required to elicit stress-related behaviors [10].
The forced swim test (FST) is used to study depression-like behaviors in rodents [51]. Sperling and colleagues showed that nor-BNI lowers the enhanced ethanol intake caused by forced-swim stress, whereas the KOR agonist U50,488 increases ethanol preference and ethanol drinking in mice [45], implying that similar processes are involved in the development of ethanol withdrawal- and KOR agonist-induced behavioral alterations [12].
FST was also used to examine the ability of nor-BNI to reverse depressive-like behavior in rats chronically exposed to ethanol. Results showed that rats chronically exposed to ethanol exhibited increased immobility time in the FST during acute ethanol withdrawal and protracted ethanol abstinence, which were both reversed by nor-BNI, suggesting that the DYN/KOR system mediates depressive-like states linked to alcohol withdrawal [34]. Overall, these findings suggest that the DYN/KOR system mediates the negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal.
3.5. Neuroanatomical Sites of Actions of the DYN/KOR System in Regulating Alcohol Consumption and Affective Signs of Ethanol Withdrawal
Different brain regions have been implicated in the regulatory actions of the DYN/KOR system on alcohol consumption. Likewise, as described above, alcohol induces alterations in the DYN/KOR system in different brain regions. Several techniques have been used to investigate the role of the DYN/KOR system in these brain regions in response to alcohol consumption and withdrawal. The CeA expresses a high level of DYN and KOR [25]. This brain region has also been associated with binge drinking and alcohol intake linked to dependency [31]. One study found that binge-like alcohol consumption is mediated, at least in part, by DYN/KOR signaling in the CeA. Acute alcohol administration causes the release of DYN in the CeA [35], and persistent alcohol vapor exposure increases DYN peptide expression as well as KOR signaling in the CeA [37]. In this study, one experiment looked into the effect of intra-CeA injections of a KOR antagonist on binge-like alcohol consumption using the dinking in the dark approach. Mice were given microinjections of nor-BNI into the CeA, which reduced alcohol consumption. They also used a chemogenetic approach to deactivate DYN-containing neurons to recapitulate the results obtained with nor-BNI. Adult male pDYN-IRES-Cre mice were sacrificed for in situ hybridization or injected with a virus harboring Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs (DREADDs) that targeted the CeA. The membrane potential of DREADD-expressing neurons was significantly reduced after a bath injection of clozapine-N-oxide. Thus, these findings demonstrate that direct inhibition of KOR in the CeA reduces alcohol consumption, implying that KOR signaling within the CeA plays a functional role in regulating binge-like alcohol intake [25].
Another study investigated the role of KORs in the extended amygdala in alcohol dependence. Alterations in the expression of DYN or KOR caused by chronic alcohol consumption can affect areas such as the NAc shell and the CeA. Previous studies have suggested that KOR may mediate the negative reinforcing actions of alcohol consumption rather than its positive reinforcing effects. Thus, negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal are hypothesized to make alcohol a negative reinforcer. KOR antagonists decrease the negative affective state associated with alcohol withdrawal. These results suggest that a KOR antagonist may enable the subjects to stay sober for a longer time and make abstinent individuals seek therapy and compel them to stay on medications for the management of their AUD [47].
Studies by Haun and colleagues (2020) have examined the role of the KOR system in the BNST in binge drinking in male and female mice. They also measured the impact of a KOR antagonist on sucrose intake. Females consumed more alcohol and sucrose during the first two hours than male mice. Bilateral intra-BNST injections of nor-BNI decreased binge drinking and blood alcohol levels in both male and female mice and also reduced sucrose intake, but to a lesser extent than alcohol consumption. Locomotor activity was unaffected by nor-BNI. U50,488 was also administered systemically in mice and resulted in a large increase in alcohol consumption. When nor-BNI was administered in the BNST after systemic U50,488 injection, nor-BNI blocked U50,488-induced increases in alcohol intake and blood alcohol levels. The authors concluded that the DYN/KOR system in the BNST plays a role in binge drinking in both male and female mice [28].
3.6. Impacts of Gender/Sex
Past research has shown a significant difference in alcohol consumption between the sexes in both biological and social contexts [52]. Women have been shown to drink less in a social setting where they are excluded than men [53]. Interestingly, women are more likely to be lifetime abstainers and less likely to consume alcohol, engage in problem drinking, develop AUDs, and experience withdrawal after a drinking episode compared to men [54]. Although there is a large body of evidence exploring the bidirectional relationship between sex and alcohol consumption, there is little research regarding the role of DYN/KOR in these mechanisms in humans. A previous study reported a higher level of available KOR in healthy males than females [55]. This appears to change in subjects with AUDs, in which there is reduced KOR availability in the amygdala and pallidum of males with AUDs than in healthy controls. This difference was only significant in the amygdala between females with AUDs and their healthy controls [56]. Interestingly, KOR upregulation has been suggested to enhance the reward-related effects of addictive drugs in males only (for a review, see [57]). On the other hand, KOR availability was reduced in subjects with decreased craving and alcohol intake following naltrexone treatment [58], as naltrexone may cause the release of endogenous DYN to reduce drinking and craving and downregulate KORs. Future studies are needed to test this possibility.
Preclinical data show that KOR-induced antinociception but not aversion is attenuated in female C57BL/6N mice rather than male mice [59]. Differences in the consumption of alcohol may also depend on sex in rodents. Evidence suggests that males and females respond differently to KOR manipulation in drug-related behaviors (for a review, see [57]). The sex-related differences in the action of nor-BNI to regulate ethanol consumption that have been observed in adults may be due to females being more stressed and anxious when housed individually. This may have caused the females to consume less ethanol following the KOR blockade because nor-BNI successfully relieved their anxiety, so ethanol was no longer needed to relieve their anxiety.
Adult males and females exhibited higher blood ethanol concentrations than adolescent rats, possibly due to younger rats metabolizing ethanol faster than adults when administered a small dose of ethanol. Male and female adolescent mice showed greater locomotor activity than their adult counterparts, and female adults exhibited greater locomotor activity than male adults, which could impact alcohol intake [60]. As stated above, female but not male mice lacking the ppDYN gene consumed reduced amounts of alcohol compared to their wild-type counterparts [27]. Overall, these observations suggest that there may be male/female differences in alcohol consumption mediated by the DYN/KOR receptor system or, at least, that adult males and females respond differently to KOR ligands to alter alcohol consumption.
3.7. Impacts of Age
Age-related differences in alcohol consumption are well documented [61,62]. More recent data show that 39.7% of 12- to 20-year-olds have admitted to having at least one drink in their lifetimes, showing how, as time progresses, the consumption of alcohol in the young decreases. Moreover, elevated levels of ethanol at this age can be problematic as early ethanol use and abuse is a strong predictor of lifetime alcohol abuse and dependence [63]. With regards to receptor availability, it was found that KOR availability in the amygdala and pallidum is reduced in males with AUDs than in healthy controls. Still, there was no effect of age in this regard [56]. Considering that there are limited human studies assessing the impact of age concerning the role of the DYN/KOR system in AUDs, further studies are needed to determine the role of endogenous and exogenous DYN and other KOR ligands in different age groups with AUDs.
Preclinical data suggest that adolescents may be less sensitive to the aversive properties of drugs of abuse than adults, and they also appear more sensitive to the rewarding actions of addictive drugs [64,65,66]. The DYN/KOR receptor system may be important in this age-related difference in alcohol consumption [60]. There was an age-related difference in alcohol consumption where adolescent males consumed more ethanol than adults. However, adolescent males had a significantly lower blood ethanol concentration than adults. The ability of the KOR antagonist to impact ethanol consumption varied based on age, as nor-BNI did not alter alcohol consumption in adolescents of either sex. On the other hand, nor-BNI increased alcohol intake in male adults and decreased ethanol consumption in female adults. These results suggest that the DYN/KOR system regulates alcohol intake differently between adolescents and adults as well as in male and female adults [60].
4. Conclusions and Application
The DYN/KOR system plays a functional role in regulating the negative symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. This system is involved in regulating the depressive-like states associated with alcohol dependence. Moreover, KORs have been seen to regulate stress-mediated anxiety and the anxiety caused by alcohol withdrawal. KOR antagonists can help decrease increased alcoholism in both long-term and short-term addictive states. Moreover, this system is key in alleviating the negative affective states in both adolescents and adults with AUDs. The studies above show how targeting KORs directly impacts the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. The CeA and BNST may be prominent brain areas where DYN exerts its regulatory action on the negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal.
KOR agonists and antagonists have been successful in reducing the intake of alcohol in animals and possibly in humans. However, KOR agonists devoid of aversive effects need to be developed to promote patient compliance. On the other hand, a KOR antagonist might be a better option to reduce or prevent negative affective states associated with alcohol withdrawal. However, one should be cautious about the promise of KOR antagonists, given that some of these ligands have failed to provide efficacy in clinical trials [67,68]. Additionally, some of these antagonists have unusual pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics when administered to rodents, such as JTDic, GNTI, and nr-BNI. They have a slow onset of action but a long-lasting effect with poor solubility [69]. Thus, novel ligands that only show selectivity toward KORs and act faster are preferable. One such compound is LY2456302, which displays selectivity for KORs [70]. This KOR antagonist also had good safety and tolerability when injected with ethanol [71] in cocaine-dependent subjects and healthy volunteers [72].
Interestingly, this KOR antagonist was efficacious in decreasing alcohol consumption and motivation to self-administer alcohol. It also attenuated the reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior in rats [70,73]. Another KOR antagonist, CERC-501, also shows some efficacy in a preclinical model of alcoholism, but it has a half-life of 40 h, which may not be ideal clinically [69]. However, some of these KOR antagonists failed to show efficacy in altering drug use metrics in nicotine- or cocaine-dependent individuals (for a review, see [74]). Therefore, more research is needed to show the efficacy and safety of these ligands in subjects with AUDs or addictive drug dependence.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.L.; methodology, J.G., M.T., S.M., K.S. and K.L.; software, J.G., M.T., K.S., S.M., S.M.A. and K.L.; validation, K.S. and K.L.; formal analysis, J.G., M.T., K.S., S.M. and K.L.; investigation, J.G., M.T., K.S., S.M., S.M.A. and K.L.; resources, K.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.G., M.T., K.S., S.M. and K.L.; writing—review and editing, K.S. and K.L.; visualization, S.M.A., K.S. and K.L.; supervision, K.L.; project administration, K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. This work was a part of a summer internship involving high school students, undergraduate volunteers, and laboratory member(s).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the summer internship program at Valencia High School (Placentia, CA, USA).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Osna, N.A.; Donohue, T.M., Jr.; Kharbanda, K.K. Alcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current Management. Alcohol Res. 2017, 38, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Islami, F.; Goding Sauer, A.; Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Fedewa, S.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; McCullough, M.L.; Patel, A.V.; Ma, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; et al. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Marks, J.S.; Stroup, D.F.; Gerberding, J.L. Actual causes of death in the United States, 2000. JAMA 2004, 291, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, H.J.; Fountain, D.; Livermore, G. Economic costs of alcohol abuse and alcoholism. Recent Dev. Alcohol. 1998, 14, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grant, B.F. The impact of a family history of alcoholism on the relationship between age at onset of alcohol use and DSM-IV alcohol dependence: Results from the National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey. Alcohol Health Res. World 1998, 22, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.I.; Becker, H.C. Role of the Dynorphin/Kappa Opioid Receptor System in the Motivational Effects of Ethanol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1402–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, H.C. Influence of stress associated with chronic alcohol exposure on drinking. Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F. Neurocircuitry of alcohol addiction: Synthesis from animal models. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 125, 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Koob, G.F. Neurobiology of Opioid Addiction: Opponent Process, Hyperkatifeia, and Negative Reinforcement. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillett, K.; Harshberger, E.; Valdez, G.R. Protracted withdrawal from ethanol and enhanced responsiveness stress: Regulation via the dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor system. Alcohol 2013, 47, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshberger, E.; Gilson, E.A.; Gillett, K.; Stone, J.H.; El Amrani, L.; Valdez, G.R. nor-BNI Antagonism of Kappa Opioid Agonist-Induced Reinstatement of Ethanol-Seeking Behavior. J. Addict. 2016, 2016, 1084235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, G.R.; Harshberger, E. κ opioid regulation of anxiety-like behavior during acute ethanol withdrawal. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elholm, B.; Larsen, K.; Hornnes, N.; Zierau, F.; Becker, U. Alcohol withdrawal syndrome: Symptom-triggered versus fixed-schedule treatment in an outpatient setting. Alcohol Alcohol. 2011, 46, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkhanis, A.N.; Al-Hasani, R. Dynorphin and its role in alcohol use disorder. Brain Res. 2020, 1735, 146742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, J.H.; Leslie, F.M. Distribution of dynorphin and enkephalin peptides in the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1986, 249, 293–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Ghazarossian, V.E. Immunoreactive dynorphin in pituitary and brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 6207–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzer, C. 30 years of dynorphins--new insights on their functions in neuropsychiatric diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 123, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavkin, C.; Koob, G.F. Dynorphin, Dysphoria, and Dependence: The Stress of Addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 373–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, R.F.; Herz, A. Motivational properties of kappa and mu opioid receptor agonists studied with place and taste preference conditioning. Psychopharmacology 1985, 86, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, A.; Brantl, V.; Herz, A.; Emrich, H.M. Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 1986, 233, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shippenberg, T.S.; Zapata, A.; Chefer, V.I. Dynorphin and the pathophysiology of drug addiction. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 116, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, S.; Ploj, K.; Franck, J.; Nylander, I. Repeated ethanol administration induces short- and long-term changes in enkephalin and dynorphin tissue concentrations in rat brain. Alcohol 2000, 22, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przewlocka, B.; Turchan, J.; Lason, W.; Przewlocki, R. Ethanol withdrawal enhances the prodynorphin system activity in the rat nucleus accumbens. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 238, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.I.; Lopez, M.F.; Griffin, W.C.; Haun, H.L.; Bloodgood, D.W.; Pati, D.; Boyt, K.M.; Kash, T.L.; Becker, H.C. Dynorphin-kappa opioid receptor activity in the central amygdala modulates binge-like alcohol drinking in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazov, I.; Sarkisyan, D.; Kononenko, O.; Watanabe, H.; Yakovleva, T.; Hansson, A.C.; Sommer, W.H.; Spanagel, R.; Bakalkin, G. Dynorphin and κ-Opioid Receptor Dysregulation in the Dopaminergic Reward System of Human Alcoholics. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 7049–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blednov, Y.A.; Walker, D.; Martinez, M.; Harris, R.A. Reduced alcohol consumption in mice lacking preprodynorphin. Alcohol 2006, 40, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haun, H.L.; Griffin, W.C.; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C. Kappa opioid receptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis regulate binge-like alcohol consumption in male and female mice. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 107984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logrip, M.L.; Janak, P.H.; Ron, D. Dynorphin is a downstream effector of striatal BDNF regulation of ethanol intake. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logrip, M.L.; Janak, P.H.; Ron, D. Blockade of ethanol reward by the kappa opioid receptor agonist U50,488H. Alcohol 2009, 43, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, N.W.; Herman, M.A.; Roberto, M. The central amygdala as an integrative hub for anxiety and alcohol use disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamensky, N.T.; Gianoulakis, C. Content of dynorphins and kappa-opioid receptors in distinct brain regions of C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1997, 21, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarjour, S.; Bai, L.; Gianoulakis, C. Effect of acute ethanol administration on the release of opioid peptides from the midbrain including the ventral tegmental area. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarman, S.K.; Haney, A.M.; Valdez, G.R. Kappa opioid regulation of depressive-like behavior during acute withdrawal and protracted abstinence from ethanol. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.P.; Marinelli, P.W.; Bai, L.; Gianoulakis, C. Effects of acute ethanol on opioid peptide release in the central amygdala: An in vivo microdialysis study. Psychopharmacology 2008, 201, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissler, J.L.; Sirohi, S.; Reis, D.J.; Jansen, H.T.; Quock, R.M.; Smith, D.G.; Walker, B.M. The one-two punch of alcoholism: Role of central amygdala dynorphins/kappa-opioid receptors. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissler, J.L.; Walker, B.M. Dissociating Motivational From Physiological Withdrawal in Alcohol Dependence: Role of Central Amygdala κ-Opioid Receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, K.M.; Szakall, I.; O’Brien, D.; Wang, R.; Vinod, K.Y.; Saito, M.; Simonin, F.; Kieffer, B.L.; Vadasz, C. Decreased oral self-administration of alcohol in kappa-opioid receptor knock-out mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, S.; Werme, M.; Brené, S.; Franck, J. The selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist U50,488H attenuates voluntary ethanol intake in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 120, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, P.W.; Lam, M.; Bai, L.; Quirion, R.; Gianoulakis, C. A microdialysis profile of dynorphin A(1–8) release in the rat nucleus accumbens following alcohol administration. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.M.; Liang, M.T.; Fields, H.L. A single injection of the kappa opioid antagonist norbinaltorphimine increases ethanol consumption in rats. Psychopharmacology 2005, 182, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Tseng, A.; Marquez, P.; Hamid, A.; Lutfy, K. The role of endogenous dynorphin in ethanol-induced state-dependent CPP. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploj, K.; Roman, E.; Gustavsson, L.; Nylander, I. Basal levels and alcohol-induced changes in nociceptin/orphanin FQ, dynorphin, and enkephalin levels in C57BL/6J mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2000, 53, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirohi, S.; Aldrich, J.V.; Walker, B.M. Species differences in the effects of the κ-opioid receptor antagonist zyklophin. Alcohol 2016, 51, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.E.; Gomes, S.M.; Sypek, E.I.; Carey, A.N.; McLaughlin, J.P. Endogenous kappa-opioid mediation of stress-induced potentiation of ethanol-conditioned place preference and self-administration. Psychopharmacology 2010, 210, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Veer, A.; Smith, K.L.; Cohen, B.M.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Bechtholt, A.J. Kappa-opioid receptors differentially regulate low and high levels of ethanol intake in female mice. Brain Behav. 2016, 6, e00523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.M.; Koob, G.F. Pharmacological evidence for a motivational role of kappa-opioid systems in ethanol dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.M.; Valdez, G.R.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Bakalkin, G. Targeting dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor systems to treat alcohol abuse and dependence. Alcohol 2012, 46, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.; Shippenberg, T.S. Endogenous kappa opioid receptor systems modulate the responsiveness of mesoaccumbal dopamine neurons to ethanol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, A.; Sandin, J.; Terenius, L.; Ogren, S.O. Dose- and time-dependent bimodal effects of kappa-opioid agonists on locomotor activity in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 295, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Porsolt, R.D. Animal model of depression. Biomedicine 1979, 30, 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Bonilla, A.; Richardson, H.N. Sex Differences in the Neurobiology of Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol Res. 2020, 40, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, A.K.; Cranford, A.N.; Blumenthal, H. Effects of ostracism and sex on alcohol consumption in a clinical laboratory setting. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2015, 29, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, A.; Karpyak, V.M. Sex and gender-related differences in alcohol use and its consequences: Contemporary knowledge and future research considerations. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 156, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Wang, S.; Worhunsky, P.; Zheng, M.Q.; Nabulsi, N.; Ropchan, J.; Krishnan-Sarin, S.; Huang, Y.; Morris, E.D. PET imaging reveals sex differences in kappa opioid receptor availability in humans, in vivo. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 6, 205–214. [Google Scholar]
- Vijay, A.; Cavallo, D.; Goldberg, A.; de Laat, B.; Nabulsi, N.; Huang, Y.; Krishnan-Sarin, S.; Morris, E.D. PET imaging reveals lower kappa opioid receptor availability in alcoholics but no effect of age. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartoff, E.H.; Mavrikaki, M. Sex Differences in Kappa Opioid Receptor Function and Their Potential Impact on Addiction. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laat, B.; Goldberg, A.; Shi, J.; Tetrault, J.M.; Nabulsi, N.; Zheng, M.-Q.; Najafzadeh, S.; Gao, H.; Kapinos, M.; Ropchan, J.; et al. The Kappa Opioid Receptor Is Associated With Naltrexone-Induced Reduction of Drinking and Craving. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 86, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.D.; Schattauer, S.S.; Reichard, K.L.; Cohen, J.H.; Fontaine, H.M.; Song, A.J.; Johnson, S.D.; Land, B.B.; Chavkin, C. Estrogen Regulation of GRK2 Inactivates Kappa Opioid Receptor Signaling Mediating Analgesia, But Not Aversion. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 8031–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.; Anderson, R.I.; Spear, L.P.; Varlinskaya, E.I. Effects of the kappa opioid receptor antagonist, nor-binaltorphimine, on ethanol intake: Impact of age and sex. Dev. Psychobiol. 2014, 56, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Villaça, Y.; Manhães, A.C.; Krahe, T.E.; Filgueiras, C.C.; Ribeiro-Carvalho, A. Tobacco and alcohol use during adolescence: Interactive mechanisms in animal models. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 144, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lannoy, S.; Sullivan, E.V. Trajectories of brain development reveal times of risk and factors promoting resilience to alcohol use during adolescence. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2021, 160, 85–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grant, B.F.; Dawson, D.A. Age at onset of alcohol use and its association with DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: Results from the National Longitudinal Alcohol Epidemiologic Survey. J. Subst. Abuse 1997, 9, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badanich, K.A.; Maldonado, A.M.; Kirstein, C.L. Chronic ethanol exposure during adolescence increases basal dopamine in the nucleus accumbens septi during adulthood. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.V.; Tejeda, H.A.; Natividad, L.A.; O’Dell, L.E. Enhanced vulnerability to the rewarding effects of nicotine during the adolescent period of development. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, E.; Wade, D.; Izenwasser, S. Sensitivity to cocaine conditioned reward depends on sex and age. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 92, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, J.J.; I Carroll, F.; Kosten, T.R.; Swearingen, D.; Walters, B.B. A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Single, Escalating Oral Doses of JDTic. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2059–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlezon, W.A.; Krystal, A.D. Kappa-Opioid Antagonists for Psychiatric Disorders: From Bench to Clinical Trials. Depression Anxiety 2016, 33, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbano, M.; Guerrero, M.; Rosen, H.; Roberts, E. Antagonists of the kappa opioid receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 2021–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorick-Kehn, L.M.; Witkin, J.M.; Statnick, M.A.; Eberle, E.L.; McKinzie, J.H.; Kahl, S.D.; Forster, B.M.; Wong, C.J.; Li, X.; Crile, R.S.; et al. LY2456302 is a novel, potent, orally-bioavailable small molecule kappa-selective antagonist with activity in animal models predictive of efficacy in mood and addictive disorders. Neuropharmacology 2014, 77, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.L.; Wong, C.J.; Witcher, J.; Gonzales, C.R.; Dickinson, G.L.; Bell, R.L.; Rorick-Kehn, L.; Weller, M.; Stoltz, R.R.; Royalty, J.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic evaluation of single- and multiple-ascending doses of a novel kappa opioid receptor antagonist LY2456302 and drug interaction with ethanol in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 54, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, B.; Butelman, E.R.; Fry, R.S.; Kimani, R.; Kreek, M.J. Repeated Administration of Opra Kappa (LY2456302), a Novel, Short-Acting, Selective KOP-r Antagonist, in Persons with and without Cocaine Dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domi, E.; Barbier, E.; Augier, E.; Augier, G.; Gehlert, D.; Barchiesi, R.; Thorsell, A.; Holm, L.; Heilig, M. Preclinical evaluation of the kappa-opioid receptor antagonist CERC-501 as a candidate therapeutic for alcohol use disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, M.L. The Rise and Fall of Kappa-Opioid Receptors in Drug Abuse Research. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2020, 258, 147–165. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).