Visual Rehabilitation in Post Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Case-Based Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case History
2.1. Pre-Treatment Clinical Findings
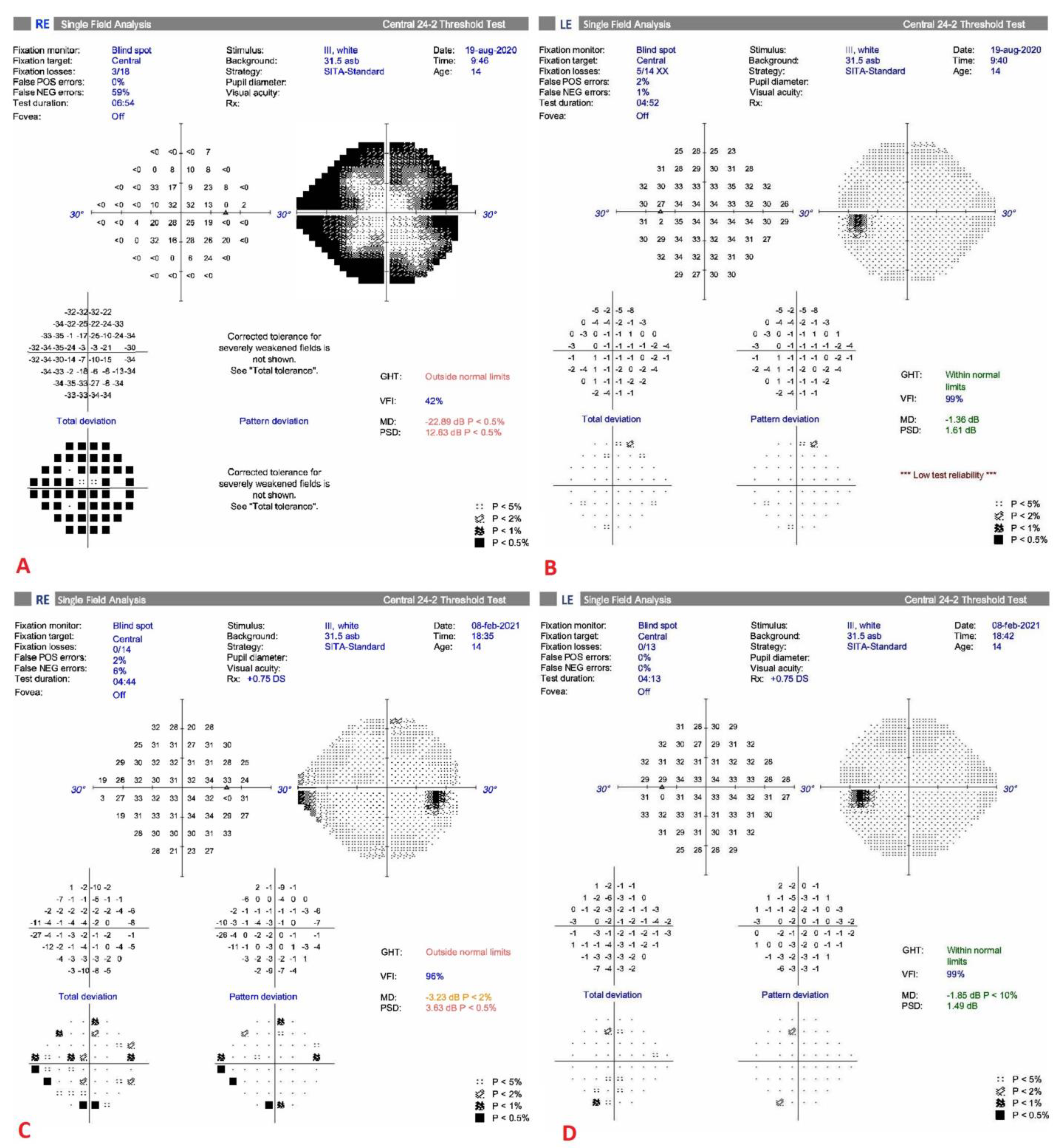
2.2. Treatment Timeline and Therapeutic Interventions
3. Follow-Up and Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, J.; Olavarria, G.; Stanton, B. Pediatric Neurosurgery in Primary Care, an Issue of Pediatric Clinics of North America, Ebook ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; Volume 68, No. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Crampton, A.; Teel, E.; Chevignard, M.; Gagnon, I. Vestibular-ocular Reflex Dysfunction Following Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Narrative Review. Neurochirurgie 2021, 67, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padula, W.V.; Capo-Aponte, J.E.; Padula, W.V.; Singman, E.L.; Jenness, J. The Consequence of Spatial Visual Processing Dysfunction Caused by Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). Brain Inj. 2017, 31, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, J.D.; Cancelliere, C.; Carroll, L.J.; Côté, P.; Hincapié, C.A.; Holm, L.W.; Hartvigsen, J.; Donovan, J.; Nygren-de Boussard, C.; Kristman, V.L.; et al. Systematic Review of Self-Reported Prognosis in Adults After Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: Results of the International Collaboration on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Prognosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, S132–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, S.; Parrington, L.; Martini, D.; Peterka, R.; Chesnutt, J.; King, L. The Measurement of Eye Movements in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Structured Review of an Emerging Area. Front. Sport. Act. Living 2020, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benassi, M.; Frattini, D.; Garofalo, S.; Bolzani, R.; Pansell, T. Visuo-motor Integration, Vision Perception and attention in mTBI Patients. Preliminary Findings. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fimreite, V.; Willeford, K.T.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Effect of Chromatic Filters on Visual Performance in Individuals with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI): A pilot study. J. Optom. 2016, 9, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, K.; Ward, A.B.; Boughey, A.; Jones, M.; Mychalkiw, W. Sequelae of Minor Head Injury: The Natural History of Post-Concussive Symptoms and their Relationship to Loss of Consciousness and Follow-up. Emerg. Med. J. 1994, 11, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengo-Kahn, A.M.; Reynolds, R.A.; Bonfield, C.M. Mild Traumatic Brain Injury in Children. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 68, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuffreda, K.J.; Thiagarajan, P. Objectively-based Vergence and Accommodative Dynamics in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI): A mini review. Vision Res. 2022, 191, 107967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.L.; de Haerne, C.M.; Malvankar-Mehta, M.S.; Bursztyn, L.L.C.D. Visual Abnormalities in Chronic Post-Concussion Syndrome. Adv. Ophthalmol. Optom. 2020, 5, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, J.; Ranalli, P. Vision tHerapy: Occlusion, Prisms, Filters, and vEstibular Exercises for Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2020, 66, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallaway, M.; Scheiman, M.; Mitchell, G.L. Vision Therapy for Post-Concussion Vision Disorders. Optom. Vis. Sci. Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Optom. 2017, 94, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheiman, M.; Wick, B. Clinical Management of Binocular Vision: Heterophoric, Accommodative, and Eye Movement Disorders; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiman, M.; Grady, M.F.; Jenewein, E.; Shoge, R.; Podolak, O.E.; Howell, D.H.; Master, C.L. Frequency of Oculomotor Disorders in Adolescents 11 to 17 yEars of aGE with Concussion, 4 to 12 Weeks Post Injury. Vision Res. 2021, 183, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuram, A.; Cotter, S.A.; Gowrisankaran, S.; Kanji, J.; Howell, D.R.; Meehan, W.P., 3rd; Shah, A.S. Postconcussion: Receded Near Point of Convergence is not Diagnostic of Convergence Insufficiency. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 206, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.A.; Wilson, J.C.; Seehusen, C.N.; Provance, A.J.; Howell, D.R. Is Near Point of Convergence Associated with Symptom Profiles or Recovery in Adolescents After Concussion? Vision Res. 2021, 184, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanowicz, D.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Thiagarajan, P.; Ludlam, D.P.; Green, W.; Kapoor, N. Vergence in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Pilot Study. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2012, 49, 1083–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, P.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Ludlam, D.P. Vergence Dysfunction in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI): A Review. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. J. Br. Coll. Ophthalmic Opt. 2011, 31, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Thiagarajan, P.; Szymanowicz, D.; Ludlam, D.P.; Kapoor, N. Accommodation in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2010, 47, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, C.L.; Scheiman, M.; Gallaway, M.; Goodman, A.; Robinson, R.L.; Master, S.R.; Grady, M.F. Vision Diagnoses Are Common After Concussion in Adolescents. Clin. Pediatr. 2016, 55, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, K.; Rubin, L.H.; Lee, J.H.; Sim, T.; Takahagi, M.; Szwanki, V.; Bellamy, A.; Darvish, K.; Assari, S.; Henderer, J.D.; et al. Association of Football Subconcussive Head Impacts with Ocular Near Point of Convergence. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiecek, E.K.; Roberts, T.L.; Shah, A.S.; Raghuram, A. Vergence, Accommodation, and Visual Tracking in Children and Adolescents Evaluated in a Multidisciplinary Concussion Clinic. Vision Res. 2021, 184, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, T.L.; Yaramothu, C.; Scheiman, M.; Goodman, A.; Cotter, S.A.; Huang, K.; Chen, A.M.; Grady, M.; Mozel, A.E.; Podolak, O.E.; et al. Disparity Vergence Differences Between Typically Occurring and Concussion-related Convergence Insufficiency Pediatric Patients. Vision Res. 2021, 185, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffreda, K.J.; Ludlam, D.P.; Yadav, N.K.; Optom, B.S. Convergence Peak Velocity: An Objective, Non-Invasive, Oculomotor-Based Biomarker for Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI)/Concussion. Vis. Dev. Rehabil. 2018, 4, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ciuffreda, K.J.; Joshi, N.R.; Truong, J.Q. Understanding the Effects of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury on the Pupillary Light Reflex. Concussion 2017, 2, CNC36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapoor, N.; Ciuffreda, K.J.; Han, Y. Oculomotor Rehabilitation in Acquired Brain Injury: A Case Series. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan, P.; Ciuffreda, K.J. Article 4 Accommodative and Vergence Dysfunctions in mTBI: Treatment Effects and Systems Correlations; State University of New York: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiman, M.M.; Talasan, H.; Mitchell, G.L.; Alvarez, T.L. Objective Assessment of Vergence after Treatment of Concussion-Related CI: A Pilot Study. Optom. Vis. Sci. Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Optom. 2017, 94, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barton, J.J.S.; Ranalli, P.J. Vision Therapy: Ocular Motor Training in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candy, T.R.; Cormack, L.K. Recent Understanding of Binocular Vision in the Natural Environment with Clinical Implications. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 88, 101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Guidelines|AOA [Internet]. Available online: https://www.aoa.org/practice/clinical-guidelines?sso=y (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Scheiman, M.; Wick, B. Clinical Management of Binocular Vision, 4th ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, J.R.; Grisham, J.D. Binocular Anomalies. Diagnosis and Vision Therapy, 4th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Portela-Camino, J.A.; Martín-González, S.; Ruiz-Alcocer, J.; Illarramendi-Mendicute, I.; Garrido-Mercado, R. An Evaluation of the Agreement between a Computerized Stereoscopic Game Test and the TNO Stereoacuity Test. Clin. Optom. 2021, 13, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela-Camino, J.A.; Martín-González, S.; Ruiz-Alcocer, J.; Illarramendi-Mendicute, I.; Garrido-Mercado, R. A Random Dot Computer Video Game Improves Stereopsis. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2018, 95, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test | Pre-Treatment Vision Exam Results | Post-Treatment Vision Exam Results | Normal Range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncorrected VA (Snellen) (RE/LE) | 20/32 | 20/16 | 20/16 | 20/16 | 20/20 |
| Cycloplegic refraction (RE/LE) | +1.75 D − 0.50 D × 180° | +1.25 D − 0.50 D × 180° | +1.50 D −0.50 D × 5° | +1.50 D | N/A |
| Non-cycloplegic refraction (RE/LE) | +0.00 D | +0.25 D | +1.25 D − 0.50 D × 5° | +1.25 D | N/A |
| Stereopsis (Random Dot 2-S Test) | 200” | 30” | 20” | ||
| Worth test | Fusion | Fusion | Fusion | ||
| Cover test (distance) | 8 Δ esophoria, 2 Δ hyperphoria RE | Ortophoria | 0–2 ∆ exophoria | ||
| Cover test (near) | 8 Δ esophoria, 2 Δ hyperphoria RE | Ortophoria | 0–6 ∆ exophoria | ||
| Maddox (distance) | 8 ∆ esophoria, 6 ∆ hyperphoria RE | 6 ∆ esophoria, 2 ∆ hyperphoria RE | 0–2 ∆ exophoria | ||
| Maddox (near) | 8 ∆ esophoria, 5 ∆ hyperphoria RE | 8 ∆ esophoria, 2 ∆ hyperphoria RE | 0–6 ∆ exophoria | ||
| NPC (break/recovery) | 11 cm/15 cm | 7/8 cm | 1–3” break/3–5” recovery | ||
| NFV prism bar (near) | −/10/6 ∆ | 8/14/8 ∆ | 13/10 ∆ | ||
| PFV prism bar (near) | 6/14/14 ∆ | 18/25/20 ∆ | 19/14 ∆ | ||
| NFV prism bar (distance) | −/6/4 ∆ | 6/8/4 ∆ | 7/4 ∆ | ||
| PFV prism bar (distance) | 8/20/18 ∆ | 6/12/8 ∆ | 11/7 ∆ | ||
| Vergence facility 3/12 ∆ | 4 cpm | 9 cpm | 15 cpm | ||
| Monocular AA (RE/LE) | 8.00 D | 13.00 D | 10.5 D | 13 D | 13 D |
| Monocular accommodative facility (RE/LE) | 8 cpm difficulty clearing negative and positive lenses | 13 cpm | 9 cpm | 10 cpm | 11 cpm |
| NRA/PRA | +1.75/−0.50 D | +2.25/−1.50 D | +2.00/−2.37 D | ||
| MEM (RE/LE) | Fluctuating value | +1.50 D | +2.00 D | +2.00 D | +0.50 D |
| Pursuits (NSUCO) | 5/1/4/4 | 5/3/5/5 | 5/4/4/5 | ||
| Saccades (NSUCO) | 5/1/4/4 | 5/5/5/5 | 5/3/4/5 | ||
| Dextroversion | Central Area | Levoversion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Δ BO | 5 Δ BU LE | - | 8 Δ BO | 5 Δ BU LE |
| 10 Δ BO | 8 Δ BU LE | - | 12 Δ BO | 5 Δ BD LE |
| 16 Δ BO | 8 Δ BU LE | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-de-la-Fuente, C.; Barriga-Longás, H.; Orduna-Hospital, E. Visual Rehabilitation in Post Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Case-Based Review. J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2023, 1, 25-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto1010005
López-de-la-Fuente C, Barriga-Longás H, Orduna-Hospital E. Visual Rehabilitation in Post Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Case-Based Review. Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology. 2023; 1(1):25-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto1010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-de-la-Fuente, Carmen, Hermes Barriga-Longás, and Elvira Orduna-Hospital. 2023. "Visual Rehabilitation in Post Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Case-Based Review" Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology 1, no. 1: 25-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto1010005
APA StyleLópez-de-la-Fuente, C., Barriga-Longás, H., & Orduna-Hospital, E. (2023). Visual Rehabilitation in Post Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Case-Based Review. Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology, 1(1), 25-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto1010005






