1. Introduction
Septic arthritis, characterized by inflammation of the joints due to an infectious etiology, can be caused by various pathogens, with staphylococcus aureus being the leading cause of infection and
Streptococcus species being the least [
1,
2]. The introduction of bacterial organisms into the synovial fluid develops as a result of contiguous spread from adjacent areas such as soft tissue infections, hematogenous spread, or from direct penetration into the synovial cavity. Invasion of bacterial organisms into the synovial fluid results in a clinical presentation of septic arthritis in native joints and is manifested through painful, inflamed joints with or without fever. However, clinical signs and symptoms must be accompanied by aspiration of synovial fluid for analysis of leukocytes and bacterial identification to rule out other causes of joint pain such as rheumatoid arthritis or crystal-induced arthritis (such as gout, tears, or fractures). A synovial white blood cell count exceeding 75,000 cells/mm
3 and clinical suspicion are key indicators of septic arthritis [
3]. In contrast, patients who are found to have crystal-induced arthritis are found to have synovial white blood cells of less than 1650 cells/mm
3 [
4].
Current guidelines recommend 6 weeks of antibiotics in bone and joint infections for 6 weeks with an initial 1 to 2 weeks of intravenous (IV) antibiotics, followed by an oral treatment course lasting 2 to 4 weeks upon clinical improvement. For the characteristics of transitioning to oral administration to be ideal, patients must show signs of clinical improvement including defervescence and a reduction in redness, swelling, and pain, as well as improvement in CRP levels and leukocyte count. Prior to the initiation of oral antibiotics, clinicians must evaluate antibiotics for high bioavailability, tolerability of oral intake for patients, and adequate penetration into the infected tissues [
1]. Other considerations include health and economic disparities that prohibit adequate completion of antibiotic therapy. A meta-analysis demonstrated the effective use of dalbavancin when compared to standard-of-care in patients with osteoarthritis infections, resulting in significant reduction in hospital length of stay and treatment emergent side effects [
5,
6].
An alternative to daily oral and intravenous antibiotics is dalbavancin. Dalbavancin is a second-generation, semi-synthetic lipoglycopeptide and was developed as an enhancement over its predecessor, vancomycin. It has been approved for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by gram-positive microorganisms such as
Staphylococcus,
Streptococcus, and
Enterococcus. Notably, dalbavancin’s extended half-life of 346 h enables the possibility of a single infusion or weekly dosing intervals in contrast to the more frequent dosing required for antibiotics like vancomycin, which are also associated with a higher likelihood of adverse reactions [
4]. In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) introduced its inaugural AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) classification of antibiotics as a strategic framework to guide global antibiotic stewardship, with a focus on mitigating antimicrobial resistance. By 2023, WHO categorized dalbavancin under the Reserve group (ATC Code J01XA04), designating it as a critical last-line therapy for multidrug-resistant infections, and it is tailored to patient-specific settings when alternatives have failed [
7].
A phase 3 subgroup analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety of dalbavancin in obese and diabetic patients. Those patients with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m
2 were found to have 95.2% (95% CI, 91.3 to 97.3) clinical success at the end of treatment of ABSSI [
8,
9]. Treatment-related adverse events in patients with higher BMI experiencing one or more events were found to be 31.7% in the dalbavancin group while the vancomycin group had 47.7% of the patients experiencing similar treatment-related adverse events. Additionally, Morata et al. conducted a multicenter study that has shown successful clinical outcomes in the treatment of bone and joint infections with more than two doses of weekly dalbavancin [
10]. While vancomycin has been the drug of choice for all bone and joint infections, dalbavancin has demonstrated a two-week post-dose concentration in synovial fluid of 6.3 μg/mL, surpassing the concentrations achieved by vancomycin [
11]. Although precise vancomycin levels in synovial fluid have not been extensively studied, it is known that vancomycin concentrations generally exceed the MIC
90 for
Staphylococcus aureus and
Streptococcus pneumoniae but not
Enterococcus spp. [
12]. Although studies on dalbavancin primarily assessed its efficacy with a weekly dosing regimen, several investigations have also examined biweekly dosing in patients, demonstrating high successful treatment outcomes (89%) for gram-positive infections, including endocarditis and bone and joint infections [
13,
14,
15].
The aim of this case study is to report the successful treatment of Enterococci and S. Pneumoniae septic arthritis and bacteremia with dalbavancin in an obese patient with an extended dosing interval of every two weeks.
2. Case Presentation
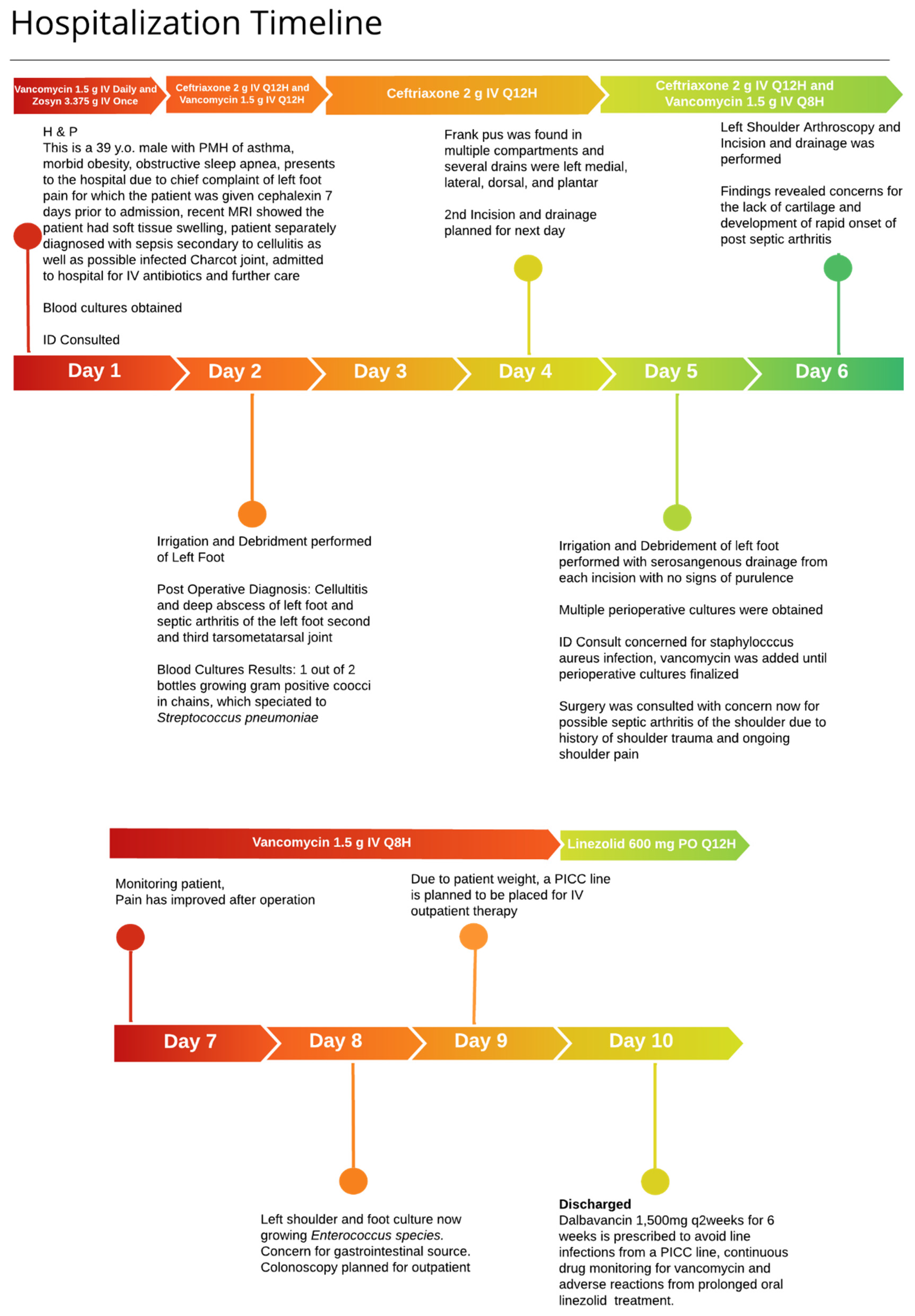
A 38-year-old male, weighing 145 kg with a history of asthma, morbid obesity, and obstructive sleep apnea, presented to the emergency department with worsening pain and swelling in the left foot and shoulder. The patient had previously visited the emergency department one week earlier for similar symptoms following a mechanical fall. An outpatient orthopedic follow-up included magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which suggested a possible Lisfranc injury with associated soft tissue swelling and potential fluid collection at the plantar apex of the midfoot.
In the emergency department, the patient was febrile with a temperature of 38.2 °C, a heart rate of 119 beats per minute, a respiratory rate of 36 breaths per minute, and an oxygen saturation of 92% on room air. Physical examination revealed diffuse swelling in the left foot, fluctuance over the dorsal aspect, and tenderness at the medial plantar column. Laboratory tests and blood cultures were performed, and the patient was empirically started on ceftriaxone 2 g IV daily and vancomycin. Significant laboratory findings included a white blood cell count (WBC) of 21,000 cells/µL, serum creatinine (SCr) of 1 mg/dL, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) of 43 U/L, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) of 112 U/L, C-reactive protein (CRP) of 21.43 mg/dL, and glucose of 132 mg/dL. Additionally, MRI of the left foot indicated subcutaneous edema suggestive of cellulitis, with marrow changes and fluid around the midfoot, where abscess and infection could not be excluded.
An infectious diseases (ID) physician was consulted on day 2 of hospitalization to determine the source of bacteremia. Blood cultures identified gram-positive cocci in chains in one of two bottles, which were identified as Streptococcus pneumoniae. Given the uncertainty regarding the source of infection—whether originating from the foot or possibly seeded from another site—it was recommended to repeat blood cultures and continue ceftriaxone monotherapy at a dosage of 2 g IV twice daily to ensure adequate antimicrobial penetration given the patient’s body weight. Further imaging included computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses, which showed no definitive acute or chronic sinusitis but revealed mild bilateral mastoid effusions. Additionally, a discussion with cardiology evaluated the utility of a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) due to suspicion of endocarditis from the bacteremia. The TEE revealed no major valvular disease, thus lowering the suspicion of endocarditis.
Incision and drainage (I&D) of the foot was performed on the second day of admission due to concern for the presence of a foot abscess, yielding serosanguinous fluid with frank pus in multiple compartments. Repeat blood cultures were obtained, which yielded no growth after 5 days. Drains were placed in the second and third tarsometatarsal joints, dorsal compartment, and the second and third interossei compartments. While awaiting cultures from the foot, ID was concerned about Staphylococcus aureus as the cause of the abscess and initiated vancomycin. The next day, cultures from the I&D grew Enterococcus species with a vancomycin MIC of 1 µg/mL, prompting discontinuation of ceftriaxone and raising suspicion of an intra-abdominal source. However, abdominal ultrasound imaging was negative, and an outpatient colonoscopy was planned.
On day 6 of admission, surgery was consulted for persistent shoulder pain, which began before admission, and a left shoulder arthroscopy was performed. Findings included concerns about a lack of cartilage and rapid onset of septic arthritis. Consequently, the diagnosis included Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia and cellulitis, as well as Enterococcus bacteremia secondary to septic arthritis.
Given the patient’s weight, there were concerns about the adequate penetration of oral antibiotics, and therefore the infectious diseases physician recommended the continuation of IV antibiotics to be continued in the outpatient setting. The ID physician recommended three doses of dalbavancin 1500 mg IV every two weeks for a total duration of six weeks, covering
Enterococcus spp. and
Streptococcus pneumoniae, to be started upon discharge. Dalbavancin was preferred over vancomycin to avoid placing a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line, reducing the risk of line infections and the need for continuous therapeutic drug monitoring. The decision to administer dalbavancin biweekly was primarily driven by the need to reduce costs associated with manual labor and medical supplies, while also improving patient adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen. The extended dosing interval aimed to ensure complete treatment adherence (
Figure 1).
After discharge, the patient was closely monitored in an outpatient setting, including follow-up with physical therapy. Despite these interventions, severe shoulder pain persisted, necessitating evaluation by orthopedic surgery. Consequently, the decision was made to perform a shoulder replacement. The patient recovered well postoperatively, with minimal residual pain and no recurrence of infection after a year of follow up appointments with the infectious diseases physician.
3. Discussion
This case report, though limited in scope, aligns with previous research on the efficacy of dalbavancin in treating gram-positive bacteremia. Alternatives such as linezolid were not chosen due to the risk of thrombocytopenia with extended duration, as well as the need for regular monitoring and the associated costs of vancomycin administration; therefore, dalbavancin emerged as the preferred therapeutic option while considering the World Health Organization’s classification of dalbavancin. In clinical trials, dalbavancin was administered as a single or double dose to patients with confirmed
S. aureus bacteremia, identified through blood cultures. Vancomycin (intravenous) and linezolid (both intravenous and oral) were used as comparators over a 10–14-day period. Overall, 100% of patients treated with dalbavancin successfully cleared the bacteremia in a shorter time frame, while the comparators achieved a 95% successful clearance rate among all patients who received the controlled therapy [
8]. Additionally, there have been multiple reports to support the safety and efficacy of biweekly administration of dalbavancin for patients requiring long-term suppressive therapy [
16,
17]. This case is unique, as it represents the first reported instance of treating gram-positive polymicrobial septic arthritis using a biweekly administration of dalbavancin over a six-week period. The significance of this treatment approach lies in its potential to enhance patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes in outpatient settings. Traditionally, the management of septic arthritis, particularly when caused by multiple gram-positive organisms, involves the use of intravenous antibiotics such as vancomycin, which require frequent dosing and often necessitate prolonged hospital stays or the placement of peripherally inserted central catheters for outpatient administration or oral therapy with linezolid. These methods are associated with various challenges, including the risk of catheter-related infections and the need for regular therapeutic drug monitoring. Furthermore, oral linezolid has been well documented to cause myelosuppression with long durations of therapy, deeming it an unfavorable treatment option for this patient.
The understanding of dalbavancin’s use in morbidly obese patients remains limited. Pharmacokinetic studies have shown comparable outcomes in normal-weight, overweight, and obese patients for the treatment of ABSSSI [
9]. However, there are very few, if any, studies that document the successful use of dalbavancin for the treatment of bacteremia and septic arthritis in the morbidly obese population [
18]. Furthermore, this case report does not address the cost-effectiveness comparison between dalbavancin and its alternative, vancomycin. Despite the higher cost associated with dalbavancin, many healthcare providers have been reluctant to adopt its use. However, recent research has evaluated the overall cost of administering dalbavancin in outpatient settings and has concluded that the expenses are offset by savings from reduced inpatient stays, fewer PICC line complications, and decreased reliance on home health services [
19]. Therefore, dalbavancin offers substantial financial and logistical advantages. It eliminates the necessity for routine laboratory monitoring and the need for staff to perform pharmacokinetic calculations, thereby enhancing its logistical feasibility as a preferred treatment option.
Several limitations are noted in this study. First, dalbavancin was administered only at discharge following prior intravenous antibiotic therapy, making it uncertain whether dalbavancin given biweekly as an initial therapy would be equally effective. Second, as this is a single-patient case report without a comparative group, larger studies are needed to assess the efficacy of biweekly dalbavancin administration, particularly in obese patients. Finally, follow-up cultures were not obtained after one year, leaving the possibility of recurrence undetermined beyond the one-year follow-up period.
This case report demonstrates the successful biweekly administration of dalbavancin, which, while not yet studied extensively, shows promise for improving patient compliance in outpatient settings. By highlighting this case, the report opens a discussion on the safety and efficacy of dalbavancin in treating septic arthritis and emphasizes the need for further research into pharmacokinetic adjustments, particularly for the obese population.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, this report highlights the successful treatment of Enterococcus spp. and Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia secondary to septic arthritis using dalbavancin. The positive clinical outcomes observed suggest that biweekly dalbavancin administration is a promising therapeutic option for managing septic arthritis. Additionally, notable cost-saving benefits, such as reduced reliance on intravenous lines and staff resources, make dalbavancin an attractive choice for outpatient parenteral therapy. However, to align with antibiotic stewardship initiatives, manage costs, and adherence to WHO’s AWaRe classification, dalbavancin should be reserved as a last-line therapy when other antibiotic alternatives are not viable.