Step-by-Step Development of a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Assay for Sex Identification in Papaya
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The T4 Enzymes uvsX, gp32, uvsY, and Bsu DNA Polymerase
2.2. RPA Primer Design
2.3. Preparation of the DNA Used as Standard
2.4. Setting the Conditions for the RPA Reaction
3. Results
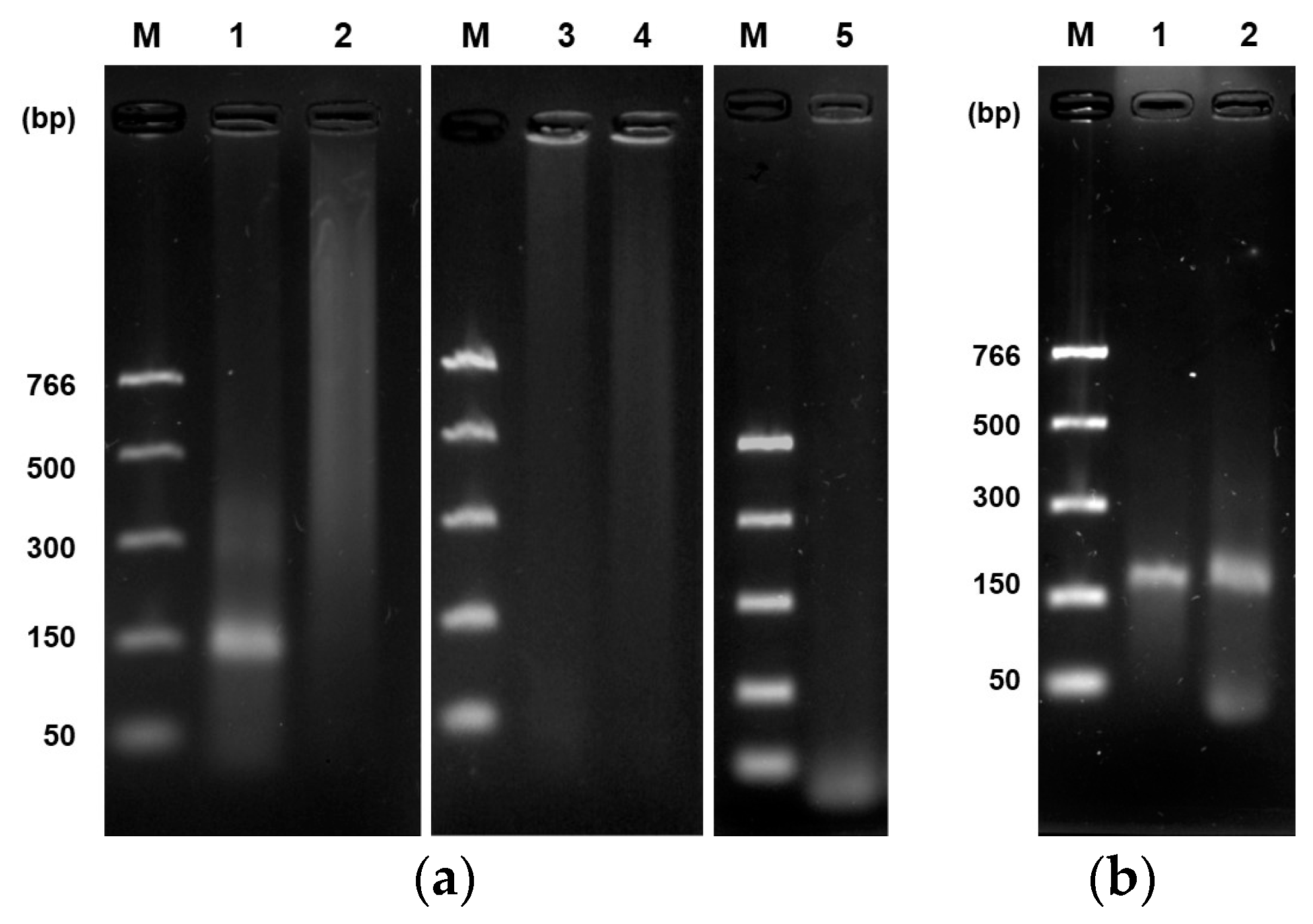
3.1. Expression and Purification of Recombinant Enzymes uvsX, uvsY, gp32, and Bsu DNA Polymerase
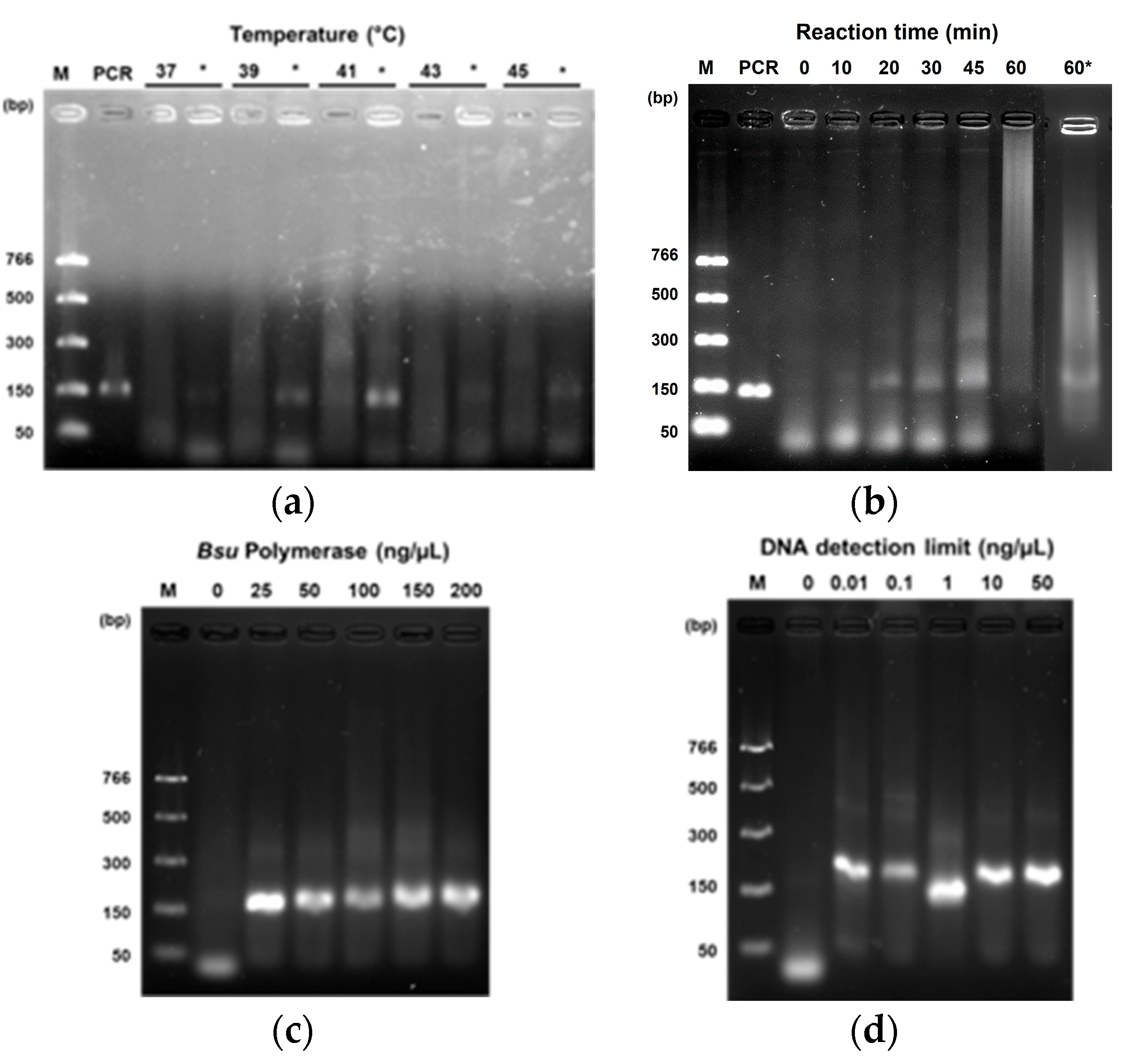
3.2. RPA Assay Optimization for Papaya Sex Determination
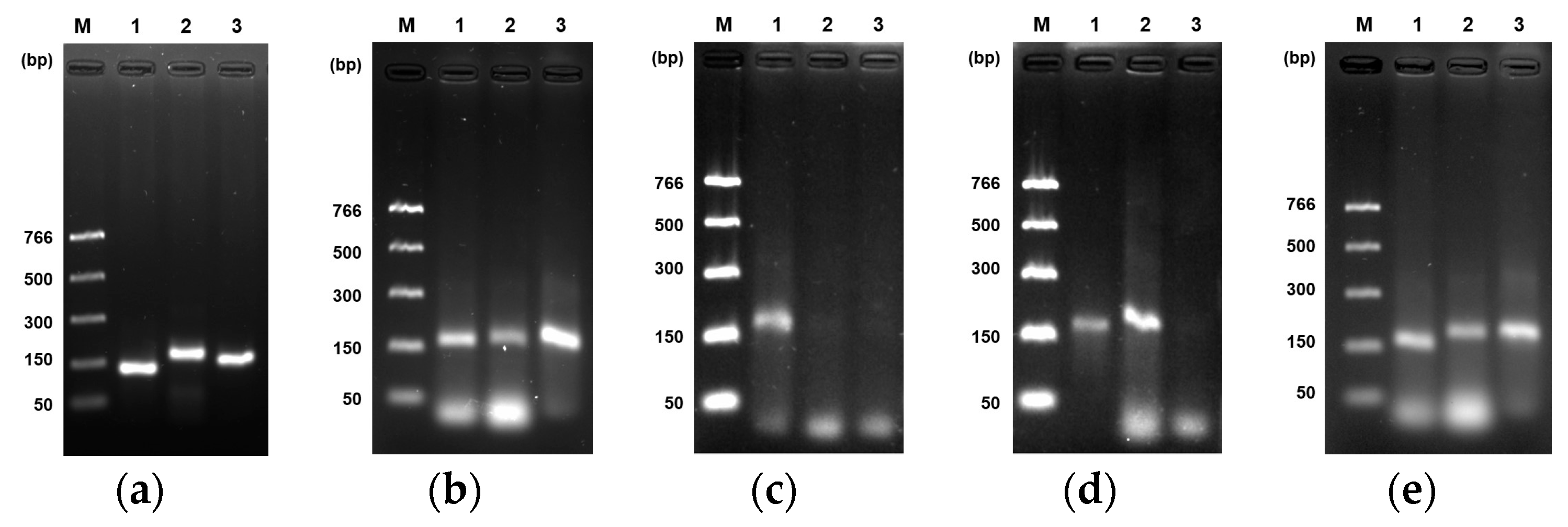
3.3. Performance of Enzymes in RPA Reaction
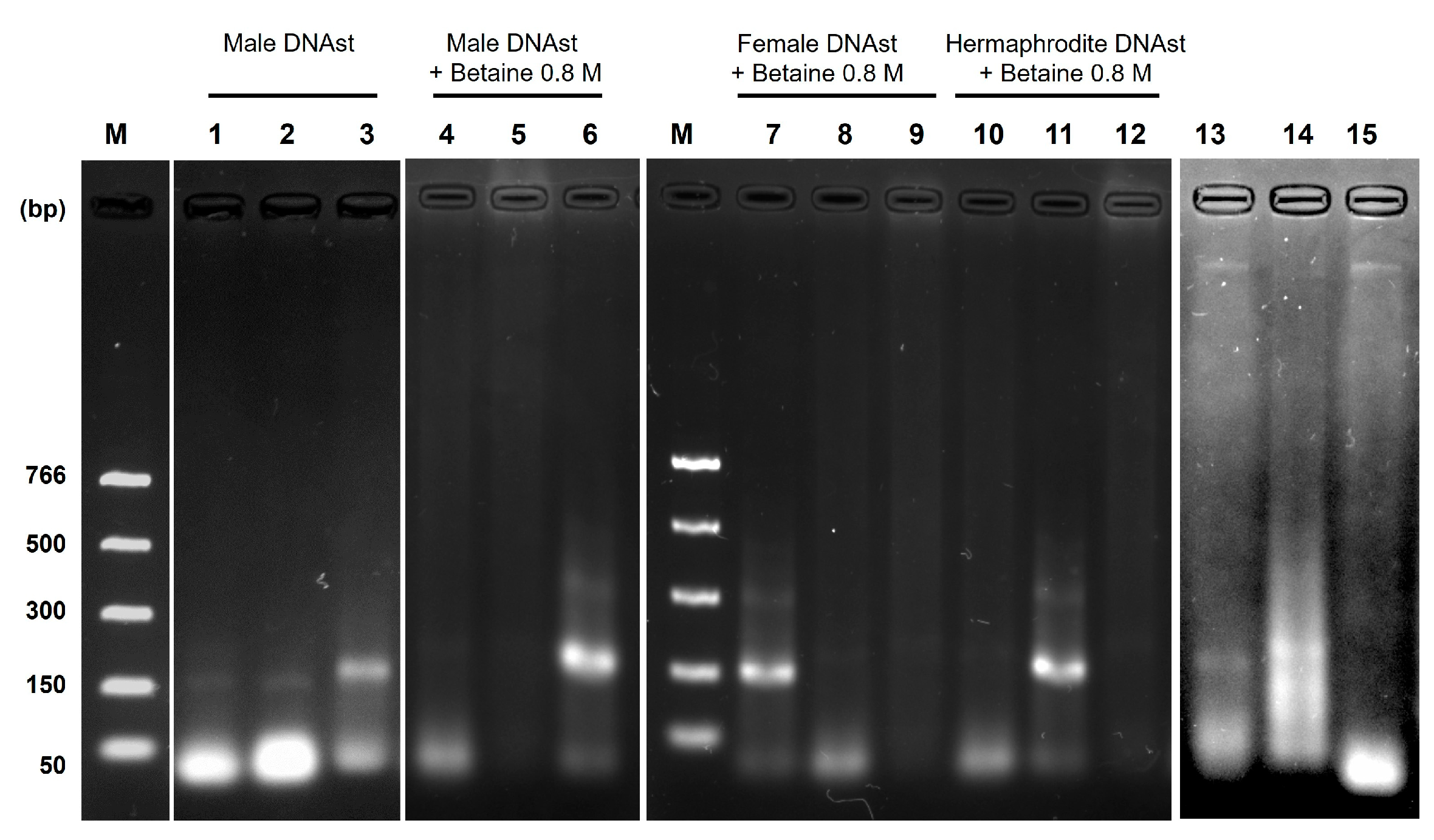
3.4. Evaluation of Betaine Addition on the RPA Efficiency and Primer Specificity Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deputy, J.; Ming, R.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Fitch, M.; Wang, M.; Manshardt, R.; Stiles, J. Molecular markers for sex determination in papaya (Carica papaya L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 106, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saalau-Rojas, E.; Barrantes-Santamaría, W.; Loría-Quirós, C.L.; Brenes-Angulo, A.; Gómez-Alpízar, L. Identificación mediante PCR del sexo de la papaya (Carica papaya L.), híbrido “Pococí”. Agron. Mesoam. 2009, 20, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aspeitia-Echegaray, V.; Torres-Tapia, M.A.; Mendoza-Rodríguez, D.V.; Reyes-Valdés, M.H. Evaluación de marcadores genéticos para discriminación entre hembras y hermafroditas de papaya (Carica papaya L.) variedad “Maradol”. Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2014, 37, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Ruiz, F.G.; Anaya López, J.L.; Rodríguez Vera, A.P. Evaluación de marcadores moleculares en la predicción temprana de plantas de papaya (Carica papaya L.) de tipo hermafrodita var. Maradol en la zona Costa de Oaxaca. Temas Cienc. Tecnol. 2017, 21, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Araya-Valverde, E.; Bogantes, A.; Holst, A.; Vargas-Mora, C.; Gómez-Alpízar, L.; Brenes, A.; Sánchez-Barrantes, E.; Chavarría, M.; Barboza-Barquero, L. Field performance of hermaphrodite papaya plants obtained through molecular selection and micropropagation. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification. Nature 1991, 350, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.T.; Fraiser, M.S.; Schram, J.L.; Little, M.C.; Nadeau, J.G.; Malinowski, D.P. Strand displacement amplification—An isothermal, in vitro DNA amplification technique. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banér, J.; Nilsson, M.; Mendel-Hartvig, M.; Landegren, U. Signal amplification of padlock probes by rolling circle replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 5073–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepenburg, O.; Williams, C.H.; Stemple, D.L.; Armes, N.A. DNA detection using recombination proteins. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Sidas, D.A.; Vargas-Hernández, B.Y.; Ramírez-Pool, J.A.; Núñez-Muñoz, L.A.; Calderón-Pérez, B.; González-González, R.; Brieba, L.G.; Lira-Carmona, R.; Ferat-Osorio, E.; López-Macías, C.; et al. Starting from scratch: Step-by-step development of diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2 detection by RT-LAMP. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Wu, R.; Xiao, X.; Xing, F. Development of an on-spot and rapid recombinase polymerase amplification assay for Aspergillus flavus detection in grains. Food Control 2021, 125, 107957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, N.I.V.; Bonney, L.C.; Watson, R.J.; Graham, V.; Hewson, R. Point-of-care diagnostic assay for the detection of Zika virus using the recombinase polymerase amplification method. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1012–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Mason, M.G.; Botella, J.R. Evaluation and improvement of isothermal amplification methods for point-of-need plant disease diagnostics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, T.; Yang, X.; Hu, T.; Jiao, B.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Shen, D. Comparative evaluation of a novel recombinase polymerase amplification-lateral flow dipstick (RPA-LFD) assay, LAMP, conventional PCR, and leaf-disc baiting methods for detection of Phytophthora sojae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Wahed, A.A.; Patel, P.; Maier, M.; Pietsch, C.; Rüster, D.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Kissenkötter, J.; Behrmann, O.; Frimpong, M.; Diagne, M.M. Suitcase lab for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 based on recombinase polymerase amplification assay. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 2627–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Prasad, D. Isothermal nucleic acid amplification and its uses in modern diagnostic technologies. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, M.; Toljamo, A.; Martin, F.; Kokko, H. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for fast, sensitive and on-site detection of Phytophthora cactorum without DNA extraction. Eur. J. Hortic. 2019, 84, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrea-Sarmiento, A.; Stack, J.P.; Alvarez, A.M.; Arif, M. Multiplex recombinase polymerase amplification assay developed using unique genomic regions for rapid on-site detection of genus Clavibacter and C. nebraskensis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.M.; Yang, J.T. Visual DNA diagnosis of tomato yellow leaf curl virus with integrated recombinase polymerase amplification and a gold-nanoparticle probe. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Kapoor, R.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Saritha, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Baranwal, V.K. Rapid diagnosis of Cucumber mosaic virus in banana plants using a fluorescence-based real-time isothermal reverse transcription-recombinase polymerase amplification assay. J. Virol. Methods 2019, 270, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babujee, L.; Witherell, R.A.; Mikami, K.; Aiuchi, D.; Charkowski, A.O.; Rakotondrafara, A.M. Optimization of an isothermal recombinase polymerase amplification method for real-time detection of Potato virus Y O and N types in potato. J. Virol. Methods 2019, 267, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobato, I.M.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Recombinase polymerase amplification: Basics, applications and recent advances. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Juma, K.M.; Akagi, S.; Hayashi, K.; Takita, T.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; Fujiwara, S.; Nakura, Y.; Yanagihara, I.; Yasukawa, K. Solvent engineering studies on recombinase polymerase amplification. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 131, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Morimoto, K.; Juma, K.M.; Takita, T.; Saito, K.; Yanagihara, I.; Fujiwara, S.; Yasukawa, K. Application of recombinant human pyruvate kinase in recombinase polymerase amplification. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2023, 136, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juma, K.M.; Inoue, E.; Asada, K.; Fukuda, W.; Morimoto, K.; Yamagata, M.; Takita, T.; Kojima, K.; Suzuki, K.; Nakura, Y.; et al. Recombinase polymerase amplification using novel thermostable strand-displacing DNA polymerases from Aeribacillus pallidus and Geobacillus zalihae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2023, 135, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juma, K.M.; Kojima, K.; Takita, T.; Natsuaki, K.T.; Yasukawa, K. Comparison of sensitivity and rapidness of PCR, recombinase polymerase amplification, and RNA-specific amplification for detection of Rice yellow mottle virus. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 21, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juma, K.M.; Takita, T.; Ito, K.; Yamagata, M.; Akagi, S.; Arikawa, E.; Kojima, K.; Biyani, M.; Fujiwara, S.; Nakura, Y.; et al. Optimization of reaction condition of recombinase polymerase amplification to detect SARS-CoV-2 DNA and RNA using a statistical method. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 567, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juma, K.M.; Takita, T.; Yamagata, M.; Ishitani, M.; Hayashi, K.; Kojima, K.; Suzuki, K.; Ando, Y.; Fukuda, W.; Fujiwara, S.; et al. Modified uvsY by N-terminal hexahistidine tag addition enhances efficiency of recombinase polymerase amplification to detect SARS-CoV-2 DNA. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidman, C.E.; Struhl, K.; Sheen, J.; Jessen, T. Introduction of plasmid DNA into cells. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 1997, 37, 1.8.1–1.8.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba-Andrade, F.; Peralta-Castro, A.; García-Medel, P.L.; Castro-Torres, E.; González-González, R.; Castro-Lara, A.Y.; Mora Garduño, J.D.; Raygoza, C.D.; Baruch-Torres, N.; Peñafiel-Ayala, A.; et al. An open-source bacteriophage T4 recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) system for pathogen detection: A proof of concept on SARS-CoV-2 detection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 2024. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Meneses, E.; Cárdenas, H.; Zárate, S.; Brieba, L.G.; Orozco, E.; López-Camarillo, C.; Azuara-Liceaga, E. The R2R3 Myb protein family in Entamoeba histolytica. Gene 2010, 455, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baruch-Torres, N.; Brieba, L.G. Plant organellar DNA polymerases are replicative and translesion DNA synthesis polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 10751–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peralta-Castro, A.; Baruch-Torres, N.; Brieba, L.G. Plant organellar DNA primase-helicase synthesizes RNA primers for organellar DNA polymerases using a unique recognition sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 10764–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Strayer-Scherer, A.; Jones, J.B.; Paret, M.L. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for field detection of tomato bacterial spot pathogens. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ávila-Hernández, J.G.; Camas-Reyes, A.; Martínez-Antonio, A. Sex determination of papaya var. ‘Maradol’ reveals hermaphrodite-to-male sex reversal under greenhouse conditions. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2023, 23, e457923312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.C.; Yi, T.T.; Jiang, B.; Guo, X.L.; Zhang, G.Y. Betaine-assisted recombinase polymerase assay with enhanced specificity. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 575, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satya, P.; Mitra, S.; Ray, D.P.; Mahapatra, B.S.; Karan, M.; Jana, S.; Sharma, D.A. Rapid and inexpensive NaOH based direct PCR for amplification of nuclear and organelle DNA from ramie (Boehmeria nivea), a bast fibre crop containing complex polysaccharides. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londoño, M.A.; Harmon, C.L.; Polston, J.E. Evaluation of recombinase polymerase amplification for detection of begomoviruses by plant diagnostic clinics. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.H.; Gwo, J.C.; Lin, K.H. Rapid sex identification of papaya (Carica papaya) using multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification (mLAMP). Planta 2012, 236, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.C.; Shih, H.C.; Ko, Y.Z.; Wang, R.H.; Li, S.J.; Chiang, Y.C. Direct LAMP assay without prior DNA purification for sex determination of papaya. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, I.; Ianc, M.B.; Ochis, C.; Popescu, O. The evidence of contaminant bacterial DNA in several commercial Taq polymerases. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 18, 8007–8012. [Google Scholar]
- Ávila-Hernández, J.G.; Cárdenas-Aquino, M.d.R.; Camas-Reyes, A.; Martínez-Antonio, A. Sex determination in papaya: Current status and perspectives. Plant Sci. J. 2023, 335, 111814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, C. Accelerated isothermal nucleic acid amplification in betaine-free reaction. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 530, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intha, N.; Chaiprasart, P. Sex determination in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) by PCR based marker analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 236, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flajšman, M.; Slapnik, M.; Murovec, J. Production of feminized seeds of high CBD Cannabis sativa L. by manipulation of sex expression and its application to breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 718092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, N.; Ayukawa, Y.; Fuke, M.; Teraoka, T.; Watanabe, K.; Arie, T.; Komatsu, K. Rapid sex identification method of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) in the vegetative stage using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Planta 2017, 245, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sex to Identify | Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Size of RPA Product | %GC Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | rpaCpTrnL-F rpaCpTrnL-R | GGGGATATGGCGAAATCGGTAGACGCTACGGA TGTTTGTTCTCGTAAAACAGGATTTGGCTCAG | 150 bp | 56 41 |
| Hermaphrodite | rpaW11-F rpaW11-R | TGGATCGTGCTCCTAGTGCTCATGGTGACACC CTGATGCGTGTGTGGCTCTATCTATATGTGTG | 165 bp | 56 47 |
| Male | rpaPMSM2-F rpaPMSM2-R | GCGATGCTTCAAGTGTTGACATAAAGGCAGTT AATATCCCTCTAATACTCTCACCAAGGCATAC | 150 bp | 44 41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ávila-Hernández, J.G.; Coreño-Alonso, A.; Pantoja-Alonso, M.A.; Córdoba-Andrade, F.J.; González-González, R.; Díaz-Quezada, C.E.; Camas-Reyes, A.; Martínez-Antonio, A. Step-by-Step Development of a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Assay for Sex Identification in Papaya. Appl. Biosci. 2024, 3, 426-437. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3040027
Ávila-Hernández JG, Coreño-Alonso A, Pantoja-Alonso MA, Córdoba-Andrade FJ, González-González R, Díaz-Quezada CE, Camas-Reyes A, Martínez-Antonio A. Step-by-Step Development of a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Assay for Sex Identification in Papaya. Applied Biosciences. 2024; 3(4):426-437. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3040027
Chicago/Turabian StyleÁvila-Hernández, José Guadalupe, Alejandro Coreño-Alonso, Mario Alberto Pantoja-Alonso, Francisco Javier Córdoba-Andrade, Rogelio González-González, Corina E. Díaz-Quezada, Alberto Camas-Reyes, and Agustino Martínez-Antonio. 2024. "Step-by-Step Development of a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Assay for Sex Identification in Papaya" Applied Biosciences 3, no. 4: 426-437. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3040027
APA StyleÁvila-Hernández, J. G., Coreño-Alonso, A., Pantoja-Alonso, M. A., Córdoba-Andrade, F. J., González-González, R., Díaz-Quezada, C. E., Camas-Reyes, A., & Martínez-Antonio, A. (2024). Step-by-Step Development of a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA) Assay for Sex Identification in Papaya. Applied Biosciences, 3(4), 426-437. https://doi.org/10.3390/applbiosci3040027








