Abstract
It has been previously reported that time-varying EMFs and LEDs have the potential to modulate cellular activity and cell viability. It has also been shown that cellular activity and state can be inferred by measuring the biophoton emission derived from these same cells. To identify if the brief application (15 min) of an LED (635 nm at 3 klx) or EMF (1–3 uT) could influence cell growth and subsequent biophoton emission characteristics, B16-BL6 cells were grown to confluence and exposed to a time-varying, frequency-modulated EMF, LED, or both. Before and after EMF and LED exposure, photon emission measurements were taken for 1 min at a 50 Hz sampling rate. Following the exposure and photon emission measurements, cell viability was assessed via the use of a hemocytometer. The results demonstrated that after only 15 min of exposure to a time-varying EMF, there was a 41.6% reduction in viable cells when compared to sham controls [t(25) = 2.4, p = 0.02]. This effect approached significance in the LED alone condition [p = 0.07] but was completely absent in the condition wherein the LED and EMF were applied simultaneously [p < 0.8]. Additionally, following exposure to only the LED, there was a significant increase in biophoton emission SPD values at 13 Hz from whole cell cultures [t(60) = 2.3, p = 0.021]. This biophoton emission frequency was also strongly correlated with the number of nonviable cells [r = −0.514] in the dish. Taken together, these data point to biophotons emitted from cell cultures at 13 Hz as a potential indicator of the number of nonviable cells in vitro. The summation of data here corroborates previous work demonstrating the efficacy of specific time-varying EMFs as a novel therapeutic for the inhibition of cancer cell growth. It also furthers our assertion that biophoton emission can be used as a novel detection tool for cell activity.
1. Introduction
The application of a light-emitting diode (LED) or an electromagnetic field (EMF) to biological systems have been shown to affect growth rates and cell proliferation in both in vitro and in vivo models [1,2,3]. Throughout these studies, the results were influenced by the specific wavelength, energy strength, and pattern of application of EMF or LED. Specific patterns of LED application have been associated with increased rates of recovery and a reduction in inflammation in living systems [4,5,6]. A study conducted by Wu and Persinger [7] reported increased stem cell proliferation in amputated planaria, with higher densities of stem cells in planaria treated with an 880 nm LED. In a similar study involving the use of freshwater planaria, the authors observed increased regeneration rates when stimulating head blastemas with red LEDs in comparison to diminishing or slower regeneration rates when exposed to green LEDs [5]. Alongside this, the existing literature also contains experiments demonstrating the effectiveness of LEDs in inducing neurite outgrowth in rat cortical neurons in vitro. The results from these experiments demonstrated an increase in MAP-Kinase activity and ultimately an increase in neurite outgrowth after exposure to 710 nm LED [8]. Matsumoto and colleagues [9] sought to observe the different responses that human colon cancer cells had to varying wavelengths of LEDs. Using different wavelengths of 465 nm (blue light), 525 nm (green light), and 635 nm (red light) LEDs, the researchers attempted to irradiate and inhibit the proliferation of human colon cancer cells. The results displayed a lower viability outcome for cells irradiated with 465 nm LEDs than for the control groups. No significant results were found for the 525 nm or 635 nm LEDs. In a similar study, researchers observed the inhibition of cell growth from B16 melanoma cells, again from the application of a blue LED (470 nm). Ohara and colleagues [10] discovered that the application of the blue light (not red or green) inhibited cell proliferation from B16 melanoma cells and reduced subsequent colony sizes. Interestingly, there was no reduction in the number of colonies observed after application from any light, including the blue LED. However, the blue light only showed a decrease in the size of the colonies as well as the number of cells per colony compared to the control and other LED groups [10]. Taken together, these findings provide insights into the specificity needed in identifying specific wavelengths that produce effects on cell populations.
Additionally, the application of an exogenous EMF has been shown to have a variety of effects on biological systems [11,12,13,14]. With the advancement of technology in today’s society, it has become apparent that exogenous EMFs have an impact on biological structures [15,16,17]. However, it is important to note that not all EMFs are analogous and that they can differ tremendously in both form and function [18]. Buckner and colleagues [19] demonstrated the capacity for the inhibition of malignant cell growth in B16-BL6 melanoma cells through the application of an EMF. They utilized a low-intensity, low-frequency EMF in the form of the ‘Thomas’ pattern. The Thomas EMF is a low-intensity modulated EMF pattern that contains frequencies ranging from 25 Hz to 6 Hz. Importantly, Buckner [19] demonstrated that the application of the Thomas EMF can specifically damage cancer cells while leaving non-malignant cell lines intact. This was hypothesized to be due to the biological properties of cancer cells expressing T-type Ca2+ channels, whereas the same expression is not found in non-malignant cells. Overall, they were able to demonstrate the inhibition of the proliferation of malignant cells through exposure to Thomas EMF for one hour a day over five consecutive days [19]. An interesting feature of this experiment lies within the structural component of the Thomas EMF itself. When the Thomas EMF pattern was reversed (now containing frequency ranges of 6 Hz–25 Hz), no effect was found regarding cell proliferation [19]. This highlights the importance of the specificity component regarding the effect a field can have on a population of cells.
Biophotons emitted from biological systems can be used as a prediction tool for cell density and overall state [20,21]. When measuring photon emission from biological systems, two notable variables are photon intensity and photon periodicity. Alternatively, diagnoses can be delineated from the frequency of photon production; this is the quality of information that the light is producing, which the observer can detect through spectral analysis [22]. B16-BL6 melanoma cells have been shown to emit photons of different wavelengths over a period of time outside of the incubator [23]. Over a 24 h period, varying wavelength filters were applied to B16-BL6 cells to demonstrate the shifts in emission frequencies from melanoma cells in a stressed environment. Increases in infrared (950 nm), ultraviolet (370 nm), and wavelengths within the visible spectrum (400 nm–800 nm) were all detected at specific time intervals with B16-BL6 cells left outside of the incubator. Additionally, specific activators and inhibitors corresponding to specific wavelengths were introduced to cells. This resulted in an increase or decrease in photon emissions at the respective wavelength corresponding to the activator introduced. These results display energy shifts within the electromagnetic spectrum over time in a changed environment. Moreover, the results display a relationship between electromagnetic activity and molecular structures. Additionally, we have also observed that there is a conspicuous relationship between electromagnetic energy and photon emission [24,25,26,27]. The results reported by Persinger and colleagues (2015) demonstrate that local magnetic field measurements and biophoton emission measurements are inversely related. Hence, there must be reciprocal or demonstrable biophoton emission changes in cell cultures exposed to EMF or LED stimulation.
Overall, applying LEDs or EMFs to cell cultures can influence cell density and, potentially, photon emissions from cells. Depending on the application characteristics of an LED or EMF, the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation [28] or an increase in cell proliferation during wound healing [7] can be observed. Here, we propose that the brief application of an LED and EMF to B16-BL6 cells (malignant cell line) will reduce cell proliferation and induce photon emission changes following LED and EMF stimulation. The objective is to identify what patterns of EMF and LED induce viability changes in B16-BL6 cells and what, if any, biophoton emission changes occur.
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Cells
A B16-BL6 mouse melanoma cancerous cell line was used. The B16BL6 cell line was obtained from Dr. Robert Lafrenie [19]. Cell cultures were maintained in 150 × 20 mm cell culture plates using Dulbecco’s Modified Essential Medium. Media consisted of 10% Fetal Bovine Serum and 1% Antibiotic + Antimycotic. The cell cultures were incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2. For the experiment, cell monolayers were washed with a neutral pH PBS. Plates were then exposed to a 0.25% trypsin solution to restrict the cells from adhering to the cell plates. After centrifugation at 850 RPM for 5 min, pellets were re-suspended and plated onto 60 × 15 mm cell plates. The final cell density for each plate was 1.0 × 106 cells, with the volume of media being 2.5 cm3. The cell plates were left in an incubator to grow for approximately 3 days to reach 95% confluence.
2.2. Procedure
The plates were removed from an incubator heated to 37 °C and immediately placed onto the aperture of a Model DM0090C digital photomultiplier tube (PMT) (SENS-TECH Sensory Technologies, Surrey, UK). This PMT model has a spectral response range of 280 to 850 nm and a peak QE at 400 nm. The PMT was housed within a dark box in a dark room adjacent to where cells are housed in the incubator. The dark box was a 15 × 15 × 15 cm box composed of wood that had been painted black. The top portion of the box is lifted to allow access to the PMT device and ease the placing and taking out of cell dishes placed on top of the PMT. The PMT itself was connected to a laptop adjacent to the dark box with a Counter Timer software installed on the laptop. This software allows for the collection of photon measurements. Photon measurements were recorded for 1 minute every 20 milliseconds (50 Hz) for a total of 3000 samples. Two recordings were taken for each cell plate. Furthermore, the dark box was covered with multiple layers of thick black cloth to ensure the absence of any external light that may affect the photon readings taken by the PMT.
After initial photon intensity measurements were taken using the PMT, the cell plates were then taken to the exposure room, where they were exposed to varying patterns of electromagnetic fields (EMFs) or LEDs or both simultaneously. The time-varying patterns that were applied to the cell plates (as either LED, EMF, or both) were 40 Hz Sine or Thomas. The plates were then exposed to one of the previously mentioned patterns in the form of an EMF, LED, or both an EMF and LED applied simultaneously. The patterns were applied to the plates for a total of 15 min. The LED was a red light with a wavelength of 635 nm (0.5 klx). The EMF was applied at 1–3 uT. The software and LED hardware utilized to produce these patterns have been described elsewhere [23,29]. After this 15 min exposure period, the cell plates were taken back to the dark box, where photon measurements were taken again. At three hours following exposure, the cell plates were then counted for cell viability using a hemocytometer. The counts included both viable and non-viable cells within the cell plate. This process involves washing media plates with PBS and then adding in 25% trypsin to remove cells from the cell plate. This is then neutralized using medium and centrifuged. Once the pellet had been re-suspended and mixed with Trypan Blue, the cell counts were taken under a microscope using a hemocytometer. The number of viable and non-viable cells was then compared with both photon intensity and the spectral power density emitted by each cell plate. A schematic of the patterns of the EMFs and LEDs we used, as well as a representation of our methodology, can be seen in Figure 1.
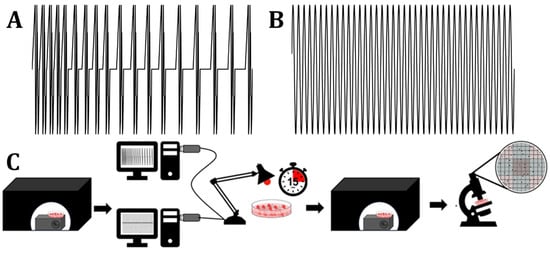
Figure 1.
The two EMFs utilized in this study were Thomas (A) and 40 Hz (B); a representation of the procedure can be seen in (C).
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability with LED and EMF Application
The initial results demonstrated that the number of viable cells decreased by 41.6% when the Thomas pattern was applied through the EMF alone condition when compared to the controls. The Thomas EMF alone condition displayed significantly fewer viable cells when compared to the sham conditions [t(25) = 2.4, p = 0.02] (Figure 2). There was no difference in cell viability when a 40 Hz Sine wave was applied as an EMF. Additionally, when the Thomas pattern was applied as an LED alone, there was a 33% decrease in viable cells. This decrease, while consistent with the EMF application, was not statistically significant [p = 0.07]. There was, however, a 47.9% decrease in the number of non-viable cells from the Thomas LED alone condition when compared to the control conditions. When the Thomas pattern was applied as an LED alone, there were statistically fewer non-viable cells observed when compared to the sham controls [t(25) = 3.1, p = 0.004] (Figure 3). Again, no differences in cell viability were observed when a 40 Hz Sine wave was applied. Interestingly, the observed decrease in viable cells in the EMF alone condition and the LED alone condition (albeit to a lesser extent in the latter) was not observed when the EMF and LED were applied simultaneously [p = 0.728] (Figure 4).
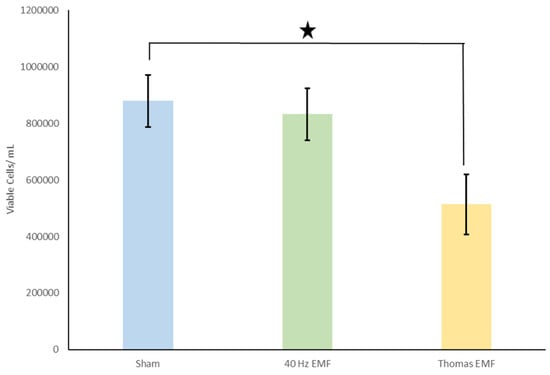
Figure 2.
Number of viable cells for EMF alone condition. The Thomas EMF displayed significantly fewer numbers of viable cells compared to the sham controls (denoted by asterisk). Means and SEMs are presented.
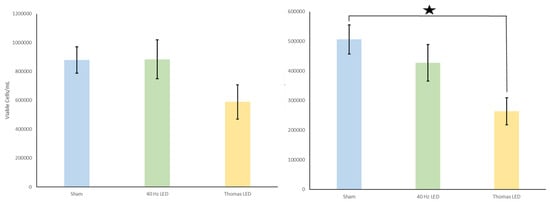
Figure 3.
(left): Number of viable cells for LED alone condition. No significant differences were found. (right): Number of non-viable cells for the LED alone condition. The Thomas pattern applied as an LED produced significantly fewer non-viable cells when compared to the controls (denoted by asterisk). Means and SEMs are presented.
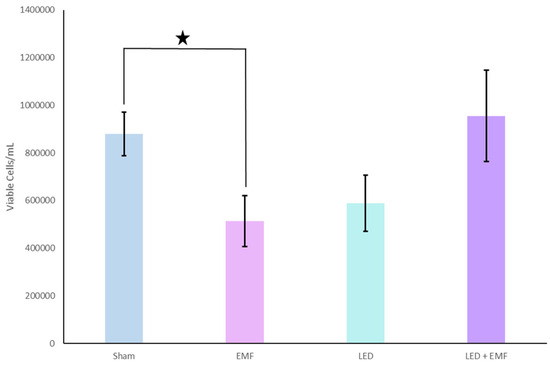
Figure 4.
The number of viable cells regarding Thomas pattern application geometry. When the Thomas pattern was applied as an EMF alone, there was a significant reduction in the number of viable cells (denoted by asterisk). This trend continued and approached significance in the LED alone condition. The LED and EMF simultaneous application condition displayed no difference in the number of viable cells when compared to the controls.
3.2. Biophoton Emission Periodicity and Cell Viability
Biophoton emission intensity was measured from the cells before and after each LED and EMF exposure condition (LED alone, EMF alone, and EMF and LED simultaneously). There were no differences in biophoton emission intensity between any of the groups. There was one consistent biophoton emission frequency associated with viable cell counts before exposures: 7.3 Hz (r = 0.288, p = 0.006). The greater the intensity of this frequency before any LED or EMF exposure, the greater the number of viable cells observed in the cultures 3 days later. This relationship was not apparent when investigating the nonviable cells. However, when observing biophoton emission frequency after exposure to the LED alone, significant results were revealed regarding the nonviable cell count predictions. The 13 Hz frequency was strongly correlated with the number of nonviable cells three hours later (r = −0.514, p < 0.01). Additionally, this exact frequency increased following the LED alone condition (t(60) = 2.3, p = 0.021). This increase in the 13 Hz frequency was not seen in the EMF alone condition or the condition wherein the EMF and LED were applied simultaneously. The same is true with the observed reduction in nonviable cells, where a reduction in nonviable cells was seen in the LED alone condition, but not in the EMF alone condition or the condition wherein the EMF and LED were applied simultaneously.
4. Discussion
The data presented here corroborate previously reported work on the efficacy of LED and EMF application on cell density and planarian regeneration [5,28,29]. A novel finding of this study is that the effects of cell viability were apparent after only a few hours and only 15 min of LED or EMF exposure. Buckner and colleagues [28] found that exposing B16-BL6 cells to the Thomas field for 1 h a day for 5 days dropped cell proliferation by 45 ± 6%. Our data revealed a decrease in cell counts of 41.6%. This drop falls in line with their previously reported data. This rapid reduction in viable cells could possibly be a result of apoptosis, as previous work from our laboratory has demonstrated that single exposure to time-varying EMFs produces apoptosis in B16-BL6 cells [30]. This hypothesis is made more plausible by previously reported data on the speed with which cellular apoptosis can occur [31]. While the LED alone and the LED and EMF together conditions were unable to significantly reduce the number of viable cells (the LED alone condition approached significance p = 0.07), there was a reduction in the number of nonviable cells when the LED was applied alone (Figure 3).
This reduction in nonviable cells is of interest, as this was the main measure associated with biophoton emission. As the number of nonviable cells increased, the number of biophotons emitted at the 13 Hz frequency decreased (Figure 5). What was most interesting is that when the Thomas LED was presented alone, there was an immediate increase in the 13 Hz frequency band. This was the same condition (Thomas LED alone) that produced a significant decrease in nonviable cells. A core feature of the Thomas pattern is that it is frequency-modulated between 25 Hz and 6 Hz. So, the increase in the 13 Hz frequency following the application of the Thomas LED is fitting, given the characteristics associated with the applied Thomas pattern. It is intriguing that this frequency predicts the number of nonviable cells in the dish but is also re-emitted as a biophoton following the application of the LED.
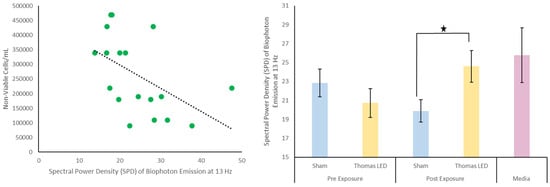
Figure 5.
(left): Scatterplot of non-viable cell counts by SPD of biophoton emission at 13 Hz after exposure to a lone LED. (right): Spectral Power Density of biophoton emission at 13 Hz via LED condition. The only significant result was an increase in SPD at 13 Hz for the Thomas condition following LED exposure (denoted by asterisk).
That the reduced cell viability effect seen in the Thomas EMF alone condition was absent in the Thomas EMF and LED simultaneous condition is of interest. It was somewhat surprising that no synergistic effects were observed when the two devices were paired together. This may be explained by interference patterns. It has previously been reported that the application of a physiologically based EMF before spatial learning impaired an animal’s ability to learn [32]. The simultaneous application of an EMF that mimicked the brain’s activity while learning appeared to saturate the animal’s ability to acquire new information, thus creating an interference pattern. While more data are required to know for certain why the simultaneous application of EMF and LED produced no effects, it is reasonable to suggest that the cell system was saturated with the frequency-modulated signal from two separate sources and produced interference.
The data presented here support our contention that dynamic, time-varying EMFs are able to induce strong effects within biological systems at lower intensities. Our data also demonstrate the reliable relationship between biophoton emission and cell systems. This further supports the notion that biophoton emission can be a measure of cell viability and that the application of specific time-varying patterns through LEDs can induce similar patterns of biophoton emission output from cell cultures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.R., K.S.B. and B.T.D.; methodology, R.R., K.S.B. and B.T.D.; formal analysis, R.R. and B.T.D.; investigation, R.R., K.S.B., L.M.L. and B.T.D.; resources, B.T.D.; data curation, R.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.R. and B.T.D.; writing—review and editing, R.R., K.S.B., L.M.L. and B.T.D.; supervision, B.T.D.; project administration, B.T.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tafur, J.; Van Wijk, E.P.A.; Van Wijk, R.; Mills, P.J. Biophoton Detection and Low-Intensity Light Therapy: A Potential Clinical Partnership. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2010, 28, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Vo, N.T.K.; Chettle, D.R.; McNeill, F.E.; Seymour, C.B.; Mothersill, C.E. Quantifying Biophoton Emissions from Human Cells Directly Exposed to Low-Dose Gamma Radiation. Dose Response 2020, 18, 1559325820926763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, C.A.; Buckner, A.L.; Koren, S.A.; Persinger, M.A.; Lafrenie, R.M. Exposure to a specific time-varying electromagnetic field inhibits cell proliferation via cAMP and ERK signaling in cancer cells. Bioelectromagnetics 2018, 39, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, N.; Denegar, C.R.; Preische, J. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of tibial fractures: A systematic review. J. Athl. Train. 2007, 42, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ermakov, A.M.; Ermakova, O.N.; Popov, A.L.; Manokhin, A.A.; Ivanov, V.K. Opposite effects of low intensity light of different wavelengths on the planarian regeneration rate. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 202, 111714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindl, A.; Merwald, H.; Schindl, L.; Kaun, C.; Wojta, J. Direct stimulatory effect of low-intensity 670 nm laser irradiation on human endothelial cell proliferation. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 148, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.P.P.; Persinger, M.A. Increased mobility and stem-cell proliferation rate in Dugesia tigrina induced by 880 nm light emitting diode. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2011, 102, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, J. Effect of 710 nm visible light irradiation on neurite outgrowth in primary rat cortical neurons following ischemic insult. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, N.; Yoshikawa, K.; Shimada, M.; Kurita, N.; Sato, H.; Iwata, T.; Higashijima, J.; Chikakiyo, M.; Nishi, M.; Kashihara, H.; et al. Effect of light irradiation by light emitting diode on colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res. Sep. 2014, 34, 4709–4716. [Google Scholar]
- Ohara, M.; Kawashima, Y.; Katoh, O.; Watanabe, H. Blue light inhibits the growth of B16 melanoma cells. JPN J. Cancer Res. 2002, 93, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walleczek, J. Electromagnetic field effects on cells of the immune system: The role of calcium signalling. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 3177–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.L.; Harrison, B.S. Effect of time-varied magnetic field on inflammatory response in macrophage cell line RAW 264.7. Electromag. Biol. Med. 2013, 32, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Bai, L.; Bai, W.; Xu, W.; Zhu, H. Effects of 50 Hz pulsed electromagnetic fields on the growth and cell cycle arrest of mesenchymal stem cells: An in vitro study. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2012, 31, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whissell, P.D.; Persinger, M.A. Emerging synergisms between drugs and physiologically- patterned weak magnetic fields: Implications for neuropharmacology and the human population in the twenty-first century. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2007, 5, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivrak, E.G.; Yurt, K.K.; Kaplan, A.A.; Alkan, I.; Altun, G. Effects of Electromagnetic Field Exposure on the Antioxidant Defense System. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2017, 5, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, K.B.; Kim, H.R. Possible Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Exposure on Central Nerve System. Biomol. Ther. 2019, 27, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, N.; Bono, D.; Dedic, N.; Kodandaramaiah, S.B.; Rudenko, A.; Suk, H.J.; Cassara, A.M.; Neufeld, E.; Kuster, N.; Tsai, L.H.; et al. Noninvasive Deep Brain Stimulation via Temporally Interfering Electric Fields. Cell 2017, 169, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifra, M.; Fields, J.Z.; Farhadi, A. Electromagnetic cellular interactions. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 105, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckner, C.A.; Buckner, A.L.; Koren, S.A.; Persinger, M.A.; Lafrenie, R.M. The effects of electromagnetic fields on B16-BL6 cells are dependent on their spatial and temporal character. Bioelectromagnetics 2016, 38, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotta, B.T.; Buckner, C.A.; Cameron, D.; Lafrenie, R.F.; Persinger, M.A. Biophoton emissions from cell cultures: Biochemical evidence for the plasma membrane as the primary source. Gen. Phys. Biophys. 2011, 3, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, H. Super-high sensitivity systems for detection and spectral analysis of ultraweak photon emission from biological cells and tissues. Experientia 1988, 44, 530–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.J.; Persinger, M.A.; Karbowski, L.M.; Dotta, B.T. Ultraweak Photon Emissions as a Non-Invasive, Early-Malignancy Detection Tool: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotta, B.T.; Lafrenie, R.M.; Karbowski, L.M.; Persinger, M.A. Photon emission from melanoma cells during brief stimulation by patterned magnetic fields: Is the source coupled to rotational diffusion within the membrane? Gen. Phys. Biophys. 2014, 33, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Persinger, M.A.; Dotta, B.T.; Karbowski, L.M.; Murugan, N.J. Inverse relationship between photon flux densities and nanotesla magnetic fields over cell aggregates: Quantitative evidence for energetic conservation. FEBS Open Bio 2015, 5, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, U.A.M.; Khalifa, I.A.; EL-Sheikh, I.A. The biological effects of the Magnetic Field in Healing Humans and Preventing Insects from Infecting and Harming Plants Using Schrodinger Quantum and Maxwell’s Equations. J. Surv. Fish. Sci. 2023, 10, 790–799. [Google Scholar]
- Sefidbakht, Y.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.M.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Khodagholi, F.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Foolad, F.; Faraji-Dana, R. Effects of 940 MHz EMF on bioluminescence and oxidative response of stable luciferase producing HEK cells. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2014, 13, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereta, M.; Janousek, L.; Cifra, M.; Cervinoka, K. Low frequency electromagnetic field effects on ultra-weak photon emission from yeast cells. In Proceedings of the 2016 ELEKTRO, Strbske Pleso, Slovakia, 16–18 May 2016; pp. 478–481. [Google Scholar]
- Buckner, C.A.; Buckner, A.L.; Koren, S.A.; Persinger, M.A.; Lafrenie, R.M. Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by Exposure to a Specific Time-Varying Electromagnetic Field Involves T-Type Calcium Channels. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.J.; Karbowski, L.M.; Persinger, M.A. Synergistic interactions between temporal coupling of complex light and magnetic pulses upon melanoma cell proliferation and planarian regeneration. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2017, 36, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rain, B.D.; Plourde-Kelly, A.D.; Lafrenie, R.M.; Dotta, B.T. Induction of apoptosis in B16-BL6 Melanoma Cells Following Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields modelled after Intercellular Calcium Waves. FEBS Open Bio 2023. in submission. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, Q.H.; Persinger, M.A. Behavioral changes with brief exposures to weak magnetic fields patterned to stimulate long-term potentiation. Brain Res. 2009, 1261, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





