Effects of Clay Minerals on Enzyme Activity as a Potential Biosensor of Soil Pollution in Alice Township
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
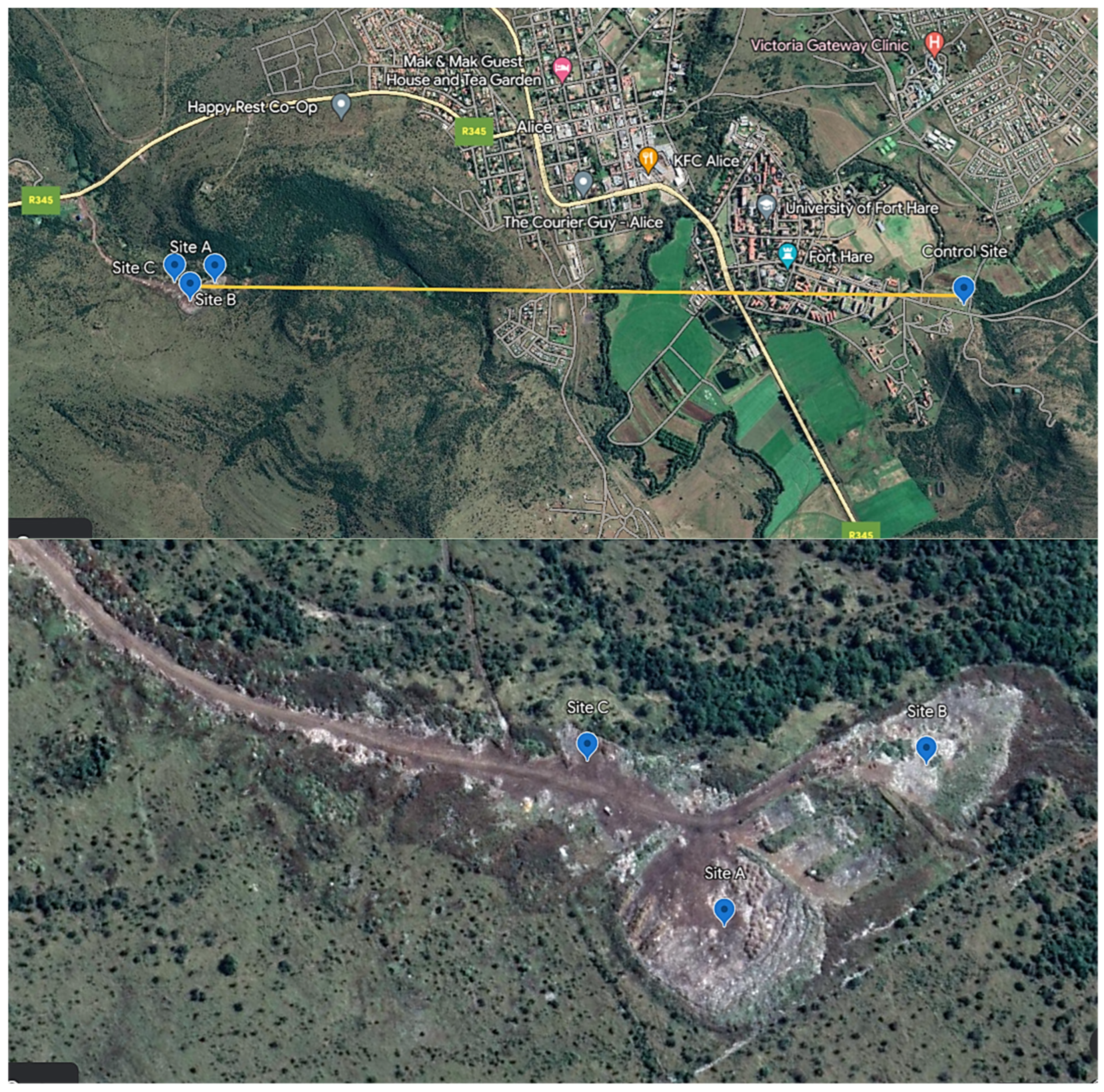
2.1. Sample Sites Description
2.2. Elemental Analysis
2.3. Enzyme Activity Analysis
2.3.1. Invertase Activity
2.3.2. Urease Activity
2.3.3. Phosphatase Activity
2.3.4. Catalase Activity
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
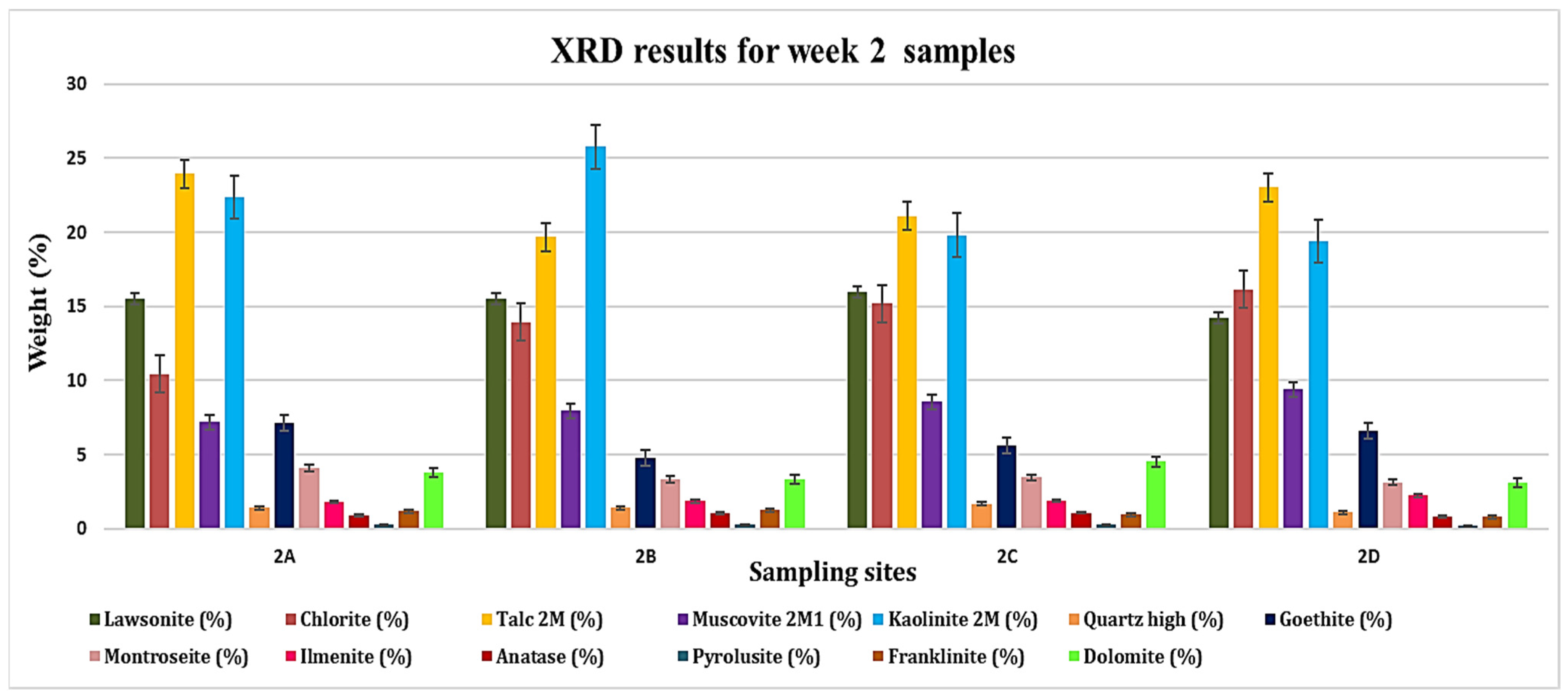
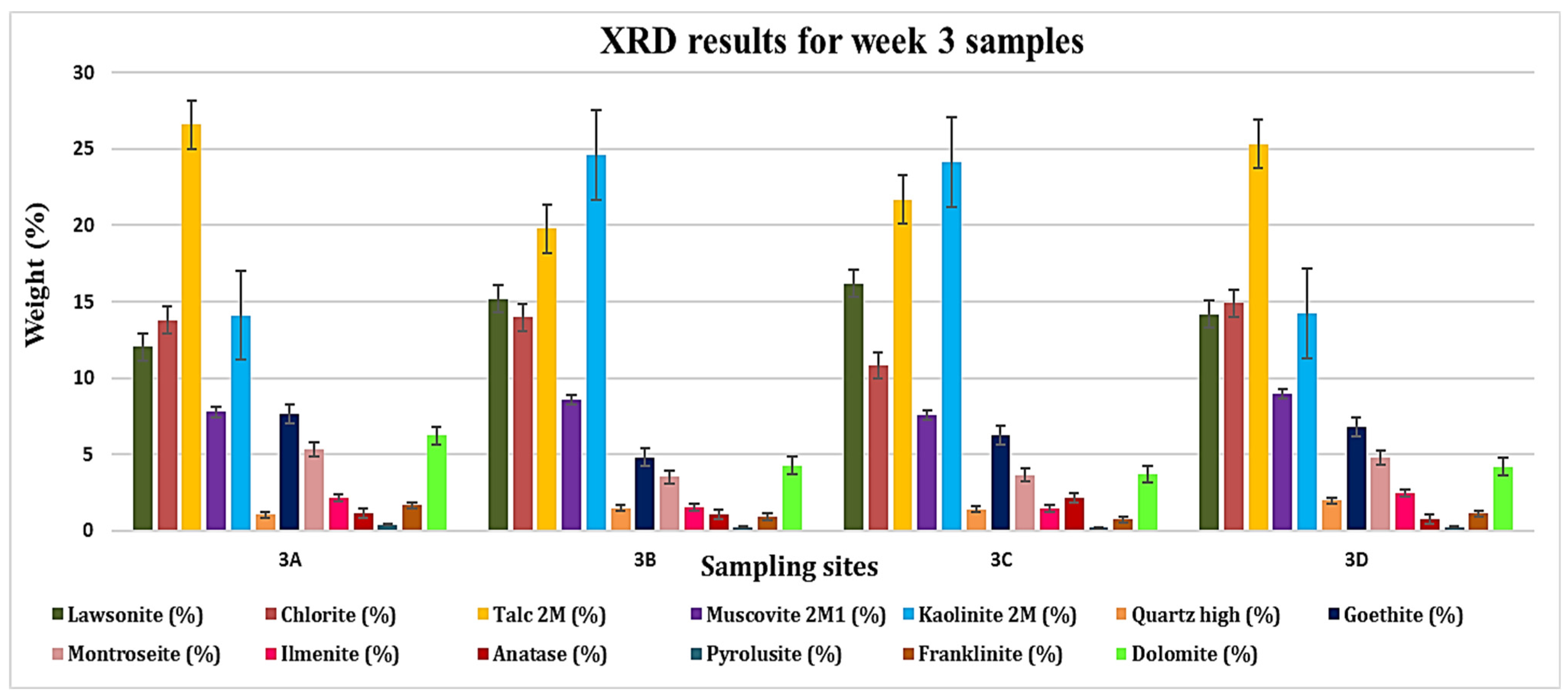
3.1. XRD Analysis
3.2. Enzyme Activity Analysis in Soil
3.3. The Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Recommendations and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| MPI | Significance | Remarks |
| <0.1 | Very slight contamination | No negative effect on soil, plant and, environment |
| 0.10–0.25 | Slight contamination | No negative effect on soil, plant and, environment |
| 0.26–0.5 | Moderate contamination | No negative effect on soil, plant and, environment |
| 0.51–0.75 | Severe contamination | No negative effect on soil, plant and, environment |
| 0.76–1.00 | Very severe contamination | No negative effect on soil, plant and, environment |
| 1.1–2.0 | Slight pollution | Will pose a negative impact on soil, plants, and environment |
| 2.1–4.0 | Moderate pollution | Will pose a negative impact on soil, plants, and environment |
| 4.1–8.0 | Severe pollution | Will pose a negative impact on soil, plants, and environment |
| 8.1–16.0 | Very severe pollution | Will pose a negative impact on soil, plants, and environment |
| >16.0 | Excessive pollution | Will pose a negative impact on soil, plants, and environment. |
References
- Tindwa, H.J.; Singh, B.R. Soil pollution and agriculture in sub-Saharan Africa: State of the knowledge and remediation technologies. Front. Soil Sci. 2023, 2, 1101944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, M.; Ramamoorthy, D.; Savitha, V.; Kirubakaran, N. Soil Enzyme Activities and Their Relationship with Soil Physico-Chemical Properties and Oxide Minerals in Coastal Agroecosystem of Puducherry. Geomicrobiol. J. 2019, 36, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utobo, E.B.; Tewari, L. Soil enzymes as bioindicators of soil ecosystem status. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Zwydak, M. The relationship between soil properties, enzyme activity, and land use. For. Res. Pap. 2017, 78, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igalavithana, A.D.; Lee, S.S.; Niazi, N.K.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Moon, D.H.; Ok, Y.S. Assessment of soil health in urban agriculture: Soil enzymes and microbial properties. Sustainability 2017, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karigar, C.S.; Rao, S.S. Role of microbial enzymes in the bioremediation of pollutants: A review. Enzym. Res. 2011, 2011, 805187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Google Earth. Alice landfillsite 32°48′24.88″ S and 26°49′33.37. Available online: https://earth.google.com/web/@-32.80488462,26.82628862,568.55580416a,550.09844115d,35y,40.42744424h,59.95875558t,0r/data=CjYaNBIuCiUweDFlNjNmNDgyNGZhZDE1YzM6MHg4ZjkxYzM5MzhkOGI1ZWQ4KgVBbGljZRgBIAE6AwoBMA (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Parajuli, P.B.; Duffy, S. Evaluation of soil organic carbon and soil moisture content from agricultural fields in Mississippi. Open J. Soil Sci. 2013, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyika, J.; Onyari, E.; Dinka, M.; Mishra, S. Analysis of particle size distribution of landfill contaminated soils and their mineralogical composition. Part. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motsara, M.R.; Roy, R.N. Guide to Laboratory Establishment for Plant Nutrient Analysis; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2008; Volume 19, pp. 101–122. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Xu, S.; Li, D.; Li, J. An Experimental Study of Mineral and Microstructure for Undisturbed Loess Polluted by Landfill Leachate. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 4891–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomina, M.; Skorochod, I. Microbial interaction with clay minerals and its environmental and biotechnological implications. Minerals 2020, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhu, W.; Amombo, E.; Lou, Y.; Chen, L.; Fu, J. Effect of heavy metals pollution on soil microbial diversity and bermudagrass genetic variation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, C.D.; Karathanasis, A.D. Clay minerals. In Encyclopedia of Soil Science; Lal, R., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio, P.; Ferrell, R.E. An application of profile fitting and CLAY++ for the quantitative representation (QR) of mixed-layer clay minerals. Clay Miner. 2001, 36, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekosse, G.I.E. Kaolin deposits and occurrences in Africa: Geology, mineralogy, and utilization. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 212–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olokode, O.S.; Aiyedun, P.O. Mineralogical characteristics of natural kaolins from Abeokuta, South-West Nigeria. Pac. J. Sci. Technol. 2011, 12, 558–565. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Jin, X.; Chen, H.; He, Z.; Qiu, L.; Duan, H. Grain Size Distribution and Clay Mineral Distinction of Rare Earth Ore through Different Methods. Minerals 2020, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbugadu, A.A.; Igwe, O. Mineralogical and major oxide characterization of Panyam clays, North-Central Nigeria. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2019, 14, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, L. X-Ray Diffraction and Mineralogical Analysis of Expansive Soils InKibaha, Tanzania. Int. J. Eng. Invent. 2016, 5, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Olagoke, F.K.; Kalbitz, K.; Vogel, C. Control of soil extracellular enzyme activities by clay minerals-Perspectives on microbial responses. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonious, G.F.; Turley, E.T. Trace Elements Composition and Enzymes Activity of Soil Amended with Municipal Sewage Sludge at Three Locations in Kentucky. Int. J. Appl. Agric. Sci. 2020, 6, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietjen, T.; Wetzel, R.G. Extracellular enzyme-clay mineral complexes: Enzyme adsorption, alteration of enzyme activity, and protection from photodegradation. Aquat. Ecol. 2003, 37, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzaioli, R.; Trifuoggi, M.; Rutigliano, F.A. Soil microbial biomass, activities and diversity in Southern Italy areas chronically exposed to trace element input from industrial and agricultural activities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 174, 104392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeboah, J.O.; Shi, G.; Shi, W. Effect of heavy metal contamination on soil enzymes activities. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2021, 9, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, H.; Meli, P.; Butler, B.; Paolini, J.; Matus, F.; Merino, C.; Cornejo, P.; Kuzyakov, Y. Meta-analysis of heavy metal effects on soil enzyme activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Clay Minerals Change the Toxic Effect of Cadmium on the Activities of Leucine Aminopeptidase. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 1024085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Dong, H.; Coffin, E.; Myrold, D.; Kleber, M. The Important Role of Enzyme Adsorbing Capacity of Soil Minerals in Regulating β-Glucosidase activity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, P.O.; Edokpayi, J.N.; Odiyo, J.O. Health and environmental risks of residents living close to a landfill: A case study of Thohoyandou Landfill, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sampling Sites | Lawsonite (%) SrMn2(Si2O7)(OH)2.H2O | Chlorite (%) Mg3Si2O5(OH)4 | Talc 2M (%) Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 | Muscovite 2M1 (%) KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2 | Kaolinite 2M (%) Al2Si2O5(OH)4 | Quartz high (%) α-SiO2 | Goethite (%) α-FeOOH | Montroseite (%) V875Fe125OOH | Ilmenite (%) FeTiO3 | Anatase (%) TiO2 | Pyrolusite (%) β-MnO2 | Franklinite (%) ZnFe2O4 | Dolomite (%) CaMg (CO3)2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 12.34 | 12.21 | 20.25 | 7.88 | 26.48 | 1.85 | 5.12 | 3.31 | 1.57 | 6.69 | 0.31 | 0.85 | 1.15 |
| 1B | 7.12 | 17.29 | 25.88 | 8.88 | 19.20 | 1.70 | 6.65 | 4.57 | 2.52 | 1.10 | 0.32 | 2.18 | 2.58 |
| 1C | 7.23 | 17.29 | 29.04 | 8.28 | 12.06 | 1.38 | 8.74 | 5.49 | 2.20 | 1.71 | 0.40 | 1.09 | 5.09 |
| 1D | 18.24 | 11.25 | 18.90 | 8.83 | 26.52 | 1.08 | 4.73 | 4.30 | 1.58 | 1.65 | 0.16 | 0.88 | 1.88 |
| 2A | 15.54 | 10.44 | 23.95 | 7.17 | 22.35 | 1.41 | 7.12 | 4.10 | 1.79 | 0.86 | 0.29 | 1.16 | 3.80 |
| 2B | 15.49 | 13.93 | 19.70 | 7.94 | 25.77 | 1.41 | 4.74 | 3.32 | 1.85 | 1.01 | 0.25 | 1.26 | 3.34 |
| 2C | 15.95 | 15.19 | 21.11 | 8.55 | 19.81 | 1.68 | 5.58 | 3.45 | 1.88 | 1.07 | 0.26 | 0.94 | 4.51 |
| 2D | 14.19 | 16.14 | 23.03 | 9.38 | 19.41 | 1.09 | 6.57 | 3.12 | 2.22 | 0.79 | 0.22 | 0.77 | 3.08 |
| 3A | 12.03 | 13.79 | 26.59 | 7.78 | 14.11 | 1.05 | 7.64 | 5.34 | 2.18 | 1.18 | 0.40 | 1.68 | 6.23 |
| 3B | 15.19 | 13.99 | 19.76 | 8.59 | 24.60 | 1.48 | 4.81 | 3.53 | 1.53 | 1.06 | 0.26 | 0.92 | 4.28 |
| 3C | 16.19 | 10.82 | 21.69 | 7.59 | 24.11 | 1.42 | 6.26 | 3.66 | 1.44 | 2.17 | 0.20 | 0.75 | 3.70 |
| 3D | 14.15 | 14.90 | 25.31 | 8.95 | 14.26 | 1.98 | 6.81 | 4.80 | 2.44 | 0.79 | 0.25 | 1.14 | 4.20 |
| 4A | 13.20 | 12.77 | 24.96 | 7.92 | 17.50 | 1.41 | 6.42 | 6.05 | 2.39 | 0.98 | 0.27 | 1.03 | 5.11 |
| 4B | 15.81 | 12.53 | 21.89 | 7.34 | 21.22 | 1.79 | 5.28 | 3.75 | 2.20 | 1.74 | 0.18 | 1.32 | 4.95 |
| 4C | 15.58 | 12.57 | 20.39 | 8.48 | 23.31 | 1.75 | 5.47 | 4.72 | 1.71 | 1.07 | 0.25 | 0.90 | 3.80 |
| 4D | 12.69 | 16.20 | 24.54 | 7.30 | 13.51 | 1.90 | 6.98 | 4.77 | 2.77 | 0.69 | 0.43 | 1.12 | 7.09 |
| Major Elements | Observed Element Complexes by XRD in Soil Samples |
|---|---|
| Mn | SrMn2(Si2O7) (OH)2·H2O (lawsonite), MnO2 (pyrolusite) |
| Mg | Mg3Si4O10(OH)2 (talc 2M), Mg3Si2O5(OH)4 (Chlorite) |
| Al | Al2Si2O5(OH)4 [kaolinite], KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2 (muscovite) |
| K | KAl2(AlSi3O10) (OH)2 (muscovite) |
| Fe | FeOOH (goethite) |
| Ti | TiO2 (anatase), FeTiO3 (ilmenite) |
| V | V875Fe125OOH (Montroseite) |
| Ca | CaMg (CO3)2 (dolomite) |
| Zn | ZnFe2O4 (franklinite) |
| Si | SiO2 (quartz) |
| Sr | SrMn2(Si2O7) (OH)2·H2O (lawsonite) |
| Sites | Mn | Mg | Al | Fe | Ti | V | Ca | Zn | Si | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1A | 0.68 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 1.08 | 1.05 | 0.77 | 0.61 | 0.97 | 1.71 | 0.89 |
| 1B | 0.39 | 1.37 | 0.72 | 1.41 | 0.67 | 1.06 | 1.37 | 2.48 | 1.57 | 1.01 |
| 1C | 0.40 | 1.54 | 0.45 | 1.85 | 1.04 | 1.28 | 2.71 | 1.24 | 1.28 | 0.94 |
| 2A | 1.10 | 1.04 | 1.15 | 1.08 | 1.09 | 1.31 | 1.23 | 1.51 | 1.29 | 0.80 |
| 2B | 1.09 | 0.86 | 1.33 | 0.72 | 1.28 | 1.06 | 1.08 | 1.64 | 1.28 | 0.85 |
| 2C | 1.12 | 0.92 | 1.02 | 0.85 | 1.35 | 1.11 | 1.46 | 1.22 | 1.54 | 0.91 |
| 3A | 0.85 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 1.12 | 1.49 | 1.11 | 1.48 | 1.47 | 0.53 | 0.87 |
| 3B | 1.07 | 0.89 | 1.73 | 0.71 | 1.34 | 0.74 | 1.02 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.96 |
| 3C | 1.14 | 0.83 | 1.69 | 0.92 | 2.75 | 0.76 | 0.88 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.85 |
| 4A | 1.04 | 1.02 | 1.30 | 0.92 | 1.42 | 1.27 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 1.08 |
| 4B | 1.25 | 0.89 | 1.57 | 0.76 | 2.52 | 0.79 | 0.70 | 1.18 | 0.94 | 1.01 |
| 4C | 1.23 | 0.83 | 1.73 | 0.92 | 1.55 | 0.99 | 0.54 | 0.80 | 0.92 | 1.16 |
| Urease (µg NH4- N·g−1 Soil·h−1) | Invertase (µg Glucose·g−1 Soil·h−1) | Catalase (mL KMnO4·g−1 Soil·h−1) | Phosphatase (µg Phenol·g−1 Soil·h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Site 1A | 0.09 ± 0.05 c | 3.35 ± 1.94 d | 2.80 ± 1.62 d | 1.16 ± 0.67 d |
| Site 1B | 0.12 ± 0.07 c | 3.48 ± 2.01 d | 0.90 ± 0.52 cd | 2.66 ± 1.54 a | |
| Site 1C | 0.10 ± 0.06 c | 3.49 ± 2.01 d | 1.25 ± 0.72 a | 2.34 ± 1.35 c | |
| Site 2 | 0.12 ± 0.07 c | 3.48 ± 2.01 d | 1.50 ± 0.87 a | 1.34 ± 0.77 d | |
| Week 2 | Site 1A | 0.09 ± 0.05 c | 3.66 ± 2.11 d | 0.65 ± 0.37 b | 1.59 ± 0.92 d |
| Site 1B | 0.11 ± 0.06 c | 3.65 ± 2.10 d | 0.80 ± 0.46 cd | 3.49 ± 2.01 ab | |
| Site 1C | 0.12 ± 0.07 c | 3.66 ± 2.11 d | 1.36 ± 0.78 a | 3.66 ± 2.11 e | |
| Site 2 | 0.10 ± 0.06 c | 3.60 ± 2.08 d | 0.87 ± 0.50 cd | 1.42 ± 0.82 d | |
| Week 3 | Site 1A | 0.11 ± 0.06 c | 3.35 ± 1.93 d | 0.97 ± 0.56 cd | 2.37 ± 1.37 c |
| Site 1B | 0.10 ± 0.05 c | 3.48 ± 2.01 d | 0.46 ± 0.27 ab | 3.49 ± 2.01 ab | |
| Site 1C | 0.12 ± 0.07 c | 3.18 ± 1.83 d | 1.14 ± 0.66 a | 2.79 ± 1.61 a | |
| Site 2 | 0.13 ± 0.07 c | 3.47 ± 2.01 d | 0.65 ± 0.37 b | 2.33 ± 1.34 c | |
| Week 4 | Site 1A | 0.22 ± 0.13 cd | 2.88 ± 1.66 c | 2.27 ± 1.31 e | 3.97 ± 2.29 e |
| Site 1B | 0.12 ± 0.07 c | 3.26 ± 1.88 d | 2.58 ± 1.49 d | 3.67 ± 2.12 e | |
| Site 1C | 0.15 ± 0.09 c | 2.43 ± 1.52 c | 2.63 ± 1.52 d | 3.98 ± 2.30 e | |
| Site 2 | 0.14 ± 0.0 c | 3.36 ± 1.94 d | 1.57 ± 0.91 a | 3.65 ± 2.10 e | |
| Mn | Mg | K | Al | Si | Fe | V | Ti | Zn | Ca | PHO | INV | CAT | URE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Mg | −0.774 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||
| K | −0.092 | −0.068 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Al | 0.593 * | −0.893 ** | 0.003 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Si | −0.120 | −0.029 | −0.160 | −0.094 | 1 | |||||||||
| Fe | −0.663 ** | 0.0948 ** | −0.116 | −0.844 ** | −0.132 | 1 | ||||||||
| V | −0.462 | 0.700 ** | −0.107 | −0.672 ** | −0.044 | 0.612 * | 1 | |||||||
| Ti | −0.099 | −0.263 | −0.171 | 0.397 | 0.219 | −0.251 | −0.292 | 1 | ||||||
| Zn | −0.586 * | 0.488 | −0.049 | −0.334 | 0.072 | 0.299 | 0.322 | −0.228 | 1 | |||||
| Ca | −0.150 | 0.517 * | −0.418 | −0.731 ** | 0.071 | 0.510 * | 0.514 * | −0.535 * | 0.157 | 1 | ||||
| PHO | 0.088 | −0.072 | −0.225 | −0.131 | 0.362 | −0.181 | 0.208 | −0.428 | 0.085 | 0.564 * | 1 | |||
| INV | −0.077 | 0.078 | 0.119 | −0.043 | −0.206 | 0.093 | −0.424 | −0.045 | 0.159 | −0.128 | −0.459 | 1 | ||
| CAT | 0.072 | −0.229 | −0.276 | 0.181 | 0.355 | −0.279 | 0.122 | 0.526 * | −0.221 | −0.090 | 0.212 | −0.664 ** | 1 | |
| URE | 0.044 | 0.122 | −0.050 | −0.233 | 0.140 | −0.006 | 0.613 * | −0.296 | −0.023 | 0.332 | 0.587 * | −0.643 ** | 0.398 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maphuhla, N.G.; Oyedeji, O.O. Effects of Clay Minerals on Enzyme Activity as a Potential Biosensor of Soil Pollution in Alice Township. Waste 2024, 2, 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste2010005
Maphuhla NG, Oyedeji OO. Effects of Clay Minerals on Enzyme Activity as a Potential Biosensor of Soil Pollution in Alice Township. Waste. 2024; 2(1):85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste2010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaphuhla, Nontobeko Gloria, and Opeoluwa Oyehan Oyedeji. 2024. "Effects of Clay Minerals on Enzyme Activity as a Potential Biosensor of Soil Pollution in Alice Township" Waste 2, no. 1: 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste2010005
APA StyleMaphuhla, N. G., & Oyedeji, O. O. (2024). Effects of Clay Minerals on Enzyme Activity as a Potential Biosensor of Soil Pollution in Alice Township. Waste, 2(1), 85-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste2010005








