Efficient Al Recovery from Aluminum Dross with Simultaneous AlN Separation by a Mechanical Method
Abstract
:Highlights
- Metallic Al in aluminum dross was separated by a milling method via size control.
- Ball medias decreased the fraction of large particles. Metallic Al particle with a size of 0.15–2 mm were targeted, which improved Al recovery to 65%. Most AlN was collected simultaneously in particles with size < 0.425 mm.
- Size control of aluminum dross was achieved by ball milling.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Size Distribution
2.3. Composition Estimation
2.4. Characterization Method
3. Results and Discussion
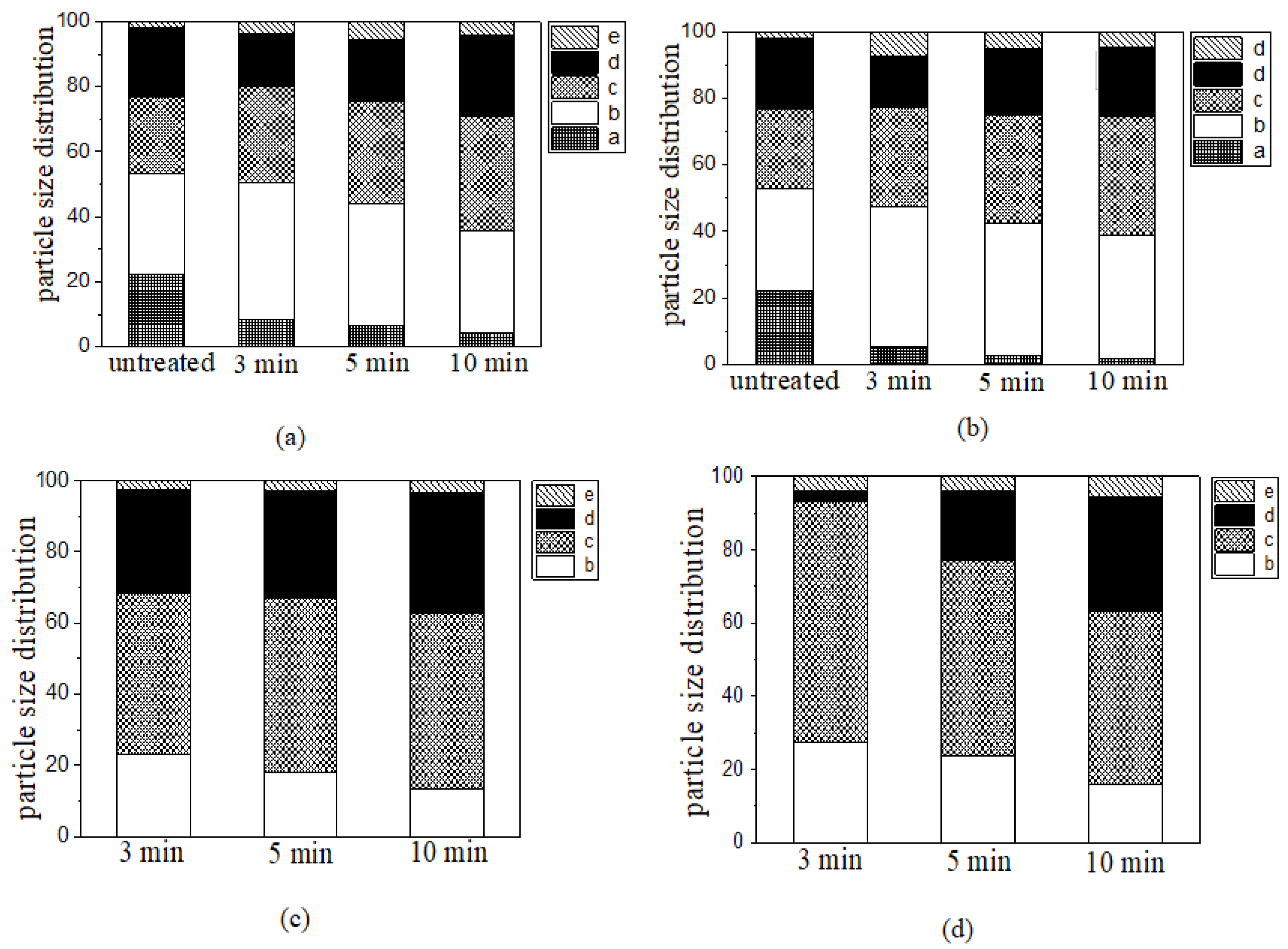
3.1. Size Distribution
3.2. Element Distribution
3.3. Aluminum Recovery (Recoverable Aluminum Metal)
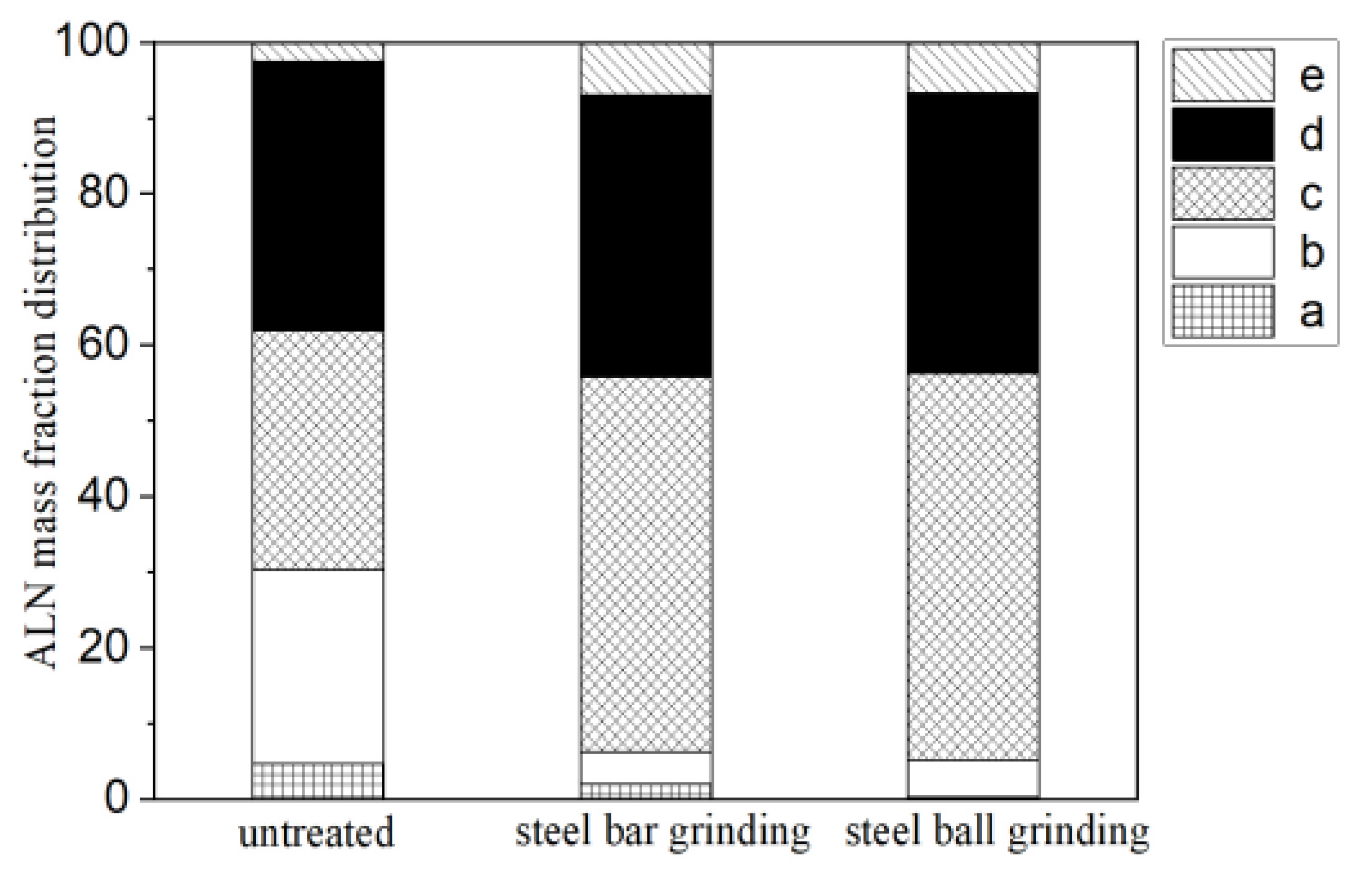
3.4. Simultaneous AlN Separation
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The fraction of Dp < 0.08 mm in untreated AD is lower, while the fraction of other particle sizes of AD is uniform. After ball milling, the particle size distribution is centered at Dp0.425–0.08 mm AD. Grinding with steel bar and steel ball media has obvious impacts on coarse AD particles. Steel ball grinding media have a better impact than steel ball media.
- (2)
- After ball milling, the element fractions of different particle sizes of AD vary. Metallic Al is concentrated in the Dp2–0.425 mm fraction of AD, and AlN is concentrated in the Dp0.425–0.15 mm fraction of AD.
- (3)
- The metallic Al recovery rate reached 65% after 10 min of steel ball grinding.
- (4)
- The AlN mass fraction reached approximately 90% after 10 min of steel ball grinding.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahinroosta, M.; Allahverdi, A. A promising green process for synthesis of high purity activated-alumina nanopowder from secondary aluminum dross. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 179, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiridis, P.E. Aluminium salt slag characterization and utilization—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elseknidy, M.; Salmiaton, A.; Shafizah, I.N.; Saad, A. A Study on Mechanical Properties of Concrete Incorporating Aluminum Dross, Fly Ash, and Quarry Dust. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Maghool, F.; Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S. Engineering Characteristics and Environmental Risks of Utilizing Recycled Aluminum Salt Slag and Recycled Concrete as a Sustainable Geomaterial. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-P.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.-Y.; Sun, B.-D.; Li, J.-J.; Chen, C. Process of aluminum dross recycling and life cycle assessment for Al-Si alloys and brown fused alumina. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Forssberg, E. An overview of recovery of metals from slags. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, A.; Singh, K.K. Recovery of valuable products from hazardous aluminum dross: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 130, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H. Evaluation of aluminum dross as raw material for high-alumina refractory. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 12585–12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, B. Microstructure observation of β-sialon-15R ceramics synthesized from aluminum dross. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 3075–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahinroosta, M.; Allahverdi, A. Hazardous aluminum dross characterization and recycling strategies: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Reuter, M.; Boin, U. Aluminium recycling and environmental issues of salt slag treatment. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2005, 40, 1861–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraki, T.; Miki, T.; Nakajima, K.; Matsubae, K.; Nakamura, S.; Nagasaka, T. Thermodynamic Analysis for the Refining Ability of Salt Flux for Aluminum Recycling. Materials 2014, 7, 5543–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Han, Z.; Xiao, X. Effect of rare earth oxides doping on MgAl2O4 spinel obtained by sintering of secondary aluminium dross. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 2597–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H.; Abreu, A.; Molisani, A.L.; de Camargo, A.C.; Portela, J.; Narita, N. Evaluation of aluminum dross waste as raw material for refractories. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.R.; Sahai, Y. Interfacial tension between aluminum alloy and molten salt flux. Mater. Trans. JIM 1997, 38, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudyba, A.; Akhtar, S.; Johansen, I.; Safarian, J. Aluminothermic Reduction of Manganese Oxide from Selected MnO-Containing Slags. Materials 2021, 14, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, M.; Altıner, M.; Top, S.; Karaca, S.; Bouchekrit, C. Production of Alpha-Alumina from Black Aluminum Dross Using NaOH Leaching Followed by Calcination. JOM 2020, 72, 3358–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Q.; Xun, L.; Zhen, S.; Liu, D. The Investigation of Optimizing Leaching Efficiency of Al in Secondary Aluminum Dross via Pretreatment Operations. Processes 2020, 8, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Lu, F.-H. Oxidation behavior of AlN films at high temperature under controlled atmosphere. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 28, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajare, D.; Korjakins, A.; Kazjonovs, J.; Rozenstrauha, I. Pore structure of lightweight clay aggregate incorporate with non-metallic products coming from aluminium scrap recycling industry. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zuo, Z.; Han, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, R. Removal Process and Kinetics of Nitrogen and Chlorine Removal from Black Aluminum Dross. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.-A. Dependence on the distribution of valuable elements and chemical characterizations based on different particle sizes of high alumina fly ash. Fuel 2021, 291, 120225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, C.; Qu, Y.; Wang, H.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y. Hazardous characteristics and transformation mechanism in hydrometallurgical disposing strategy of secondary aluminum dross. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi-Tousi, S.S.; Szpunar, J.A. Mechanism of Corrosion of Activated Aluminum Particles by Hot Water. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 127, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.H.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hashim, N.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J.; Hubadillah, S.K.; Tai, Z.S. Pretreated aluminium dross waste as a source of inexpensive alumina-spinel composite ceramic hollow fibre membrane for pretreatment of oily saline produced water. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.; Misol, A.; Morato, Á.; Rives, V.; Vicente, M.A.; Gil, A. Synthesis of pollucite and analcime zeolites by recovering aluminum from a saline slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorab, H.Y.; Rizk, M.; Matter, A.; Salama, A.A. Characterization and Recycling of Aluminum Slag. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2004, 43, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Lv, H.; Li, R.; Liu, F.; Zhao, H. A new approach to recover the valuable elements in black aluminum dross. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Time | Element | >2 mm | 0.425–2 mm | 0.15–0.425 mm | 0.08–0.15 mm | <0.08 mm | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 min | Al (%) | 2.9 | 15.0 | 11.2 | 6.4 | 1.4 | 36.9 |
| Si (%) | 0.9 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 9.0 | |
| 5 min | Al (%) | 2.0 | 14.3 | 12.1 | 7.6 | 2.2 | 38.2 |
| Si (%) | 0.9 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 8.3 | |
| 10 min | Al (%) | 1.5 | 12.1 | 13.2 | 10.0 | 1.6 | 38.3 |
| Si (%) | 0.4 | 2.9 | 3.0 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 8.2 |
| Time | Element | >2 mm | 0.425–2 mm | 0.15–0.425 mm | 0.08–0.15 mm | <0.08 mm | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 min | Al (%) | 1.3 | 19.4 | 15.2 | 4.2 | 0.3 | 40.4 |
| Si (%) | 0.3 | 3.2 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 8.4 | |
| 5 min | Al (%) | 0.4 | 22.1 | 10.6 | 5.3 | 1.7 | 40.1 |
| Si (%) | 0.5 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 1.1 | 8.6 | |
| 10 min | Al (%) | 0.1 | 16.3 | 12.6 | 6.9 | 2.2 | 38.1 |
| Si (%) | 0.1 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 1.1 | 9 |
| Grinding Time | >2 mm | 0.425–2 mm | 0.15–0.425 mm | 0.08–0.15 mm | <0.08 mm | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 min (%) | 0.30 | 19.91 | 9.96 | 2.61 | 0.59 | 33.37 |
| 5 min (%) | 0.07 | 16.96 | 11.56 | 4.17 | 0.29 | 33.06 |
| 10 min (%) | 0.03 | 14.47 | 13.41 | 4.62 | 0.24 | 32.77 |
| Grinding Time | >2 mm | 0.425–2 mm | 0.15–0.425 mm | 0.08–0.15 mm | <0.08 mm | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 min (%) | 0.01 | 2.11 | 15.26 | 5.66 | 0.49 | 23.53 |
| 5 min (%) | 0.01 | 1.98 | 16.74 | 7.29 | 0.35 | 26.36 |
| 10 min (%) | 0.00 | 1.84 | 18.17 | 7.73 | 0.32 | 28.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Efficient Al Recovery from Aluminum Dross with Simultaneous AlN Separation by a Mechanical Method. Waste 2023, 1, 40-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1010004
Xue Y, Zhang M, Zhou J, Zhang Y. Efficient Al Recovery from Aluminum Dross with Simultaneous AlN Separation by a Mechanical Method. Waste. 2023; 1(1):40-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Yujie, Mingqi Zhang, Jizhi Zhou, and Yufeng Zhang. 2023. "Efficient Al Recovery from Aluminum Dross with Simultaneous AlN Separation by a Mechanical Method" Waste 1, no. 1: 40-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1010004
APA StyleXue, Y., Zhang, M., Zhou, J., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Efficient Al Recovery from Aluminum Dross with Simultaneous AlN Separation by a Mechanical Method. Waste, 1(1), 40-51. https://doi.org/10.3390/waste1010004





