Kv3.1 and Kv3.4, Are Involved in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
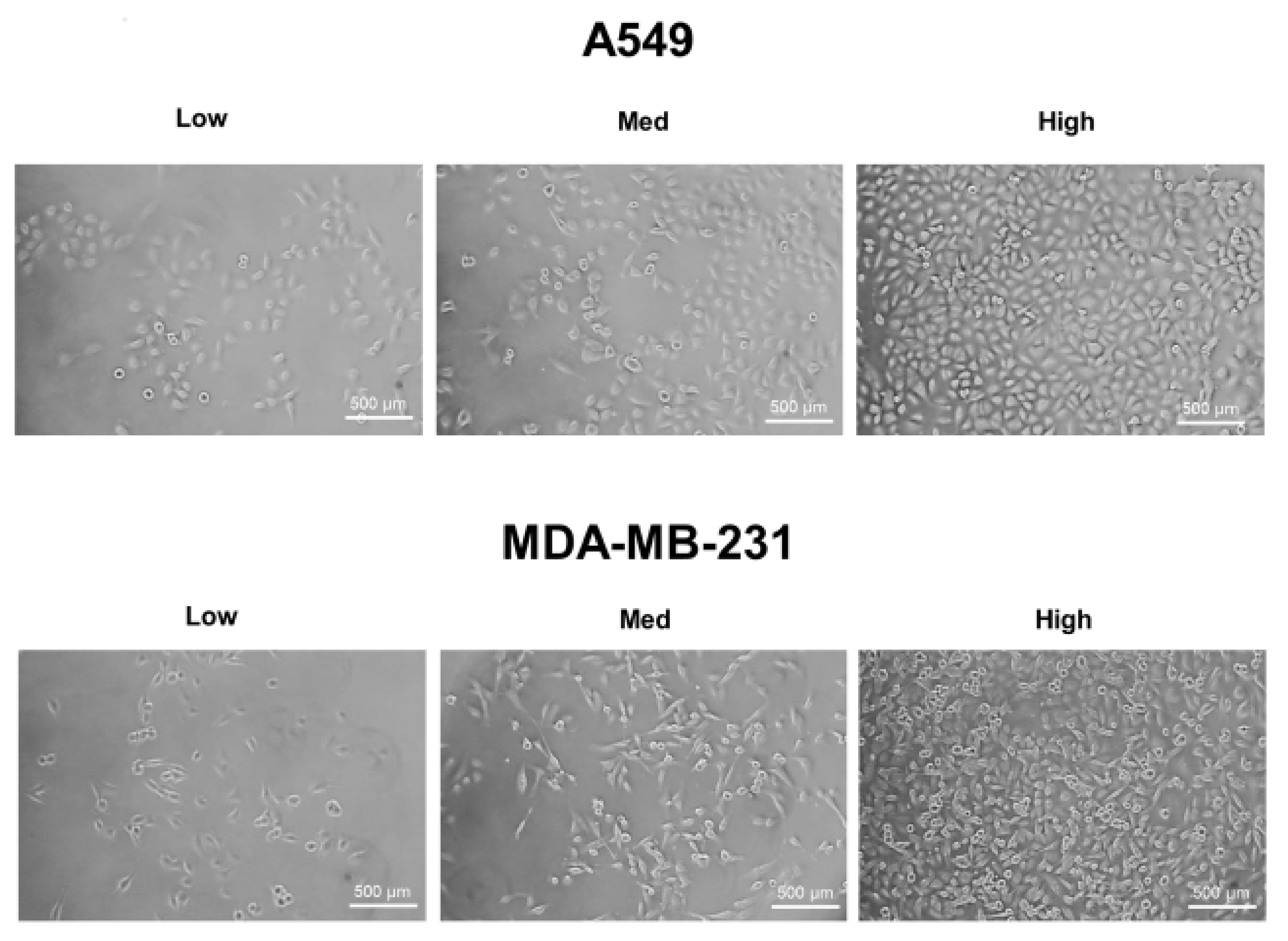
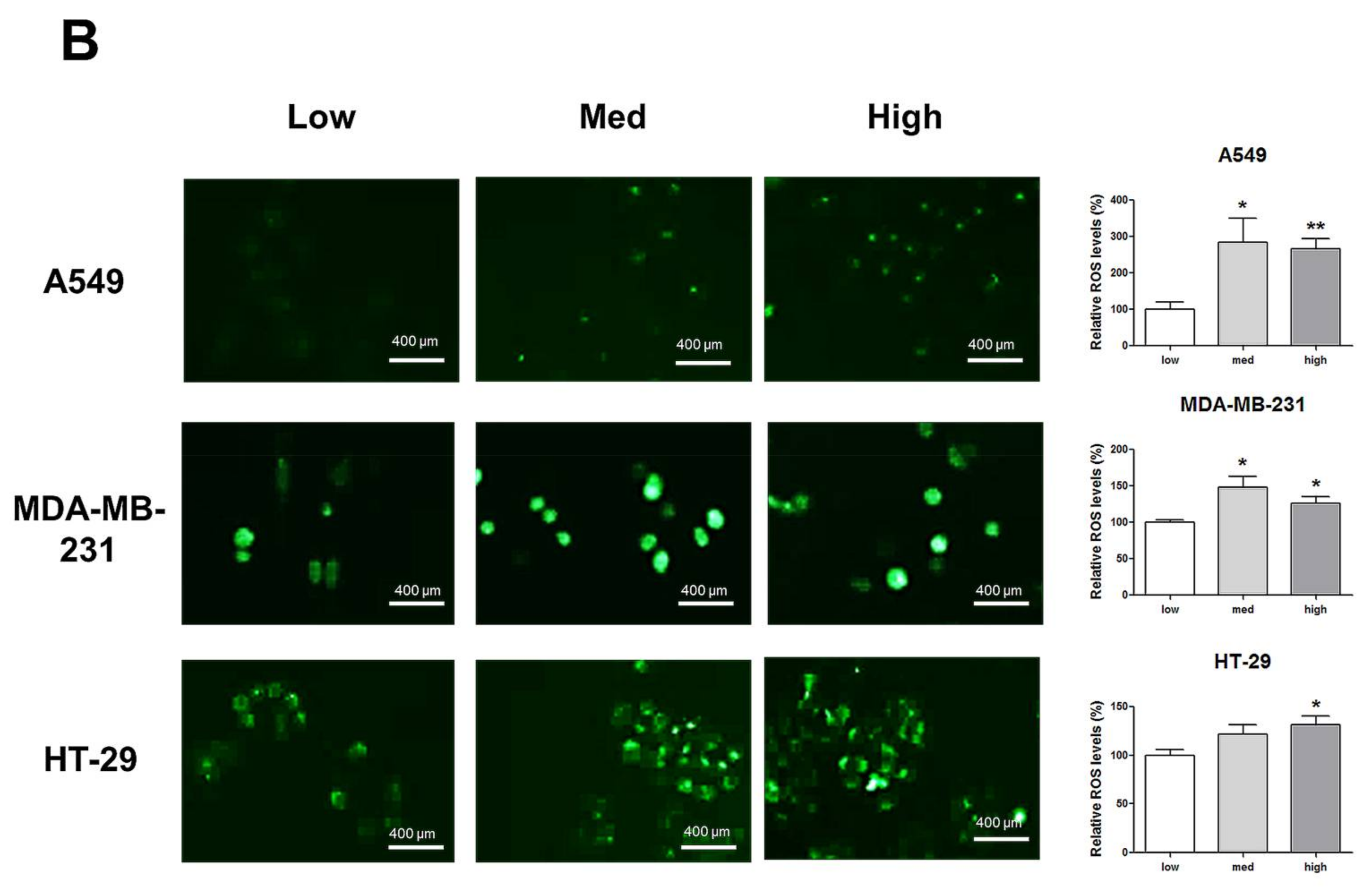
2.1. Increases in HIF-1α and ROS Levels Related to Increased Cell Density
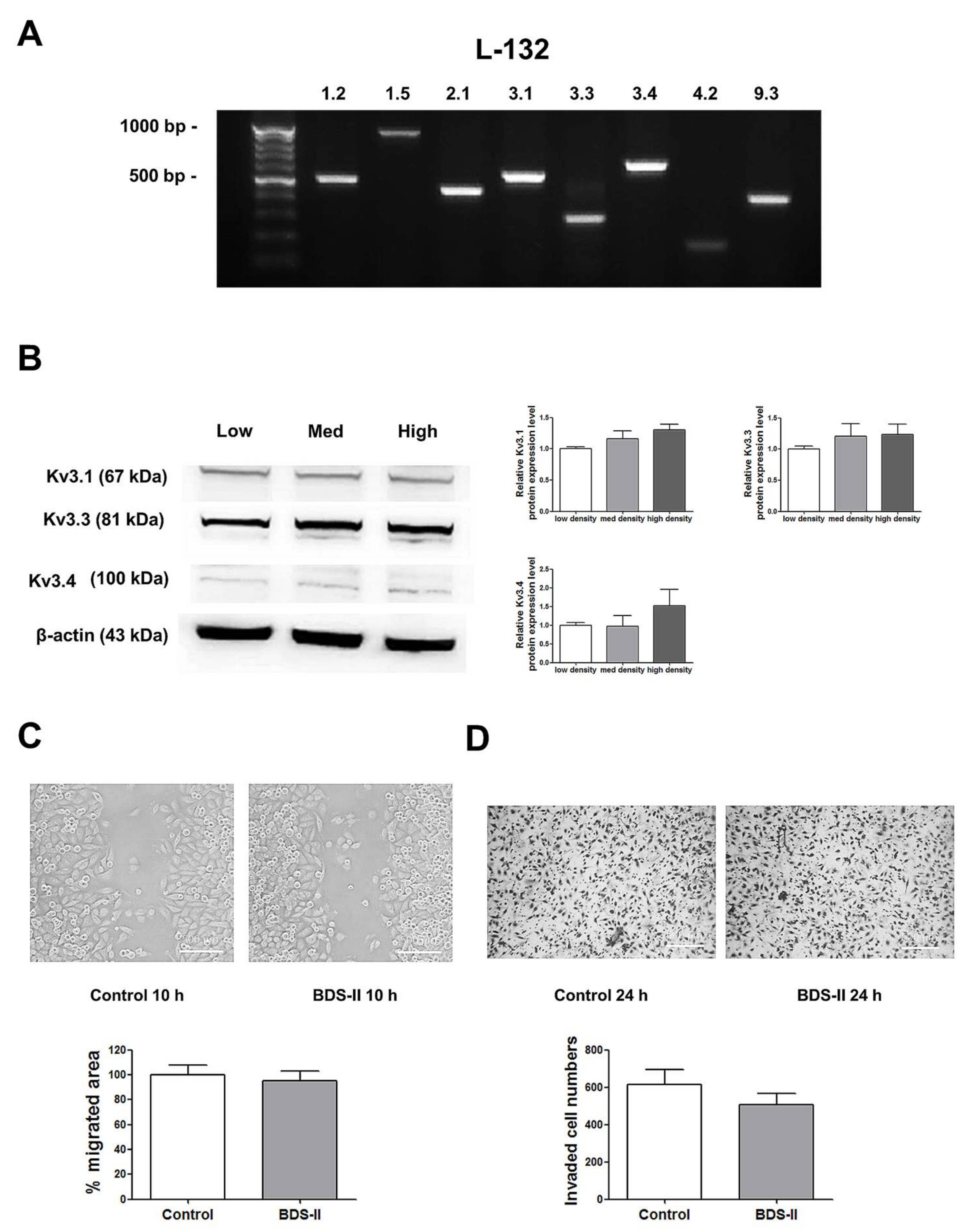
2.2. mRNA and Protein Expression Changes According to Increased Cell Density
2.3. The Effect of BDS-II-Mediated Kv3.1 and Kv3.4 Inhibition on Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion
2.4. Cell Density-Dependent Kv Channel Expression and the Effect of BDS-II on L-132 Cells
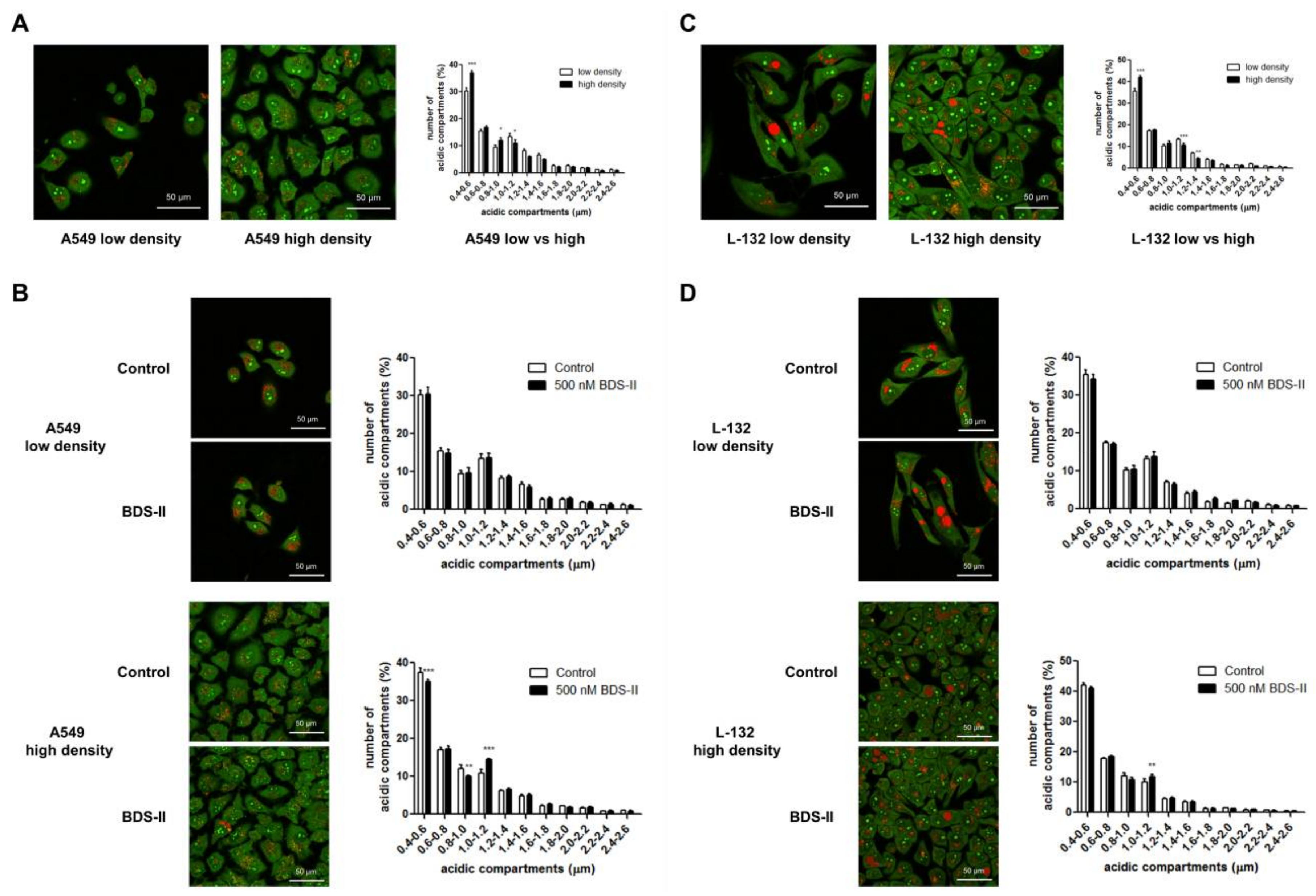
2.5. Cell Density-Dependent Alterations in the Diameter of Acidic Compartments in A549 and L-132 Cells
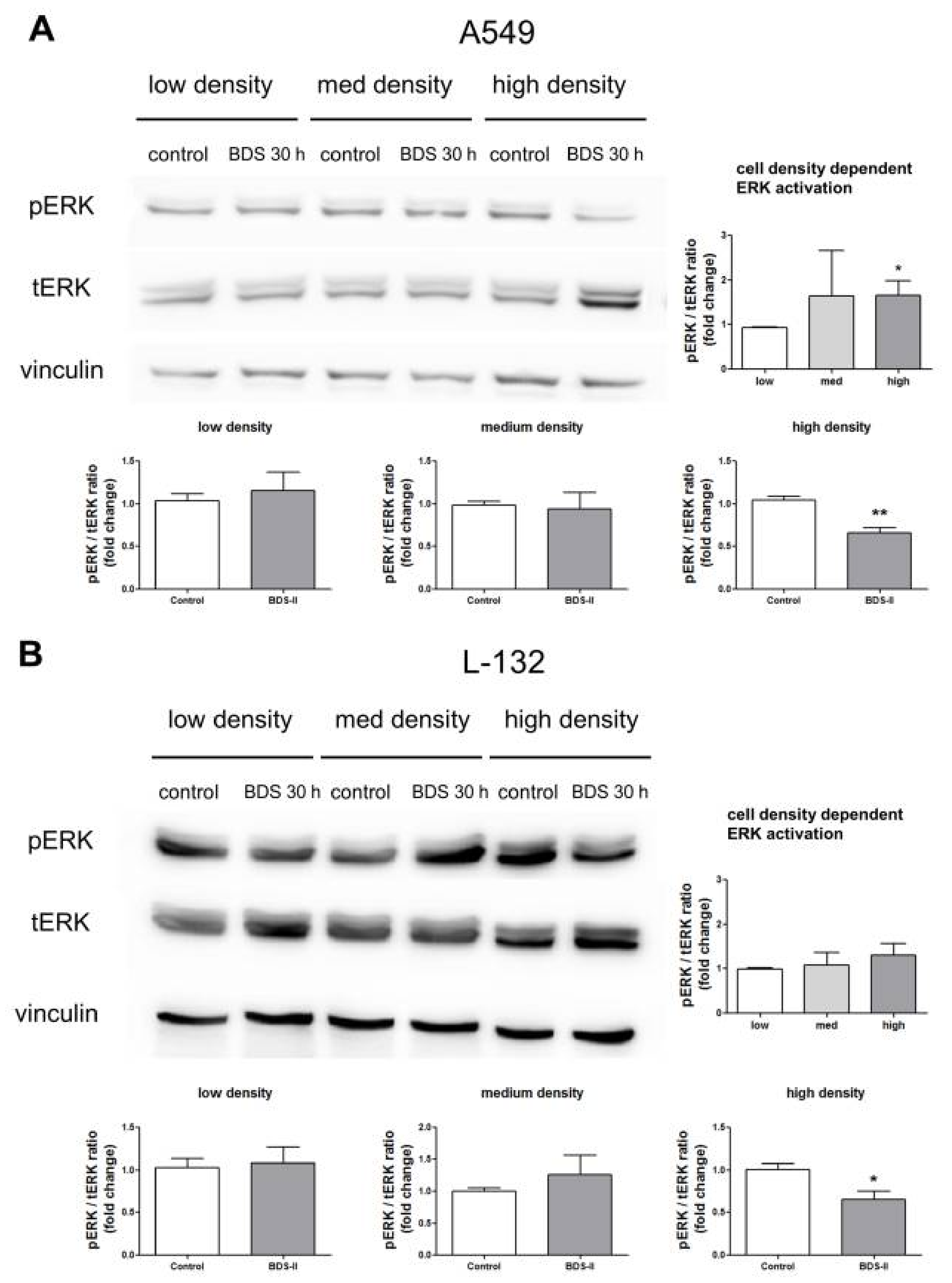
2.6. Effect of BDS-II on ERK Activation According to Increased A549 and L-132 Cell Density
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.3. Western Blotting
4.4. ROS Detection
4.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.6. Cell Migration and Invasion Assay
4.7. Acridine Orange Staining
4.8. siRNA Transfection
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Kv channels | voltage-gated potassium channels |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| BDS | blood depressing substance |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
References
- Spill, F.; Reynolds, D.S.; Kamm, R.D.; Zaman, M.H. Impact of the physical microenvironment on tumor progression and metastasis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 40, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilkes, D.M.; Semenza, G.L.; Wirtz, D. Hypoxia and the extracellular matrix: Drivers of tumour metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockel, M.; Vaupel, P. Tumor hypoxia: Definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Mayer, A.; Hockel, M. Tumor hypoxia and malignant progression. Methods Enzymol. 2004, 381, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.J.; Honore, E. Molecular physiology of oxygen-sensitive potassium channels. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 18, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaccia, A.J.; Simon, M.C.; Johnson, R. The biology of hypoxia: The role of oxygen sensing in development, normal function, and disease. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckler, K.J. A novel oxygen-sensitive potassium current in rat carotid body type I cells. J. Physiol. 1997, 498 Pt 3, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaab, S.; Miguel-Velado, E.; Lopez-Lopez, J.R.; Perez-Garcia, M.T. Down regulation of Kv3.4 channels by chronic hypoxia increases acute oxygen sensitivity in rabbit carotid body. J. Physiol. 2005, 566 Pt 2, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, M.; Gu, X.Q.; Pak, O.; Pamenter, M.E.; Haag, D.; Fuchs, D.B.; Schermuly, R.T.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Brandes, R.P.; Seeger, W.; et al. Hypoxia induces Kv channel current inhibition by increased NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, L.A.; Manalo, D.J.; Sham, J.S.; Semenza, G.L.; Sylvester, J.T. Partial HIF-1α deficiency impairs pulmonary arterial myocyte electrophysiological responses to hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 281, L202–L208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, D.D.; Peng, Y.J.; Manalo, D.J.; Semenza, G.L.; Prabhakar, N.R. Defective carotid body function and impaired ventilatory responses to chronic hypoxia in mice partially deficient for hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Barneo, J.; del Toro, R.; Levitsky, K.L.; Chiara, M.D.; Ortega-Saenz, P. Regulation of oxygen sensing by ion channels. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.A.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5510–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 and tumor progression: Pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaupel, P. The role of hypoxia-induced factors in tumor progression. Oncologist 2004, 9 (Suppl. S5), 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 mediates metabolic responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatrowski, T.P.; Nathan, C.F. Production of large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Storz, P. Reactive oxygen species in tumor progression. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 1881–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, G.Y.; Storz, P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, L.A.; Zanella, C.; Fung, H.; Janssen, Y.M.; Vacek, P.; Charland, C.; Goldberg, J.; Mossman, B.T. Role of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases in apoptosis by asbestos and H2O2. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, L1029–L1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Wong, E.W.; Chang, F.; Lehmann, B.; Terrian, D.M.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A.; et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppersberg, J.P.; Stocker, M.; Pongs, O.; Heinemann, S.H.; Frank, R.; Koenen, M. Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IK(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature 1991, 352, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Jan, L.Y. Targeting potassium channels in cancer. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 206, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, L.A.; Stuhmer, W. The roles of K+ channels in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, F.; Kajiya, H.; Toh, K.; Uchida, S.; Yoshikawa, M.; Sasaki, S.; Kido, M.A.; Tanaka, T.; Okabe, K. Intracellular ClC-3 chloride channels promote bone resorption in vitro through organelle acidification in mouse osteoclasts. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 294, C693–C701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, J.A.; Pollard, J.W. Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, G.; Galeotti, T.; Chiarugi, P. Metastasis: Cancer cell’s escape from oxidative stress. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudy, B.; McBain, C.J. Kv3 channels: Voltage-gated K+ channels designed for high-frequency repetitive firing. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonello, S.; Zahringer, C.; BelAiba, R.S.; Djordjevic, T.; Hess, J.; Michiels, C.; Kietzmann, T.; Gorlach, A. Reactive oxygen species activate the HIF-1α promoter via a functional NFkappaB site. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qutub, A.A.; Popel, A.S. Reactive oxygen species regulate hypoxia-inducible factor 1α differentially in cancer and ischemia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5106–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, T. Oxygen versus Reactive Oxygen in the Regulation of HIF-1α: The Balance Tips. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 436981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, S.; Michelakis, E.D.; Porter, C.J.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Thebaud, B.; Haromy, A.; Harry, G.; Moudgil, R.; McMurtry, M.S.; Weir, E.K.; et al. An abnormal mitochondrial-hypoxia inducible factor-1α-Kv channel pathway disrupts oxygen sensing and triggers pulmonary arterial hypertension in fawn hooded rats: Similarities to human pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 2006, 113, 2630–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsters, P.; Alhamdan, R.; Campbell, B.K. Cell density-mediated pericellular hypoxia and the local dynamic regulation of VEGF-A splice variants in ovine ovarian granulosa cells. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, J.P.; Garcia-Pedrero, J.M.; Suarez, C.; Takes, R.P.; Thompson, L.D.; Slootweg, P.J.; Woolgar, J.A.; Westra, W.H.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Rinaldo, A.; et al. Biomarkers predicting malignant progression of laryngeal epithelial precursor lesions: A systematic review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 269, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, S.T.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Allonca, E.; Garcia-Carracedo, D.; Alvarez-Alija, G.; Casado-Zapico, S.; Fresno, M.F.; Rodriguez, C.; Suarez, C.; Garcia-Pedrero, J.M. Expression and clinical significance of the Kv3.4 potassium channel subunit in the development and progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fais, S.; De Milito, A.; You, H.; Qin, W. Targeting vacuolar H+-ATPases as a new strategy against cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10627–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glunde, K.; Guggino, S.E.; Solaiyappan, M.; Pathak, A.P.; Ichikawa, Y.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Extracellular acidification alters lysosomal trafficking in human breast cancer cells. Neoplasia 2003, 5, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bewick, M.; Lafrenie, R.M. Role of Raf-1 and FAK in cell density-dependent regulation of integrin-dependent activation of MAP kinase. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayne, J.; Sielski, J.; Rizvi, A.; Georges, K.; Hutter, D. ERK regulation upon contact inhibition in fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 286, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Culture Place | Cell Name | Cell Density | Number of Cells | Culture Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-well plate | A549 | low | 2 × 104 | 2~3 days |
| med | 4 × 104 | |||
| high | 1.2 × 105 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | low | 2 × 104 | ||
| med | 4 × 104 | |||
| high | 1.2 × 105 | |||
| HT-29 | low | 5 × 104 | ||
| med | 1.5 × 105 | |||
| high | 5 × 105 | |||
| L-132 | low | 1 × 104 | ||
| med | 4 × 104 | |||
| high | 1.2 × 105 | |||
| 100 mm dish | A549 | low | 2 × 105 | 2~3 days |
| med | 4 × 105 | |||
| high | 1 × 106 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | low | 2 × 105 | ||
| med | 4 × 105 | |||
| high | 1 × 106 | |||
| HT-29 | low | 5 × 105 | ||
| med | 1.5 × 106 | |||
| high | 1 × 107 |
| Subtype | Accession No. | Size (bp) | Primer Sequence (Forward/Reverse) | Annealing (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kv1.2 | L02752 | 513 | 5′-GGGACAGAGTTGGCTGAGAA-3′ | 60 |
| 5′-GGAGGATGGGATCTTTGGAC-3′ | ||||
| Kv1.5 | M55513 | 917 | 5′-TGCGTCATCTGGTTCACCTTCG-3′ | 60 |
| 5′-TGTTCAGCAAGCCTCCCATTCC-3′ | ||||
| Kv2.1 | L02840 | 451 | 5′-GGAAGCCTGCTGTCTTCTTG-3′ | 65 |
| 5′-CTTCATCTGAGAGCCCAAGG-3′ | ||||
| Kv3.1 | S56770 | 550 | 5′-AACCCCATCGTGAACAAGACGG-3′ | 60 |
| 5′-TCATGGTGACCACGGCCCA-3′ | ||||
| Kv3.3 | AF055989 | 284 | 5′-CCTCATCTCCATCACCACCT-3′ | 60 |
| 5′-CGAGATAGAAGGGCAGGATG-3′ | ||||
| Kv3.4 | M64676 | 631 | 5′-TTCAAGCTCACACGCCACTTCG-3′ | 65 |
| 5′-TGCCAAATCCCAAGGTCTGAGG-3′ | ||||
| Kv4.2 | NM_012281.2 | 157 | 5′-GCCTTCTTCTGCTTGGACAC-3′ | 60 |
| 5′-TCATCACCAGCCCAATGTAA-3′ | ||||
| Kv9.3 | AF043472 | 395 | 5′-CTGGGGAAGCTGCTTACTTG-3′ | 60 |
| 5′-CAGATTTTCTTCCGGAGCTG-3′ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, M.S.; Park, S.M.; Park, J.S.; Byun, J.H.; Jin, H.J.; Seo, S.H.; Ryu, P.D.; Lee, S.Y. Kv3.1 and Kv3.4, Are Involved in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041061
Song MS, Park SM, Park JS, Byun JH, Jin HJ, Seo SH, Ryu PD, Lee SY. Kv3.1 and Kv3.4, Are Involved in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041061
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Min Seok, Su Min Park, Jeong Seok Park, Jin Ho Byun, Hee Jung Jin, Seung Hyun Seo, Pan Dong Ryu, and So Yeong Lee. 2018. "Kv3.1 and Kv3.4, Are Involved in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041061
APA StyleSong, M. S., Park, S. M., Park, J. S., Byun, J. H., Jin, H. J., Seo, S. H., Ryu, P. D., & Lee, S. Y. (2018). Kv3.1 and Kv3.4, Are Involved in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041061





