Objective Assessment of Orofacial Muscle Strength: Validation of an Alternative Low-Cost Measurement Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Measurements
2.2. Observational Study
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sandway® Reliability
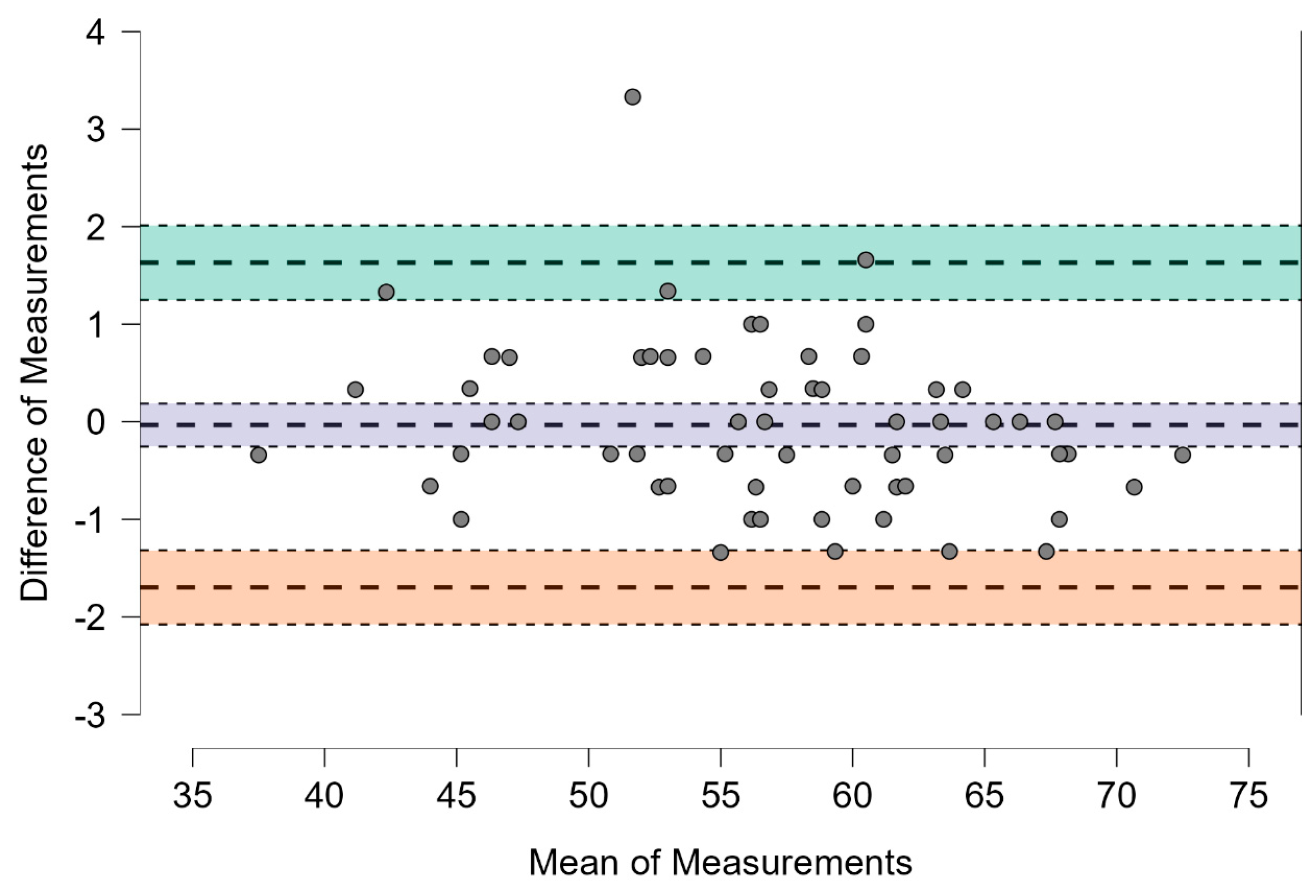
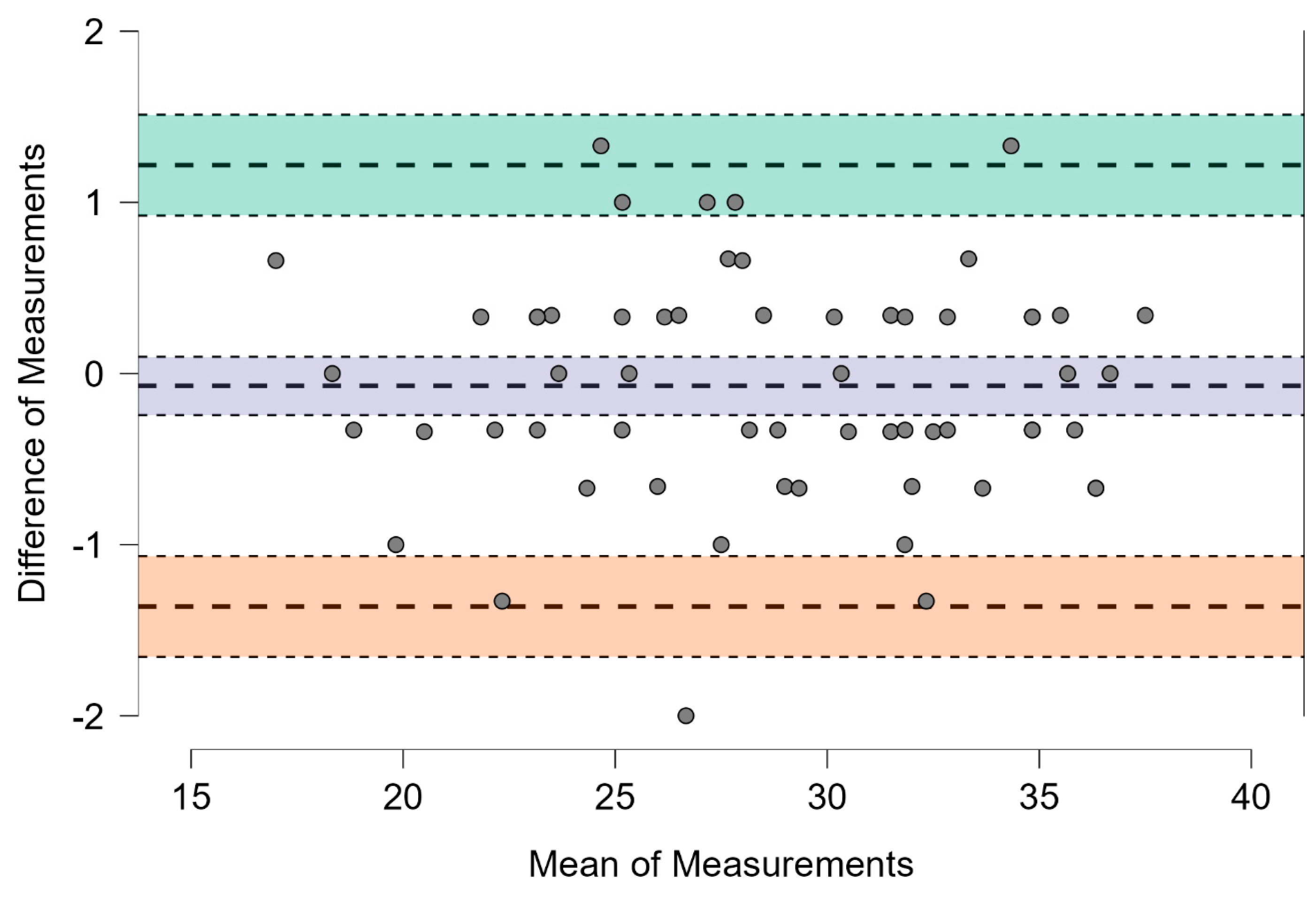
3.2. Level of Agreement Between Sandway® and IOPI®
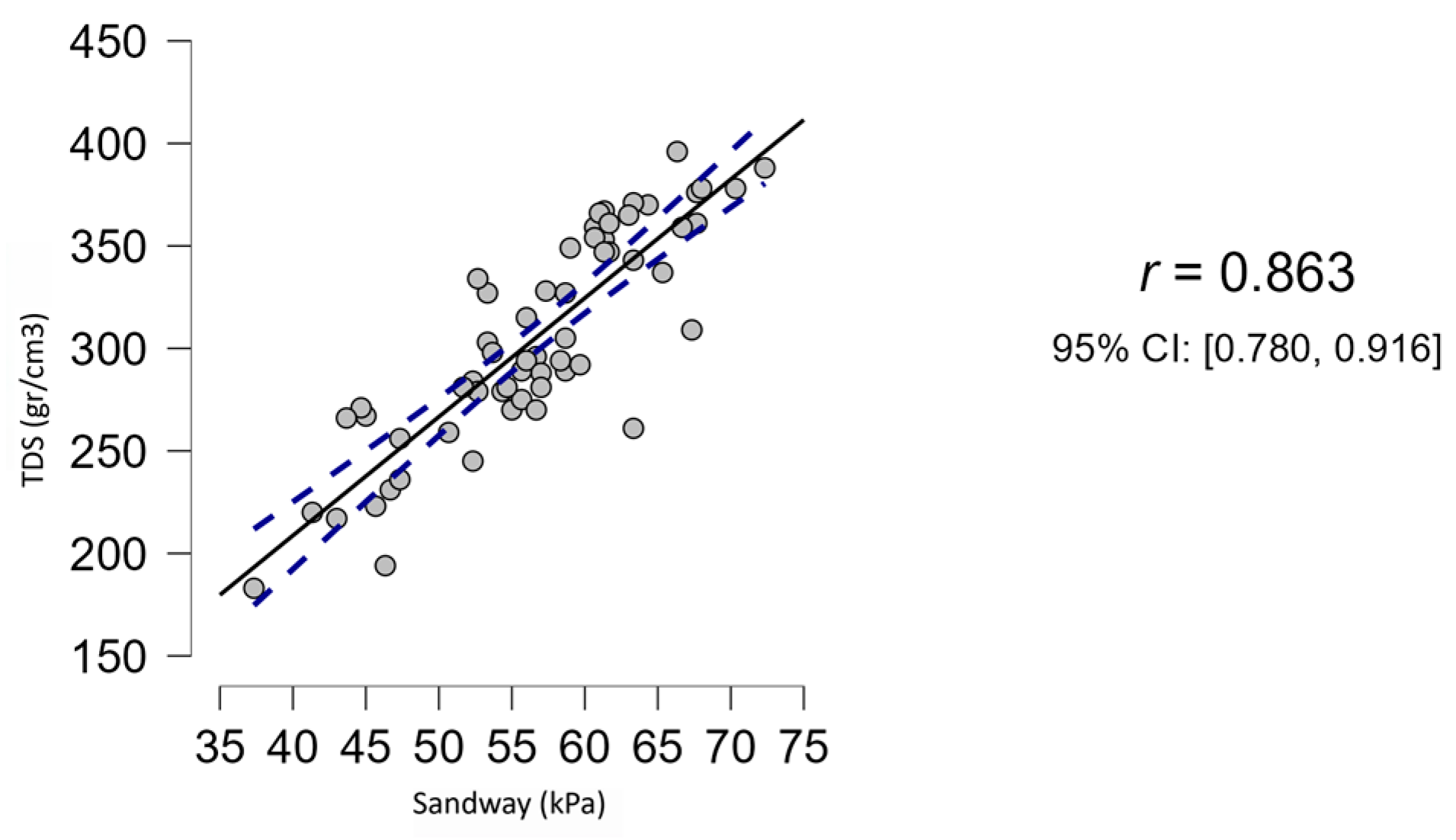
3.3. Correlation Sandway®—Tongue Digital Spoon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjafield, A.V.; Ayas, N.T.; Eastwood, P.R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M.S.M.; Morrell, M.J.; Nunez, C.M.; Patel, S.R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J.-L.; et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: A literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drager, L.F.; Togeiro, S.M.; Polotsky, V.Y.; Lorenzi-Filho, G. Obstructive sleep apnea: A cardiometabolic risk in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 62, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Smith, C.M.; Isaiah, A.; Melendres, M.C.; Mahgerefteh, J.; Lasso-Pirot, A.; Mayo, S.; Gooding, H.; Zachariah, J.; American Heart Association Athero, Hypertension and Obesity in the Young Committee of the Council on Lifelong Congenital Heart Disease and Heart Health in the Young. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease in children and adolescents: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e022427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, C.L.A.; Randerath, W.; Vignatelli, L.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Brill, A.K.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Grote, L.; Jennum, P.; Leys, D.; Minnerup, J.; et al. EAN/ERS/ESO/ESRS statement on the impact of sleep disorders on risk and outcome of stroke. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, D.J.; White, D.P.; Jordan, A.S.; Malhotra, A.; Wellman, A. Defining phenotypic causes of obstructive sleep apnea: Identification of novel therapeutic targets. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, V.; Mathisen, B.; Baines, S.; Lazarus, C.; Callister, R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of measurements of tongue and hand strength and endurance using the Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI). Dysphagia 2013, 28, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.; Martínez, J.M.L.; O’Connor-Reina, C.; Plaza, G. Assessment of muscular tone of the tongue using a digital measure spoon in a healthy population: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shortland, H.A.; Webb, G.; Vertigan, A.; Hewat, S. Speech-language pathologists’ use of myofunctional devices in therapy programs. Perspect. ASHA Spec. Interest Groups 2022, 7, 2012–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.A.; Diaz, C.; Lee, T.; Rameau, A. Validation of a low-cost manometer to assess of tongue, lip, cheek, and respiratory strength: A laboratory-based study. Laryngoscope 2025, 135, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alcalá, L.; Ignacio-García, J.; Serrano Angulo, M.S.; Casado Morente, J.C.; Benjumea Flores, F.; O’Connor-Reina, C. Tongue+ protocol for the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnoea in Quirónsalud Marbella hospital. F1000Research 2022, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Felício, C.M.; Ferreira, C.L.P. Protocol of orofacial myofunctional evaluation with scores. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 72, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljequist, D.; Elfving, B.; Skavberg Roaldsen, K. Intraclass correlation—A discussion and demonstration of basic features. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Pérez, J.A.; Pérez Martin, P.S. Coeficiente de correlación intraclase [Intraclass correlation coefficient]. Semergen 2023, 49, 101907. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A.; Mesarwi, O.; Pepin, J.L.; Owens, R.L. Endotypes and phenotypes in obstructive sleep apnea. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2020, 26, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, M.; Owens, R.L.; Schmickl, C.N.; Malhotra, A. Precision medicine for obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. Clin. 2019, 14, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, E.J.; Conti, D.M.; Gozal, D.; O’Connor-Reina, C. Preventive medicine in obstructive sleep apnea-–a systematic review and a call to action. Sleep 2024, 47, zsae164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Sullivan, S.S.; Huang, Y.S. Sleep-disordered breathing, orofacial growth, and prevention of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Med. Clin. 2019, 14, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Felício, C.M.; da Silva Dias, F.V.; Trawitzki, L.V.V. Obstructive sleep apnea: Focus on myofunctional therapy. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2018, 10, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botzer, E.; Quinzi, V.; Salvati, S.E.; Paskay, L.C.; Saccomanno, S. Myofunctional therapy Part 3: Tongue function and breastfeeding as precursor of oronasal functions. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2021, 22, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, N.L.; Short, R. Maximal tongue strength in typically developing children and adolescents. Dysphagia 2009, 24, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOPI Medical. Qualitative Guidelines for Interpreting Tongue Elevation Strength (Pmax). IOPI Normal Values. 2025. Available online: https://iopimedical.com/normal-values/ (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor-Reina, C.; Plaza, G.; Garcia-Iriarte, M.T.; Ignacio-Garcia, J.M.; Baptista, P.; Casado-Morente, J.C.; De Vicente, E. Tongue peak pressure: A tool to aid in the identification of obstruction sites in patients with obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, C.d.C.; Weber, S.A.T.; Evangelisti, M.; Villa, M.P. The short evaluation of orofacial myofunctional protocol (ShOM) and the sleep clinical record in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 137, 110240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakke, M.; Bergendal, B.; McAllister, A.; Sjögreen, L.; Asten, P. Development and evaluation of a comprehensive screening for orofacial dysfunction. Swed. Dent. J. 2007, 31, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villa, M.P.; Evangelisti, M.; Martella, S.; Barreto, M.; Del Pozzo, M. Can myofunctional therapy increase tongue tone and reduce symptoms in children with sleep-disordered breathing? Sleep Breath. 2017, 21, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieto, V.; Kayamori, F.; Montes, M.I.; Hirata, R.P.; Gregório, M.G.; Alencar, A.M.; Drager, L.F.; Genta, P.R.; Lorenzi-Filho, G. Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on snoring: A randomized trial. Chest 2015, 148, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, K.C.; Drager, L.F.; Genta, P.R.; Marcondes, B.F.; Lorenzi-Filho, G. Effects of oropharyngeal exercises on patients with moderate obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koka, V.; De Vito, A.; Roisman, G.; Petitjean, M.; Filograna Pignatelli, G.R.; Padovani, D.; Randerath, W. Orofacial myofunctional therapy in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: A pathophysiological perspective. Medicina 2021, 57, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.P.; Brasili, L.; Ferretti, A.; Vitelli, O.; Rabasco, J.; Mazzotta, A.R.; Pietropaoli, N.; Martella, S. Oropharyngeal exercises to reduce symptoms of OSA after AT. Sleep Breath. 2015, 19, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.; Martínez, J.M.L.; Baptista, P.; Ríos Fernández, R.; Javier Gómez, F.; Parejo Santaella, J.; Plaza, G. Sensorimotor tongue evaluation and rehabilitation in patients with sleep-disordered breathing: A novel approach. J. Oral Rehabil. 2021, 48, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciotti, R.; Di Maria, E.; D’Attilio, M.; Aprile, G.; Cosentino, F.G.; Perrotti, V. Quantitative Measurement of Swallowing Performance Using Iowa Oral Performance Instrument: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.C. Effects of Effortful Swallowing Exercise with Progressive Anterior Tongue Press Using Iowa Oral Performance Instrument (IOPI) on the Strength of Swallowing-Related Muscles in the Elderly: A Preliminary Study. Dysphagia 2022, 37, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitts, L.L.; Cox, A.; Morales, S.; Tiffany, H. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Iowa Oral Performance Instrument Measures in Persons with Parkinson’s Disease Compared to Healthy Adults. Dysphagia 2022, 37, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.A.; Mocchetti, V.; Rameau, A. Concurrent Validity of the IOPI and Tongueometer Orofacial Strength Measurement Devices. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 3123–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
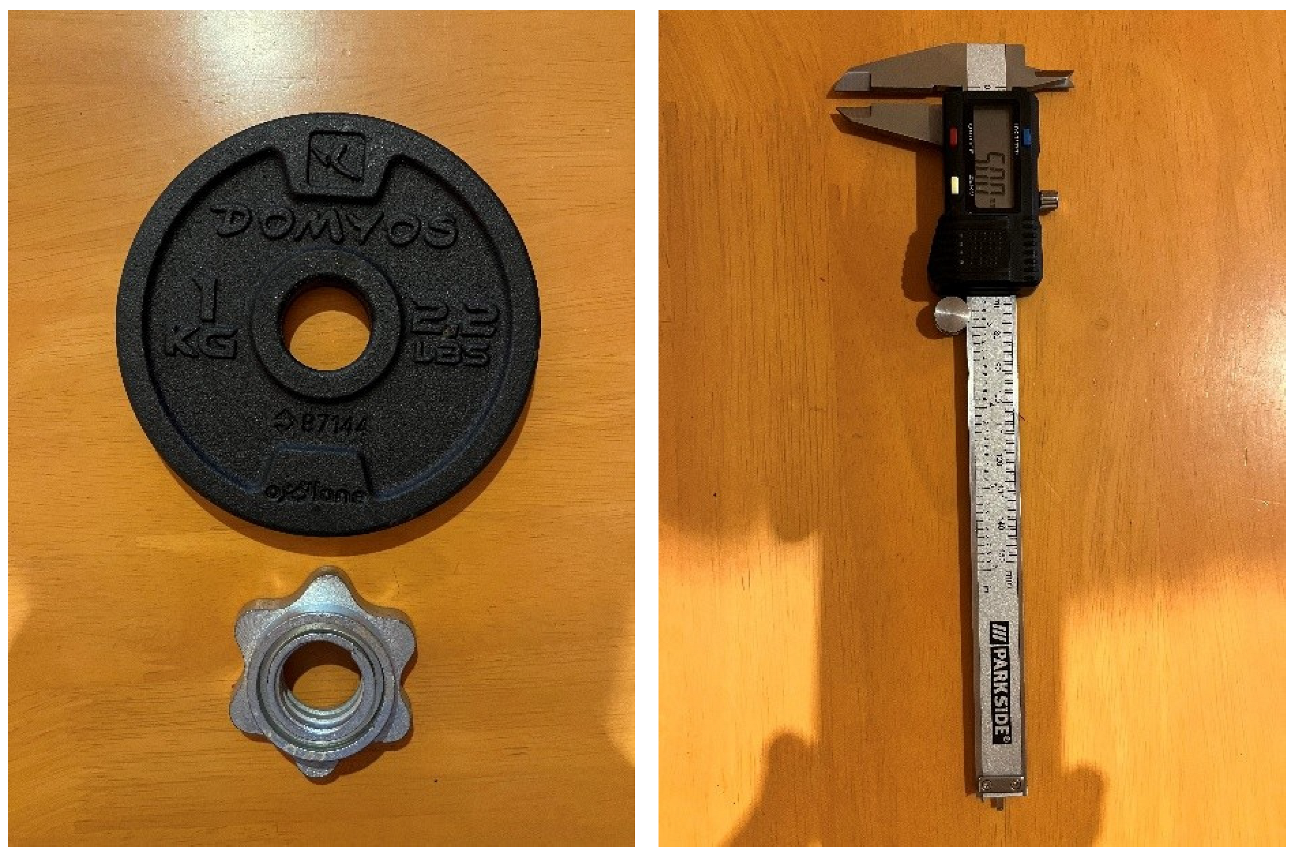

| IOPI vs. Sandway Measurements | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model: Digital Calliper | |||
| Measurement (kPa) | |||
| Sample | Pressure Applied in mm | IOPI | Sandway |
| 1 | 9 | 5 | 5.33 |
| 2 | 8 | 9 | 9.12 |
| 3 | 7 | 14 | 14.15 |
| 4 | 6 | 21 | 21.09 |
| 5 | 5 | 29 | 29.63 |
| 6 | 4 | 39 | 39.85 |
| 7 | 3 | 52 | 52.58 |
| 8 | 2 | 66 | 66.95 |
| Model: Weight Plate | |||
| Measurement (kPa) | |||
| Sample | Plate | IOPI | Sandway |
| 1 | Screw | 8 | 8.05 |
| 2 | 1kg | 25 | 25.6 |
| 3 | 2kg | 41 | 41.53 |
| 4 | 3kg | 58 | 58.24 |
| 5 | 4kg | 64 | 64.63 |
| Age | |
| Mean | 46.05 |
| SD | 16.67 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 35 (58.33%) |
| Female | 25 (41.67%) |
| BMI | n (%) |
| Normal | 15 (25%) |
| Overweight | 17 (28.34%) |
| Obesity Type 1 | 18 (30%) |
| Obesity Type 2 | 8 (13.33%) |
| Obesity Type 3 | 2 (3.33%) |
| AHI | n (%) |
| Moderate | 35 (58.33%) |
| Severe | 25 (41.67%) |
| Sandway® Intraclass Correlation 3,1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Point Estimate | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI |
| ICC 3,1 | 0.978 | 0.967 | 0.986 |
| Sandway®—IOPI® Tongue | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bias and Limits | Point Value | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI |
| Mean difference + 1.96 SD | 1.631 | 1.251 | 2.011 |
| Mean difference | −0.034 | −0.253 | 0.186 |
| Mean difference − 1.96 SD | −1.698 | −2.078 | −1.318 |
| Sandway®—IOPI® Lips | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bias and Limits | Point Value | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI |
| Mean difference + 1.96 SD | 1.217 | 0.923 | 1.512 |
| Mean difference | −0.072 | −0.242 | 0.098 |
| Mean difference − 1.96 SD | – | −1.656 | −1.067 |
| Pearson’s Correlation Analysis - Sandway® and Tongue Digital Spoon | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson’s r | p Value | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | |
| Sandway® - TDS | 0.863 | <0.001 | 0.780 | 0.916 |
| Shapiro - Wilk Test for Multivariate Normality | 0.962 | p = 0.024 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Association of Orofacial Myology (IAOM). Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Correa, E.J.; Curtis, J.; Rodriguez Alcalá, L.; Ibañez-Rodriguez, J.A.; Morato-Galán, M.; Folha, G.A.; Alcalá, C.R.; García Iriarte, M.T.; Plaza, G.; O'Connor-Reina, C. Objective Assessment of Orofacial Muscle Strength: Validation of an Alternative Low-Cost Measurement Device. Int. J. Orofac. Myol. Myofunct. Ther. 2025, 51, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijom51020009
Correa EJ, Curtis J, Rodriguez Alcalá L, Ibañez-Rodriguez JA, Morato-Galán M, Folha GA, Alcalá CR, García Iriarte MT, Plaza G, O'Connor-Reina C. Objective Assessment of Orofacial Muscle Strength: Validation of an Alternative Low-Cost Measurement Device. International Journal of Orofacial Myology and Myofunctional Therapy. 2025; 51(2):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijom51020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorrea, Eduardo J., James Curtis, Laura Rodriguez Alcalá, Juan Antonio Ibañez-Rodriguez, Marta Morato-Galán, Gislaine Aparecida Folha, Cristina Rodriguez Alcalá, María Teresa García Iriarte, Guillermo Plaza, and Carlos O'Connor-Reina. 2025. "Objective Assessment of Orofacial Muscle Strength: Validation of an Alternative Low-Cost Measurement Device" International Journal of Orofacial Myology and Myofunctional Therapy 51, no. 2: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijom51020009
APA StyleCorrea, E. J., Curtis, J., Rodriguez Alcalá, L., Ibañez-Rodriguez, J. A., Morato-Galán, M., Folha, G. A., Alcalá, C. R., García Iriarte, M. T., Plaza, G., & O'Connor-Reina, C. (2025). Objective Assessment of Orofacial Muscle Strength: Validation of an Alternative Low-Cost Measurement Device. International Journal of Orofacial Myology and Myofunctional Therapy, 51(2), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijom51020009








