Abstract
The purpose of the present study was to investigate the relationship between multidirectional lip closing force and the three-dimensional morphology of perioral soft tissue in adults. Twenty-three Japanese adults with straight facial profiles participated in this study. The signals of directional lip closing force (DLCF) were investigated in 8 directions. Three-dimensional morphology of perioral soft tissue was recorded using a 30 surface-imaging device. Correlations between lip-closing force and the three-dimensional morphology of the perioral soft tissue were analyzed statistically. Upper lip-closing force significantly correlated with the anteroposterior, vertical, transverse morphology of the upper lip, while lower lip-closing force did not correlate with the anteroposterior, vertical, or transverse morphology of the lower lip. In adults with straight facial profiles, associations were found between upper lip-closing force and upper lip morphology. There were no associations between lower lip-closing force and lower lip morphology.
INTRODUCTION
Lip function has been thought to be one of the chief factors in determining tooth position (Brodie, 1953; Posen, 1972; Proffit, 1975; Posen, 1976). A child with a missing lower lip has been reported to exhibit severely proclined lower incisors (Safeena, Najmuddin & Reddy, 2012). As a result of orthodontic treatment, when the lower lip is distracted by the lip bumper, the labial incisor is proclined due to unopposed tongue pressure (Davidovitch, Mcinnis & Lindauer, 1997). Mandibular proclined incisors have been shown to easily relapse, probably due to lip function (Mills, 1966; Artun, Krogstad & Little, 1990). Thus, assessing lip function is significant for diagnosis, treatment planning, and increased stability of post treatment orthodontic results.
Lip-closing force measurement has been shown to be preferable among several lip function measurements because it can be simply and easily implemented (Jung, Yang & Nahm, 2003). Regarding the relationship between lip-closing force and dental characteristics, the lip-closing force of the upper lip has been reported to have a strong influence on maxillary incisor angulation (Posen, 1976; Thuer & Ingervall, 1986; Yamaguchi, Morimoto, Nanda, Ghosh & Tanne, 2000; Jung et al., 2003; Jung, Yang & Nahm, 2010). However, there is little information as to what characteristics of craniofacial morphology are associated with the lip-closing force. The values for maximum lip-closing force have been shown to have a relationship with the vertical skeletal pattern and lip protrusion in Class II subjects (Jung et al., 2010), while the horizontal skeletal pattern or the degree of maxillary protrusion have not been found to be significantly related to upper lip-closing force (Jung et al., 2003). Even when variations in subjects and measurement methods are taken into account, there has been no agreement on the association between lip-closing force and craniofacial morphology. To understand the relationships between the lip-closing force and craniofacial morphology, the authors believe it is indispensable to examine the association between lip-closing force and the characteristics of the regional perioral structures, particularly soft tissue, rather than examining associations between lip-closing force and overall craniofacial structure.
When the lips close, many muscle fascicles with various directions are involved (Rogers, Mooney, Smith, Weinberg, Waller, Parr, Docherty, Bonar, Reinholt, Deleyiannis, Siegel, Marazita & Burrows, 2009), Recently, a multidirectional lip-closing force measurement device has been developed which allows the direction of lip-closing force to be evaluated (Nakatsuka, Adachi, Kato, Oishi, Murakami, Okada & Masuda, 2011). Concerning the relationship between lip-closing force and lip morphology, a weak correlation between lip closing force and lower labial ratio (Ooishi, Adachi, Yasutomi, Nakatsuka, Yamada & Masuda, 20111) has been shown, and, when mandibular deviation is greater, the upper deviated lip-closing force has been shown to be smaller (Kawabata, Kobayashi, Takagi, Kuroyanagi, Washino, Sabashi & Kitai, 2013). However, no study of the relationship between multidirectional lip-closing force and three dimensional morphology of perioral soft tissue structure has been reported. Evaluating the relationship between multidirectional lip-closing force and the three-dimensional morphology of perioral structures would seem to be contributory to understanding orofacial muscle activity.
The purpose of the present study was to investigate the relationship between multidirectional lip-closing force and the three-dimensional morphology of perioral soft tissue in adults.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
- Subjects
Twenty-three Japanese adults with straight facial profiles (Proffit, Fields & Sarver, 2007) and without mandibular deviation participated in this study (13 males, 10 females; ages 22 years 6 months to 35 years 8 months). Subjects had good general and oral health and no history of orthodontic treatment, facial injury, or facial surgery. The subjects gave consent to participate after receiving a full explanation of the aim and design of the study. The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Asahi University Graduate School of Dentistry (No. 23118).
- Recording method
Directional lip-closing force (DLCF) was recorded using a multidirectional lip-closing force measurement device (PROCEED, Nagano, Japan) (Figure 1). The measurement device consists of a fixed stand with two handgrips, a measurement probe, and a head fastening arrangement. The measurement probe and the head-fastening arrangement are adjustable vertically to fit the position of the subject’s lips and head. The measurement probe is composed of 8 phosphor-bronze plates (height 2 mm, width 5 mm, depth 100 mm) with strain gauges. The 5 mm side of the plates is arranged in an octagonal shape. The probe is surrounded by the columnar plastic tube, which is replaced with a new tube for each subject. For this study, each subject was seated with the head fixed using ear rods and with the Camper plane parallel to the floor. With the probe held within the oral vestibule without tooth contact, the subject was instructed to position the tip of probe as close to the anterior teeth as possible and to purse the lips as firmly as possible. Each set consisted of three trials of 5 seconds each. The interval between each trial within a set was 5 seconds. Each set of measurements was repeated three times with 1 minute breaks to avoid muscle fatigue. Utilizing a 3D surface-imaging device (3dMDcranial System, 3dMD, USA), 3D images of the face at rest were recorded with the subject in a seated natural head position with the teeth in light occlusal contact (Figure 2).
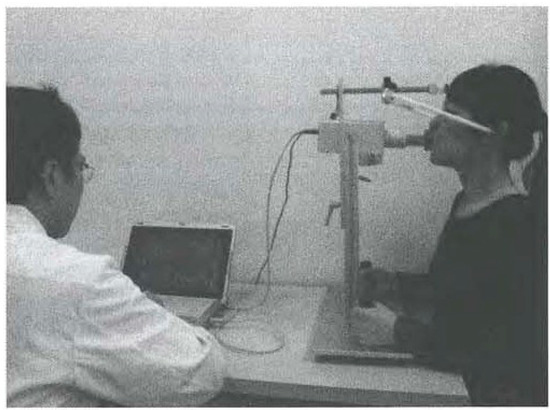
Figure 1.
Full view of device for measuring lip-closing force (a multidirectional lip closing force measurement system, PROCEED, Nagano, Japan).
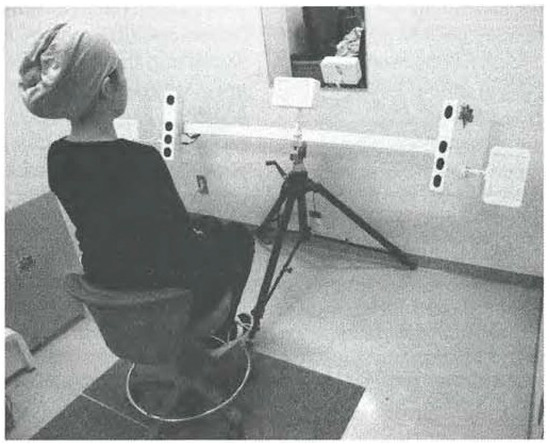
Figure 2.
3D surface-imaging device (3dMDcranial System, 3dMD, USA).
- Data analysesLip-closing force
The DLCF signals were analyzed in eight directions (Figure 3) using a personal computer (CF..f10, Panasonic Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The DLCF in each direction was assessed in terms of the impulse (Nxs) in physics. The impulse was calculated between 1 second and 4 seconds after the onset of measurement. The mean value for the DLCFs obtained from nine recordings (3 trialsx 3 sets) was defined as a representative value for each subject. The eight directions of the DLCFs are defined as: upper, upper-right, right, lower right, lower, lower-left, left, upper-left. Total upper lip-closing force was calculated by adding upper, upper-right, and upper-left DLCFs. Total lower lip-closing force was calculated by adding lower, lower-right, and lower-left DLCFs.
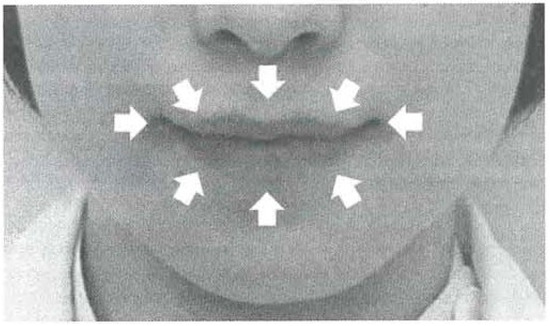
Figure 3.
The direction of directional lip-closing force (DLCF).
In horizontal directions, the weakest and the least stable forces were always recorded by the system, suggesting the relatively poor reliability of the measurements obtained similarly in the previous study (Nakatsuka et al., 2011; Murakami, Adachi, Nakatsuka Kato Oishi & Masuda, 2012). Accordingly, the data o closing-force in horizontal directions were excluded from analysis in this report.
- Three-dimensional image of the soft tissue around the lip
Three-dimensional image data were transferred to a personal computer (HP 221O CMT Workstation, Hewlett-Packard Japan, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Several anatomical landmark positions were identified on the axial coronal, and sagittal slices using image-analyzing software (3D-Rugle, Medic Engineering, Kyoto, Japan).
Definitions of reference points are shown in Table 1 and Figure 4. The reference planes were determined using the reference points. Mid-sagittal plane (MSP) was defined as a plane through ebm, enm, and aim. Axial plane (AP) was defined as a plane parallel to the straight line through trI, and orI which is perpendicular to the MSP. Frontal plane (FP) was defined as a plane through enm perpendicular to the AP and the MSP.

Table 1.
Definitions of reference points.
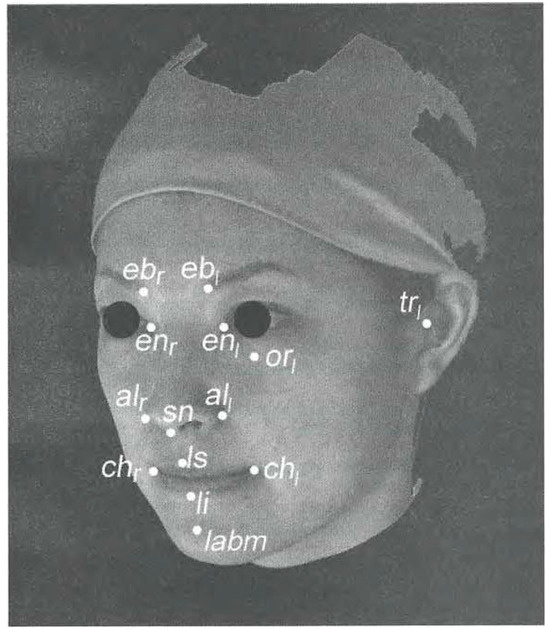
Figure 4.
Reference points of the perioral soft tissue (ebr: Eyebrow right; ebI: Eyebrow left; enr: Entocanthion right; enI: Entocanthion left; air: Alare right; all: Alare left; sn: Subnasale; orI: Orbitale left; trI: Tragion left; chr: Cheilion right; chI: Cheilion left; ls: Labral superiors; li: Labral inferiors; lamb: Labiodental).
Regarding the coordinates system used for the measurements, enm was designated as the original point The X-axis was defined as a line with lateral direction, the Y-axis as a line with vertical direction, and Z-axis as a line with anteroposterior direction. If the point of measurement was leftward or upward or forward from the original point, the value was defined as positive. The definitions of 30 soft tissue variables around the lip are shown in Table 2, Figure 5, and Figure 6.

Table 2.
Definitions of craniofacial variables.
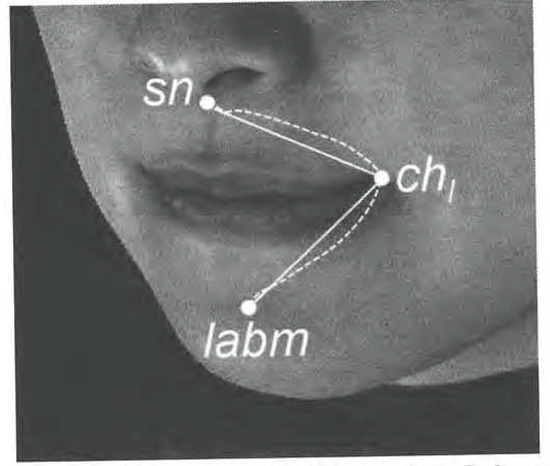
Figure 5.
Linear variables for perioral soft tissue (sn: Subnasale; ch1: Cheilion left; lamb: Labiodental).
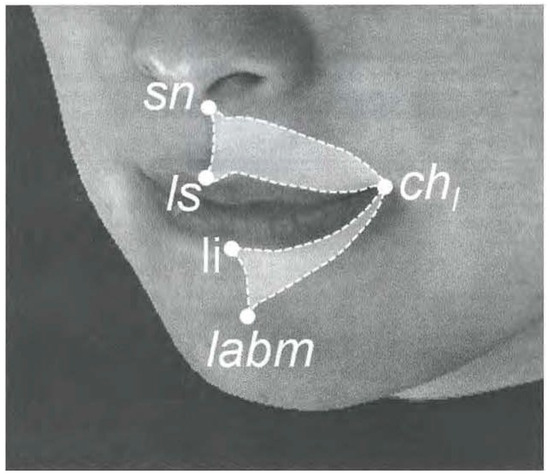
Figure 6.
Area variables for perioral soft tissue (sn: Subnasale; ls: Labral superiors; li: Labral inferiors; chI: Cheilion left; lamb: Labiodental).
- Statistical analysis
Spearman rank correlation coefficients of upper and lower lip-closing force with lip width height, and depth were calculated. Spearman’ rank correlation coefficients were calculated between the upper-right DLCF and upper-right lip variables, between the lower-right DLCF and tower-right lip variables, between the upper-left DLCF and upper left lip variables, and between the lower-left DLCF and lower left lip variables. The level of significance p < 0.05 was chosen for all tests. Analyses were performed using statistical software (SPSS 14.0, IBM, NY, USA).
RESULTS
Medians, minima, and maxima for DLCFs are shown in Table 3. Table 4 shows medians, minima, and maxima for each lip variable.

Table 3.
Directional lip-closing force (DLCF).

Table 4.
Measurement variables of craniofacial morphology.
Correlation coefficients between DLCFs and lip variables are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Correlation coefficients between DLCFs and lip variables.
Total upper lip-closing force showed significant positive correlation with upper lip width, upper lip height, and upper lip depth (p < 0.01). Total lower lip-closing force did not exhibit significant correlation with lower lip width, lower lip height, or lower lip depth.
Upper-right DLCFs significantly correlated with the upper right lip base length, upper right lip surface length, and upper right lip surface area (p < 0.01). Lower-right DLCFs did not exhibit significant differences with the lower right lip base length, lower right lip surface length, or lower right lip surface area.
Upper-left DLCFs significantly correlated with the upper left lip base length, upper left lip surface length, and upper left lip surface area (p < 0.01). Lower-left DLCFs did not exhibit significant differences with the lower left lip base length, lower left lip surface length, or lower left lip surface area.
DISCUSSION
The multidirectional lip-closing force measurement device utilized in the present study allows evaluation of lip-closing force in 8 directions, upper, upper-right, right, lower-right, lower, lower-left, left, upper-left. This system affords reasonably good quality and reliability for quantitative measurements of lip-closing force in the previous study (Nakatsuka et al., 2011).
To investigate the association between regional lip morphology and lip-closing force, it is necessary to determine where the lip begins and ends. The superficial lip is comprised of the Vermillion, the skin above the vermilion border and below the nares, and the skin below the vermilion border and above the labiomental sulcus (Rogers et al., 2009). The skin around the vermillion can be described as consisting of horizontal, oblique, and longitudinal fiber bands, whereas the vermillion can be described as having only horizontal fiber bands (Rogers et al., 2009). The vermillion, which functions to press the lip to the maxillary teeth or invert it closer to the oral cavity, does not participate directly in pursing type lip-closure (Ooishi et al., 2011). Therefore, only the skin around the vermillion was analyzed.
In the present study, the total upper lip-closing force correlated with the anteroposterior, vertical, transverse linear measurement of the upper lip, whereas the total lower lip-closing force did not correlate with the anteroposterior, vertical, transverse linear measurement of the lower lip. In a previous study, no correlation was found between lip-closing force and upper lip morphology, whereas lip-closing force did correlate with lower lip morphology (Maeda, Ooshima, Saitoh, Kawashima, Hayashi, Aoki. Yamaguchi & Kasai, 2009). The difference in those results from those of the present report may be due in part to use of a different device and different measuring variables. The previous device measured reciprocal compression of the lips, which seems to include the function of the masticatory muscles. The subjects close their mouths from the mouth opening position during compressing the lips together because the previous device is large. Accordingly, lip closing force including masticatory muscle function is considered to reflect the lower lip morphology. The measuring variables in the previous study include the vermillion, which does not seem to be related to the pursing-like lip closure task (Rogers et al., 2009). In an another earlier study using the same device as in the present report, no correlation was found between lip-closing force and the upper labial ratio, whereas lip-closing force did correlate with the lower labial ratio. The upper or lower labial ratio, used in the previous study, is the ratio of the upper or lower lip height to lower face height, respectively. The values of the variables are influenced by lower face height, i.e., mental height. Accordingly, the previous study could be thought to investigate the fact that mandibular overall structures seem to have a relationship to lip-closing force.
When the lip-closing force is evaluated separately on right and left sides, similar results were found between the data for right and left lip variables. The greater the upper lip closing force, the larger the upper lip base length, upper lip surface length, and upper lip surface area. The surface length, base length, and surface area of the upper lip are assumed to correspond to the upper portion of the orbicularis oris muscle. This suggests that lip closing force may have a relationship with the size of the orbicularis oris muscle in the upper lip. It seems that lip-closing force is predicted by the three-dimensional morphology of the upper lip.
The lower lip-closing force did not significantly correlate with the base length, surface length, and surface area of the lower lip, which are assumed to be part of the lower orbicularis oris muscle. This result suggests that the lip-closing force of the lower lip has no correlation with the size of the orbicularis oris muscle in the lower lip. In closing the lower lip, the mentalis muscle is involved in addition to the orbicularis oris muscle (Wakabayashi, 2002). The mentalis muscle originates from the incisive fossa of mandible and descends to be inserted into the integument of the chin (Standring, 2008). The muscle has been reported to lift the lower lip and assist in vertical movement of the lower lip (Rubens & West, 1989). Therefore, the present results suggest that the mentalis muscle may have a greater relationship with lower lip closing force than the orbicularis oris muscle in the lower lip.
The results of the present study characterize that the three-dimensional morphology of the upper lip is important for upper lip function. These findings can be expected to be contributory to estimations of the lip function in orthodontic treatment planning and in the evaluation of the stability of orthodontic treatment results.
CONCLUSIONS
In adults with straight facial profiles:
- (1)
- Significant correlations were found between upper lip-closing force and upper lip morphology.
- (2)
- No correlation between tower lip-closing force and lower lip morphology was found.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Ms. Nellie W. Kremenak for grammatical correction of the manuscript.
References
- Artun, J., O. Krogstad, and R. M. Little. 1990. Stability of mandibular incisors following excessive proclination: A study in adults with surgically treated mandibular prognathism. Angle Orthodontist 60: 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Brodie, A. 1953. Muscular factors in the diagnosis and treatment of malocclusions. Angle Orthodontist 23: 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovitch, M., D. Mcinnis, and S. J. Lindauer. 1997. The effects of lip bumper therapy in the mixed dentition. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 111: 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M. H., W. S. Yang, and D. S. Nahm. 2003. Effects of upper lip closing force on craniofacial structures. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 123: 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M. H., W. S. Yang, and D. S. Nahm. 2010. Maximum closing force of mentolabial muscles and type of malocclusion. Angle Orthodontist 80: 72–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, A., T. Kobayashi, A. Takagi, F. Kuroyanagi, K. Washino, K. Sabashi, and N. Kitai. 2013. Multidirectional lip-closing force in adults with mandibular deviation. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 40: 664–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeda, J., C. Ooshima, K. Saitoh, R. Kawashima, R. Hayashi, Y. Aoki, M. Yamaguchi, and K. Kasai. 2009. The correlation between the force of lip closure, the lip forms, and the upper and tower anterior teeth. Nihon University Journal of Oral Science 35: 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, J. R. 1966. The long-term results of the proclination of lower incisors. British Dental Journal 120: 355–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M., T. Adachi, K. Nakatsuka, T. Kato, M. Oishi, and Y. Masuda. 2012. Gender differences in maximum voluntary lip-closing force during lip pursing in healthy young adults. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 39: 399–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, K., T. Adachi, T. Kato, M. Oishi, M. Murakami, Y. Okada, and Y. Masuda. 2011. Reliability of novel multidirectional lip-closing force measurement system. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 38: 18–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ooishi, M., T. Adachi, K. Yasutomi, K. Nakatsuka, K. Yamada, and Y. Masuda. 2011. Multidirectional lip-closing force in the early stage of permanent anterior teeth occlusion (II)—Relationship between lip-closing force and lip morphology or anterior teeth occlusion. The Journal of Japanese Society of Stomatognathic Function 17: 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Posen, A. L. 1972. The influence of maximum perioral and tongue force on the incisor teeth. American Journal of Orthodontics 42: 285–309. [Google Scholar]
- Posen, A. L. 1976. The application of quantitative perioral assessment to orthodontic case analysis and treatment planning. Angle Orthodontist 46: 118–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Proffit, W. R. 1975. Muscle pressures and tooth position: North American whites and Australian aborigines. Angle Orthodontist 45: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Proffit, W. R., H. W. Fields, and O. M. Sarver. 2007. Contemporary orthodontics, 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Year Book Inc.: vol. p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, C. R., M. P. Mooney, T. O. Smith, S. M. Weinberg, B. M. Waller, L. A. Parr, B. A. Docherty, C. J. Bonar, L. E. Reinholt, F. W. Deleyiannis, M. I. Siegel, M. L. Marazita, and A. M. Burrows. 2009. Comparative microanatomy of the orbicularis oris muscle between chimpanzees and humans: Evolutionary divergence of lip function. Journal of Anatomy 214: 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubens, B. C., and R. A. West. 1989. Ptosis of the chin and lip incompetence: consequences of lost mentalis muscle support. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 47: 359–366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Safeena, S., M. Najmuddin, and K. Reddy. 2012. Presurgical management of a child With missing lower lip using a new design of fixed lower tongue crib. Journal of the Indian Society of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry 30: 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standring, S. 2008. Gray’s anatomy: The anatomical basis of clinical practice, 4th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone. [Google Scholar]
- Thuer, U., and B. Ingervall. 1986. Pressure from the lips on the teeth and malocclusion. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 90: 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K. 2002. Relationship between maxillofacial morphology and perioral muscle function. Orthodontic Waves 61: 454–465. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, K., Y. Morimoto, R. S. Nanda, J. Ghosh, and K. Tanne. 2000. Morphological differences in individuals with lip competence and incompetence based on electromyographic diagnosis. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 27: 893–901. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the author. 2015 Asuka Fujiwara, Fumi Kuroyanagi, Atsushi Kawabata, Atsushi Fujiwara, Wakako Tome and Noriyuki Kital