Potential Risk Factors Related to Antimicrobial Usage and Antimicrobial Resistance in Commercial Poultry Production—A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Charting
2.4. Presentation of Results
3. Results
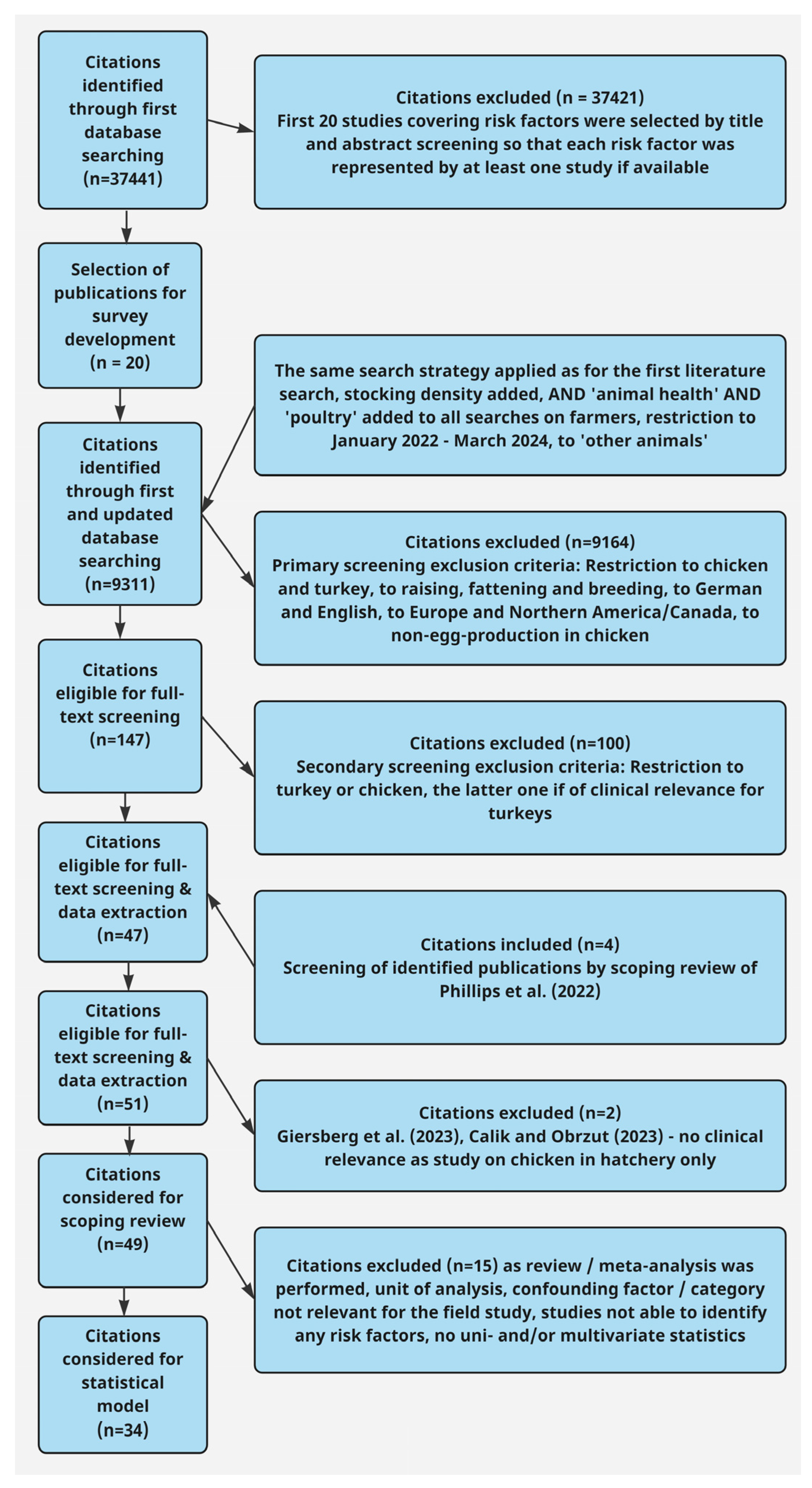
3.1. Search Results and Study Selection
3.1.1. Identified Risk Factors
3.1.2. Risk Factors Considered for Full Information Extraction
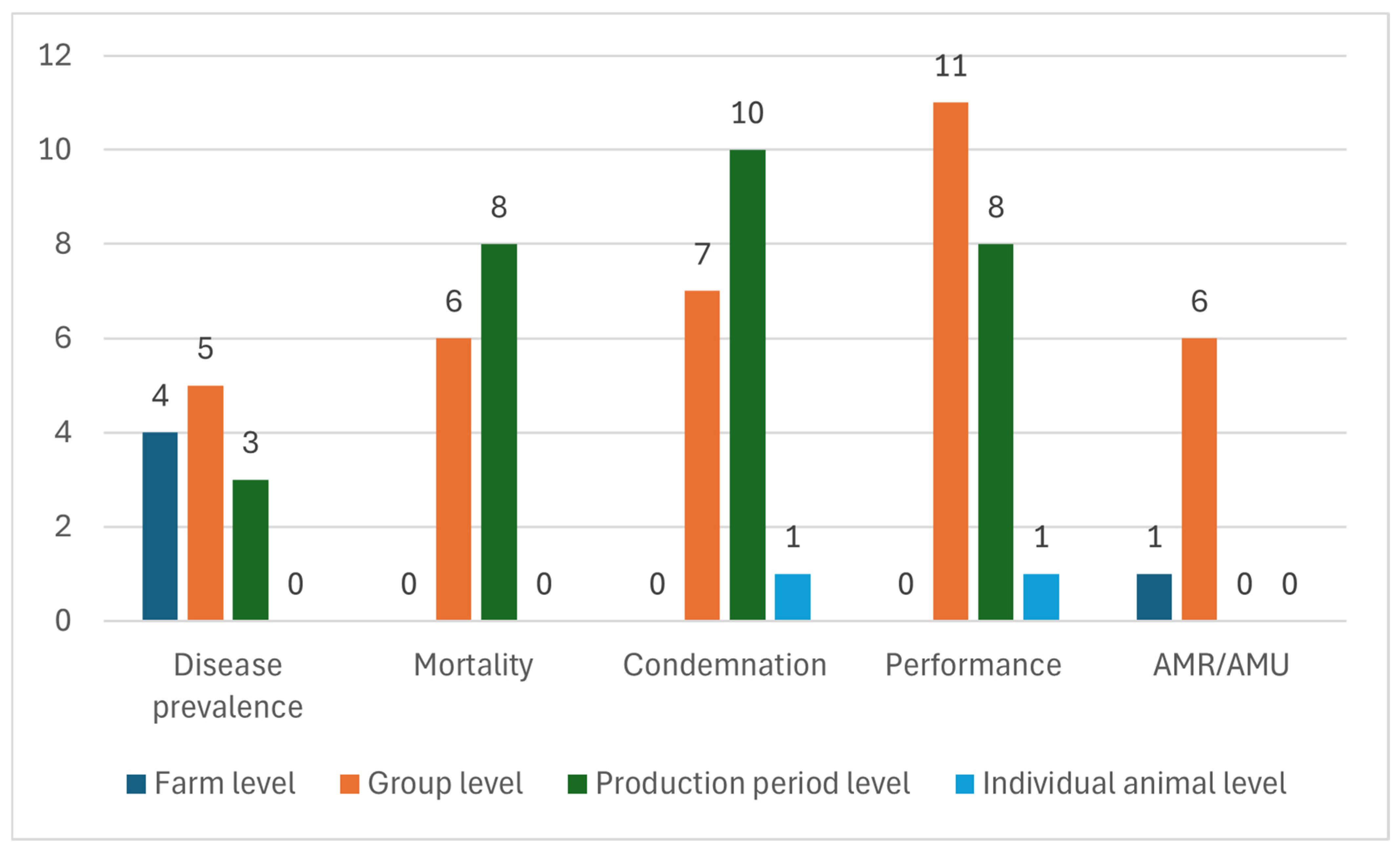
3.2. Risk Factors with Potential Impact Considering the Unit of Analysis
3.2.1. Risk Factors with Potential Impact on the Farm Level
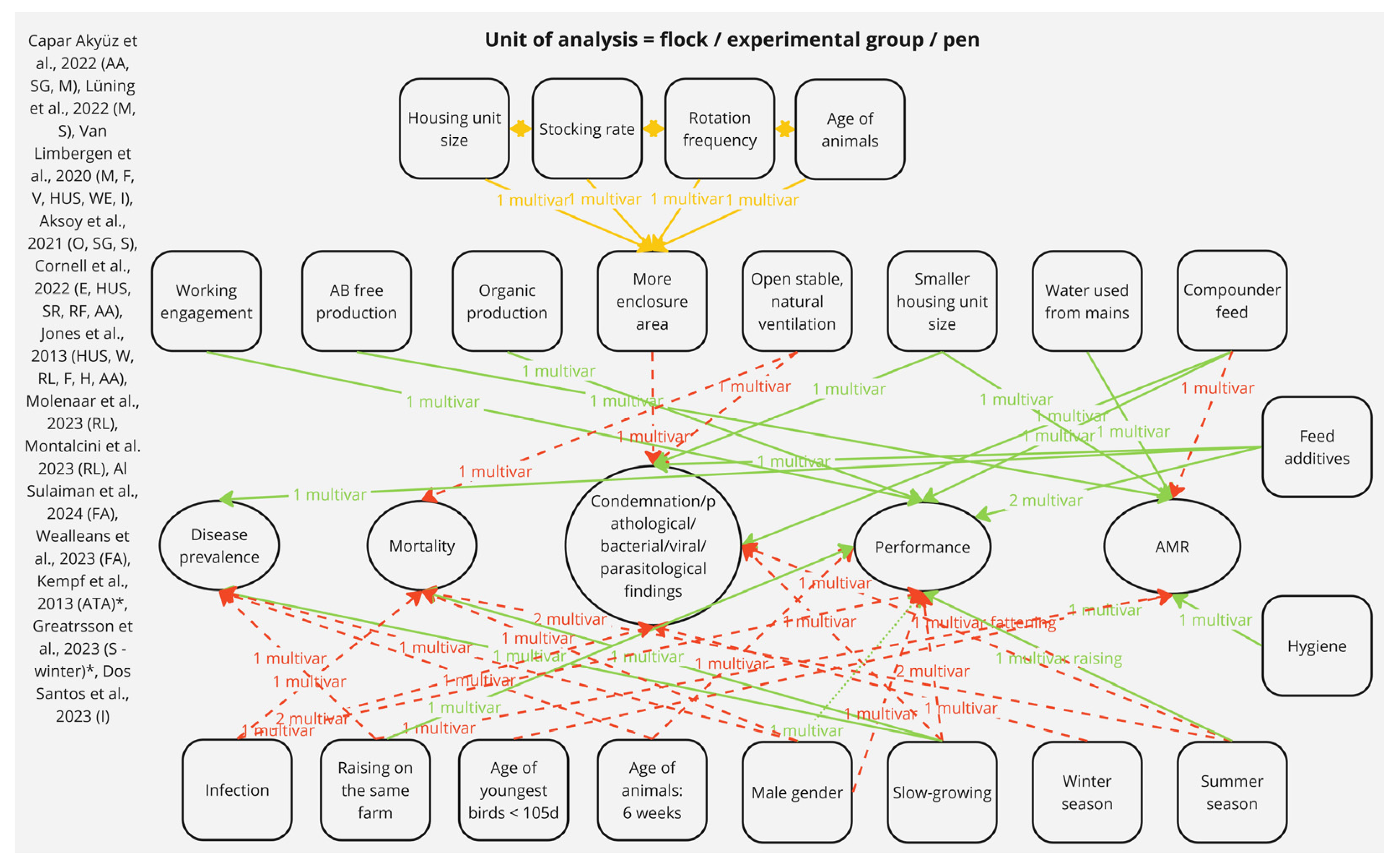
3.2.2. Risk Factors with Potential Impact on the Group Level
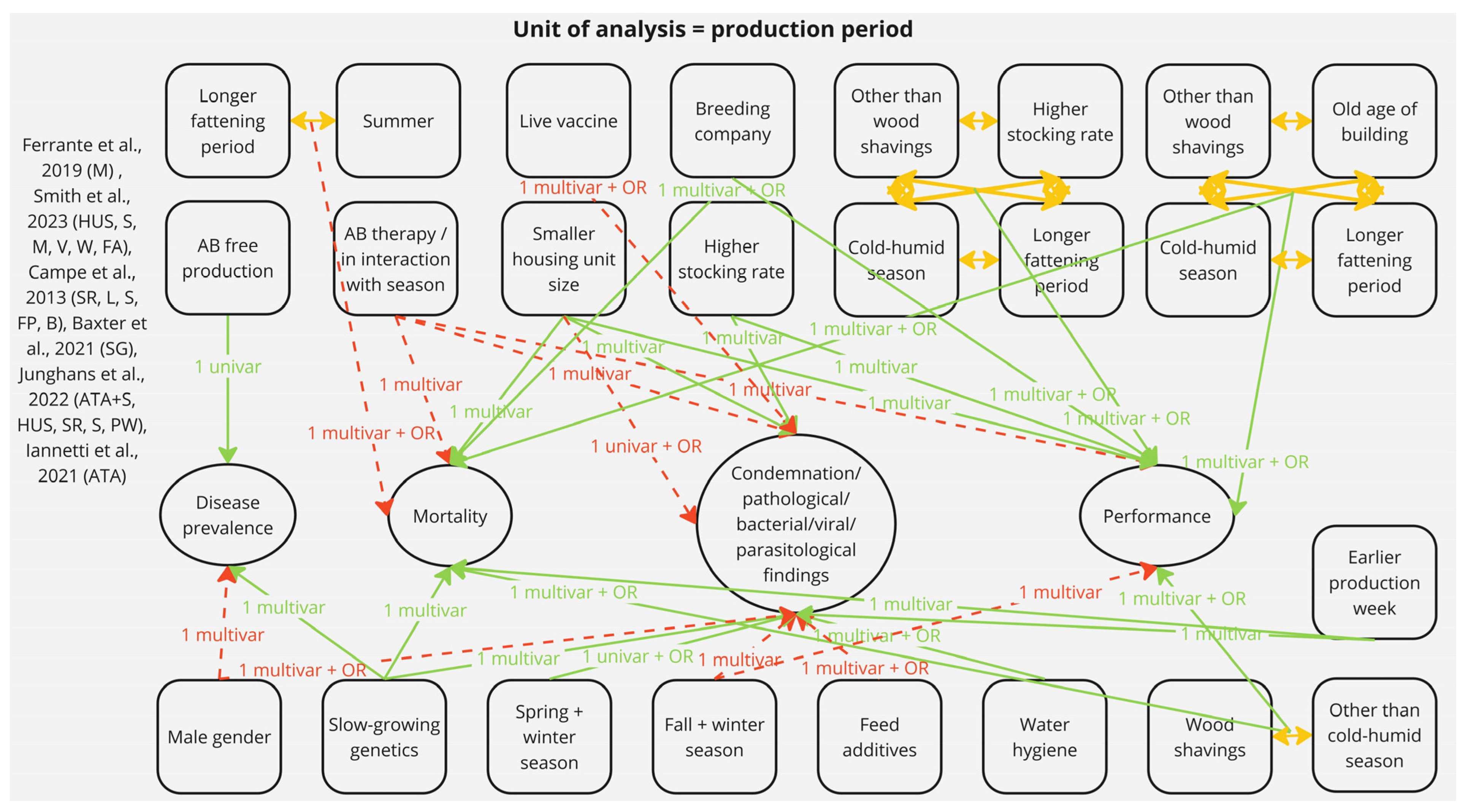
3.2.3. Risk Factors with Potential Impact on the Production Period Level
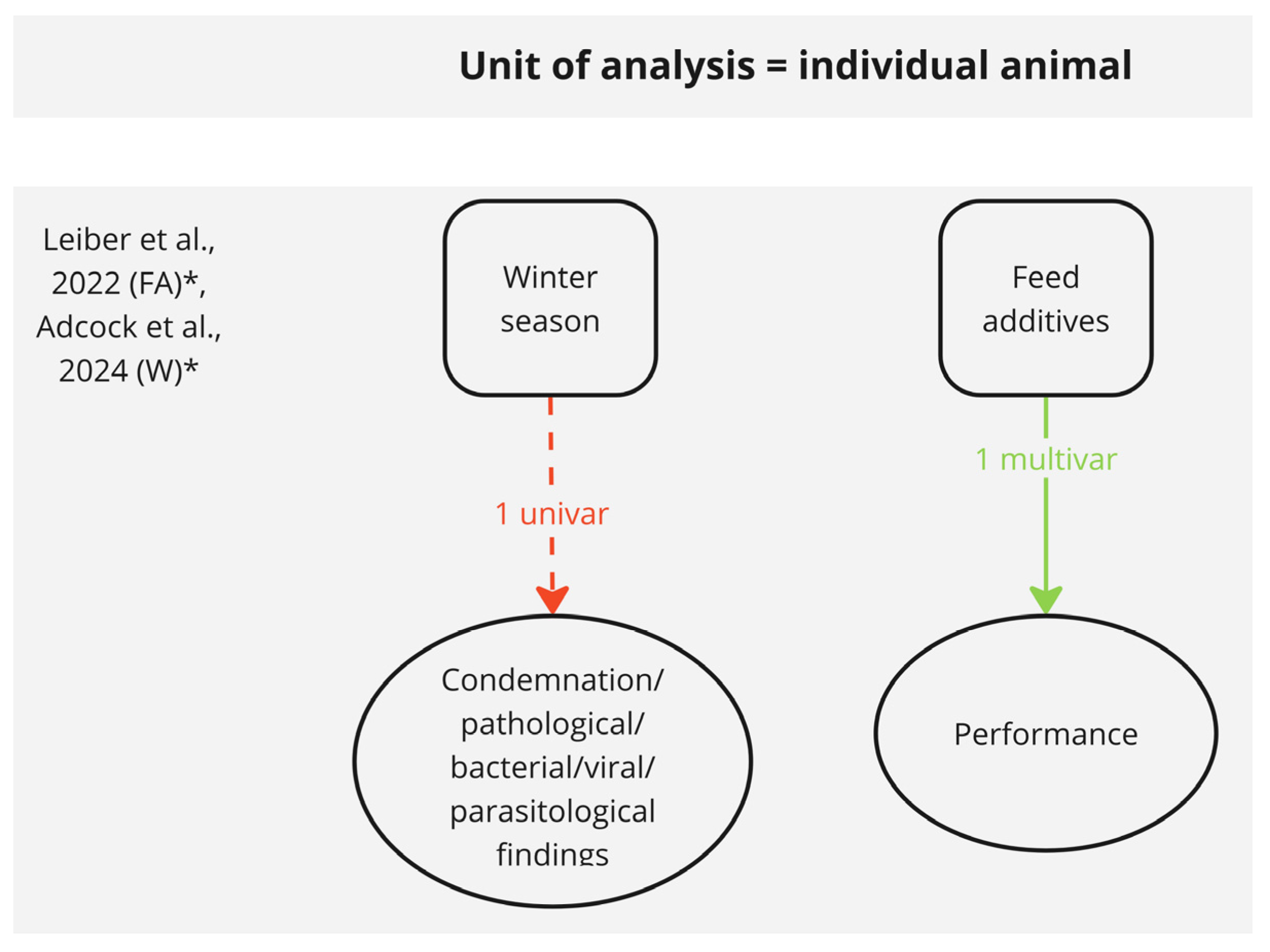
3.2.4. Risk Factors with Potential Impact on the Individual Animal Level
3.2.5. Statistical Models Used in the Identified Studies
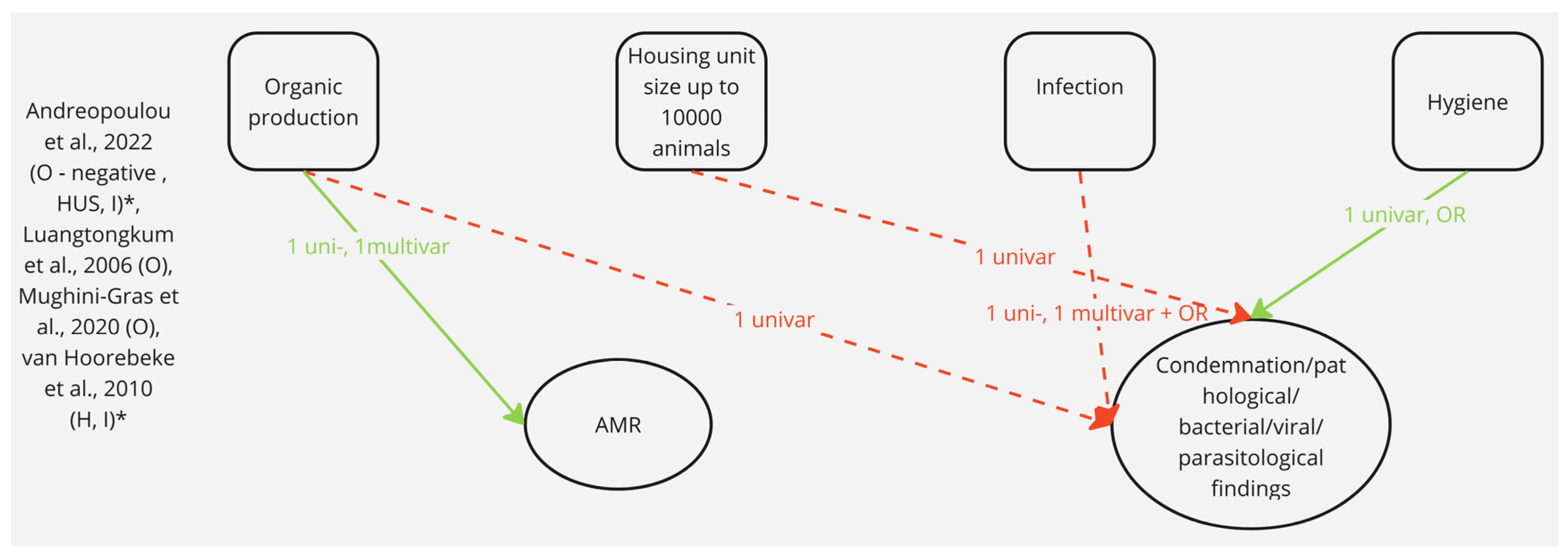
3.3. Results from Multivariable Statistical Models Only
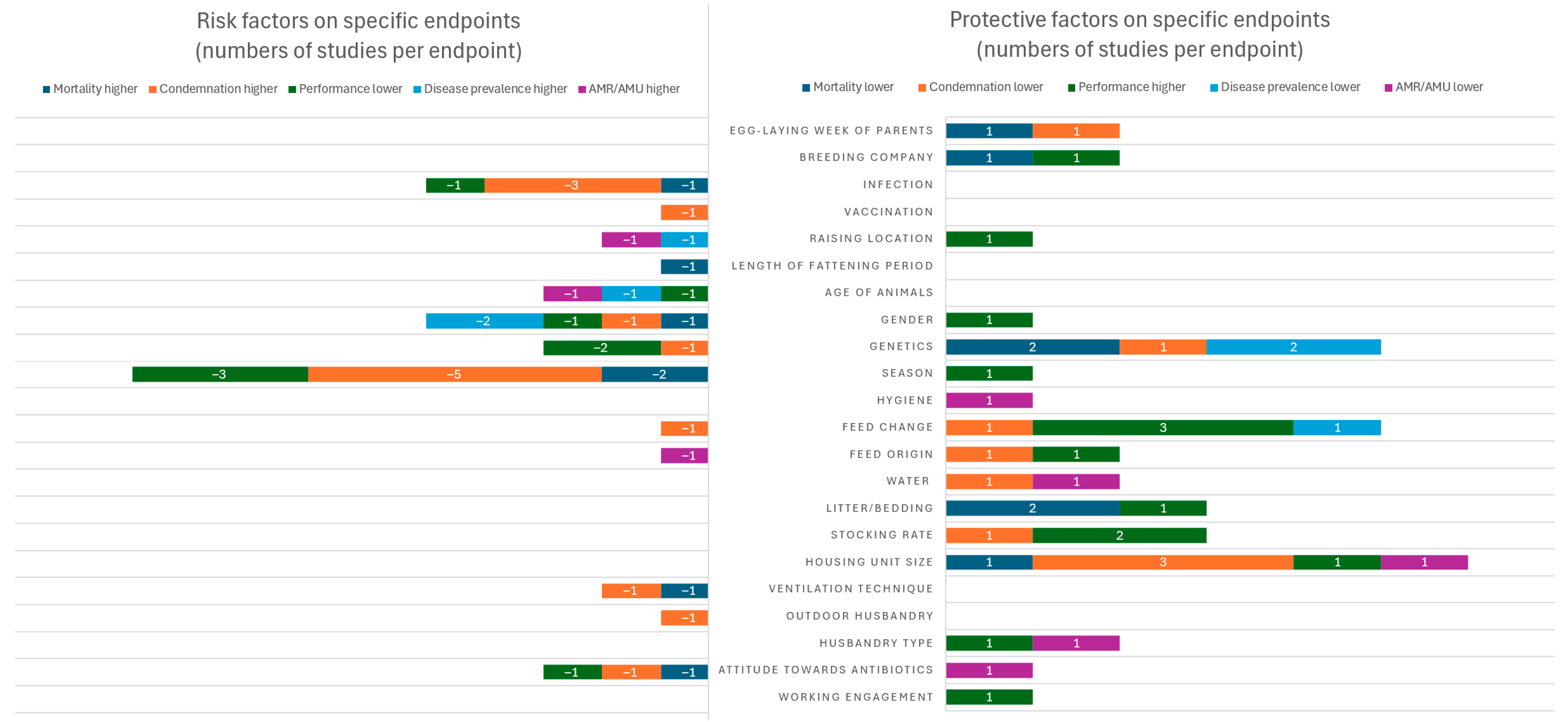
3.3.1. Synthesis of Influence of Risk Factors on All Specific Endpoints
AMR/AMU
Mortality
Disease Prevalence
Condemnation/Pathological/Bacterial/Viral/Parasitological Findings
Performance Parameters
3.3.2. Robustness of Evidence of Influence of Risk Factors on Specific Endpoints
| Risk Factor | Negative Influence (Higher AMR/AMU, Mortality, Disease Prevalence, Condemnation/Pathological/Bacterial/Viral/Parasitological Findings, Lower Performance) | Positive Influence (Lower AMR/AMU, Mortality, Disease Prevalence, Condemnation/Pathological/Bacterial/Viral/Parasitological Findings, Higher Performance) |
|---|---|---|
| Factors related to farmers | ||
| Working engagement (1) | 0 | 1x higher working engagement (P(1)) |
| Attitude towards antibiotics (4) | 2x positive attitude towards antibiotic treatment/AMU (M(1)/C(1)), 1x positive attitude towards antibiotic treatment/AMU in interaction with season (P(1)) | 1x negative attitude towards antibiotics/antibiotic-free production (AMR(1)) |
| Housing conditions and management-related factors | ||
| Husbandry type (2) | 0 | 2x organic husbandry type (P(1)/AMR(1)) |
| Outdoor husbandry (1) | 1x outdoor husbandry in correlation with housing unit size, stocking rate, rotation frequency and age of animals (C(1)) | 0 |
| Ventilation technique (1) | 1x roof or tunnel ventilation (natural ventilation) (M(1)/C(1)) | 0 |
| Housing unit size (3) | 0 | 3x smaller housing unit size (M(1)/C(3)/P(1)/AMR(1)) |
| Stocking rate (3) | 0 | 2x higher stocking rate (C(1)/P(1)), 1x higher stocking rate or old age of building in interaction with other than wood shavings, with cold-humid season and longer fattening period (P(1)) |
| Litter/bedding (2) | 0 | 1x old age of building in interaction with other than wood shaving litter/bedding, with cold-humid season and with longer fattening period (M(1)), 1x other than cold-humid seasons in interaction with wood shaving litter/bedding (M(1)/P(1)) |
| Water (2) | 0 | 1x use of water from mains (AMR(1)), 1x application of water hygiene (C(1)) |
| Feed origin (2) | 1x compounder feed origin (AMR(1)) | 1x compounder feed origin (C(1)/P(1)) |
| Feed change (5) | 1x feed supplements (C(1)) | 4x feed supplements (C(1)/P(3)/D(1)) |
| Hygiene (1) | 0 | 1x application of good hygiene principles (AMR(1)) |
| Season (8) | 2x summer (M(2)/C(1)), 1x summer (fattening) (P(1)), 1x fall (C(1)/P(1)), and 3x winter season (P(1)/C(3)) | 1x summer season (raising) (P(1)) |
| Animal-related factors | ||
| Genetics (5) | 2x slow growing genetics (C(1)/P(2)) | 3x slow-growing genetics (M(2)/C(1)/D(2)) |
| Gender (5) | 4x male gender (M(1)/C(1)/P(1)/D(2)) | 1x male gender (P(1)) |
| Age of animals (2) | 1x 6 weeks of age (P(1)/D(1)), 1x age of the youngest birds < 105d (AMR(1)) | 0 |
| Length of fattening period (1) | 1x longer fattening period with summer (M (1)) | 0 |
| Raising location (2) | 1x raising on the same farm (D(1)/AMR(1)) | 1x raising on the same farm (P(1)) |
| Vaccination (1) | 1x application of routine vaccination scheme with live vaccines (C(1)) | 0 |
| Infection (3) | 3x infection (M(1)/C(3)/P(1)) | 0 |
| Documentation criteria | ||
| Breeding company (1) | 0 | 1x certain breeding company (M(1)/P(1)) |
| Egg-laying week of parents (1) | 0 | 1x earlier production week of parents (M(1)/C(1)) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Aguilar, G.R.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.M.; Dolk, F.C.K.; Pouwels, K.B.; Christie, M.; Robotham, J.V.; Smieszek, T. Defining the appropriateness and inappropriateness of antibiotic prescribing in primary care. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, ii11–ii18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC. Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance in Bacteria from Humans and Food-Producing Animals (JIACRA IV–2019−2021). Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/antimicrobial-consumption-and-resistance-bacteria-humans-and-food-producing (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Berthe, F.C.J.; Bouley, T.; Karesh, W.; Le Gall, F.G.; Machalaba, C.C.; Plante, C.A.; Seifman, R.M. Operational Framework for Strengthening Human, Animal and Environmental Public Health Systems at Their Interface (English). Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/703711517234402168/Operational-framework-for-strengthening-human-animal-and-environmental-public-health-systems-at-their-interface (accessed on 28 May 2023).
- Viñes, J.; Cuscó, A.; Napp, S.; Alvarez, J.; Saez-Llorente, J.L.; Rosàs-Rodoreda, M.; Francino, O.; Migura-Garcia, L. Transmission of Similar Mcr-1 Carrying Plasmids among Different Escherichia coli Lineages Isolated from Livestock and the Farmer. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions a Farm to Fork Strategy for a Fair, Healthy and Environmentally-Friendly Food System. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52020DC0381 (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Smith, J.; Gheyas, A.; Burt, D.W. Animal genomics and infectious disease resistance in poultry. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2016, 35, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Limbergen, T.; Sarrazin, S.; Chantziaras, I.; Dewulf, J.; Ducatelle, R.; Kyriazakis, I.; McMullin, P.; Méndez, J.; Niemi, J.K.; Papasolomontos, S.; et al. Risk factors for poor health and performance in European broiler production systems. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannetti, L.; Romagnoli, S.; Cotturone, G.; Vulpiani, M.P. Animal Welfare Assessment in Antibiotic-Free and Conventional Broiler Chicken. Animals 2021, 11, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junghans, A.; Deseniß, L.; Louton, H. Data evaluation of broiler chicken rearing and slaughter-An exploratory study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 957786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughini-Gras, L.; Di Martino, G.; Moscati, L.; Buniolo, F.; Cibin, V.; Bonfanti, L. Natural immunity in conventionally and organically reared turkeys and its relation with antimicrobial resistance. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, K.A.; Smith, O.M.; Crespo, R.; Jones, M.S.; Crossley, M.S.; Snyder, W.E.; Owen, J.P. Prevalence Patterns for Enteric Parasites of Chickens Managed in Open Environments of the Western United States. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüning, J.; Wunderl, D.; Rautenschlein, S.; Campe, A. Histomonosis in German turkey flocks: Possible ways of pathogen introduction. Avian Pathol. 2023, 52, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.P.; Lawes, J.; Davies, R.H.; Hutchison, M.L.; Vidal, A.; Gilson, D.; Rodgers, J. UK-wide risk factor study of broiler carcases highly contaminated with Campylobacter. Zoonoses Public Health 2023, 70, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campe, A.; Koesters, S.; Niemeyer, M.; Klose, K.; Ruddat, I.; Baumgarte, J.; Kreienbrock, L. Epidemiology of influences on the performance in broiler flocks--a field study in Germany. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2576–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhetam, S.; Buchynski, K.; Shynkaruk, T.; Schwean-Lardner, K. Evaluating the effects of stocking density on the behavior, health, and welfare of turkey hens to 11 weeks of age. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüning, J.; Auerbach, M.; Lindenwald, R.; Campe, A.; Rautenschlein, S. Retrospective Investigations of Recurring Histomonosis on a Turkey Farm. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiber, F.; Amsler, Z.; Bieber, A.; Quander-Stoll, N.; Maurer, V.; Lambertz, C.; Früh, B.; Ayrle, H. Effects of riboflavin supplementation level on health, performance, and fertility of organic broiler parent stock and their chicks. Animal 2022, 16, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.; Chapman, B.; Agunos, A.; Carson, C.A.; Parmley, E.J.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Smith, B.A.; Murphy, C.P. A scoping review of factors potentially linked with antimicrobial-resistant bacteria from turkeys (iAM.AMR Project). Epidemiol. Infect. 2022, 150, e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.M.; Cardo, M.; Ruano, Z.; Alho, A.M.; Dinis-Teixeira, J.; Aguiar, P.; Leite, A. Effectiveness of antimicrobial interventions directed at tackling antimicrobial resistance in animal production: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 218, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey-Murto, S.; Varpio, L.; Wood, T.J.; Gonsalves, C.; Ufholz, L.A.; Mascioli, K.; Wang, C.; Foth, T. The Use of the Delphi and Other Consensus Group Methods in Medical Education Research: A Review. Acad. Med. 2017, 92, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baur-Bernhardt, S.; Käsbohrer, A.; Doherr, M.G.; Meemken, D.; Sonnenschein-Swanson, L.; Stetina, B.U.; Sommer, M.A.; Weiermayer, P. Assessing the Feasibility of a Two-Cohort Design to Assess the Potential of Homeopathic Medicinal Products to Reduce Antimicrobial Resistance in Turkeys (The HOMAMR Project)-Study Protocol. Homeopathy 2025, 114, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkman, I.; Röing, M.; Sternberg Lewerin, S.; Stålsby Lundborg, C.; Eriksen, J. Animal Production With Restrictive Use of Antibiotics to Contain Antimicrobial Resistance in Sweden-A Qualitative Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 619030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, K.A.; Alter, T.; Doherr, M.G.; Merle, R. From Stable to Table: Determination of German Consumer Perceptions of the Role of Multiple Aspects of Poultry Production on Meat Quality and Safety. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefania, C.; Alessio, M.; Paolo, M.; Tiziano, D.; Favretto, A.R.; Francesca, Z.; Giulia, M.; Giandomenico, P. The application of biosecurity practices for preventing avian influenza in North-Eastern Italy turkey farms: An analysis of the point of view and perception of farmers. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 222, 106084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.M.; Snow, L.C.; Carrique-Mas, J.J.; Gosling, R.J.; Clouting, C.; Davies, R.H. Risk factors for antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli found in GB turkey flocks. Vet. Rec. 2013, 173, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, I.; Le Roux, A.; Perrin-Guyomard, A.; Mourand, G.; Le Devendec, L.; Bougeard, S.; Richez, P.; Le Pottier, G.; Eterradossi, N. Effect of in-feed paromomycin supplementation on antimicrobial resistance of enteric bacteria in turkeys. Vet. J. 2013, 198, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Purswell, J.L.; Chesser, G.D.; Lowe, J.W.; Wu, T.L. Effects of antibiotic-free diet and stocking density on male broilers reared to 35 days of age. Part 2: Feeding and drinking behaviours of broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangtongkum, T.; Morishita, T.Y.; Ison, A.J.; Huang, S.; McDermott, P.F.; Zhang, Q. Effect of conventional and organic production practices on the prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter spp. in poultry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3600–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoorebeke, S.; Van Immerseel, F.; De Vylder, J.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F.; de Kruif, A.; Dewulf, J. The age of production system and previous Salmonella infections on-farm are risk factors for low-level Salmonella infections in laying hen flocks. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.S.; Waits, K.; Nordstrom, L.; Grande, H.; Weaver, B.; Papp, K.; Horwinski, J.; Koch, B.; Hungate, B.A.; Liu, C.M.; et al. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli from retail poultry meat with different antibiotic use claims. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, T.; Çürek, D.; Narinç, D.; Önenç, A. Effects of season, genotype, and rearing system on broiler chickens raised in different semi-intensive systems: Performance, mortality, and slaughter results. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreopoulou, M.; Chaligiannis, I.; Sotiraki, S.; Daugschies, A.; Bangoura, B. Prevalence and molecular detection of Eimeria species in different types of poultry in Greece and associated risk factors. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 2051–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.V.; Skånberg, L.; Keeling, L.J.; Estevez, I.; Newberry, R.C. Resource choice during ontogeny enhances both the short- and longer-term welfare of laying hen pullets. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, J.; Wartemann, S. Influence of a turkey stable with a veranda on performance, behaviour and health of male turkeys. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2006, 113, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baxter, M.; Richmond, A.; Lavery, U.; O’Connell, N.E. A comparison of fast growing broiler chickens with a slower-growing breed type reared on Higher Welfare commercial farms. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krautwald-Junghanns, M.E.; Sirovnik, J. The influence of stocking density on behaviour, health, and production in commercial fattening turkeys-a review. Br. Poult. Sci. 2022, 63, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.N.; Widowski, T.M.; Kiarie, E.G.; Guerin, M.T.; Edwards, A.M.; Torrey, S. In pursuit of a better broiler: Walking ability and incidence of contact dermatitis in conventional and slower growing strains of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmuş, M.; Kurşun, K.; Polat Açık, I.; Tufan, M.; Kutay, H.; Benli, H.; Baylan, M.; Kutlu, H.R. Effect of different litter materials on growth performance, the gait score and footpad dermatitis, carcass parameters, meat quality, and microbial load of litter in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelsen, K.E.; Vasdal, G.; Moe, R.O.; Steinhoff, F.S.; Tahamtani, F.M. Health effects of feed dilution and roughage in Ross 308 broiler breeder cockerels. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, L.P.; Sweeney, K.M.; Evans, C.R.; White, D.L.; Kim, W.K.; Regmi, P.; Williams, S.M.; Nicholds, J.; Wilson, J.L. Body composition, gastrointestinal, and reproductive differences between broiler breeders fed using everyday or skip-a-day rearing programs. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, L.P.; Leiva, S.F.; Abascal-Ponciano, G.A.; Flees, J.J.; Sweeney, K.M.; Wilson, J.L.; Meloche, K.J.; Turner, B.J.; Litta, G.; Waguespack-Levy, A.M.; et al. Effect of combined maternal and post-hatch dietary 25-hydroxycholecalciferol supplementation on broiler chicken Pectoralis major muscle growth characteristics and satellite cell mitotic activity. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Mohammed, A.A.; Murugesan, G.R.; Cheng, H.W. Effect of a synbiotic supplement as an antibiotic alternative on broiler skeletal, physiological, and oxidative parameters under heat stress. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, T.S.; Augusto, K.V.Z.; Han, Y.; Sartori, M.M.P.; Batistioli, J.S.; Contin Neto, A.C.; Ferreira Netto, R.G.; Zanetti, L.H.; Pasquali, G.A.M.; Muro, E.M.; et al. Effects of dietary copper and zinc hydroxychloride supplementation on bone development, skin quality and hematological parameters of broilers chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 107, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, L.F.V.; Dorigam, J.C.P.; Reis, M.P.; Horna, F.; Fernandes, J.B.K.; Sakomura, N.K. Eimeria maxima infection impacts the protein utilisation of broiler chicks from 14 to 28 days of age. Animal 2023, 17, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholikin, M.M.; Sadarman; Irawan, A.; Sofyan, A.; Jayanegara, A.; Rumhayati, B.; Hidayat, C.; Adli, D.N.; Julendra, H.; Herdian, H.; et al. A meta-analysis of the effects of clay mineral supplementation on alkaline phosphatase, broiler health, and performance. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Sulaiman, A.R.; Abudabos, A.M.; Alhotan, R.A. Protective influence of supplementary betaine against heat stress by regulating intestinal oxidative status and microbiota composition in broiler chickens. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2024, 68, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wealleans, A.L.; Desbruslais, A.; Goncalves, R.; Scholey, D.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, D.; Burton, E.; Spaepen, R.; Elliott, A.; Currie, D. Research Note: Comparative effects of liquid and dry applications of a combination of lysolecithin, synthetic emulsifier, and monoglycerides on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and litter moisture in broilers fed diets of differing energy density. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvon, S.; Beaumont, M.; Dayonnet, A.; Eutamène, H.; Lambert, W.; Tondereau, V.; Chalvon-Demersay, T.; Belloir, P.; Paës, C. Effect of diet supplemented with functional amino acids and polyphenols on gut health in broilers subjected to a corticosterone-induced stress. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Nam, H.; Wickramasuriya, S.S.; Lee, Y.; Wall, E.H.; Ravichandran, S.; Lillehoj, H.S. Host-mediated beneficial effects of phytochemicals for prevention of avian coccidiosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1145367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzieciolowski, T.; Boqvist, S.; Rydén, J.; Hansson, I. Cleaning and disinfection of transport crates for poultry-comparison of four treatments at slaughter plant. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuder, J.; Simitopoulou, M.; Angastiniotis, K.; Ferrari, P.; Wolthuis-Fillerup, M.; Kefalas, G.; Papasolomontos, S. Development and implementation of a risk assessment tool for broiler farm biosecurity and a health intervention plan in the Netherlands, Greece, and Cyprus. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gretarsson, P.; Kittelsen, K.; Oppermann Moe, R.; Toftaker, I. Causes of carcass condemnation in Norwegian aviary housed layers. Acta Vet. Scand. 2023, 65, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, K.G.; Berghaus, R.D.; Goodwin, C.C.; Ruder, M.G.; Yabsley, M.J.; Mead, D.G.; Nemeth, N.M. Lymphoproliferative Disease Virus and Reticuloendotheliosis Virus Detection and Disease in Wild Turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo). J. Wildl. Dis. 2024, 60, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çapar Akyüz, H.; Onbaşılar, E.E.; Bayraktaroğlu, A.G.; Ceylan, A. Age and sex related changes in fattening performance, dermatitis, intestinal histomorphology, and serum IgG level of slow- and fast-growing broilers under the intensive system. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, V.; Lolli, S.; Ferrari, L.; Watanabe, T.T.N.; Tremolada, C.; Marchewka, J.; Estevez, I. Differences in prevalence of welfare indicators in male and female turkey flocks (Meleagris gallopavo). Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenaar, R.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Giersberg, M.F.; Rodenburg, T.B.; Kemp, B.; van den Brand, H.; de Jong, I.C. Effects of hatching system on chick quality, welfare and health of young breeder flock offspring. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalcini, C.M.; Petelle, M.B.; Toscano, M.J. Commercial hatchery practices have long-lasting effects on laying hens’ spatial behaviour and health. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0295560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung. Tabellen zur Entwicklung der Therapiehäufigkeit und der Antibiotikaverbrauchsmengen 2018–2021. Available online: https://www.bfr.bund.de/cm/343/therapiehaeufigkeit-und-antibiotikaverbrauchsmengen-2018-2021-bericht.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Wehrens, R.; Oldenhof, L.; Heerings, M.; Petit-Steeghs, V.; Haperen, S.V.; Bal, R.; Greenhalgh, T. Integrating System Dynamics and Action Research: Towards a Consideration of Normative Complexity Comment on “Insights Gained From a Re-analysis of Five Improvement Cases in Healthcare Integrating System Dynamics Into Action Research”. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2023, 12, 7582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Papoutsi, C. Studying complexity in health services research: Desperately seeking an overdue paradigm shift. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzsolt, F.; Rocha, N.G.; Toledo-Arruda, A.C.; Thomaz, T.G.; Moraes, C.; Bessa-Guerra, T.R.; Leão, M.; Migowski, A.; Araujo da Silva, A.R.; Weiss, C. Efficacy and effectiveness trials have different goals, use different tools, and generate different messages. Pragmat. Obs. Res. 2015, 6, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sonnenschein-Swanson, L.; Baur-Bernhardt, S.; Käsbohrer, A.; Doherr, M.G.; Meemken, D.; Weiermayer, P. Potential Risk Factors Related to Antimicrobial Usage and Antimicrobial Resistance in Commercial Poultry Production—A Scoping Review. Poultry 2025, 4, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4030039
Sonnenschein-Swanson L, Baur-Bernhardt S, Käsbohrer A, Doherr MG, Meemken D, Weiermayer P. Potential Risk Factors Related to Antimicrobial Usage and Antimicrobial Resistance in Commercial Poultry Production—A Scoping Review. Poultry. 2025; 4(3):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4030039
Chicago/Turabian StyleSonnenschein-Swanson, Lena, Silvia Baur-Bernhardt, Annemarie Käsbohrer, Marcus Georg Doherr, Diana Meemken, and Petra Weiermayer. 2025. "Potential Risk Factors Related to Antimicrobial Usage and Antimicrobial Resistance in Commercial Poultry Production—A Scoping Review" Poultry 4, no. 3: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4030039
APA StyleSonnenschein-Swanson, L., Baur-Bernhardt, S., Käsbohrer, A., Doherr, M. G., Meemken, D., & Weiermayer, P. (2025). Potential Risk Factors Related to Antimicrobial Usage and Antimicrobial Resistance in Commercial Poultry Production—A Scoping Review. Poultry, 4(3), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4030039







