Evaluation of the Effect of In Ovo Applied Bifidobacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria on Enteric Colonization by Hatchery-Associated Opportunistic Pathogens and Early Performance in Broiler Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Lactic Acid Bacteria
2.3. Bifidobacteria
2.4. Application of Probiotic Treatments
2.5. Challenge Preparation and Application
2.6. Gastrointestinal Sampling
2.7. Animal Source
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. DOH Gut Recovery
3.2. Meta-Analysis of DOH Gut–Trials 2–4
3.3. Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalling, J.W. Pioneer Species—An overview. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery Mode Shapes the Acquisition and Structure of the Initial Microbiota across Multiple Body Habitats in Newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; La, T.-M.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, I.-S.; Song, C.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-B.; Lee, S.-W. Characterization of Microbial Communities in the Chicken Oviduct and the Origin of Chicken Embryo Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Bi, R.; Xiao, K.; Roy, A.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Peng, J.; Wang, R.; Yang, R.; Shen, X.; et al. Hen Raising Helps Chicks Establish Gut Microbiota in Their Early Life and Improve Microbiota Stability after H9N2 Challenge. Microbiome 2022, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, A.; Drigo, B.; Djordjevic, S.P.; Donner, E.; Hoye, B.J. Impacts of Coprophagic Foraging Behaviour on the Avian Gut Microbiome. Biol. Rev. 2024, 99, 582–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, J.J.; Klima, C.L.; Sylte, M.J.; Looft, T. The Microbial Pecking Order: Utilization of Intestinal Microbiota for Poultry Health. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Wang, T.; Wu, M.; Chu, Q.; Lan, H.; Lang, W.; Zhu, L.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wen, Q.; et al. Maternal Effects Drive Intestinal Development Beginning in the Embryonic Period on the Basis of Maternal Immune and Microbial Transfer in Chickens. Microbiome 2023, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edens, F.W.; Parkhurst, C.R.; Casas, I.A.; Dobrogosz, W.J. Principles of Ex Ovo Competitive Exclusion and in Ovo Administration of Lactobacillus reuteri. Poult. Sci. 1997, 76, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, W.; Ghareeb, K.; Böhm, J. Intestinal Structure and Function of Broiler Chickens on Diets Supplemented with a Synbiotic Containing Enterococcus faecium and Oligosaccharides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2205–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Moneim, A.E.-M.E.A.; El-Wardany, I.; Abu-Taleb, A.M.; Wakwak, M.M.; Ebeid, T.A.; Saleh, A.A. Assessment of In Ovo Administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Bifidobacterium bongum on Performance, Ileal Histomorphometry, Blood Hematological, and Biochemical Parameters of Broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Prot. 2020, 12, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda, C.D.; Dittoe, D.K.; Wamsley, K.G.S.; McDaniel, C.D.; Blanch, A.; Sandvang, D.; Kiess, A.S. In Ovo Inoculation of an Enterococcus Faecium–Based Product to Enhance Broiler Hatchability, Live Performance, and Intestinal Morphology. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6163–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.D.; Pedroso, A.A.; Lumpkins, B.; Cho, Y.; Maurer, J.J. Pioneer Colonizers: Bacteria That Alter the Chicken Intestinal Morphology and Development of the Microbiota. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1139321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.M.; Rodrigues, D.R.; Briggs, W.N.; Duff, A.F.; Chasser, K.M.; Bielke, L.R. Evaluation of the Impact of in Ovo Administered Bacteria on Microbiome of Chicks through 10 Days of Age. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5949–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.R.; Winson, E.; Wilson, K.M.; Briggs, W.N.; Duff, A.D.; Chasser, K.M.; Bielke, L.R. Intestinal Pioneer Colonizers as Drivers of Ileal Microbial Composition and Diversity of Broiler Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2858. [Google Scholar]
- Karaffová, V.; Marcinková, E.; Bobíková, K.; Herich, R.; Revajová, V.; Stašová, D.; Kavuľová, A.; Levkutová, M.; Levkut, M.; Lauková, A.; et al. TLR4 and TLR21 expression, MIF, IFN-β, MD-2, CD14 activation, and sIgA production in chickens administered with EFAL41 strain challenged with Campylobacter jejuni. Folia Microbiol. 2017, 62, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Alizadeh, M.; Shojadoost, B.; Astill, J.; Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Karimi, S.H.; Bavananthasivam, J.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Sharif, S. Effects of in Ovo Inoculation of Multi-Strain Lactobacilli on Cytokine Gene Expression and Antibody-Mediated Immune Responses in Chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.; Bavananthasivam, J.; Shojadoost, B.; Astill, J.; Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Alqazlan, N.; Boodhoo, N.; Shoja Doost, J.; Sharif, S. In Ovo and Oral Administration of Probiotic Lactobacilli Modulate Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immune Responses in Newly Hatched Chicks. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 664387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Sharif, S.; Hassan, H.; Alizadeh, M.; Pratt, S.; Abdelaziz, K. In Ovo Feeding of Probiotic Lactobacilli Differentially Alters Expression of Genes Involved in the Development and Immunological Maturation of Bursa of Fabricius in Pre-Hatched Chicks. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, K.D.; Graham, L.E.; Dunn, J.R.; Cheng, H.H.; Anthony, N.; Latorre, J.D.; Menconi, A.; Wolfenden, R.E.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Mahaffey, B.D.; et al. In Ovo Evaluation of FloraMax®-B11 on Marek’s Disease HVT Vaccine Protective Efficacy, Hatchability, Microbiota Composition, Morphometric Analysis, and Salmonella Enteritidis Infection in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villumsen, K.R.; Sandvang, D.; Vestergård, G.; Olsen, M.S.R.; Juul, J.; Dencker, M.; Kudsk, J.; Poulsen, L.L. Effects of a Novel, Non-Invasive Pre-Hatch Application of Probiotic for Broilers on Development of Cecum Microbiota and Production Performance. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Ren, Y.; Lu, S.; Reddyvari, R.; Venkitanarayanan, K.; Amalaradjou, M.A. In Ovo Probiotic Supplementation Supports Hatchability and Improves Hatchling Quality in Broilers. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfenden, A.D.; Vicente, J.L.; Higgins, J.P.; Andreatti Filho, R.L.; Higgins, S.E.; Hargis, B.M.; Tellez, G. Effect of Organic Acids and Probiotics on Salmonella Enteritidis Infection in Broiler Chickens. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2007, 6, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, S.; Hughes, R.J.; Hao Van, T.T.; Moore, R.J.; Stanley, D. At-Hatch Administration of Probiotic to Chickens Can Introduce Beneficial Changes in Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.D.; Selby, C.M.; Forga, A.J.; Coles, M.E.; Beer, L.C.; Graham, L.E.; Teague, K.D.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Hargis, B.M.; Vuong, C.N. Development of an Environmental Contamination Model to Simulate the Microbial Bloom That Occurs in Commercial Hatch Cabinets. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviagen. Ross Broiler Nutrition Specification. 2022. Available online: https://aviagen.com/assets/Tech_Center/Ross_Broiler/Ross-BroilerNutritionSpecifications2022-EN.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Scardovi, V. Genus Bifidobacterium. Bergey’s Man. Syst. Bacteriol. 1986, 2, 1418–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Mättö, J.; Suihko, M.-L.; Saarela, M. Comparison of Three Test Media for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Bifidobacteria Using the Etest Method. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 28, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitaram, S.N.; Siragusa, G.R.; Hinton, A. Bifidobacterium-Selective Isolation and Enumeration from Chicken Caeca by a Modified Oligosaccharide Antibiotic-Selective Agar Medium. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 41, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlková, E.; Salmonová, H.; Bunešová, V.; Geigerová, M.; Rada, V.; Musilová, Š. A New Medium Containing Mupirocin, Acetic Acid, and Norfloxacin for the Selective Cultivation of Bifidobacteria. Anaerobe 2015, 34, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, C.M.; Beer, L.C.; Forga, A.J.; Coles, M.E.; Graham, L.E.; Teague, K.D.; Tellez-Isaias, G.; Hargis, B.M.; Vuong, C.N.; Graham, B.D. Evaluation of the Impact of Formaldehyde Fumigation during the Hatching Phase on Contamination in the Hatch Cabinet and Early Performance in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango, M.; Forga, A.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Gray, L.; Moore, R.; Coles, M.; Atencio, A.; Trujillo, C.; Latorre, J.D.; et al. Characterizing the Impact of Enterococcus cecorum Infection during Late Embryogenesis on Disease Progression, Cecal Microbiome Composition, and Early Performance in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, N.A.; Bailey, J.S.; Blankenship, L.C.; Gildersleeve, R.P. Research Note: In Ovo Administration of a Competitive Exclusion Culture Treatment to Broiler Embryos. Poult. Sci. 1992, 71, 1781–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.M.L. The Role of Probiotics in the Poultry Industry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3531–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutting, S.M. Bacillus Probiotics. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, J.E.; Van Der Hoeven-Hangoor, E.; Van De Linde, I.B.; Montijn, R.C.; Van Der Vossen, J.M.B.M. In Ovo Inoculation of Chicken Embryos with Probiotic Bacteria and Its Effect on Posthatch salmonella Susceptibility. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, A.; Ju, A.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xue, L.; Ma, X.; Luan, W.; Yang, S. The Effects of In Ovo Injection of Synbiotics on the Early Growth Performance and Intestinal Health of Chicks. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 658301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplett, M.D.; Zhai, W.; Peebles, E.D.; McDaniel, C.D.; Kiess, A.S. Investigating Commercial in Ovo Technology as a Strategy for Introducing Probiotic Bacteria to Broiler Embryos. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biavati, B.; Mattarelli, P.; Crociani, F. Bifidobacterium saeculare: A new species isolated from feces of rabbit. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 14, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Kong, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, X.; Seviour, R.; Kong, Y. Effects of Dietary Inulin Supplementation on the Composition and Dynamics of Cecal Microbiota and Growth-Related Parameters in Broiler Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6942–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasatikova, L.; Zeman, M.; Crhanova, M.; Matiasovicova, J.; Karasova, D.; Faldynova, M.; Prikrylova, H.; Sebkova, A.; Rychlik, I. Colonization of Chickens with Competitive Exclusion Products Results in Extensive Differences in Metabolite Composition in Cecal Digesta. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasova, T.; Kollarcikova, M.; Crhanova, M.; Karasova, D.; Cejkova, D.; Sebkova, A.; Matiasovicova, J.; Faldynova, M.; Sisak, F.; Babak, V.; et al. Gut Anaerobes Capable of Chicken Caecum Colonisation. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papouskova, A.; Rychlik, I.; Harustiakova, D.; Cizek, A. Research Note: A Mixture of Bacteroides Spp. and Other Probiotic Intestinal Anaerobes Reduces Colonization by Pathogenic E. Coli Strain O78:H4-ST117 in Newly Hatched Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.N.; McDaniel, C.D.; Wamsley, K.G.S.; Kiess, A.S. The Potential for Inoculating Lactobacillus animalis and Enterococcus faecium Alone or in Combination Using Commercial in Ovo Technology without Negatively Impacting Hatch and Post-Hatch Performance. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 7050–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagini, L.; Galosi, L.; Tambella, A.M.; Roncarati, A.; De Bellis, D.; Pesaro, S.; Attili, A.-R.; Berardi, S.; Rossi, G. Effect of In Ovo Supplementation of Slab51 Probiotic Mixture, Associated with Marek’s Disease Vaccine, on Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology and Eimeria Spp. Infection in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2024, 14, 3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
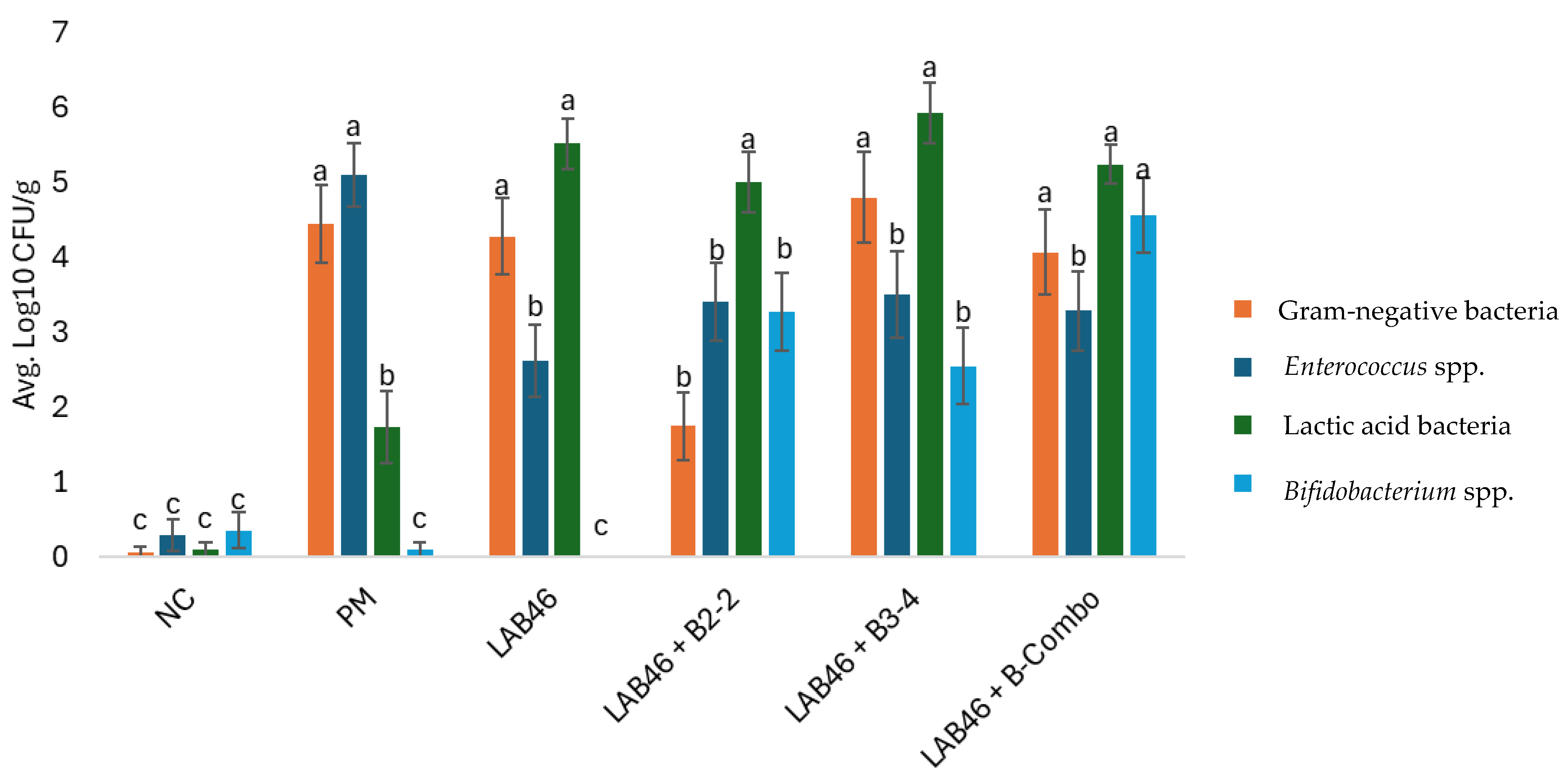
| Trial | Treatment 1 | Gram-Negative Bacteria | Bifidobacterium spp. | Lactic Acid Bacteria | Enterococcus spp. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trial 1 | NC | 1.64 ± 0.62 cde | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.98 ± 0.70 d | 0.00 ± 0.00 e |
| PM | 1.32 ± 0.75 cde | 0.22 ± 0.22 bc | 2.61 ± 0.89 cd | 0.64 ± 0.64 de | |
| LAB18 | 3.82 ± 0.68 b | 0.73 ± 0.39 abc | 4.94 ± 0.70 ab | 2.36 ± 0.90 cd | |
| LAB46 | 0.99 ± 0.69 de | 0.28 ± 0.28 bc | 4.65 ± 0.56 ab | 1.90 ± 0.84 cde | |
| B2-2 | 2.47 ± 0.82 bcd | 0.53 ± 0.53 bc | 5.03 ± 0.74 ab | 5.38 ± 0.81 ab | |
| B3-4 | 3.18 ± 0.86 bc | 1.49 ± 0.69 ab | 6.57 ± 0.34 a | 6.05 ± 0.66 a | |
| LAB18 + B2-2 | 5.93 ± 0.63 a | 1.23 ± 0.83 abc | 5.88 ± 0.64 a | 1.87 ± 0.98 cde | |
| LAB46 + B3-4 | 0.24 ± 0.24 e | 2.13 ± 0.71 a | 3.07 ± 0.70 bc | 3.65 ± 0.99 bc | |
| LAB18 + B3-4 | 1.61 ± 0.71 cde | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 3.08 ± 0.85 bc | 0.24 ± 0.24 de | |
| LAB46 + B2-2 | 4.40 ± 0.88 ab | 1.10 ± 0.74 abc | 2.39 ± 0.80 cd | 2.35 ± 0.86 cd | |
| Trial 2 | NC | 0.22 ± 0.22 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 c |
| PM | 2.77 ± 0.84 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 4.11 ± 0.86 a | |
| LAB46 | 2.63 ± 0.88 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 5.57 ± 0.58 a | 1.86 ± 0.69 bc | |
| LAB46 + B2-2 | 2.28 ± 0.98 ab | 2.81 ± 0.92 b | 3.49 ± 0.88 b | 1.81 ± 0.84 bc | |
| LAB46 + B3-4 | 2.64 ± 0.90 a | 1.16 ± 0.64 c | 5.75 ± 0.63 a | 3.57 ± 0.86 ab | |
| LAB46 + B-Combo | 3.09 ± 0.86 a | 5.79 ± 0.58 a | 4.60 ± 0.26 ab | 1.43 ± 0.57 c | |
| Trial 3 | NC | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 c |
| PM | 3.51 ± 0.83 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.84 ± 0.45 b | 4.75 ± 0.69 a | |
| LAB46 | 3.96 ± 0.89 b | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 5.45 ± 0.58 a | 2.76 ± 0.89 ab | |
| LAB46 + B2-2 | 0.38 ± 0.38 c | 1.92 ± 0.74 a | 5.14 ± 0.54 a | 4.24 ± 0.72 a | |
| LAB46 + B3-4 | 6.11 ± 0.69 a | 3.01 ± 0.81 a | 4.97 ± 0.71 a | 1.10 ± 0.75 bc | |
| LAB46 + B-Combo | 2.57 ± 1.11 b | 2.67 ± 0.76 a | 5.82 ± 0.37 a | 2.16 ± 0.84 b | |
| Trial 4 | NC | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 1.04 ± 0.70 b | 0.31 ± 0.31 c | 0.87 ± 0.61 d |
| PM | 7.05 ± 0.42 a | 0.31 ± 0.31 b | 4.38 ± 0.99 b | 6.45 ± 0.49 a | |
| LAB46 | 6.26 ± 0.57 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 5.52 ± 0.68 ab | 3.24 ± 0.91 c | |
| LAB46 + B2-2 | 2.60 ± 0.77 b | 5.10 ± 0.84 a | 6.26 ± 0.38 a | 4.17 ± 1.01 bc | |
| LAB46 + B3-4 | 5.64 ± 1.21 a | 3.50 ± 1.08 a | 7.08 ± 0.70 a | 5.87 ± 0.92 ab | |
| LAB46 + B-Combo | 6.55 ± 0.56 a | 5.26 ± 0.97 a | 5.32 ± 0.60 ab | 6.27 ± 0.67 ab |
| Treatment 1 | Trial 2 | Trial 3 | Trial 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 237/239 (99.16) | 357/354 (99.16) | 432/441 (97.96) |
| PM | 230/236 (97.46) | 356/351 (98.60) | 439/446 (98.43) |
| LAB46 | 237/238 (99.58) | 358/357 (99.71) | 221/223 (99.10) |
| LAB46 + B3-4 | 215/219 (98.17) | 359/352 (98.06) | 208/209 (99.52) |
| LAB46 + B2-2 | 230/230 (100) | 357/353 (98.88) | 206/207 (99.52) |
| LAB46 + B-Combo | 224/225 (99.56) | 354/352 (99.42) | 206/208 (99.04) |
| Trial | Treatment 1 | BW (g) | BWG (g) | FCR | Mortality (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d0 | d7 | d14 | d0–7 | d0–14 | d0–7 | d0–14 | d0–7 | d0–14 | ||
| Trial 2 | NC | 38.5 ± 0.02 c | 143.4 ± 1.97 | 394.1 ± 7.41 | 103.85 ± 1.85 | 398.83 ± 5.63 ab | 1.27 ± 0.04 b | 1.37 ± 0.03 | 1/160 (0.63) | 2/160 (1.25) |
| PM | 38.6 ± 0.06 c | 144.0 ± 2.67 | 358.9 ± 10.40 | 105.46 ± 2.65 | 375.83 ± 10.27 b | 1.41 ± 0.10 ab | 1.55 ± 0.11 | 0/160 (0) | 0/160 (0) | |
| LAB46 | 38.5 ± 0.02 c | 148.9 ± 4.44 | 399.5 ± 4.13 | 110.34 ± 4.44 | 417.22 ± 3.70 a | 1.30 ± 0.03 ab | 1.32 ± 0.02 | 0/160 (0) | 0/160 (0) | |
| LAB46 + B2-2 | 39.3 ± 0.06 a | 141.8 ± 5.88 | 400.2 ± 17.53 | 102.54 ± 5.85 | 415.97 ± 17.60 a | 1.53 ± 0.15 a | 1.53 ± 0.21 | 0/160 (0) | 1/160 (0.63) | |
| LAB46 + B3-4 | 38.8 ± 0.04 b | 146.8 ± 1.55 | 387.4 ± 12.03 | 107.99 ± 1.56 | 404.39 ± 12.27 ab | 1.33 ± 0.06 ab | 1.39 ± 0.03 | 0/160 (0) | 0/160 (0) | |
| LAB46 + B-Combo | 38.5 ± 0.04 c | 148.3 ± 2.52 | 389.3 ± 12.92 | 108.94 ± 2.69 | 405.76 ± 13.29 a | 1.38 ± 0.04 ab | 1.39 ± 0.04 | 1/160 (0.63) | 1/160 (0.63) | |
| Trial 4 | NC | 38.7 ± 0.04 ab | 133.4 ± 3.21 ab | 346.5 ± 9.31 | 90.86 ± 3.21 | 299.00 ± 9.39 | 1.56 ± 0.10 | 1.74 ± 0.10 | 4/264 (1.52) | 4/264 (1.52) |
| PM | 38.6 ± 0.06 b | 134.0 ± 3.26 b | 344.9 ± 12.73 | 91.37 ± 3.21 | 296.80 ± 12.58 | 1.54 ± 0.09 | 1.64 ± 0.06 | 1/242 (0.41) | 4/242 (1.65) | |
| LAB46 | 38.5 ± 0.06 b | 140.1 ± 3.62 ab | 360.6 ± 9.42 | 97.70 ± 3.59 | 312.40 ± 9.64 | 1.49 ± 0.11 | 1.62 ± 0.09 | 1/198 (0.51) | 4/198 (2.02) | |
| LAB46 + B2-2 | 38.5 ± 0.06 b | 142.1 ± 5.14 ab | 361.8 ± 15.88 | 99.81 ± 5.12 | 314.80 ± 15.86 | 1.30 ± 0.07 | 1.51 ± 0.09 | 0/154 (0) | 0/154 (0) | |
| LAB46 + B3-4 | 38.5 ± 0.04 b | 140.1 ± 1.51 ab | 363.3 ± 1.18 | 95.36 ± 2.49 | 314.60 ± 1.74 | 1.50 ± 0.11 | 1.63 ± 0.09 | 3/132 (2.27) | 5/132 (3.79) | |
| LAB46 + B-Combo | 38.9 ± 0.25 a | 144.3 ± 4.44 a | 365.2 ± 11.38 | 100.10 ± 4.60 | 316.80 ± 11.15 | 1.46 ± 0.10 | 1.63 ± 0.09 | 4/154 (2.60) | 5/154 (3.25) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rowland, M.C.; Teague, K.D.; Forga, A.J.; Higuita, J.; Coles, M.E.; Hargis, B.M.; Vuong, C.N.; Graham, D. Evaluation of the Effect of In Ovo Applied Bifidobacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria on Enteric Colonization by Hatchery-Associated Opportunistic Pathogens and Early Performance in Broiler Chickens. Poultry 2025, 4, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4020015
Rowland MC, Teague KD, Forga AJ, Higuita J, Coles ME, Hargis BM, Vuong CN, Graham D. Evaluation of the Effect of In Ovo Applied Bifidobacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria on Enteric Colonization by Hatchery-Associated Opportunistic Pathogens and Early Performance in Broiler Chickens. Poultry. 2025; 4(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRowland, Mitchell C., Kyle D. Teague, Aaron J. Forga, James Higuita, Makenly E. Coles, Billy M. Hargis, Christine N. Vuong, and Danielle Graham. 2025. "Evaluation of the Effect of In Ovo Applied Bifidobacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria on Enteric Colonization by Hatchery-Associated Opportunistic Pathogens and Early Performance in Broiler Chickens" Poultry 4, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4020015
APA StyleRowland, M. C., Teague, K. D., Forga, A. J., Higuita, J., Coles, M. E., Hargis, B. M., Vuong, C. N., & Graham, D. (2025). Evaluation of the Effect of In Ovo Applied Bifidobacteria and Lactic Acid Bacteria on Enteric Colonization by Hatchery-Associated Opportunistic Pathogens and Early Performance in Broiler Chickens. Poultry, 4(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/poultry4020015






