The Arg753Gln Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 2 in a Syphilis-Infected and Control Population in The Netherlands: Can Differences in the Number of Self-Reported Sexual Contacts Indicate Protection against Syphilis?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population: Amsterdam Cohort Study
2.2. Collection of Samples
2.3. Isolation of Human DNA and PCR Amplification
2.4. Statistical Methods
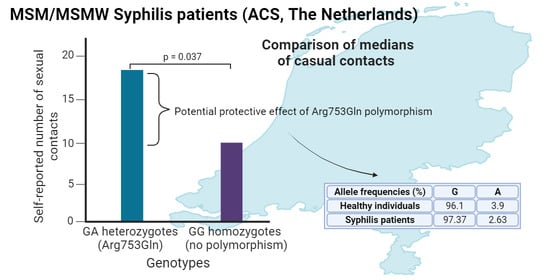
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirschning, C.J.; Schumann, R.R. TLR2: Cellular Sensor for Microbial and Endogenous Molecular Patterns. In Toll-Like Receptor Family Members and Their Ligands; Beutler, B., Wagner, H., Eds.; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 121–144. ISBN 978-3-642-59430-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.J.; Yeum, C.E.; Kim, B.C.; You, E.-Y.; Chae, G.-T. Differential production of interleukin-10 and interleukin-12 in mononuclear cells from leprosy patients with a Toll-like receptor 2 mutation. Immunology 2004, 112, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ali, M.; Barbouche, M.-R.; Bousnina, S.; Chabbou, A.; Dellagi, K. Toll-Like Receptor 2 Arg677Trp Polymorphism Is Associated with Susceptibility to Tuberculosis in Tunisian Patients. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2004, 11, 625–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozen, S.; Berdeli, A.; Türel, B.; Kutlay, S.; Yalcinkaya, F.; Arici, M.; Besbas, N.; Bakkaloglu, A.; Yilmaz, E. Arg753Gln TLR-2 polymorphism in familial mediterranean fever: Linking the environment to the phenotype in a monogenic inflammatory disease. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 2498–2500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, E.; Mira, J.P.; Cornish, K.L.; Arbour, N.C.; Schwartz, D.A. A Novel Polymorphism in the Toll-like Receptor 2 Gene and Its Potential Association with Staphylococcal Infection. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6398–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Texereau, J.; Chiche, J.-D.; Taylor, W.; Choukroun, G.; Comba, B.; Mira, J.-P. The Importance of Toll-like Receptor 2 Polymorphisms in Severe Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, S408–S415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, N.W.J.; Diterich, I.; Zinke, A.; Eckert, J.; Draing, C.; Baehr, V.V.; Hassler, D.; Priem, S.; Hahn, K.; Michelsen, K.S.; et al. Heterozygous Arg753Gln Polymorphism of Human TLR-2 Impairs Immune Activation by Borrelia burgdorferi and Protects from Late Stage Lyme Disease1. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2534–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozman, M.; Zidovec-Lepej, S.; Jambrosic, K.; Babić, M.; Drmić Hofman, I. Role of TLRs in HIV-1 Infection and Potential of TLR Agonists in HIV-1 Vaccine Development and Treatment Strategies. Pathogens 2023, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawn, T.R.; Scholes, D.; Li, S.S.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Roberts, P.L.; Stapleton, A.E.; Janer, M.; Aderem, A.; Stamm, W.E.; et al. Toll-like Receptor Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Urinary Tract Infections in Adult Women. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijpittayarit, S.; Eid, A.J.; Brown, R.A.; Paya, C.V.; Razonable, R.R. Relationship between Toll-like receptor 2 polymorphism and cytomegalovirus disease after liver transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Abdel-Massih, R.C.; Brown, R.A.; Dierkhising, R.A.; Kremers, W.K.; Razonable, R.R. Homozygosity for the toll-like receptor 2 R753Q single-nucleotide polymorphism is a risk factor for cytomegalovirus disease after liver transplantation. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 205, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad-Nejad, P.; Denz, C.; Zimmer, W.; Wacker, J.; Bugert, P.; Weiss, C.; Quintel, M.; Neumaier, M. The presence of functionally relevant toll-like receptor polymorphisms does not significantly correlate with development or outcome of sepsis. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2011, 15, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgel, P.; Macquin, C.; Bahram, S. The Heterogeneous Allelic Repertoire of Human Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) Genes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogus, A.C.; Yoldas, B.; Ozdemir, T.; Uguz, A.; Olcen, S.; Keser, I.; Coskun, M.; Cilli, A.; Yegin, O. The Arg753GLn polymorphism of the human toll-like receptor 2 gene in tuberculosis disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Chen, C.-J.; Chin, C.-H.; Liu, S.-F.; Wu, C.-C.; Eng, H.-L.; Chao, T.-Y.; Tsen, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; et al. Toll-like receptor 2 gene polymorphisms, pulmonary tuberculosis, and natural killer cell counts. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.A.; Ramadan, M.M.; Arram, E.O. Toll-like receptor-2 Arg753Gln and Arg677Trp polymorphisms and susceptibility to pulmonary and peritoneal tuberculosis. Apmis 2017, 125, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cédola, M.; Chiani, Y.; Pretre, G.; Alberdi, L.; Vanasco, B.; Gómez, R.M. Association of Toll-like receptor 2 Arg753Gln and Toll-like receptor 1 Ile602Ser single-nucleotide polymorphisms with leptospirosis in an Argentine population. Acta Trop. 2015, 146, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillová, L.; Musilová, J.; Janečková, K.; Pospíšilová, P.; Kuklová, I.; Woznicová, V.; Zákoucká, H.; Šmajs, D. The Arg753Gln Polymorphism of Toll-Like Receptor 2 Has a Lower Occurrence in Patients with Syphilis, Suggesting Its Protective Effect in Czech and Slovak Individuals. Infect. Immun. 2020, 89, e00503–e00520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabel, Y.; Berdeli, A.; Mir, S. Association of TLR2 gene Arg753Gln polymorphism with urinary tract infection in children. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2007, 34, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Candore, G.; Mirabile, M.; Lio, D.; Caimi, G.; Incalcaterra, E.; Caruso, M.; Hoffmann, E.; Caruso, C. TLR2 and age-related diseases: Potential effects of Arg753Gln and Arg677Trp polymorphisms in acute myocardial infarction. Rejuven. Res. 2008, 11, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomsma, D.I.; Wijmenga, C.; Slagboom, E.P.; Swertz, M.A.; Karssen, L.C.; Abdellaoui, A.; Ye, K.; Guryev, V.; Vermaat, M.; van Dijk, F.; et al. The Genome of the Netherlands: Design, and project goals. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 22, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krediet, T.G.; Wiertsema, S.P.; Vossers, M.J.; Hoeks, S.B.E.A.; Fleer, A.; Ruven, H.J.T.; Rijkers, G.T. Toll-like Receptor 2 Polymorphism Is Associated with Preterm Birth. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 62, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioana, M.; Ferwerda, B.; Plantinga, T.S.; Stappers, M.; Oosting, M.; McCall, M.; Cimpoeru, A.; Burada, F.; Panduru, N.; Sauerwein, R.; et al. Different Patterns of Toll-like Receptor 2 Polymorphisms in Populations of Various Ethnic and Geographic Origins. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, C.M.; Sahi, S.K.; Tantalo, L.C.; Godornes, C.; Reid, T.; Behets, F.; Rompalo, A.; Klausner, J.D.; Yin, Y.P.; Mulcahy, F.; et al. Enhanced molecular typing of treponema pallidum: Geographical distribution of strain types and association with neurosyphilis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, I.A.V.; Geskus, R.B.; Davidovich, U.; Jurriaans, S.; Coutinho, R.A.; Prins, M.; Stolte, I.G. Ongoing HIV-1 transmission among men who have sex with men in Amsterdam: A 25-year prospective cohort study. AIDS 2011, 25, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, M.; Zorgdrager, F.; Bruisten, S.M.; Bakker, M.; Berkhout, B.; van der Kuyl, A.C. Widespread hepatitis B virus genotype G (HBV-G) infection during the early years of the HIV epidemic in the Netherlands among men who have sex with men. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. European Environment Agency. 2020. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/oxygen-consuming-substances-in-rivers/r-development-core-team-2006 (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- rs5743708 RefSNP Report—dbSNP—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/rs5743708#frequency_tab (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Jongen, V.W.; Reyniers, T.; Ypma, Z.M.; Schim van der Loeff, M.F.; Davidovich, U.; Zimmermann, H.M.; Coyer, L.; van den Elshout, M.A.; de Vries, H.J.; Wouters, K.; et al. Choosing event-driven and daily HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis—Data from two European PrEP demonstration projects among men who have sex with men. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2021, 24, e25768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, V.; Tiecco, G.; Storti, S.; Degli Antoni, M.; Calza, S.; Gulletta, M.; Viola, F.; Focà, E.; Matteelli, A.; Castelli, F.; et al. Syphilis Infections, Reinfections and Serological Response in a Large Italian Sexually Transmitted Disease Centre: A Monocentric Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Control Group (n = 90) | Case Group (n = 95) | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median age in years (IQR) | 44 (20.75) | 46 (12.5) | 0.074 |
| Age range (years) | 22–80 | 24–73 | |
| Different ethnicity * | 22 (24.4%) | 22 (24.4%) | 0.864 |
| HIV status (pos./neg.) | 1/73 | 10/61 | 0.004 |
| Mean no. of sexual contacts (no. of participants) ** | 9.97 (n = 39) 95%CI [5.539–14.401] | 17.69 (n = 49) 95% CI [10.301–25.079] | 0.006 |
| Arg753Gln polymorphism frequency | 7/180 (3.9%) | 5/190 (2.63%) | 0.566 |
| GG genotype frequency | 83 (92.2%) | 90 (94.7%) | 0.559 |
| GA genotype frequency | 7 (7.8%) | 5 (5.3%) | |
| AA genotype frequency | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium | 0.929 | 0.966 | 0.901 |
| Tyr715Asn polymorphism frequency *** | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | not tested |
| Glu738Gln polymorphism frequency *** | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | not tested |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrbová, E.; Zondag, H.; Bruisten, S.; Šmajs, D. The Arg753Gln Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 2 in a Syphilis-Infected and Control Population in The Netherlands: Can Differences in the Number of Self-Reported Sexual Contacts Indicate Protection against Syphilis? Venereology 2024, 3, 26-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/venereology3010003
Vrbová E, Zondag H, Bruisten S, Šmajs D. The Arg753Gln Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 2 in a Syphilis-Infected and Control Population in The Netherlands: Can Differences in the Number of Self-Reported Sexual Contacts Indicate Protection against Syphilis? Venereology. 2024; 3(1):26-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/venereology3010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrbová, Eliška, Helene Zondag, Sylvia Bruisten, and David Šmajs. 2024. "The Arg753Gln Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 2 in a Syphilis-Infected and Control Population in The Netherlands: Can Differences in the Number of Self-Reported Sexual Contacts Indicate Protection against Syphilis?" Venereology 3, no. 1: 26-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/venereology3010003
APA StyleVrbová, E., Zondag, H., Bruisten, S., & Šmajs, D. (2024). The Arg753Gln Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptor 2 in a Syphilis-Infected and Control Population in The Netherlands: Can Differences in the Number of Self-Reported Sexual Contacts Indicate Protection against Syphilis? Venereology, 3(1), 26-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/venereology3010003