Physiopathological Aspects of Synovial Fluid and Membrane in Psoriatic Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
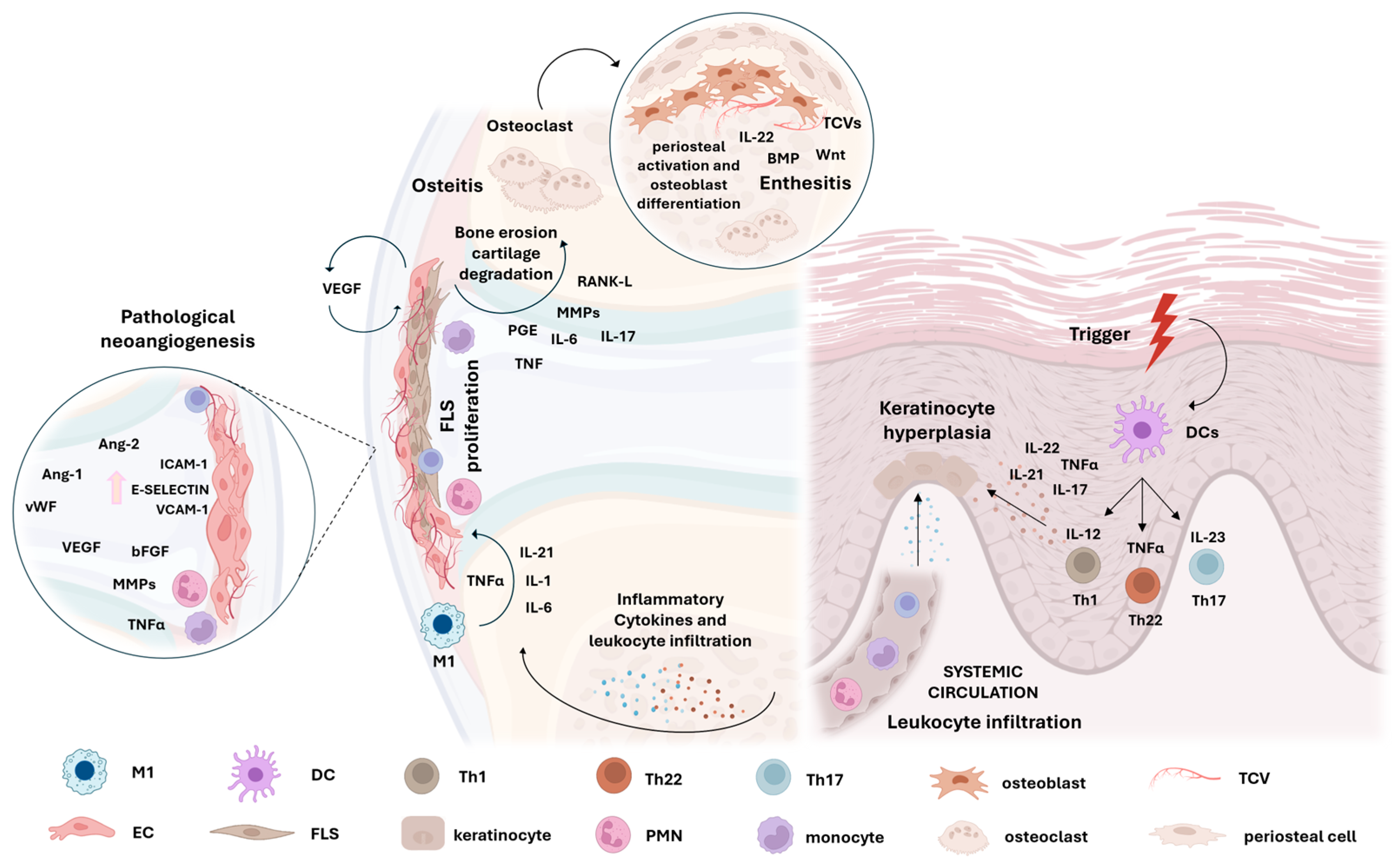
2. Synovitis in Psoriatic Arthritis
2.1. Lining Hyperplasia
2.2. Synovial Sublining Vascularization
2.3. Sublining Influx of Innate and Adaptative Immunity Cells
2.4. Inflammatory Mediators Involved in PsA Synovitis
2.5. Tissue Damage and Bone Remodelling in PsA
3. Synovial Fluid in PsA
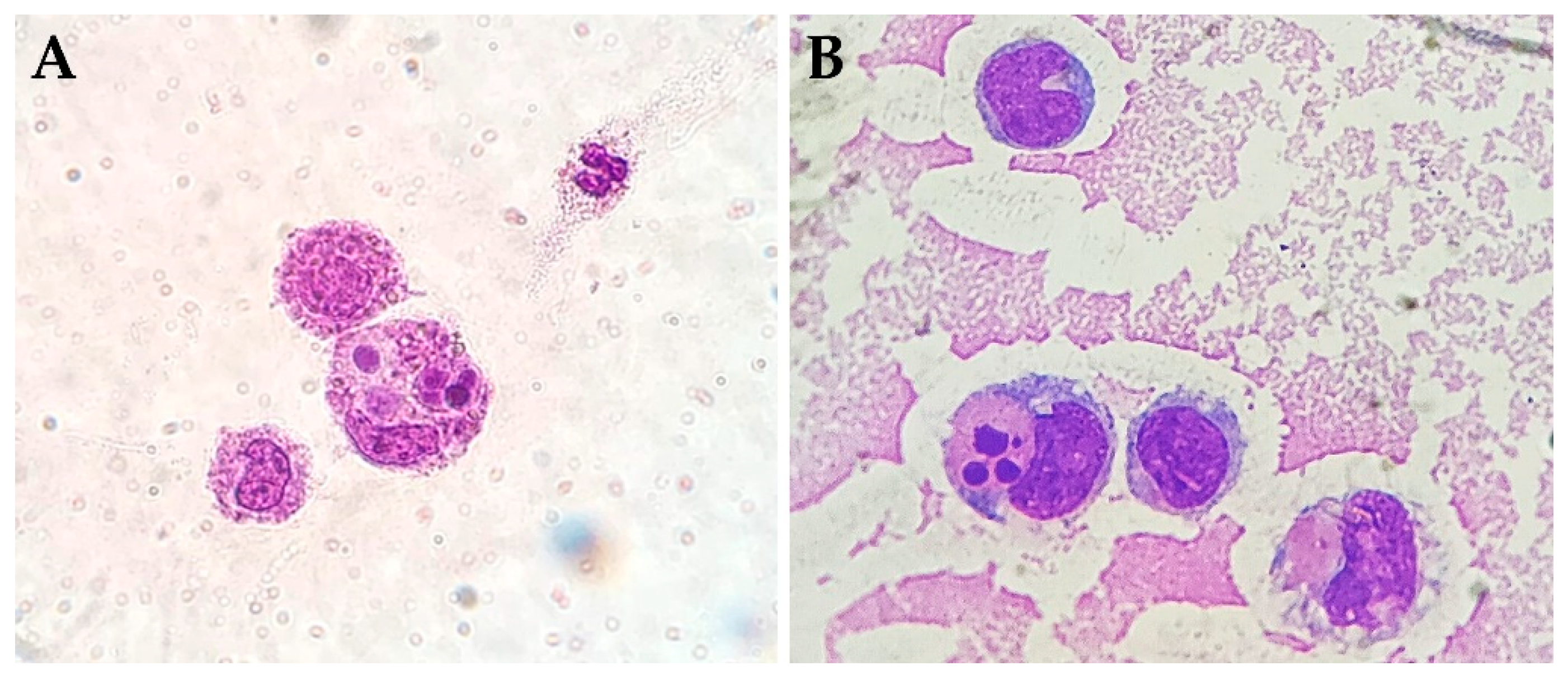
3.1. Inflammatory Cells
3.2. Cytophagocytic Mononuclear Cells
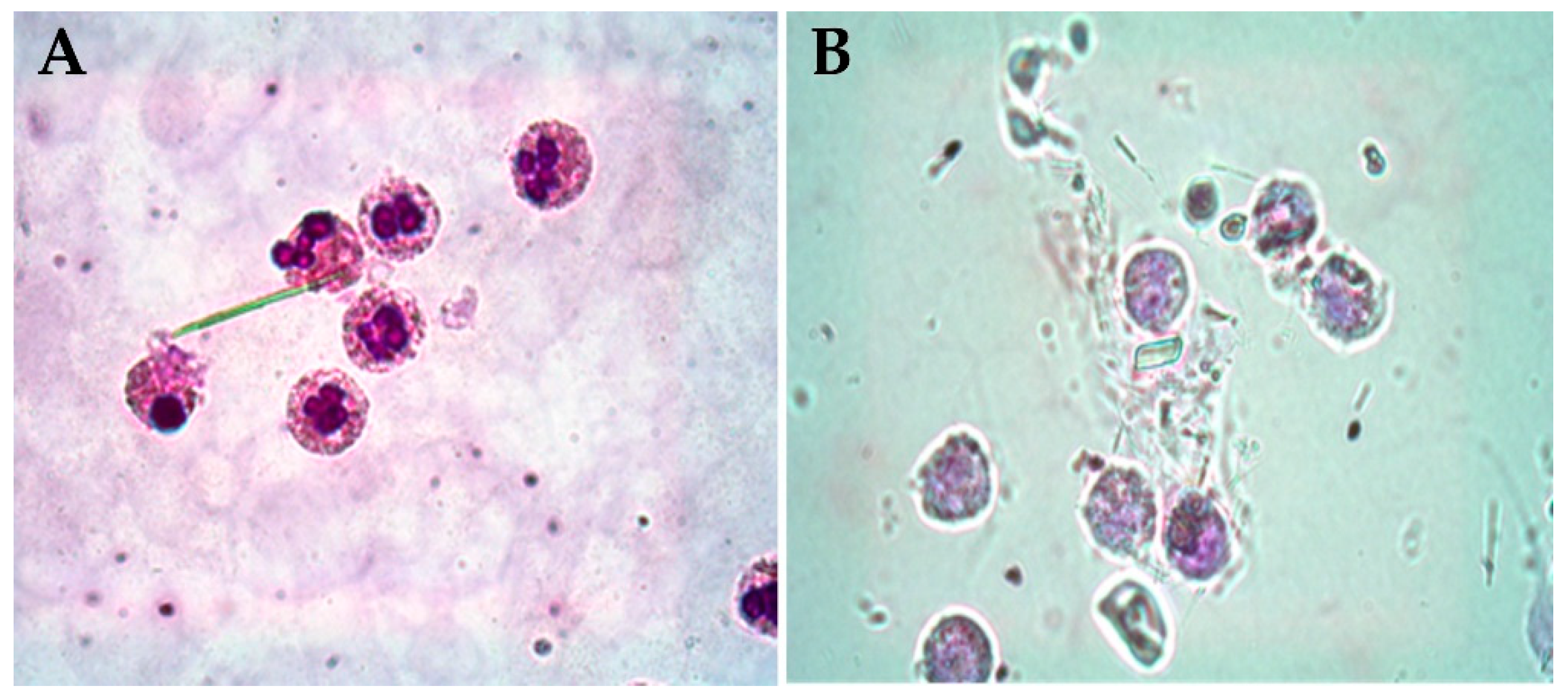
3.3. Pathogenic Crystals
3.4. Synovial Biomarkers in SF
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jose, A.M.; Rasool, M. A glimpse on the role of IL-21 in psoriatic arthritis pathogenesis. Life Sci. 2024, 350, 122766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G.; Rahman, P.; Ritchlin, C.; McInnes, I.B.; Elewaut, D.; Scher, J.U. Psoriatic arthritis from a mechanistic perspective. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celis, R.; Cuervo, A.; Ramírez, J.; Cañete, J.D. Psoriatic Synovitis: Singularity and Potential Clinical Implications. Front. Med. 2019, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougados, M.; Van der Linden, S.; Juhlin, R.; Huitfeldt, B.; Amor, B.; Calin, A.; Cats, A.; Dijkmans, B.; Olivieri, I.; Pasero, G.; et al. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kuijk, A.W.; Tak, P.P. Synovitis in psoriatic arthritis: Immunohistochemistry, comparisons with rheumatoid arthritis, and effects of therapy. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2011, 13, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mease, P. Psoriatic arthritis and spondyloarthritis assessment and management update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2013, 25, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziade, N.; Bou, A.M.; Baraliakos, X. Peripheral spondyloarthritis and psoriatic arthritis sine psoriase: Are we dealing with semantics or clinically meaningful differences? RMD Open 2022, 8, e002592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruithof, E.; Baeten, D.; De Rycke, L.; Vandooren, B.; Foell, D.; Roth, J.; Cañete, J.D.; Boots, A.M.; Veys, E.M.; De Keyser, F. Synovial histopathology of psoriatic arthritis, both oligo- and polyarticular, resembles spondyloarthropathy more than it does rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R569–R580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogdie, A.; Gelfand, J.M. Clinical Risk Factors for the Development of Psoriatic Arthritis Among Patients with Psoriasis: A Review of Available Evidence. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2015, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, E.; Harrison, B.J.; Griffiths, C.E.; Silman, A.J.; Bruce, I.N. Environmental risk factors for the development of psoriatic arthritis: Results from a case-control study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrastardottir, T.; Meer, E.; Hauksdottir, A.; Gudbjornsson, B.; Kristinsson, S.Y.; Ogdie, A.; Love, T.J. Strong Site-Specific Association of Pharyngeal Cultures with the Onset of Psoriatic Arthritis and Psoriasis, Regardless of Pathogen. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuaga, A.B.; Ramírez, J.; Cañete, J.D. Psoriatic Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Targeted Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.W.; Moon, S.J. Inflammatory Cytokines in Psoriatic Arthritis: Understanding Pathogenesis and Implications for Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E. T cells in psoriatic arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2007, 9, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakin, S.G.; Coles, M.; Sherlock, J.P.; Powrie, F.; Carr, A.J.; Buckley, C.D. Pathogenic stromal cells as therapeutic targets in joint inflammation. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; McGarry, T.; Orr, C.; McCormick, J.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Tofacitinib regulates synovial inflammation in psoriatic arthritis, inhibiting STAT activation and induction of negative feedback inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenazinha, C.; Barros, R.; Fonseca, J.E.; Vieira-Sousa, E. Histopathology of Psoriatic Arthritis Synovium-A Narrative Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 860813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Ogdie, A.R.; Schumacher, H.R. Light and electron microscopic features of synovium in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2012, 36, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, R.J.; Canete, J.D.; Parsons, W.J.; Emery, P.; Veale, D.J. Distinct vascular patterns of early synovitis in psoriatic, reactive, and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, A.; Fearon, U.; Reece, R.; Emery, P.; Veale, D.J. Matrix metalloproteinase 9, apoptosis, and vascular morphology in early arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2024–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.R.; Vasey, F.B.; Espinoza, C.G.; Bocanegra, T.S.; Germain, B.F. Vascular changes in psoriatic synovium. a light and electron microscopic study. Arthritis Rheum. 1982, 25, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, U.; Griosios, K.; Fraser, A.; Reece, R.; Emery, P.; Jones, P.F.; Veale, D.J. Angiopoietins, growth factors, and vascular morphology in early arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 260–268. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, A.; Fearon, U.; Billinghurst, R.C.; Ionescu, M.; Reece, R.; Barwick, T.; Emery, P.; Poole, A.R.; Veale, D.J. Turnover of type II collagen and aggrecan in cartilage matrix at the onset of inflammatory arthritis in humans: Relationship to mediators of systemic and local inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabala, P.A.; Malvar-Fernández, B.; Lopes, A.P.; Carvalheiro, T.; Hartgring, S.A.Y.; Tang, M.W.; Conde, C.; Baeten, D.L.; Sleeman, M.; Tak, P.P.; et al. Promotion of macrophage activation by Tie2 in the context of the inflamed synovia of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis patients. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausz, S.; Garcia, S.; Ambarus, C.A.; de Launay, D.; Foster, M.; Naiman, B.; Iverson, W.; Connor, J.R.; Sleeman, M.A.; Coyle, A.J.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 promotes inflammatory activation of human macrophages and is essential for murine experimental arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1402–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, C.; Boscaro, C.; Oliviero, F.; Trevisi, L.; Ramaschi, G.; Ramonda, R.; Bolego, C.; Cignarella, A. Gender differences and pharmacological regulation of angiogenesis induced by synovial fluids in inflammatory arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovich, S.J.; Polverini, P.J.; Shepard, H.M.; Wiseman, D.M.; Shively, V.; Nuseir, N. Macrophage-induced angiogenesis is mediated by tumour necrosis factor-α. Nature 1987, 329, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordenbos, T.; Yeremenko, N.; Gofita, I.; van de Sande, M.; Tak, P.P.; Caňete, J.D.; Baeten, D. Interleukin-17-positive mast cells contribute to synovial inflammation in spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, H.; Maier, R.; Wu, P.; Scheer, R.; Hempfing, A.; Kayser, R.; Thiel, A.; Radbruch, A.; Loddenkemper, C.; Sieper, J. Analysis of IL-17+ cells in facet joints of patients with spondyloarthritis suggests that the innate immune pathway might be of greater relevance than the Th17-mediated adaptive immune response. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leijten, E.F.; van Kempen, T.S.; Boes, M.; Michels-van Amelsfort, J.M.; Hijnen, D.; Hartgring, S.A.; van Roon, J.A.; Wenink, M.H.; Radstake, T.R. Brief report: Enrichment of activated group 3 innate lymphoid cells in psoriatic arthritis synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2673–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soare, A.; Weber, S.; Maul, L.; Rauber, S.; Gheorghiu, A.M.; Luber, M.; Houssni, I.; Kleyer, A.; von Pickardt, G.; Gado, M.; et al. Cutting Edge: Homeostasis of Innate Lymphoid Cells Is Imbalanced in Psoriatic Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Di Meglio, P.; Nestle, F.O. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, L.; Vandooren, B.; Kruithof, E.; Jacques, P.; De Vos, M.; Mielants, H.; Verbruggen, G.; De Keyser, F.; Elewaut, D. Systemic levels of IL-23 are strongly associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis but not spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, B.; Gullick, N.J.; Walter, G.J.; Rajasekhar, M.; Garrood, T.; Evans, H.G.; Taams, L.S.; Kirkham, B.W. Interleukin-17+CD8+ T cells are enriched in the joints of patients with psoriatic arthritis and correlate with disease activity and joint damage progression. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Chiricozzi, A. The Immunologic Role of IL-17 in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, N.L.; Akbar, M.; Campbell, A.L.; Reilly, J.H.; Kerr, S.C.; McLean, M.; Frleta-Gilchrist, M.; Fazzi, U.G.; Leach, W.J.; Rooney, B.P.; et al. IL-17A mediates inflammatory and tissue remodeling events in early human tendinopathy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Rodriguez, F.H.; Kanaly, S.; Stocking, K.L.; Schurr, J.; Schwarzenberger, P.; Oliver, P.; Huang, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; et al. Requirement of interleukin 17 receptor signaling for lung CXC chemokine and granulocyte colony- stimulating factor expression, neutrophil recruitment, and host defense. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafaro, G.; McInnes, I.B. Psoriatic arthritis: Tissue-directed inflammation? Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kuijk, A.W.; Wijbrandts, C.A.; Vinkenoog, M.; Zheng, T.S.; Reedquist, K.A.; Tak, P.P. TWEAK and its receptor Fn14 in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to psoriatic arthritis and its response to tumour necrosis factor blockade. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañete, J.D.; Pablos, J.L.; Sanmartí, R.; Mallofré, C.; Marsal, S.; Maymó, J.; Gratacós, J.; Mezquita, J.; Mezquita, C.; Cid, M.C. Antiangiogenic effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy with infliximab in psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1636–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigrovic, P.A.; Lee, D.M. Mast cells in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, V.E.; Luo, Y.; Colbert, R.A. IL-22 Effects on Osteoblast Mineralization and Metabolic Profile. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punzi, L.; Bertazzolo, N.; Pianon, M.; Michelotto, M.; Cesaro, G.; Gambari, P.F. The volume of synovial fluid effusion in psoriatic arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1995, 13, 535–536. [Google Scholar]
- Min, H.K.; Won, J.-Y.; Kim, B.-M.; Lee, K.-A.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.-R.; Kim, K.-W. Interleukin (IL)-25 suppresses IL-22- induced osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis via STAT3 and p38 MAPK/IκBα pathway. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belasco, J.; Wei, N. Psoriatic Arthritis: What is Happening at the Joint? Rheumatol. Ther. 2019, 6, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, C. Pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 35, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, A.; Ritchlin, C. Bone remodeling in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: An update. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2016, 28, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchlin, C.; Rahimi, H. Altered Bone Biology in Psoriatic Arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2012, 14, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, F.; Scanu, A.; Galozzi, P.; Gava, A.; Frallonardo, P.; Ramonda, R.; Punzi, L. Prevalence of calcium pyrophosphate and monosodium urate crystals in synovial fluid of patients with previously diagnosed joint diseases. Jt. Bone Spine 2013, 80, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggio, C.; Luisetto, R.; Boscaro, C.; Scanu, A.; Ramonda, R.; Albiero, M.; Sfriso, P.; Oliviero, F. Leucocyte Abnormalities in Synovial Fluid of Degenerative and Inflammatory Arthropathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornum, L.; Hansen, A.J.; Tornehave, D.; Fjording, M.S.; Colmenero, P.; Wätjen, I.F.; Søe Nielsen, N.H.; Bliddal, H.; Bartels, E.M. C5a and C5aR are elevated in joints of rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis patients, and C5aR blockade attenuates leukocyte migration to synovial fluid. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocco, U.; Sfriso, P.; Oliviero, F.; Roux-Lombard, P.; Scagliori, E.; Cozzi, L.; Lunardi, F.; Calabrese, F.; Vezzù, M.; Dainese, S.; et al. Synovial effusion and synovial fluid biomarkers in psoriatic arthritis to assess intraarticular tumor necrosis factor-α blockade in the knee joint. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, F.; Galozzi, P.; Padoan, A.; Lorenzin, M.; Scanu, A.; Ramonda, R. Seasonal variation and disease distribution of cytophagocytic mononuclear cells in synovial fluid: A medical record study. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, F.; Chimenti, M.S.; Navarini, L.; Ruscitti, P.; Peluso, R.; Girolimetto, N.; Del Puente, A.; Giacomelli, R.; Scarpa, R.; Costa, L. Metabolic Syndrome and psoriatic arthritis: Considerations for the clinician. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geneva-Popova, M.; Popova-Belova, S.; Popova, V.; Stoilov, N. Assessment of Crystals in the Synovial Fluid of Psoriatic Arthritis Patients in Relation to Disease Activity. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogera, S.; Jansen, M.P.; Bay-Jensen, A.-C.; Frederiksen, P.; Karsdal, M.A.; Thudium, C.S.; Mastbergen, S.C. Relevance of Biomarkers in Serum vs. Synovial Fluid in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivo, R.; Conigliaro, P.; Riccieri, V.; Di Franco, M.; Alessandri, C.; Spadaro, A.; Perricone, R.; Valesini, G. Distribution of interleukin-10 family cytokines in serum and synovial fluid of patients with inflammatory arthritis reveals different contribution to systemic and joint inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 179, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggino, G.; Ciccia, F.; Di Liberto, D.; Lo Pizzo, M.; Ruscitti, P.; Cipriani, P.; Ferrante, A.; Sireci, G.; Dieli, F.; Fournie, J.J.; et al. Interleukin (IL)-9/IL-9R axis drives γδ T cells activation in psoriatic arthritis patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 186, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, S.M.; Chandran, V. Exploring the Psoriatic Arthritis Proteome in Search of Novel Biomarkers. Proteomes. 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, F.; Saviano, A.; Tasso, M.; Raucci, F.; Marigliano, N.; Passavanti, S.; Frallonardo, P.; Ramonda, R.; Brancaleone, V.; Bucci, M.; et al. Analysis of rheumatoid- vs psoriatic arthritis synovial fluid reveals differential macrophage (CCR2) and T helper subsets (STAT3/4 and FOXP3) activation. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretu, D.; Prassas, I.; Saraon, P.; Batruch, I.; Gandhi, R.; Diamandis, E.P.; Chandran, V. Identification of psoriatic arthritis mediators in synovial fluid by quantitative mass spectrometry. Clin. Proteomics. 2014, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarroja, N.; López-Montilla, M.D.; Cuesta-López, L.; Pérez-Sánchez, C.; Ruiz-Ponce, M.; López-Medina, C.; Ladehesa-Pineda, M.L.; López-Pedrera, C.; Escudero-Contreras, A.; Collantes-Estévez, E.; et al. Characterization of the inflammatory proteome of synovial fluid from patients with psoriatic arthritis: Potential treatment targets. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1133435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caso, F.; Postiglione, L.; Covelli, B.; Ricciardone, M.; Di Spigna, G.; Formisano, P.; D’Esposito, V.; Girolimetto, N.; Tasso, M.; Peluso, R.; et al. Pro-inflammatory adipokine profile in psoriatic arthritis: Results from a cross-sectional study comparing PsA subset with evident cutaneous involvement and subset “sine psoriasis”. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Damasco, A.C.; Ramonda, R.; Cozzi, G.; Lorenzin, M.; Sfriso, P.; Oliviero, F.; Baggio, C. Physiopathological Aspects of Synovial Fluid and Membrane in Psoriatic Arthritis. Rheumato 2024, 4, 193-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4040015
Damasco AC, Ramonda R, Cozzi G, Lorenzin M, Sfriso P, Oliviero F, Baggio C. Physiopathological Aspects of Synovial Fluid and Membrane in Psoriatic Arthritis. Rheumato. 2024; 4(4):193-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4040015
Chicago/Turabian StyleDamasco, Amelia Carmela, Roberta Ramonda, Giacomo Cozzi, Mariagrazia Lorenzin, Paolo Sfriso, Francesca Oliviero, and Chiara Baggio. 2024. "Physiopathological Aspects of Synovial Fluid and Membrane in Psoriatic Arthritis" Rheumato 4, no. 4: 193-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4040015
APA StyleDamasco, A. C., Ramonda, R., Cozzi, G., Lorenzin, M., Sfriso, P., Oliviero, F., & Baggio, C. (2024). Physiopathological Aspects of Synovial Fluid and Membrane in Psoriatic Arthritis. Rheumato, 4(4), 193-202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rheumato4040015






