TiO2 Nanoparticles in Soil: Adsorption, Transformation, and Environmental Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Adsorption of TNPs in the Soil Environment
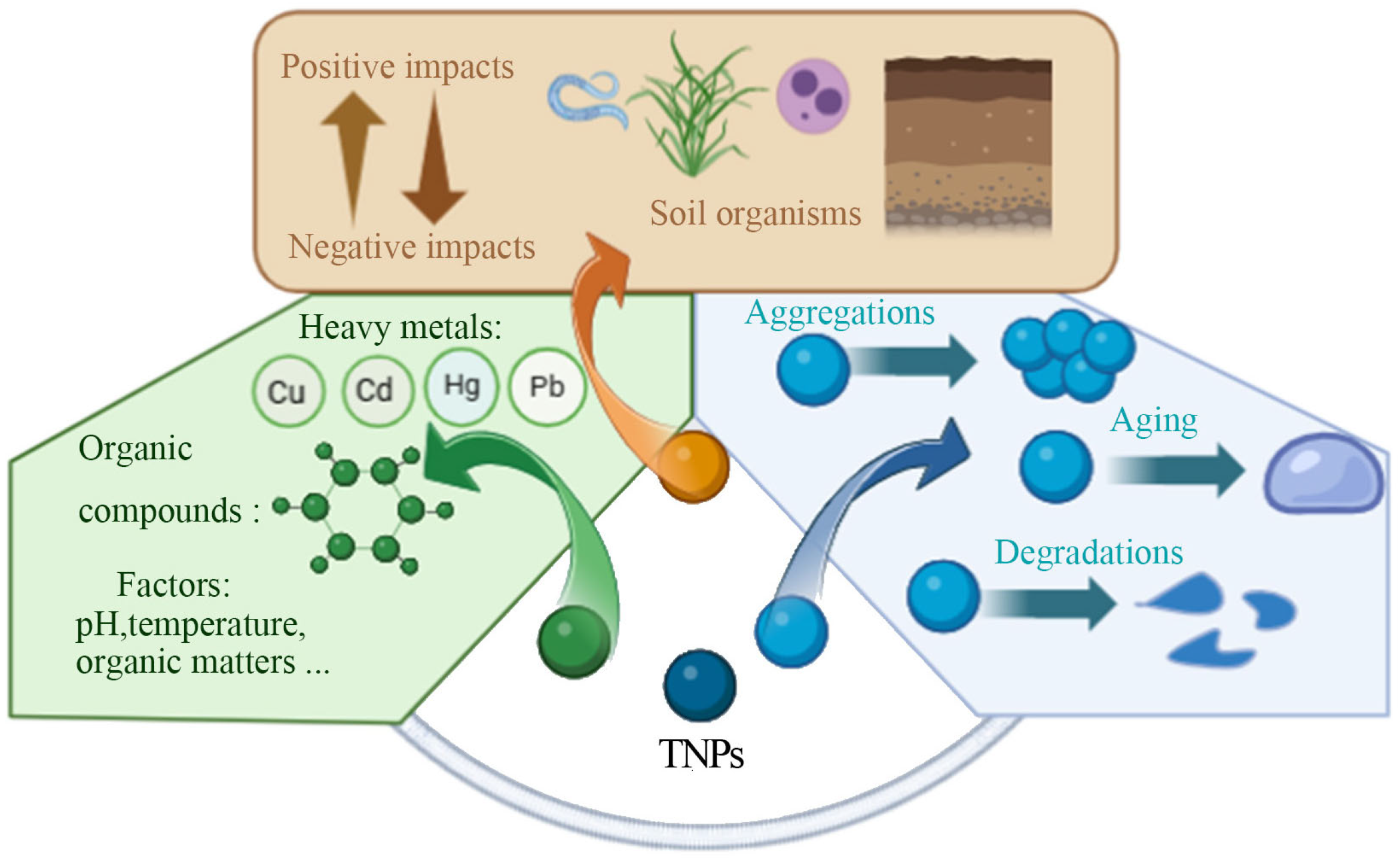
2.1. Interaction Between TNPs and Heavy Metals
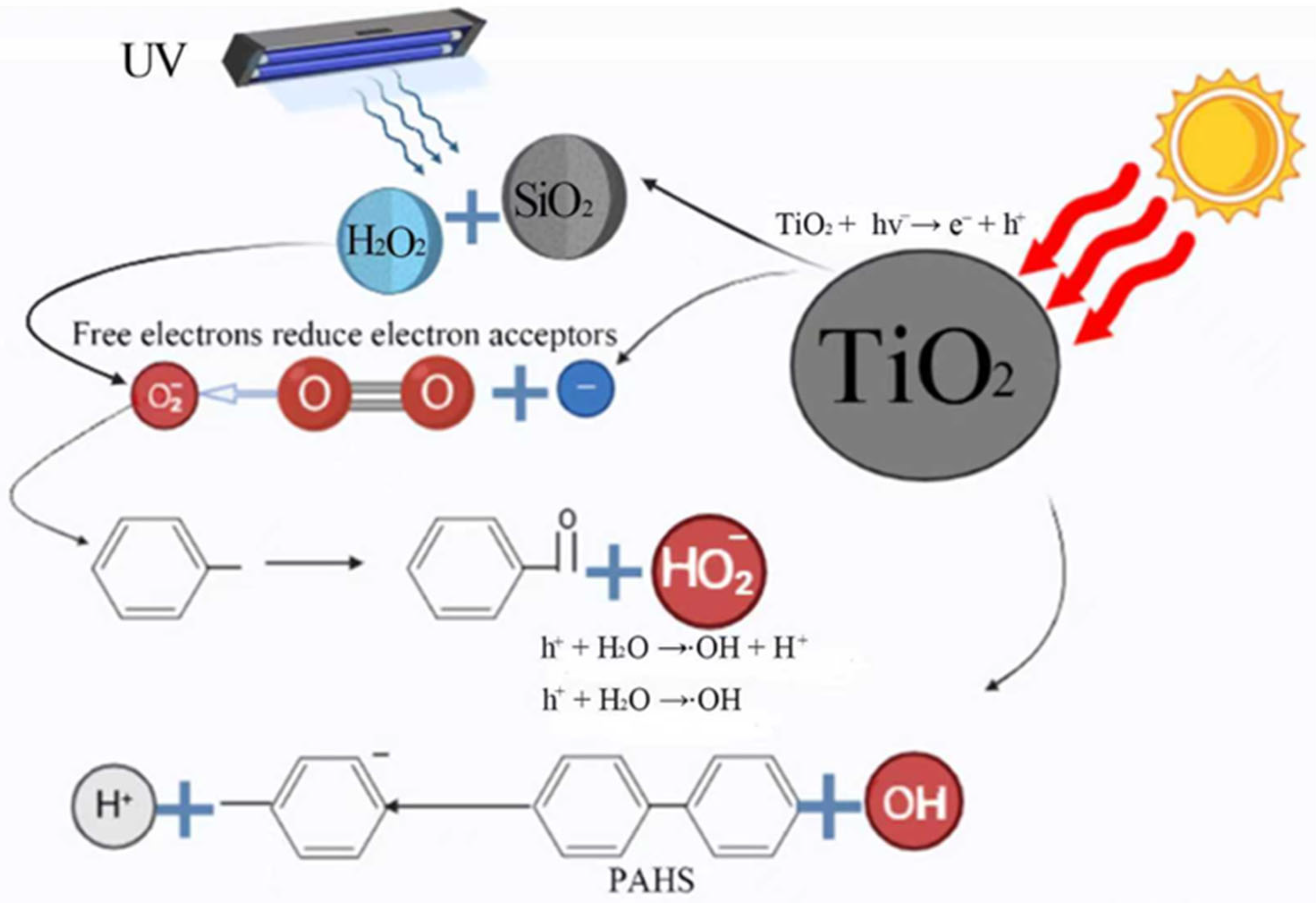
2.2. Interaction Between TNPs and Organic Compounds
2.3. Environmental Impacts on the Adsorption of TNPs
3. Transformation of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in the Soil Environment
3.1. Aggregation of TNPs in the Soil Environment
3.2. Aging Process of TNPs in the Soil Environment
3.3. Chemical/Biological Transformation of TNPs in the Soil Environment
4. Environmental Risks of TNPs in Soil
4.1. Positive Effects on Soil Organisms
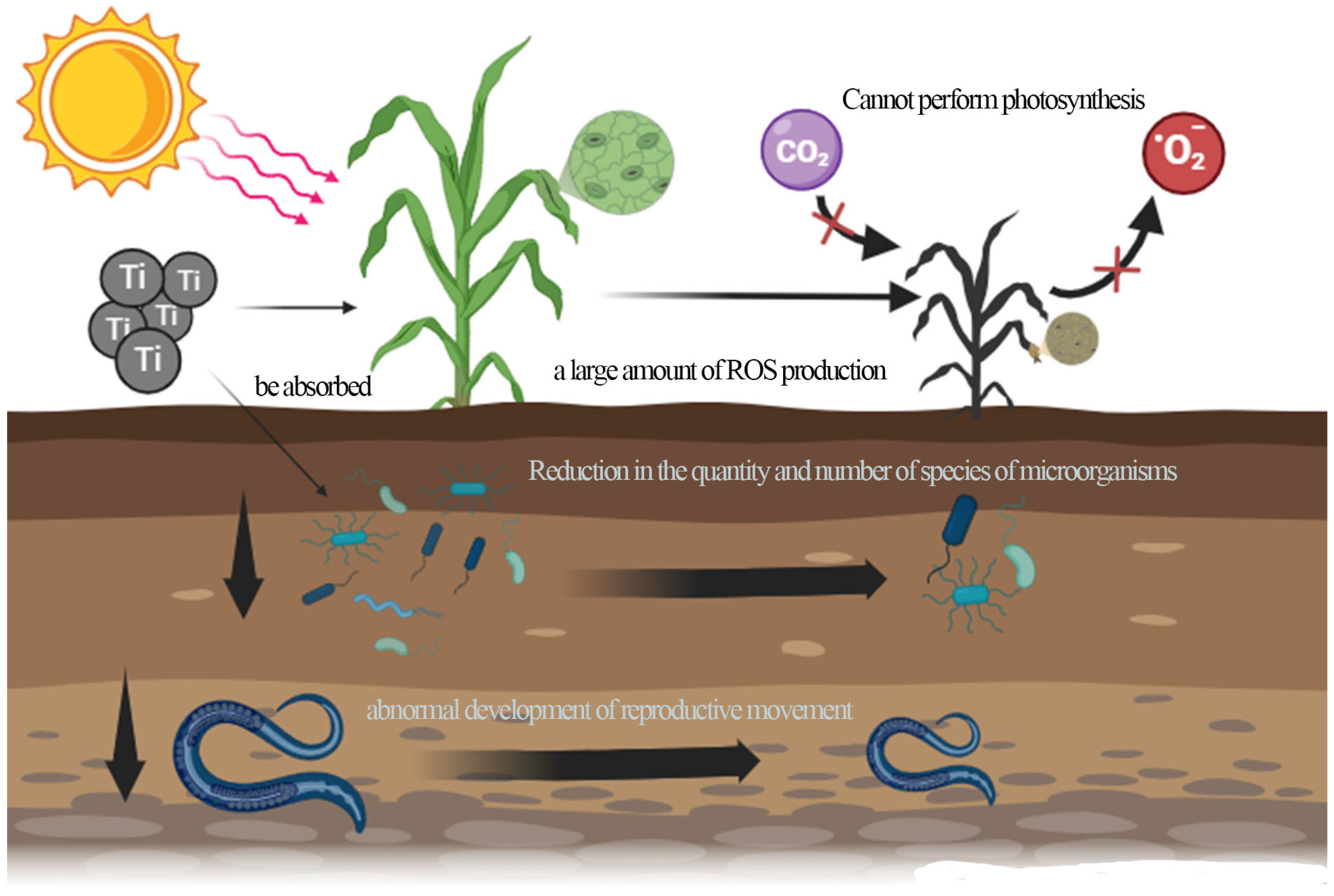
4.2. Negative Effects on Soil Organisms
| Soil Organism Group | Negative Ecological Effects | Positive Ecological Effects (Under Specific Conditions) | Key Influencing Factors | Reference Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Plants | 1. High concentration (≥2 g/L) induces ROS outburst, abnormal SOD/CAT/POD activities, and chloroplast structure disintegration; 2. Inhibits chlorophyll synthesis and causes stunted plants; 3. Toxicity is more significant under combined Cd exposure than single TNP exposure | 1. 200 mg/L TNPs can activate the antioxidant enzyme system of maize and alleviate Cd stress; 2. 0.01–0.1 mg·mL−1 TNPs enhance the resistance of tomatoes to bacterial wilt | TNP concentration, coexisting heavy metals, exposure duration | [32,37] |
| Soil Microorganisms | 1. 2000 mg/kg TNPs reduces the number of bacterial/fungal/actinomycete colonies by 45–60%; 2. 200 mg/kg TNPs decreases the Shannon diversity index (from 4.5 to 3.8) and the abundance of Proteobacteria; 3. Ammonifying bacteria/nitrifying bacteria are more sensitive to TNPs (MIC: 80–100 mg/L) | 1. Low concentration (10 mg·L−1) temporarily stimulates the metabolic activity of some microorganisms; 2. TNPs improve the living environment of microorganisms after degrading organic pollutants | TNP dosage, soil type, differences in functional genes | [35,39] |
| Soil Invertebrates | 1. Nematodes: 5 nm TNPs cause abnormalities in reproduction/movement/development; 300 nm TNPs only reduce body bending frequency; 2. Earthworms: high-concentration TNPs cause intestinal cell damage; mortality increases with concentration/duration | Soil invertebrates have extremely low demand for TiO2 | TNP particle size, exposure concentration, sensitivity of organism groups | [36] |
4.3. Cytotoxic Mechanism at the Cellular Level
5. Summary and Perspective
- Establish multitrophic microcosm models such as “soil–earthworm–bird” or “soil–plant–insect” systems to simulate the transfer process of TNPs in real food webs;
- Strengthen in vivo toxicological studies and focus on the multi-dimensional impacts of TNPs on the growth, development, reproduction, and behavior of organisms under long-term, low-dose exposure;
- Explore the connection between transformation and bioaccumulation and investigate how the chemical form transformation of TNPs in organisms affects their bioaccumulation potential and toxicity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z. Fluorine-Induced Oxygen Vacancies on TiO2 Nanosheets for Photocatalytic Indoor VOCs Degradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 348, 121610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsebigler, A.L.; Lu, G.; Yates, J.T. Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: Principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.Y. Study on the Characteristics of Nanometer Titanium Dioxide in Water and Its Interaction with Humic Acid. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.X. Preparation and Photocatalytic Performance of Mesoporous TiO2-Confined Ionic Gel Composite Particles. Master’s Thesis, Liaoning University, Shenyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.Z.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, Y.F. Study on the Aggregation Behavior of Divalent Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles in Aqueous Media. In Proceedings of the 2021 Annual Science and Technology Conference of the Chinese Society of Environmental Sciences—Environmental Engineering Technology Innovation and Application Session (IV), Tianjing, China, 20 October 2021; pp. 131–136+315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoei, A.J.; Rezaei, K. Toxicity of Titanium Nano-Oxide Nanoparticles (TiO2) on the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea gigas: Immunity and Antioxidant Defence. Toxin Rev. 2022, 1, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Study on Co-Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism of Nano-Titanium Dioxide with Tetracycline/Cadmium on Different Characteristic Soil Component Surfaces. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, D.Y.; Liang, L.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J. Effects of TNPs on the release and speciation changes of heavy metals in soil. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2016, 36, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.P. Regulation of High-Energy Facets of TiO2 and Study on Arsenic Removal. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H. Adsorption behavior of Cu2+ onto titanate nanofibers prepared by alkali treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S.; Lee, C.K.; Chen, H.Z.; Wang, C.C.; Juang, L.C. Application of titanate nanotubes for Cu2+ ions adsorptive removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 147, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liang, R.; Zhou, N.; Pan, Z. Carbon Black-Doped Anatase TiO2 Nanorods for Solar Light-Induced Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10042–10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisaksoontorn, W.; Thachepan, S.; Songsasen, A. Photodegradation of phenanthrene by n-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2009, 44, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S. Study on TiO2 Photocatalytic Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Water Bodies. Ph.D. Thesis, Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry), Guangzhou, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.J. Study on the Treatment of Printing and Dyeing Wastewater by Catalytic Ozonation Using Ti-Ce Composite Catalyst. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cao, G. Study on the photocatalytic reduction of dichromate and photocatalytic oxidation of dichlorvos. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, W. Dual photocatalytic pathways of trichloroacetate degradation on TiO2: Effects of nanosized platinum deposits on kinetics and mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 13311–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S. Study on the Adsorption Performance of Nanometer Titanium Dioxide in Heavy Metal Wastewater Treatment. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi University, Nanning, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.F. Study on the Modification of Nanometer Titanium Dioxide and Its Degradation of Organic Compounds. Master’s Thesis, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. Study on the Adsorption Performance of Heavy Metal Ions by Attapulgite Clay Supported TNPs. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Han, R.; Luan, R.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, L.D.; Qi, Z.C. Effect of phosphates on the adsorption behavior and mechanism of heavy metal ions in water by nano-titanium dioxide. Rock Miner. Anal. 2023, 42, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Hydraulic retention time governs the micro/nanostructures of titanium-incorporated diatoms and their photocatalytic activity. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J. Study on Aggregation and Deposition Characteristics of Nano-TiO2 in Water at Different Scales. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, H.J. The Influence of Aging Time of TiO2 and CeO2 Artificial Nanoparticles in Soil on the Growth of Higher Plants. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.H. The Impact of Aging and Photocatalysis Processes on the Physicochemical Properties of Titanium Dioxide Microplastics. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, F.; Pellutiè, L.; Maurino, V.; Sordello, F.; Minero, C.; Ortel, E.; Hodoroaba, V.D.; Maurino, V. Influence of agglomeration and aggregation on the photocatalytic activity of TNPS. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 217, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Zhang, X. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis: Present situation and future approaches. CR Chim. 2006, 9, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, L.H.; Guo, P. Effects of nano-TiO2 on the activity of nitrogen transformation-related bacteria in soil. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2016, 16, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Kalia, A.; Sandhu, J.; Dheri, G.S.; Kaur, G.; Pathania, S. Interaction of TiO2 nanoparticles with soil: Effect on microbiological and chemical traits. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Sun, Y.; Ji, R.; Zhu, J.; Wu, J.; Guo, H. TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles negatively affect wheat growth and soil enzyme activities in agricultural soil. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.W.; Yu, H.J.; Li, L.; Qing, M.J.; Jiang, M.; Tan, M.P. Alleviating effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the growth inhibition of maize under cadmium stress. Plant Physiol. J. 2015, 51, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.H.; Nie, D.Y.; Guo, X.P.; Xu, S.S.; Zhang, D.Y.; Cao, F.; Guan, X. Effective control of the tomato wilt pathogen using TNPS as a green nanopesticide. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Insight into the short-term effects of titanium dioxide on medicinal plant cultivation: A comprehensive analysis of ginseng physiological indices, soil physicochemical properties, and microbiome. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.T.; Tian, Y.; Zhan, Y.H.; Zhu, J. Degradation of organic pollutants in flocculated liquid digestate using photocatalytic titanate nanofibers: Mechanism and response surface optimization. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, V.A.C.; Kannan, K.; Aitken, R.J.; Naidu, R.; Mallavarapu, M. Chronic effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles to earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.W.; Cui, Y.B.; Li, D.S.; Gao, X.Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Li, M. Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cadmium uptake and phytotoxicity in maize seedlings. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2022, 39, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.M.; Wu, Z.E.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Cao, Y.L.; Jiao, Y.P.; Cao, X. Effects of Nano-TiO2 on soil microbial activity in cultivated red soil. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Thiagarajan, V.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Ravindran, B.; Mukherjee, A. Nanoplastics enhance the toxic effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticle in freshwater algae Scenedesmus obliquus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 256, 109305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, G.S.R.; Constantin, R.P.; Abrahão, J.; Foletto-Felipe, M.D.P.; Constantin, R.P.; Santos, W.D.D.; Ferrarese-Filho, O.; Marchiosi, R. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Induce Root Growth Inhibition in Soybean Due to Physical Damages. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmi, Y.; Gholinejad, Z.; Ansari, M.H.K. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce endothelial cell apoptosis via cell membrane oxidative damage and p38, PI3K/Akt, NF-κB signaling pathways modulation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 54, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.C.; Lin, W.Y.; Zainal, Z.; Williams, N.E.; Zhu, K.; Kruzic, A.P.; Smith, R.L.; Rajeshwar, K. Bactericidal Activity of TiO2 Photocatalyst in Aqueous Media: Toward a Solar-Assisted Water Disinfection System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, P. TiO2 Nanoparticles in Soil: Adsorption, Transformation, and Environmental Risks. Powders 2025, 4, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040028
Liu H, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu R, Zhang P. TiO2 Nanoparticles in Soil: Adsorption, Transformation, and Environmental Risks. Powders. 2025; 4(4):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongyu, Yaqin Wang, Xicheng Wang, Rui Liu, and Peng Zhang. 2025. "TiO2 Nanoparticles in Soil: Adsorption, Transformation, and Environmental Risks" Powders 4, no. 4: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040028
APA StyleLiu, H., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Liu, R., & Zhang, P. (2025). TiO2 Nanoparticles in Soil: Adsorption, Transformation, and Environmental Risks. Powders, 4(4), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders4040028






