Cu-10 wt.% Al Alloys Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering of Powder Blends and a Mechanically Alloyed Mixture: A Comparative Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
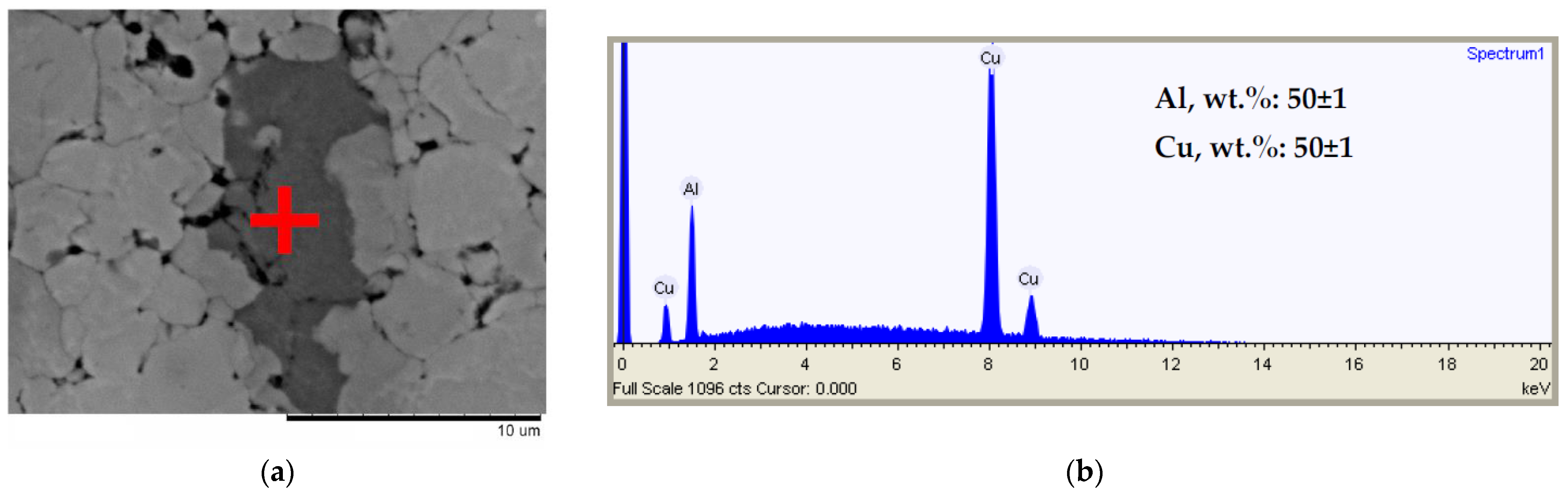
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brandes, E.A.; Brook, G.B. (Eds.) Smithells Metal Reference Handbook, 7th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Website of Copper Development Association Inc. Available online: https://www.copper.org (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- ASM International Handbook Committee. ASM Handbook, Powder Metal Technologies and Applications; ASM International: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1998; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- German, R.M. Sintering: From Empirical Observations to Scientific Principles; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2014; 544p. [Google Scholar]
- Shaik, M.A.; Golla, B.R. Densification, microstructure and properties of mechanically alloyed and hot-pressed Cu–15 wt% Al alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14694–14712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.A.; Golla, B.R. Development of highly wear resistant Cu-Al alloys processed via powder metallurgy. Tribol. Int. 2019, 136, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, M.A.; Golla, B.R. Microstructure, mechanical and wear property correlation of Al bronze alloys. Powder Metall. 2023, 66, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudina, D.V.; Grigoreva, T.F.; Kvashnin, V.I.; Devyatkina, E.T.; Vosmerikov, S.V.; Ukhina, A.V.; Novoselov, A.N.; Legan, M.A.; Esikov, M.A.; Lukyanov, Y.L.; et al. Microstructure and properties of Cu-10 wt% Al bronze obtained by high-energy mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Lett. 2022, 312, 131671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Lu, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L. Microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of nickel-aluminium bronze alloys developed via gas atomization and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 707, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, D.; Park, K.; Cho, M.; Cho, S.; Kwon, H. Effect of intermetallic compounds on the thermal and mechanical properties of Al–Cu composite materials fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Materials 2019, 12, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, K.; Kwon, H. Investigation of formation behaviour of Al–Cu intermetallic compounds in Al–50vol%Cu composites prepared by spark plasma sintering under high pressure. Materials 2021, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevas, D.; Vanmeensel, K.; Vleugels, J.; Dewulf, W.; Duflou, J.R. The use of Spark Plasma Sintering to fabricate a two-phase material from blended aluminium alloy scrap and gas atomized powder. Proc. CIRP 2015, 26, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.N.O.; da Silva, A.; Rodrigues, C.A.; de Lourdes Noronha Motta Melo, M.; Rodrigues, G.; Silva, G. Effect of high energy milling time of the aluminum bronze alloy obtained by powder metallurgy with niobium carbide addition. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.F.P.; Bayraktar, E.; Miskioglu, I.; Katundi, D. Design of hybrid composites from scrap aluminum bronze chips. In Mechanics of Composite and Multi-Functional Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 7, pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Dudina, D.V.; Bokhonov, B.B. Materials development using high-energy ball milling: A review dedicated to the memory of M.A. Korchagin. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olevsky, E.A.; Dudina, D.V. Field-Assisted Sintering: Science and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; 425p. [Google Scholar]
- Abedi, M.; Asadi, A.; Vorotilo, S.; Mukasyan, A.S. A critical review on spark plasma sintering of copper and its alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 19739–19766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Sovizi, S.; Azarniya, A.; Giuntini, D.; Seraji, M.E.; Hosseini, H.R.M.; Amutha, C.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mukasyan, A. An analytical review on Spark Plasma Sintering of metals and alloys: From processing window, phase transformation, and property perspective. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2022, 48, 169–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, J.D.; Rabson, T.A. Contactless method of measuring resistivity. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1976, 47, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvashnin, V.I.; Dudina, D.V.; Ukhina, A.V.; Koga, G.Y.; Georgarakis, K. The benefit of the glassy state of reinforcing particles for the densification of aluminum matrix composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itin, V.I.; Naiborodenko, Y.S. High-Temperature Synthesis of Intermetallic Compounds; Tomsk State University Publishing: Tomsk, Russia, 1989; 214p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, A.; Gauthier-Brunet, V.; Joulain, A.; Bonneville, J.; Dubois, S.; Monchoux, J.-P.; Pailloux, F. Mechanical properties of Al/ω-Al-Cu-Fe composites synthesized by the SPS technique. Mater. Charact. 2018, 145, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

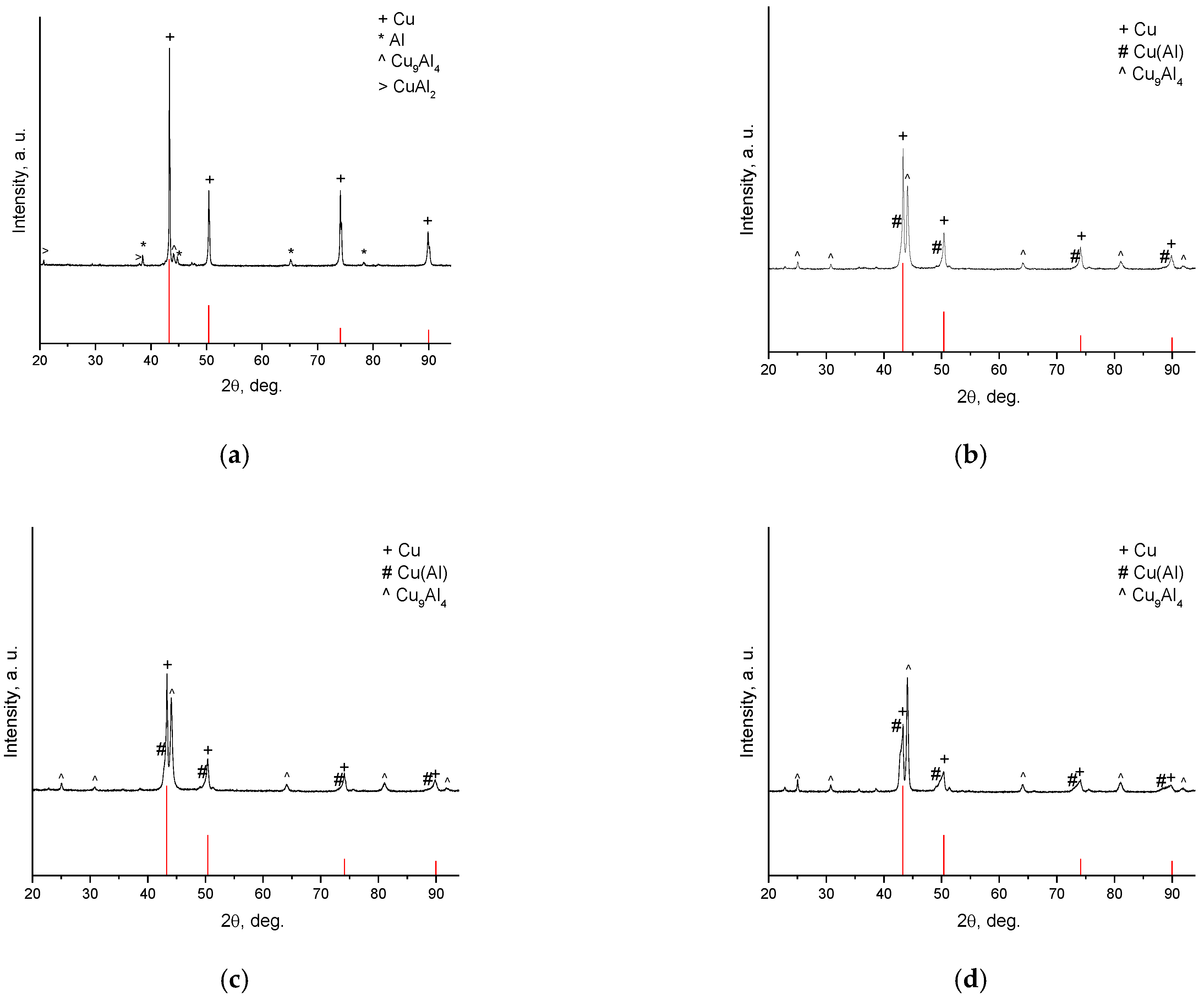
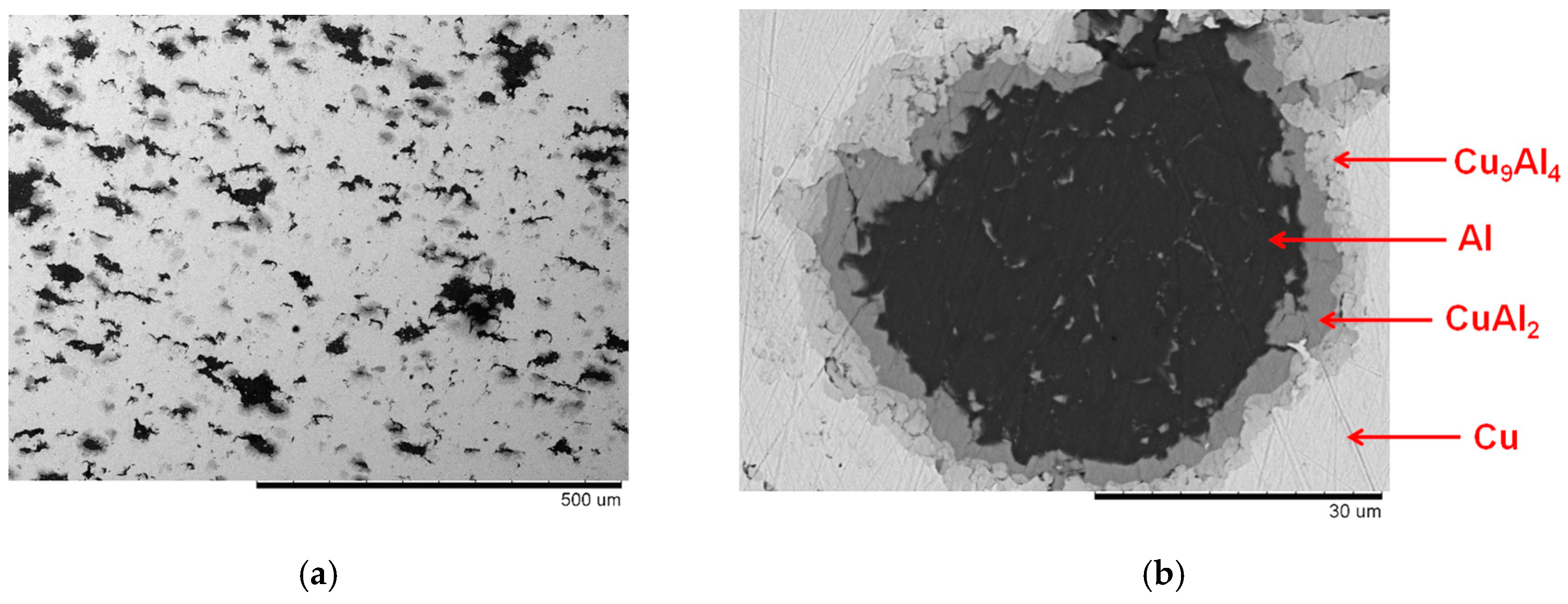
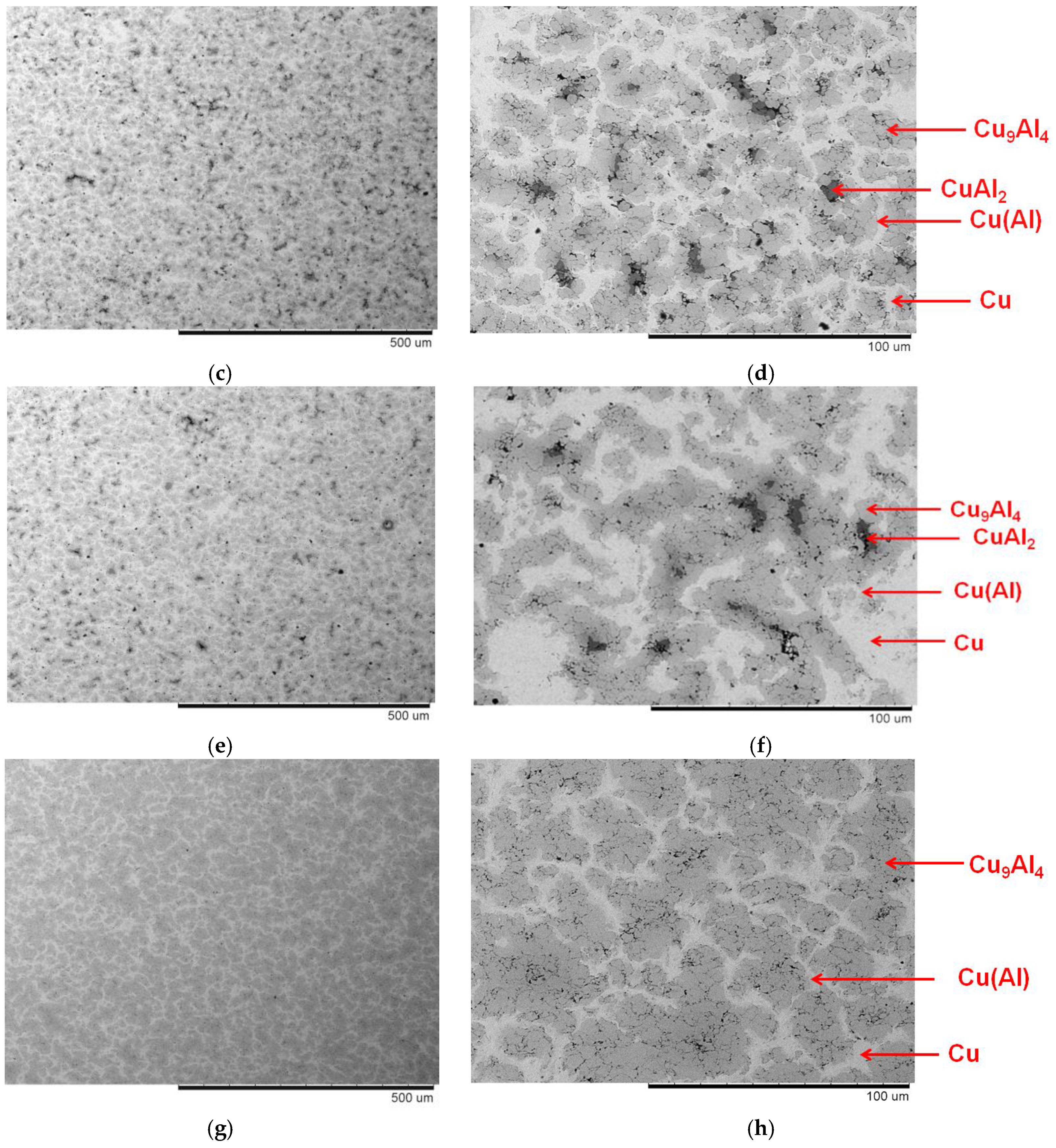

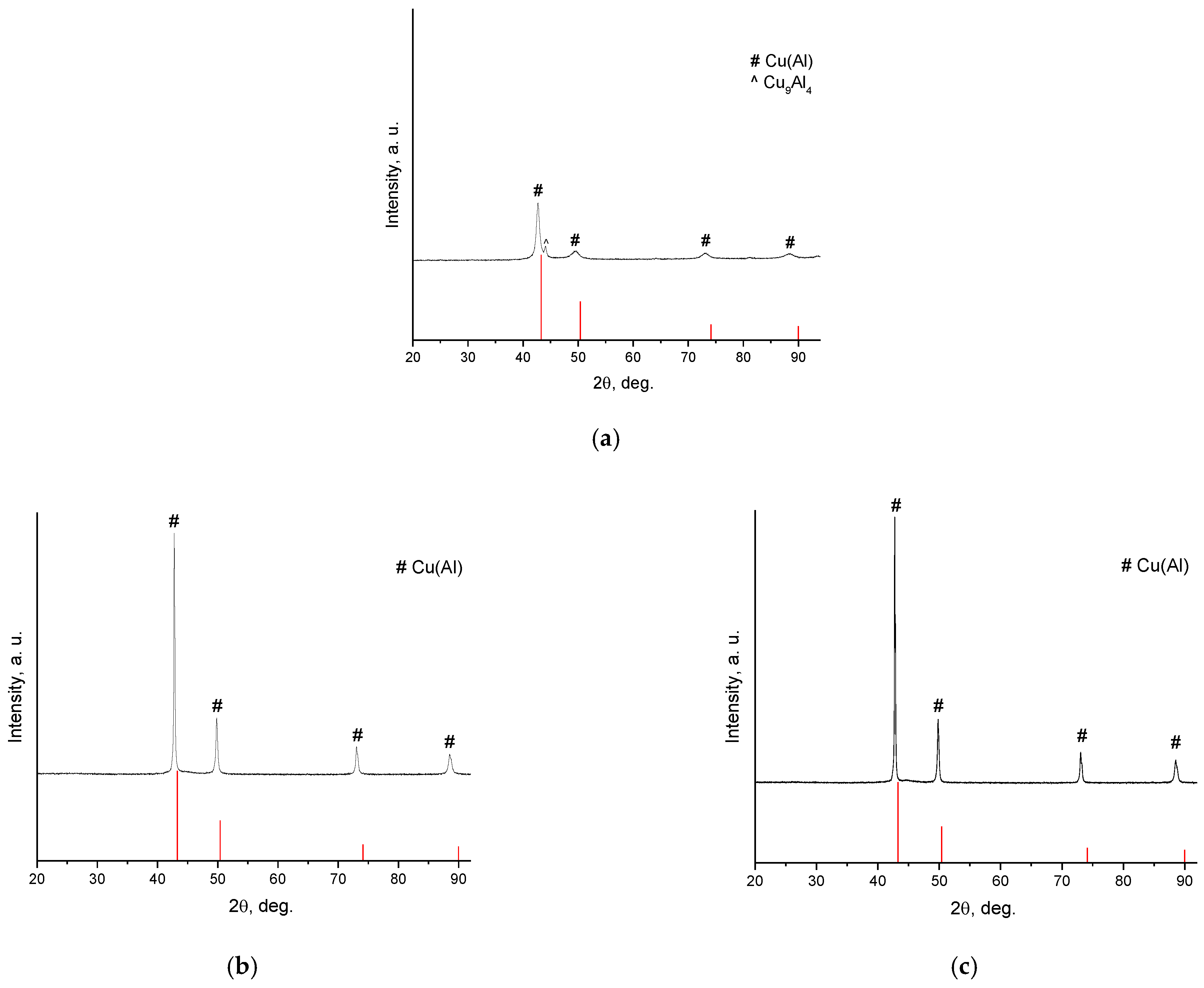
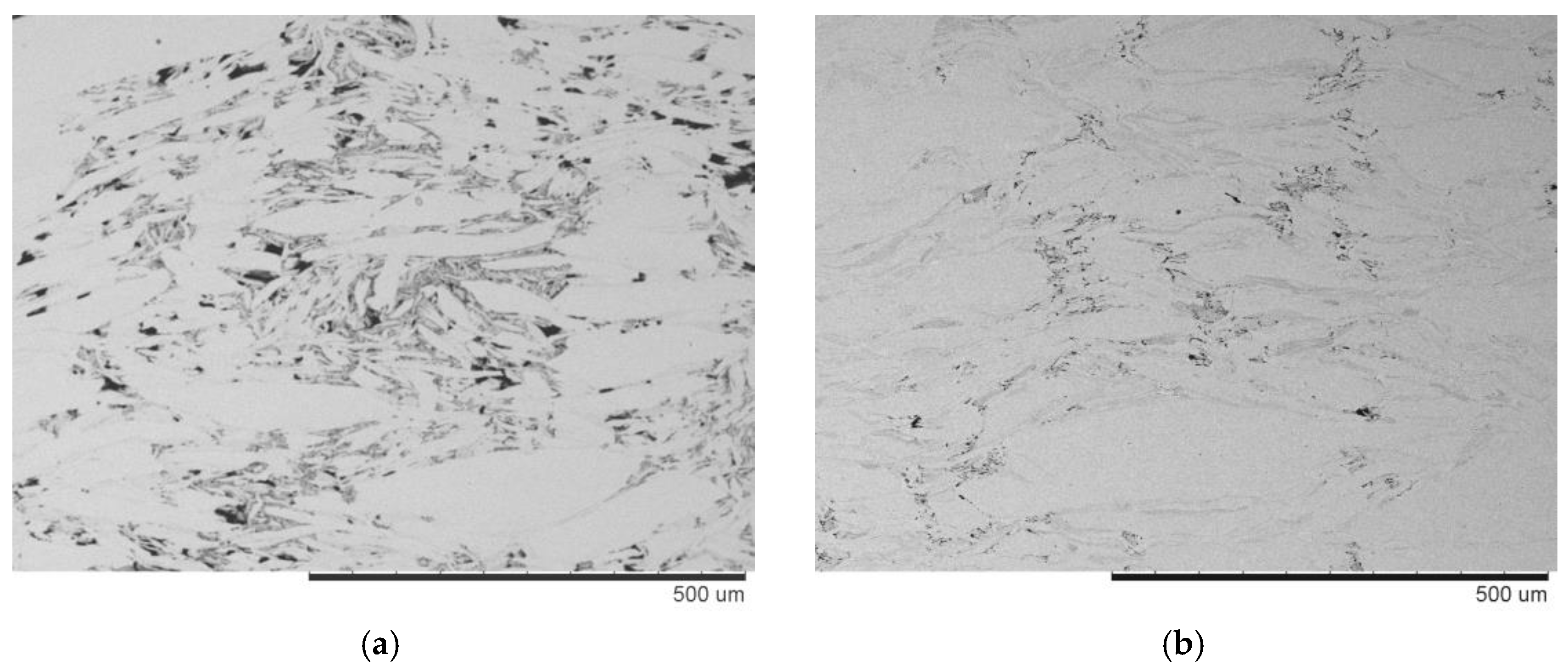
| Powder | Sintering Conditions | Phase Contents, wt.% | Residual Porosity, % | Vickers Hardness, HV1 | Electrical Conductivity, % IACS * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blend, coarse Al powder | 480 °C, 5 min, 40 MPa | Cu: 83 ± 3 CuAl2: 8 ± 1 Cu9Al4: 4 ± 1 Al: 5 ± 1 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 70 ± 3 | 56 ± 3 |
| Blend, fine Al powder | 480 °C, 5 min, 40 MPa | Cu: 35 ± 1 Cu(Al): 23 ± 1 Cu9Al4: 42 ± 1 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 160 ± 15 | 16 ± 1 |
| Blend, fine Al powder | 480 °C, 5 min, 20 MPa | Cu: 30 ± 1 Cu(Al): 25 ± 1 Cu9Al4: 45 ± 1 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 120 ± 10 | 15 ± 1 |
| Blend, fine Al powder | 480 °C, 20 min, 40 MPa | Cu: 24 ± 1 Cu(Al): 30 ± 1 Cu9Al4: 46 ± 1 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 190 ± 10 | 10 ± 1 |
| Mechanically alloyed mixture | 700 °C, 5 min, 40 MPa | Cu(Al): 100 | 15 | 280 ± 20 ** | 12 ± 1 ** |
| Mechanically alloyed mixture | 800 °C, 5 min, 40 MPa | Cu(Al): 100 | 6 | 280 ± 20 ** | 15 ± 1 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ondar, A.A.; Dudina, D.V.; Grigoreva, T.F.; Devyatkina, E.T.; Vosmerikov, S.V.; Ukhina, A.V.; Esikov, M.A.; Anisimov, A.G.; Lyakhov, N.Z. Cu-10 wt.% Al Alloys Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering of Powder Blends and a Mechanically Alloyed Mixture: A Comparative Investigation. Powders 2023, 2, 515-524. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders2030032
Ondar AA, Dudina DV, Grigoreva TF, Devyatkina ET, Vosmerikov SV, Ukhina AV, Esikov MA, Anisimov AG, Lyakhov NZ. Cu-10 wt.% Al Alloys Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering of Powder Blends and a Mechanically Alloyed Mixture: A Comparative Investigation. Powders. 2023; 2(3):515-524. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders2030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleOndar, Aigul A., Dina V. Dudina, Tatiana F. Grigoreva, Evgeniya T. Devyatkina, Sergey V. Vosmerikov, Arina V. Ukhina, Maksim A. Esikov, Alexander G. Anisimov, and Nikolay Z. Lyakhov. 2023. "Cu-10 wt.% Al Alloys Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering of Powder Blends and a Mechanically Alloyed Mixture: A Comparative Investigation" Powders 2, no. 3: 515-524. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders2030032
APA StyleOndar, A. A., Dudina, D. V., Grigoreva, T. F., Devyatkina, E. T., Vosmerikov, S. V., Ukhina, A. V., Esikov, M. A., Anisimov, A. G., & Lyakhov, N. Z. (2023). Cu-10 wt.% Al Alloys Produced by Spark Plasma Sintering of Powder Blends and a Mechanically Alloyed Mixture: A Comparative Investigation. Powders, 2(3), 515-524. https://doi.org/10.3390/powders2030032









