Wind Tunnel Experiments on Interference Effects of a High-Rise Building on the Surrounding Low-Rise Buildings in an Urban Block
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Outlines of Wind Tunnel Experiments
2.1. Experimental Models
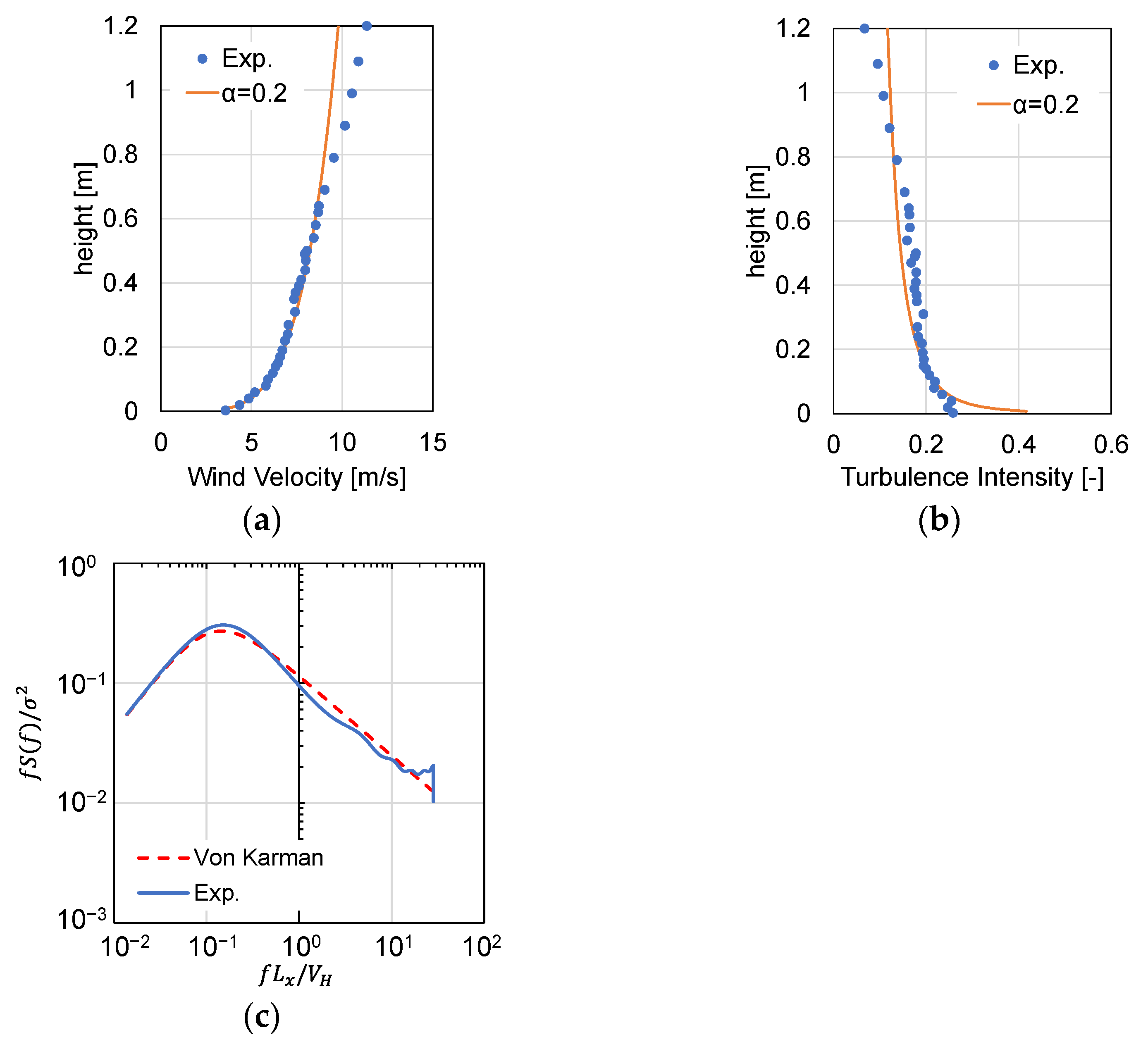
2.2. Experimental Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison with a Previous Experiment on an Isolated Cube Building
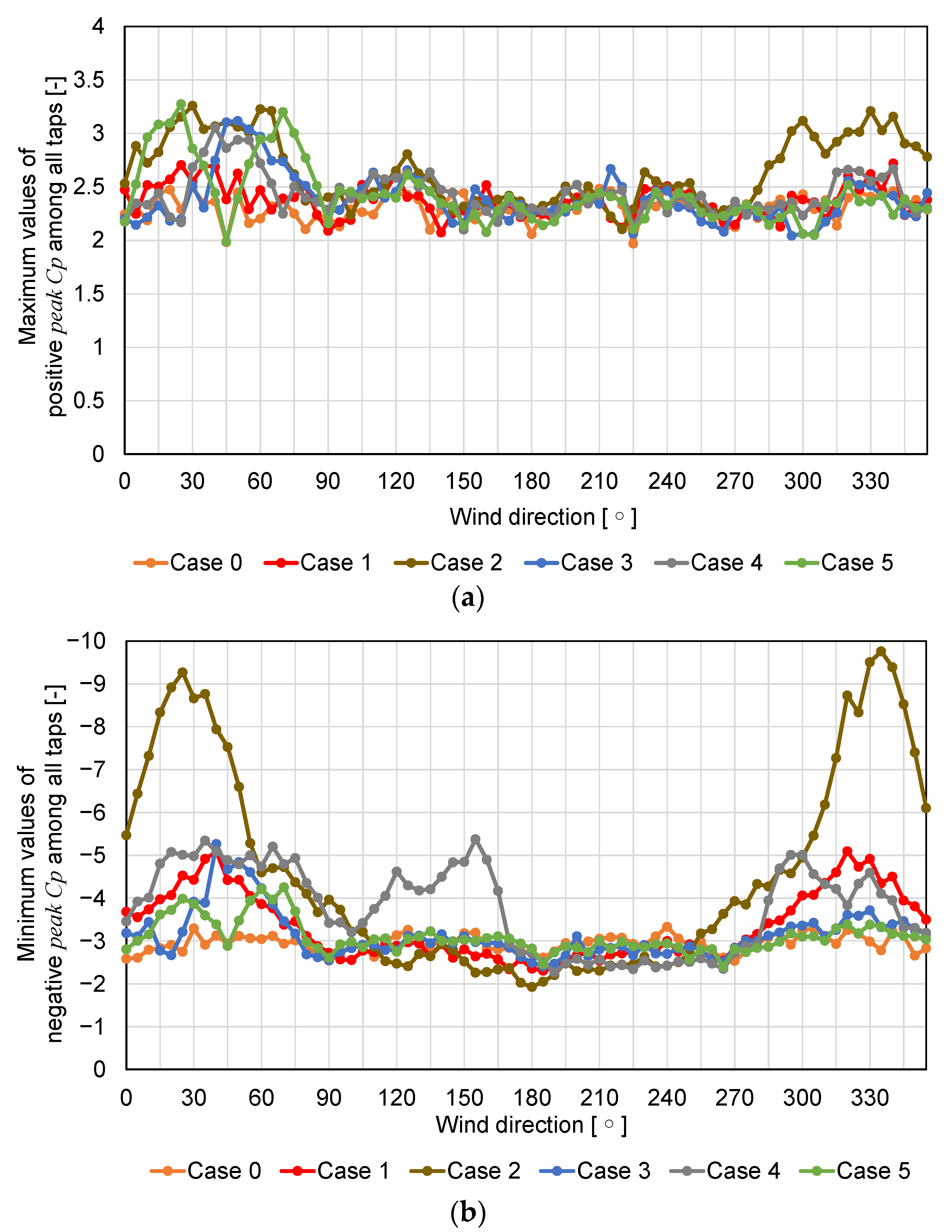
3.2. Variations in for Wind Direction and Location of a High-Rise Building
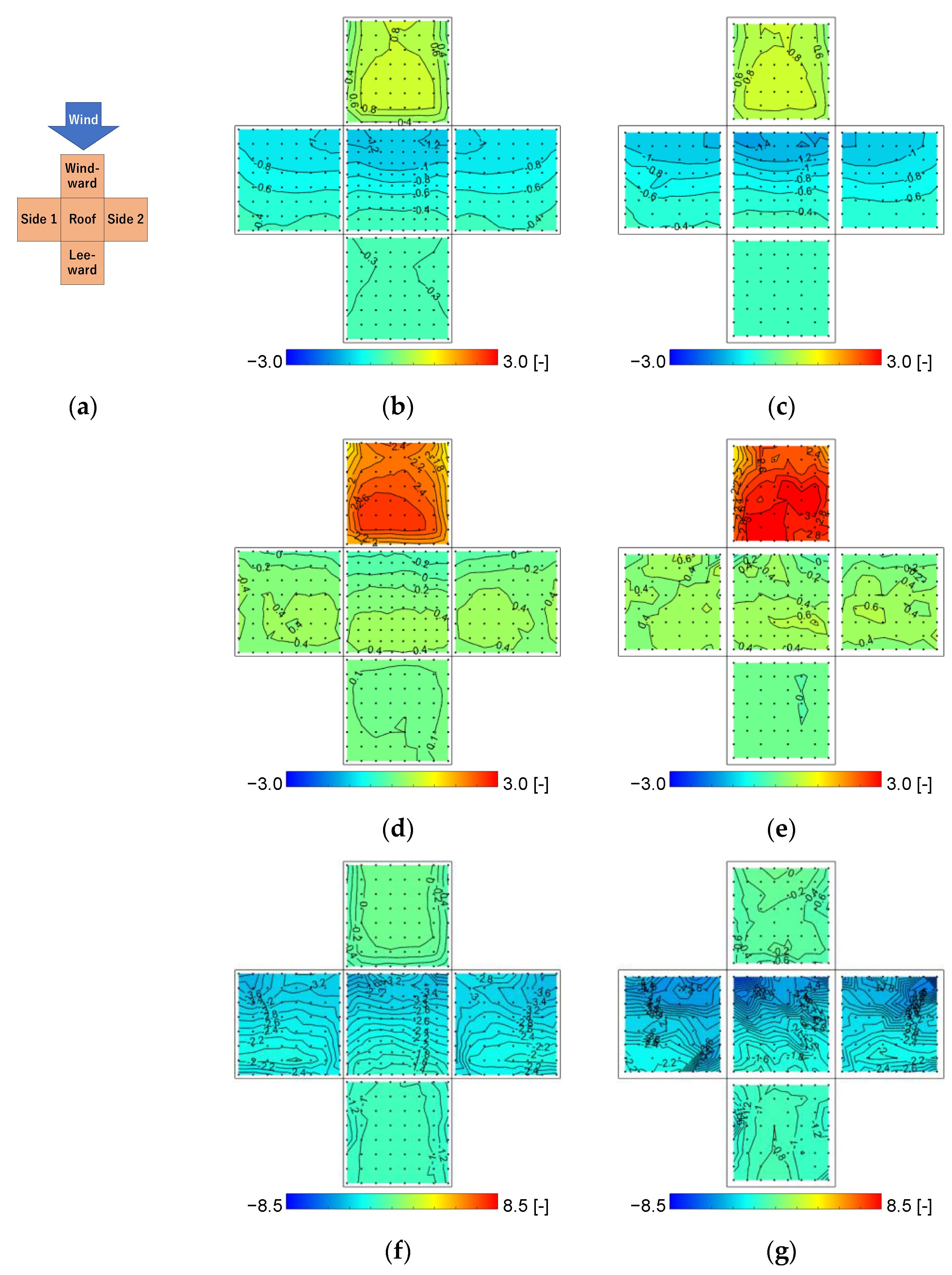
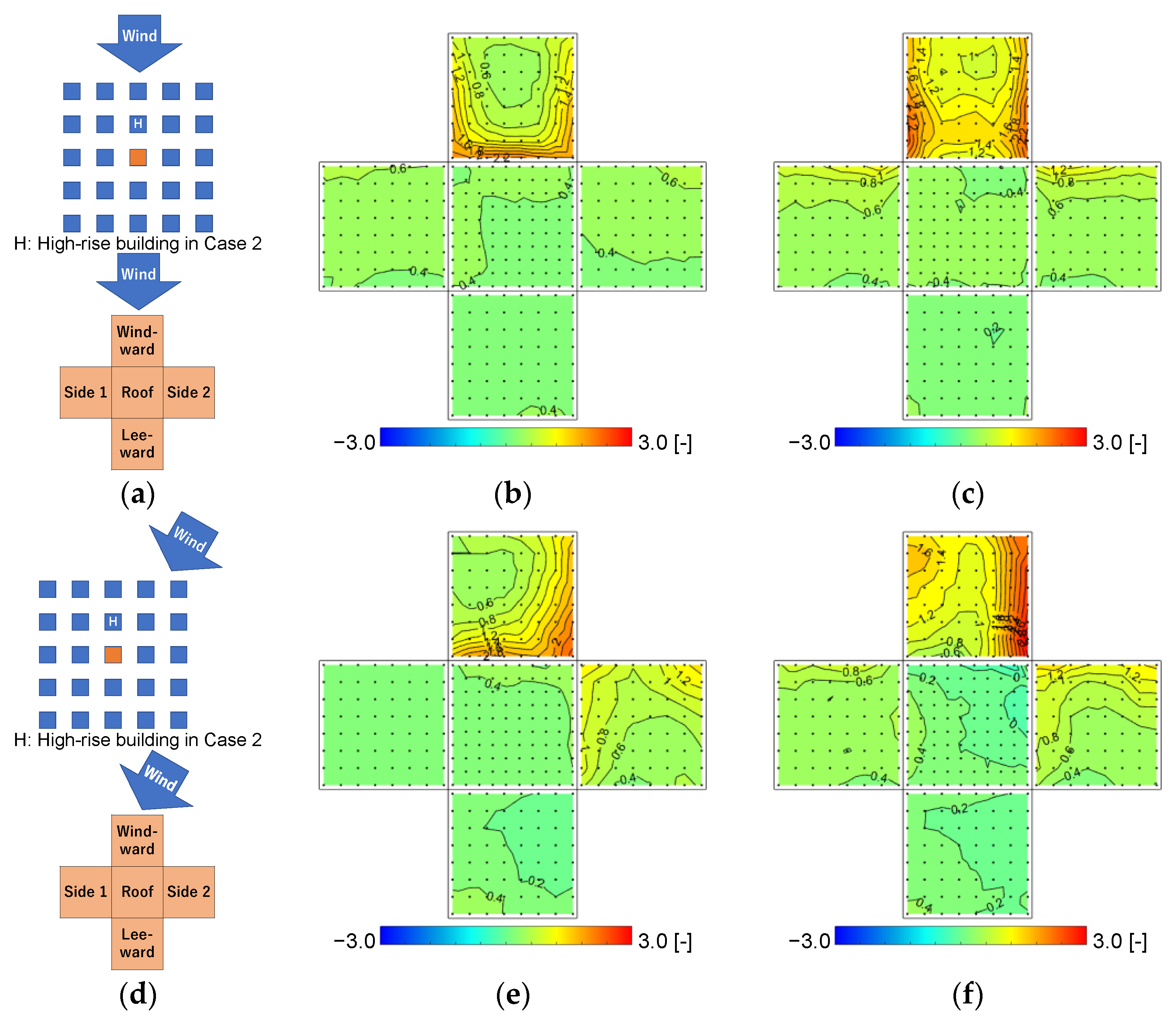
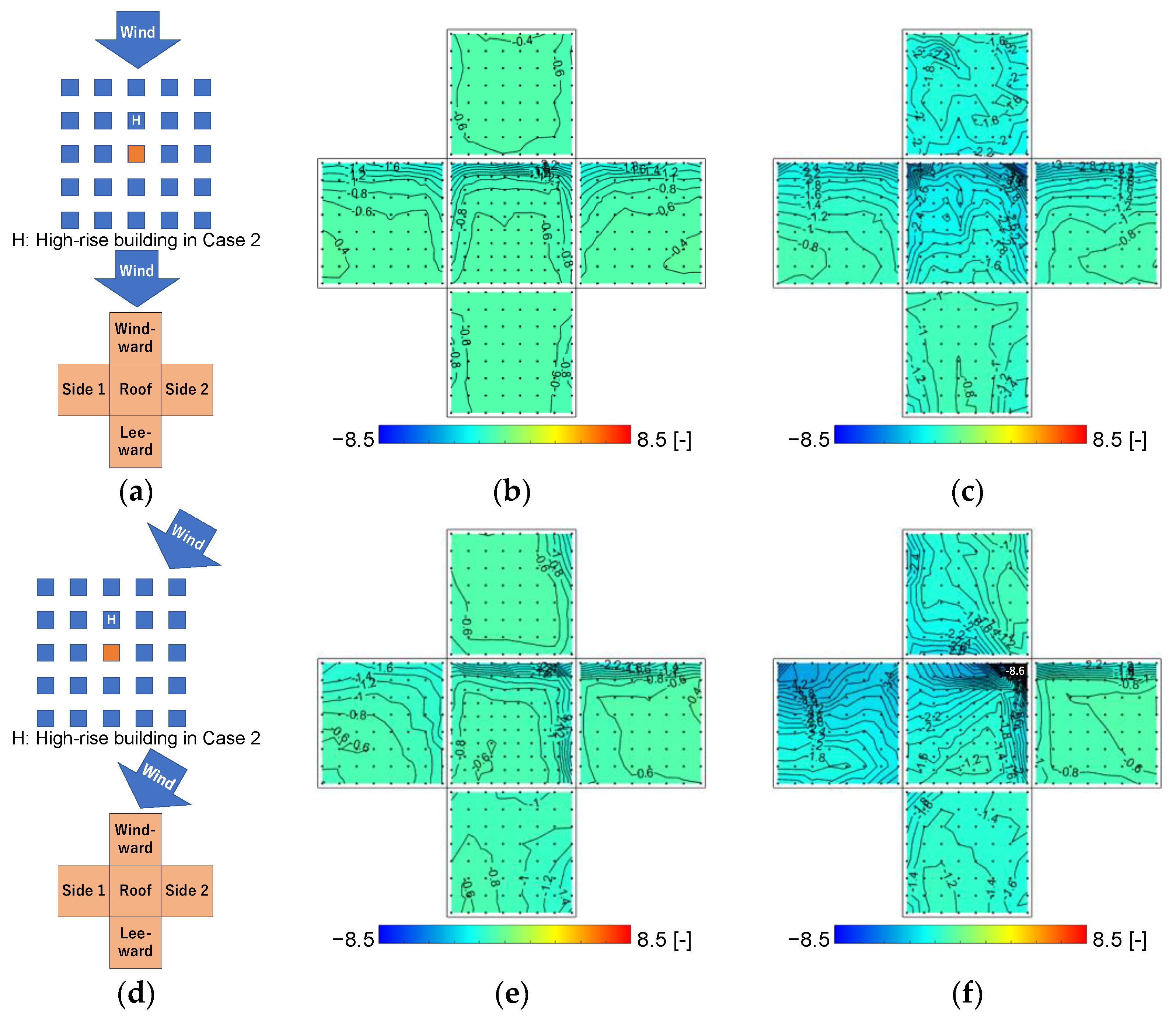
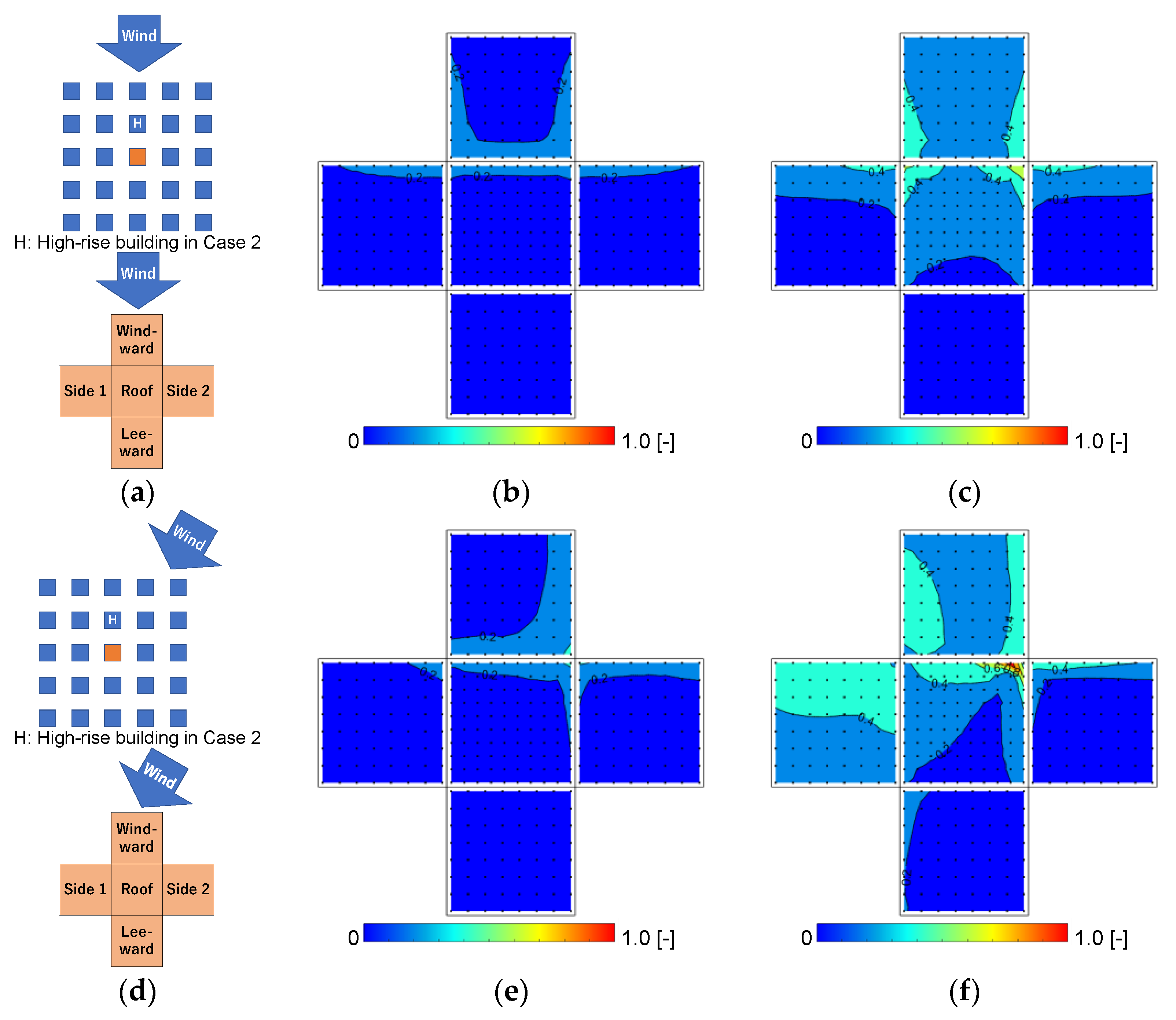
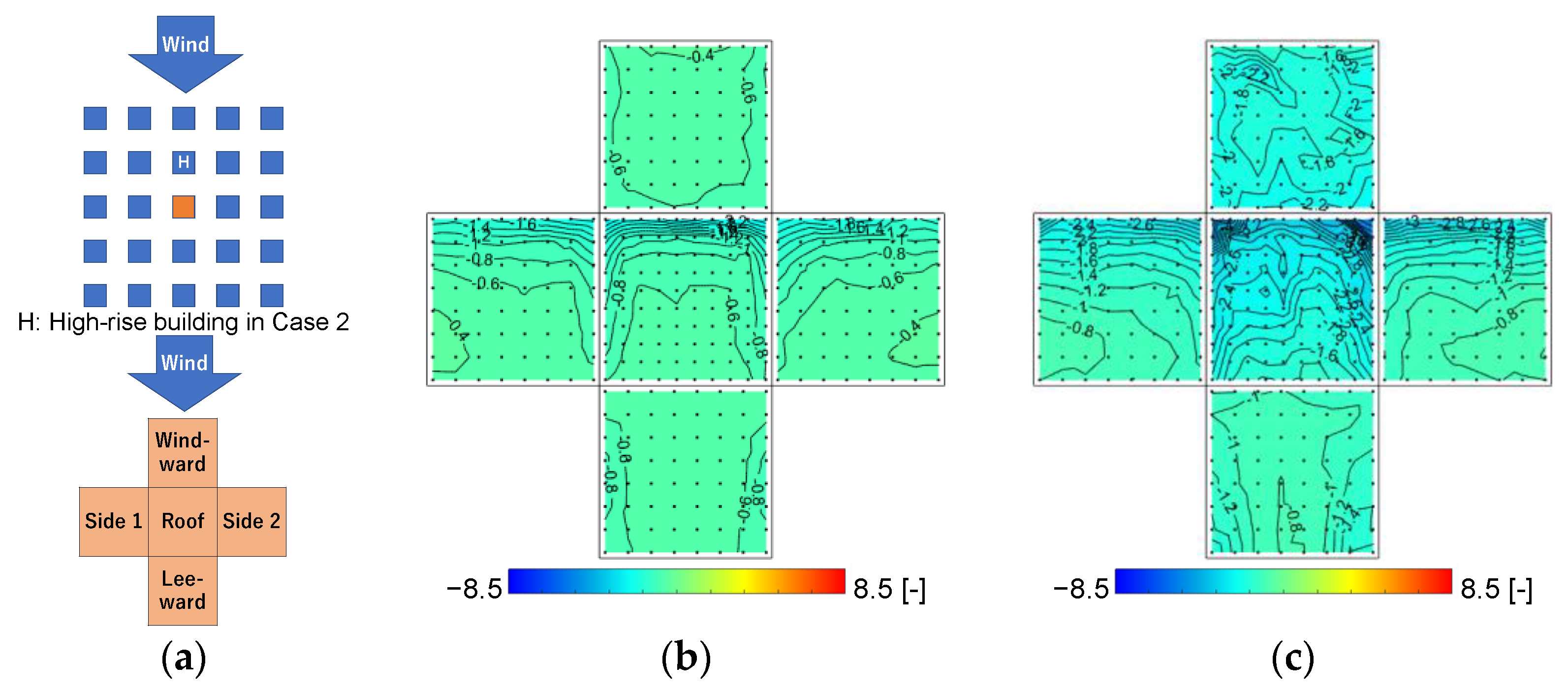
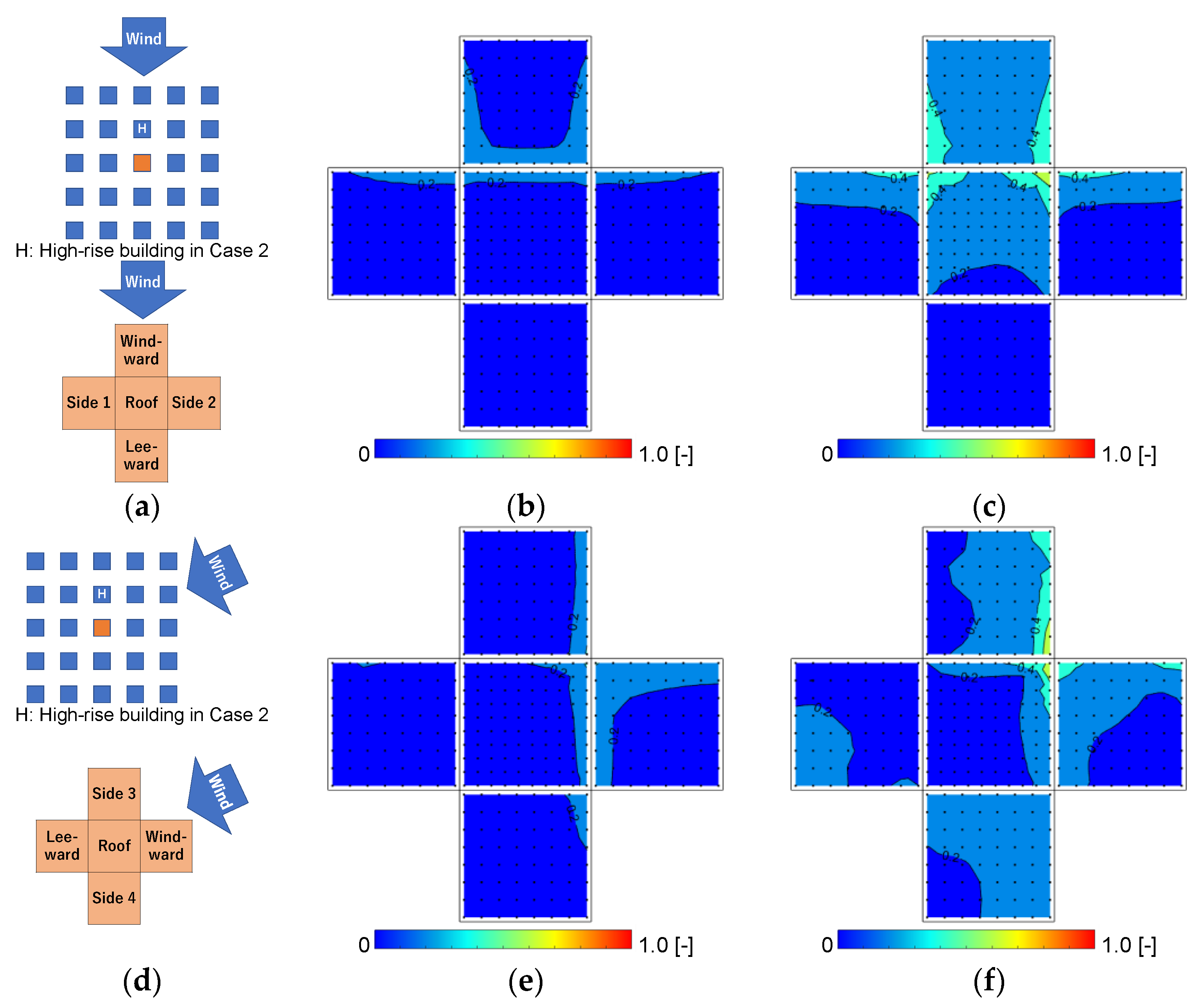
3.3. Wind Pressure Coefficient Distributions
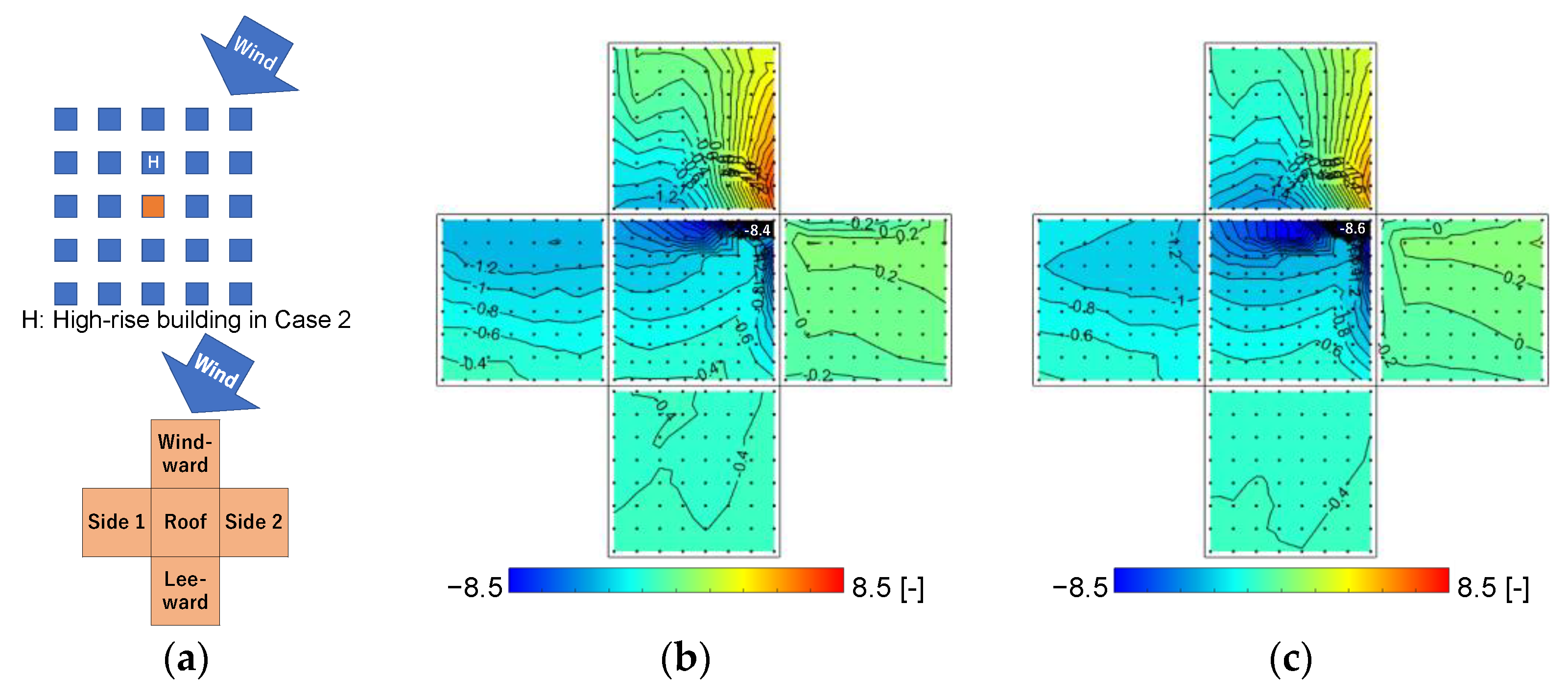
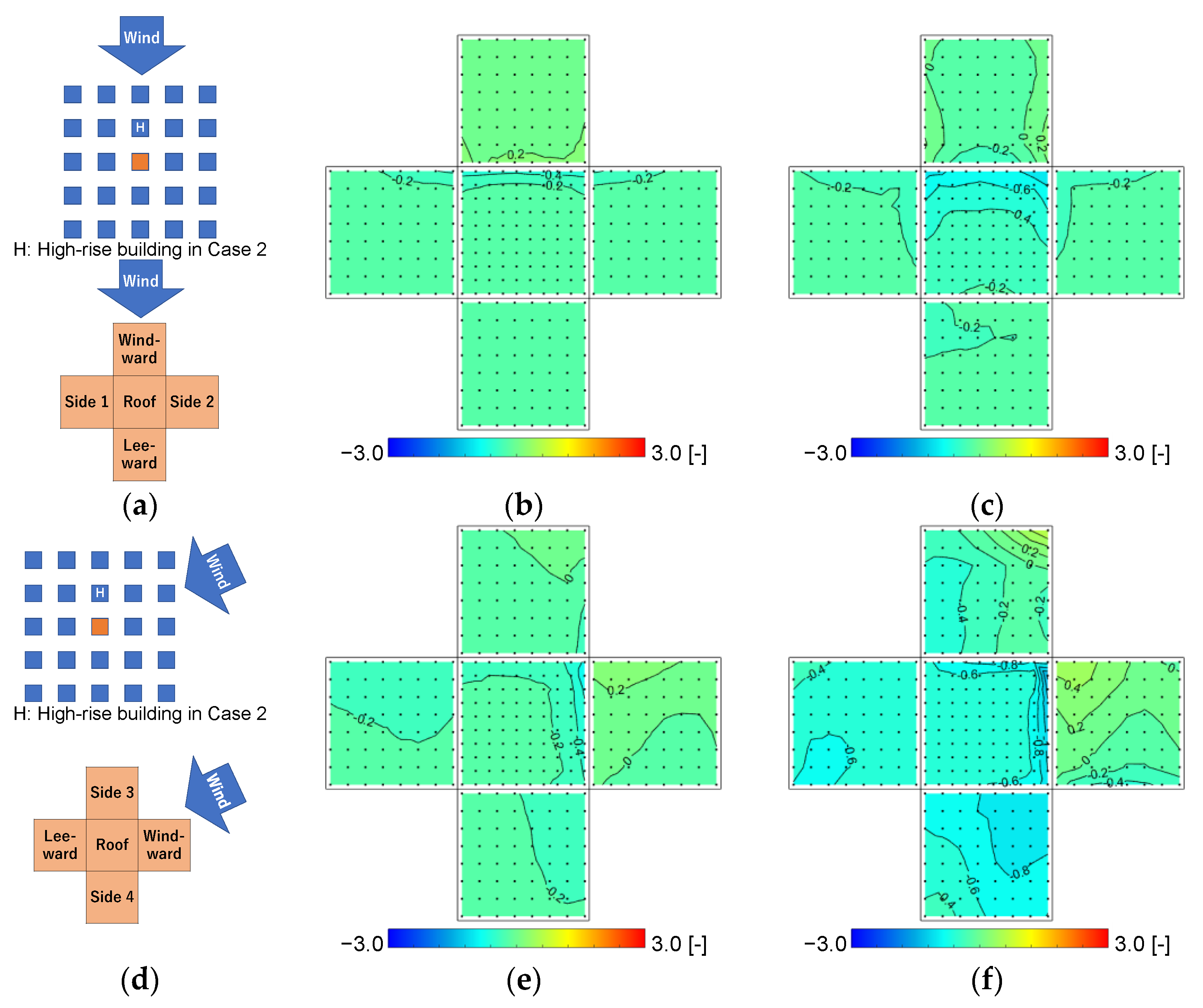
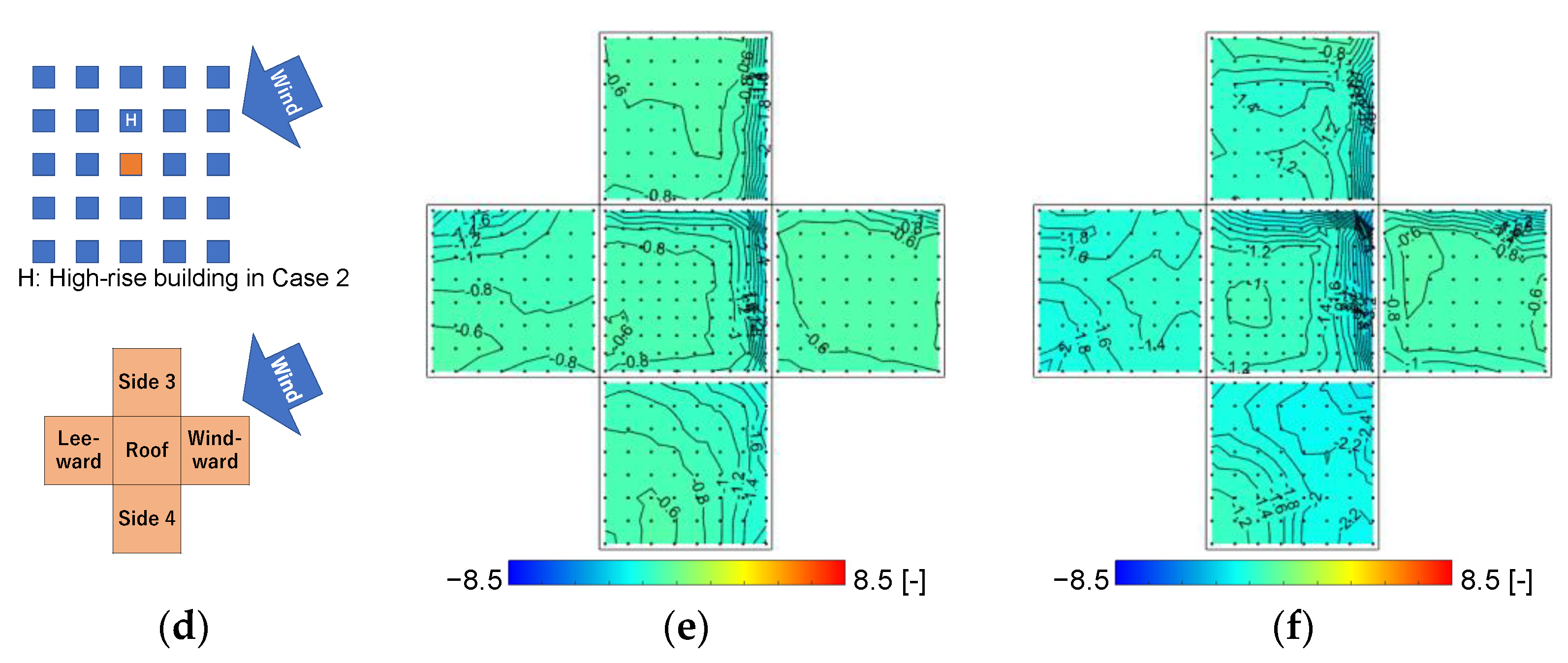
3.3.1. Wind Pressure Coefficients at 30° Wind Direction in Case 0 and Case 2
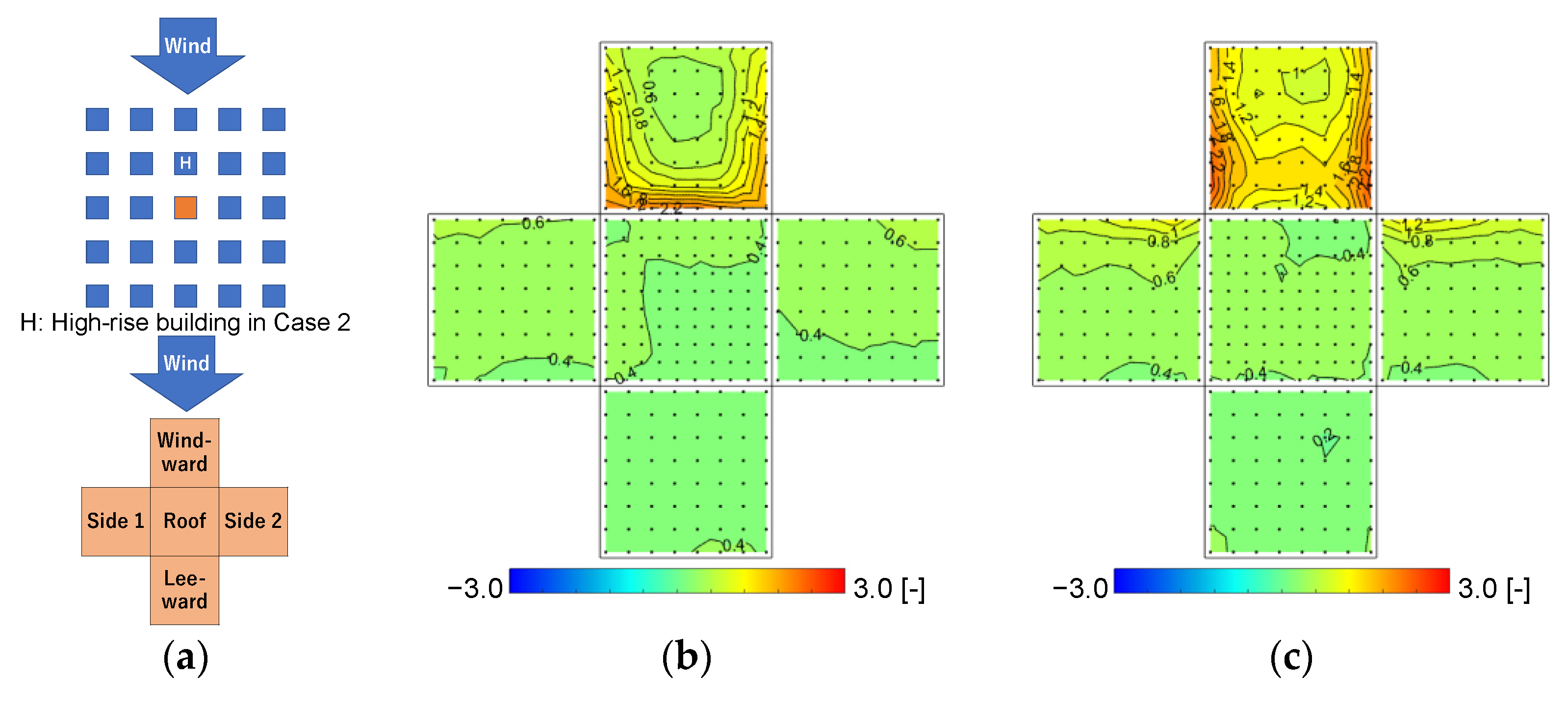
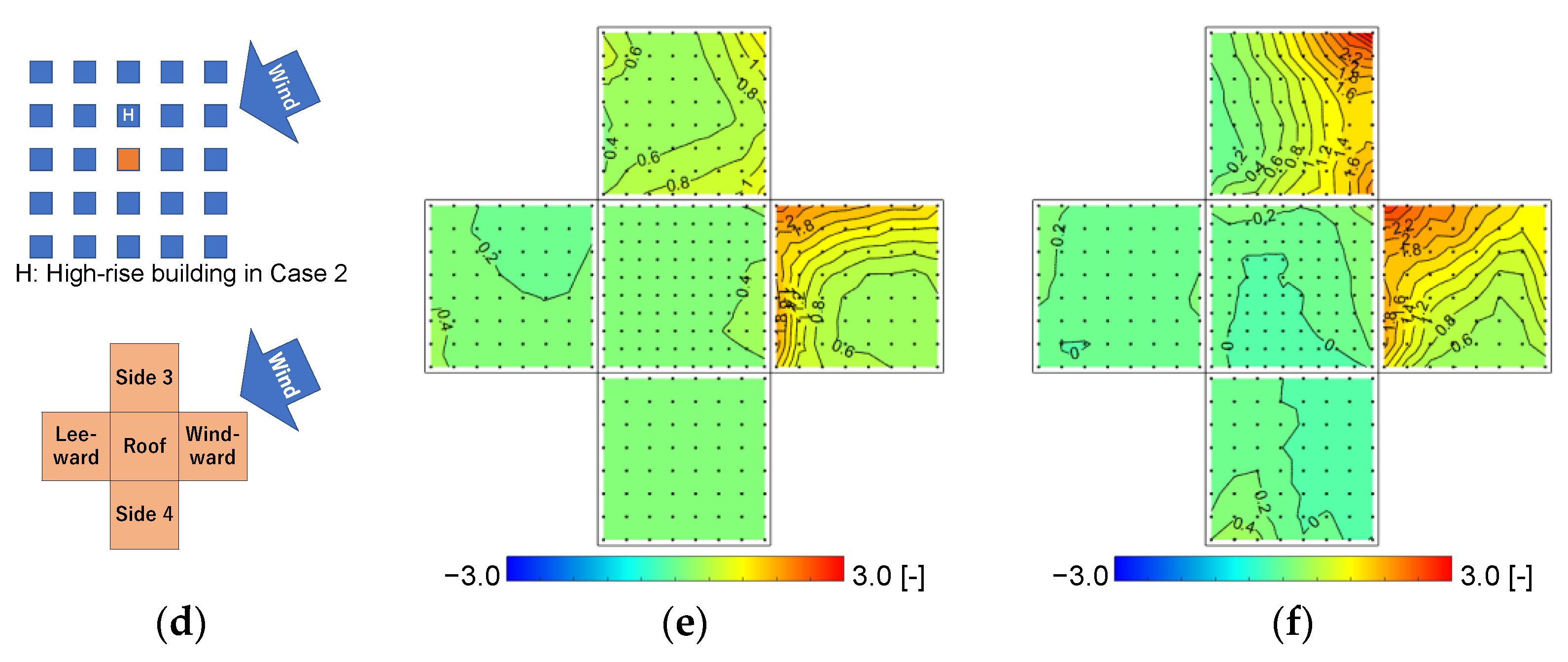
3.3.2. Wind Pressure Coefficients at a 65° Wind Direction in Case 0 and Case 2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kwok, K.C.S.; Wilhelm, P.A.; Wilkie, B.G. Effect of edge configuration on wind-induced response of tall buildings. Eng. Struct. 1988, 10, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, K.; Katagiri, J.; Nakamura, O.; Ohkuma, T.; Tamura, Y.; Itoh, M.; Mimachi, T. Wind-induced response of high-rise buildings Effects of corner cuts or openings in square buildings. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyna. 1993, 50, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kijewski, T.; Kareem, A. Along-Wind Load Effects on Tall Buildings: Comparative Study of Major International Codes and Standards. J. Struct. Eng. 2002, 128, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; You, K.P.; Ko, N.H. Across-wind responses of an aeroelastic tapered tall building. J. Fluids Struct. 2008, 96, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Tamura, Y.; Ohtake, K.; Nakai, M.; Kim, Y.C. Experimental investigation of aerodynamic forces and wind pressures acting on tall buildings with various unconventional configurations. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2012, 107–108, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocken, B. 50 years of Computational Wind Engineering: Past, present and future. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2014, 129, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, H.; Tamura, T.; Arai, M.; Sayama, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yoshie, K. Turbulence and Pressure Fluctuation around High-Rise Building with Complicated Facade in Urban Districts. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering 2018, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 18−22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Y.; Shen, G.; Yu, H.; Xie, J. Effects of Corner Modification on the Wind-Induced Responses of High-Rise Buildings. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, Q.; Yoshida, A.; Tamura, Y. Characteristics of pedestrian-level wind around super-tall buildings with various configurations. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2017, 166, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Uehara, K.; Komine, H. Amplification of wind speed at ground level due to construction of high-rise building in urban area. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1979, 4, 343–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Druenen, T.; van Hooff, T.; Montazeri, H.; Blocken, B. CFD evaluation of building geometry modifications to reduce pedestrian-level wind speed. Build. Environ. 2019, 163, 106293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanduri, A.C.; Stathopoulos, T.; Bedard, H. Wind-induced interference effects on buildings—A review of the state-of-the-art. Eng. Struct. 1998, 20, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.A.; Kwok, K.C.S. Interference Excitation of Twin Tall Buildings. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1985, 21, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Tamura, Y.; Yoshida, A. Interference effects on local peak pressures between two buildings. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Tamura, Y.; Yoshida, A. Interference effects on aerodynamic wind forces between two buildings. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2013, 147, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Tamura, Y.; Yang, Q. Analysis of interference effects on torsional moment between two high-rise buildings based on pressure and flow field measurement. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 164, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.N.; Gu, M. Simplified formulas for evaluation of wind-induced interference effects among three tall buildings. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2007, 95, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.M.; Leung, M.Y.H.; Zhao, J.G. Interference effects on wind loading of a row of closely spaced tall buildings. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 562–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Shang, L.; Qin, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, Q. Wind interference effects of high-rise building on low-rise building with flat roof. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 183, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Quan, Y.; Gu, M. Aerodynamic interference effects of a proposed super high-rise building on the aerodynamic forces and responses of an existing building. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 206, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Architectural Institute of Japan. Recommendations for Loads on Buildings; Architectural Institute of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 2015. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, H.; Cooper, K.; Girard, R. Correction of distortion effects caused by tubing systems in measurements of fluctuating pressures. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1979, 5, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.D. Equivalent time averaging in wind engineering. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1997, 72, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TPU (Tokyo Polytechnic University) Aerodynamic Database. Available online: http://db.wind.arch.t-kougei.ac.jp/ (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Hosseini, Z.; Bourgeoisa, J.A.; Martinuzzi, R.J. Large-scale structures in dipole and quadrupole wakes of a wall-mounted finite rectangular cylinder. Exp. in Fluids 2013, 54, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tamura, T.; Zhou, D.; Bao, Y.; Han, Z. Topological description of near-wall flows around a surface-mounted square cylinder at high Reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 2022, 933, A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
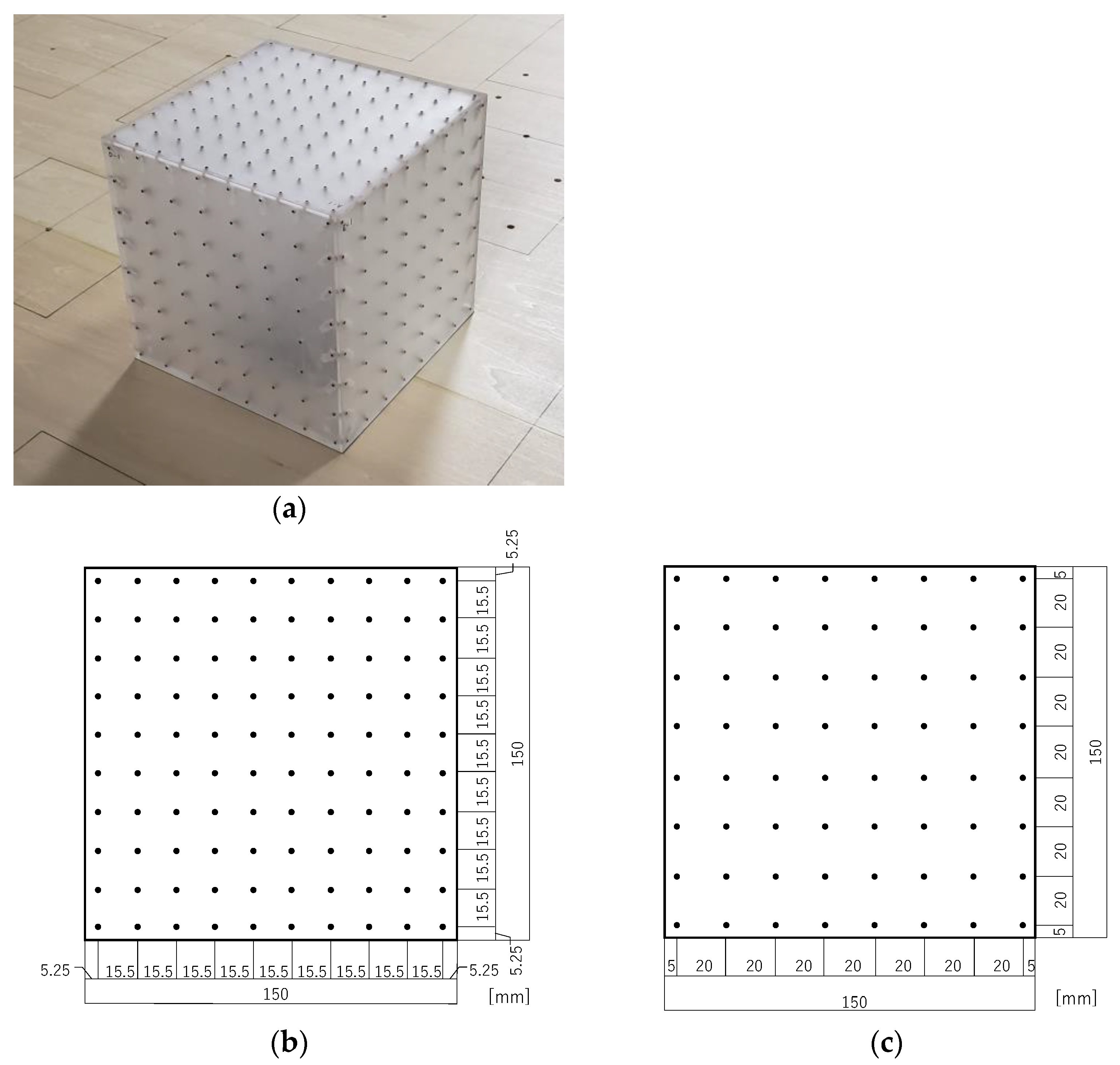
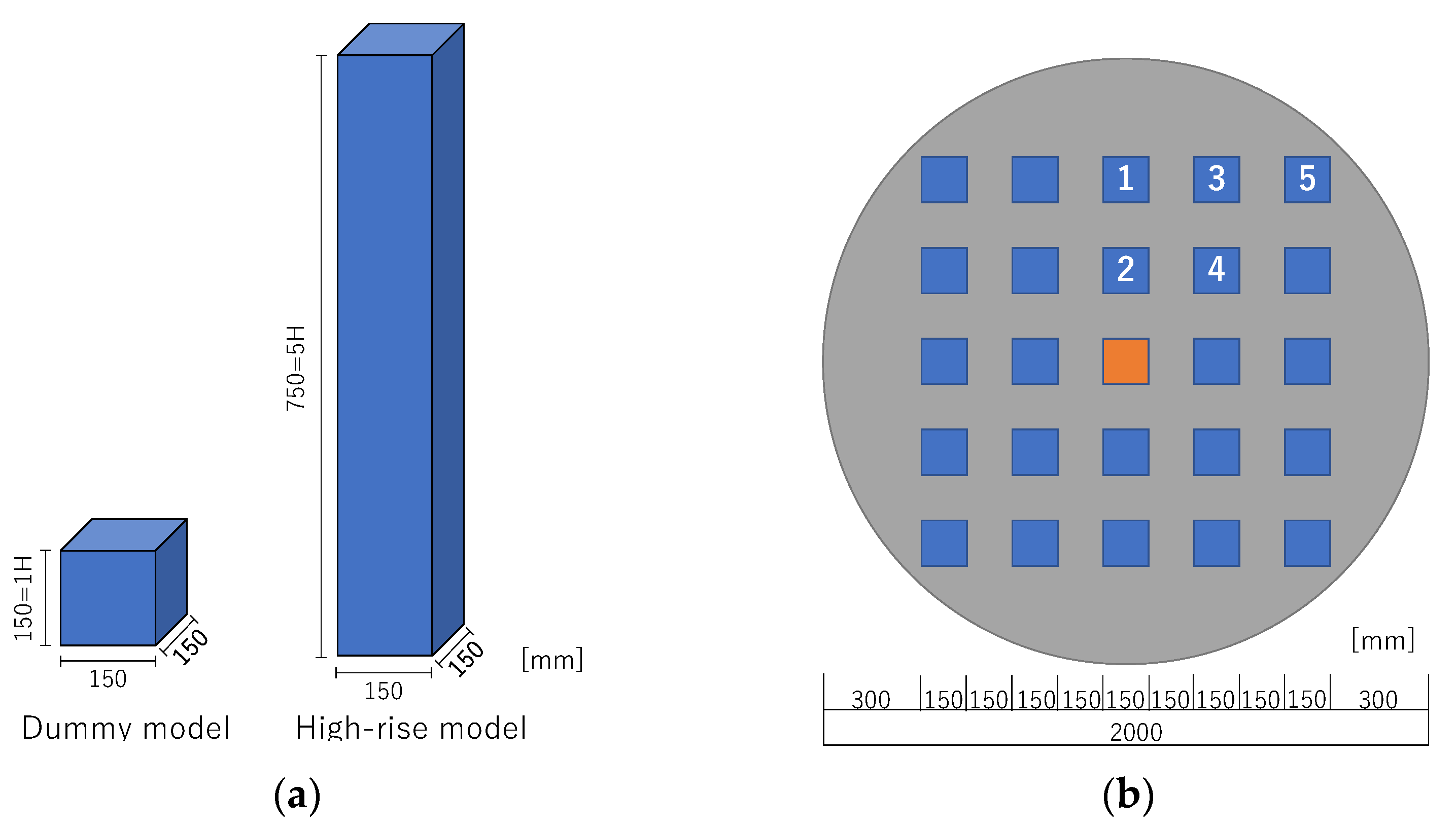


| Case Name | Location of a High-Rise Building (The Number in Figure 2) |
|---|---|
| Case 0 | Uniform height (No high-rise building) |
| Case 1 | 1 |
| Case 2 | 2 |
| Case 3 | 3 |
| Case 4 | 4 |
| Case 5 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishida, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Kamata, S.; Yamane, Y.; Mochida, A. Wind Tunnel Experiments on Interference Effects of a High-Rise Building on the Surrounding Low-Rise Buildings in an Urban Block. Wind 2023, 3, 97-114. https://doi.org/10.3390/wind3010007
Ishida Y, Yoshida A, Kamata S, Yamane Y, Mochida A. Wind Tunnel Experiments on Interference Effects of a High-Rise Building on the Surrounding Low-Rise Buildings in an Urban Block. Wind. 2023; 3(1):97-114. https://doi.org/10.3390/wind3010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshida, Yasuyuki, Akihito Yoshida, Shuhei Kamata, Yuta Yamane, and Akashi Mochida. 2023. "Wind Tunnel Experiments on Interference Effects of a High-Rise Building on the Surrounding Low-Rise Buildings in an Urban Block" Wind 3, no. 1: 97-114. https://doi.org/10.3390/wind3010007
APA StyleIshida, Y., Yoshida, A., Kamata, S., Yamane, Y., & Mochida, A. (2023). Wind Tunnel Experiments on Interference Effects of a High-Rise Building on the Surrounding Low-Rise Buildings in an Urban Block. Wind, 3(1), 97-114. https://doi.org/10.3390/wind3010007






