Influence of Chronic Dietary Nitrate on Downstream Atherogenic Metabolites and the Enteral Microbiome—A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
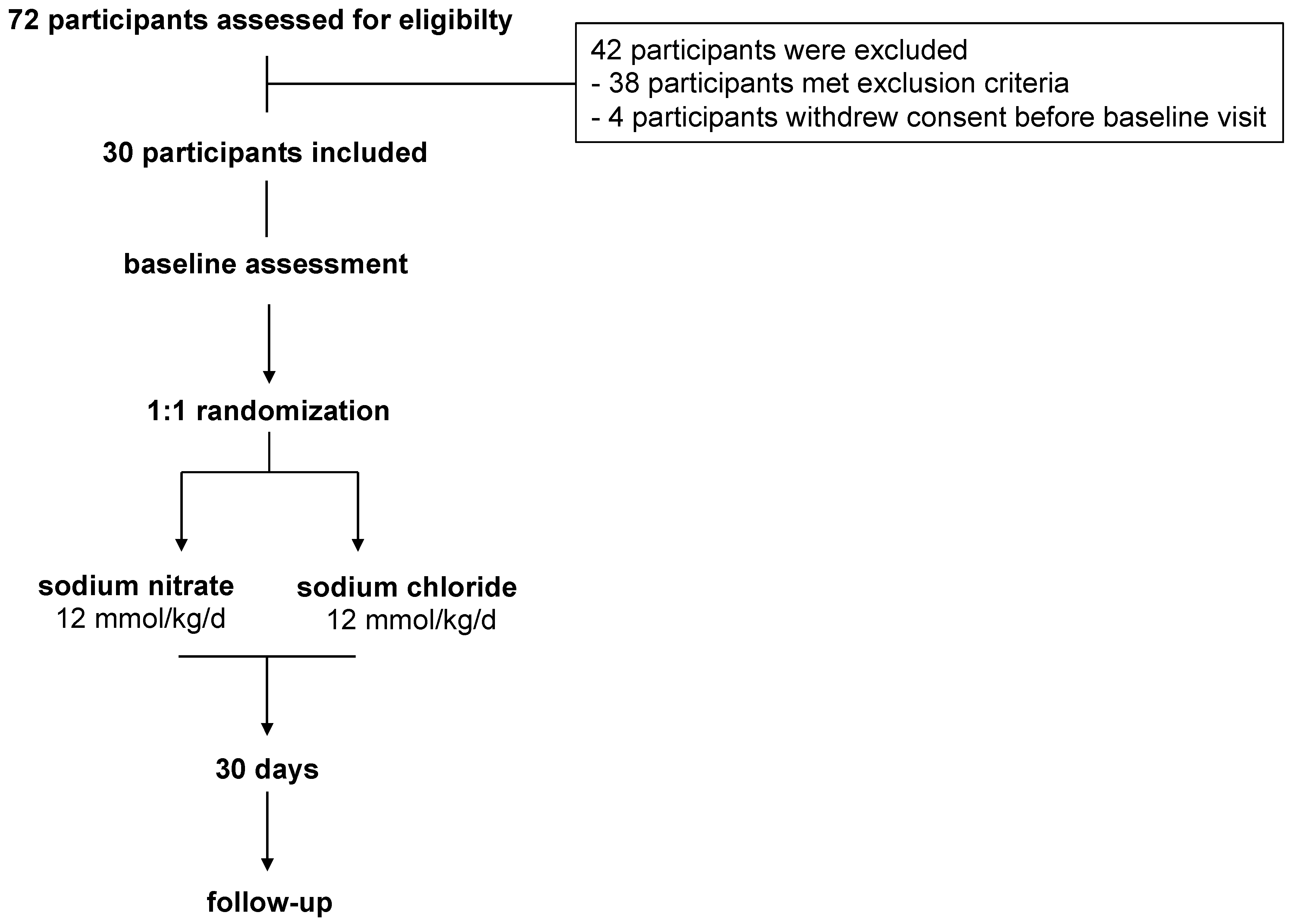
2. Methods
3. Results
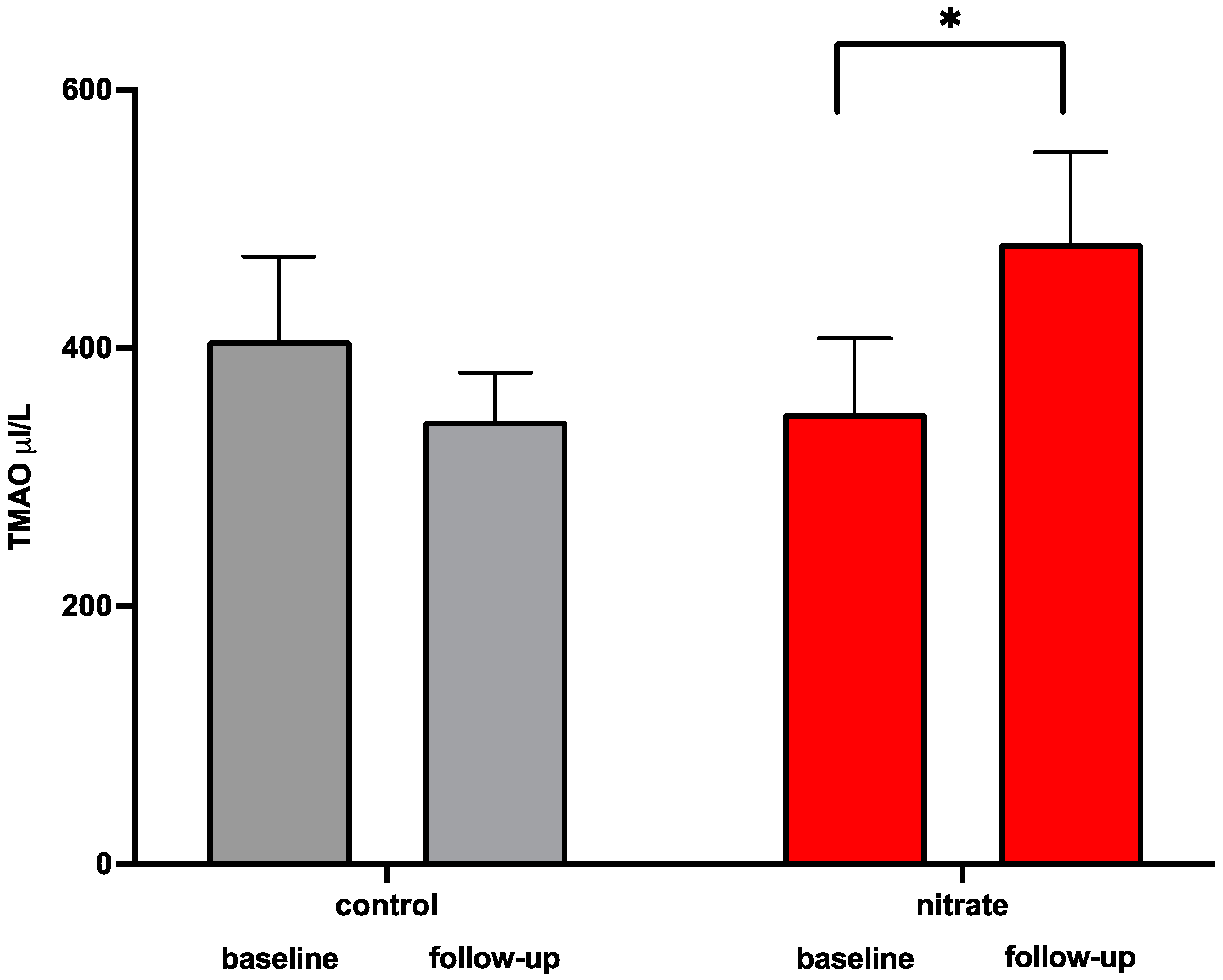
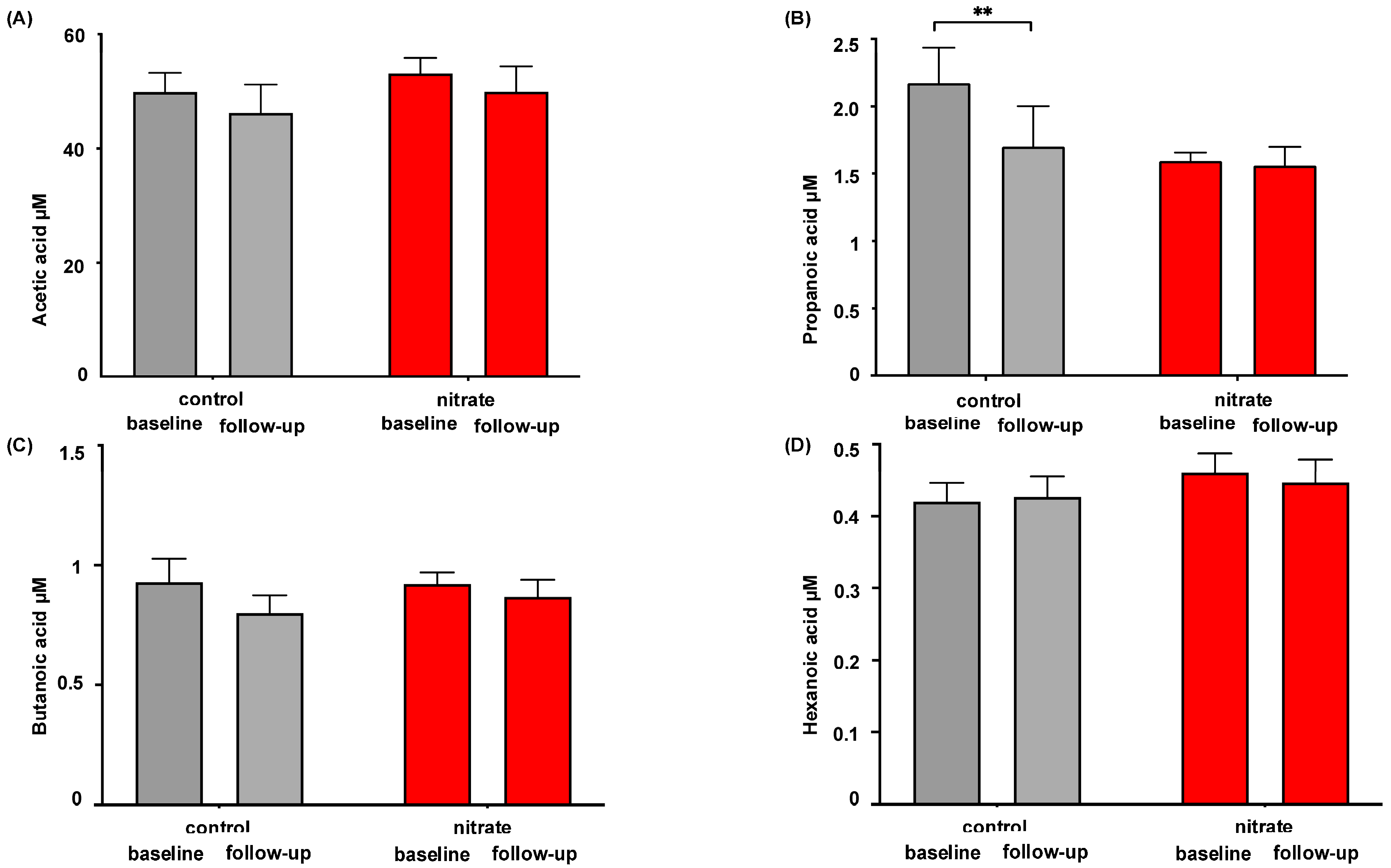
3.1. Impact of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Microbiome-Related Metabolites
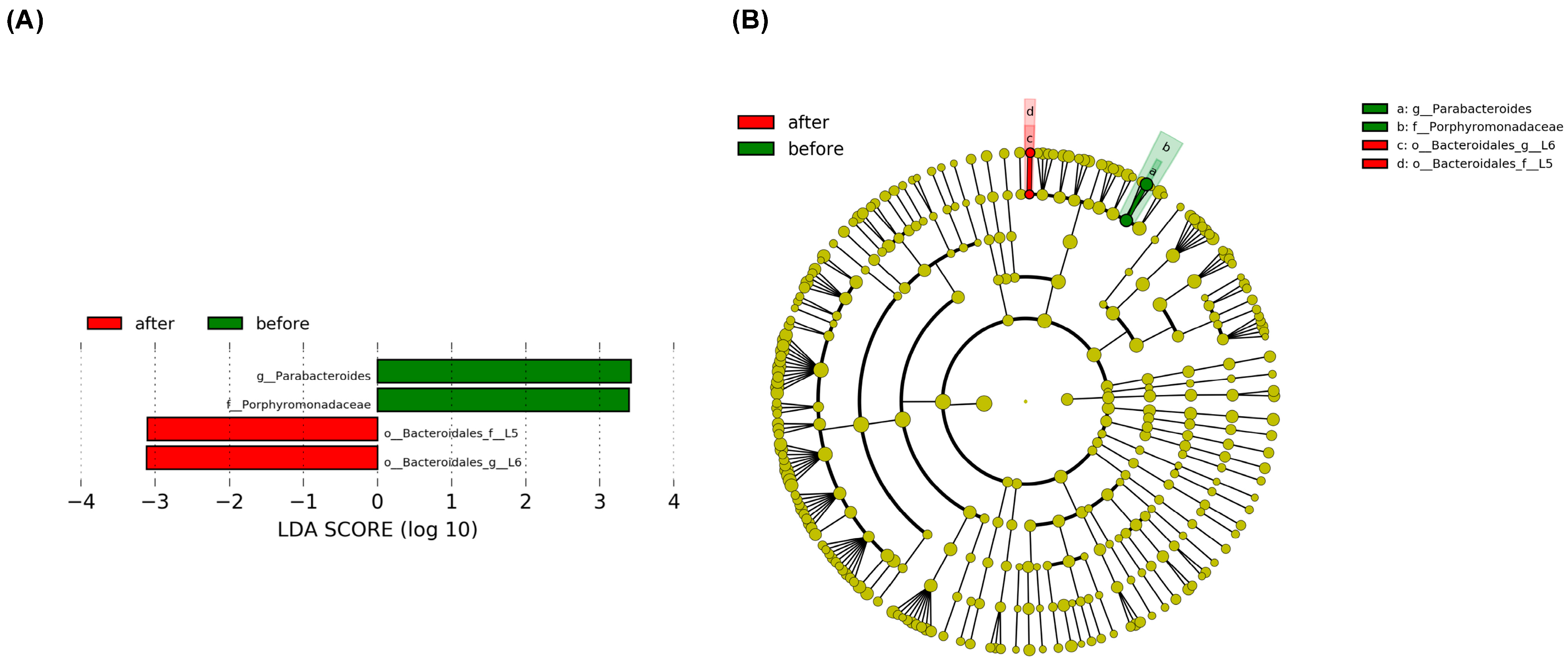
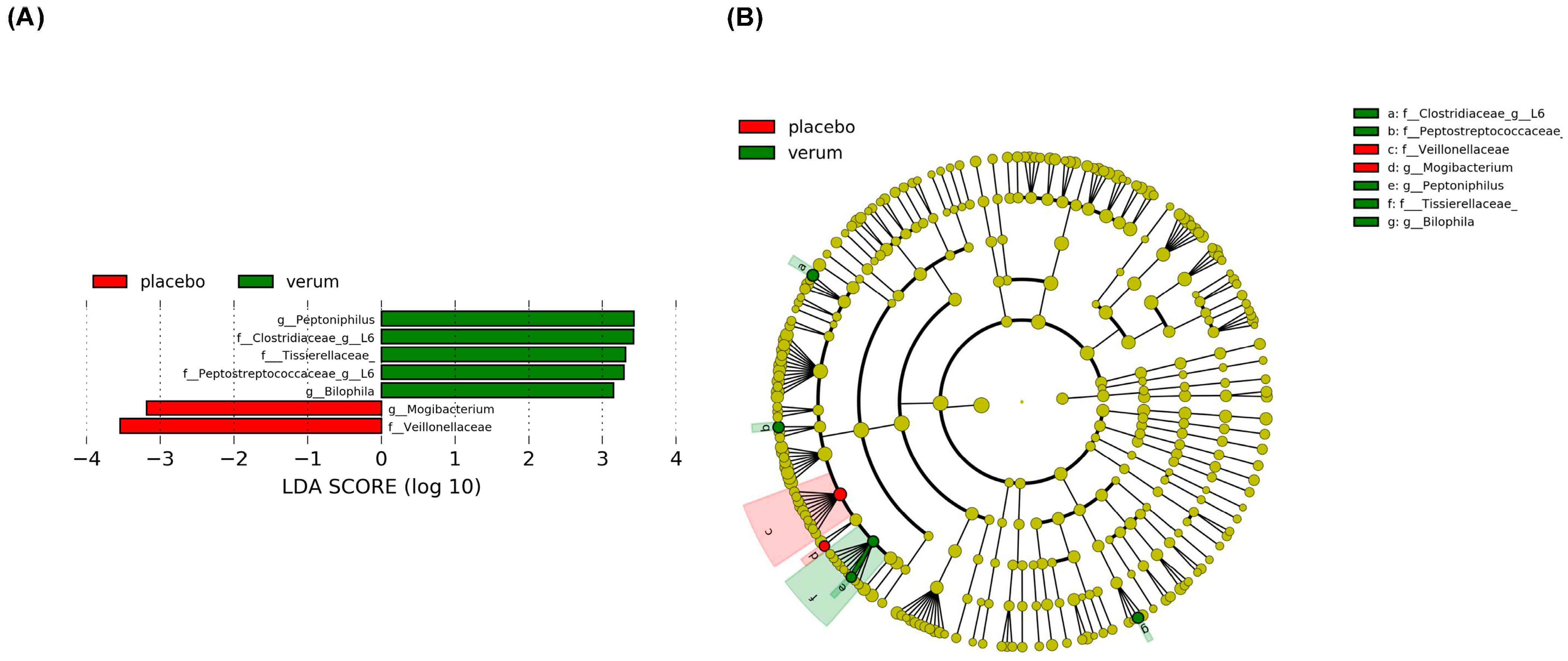
3.2. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Is Associated with a Difference in Enteral Microbiome Composition
3.3. High TMAO Levels After Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Are Associated with a Distinct Enteral Microbiome Composition
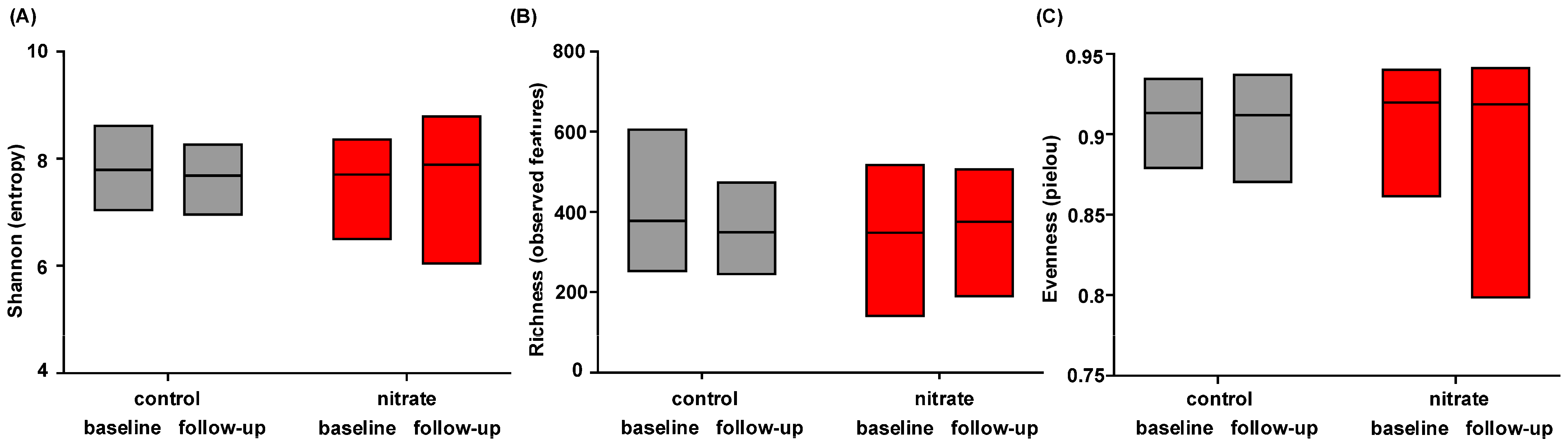
3.4. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Does Not Change Microbiome Alpha Diversity
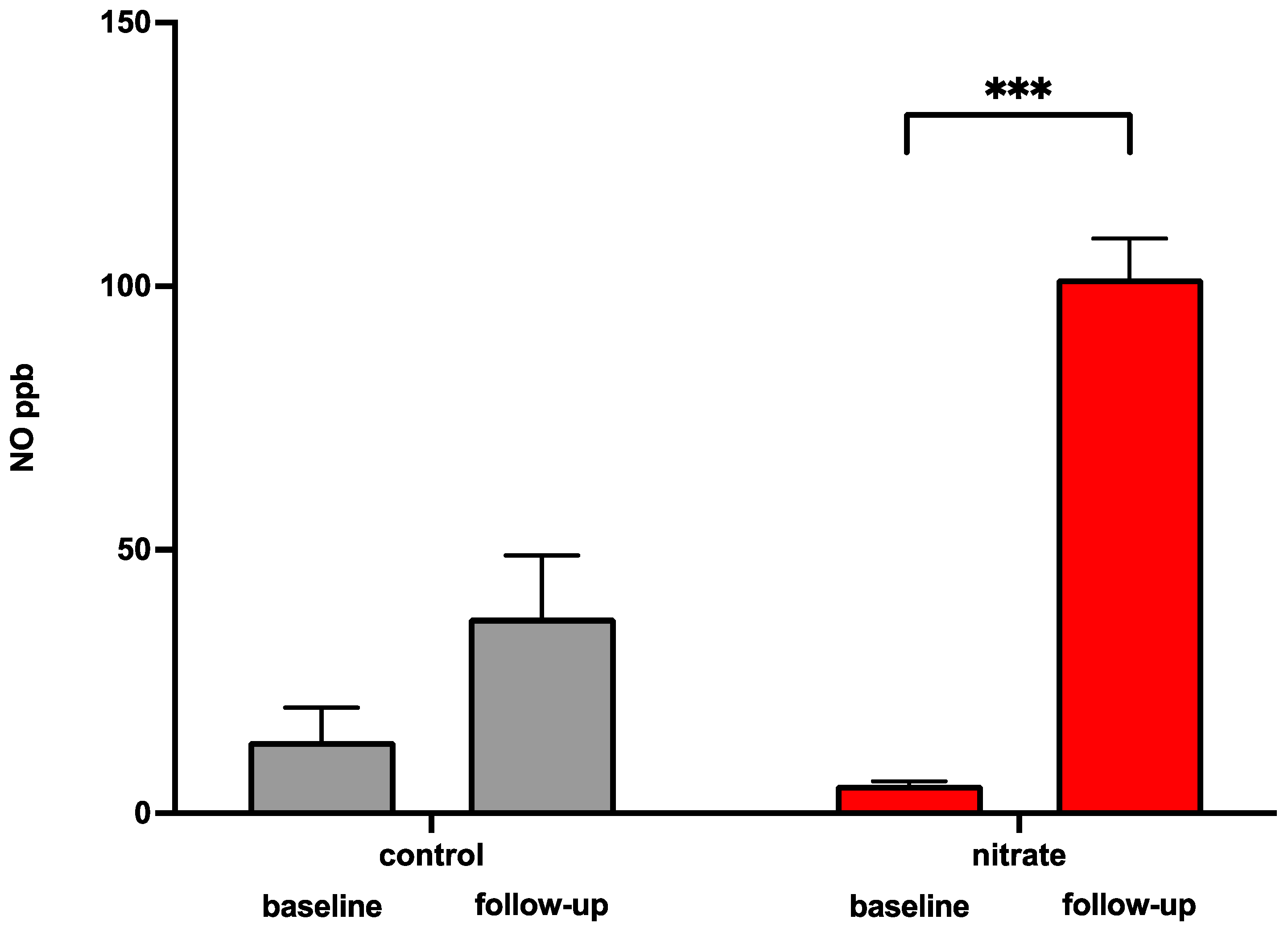
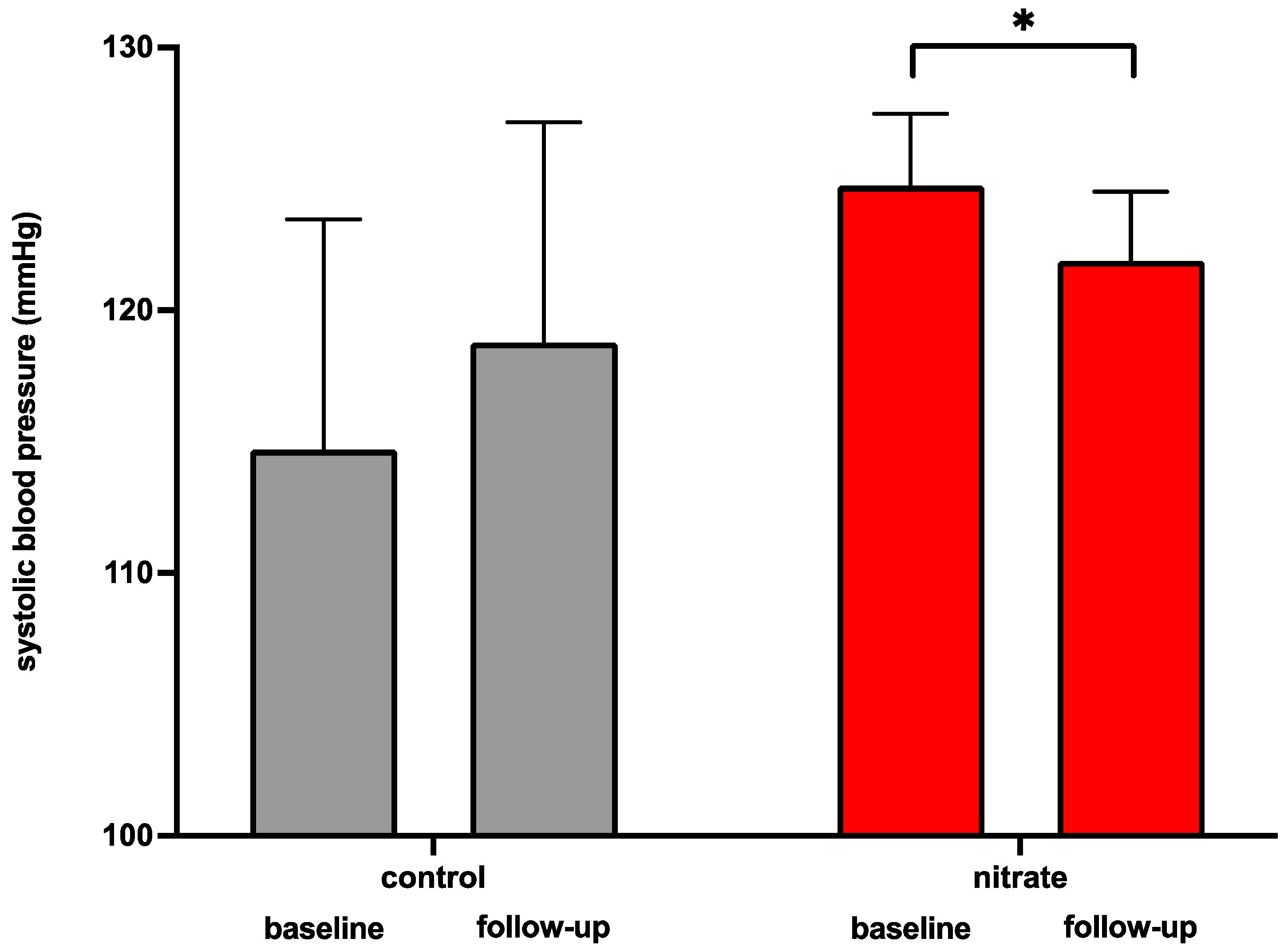
3.5. Dietary Supplementation of Inorganic Nitrate Increases Circulating Nitric Oxide Serum Levels and Reduces Systolic Blood Pressure
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stone, N.J.; Smith, S.C.; Orringer, C.E.; Rigotti, N.A.; Navar, A.M.; Khan, S.S.; Jones, D.W.; Goldberg, R.; Mora, S.; Blaha, M.; et al. Managing Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Risk in Young Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Forano, E. Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Wu, Q.; Yao, Q.; Jiang, K.; Yu, J.; Tang, Q. Short-chain fatty acid metabolism and multiple effects on cardiovascular diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 81, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; Van Der Veeken, J.; DeRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.E.; Taesuwan, S.; Malysheva, O.V.; Bender, E.; Tulchinsky, N.F.; Yan, J.; Sutter, J.L.; Caudill, M.A. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (Tmao) Response to Animal Source Foods Varies among Healthy Young Men and Is Influenced by Their Gut Microbiota Composition: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, A.; Wijayasinghe, Y.S.; Khan, I.; El Samaloty, N.M.; Adnan, M.; Dar, T.A.; Poddar, N.K.; Singh, L.R.; Sharma, H.; Khan, S. Implications of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) and Betaine in Human Health: Beyond Being Osmoprotective Compounds. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 964624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeth, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Buffa, J.A.; Org, E.; Sheehy, B.T.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Metabolism of L-Carnitine, a Nutrient in Red Meat, Promotes Atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, P.; Liu, C.; Song, L.; Liao, Z.; et al. Association between trimethylamine N-oxide and prognosis of patients with acute myocardial infarction and heart failure. ESC Hear. Fail. 2022, 9, 3846–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandsma, E.; Kloosterhuis, N.J.; Koster, M.; Dekker, D.C.; Gijbels, M.J.; van der Velden, S.; Ríos-Morales, M.; van Faassen, M.J.; Loreti, M.G.; de Bruin, A.; et al. A Proinflammatory Gut Microbiota Increases Systemic Inflammation and Accelerates Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Fuster, V.; Silla-Castro, J.C.; González, G.; Lorenzo-Vivas, E.; Alvarez, R.; Callejas, S.; Benguría, A.; Gil, E.; Núñez, E.; et al. Subclinical atherosclerosis and accelerated epigenetic age mediated by inflammation: A multi-omics study. Eur. Hear. J. 2023, 44, 2698–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, V.; Su, J.; Koprowski, S.; Hsu, A.; Tweddell, J.S.; Rafiee, P.; Gross, G.J.; Salzman, N.H.; Baker, J.E. Intestinal microbiota determine severity of myocardial infarction in rats. FASEB J. 2011, 26, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Amano, M.T.; Correa-Costa, M.; Castoldi, A.; Felizardo, R.J.; de Almeida, D.C.; Bassi, E.J.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Hiyane, M.I.; Rodas, A.C.; et al. Gut Bacteria Products Prevent AKI Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ, C.L.; Li, Z.; Sharp, T.E., 3rd; Polhemus, D.J.; Gupta, N.; Goodchild, T.T.; Tang, W.H.W.; Hazen, S.L.; Lefer, D.J. Nonlethal Inhibition of Gut Microbial Trimethylamine N-Oxide Production Improves Cardiac Function and Remodeling in a Murine Model of Heart Failure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Roth, S.; Llovera, G.; Sadler, R.; Garzetti, D.; Stecher, B.; Dichgans, M.; Liesz, A. Microbiota Dysbiosis Controls the Neuroinflammatory Response after Stroke. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7428–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.W.; Chen, H.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yen, C.Y.; Lin, C.-J.; Prajnamitra, R.P.; Chen, L.-L.; Ruan, S.-C.; Lin, J.-H.; Lin, P.-J.; et al. Loss of Gut Microbiota Alters Immune System Composition and Cripples Postinfarction Cardiac Repair. Circulation 2019, 139, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; DuGar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.-M.; et al. Gut Flora Metabolism of Phosphatidylcholine Promotes Cardiovascular Disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djekic, D.; Shi, L.; Brolin, H.; Carlsson, F.; Särnqvist, C.; Savolainen, O.; Cao, Y.; Bäckhed, F.; Tremaroli, V.; Landberg, R.; et al. Effects of a Vegetarian Diet on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, Gut Microbiota, and Plasma Metabolome in Subjects With Ischemic Heart Disease: A Randomized, Crossover Study. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2020, 9, e016518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.M.; Alving, K. Intragastric nitric oxide production in humans: Measurements in expelled air. Gut 1994, 35, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, E.R.; Andrade, F.; Vaksman, Z.; Parthasarathy, K.; Jiang, H.; Parthasarathy, D.K.; Torregrossa, A.C.; Tribble, G.; Kaplan, H.B.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of Nitrate-Reducing Bacteria in the Oral Cavity: Implications for Nitric Oxide Homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway in Physiology and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwin, M.T.; Schechter, A.N.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B.; Patel, R.P.; Hogg, N.; Shiva, S.; Cannon, R.O., 3rd; Kelm, M.; Wink, D.A.; Espey, M.G.; et al. The Emerging Biology of the Nitrite Anion. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosby, K.; Partovi, K.S.; Crawford, J.H.; Patel, R.P.; Reiter, C.D.; Martyr, S.; Yang, B.K.; Waclawiw, M.A.; Zalos, G.; Xu, X.; et al. Nitrite Reduction to Nitric Oxide by Deoxyhemoglobin Vasodilates the Human Circulation. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1498–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.D.; Gladwin, M.T.; Freeman, B.A.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Morris, A. Enterosalivary Nitrate Metabolism and the Microbiome: Intersection of Microbial Metabolism, Nitric Oxide and Diet in Cardiac and Pulmonary Vascular Health. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 105, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Govoni, M. Inorganic nitrate is a possible source for systemic generation of nitric oxide. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaf, T.; Preik, M.; Kleinbongard, P.; Lauer, T.; Heiss, C.; Strauer, B.E.; Feelisch, M.; Kelm, M. Evidence for in Vivo Transport of Bioactive Nitric Oxide in Human Plasma. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 109, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Luedike, P.; Totzeck, M.; Kropp, M.; Schicho, A.; Stock, P.; Rammos, C.; Niessen, M.; Heiss, C.; Lundberg, J.O.; et al. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Improves Revascularization in Chronic Ischemia. Circulation 2012, 126, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Merx, M.W.; Shiva, S.; Schmitz, J.; Becher, S.; Klare, J.P.; Steinhoff, H.-J.; Goedecke, A.; Schrader, J.; Gladwin, M.T.; et al. Nitrite reductase activity of myoglobin regulates respiration and cellular viability in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10256–10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaf, T.; Heiss, C.; Mangold, S.; Leyendecker, T.; Kehmeier, E.S.; Kelm, M.; Lauer, T. Vascular Formation of Nitrite After Exercise Is Abolished in Patients With Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Coronary Artery Disease. Circ. 2010, 55, 1502–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaf, T.; Poll, L.W.; Brouzos, P.; Lauer, T.; Totzeck, M.; Kleinbongard, P.; Gharini, P.; Andersen, K.; Schulz, R.; Heusch, G.; et al. Positive effects of nitric oxide on left ventricular function in humans. Eur. Hear. J. 2006, 27, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaf, T.; Totzeck, M.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Shiva, S.; Heusch, G.; Kelm, M. Circulating Nitrite Contributes to Cardioprotection by Remote Ischemic Preconditioning. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammos, C.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Sobierajski, J.; Bernard, A.; Kelm, M.; Rassaf, T. Dietary Nitrate Reverses Vascular Dysfunction in Older Adults With Moderately Increased Cardiovascular Risk. Circ. 2014, 63, 1584–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammos, C.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Totzeck, M.; Pohl, J.; Lüdike, P.; Flögel, U.; Deenen, R.; Köhrer, K.; French, B.A.; Gödecke, A.; et al. Impact of dietary nitrate on age-related diastolic dysfunction. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2016, 18, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammos, C.; Luedike, P.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.; Rassaf, T. Potential of dietary nitrate in angiogenesis. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammos, C.; Totzeck, M.; Deenen, R.; Köhrer, K.; Kelm, M.; Rassaf, T.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B. Dietary Nitrate Is a Modifier of Vascular Gene Expression in Old Male Mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, F.J.; Ekblom, B.; Sahlin, K.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Effects of Dietary Nitrate on Blood Pressure in Healthy Volunteers. New Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2792–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassaf, T.; Ferdinandy, P.; Schulz, R. Nitrite in organ protection. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 171, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totzeck, M.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Rammos, C.; Frommke, L.-M.; Knackstedt, C.; Predel, H.-G.; Kelm, M.; Rassaf, T. Higher endogenous nitrite levels are associated with superior exercise capacity in highly trained athletes. Nitric Oxide 2012, 27, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassaf, T.; Lauer, T.; Heiss, C.; Balzer, J.; Mangold, S.; Leyendecker, T.; Rottler, J.; Drexhage, C.; Meyer, C.; Kelm, M. Nitric oxide synthase-derived plasma nitrite predicts exercise capacity. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Gao, X.; Xia, G.; Chen, M.; Zeng, N.; Wang, S.; You, C.; Tian, X.; Di, H.; Tang, W.; et al. Rapid gut dysbiosis induced by stroke exacerbates brain infarction in turn. Gut 2021, 70, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebestreit, K.; Yahiaoui-Doktor, M.; Engel, C.; Vetter, W.; Siniatchkin, M.; Erickson, N.; Halle, M.; Kiechle, M.; Bischoff, S.C. Validation of the German version of the Mediterranean Diet Adherence Screener (MEDAS) questionnaire. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendgen-Cotta, U.; Grau, M.; Rassaf, T.; Gharini, P.; Kelm, M.; Kleinbongard, P. Reductive Gas-Phase Chemiluminescence and Flow Injection Analysis for Measurement of the Nitric Oxide Pool in Biological Matrices. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 441, 295–315. [Google Scholar]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Cheng, L.; Buch, H.; Zhang, F. Akkermansia muciniphila is a promising probiotic. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 1109–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, S.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Woo, C.W.; Xu, A. Akkermansia Muciniphila Protects against Atherosclerosis by Preventing Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Inflammation in Apoe-/- Mice. Circulation 2016, 133, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Duan, Y.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila prevents cold-related atrial fibrillation in rats by modulation of TMAO induced cardiac pyroptosis. EBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Du, L.; Randell, E.; Zhang, H.; Li, K.; Li, D. Effect of different phosphatidylcholines on high fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1516–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, A.P.; Murugesan, S.; Al Khodor, S.; Terranegra, A. The potential impact of a probiotic: Akkermansia muciniphila in the regulation of blood pressure—the current facts and evidence. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catry, E.; Bindels, L.B.; Tailleux, A.; Lestavel, S.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Goossens, J.-F.; Lobysheva, I.; Plovier, H.; Essaghir, A.; Demoulin, J.-B.; et al. Targeting the Gut Microbiota with Inulin-Type Fructans: Preclinical Demonstration of a Novel Approach in the Management of Endothelial Dysfunction. Gut 2018, 67, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, W.; Zieba, J.K.; Foegeding, N.J.; Torres, T.P.; Shelton, C.D.; Shealy, N.G.; Byndloss, A.J.; Cevallos, S.A.; Gertz, E.; Tiffany, C.R.; et al. High-fat diet–induced colonocyte dysfunction escalates microbiota-derived trimethylamine N -oxide. Science 2021, 373, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skye, S.M.; Zhu, W.; Romano, K.A.; Guo, C.-J.; Wang, Z.; Jia, X.; Kirsop, J.; Haag, B.; Lang, J.M.; DiDonato, J.A.; et al. Microbial Transplantation With Human Gut Commensals Containing CutC Is Sufficient to Transmit Enhanced Platelet Reactivity and Thrombosis Potential. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Leng, C.; Lin, K.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, M.; Shu, X.; Liu, W. Tangeretin Mitigates Trimethylamine Oxide Induced Arterial Inflammation by Disrupting Choline–Trimethylamine Conversion through Specific Manipulation of Intestinal Microflora. Molecules 2024, 29, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeth, R.A.; Lam-Galvez, B.R.; Kirsop, J.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Gu, X.; Copeland, M.F.; Bartlett, D.; Cody, D.B.; Dai, H.J.; et al. l-Carnitine in omnivorous diets induces an atherogenic gut microbial pathway in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 129, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic (Mean ± SD) | Both Groups | Nitrate | Placebo | p-Value (Nitrate vs. Placebo) |
| Sex, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 8 (26.7) | 4 (26.7) | 4 (26.7) | >0.9999 |
| Female | 22 (73.3) | 11 (73.3) | 11 (73.3) | >0.9999 |
| Age (years) | 50 ± 7.5 | 51 ± 6.7 | 48 ± 8.2 | 0.2611 |
| Height (cm) | 165.9 ± 32.7 | 169.1 ± 11.3 | 162.7 ± 45.4 | 0.6034 |
| Weight (kg) | 77.5 ± 18.4 | 71.8 ± 13.8 | 83.1 ± 20.9 | 0.0925 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26 ± 4.7 | 24.9 ± 2.9 | 27.2 ± 5.9 | 0.1872 |
| Omnivore, n (%) | 29 (96.7) | 14 (93.3) | 15 (100) | >0.9999 |
| Hemodynamics baseline (mean ± SD) | Both groups | Nitrate | Placebo | p-value (Nitrate vs. Placebo) |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 124.8 ± 13.9 | 125.2 ± 14.8 | 124.3 ± 13.6 | 0.6666 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 61.9 ± 9.3 | 62.8 ± 8.2 | 60.9 ±10.5 | 0.5923 |
| ABI right | 1.09 ± 0.1 | 1.11 ± 0.09 | 1.06 ± 0.09 | 0.0877 |
| ABI left | 1.06 ± 0.1 | 1.07 ± 0.09 | 1.02 ±0.11 | 0.6101 |
| PWV (m/s) | 6.9 ± 1.8 | 7.3 ± 1.7 | 6.5 ± 1.8 | 0.1891 |
| TMAO (µg/L) | 399.6 ± 253.3 | 393.6 ± 270.3 | 406 ± 243.8 | 0.8986 |
| High-sensitive CRP (mg/L) | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.08 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.1183 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 142.6 ± 40.7 | 142.3 ± 43.5 | 142.8 ± 39.2 | 0.9756 |
| Cholesterin (mg/dL) | 205.7 ± 38 | 204.7 ± 39.4 | 206.6 ± 37.8 | 0.8956 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Messiha, D.; Rinke, M.; Schultz Moreira Amos, A.; Tratnik, A.; Hendgen-Cotta, U.B.; Lortz, J.; Hogrebe, K.; Kehrmann, J.; Buer, J.; Rassaf, T.; et al. Influence of Chronic Dietary Nitrate on Downstream Atherogenic Metabolites and the Enteral Microbiome—A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Dietetics 2025, 4, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/dietetics4010001
Messiha D, Rinke M, Schultz Moreira Amos A, Tratnik A, Hendgen-Cotta UB, Lortz J, Hogrebe K, Kehrmann J, Buer J, Rassaf T, et al. Influence of Chronic Dietary Nitrate on Downstream Atherogenic Metabolites and the Enteral Microbiome—A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Dietetics. 2025; 4(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/dietetics4010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMessiha, Daniel, Miriam Rinke, Adriana Schultz Moreira Amos, Annika Tratnik, Ulrike Barbara Hendgen-Cotta, Julia Lortz, Kristina Hogrebe, Jan Kehrmann, Jan Buer, Tienush Rassaf, and et al. 2025. "Influence of Chronic Dietary Nitrate on Downstream Atherogenic Metabolites and the Enteral Microbiome—A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial" Dietetics 4, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/dietetics4010001
APA StyleMessiha, D., Rinke, M., Schultz Moreira Amos, A., Tratnik, A., Hendgen-Cotta, U. B., Lortz, J., Hogrebe, K., Kehrmann, J., Buer, J., Rassaf, T., & Rammos, C. (2025). Influence of Chronic Dietary Nitrate on Downstream Atherogenic Metabolites and the Enteral Microbiome—A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Dietetics, 4(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/dietetics4010001








