Second Order Glauber Correlation of Gravitational Waves Using the LIGO Observatories as Hanbury Brown and Twiss Detectors †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
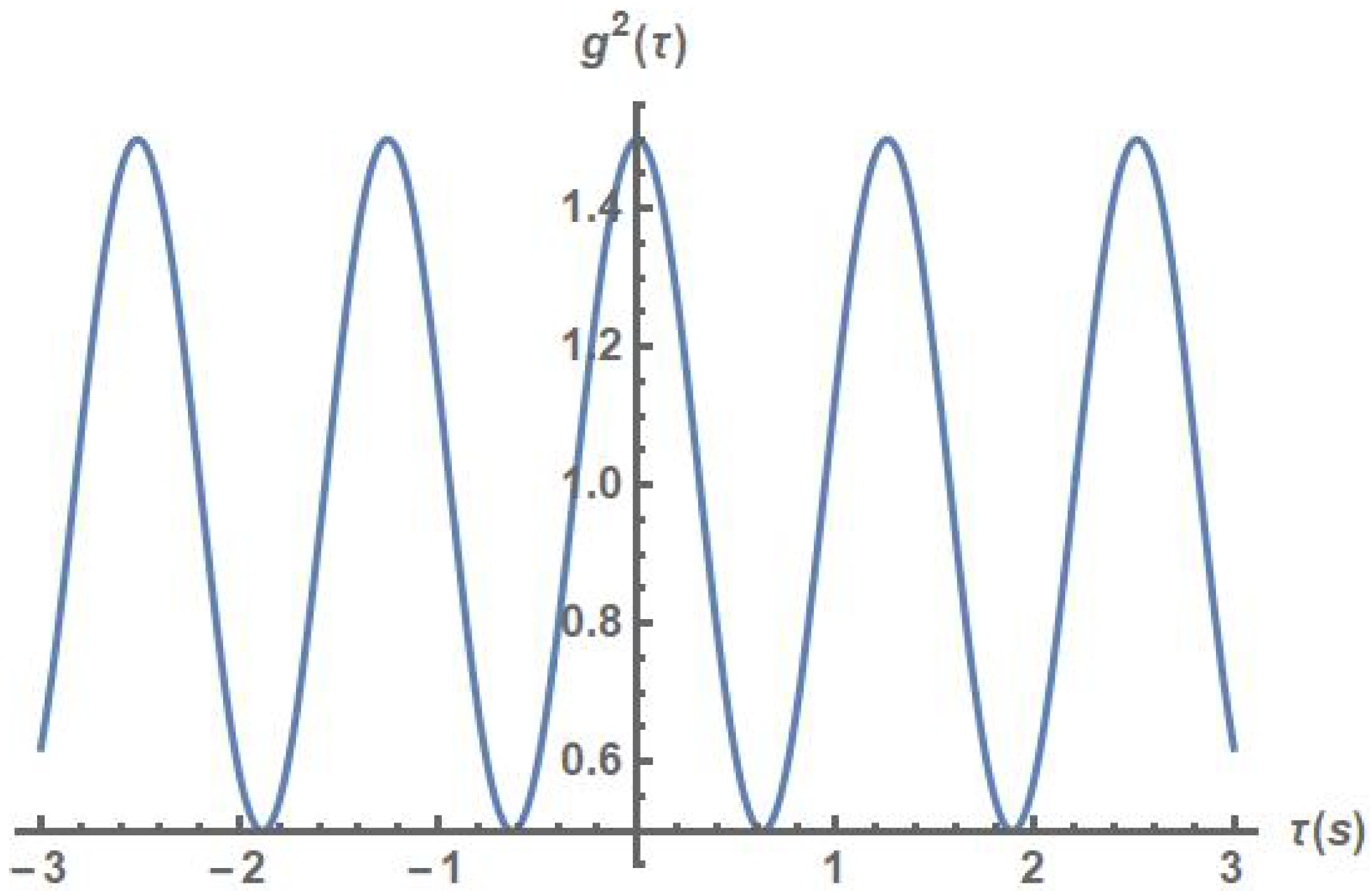
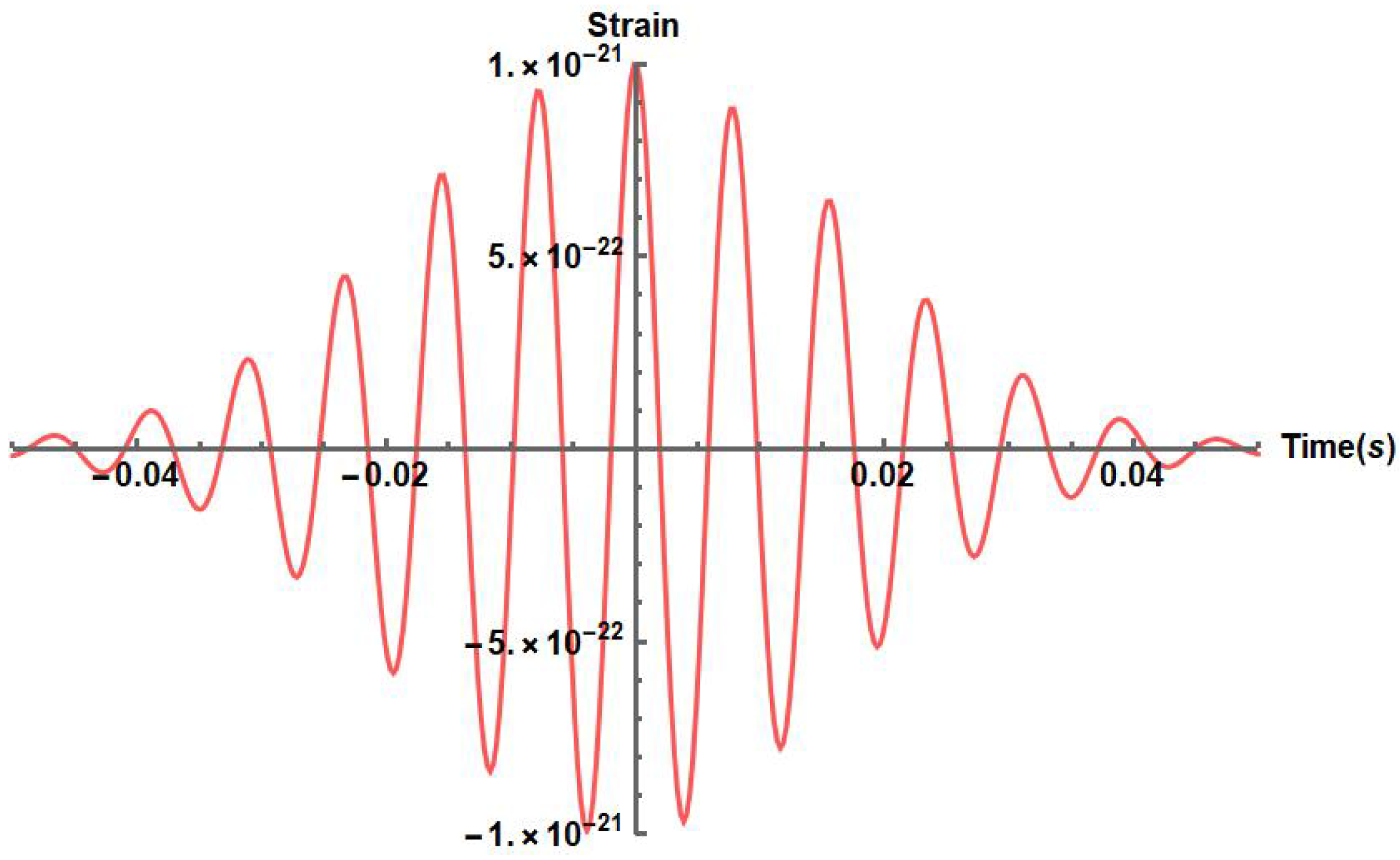
3. Results
- Coherent light of a single frequency is defined as ;
- For a laser for chaotic light;
- does not necessarily mean the signal is chaotic;
- For chaotic light .
4. Conclusions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fox, M. Quantum Optics—An Introduction; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Louden, R. The Quantum Theory of Light, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Baym, G. The physics of Hanbury Brown-Twiss intensity interferometry: From stars to nuclear collisions. Acta Phys. Pol. B 1998, 29, 1839–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Facao, M.; Lopes, A.; Silva, A.L.; Silva, P. Computer simulation for calculating the second-order correlation function of classical and quantum light. Eur. J. Phys. 2011, 32, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyaprakash, B.S.; Schutz, B.F. Physics, Astrophysics, and Cosmology, with Gravitational Waves. Living Rev. Relat. 2009, 12, 1–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lebreton, A.; Abram, I.; Braive, R.; Sagnes, I.; Robert-Philip, I.; Beveratos, A. Theory of Interferometric Photon-Correlation Measurements: Differentiating Coherent from Chaotic Light. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 013801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wikipedia Contributors. Degree of Coherence. Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Degree_of_coherence&oldid=1001227113 (accessed on 30 January 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barrett, A.; Jones, P. Second Order Glauber Correlation of Gravitational Waves Using the LIGO Observatories as Hanbury Brown and Twiss Detectors . Phys. Sci. Forum 2021, 2, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECU2021-09519
Barrett A, Jones P. Second Order Glauber Correlation of Gravitational Waves Using the LIGO Observatories as Hanbury Brown and Twiss Detectors . Physical Sciences Forum. 2021; 2(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECU2021-09519
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarrett, Alexander, and Preston Jones. 2021. "Second Order Glauber Correlation of Gravitational Waves Using the LIGO Observatories as Hanbury Brown and Twiss Detectors " Physical Sciences Forum 2, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECU2021-09519
APA StyleBarrett, A., & Jones, P. (2021). Second Order Glauber Correlation of Gravitational Waves Using the LIGO Observatories as Hanbury Brown and Twiss Detectors . Physical Sciences Forum, 2(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECU2021-09519