Applying a Wet-Type Grinder to Wheat Bran for Developing Breads †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of WG-Treated Bran
2.3. Viscosity
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5. Bread Preparation
2.6. Specific Loaf Volume
2.7. Compression Force Value (CFV)
2.8. Enzymatic Starch Digestion Assay
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
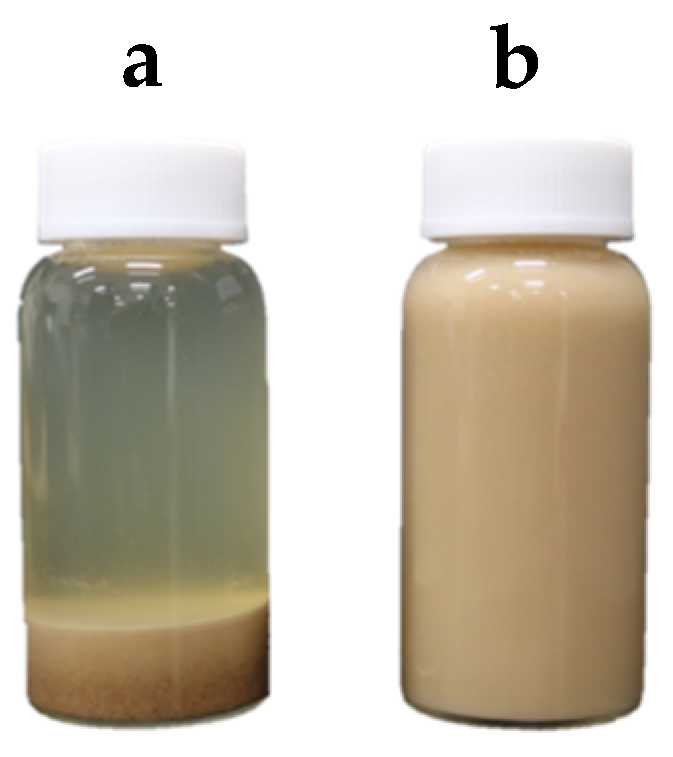
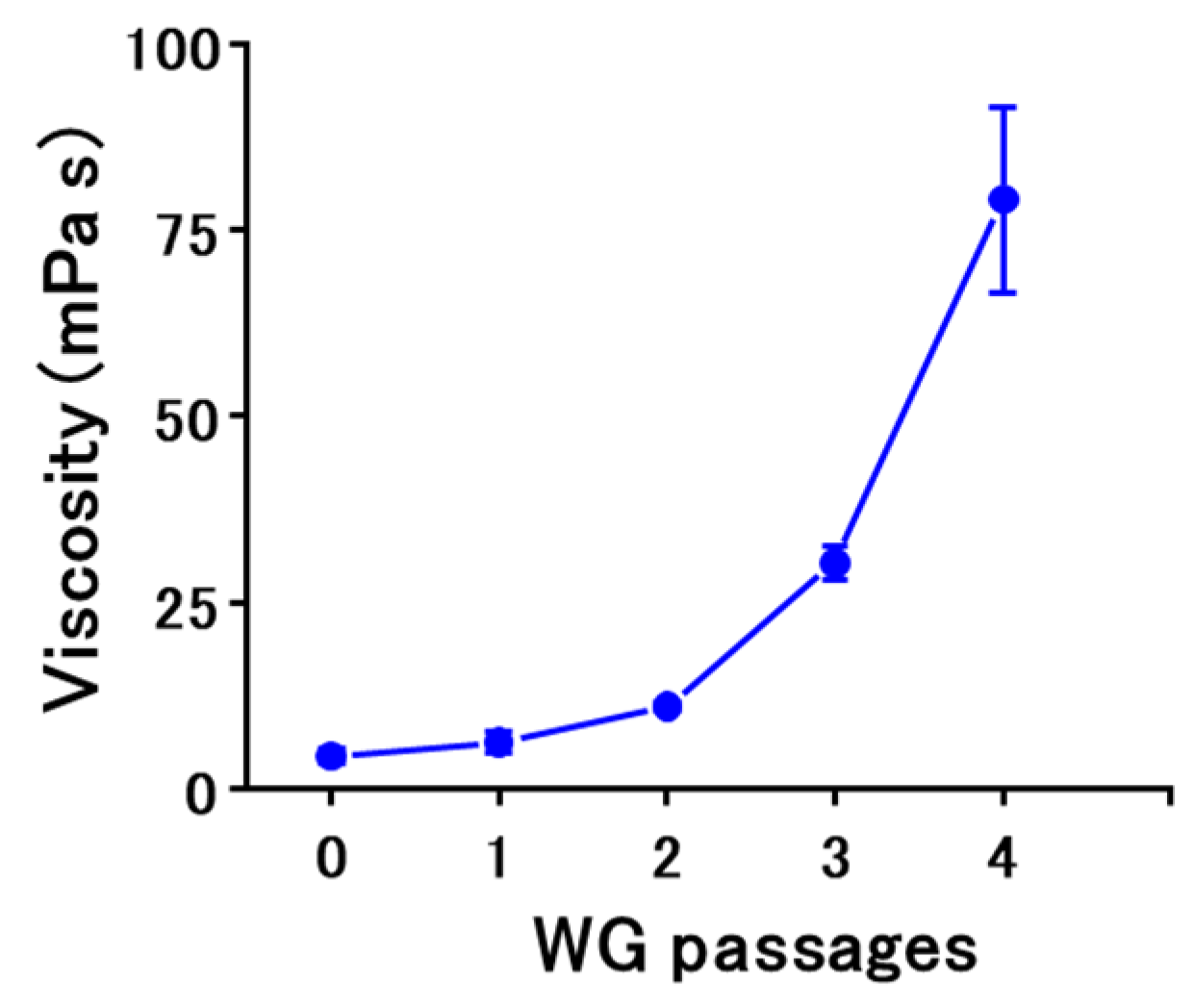
3.1. Effect of WG Treatment on Bran Properties
3.2. Bread Properties
3.3. Enzymatic Starch Digestion Assay
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosa-Sibakov, N.; Sibakov, J.; Lahtinen, P.; Poutanen, K. Wet grinding and microfluidization of wheat bran preparations: Improvement of dispersion stability by structural disintegration. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Arai, Y.; Yano, H.; Aoki, T.; Kurihara, S.; Hirano, R.; Nishinari, K. Improved physicochemical and functional properties of okara, a soybean residue, by nanocellulose technologies for food development—A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Nagano, T. Developing soybean protein gel-based foods from okara using the wet-type grinder method. Foods 2021, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AACC International. Guidelines for measurement of volume by rapeseed displacement. In Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, 11th ed.; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y. A modified American association of cereal chemists method for compressive force value determination of white bread crumb firmness. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2016, 22, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz de Erive, M.; Wang, T.; He, F.; Chen, G. Development of high-fiber wheat bread using microfluidized corn bran. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, S33–S50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Ingredient | Bran Bread | No-Bran (Control) Bread |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat flour (g) | 142.5 | 150 |
| Bran (g) | 7.5 | 0 |
| Butter (g) | 5 | 5 |
| Sugar (g) | 10 | 10 |
| Salt (g) | 3 | 3 |
| Dried yeast (g) | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Water (g) | 90 | 110 |
| Specific Loaf Volume (cm3/g) | Crumb CFV (N) | |
|---|---|---|
| Control bread | 4.00 ± 0.09 a | 0.73 ± 0.11 a |
| WG-treated bran bread | 3.09 ± 0.17 b | 1.75 ± 0.40 b |
| Untreated bran bread | 2.68 ± 0.09 c | 1.99 ± 0.28 c |
| RDS (g/100 g Bread) | SDS (g/100 g Bread) | |
|---|---|---|
| Control bread | 22.7 ± 2.9 a | 10.7 ± 5.0 a |
| WG-treated bran bread | 18.3 ± 0.8 b | 2.5 ± 1.3 b |
| Untreated bran bread | 22.8 ± 1.9 a | 1.6 ± 0.8 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, T.A.; Nakamura, K.; Arai, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Nagano, T. Applying a Wet-Type Grinder to Wheat Bran for Developing Breads. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2021, 6, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2021-10986
Le TA, Nakamura K, Arai Y, Nishinari K, Nagano T. Applying a Wet-Type Grinder to Wheat Bran for Developing Breads. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2021; 6(1):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2021-10986
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Thi Anh, Kazuyoshi Nakamura, Yuya Arai, Katsuyoshi Nishinari, and Takao Nagano. 2021. "Applying a Wet-Type Grinder to Wheat Bran for Developing Breads" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 6, no. 1: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2021-10986
APA StyleLe, T. A., Nakamura, K., Arai, Y., Nishinari, K., & Nagano, T. (2021). Applying a Wet-Type Grinder to Wheat Bran for Developing Breads. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 6(1), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2021-10986